Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Addressing Variant Pathogenicity: The TorsinA (TOR1A) Gene as a Model
- Page: v
- First Published: 14 August 2014
Spectrum of the Mutations in Bernard–Soulier Syndrome
- Pages: 1033-1045
- First Published: 16 June 2014
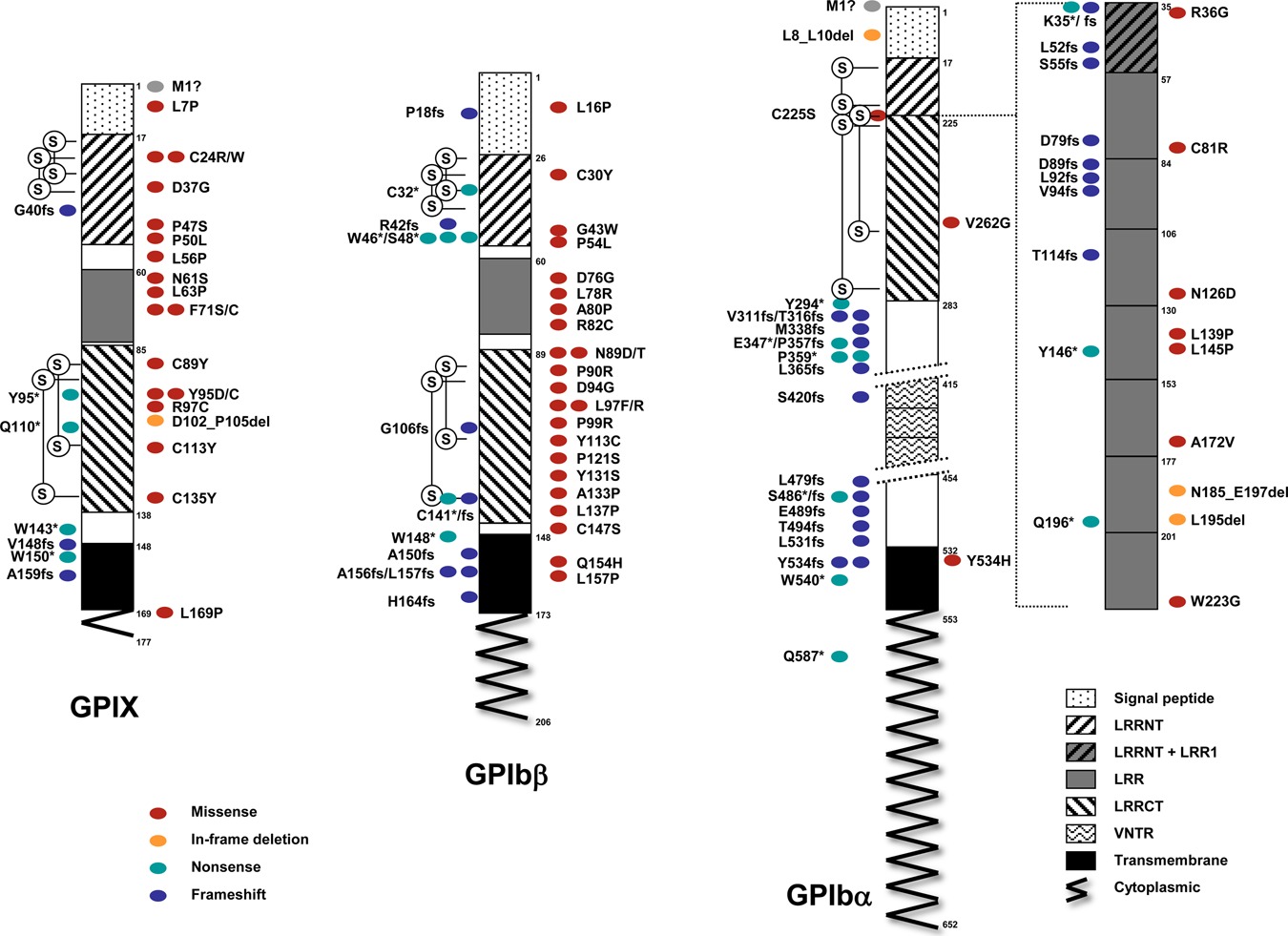
We present a comprehensive spectrum of mutations of GP1BA (GPIbα), GP1BB (GPIbβ) and GP9 (GPIX) causing Bernard-Soulier syndrome (BSS), a rare bleeding autosomal recessive disorder. Of the 211 families enrolled, 28% have mutations in GP1BA, another 28% in GP1BB and the remaining 44% in GP9. Excluding a few founder effects, most of the 112 different mutations identified are private. Missense variants, whose pathogenetic role should be determined through functional studies, accounts for more than half BSS alleles.
