Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Palindrome-Related Mutations in Neurofibromatosis 1: a New Hot-Spot, at PATRR17
- Page: v
- First Published: 10 June 2014
Mutation Update and Genotype–Phenotype Correlations of Novel and Previously Described Mutations in TPM2 and TPM3 Causing Congenital Myopathies
- Pages: 779-790
- First Published: 01 April 2014
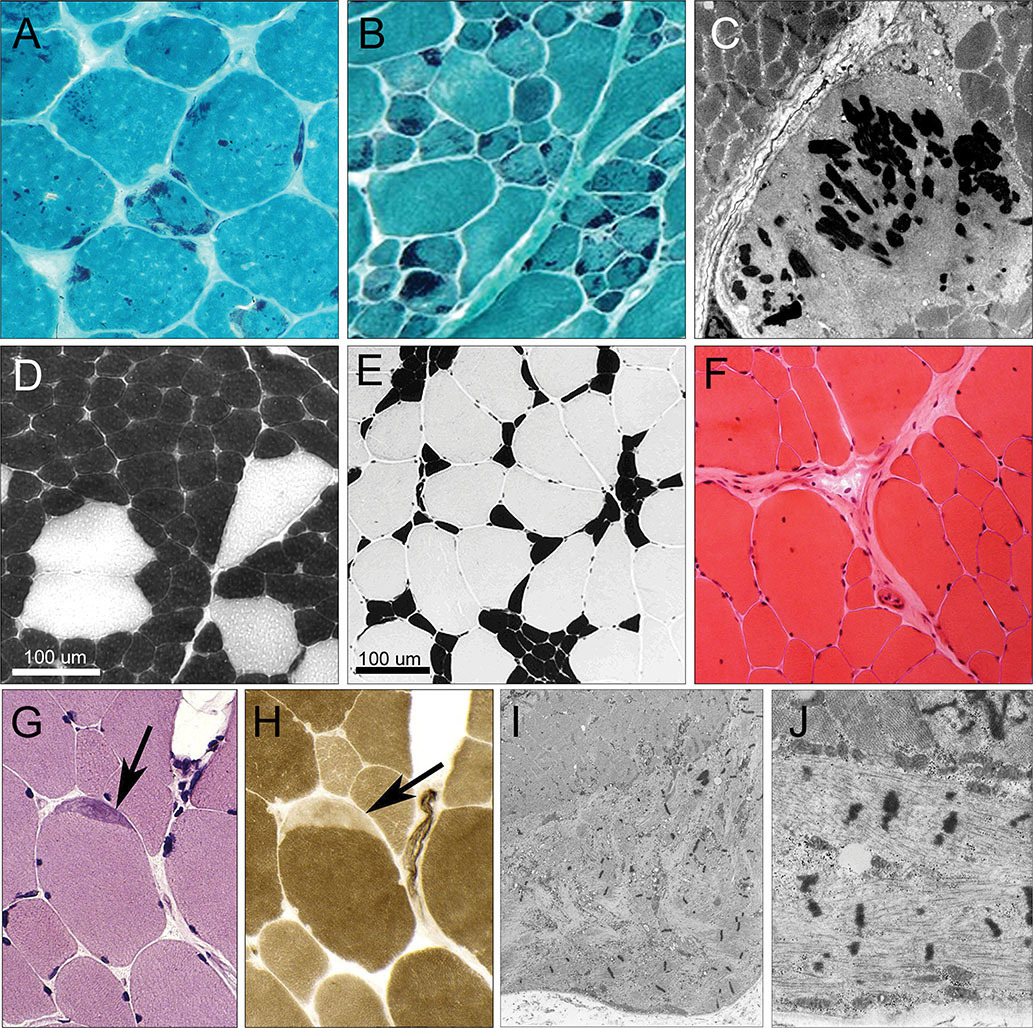
We present mutation update and genotype-phenotype correlations for novel (16) and previously reported (31) mutations of the TPM2 and TPM3 genes causing nemaline myopathy, cap myopathy, core-rod myopathy, congenital fibre-type disproportion, distal arthrogryposes and Escobar syndrome. Included are 93 families: 53 with TPM2 mutations and 40 with TPM3 mutations. Six mutations cause increased Ca2+ sensitivity resulting in hypercontractile phenotypes. Our in silico predictions show that most mutations affect tropomyosin-actin association or tropomyosin head-to-tail binding.
Mutation Databases for Inherited Renal Disease: Are They Complete, Accurate, Clinically Relevant, and Freely Available?
