Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Deciphering the cis-Regulatory Landscape of SOX9 Implicated in Craniofacial Development and Isolated Pierre Robin Sequence
- Page: v
- First Published: 17 July 2014
What Identity Crisis? Rapidly Mutating Y-STRs Facilitate Differentiation of Males
- Page: v
- First Published: 17 July 2014
The Challenge for the Next Generation of Medical Geneticists
- Pages: 909-911
- First Published: 17 May 2014
Majority Vote and Other Problems when using Computational Tools
- Pages: 912-914
- First Published: 10 June 2014
Mutation Update for GNE Gene Variants Associated with GNE Myopathy
- Pages: 915-926
- First Published: 02 May 2014
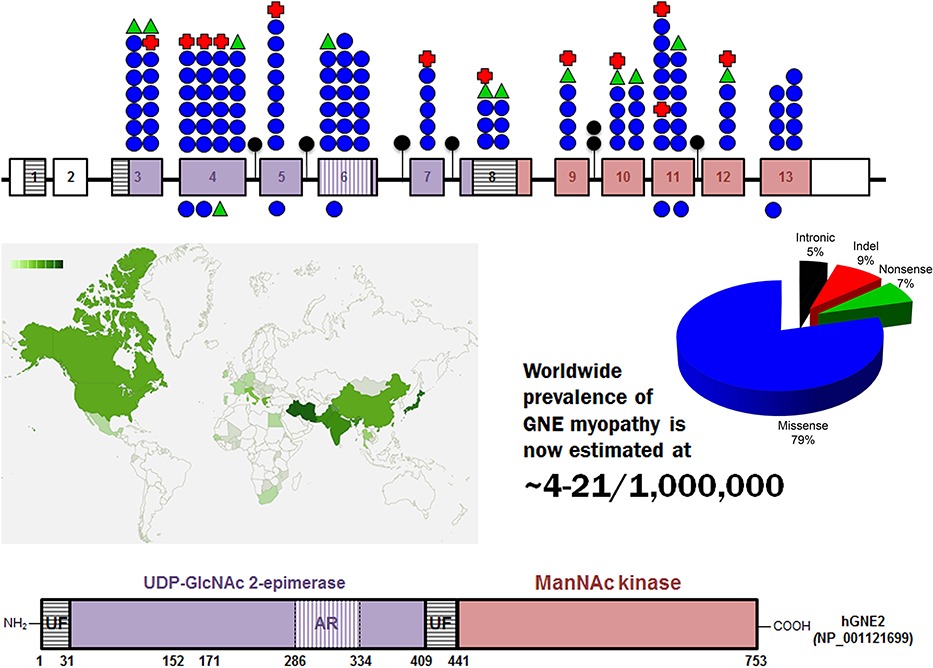
This is a comprehensive report of GNE gene mutations associated with GNE myopathy. All Reported human GNE variants are scattered all throughout the coding regions of the gene. Based on allele frequencies, the worldwide prevalence of GNE myopathy is estimated to be higher (∼4-21/1,000,000) than previously thought
Genetic Variations and Diseases in UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot: The Ins and Outs of Expert Manual Curation
- Pages: 927-935
- First Published: 21 May 2014
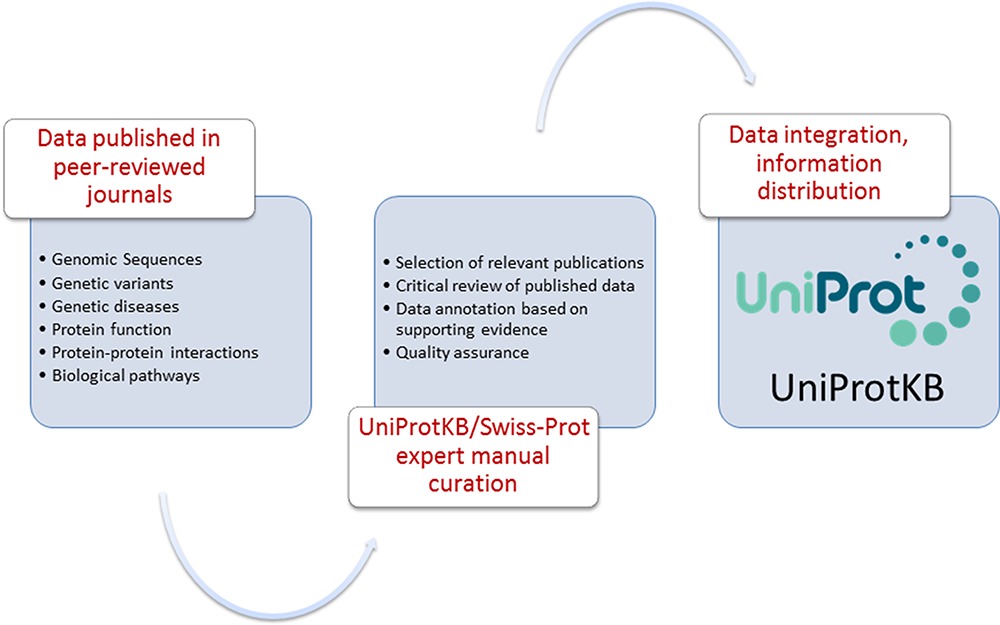
UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot is a freely accessible, expertly curated knowledgebase that offers reliable information on proteins. This manuscript describes the manual curation ofgenetic variants and diseases. The variant/disease-specific annotations are presented against the background of current physiological knowledge. This juxtaposition of physiological and pathological data can provide the researchers with a tool to elucidate the mechanisms leading from a molecular defect to a disease phenotype.
Reducing False-Positive Incidental Findings with Ensemble Genotyping and Logistic Regression Based Variant Filtering Methods
- Pages: 936-944
- First Published: 14 May 2014
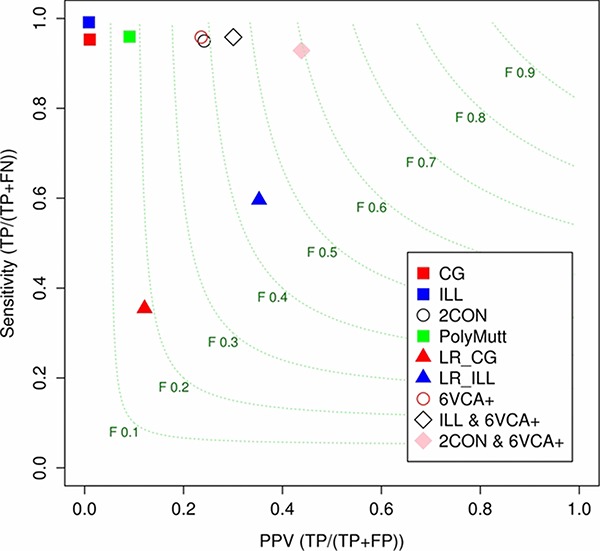
To reduce false positive incidental findings in whole genome and exome sequencing, we developed an ensemble variant calling method, and variant prioritizing methods using logistic regression. The proposed methods are especially useful for de novo mutation (DNM) discovery where positive predictive value of DNM candidates can be as low as 1% with a single platform sequencing dataset. Our approaches show significantly higher performances compared to a pedigree-aware DNM detection method (PolyMutt) or concordant DNM candidates from two sequencing platforms (2CON).