A Rising Titan: TTN Review and Mutation Update
- Pages: 1046-1059
- First Published: 30 June 2014
The 364 exon TTN gene encodes the giant protein titin, a key player in cardiac and skeletal muscles. Lately, NGS is revealing TTN as a major gene in human inherited disease, with 127 TTN disease-causing mutations reported in patients with at least 10 different conditions. Here we provide the first comprehensive update of the TTN mutations reported and discuss their distribution, molecular mechanisms, associated phenotypes, transmission pattern and phenotype-genotype correlations, alongside with their implications for basic research and human health.
GALT Protein Database: Querying Structural and Functional Features of GALT Enzyme
- Pages: 1060-1067
- First Published: 02 July 2014
Screenshot of the home page of GALT Protein Database 2.0, with the link to full access and description of its features. In this database we not only collect a list of the known missense variations for GALT enzyme, but in addition, we provide information about their effect on GALT structure and possibly, function, obtained by modeling and analyzing the structures of the missense variants.
HSF4 Mutation p.Arg116His Found in Age-Related Cataracts and in Normal Populations Produces Childhood Lamellar Cataract in Transgenic Mice
- Pages: 1068-1071
- First Published: 27 June 2014
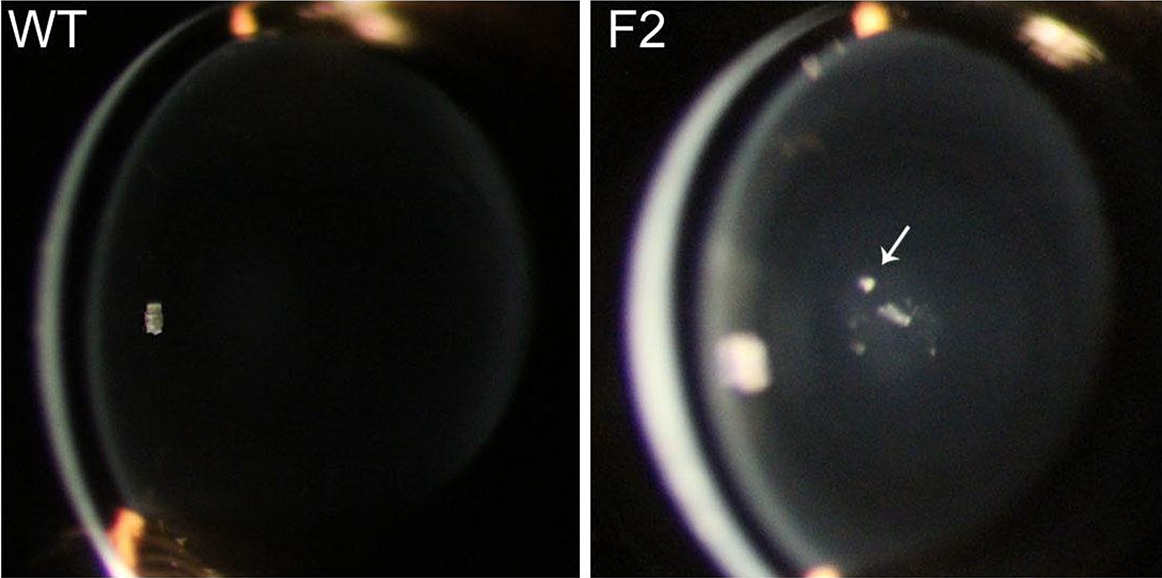
The p.Arg116His mutation in the DNA binding domain of the heat shock transcription factor HSF4, reported to be associated with age-related cataracts in humans recapitulates the most prevalent childhood lamellar cataract phenotype (arrow), when introduced into mice via bacterial artificial chromosome transgenesis. This data suggests that the presence of this mutation in ‘normal’ individuals does not impair the visual function. Slit lamp images of age matched (21 days old) wild-type (WT, left) and F2 transgenic mouse lens (right) are shown.