- Pages: 791-793
- First Published: 14 May 2014
Performance of Protein Disorder Prediction Programs on Amino Acid Substitutions
- Pages: 794-804
- First Published: 21 April 2014
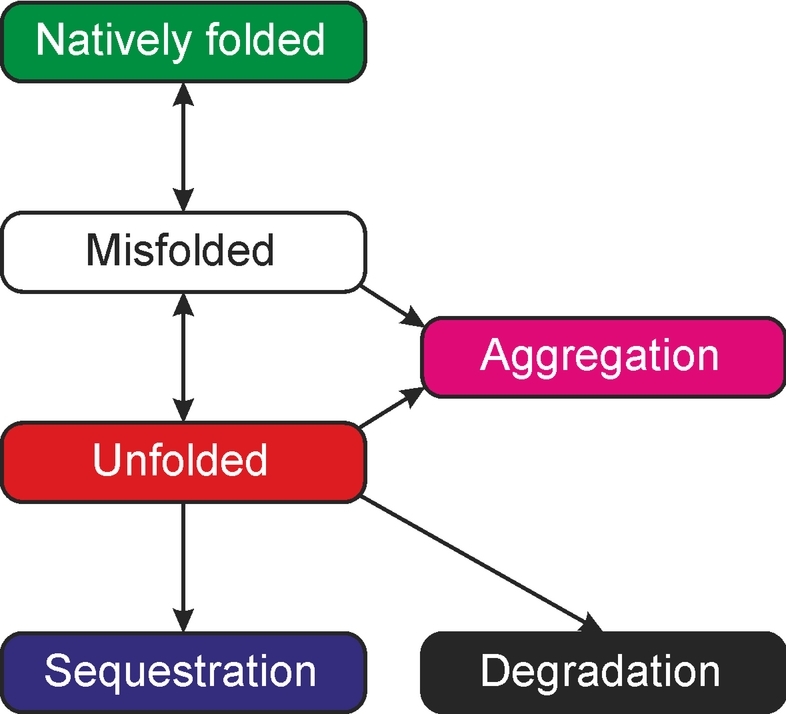
Disordered regions are proteins are rather common and variations in these proteins can have effects on structure. The performance of prediction methods to detect effects of single amino acid substitutions on protein order/disorder status was tested for 29 disorder predictors and versions with experimentally validated cases. These methods, which have been developed for detecting longer disordered segments, cannot reliably predict the effects of substitutions. A dedicated, machine learning -based tool, PON-Diso (http://structure.bmc.lu.se/PON-Diso), has superior performance with 70.5% success rate in cross-validation.
Identification of a Novel 5′ Alternative CFTR mRNA Isoform in a Patient with Nasal Polyposis and CFTR Mutations
- Pages: 805-808
- First Published: 14 March 2014
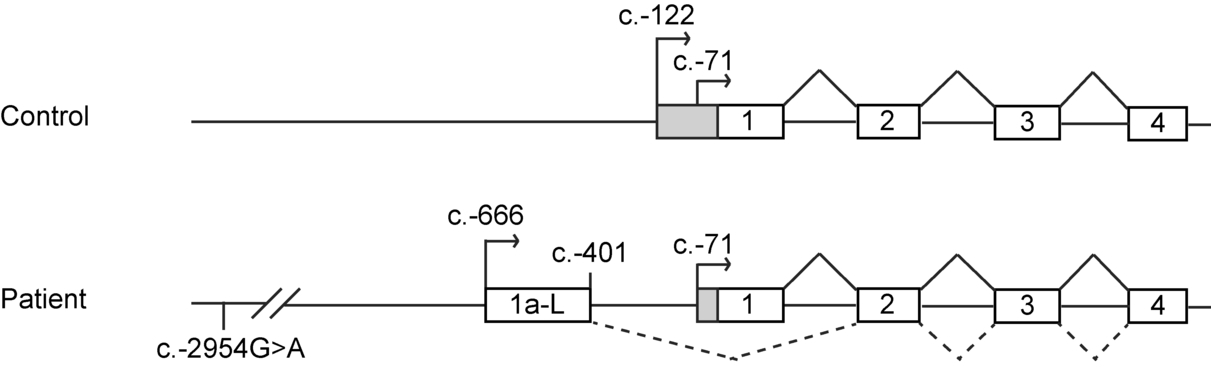
A novel 5' alternative CFTR transcript was identified in a 12y-old patient presenting with isolated nasal polyposis and being heterozygous for c.2551C>T (p.Arg851*). Its characterization was made after identification of the c.-2954G>A mutation which was shown to enhance promoter activity. The novel, presumably non-functional, transcript could represent a novel molecular CFTR defect associated with CFTR-related disorders.
Cantú Syndrome Resulting from Activating Mutation in the KCNJ8 Gene
- Pages: 809-813
- First Published: 02 April 2014
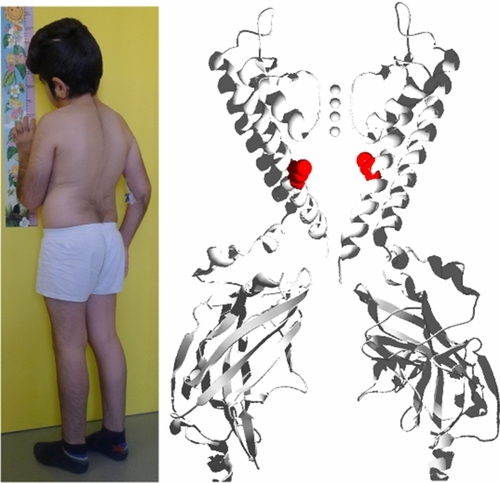
Cantu Syndrome (CS) is a rare multi-organ disorder, characterized by hypertrichosis, cranio-facial and musculo-skeletal abnormalities, lymphedema and a host of cardiovascular complications. We now show that, in addition to gain-of-function (GOF) in the ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channel regulatory sulfonylurea receptor subunit gene (ABCC9), CS can also result from GOF in the KATP pore-forming subunit gene (KCNJ8). This demonstrates a novel causal gene and confirms that CS features result from GOF in KATP channel activity, not from non-channel functions of ABCC9.
