Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover
Cover Image, Volume 118, Number 5, May 2017
- Page: i
- First Published: 19 March 2017
Cover: The cover image, by Anne E. Cress., is based on the Article Characterization of Laminin Binding Integrin Internalization in Prostate Cancer Cells, DOI: 10.1002/jcb.25673.
Issue Information
Table of Contents, Editor's Choice, Features
- Pages: 935-941
- First Published: 19 March 2017
Prospects
Environmental Impact on Intestinal Stem Cell Functions in Mucosal Homeostasis and Tumorigenesis
- Pages: 943-952
- First Published: 01 September 2016
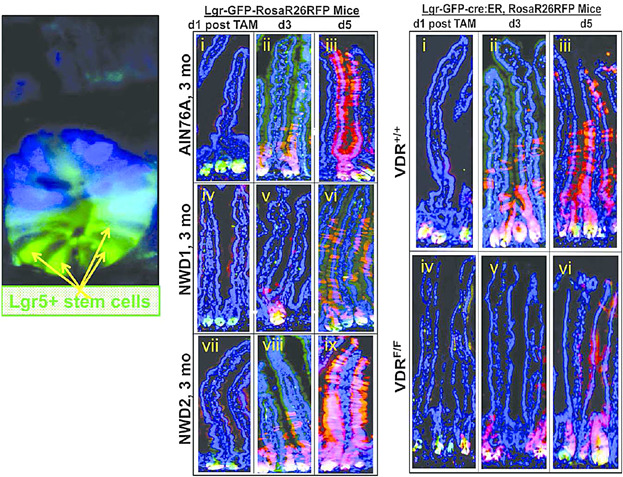
The intestinal mucosa is a rapidly turning-over tissue, completely renewing approximately every 5 days. Intestinal stem cells that maintain the mucosa and that can act as tumor initiating cells can be contributed by multiple compartments at or near the crypt base. Environmental factors—especially dietary factors—may play a major role in determining the complement of cell compartments that contribute functioning stem cells.
Precocious Phenotypic Transcription-Factor Expression During Early Development
- Pages: 953-958
- First Published: 03 September 2016
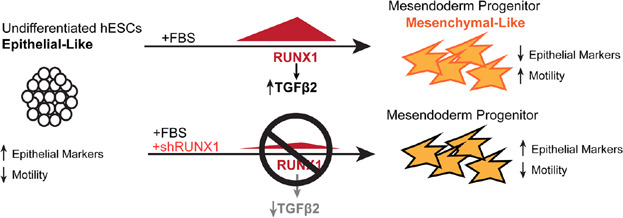
A novel role for phenotypic transcription factors in very early differentiation was recently observed and merits further study to elucidate what role this precocious expression may have in development. The RUNX1 transcription factor exhibits selective and transient upregulation during early mesenchymal differentiation.
Therapeutic Potential of Small Molecule Inhibitors
- Pages: 959-961
- First Published: 04 November 2016
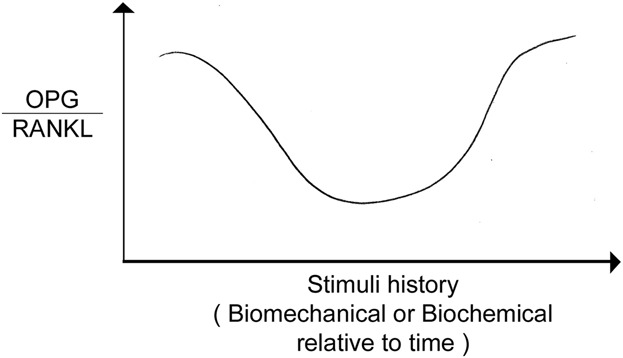
The “Mechanostat” Principle and the Osteoprotegerin—OPG/RANKL/RANK System PART II. The Role of the Hypothalamic—Pituitary Axis
- Pages: 962-966
- First Published: 15 November 2016
Articles
AQP2-Induced Acceleration of Renal Cell Proliferation Involves the Activation of a Regulatory Volume Increase Mechanism Dependent on NHE2
- Pages: 967-978
- First Published: 18 May 2016
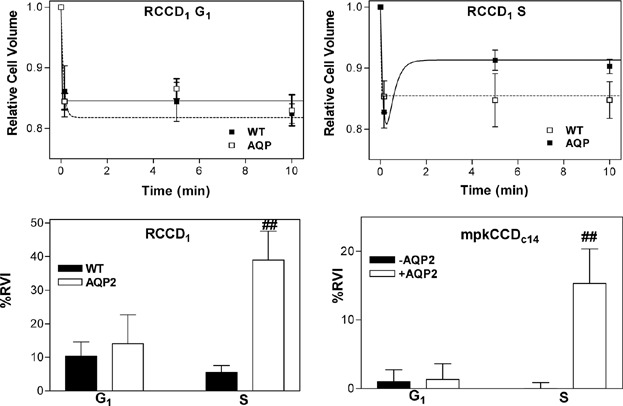
We have previously shown in renal cells that expression of the water channel Aquaporin 2 (AQP2) increases the rate of cell proliferation. In this study, we investigated if the isoform 2 of the Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE2), the main ion transporter involved in RVI responses, contributed to the AQP2-increased renal cell proliferation. Our results showed that in AQP2-expressing cells NHE2 expression and activity are higher leading to an activation of a NHE2-mediated RVI response in the S phase of the cell cycle, which may be implicated in the increase the rate of cell proliferation.