Ancient and Recent Adaptive Evolution in the Antiviral TRIM22 Gene: Identification of a Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism That Impacts TRIM22 Function
- Pages: 1072-1081
- First Published: 26 May 2014
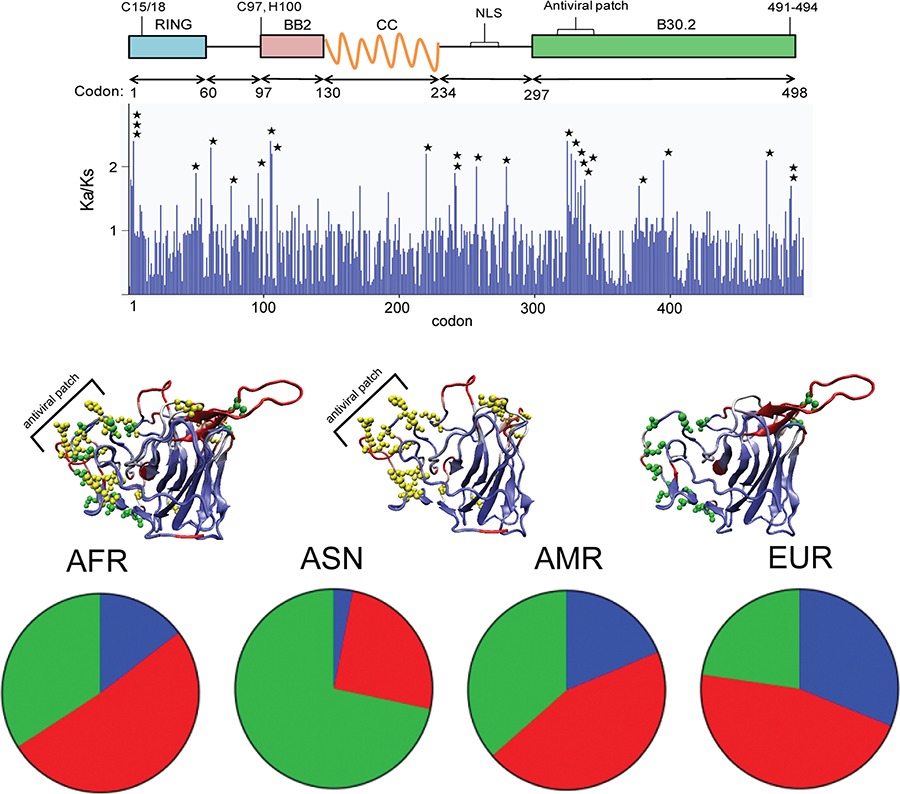
We adopted an evolution-guided functional approach to identify potential genetic determinants of TRIM22 function. We showed that positive selection is operating on multiple residues that cluster in putative functional regions and are predicted to be functionally damaging. Our data characterize the extensive genetic variation in TRIM22 and identify rs1063303:G>C as a highly prevalent SNP that influences its function.
Corneal Dystrophy-Causing SLC4A11 Mutants: Suitability for Folding-Correction Therapy
- Pages: 1082-1091
- First Published: 10 June 2014
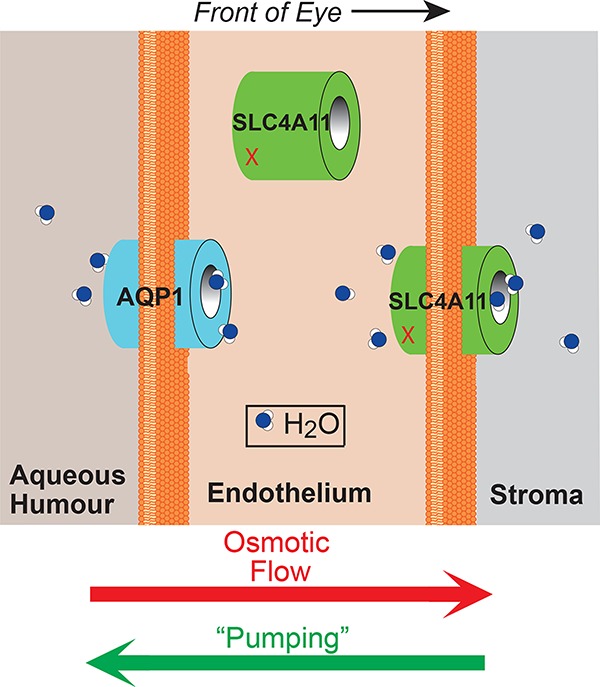
Corneal stroma accumulates water osmotically, which is countered by the “pumping” function of endothelial cells. SLC4A11 forms a water conductive pathway, whose mutations lead to blinding corneal edema. Most SLC4A11 mutants (red x) are retained in the endoplasmic reticulum, but this work found: SLC4A11 mutants could be rescued to the cell surface and are functional once rescued, providing hope for therapeutic strategies aimed at rescuing diseased SLC411 to the cell surface.