A Dominant Mutation in the Stereocilia-Expressing Gene TBC1D24 is a Probable Cause for Nonsyndromic Hearing Impairment
- Pages: 814-818
- First Published: 11 April 2014
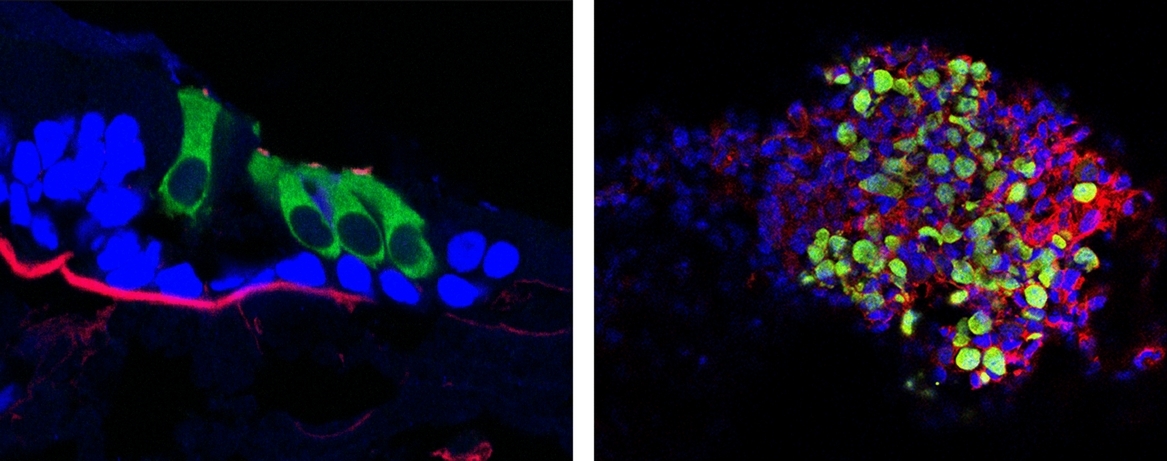
By linkage analysis and whole exome sequencing, we identified a p.Ser178Leu heterozygous mutation of TBC1D24 as a probable cause for the late-onset, progressive, non-syndromic hearing impairment in a dominant deaf family. In perinatal mouse cochlea, we detected a restricted expression of Tbc1d24 in the stereocilia of the hair cells as well as in the spiral ganglion neurons. Our findings may shed new light on the specific function of TBC1D24 in the inner ear.
TBC1D24 Mutation Causes Autosomal-Dominant Nonsyndromic Hearing Loss
- Pages: 819-823
- First Published: 11 April 2014
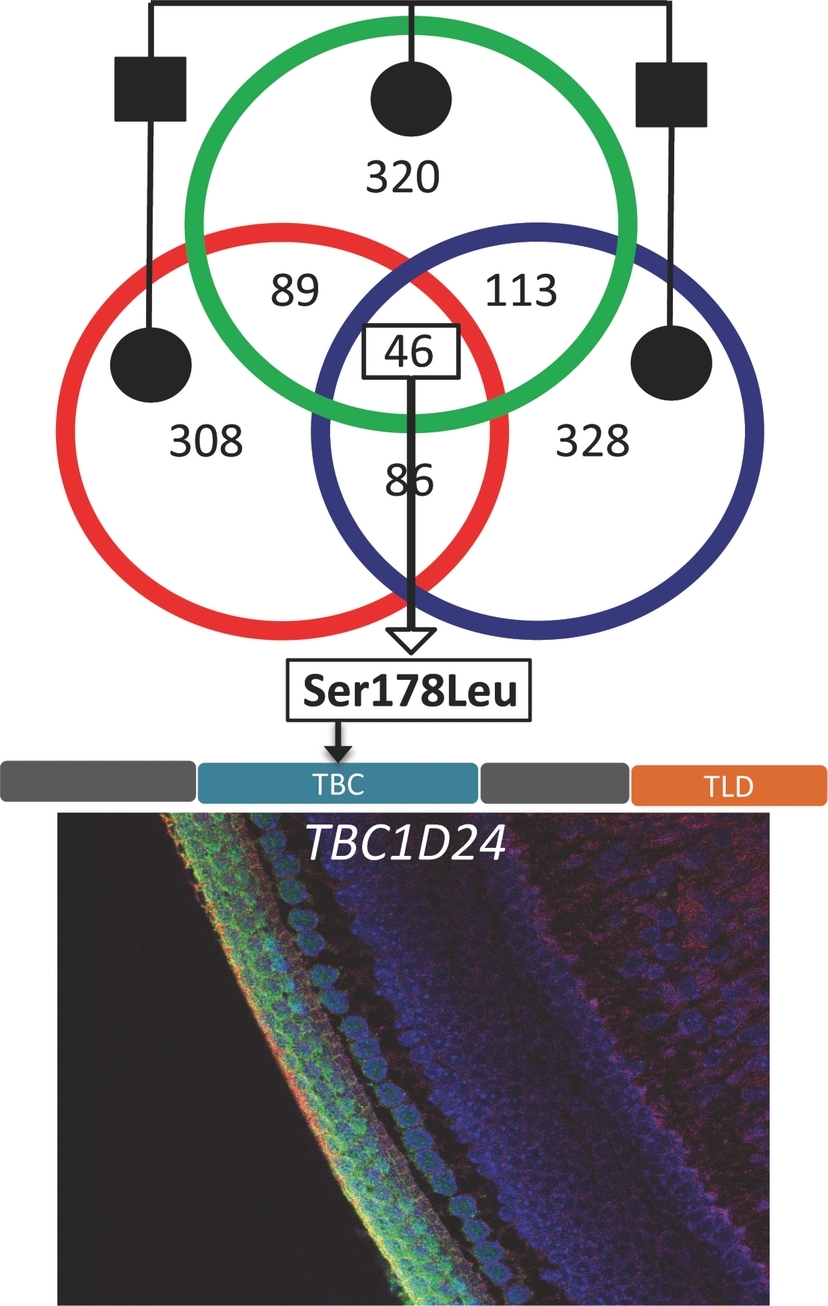