Cane Toad Skin Extract—Induced Upregulation and Increased Interaction of Serotonin 2A and D2 Receptors via Gq/11 Signaling Pathway in CLU213 Cells
- Pages: 979-993
- First Published: 13 June 2016
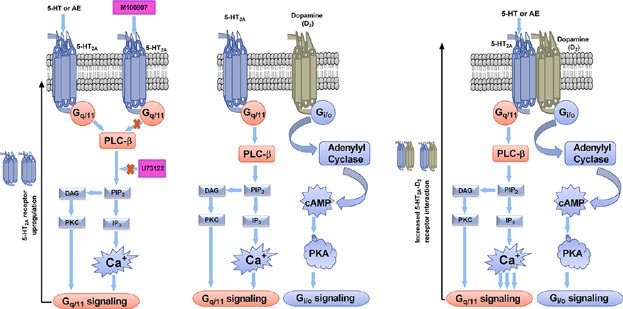
Aqueous extracts (AE) of Australian cane toad skins induce upregulation of 5-HT2A and D2 receptos and enhance their interaction in a neuronal cell (CLU213) in vitro via Gq/11 G-protein PLCβ signaling pathway and c-FOS transcription factor activation. This could provide a molecular mechanism to develop AE of Australian cane toad skins as potential novel drug candidates to ameliorate OCD symptoms.
Glucose Promotes a Pro-Oxidant and Pro-Inflammatory Stromal Microenvironment Which Favors Motile Properties in Breast Tumor Cells
- Pages: 994-1002
- First Published: 12 July 2016
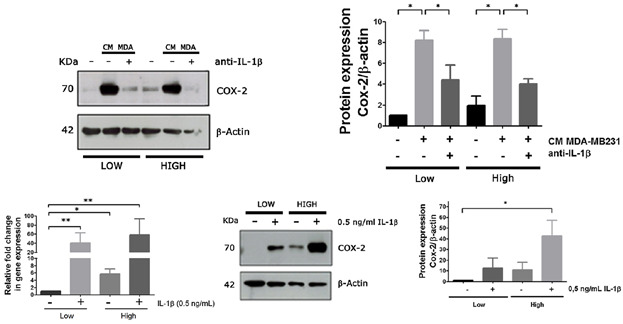
Hyperglycemic condition favors the establishment of a pro-inflammatory and pro-oxidant environment characterized by the induction of the COX-2/PGE2 axis. Stromal-derived PGE2, acting as a stimulator of IL-1 epithelial expression was one the factors that promotes the acquisition of motile properties by epithelial cells.
Elucidating the Role of Protandim and 6-Gingerol in Protection Against Osteoarthritis
- Pages: 1003-1013
- First Published: 27 July 2016
In human osteoarthritic chondrocytes, both protandim and 6-gingerol block the expression of a number of factors involved in osteoarthritis process, through Nrf2 activation. In mouse model of osteoarthritis, the intraarticular injection of protandim attenuates cartilage degradation.