Deletions in the 3′ Part of the NFIX Gene Including a Recurrent Alu-Mediated Deletion of Exon 6 and 7 Account for Previously Unexplained Cases of Marshall–Smith Syndrome
- Pages: 1092-1100
- First Published: 13 June 2014
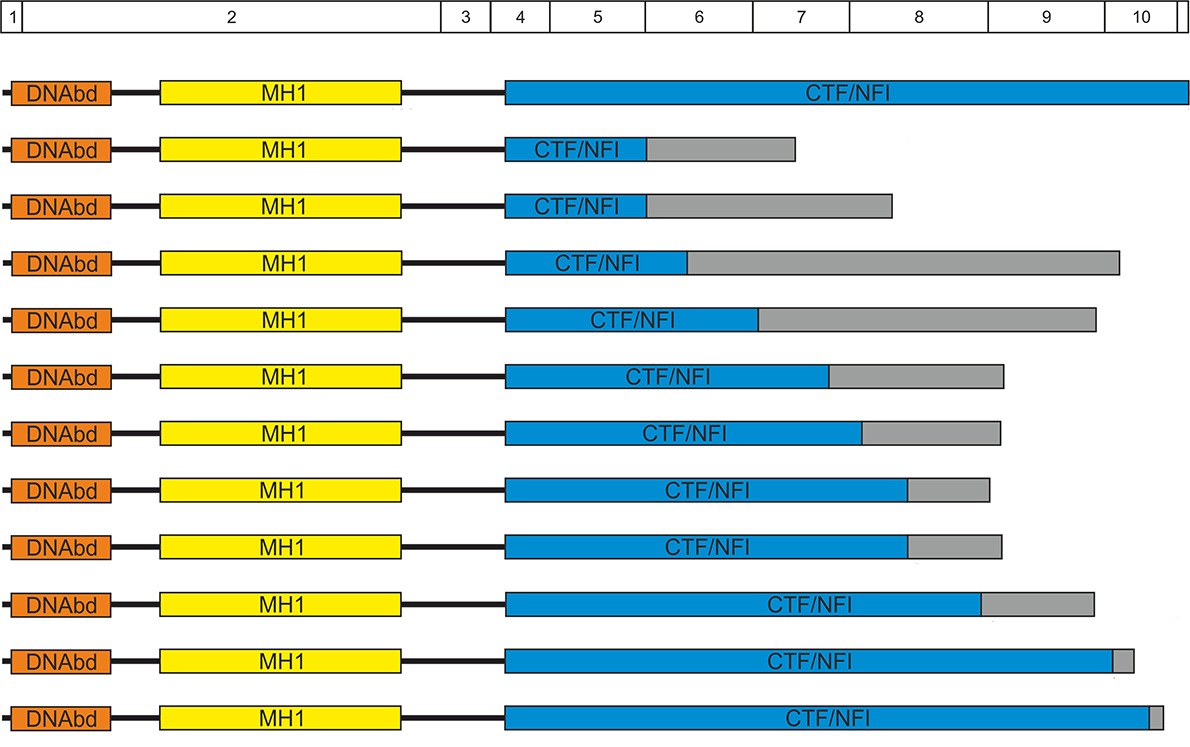
This study demonstrates that Marshall-Smith syndrome is consistently caused by de novo NFIX mutations. It is presented for the first time that exon deletions including a recurrent AluY-mediated exon 6 and 7 deletion account for roughly a quarter of cases. MSS-associated mutations lead to mutant proteins with intact DNA-binding and dimerization domains(DNAbd, MH1), while they have various alterations of their transcriptional transactivation/repression domains (CTF/NFI). Thereby they are presumed to exert dominant negative effects.