A Novel ZRS Mutation Leads to Preaxial Polydactyly Type 2 in a Heterozygous Form and Werner Mesomelic Syndrome in a Homozygous Form
- Pages: 945-948
- First Published: 28 April 2014
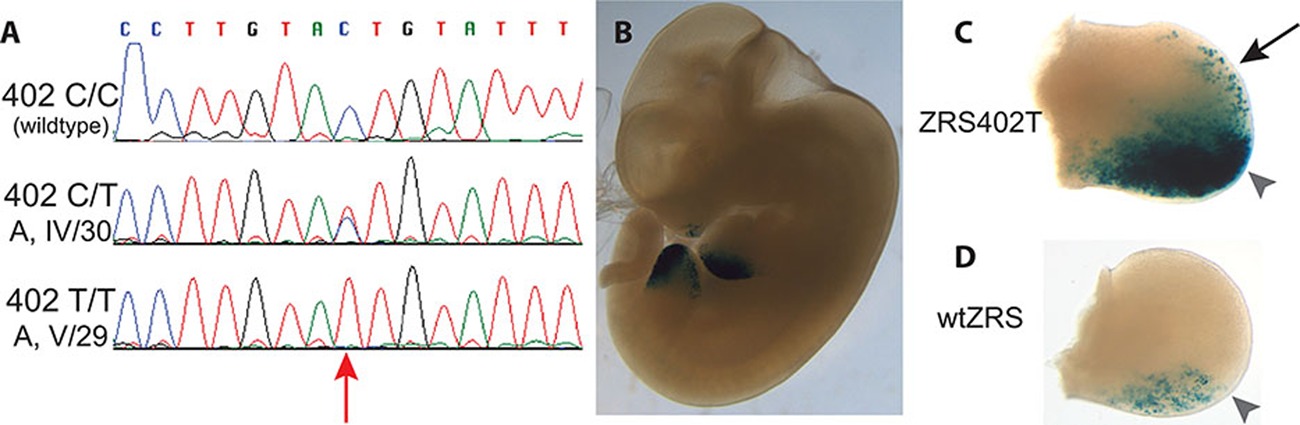
Sequencing of two Mexican families that have a variable limb malformation phenotype that includes polydactyly, triphalangeal thumb and one individual with Werner mesomelic syndrome (WMS) found a novel mutation in the zone of polarizing activity regulatory sequence (ZRS). This mutation, ZRS402, leads to an expansion of the enhancer expression in mouse embryonic limbs. The individual with WMS is the only one who is homozygous for this mutation, suggesting a dosage effect for this ZRS mutation.
Mutations in ALDH1A3 Represent a Frequent Cause of Microphthalmia/Anophthalmia in Consanguineous Families
- Pages: 949-953
- First Published: 28 April 2014
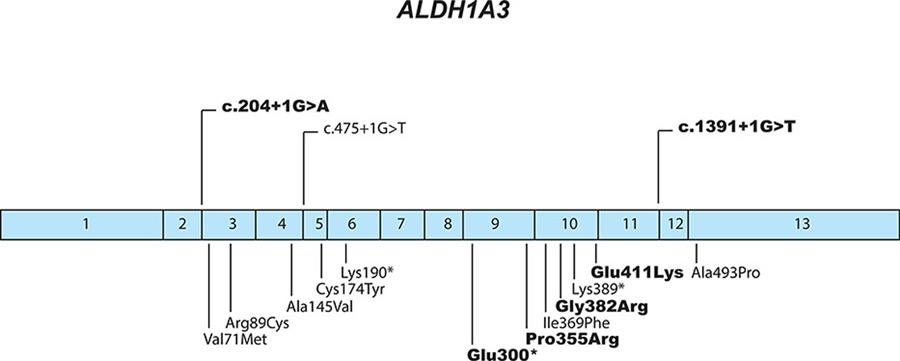
Anophthalmia/microphthalmia (A/M) is characterized by absent or small eye. Among the various genes that have recently been implicated in this malformation, aldehyde dehydrogenase family 1, member A3 (ALDH1A3) is becoming an important player. Here we show that approximately 10% of recessive A/M are due to nonsense or missense mutations in this gene.