After excluding mutations in all genes implicated in non-syndromic hearing loss, we completed segregation mapping and whole exome sequencing on 7 and 3 persons, respectively. WES data were hard filtered to identify 46 variants shared by the 3 affecteds, only one of which mapped to a segregating genomic interval. The Ser178Leu variant in TBC1D24 is highly conserved across species. The transcribed gene is expressed in inner and outer hair cells in the P2 mouse cochlea (green; actin, red; DAPI, blue).
TCIRG1-Associated Congenital Neutropenia
- Pages: 824-827
- First Published: 17 April 2014
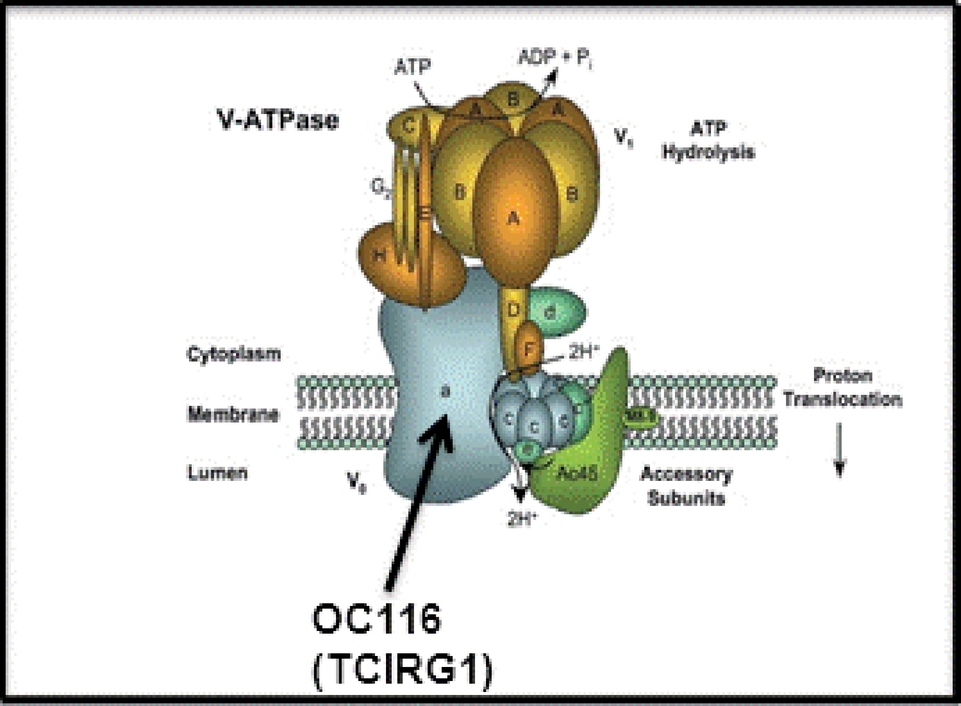
Model of VATPase showing that TClRGl protein is it's largest component. Homozygous mutations of TClRGl are a known cause of osteopetrosis. Heterozygous mutation of p.Arg736Ser in TClRGl is now associated with congenital neutropenia, presumable by impairing the differentiation or maturation or myeloid cells in the bone marrow.