Biochemical and Cellular Analysis of Human Variants of the DYT1 Dystonia Protein, TorsinA/TOR1A
- Pages: 1101-1113
- First Published: 13 June 2014
Unraveling Cellular Phenotypes of Novel TorsinA/TOR1A Mutations
- Pages: 1114-1122
- First Published: 13 June 2014
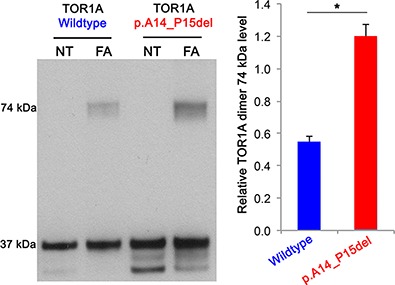
We report two new putative TOR1A mutations (p.A14_P15del and p.E121K) that we examined functionally in comparison with wildtype protein. Our findings demonstrate functional changes on different levels.Western blot analysis of cross-linking experiments with formaldehyde (FA) and quantification of TOR1A levels in SH-SY5Y cells expressing TOR1A show significantly enhanced dimerization at 74 kDa for p.A14_P15del mutant TOR1A (NT: non-treated).
Assessing How Reduced Expression Levels of the Mismatch Repair Genes MLH1, MSH2, and MSH6 Affect Repair Efficiency
- Pages: 1123-1127
- First Published: 13 June 2014
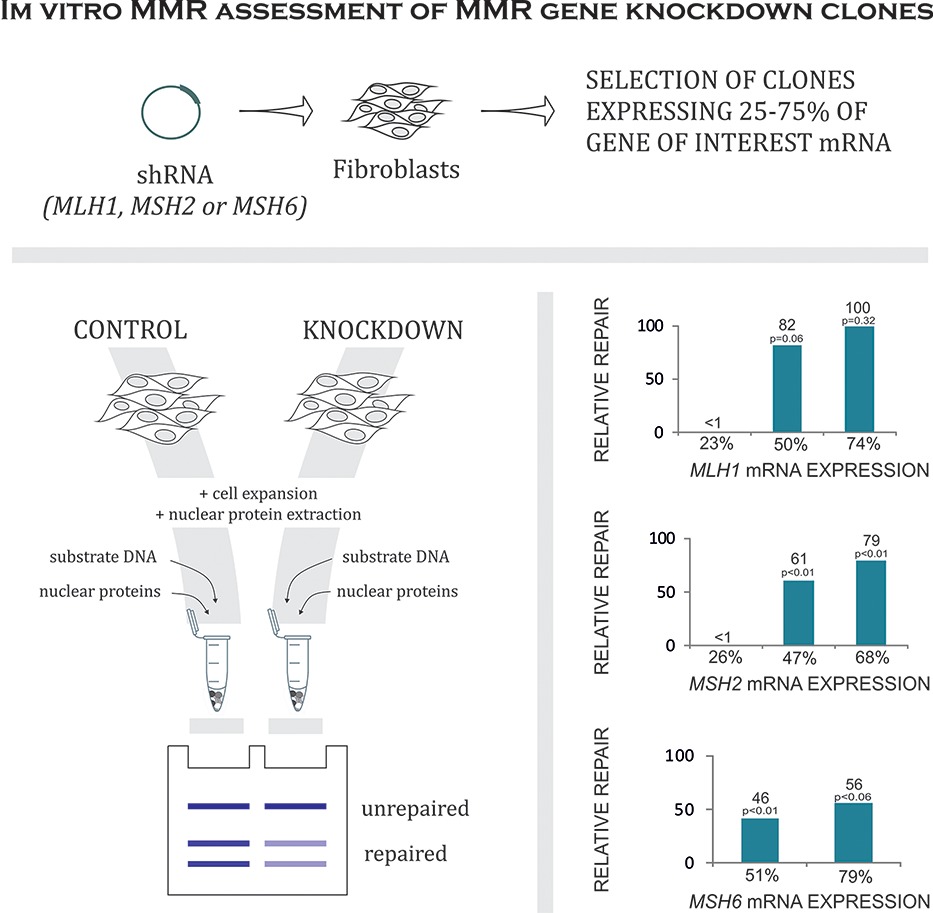
The notable effect of reduced mismatch repair gene expression on the repair efficiency provides a preliminary indication of the relative expression levelss required for wild-type function. These findings suggest that the in vitro MMR assay could be used to recognize expression levels indicative of Lynch syndrome.