A Novel in-Frame 18-bp Microdeletion in MT-CYB Causes a Multisystem Disorder with Prominent Exercise Intolerance
- Pages: 954-958
- First Published: 26 May 2014
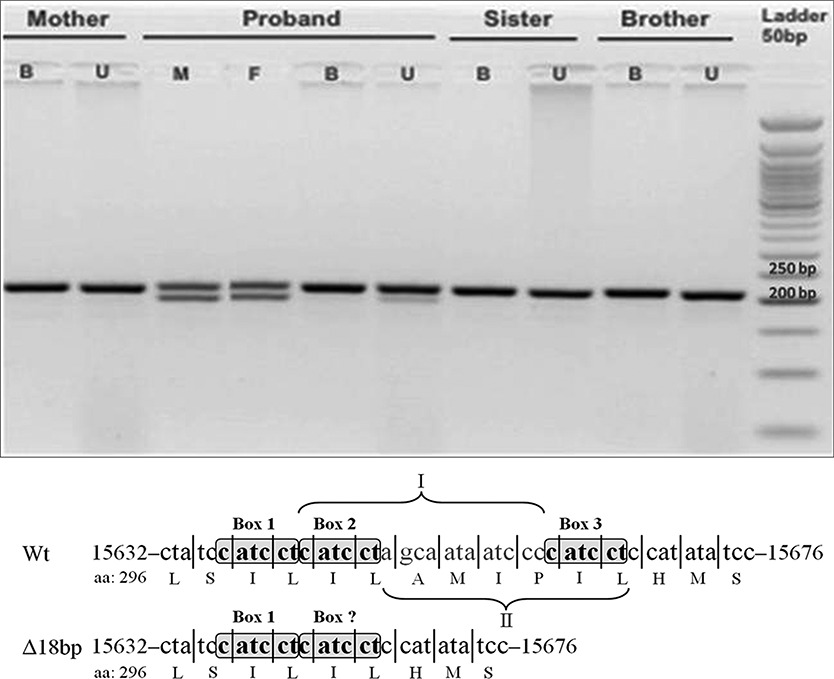
This study shows that a complex multisystem disorder with prominent exercise intolerance is associated with an 18-bp mtDNA deletion in the MT-CYB gene (m.15649_15666del18). This rearrangement, which involves two identical six bp direct repeats located 12-bp apart from each other, causes the loss of six amino acids in the protein, but leaves the remaining of the MT-CYB sequence in frame. Cybrid studies revealed that the defective complex III function was cotransferred with mutant mtDNA, thus unequivocally establishing the pathogenic role of the deletion.
A Novel Homozygous Mutation in FGFR3 Causes Tall Stature, Severe Lateral Tibial Deviation, Scoliosis, Hearing Impairment, Camptodactyly, and Arachnodactyly
- Pages: 959-963
- First Published: 26 May 2014
Genetic Screening and Functional Characterization of PDGFRB Mutations Associated with Basal Ganglia Calcification of Unknown Etiology
- Pages: 964-971
- First Published: 05 May 2014

Mutations in PDGFRB and PDGFB have recently been associated with Idiopathic Basal Ganglia Calcification (IBGC). We screened for mutations in these genes in our brain bank series and found the novel p.R695C mutation in PDGFRB. This mutation is located in the tyrosine kinase domain of PDGFRβ and results in partial loss of receptor autophosphorylation in vitro. Our study provides the first insight into the pathogenic mechanism associated with PDGFRB mutations and supports the role of the PDGF-B/PDGFRβ pathway in IBGC.