CDKN2A Unclassified Variants in Familial Malignant Melanoma: Combining Functional and Computational Approaches for Their Assessment
- Pages: 828-840
- First Published: 22 March 2014
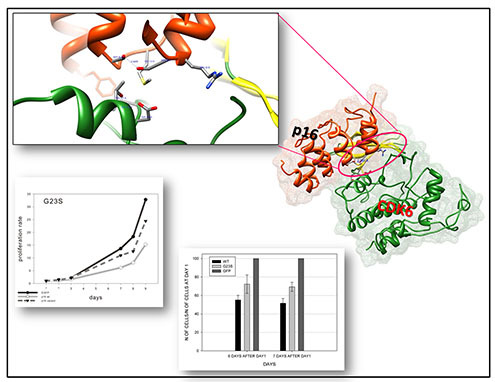
Our work tested an integrated model for the characterization of p16INK4a unclassified variants providing a robust tool for the interpretation of their structural and functional impact.
We
- assessed the ability of new in silico tools to discriminate neutral/deleterious p16INK4a variants;
- combined in silico/in vitro assays;
- used a Bayesian method to obtain a final classification
Evaluation of in silico/functional data disclosed a high agreement for 15/16 variants, suggesting that this approach could represent a pilot study.
Molecular Analysis, Pathogenic Mechanisms, and Readthrough Therapy on a Large Cohort of Kabuki Syndrome Patients
- Pages: 841-850
- First Published: 13 March 2014
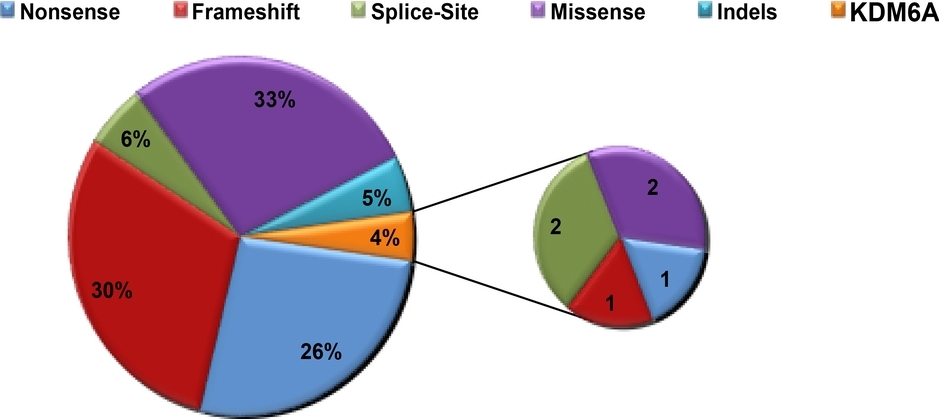
In this report, we have expanded the spectrum of mutations of KMT2D and KDM6A genes by analysing our cohort of 303 Kabuki patients by direct sequencing, MLPA and quantitative PCR. Based on KMT2D biological role, we designed functional studies that highlighted the haploinsufficiency of KMT2D as one of the mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of the disease. Moreover, we provided the first preliminary proof-of-concept that occurring nonsense mutations in KMT2D and KDM6A can be effectively suppressed and the functional endogenous protein level and biological activity of KMT2D and KDM6A proteins restored.