RNA Sequencing of Creatine Transporter (SLC6A8) Deficient Fibroblasts Reveals Impairment of the Extracellular Matrix
- Pages: 1128-1135
- First Published: 24 June 2014
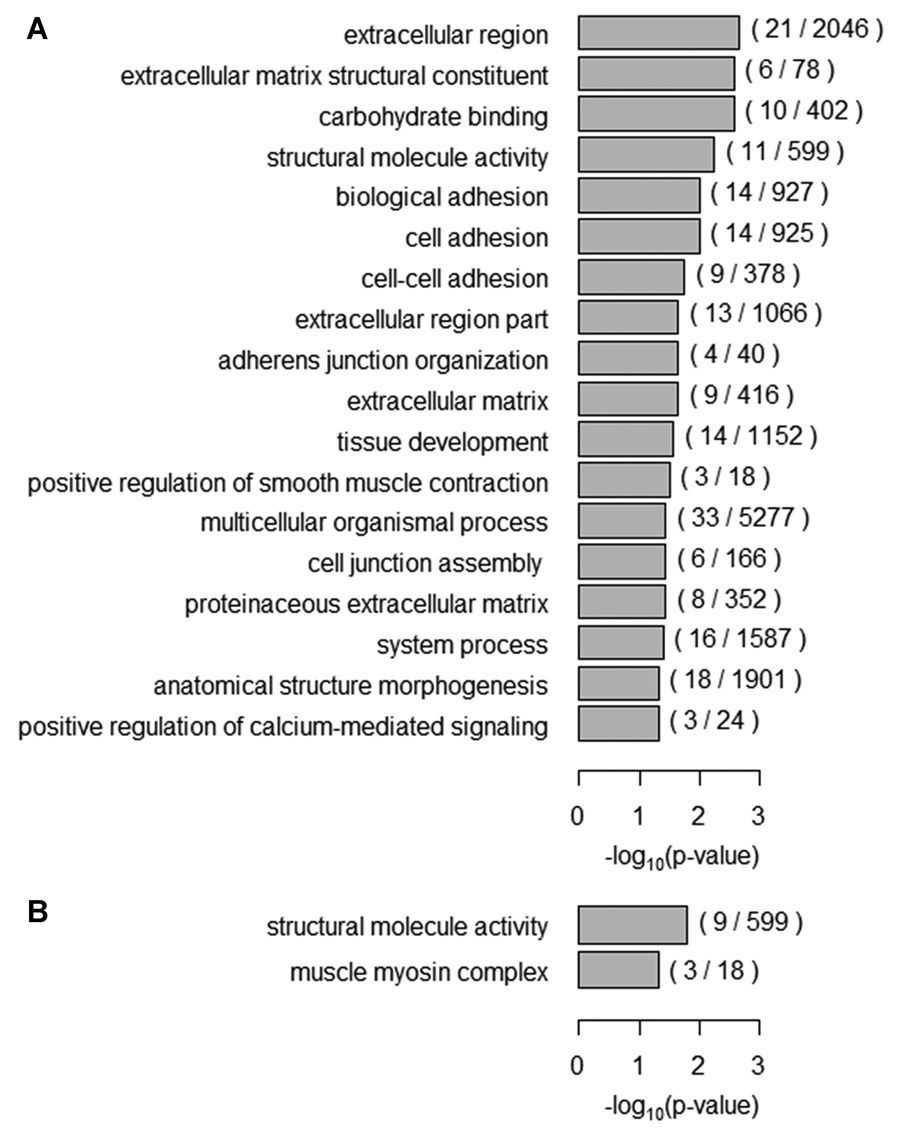
The most common cause of cerebral creatine syndromes is caused by mutations in the creatine transporter (SLC6A8), and no effective treatment is available yet. We performed RNA sequencing to investigate the molecular pathophysiology of this disorder, using fibroblast cells derived from eight unrelated individuals with SLC6A8 deficiency. Especially the expression of genes encoding components of the extracellular matrix and cytoskeleton altered due to SLC6A8 deficiency, and suggests an important role for creatine in the structural development and maintenance of cells.