Structural Genomic Variation as Risk Factor for Idiopathic Recurrent Miscarriage
- Pages: 972-982
- First Published: 14 May 2014
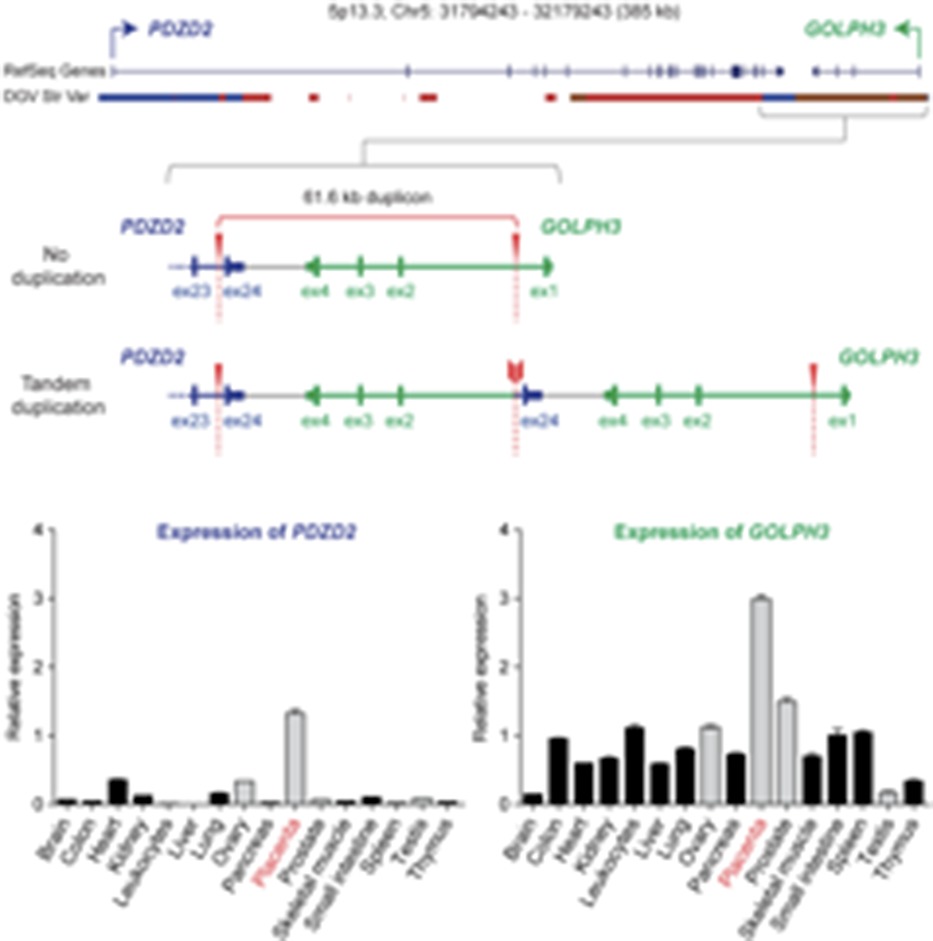
This study highlights the impact of DNA copy number variants (CNVs) as the risk factor of recurrent miscarriages. Genome-wide profile of CNVs in recurrent miscarriage cases specifically altered pathways of immune tolerance known to be essential at the fetomaternal interface of the placenta. A novel multi-copy duplication at 5p13.3 was identified conferring maternal risk to recurrent miscarriage disease and disrupting PDZD2 and GOLPH3 genes expressed in placenta and associated with early pregnancy success for the first time.
VARS2 and TARS2 Mutations in Patients with Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathies
- Pages: 983-989
- First Published: 14 May 2014
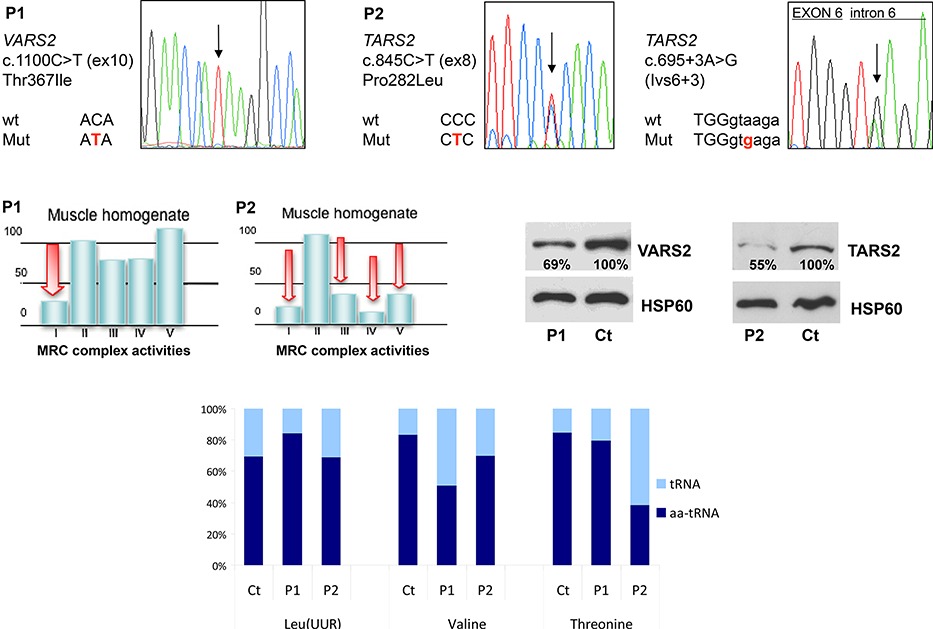
A homozygous missense mutation in VARS2 was identified in one subject with microcephaly, epilepsy and isolated deficiency of the MRC complex I
Compound heterozygous mutations in TARS2 were found in two siblings presenting with axial hypotonia and severe psychomotor delay associated with multiple MRC defects.