STK11 Domain XI Mutations: Candidate Genetic Drivers Leading to the Development of Dysplastic Polyps in Peutz–Jeghers Syndrome
- Pages: 851-858
- First Published: 20 March 2014
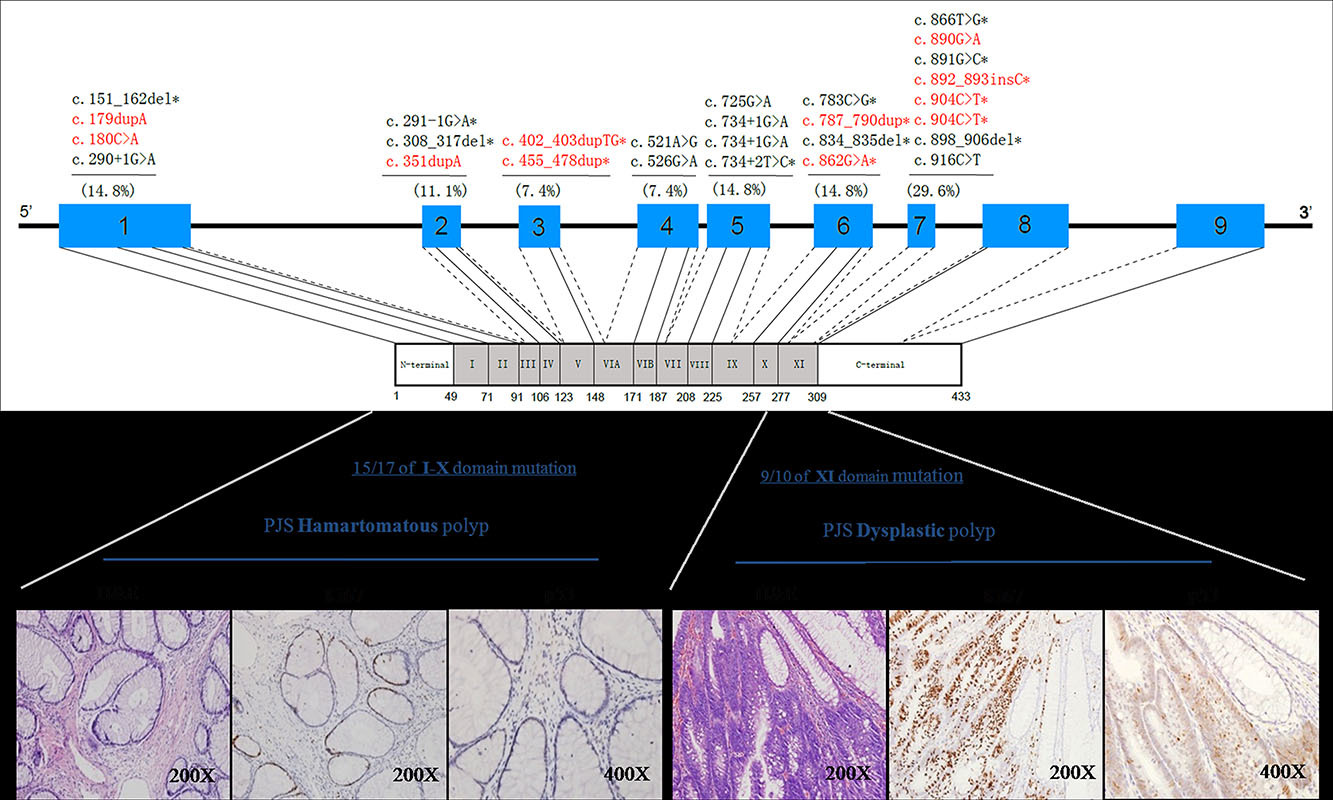
We directly interrogated STK11 gene mutations in a large cohort of 116 Chinese PJS patients representing 52 index cases. The result identified an overrepresentation of mutations within STK11's kinase domain XI and demonstrated that these mutations were strongly associated with the development of dysplastic GI polyps. These findings may prove valuable for patient counseling and provide a novel testable hypothesis for shedding light on our understanding of the development of cancer in this syndrome.
Cadherin 5 is Regulated by Corticosteroids and Associated with Central Serous Chorioretinopathy
- Pages: 859-867
- First Published: 24 March 2014
Novel Mutations Widen the Phenotypic Spectrum of Slow Skeletal/β-Cardiac Myosin (MYH7) Distal Myopathy
- Pages: 868-879
- First Published: 24 March 2014
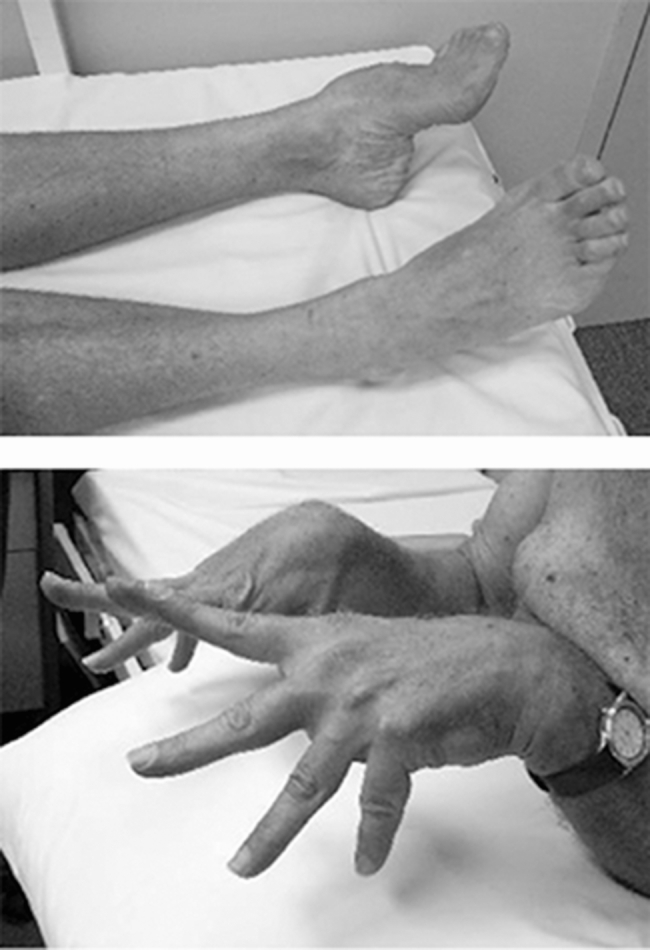
Twenty one previously unpublished families were shown to have an MYH7 gene mutation causing Laing distal myopathy (MPD1). Typical findings included footdrop and dropped fingers. Cardiac involvement was seen in 9, and spinal involvement in 12. Thirteen of these families had multiple affected members, but eight cases had no family history and de novo mutation was proven in four. A mosaic carrier was also identified. Twelve of the 21 mutations were novel.