Mutations in Exon 1 Highlight the Role of MED12 in Uterine Leiomyomas
- Pages: 1136-1141
- First Published: 30 June 2014
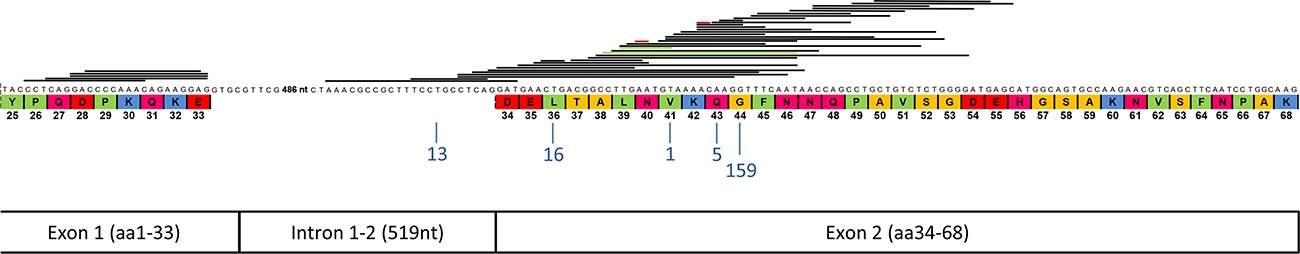
Uterine leiomyomas are the most common human tumors with highly specific mutations reported in MED12 exon 2. Here, we show that mutations occur recurrently also in MED12 exon 1. Transcriptome-wide gene expression profiling and functional analyses show that exon 1 and 2 mutations promote tumorigenesis through similar mechanism. These results bring new knowledge on MED12 function and highlight the role of MED12 in human tumorigenesis.
Destruction of DDIT3/CHOP Protein by Wild-Type SPOP but Not Prostate Cancer-Associated Mutants
- Pages: 1142-1151
- First Published: 02 July 2014
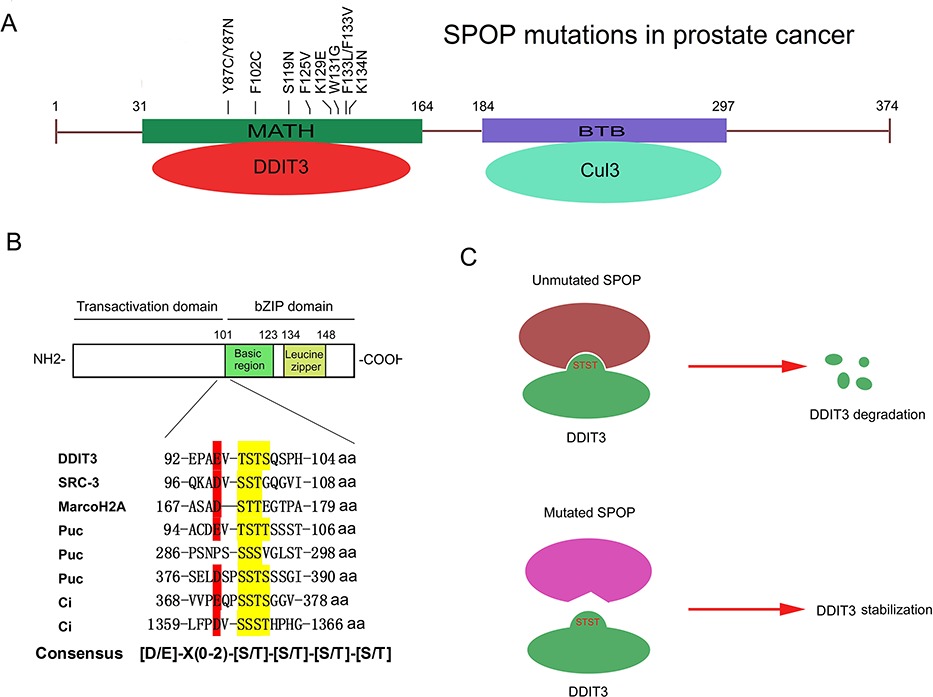
A. SPOP is one of the most frequently affected genes bysomatic point mutations in prostate cancer.
B. SPOP recognizes aSer/Thr-rich degron in the transactivation domain of DDIT3 andtriggers DDIT3 degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.
C. Prostate cancer-associated mutants of SPOP aredefective in promoting DDIT3 degradation.
Online Registry for Mutations in Hereditary Amyloidosis Including Nomenclature Recommendations
- Pages: E2403-E2412
- First Published: 17 July 2014