The amount of VARS2 and TARS2 proteins and valyl-tRNA and threonyl-tRNA levels were decreased in samples of patients according to the genetic defect; complementation studies confirmed the pathogenic effect of the identified mutations.
Genetic and Epigenetic Determinants of Low Dysferlin Expression in Monocytes
- Pages: 990-997
- First Published: 17 May 2014
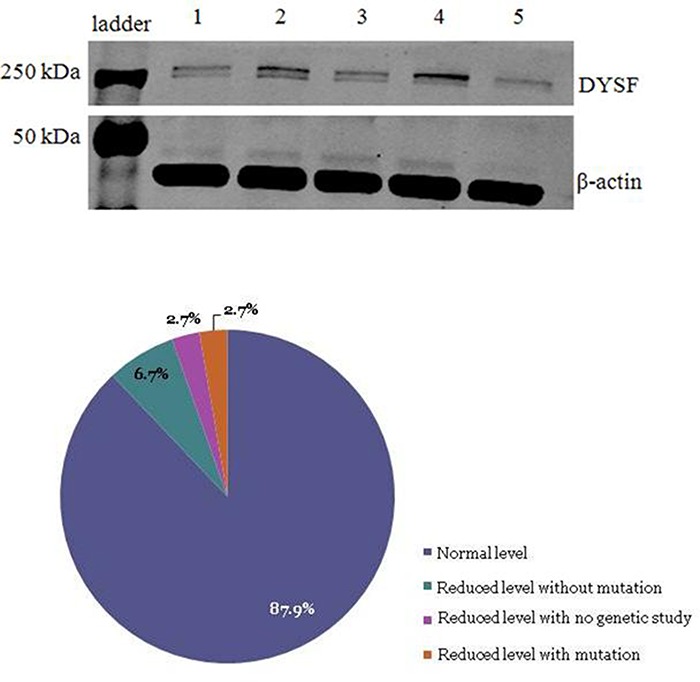
The study of dysferlin expression in monocytes of a cohort of 149 healthy volunteers showed an incidence of reduced levels (within the carrier range) of the protein higher than expected. However, only 2.7% of them presented a mutation in DYSF. DNA methylation was normal in all samples tested. Our results suggest that factors other than genetic or epigenetic changes can also influence dysferlin expression and that molecular analysis of DYSF must be performed to determine the carrier status of an individual.