Functional Studies of Tyrosine Hydroxylase Missense Variants Reveal Distinct Patterns of Molecular Defects in Dopa-Responsive Dystonia
- Pages: 880-890
- First Published: 21 April 2014
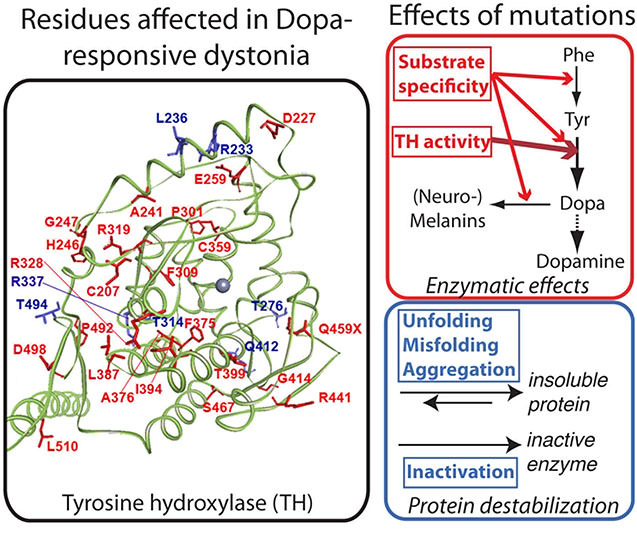
Dopa-responsive dystonia may be caused by inactivating mutations in tyrosine hydroxylase (TH). We review clinical and biochemical findings in such patients and their corresponding TH mutations. We also report a detailed investigation of 23 TH mutations previously not studied. Disease-associated TH mutations were found to affect different properties of the enzyme, including its thermal stability, solubility, enzyme activity, or substrate specificity. This exhaustive study of TH variants may guide future work to develop new and individualized therapies for dystonia patients.
Palindrome-Mediated and Replication-Dependent Pathogenic Structural Rearrangements within the NF1 Gene
- Pages: 891-898
- First Published: 23 April 2014
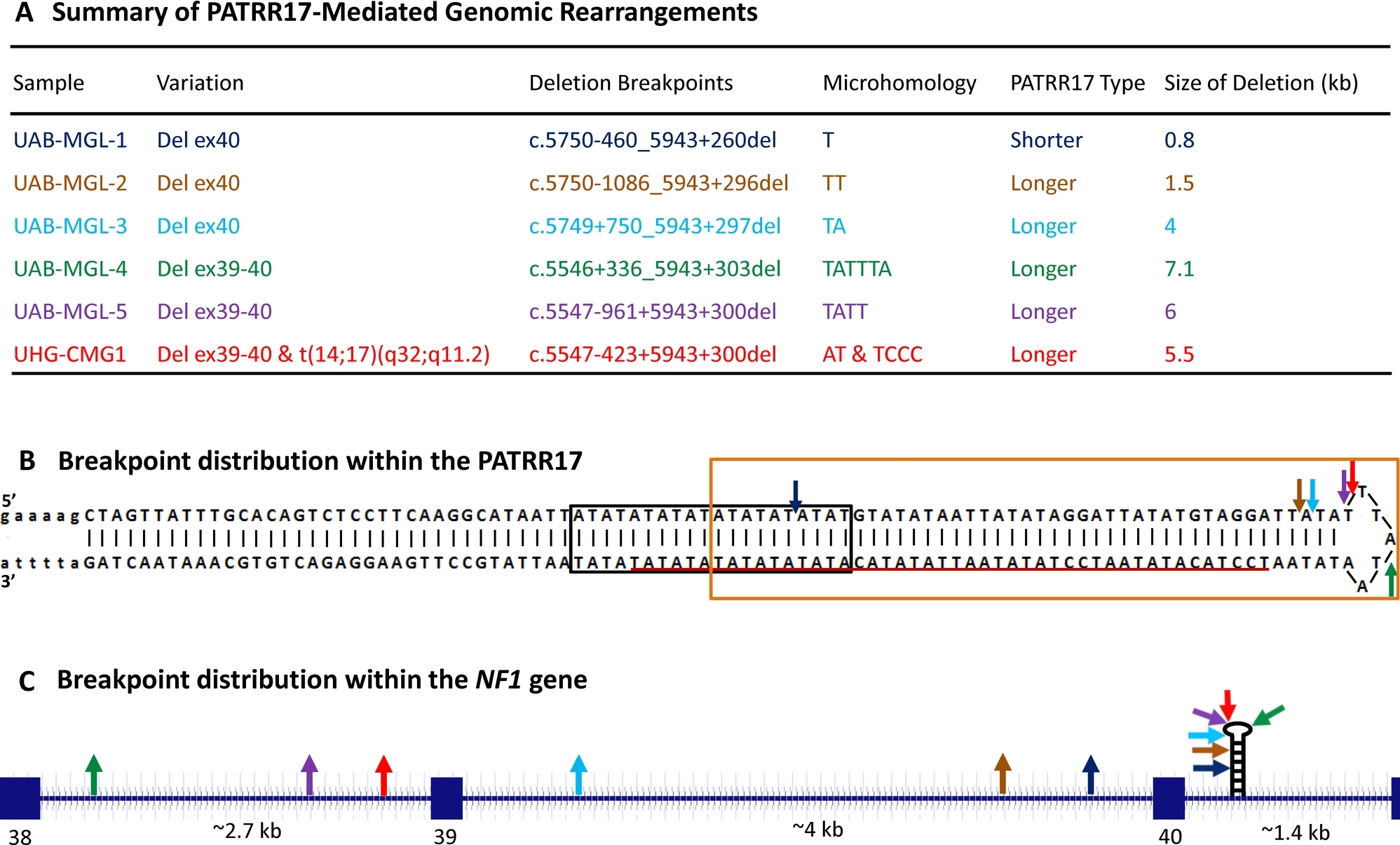
In this study, we have identified five deletions and one chromosomal translocation t(14;17)(q32;q11.2) mediated by a 197-bp long palindromic AT-rich repeat (PATRR17) within the NF1 gene. Although several previous studies indicated a purely replication-independent mechanism for PATRR-mediated translocations, the PATRR17-mediated intragenic deletions as well as the translocation are likely the result of a replication-dependent mechanism. Furthermore, we identified the PATRR17, especially the loop of PATRR17, as a significant intragenic rearrangement hotspot within the NF1 gene.
An Evaluation of Copy Number Variation Detection Tools from Whole-Exome Sequencing Data
- Pages: 899-907
- First Published: 05 March 2014
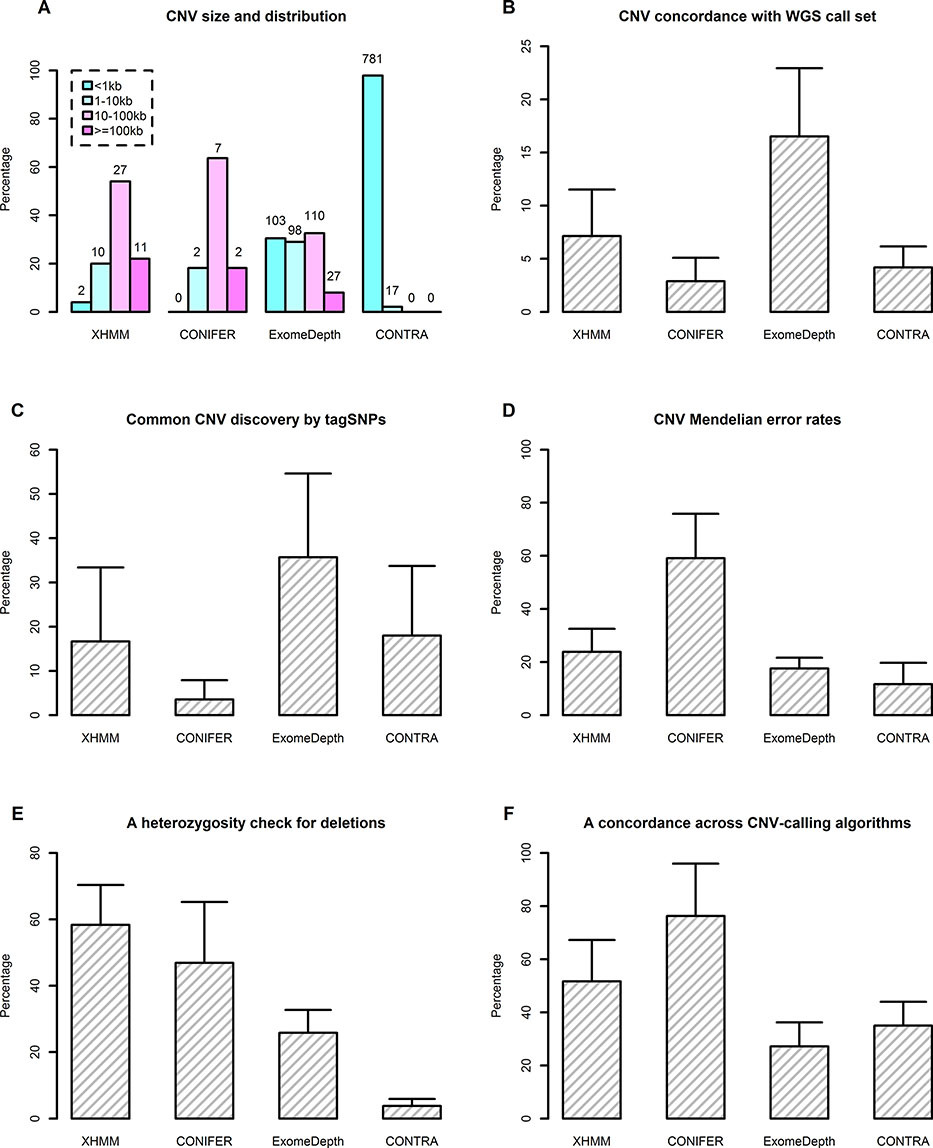
Several CNV calling tools have recently been developed on the basis of WES data. However, the comparative performance of these tools using real data remains unclear. In this study, we provided a comprehensive and objective comparison of several well-known detection tools designed for WES data. We found that the sensitive and accurate detection of CNVs in WES data remains challenging. Our evaluation results will assist researchers in choosing the most suitable tools for their research needs.