Genetic and Epigenetic Characteristics of FSHD-Associated 4q and 10q D4Z4 that are Distinct from Non-4q/10q D4Z4 Homologs
- Pages: 998-1010
- First Published: 17 May 2014
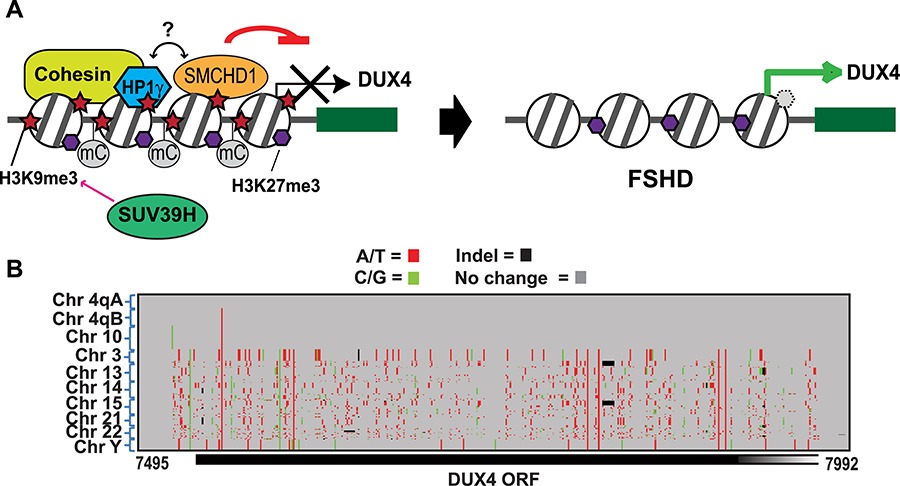
Linking epigenetic alteration and DUX4 expression in FSHD. (A) SMCHD1 is a component of the H3K9me3 heterochromatin at D4Z4 that represses the DUX4 gene. The loss of H3K9me3,an epigenetic change directly linked to FSHD,upregulatesDUX4. (B) In contrast to D4Z4 on chromosomes 4q and 10q, D4Z4 homologs on seven other chromosomes are highly heterogeneous with frequent interruptions of the DUX4 ORF and do not undergo the epigenetic alteration in FSHD. This underscoresthe unique characteristics of 4q/10q D4Z4 among the related repeats.
Identification of Novel Craniofacial Regulatory Domains Located far Upstream of SOX9 and Disrupted in Pierre Robin Sequence
- Pages: 1011-1020
- First Published: 16 June 2014

The craniofacial regulatory potential of non-coding DNA upstream of SOX9 has not been fully mapped. ChIP-Seq analysis led to the identification of candidate SOX9 craniofacial enhancers. In transgenic zebrafish embryos, one of these elements, peak 17, drove expression of a GFP reporter gene in the pharyngeal arches. This element falls with deletions observed in Pierre Robin sequence (PRS) patients; loss of the element in these patients may result in abnormal expression of SOX9, leading to the craniofacial phenotype of PRS.
Toward Male Individualization with Rapidly Mutating Y-Chromosomal Short Tandem Repeats
- Pages: 1021-1032
- First Published: 10 June 2014
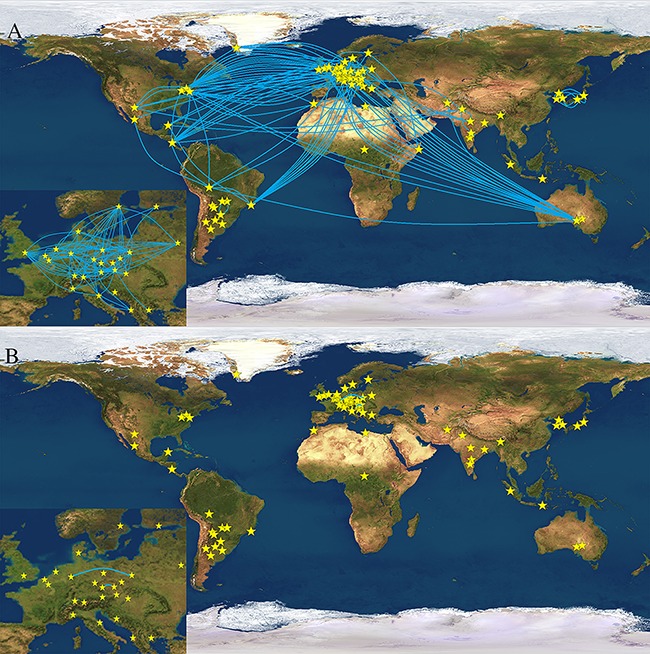
The value of 13 rapidly-mutating (RM) Y-STRs for differentiating male individuals is investigated in 14,644 related and unrelated men sampled from 111 worldwide populations. Over 99% of the 12,272 unrelated men were completely individualized. Of the 2,378 father-son pairs, 27% were separated. Figure: blue lines represent Y-STR haplotypes shared between population pairs in a subset of 7,784 males from 65 populations. Almost all shared haplotypes defined by conventional 17 Yfiler Y-STRs (above) are resolved with the 13 RM Y-STRs (below).