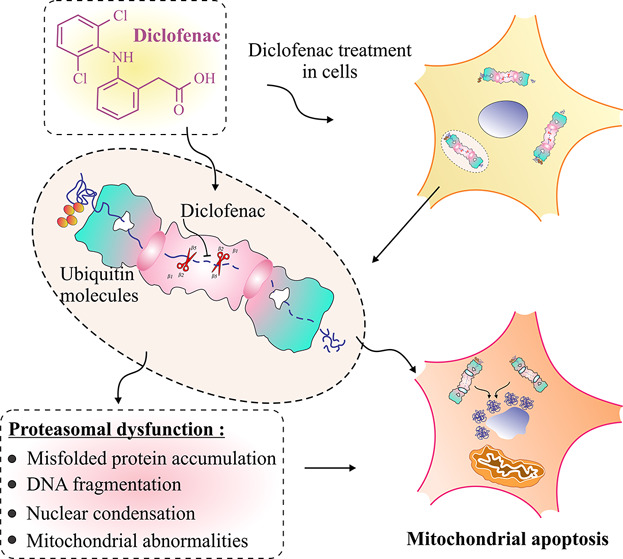
Proteasomal Dysfunction Induced By Diclofenac Engenders Apoptosis Through Mitochondrial Pathway
- Pages: 1014-1027
- First Published: 02 August 2016
Diphenyl Diselenide Reduces Oxidative Stress and Toxicity Caused by HSV-2 Infection in Mice
- Pages: 1028-1037
- First Published: 02 August 2016
Characterization of Laminin Binding Integrin Internalization in Prostate Cancer Cells
- Pages: 1038-1049
- First Published: 10 August 2016
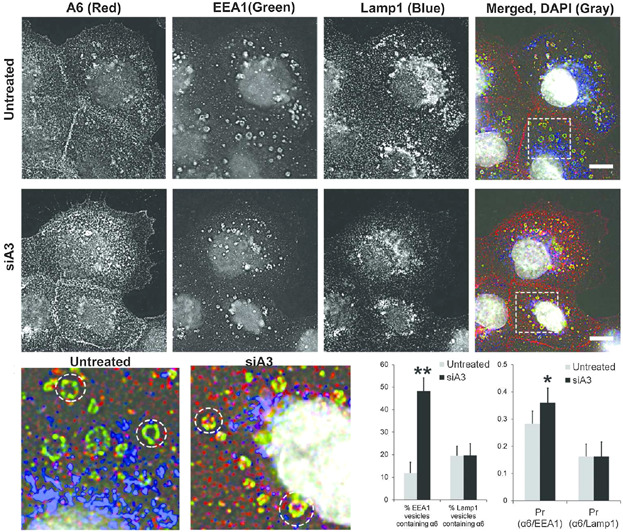
We developed a rate kinetic model of internalization and determined the basal internalization rates of laminin binding integrins (α3 and α6) to be significantly different. Coordination existed between their internalization such that, the loss of α3 integrin expression increased the internalization of α6 integrin to early endosomes and cell–cell locations. The results are important in the context of collective migration during epithelial tumor dissemination and metastasis using α6 and α3 integrins.
Absence of the Vitamin D Receptor Inhibits Atherosclerotic Plaque Calcification in Female Hypercholesterolemic Mice
- Pages: 1050-1064
- First Published: 27 August 2016
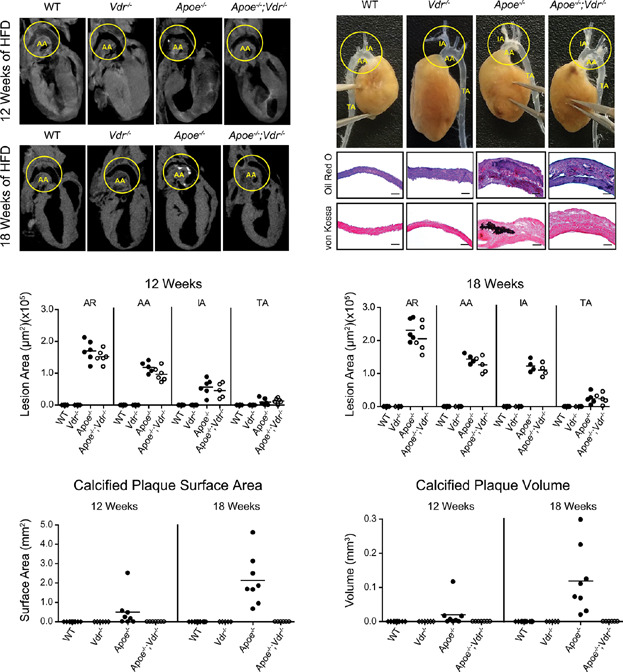
Loss of the vitamin D receptor altered mineral homeostasis, enhanced the inflammatory state, and reduced hyperlipidemic profiles in Apoe−/−;Vdr−/− mice fed a high-fat diet. While these effects of VDR loss did not alter the rate of plaque progression in the double null mice, they fully prevented calcification as assessed by µCT and histological analyses. Thus, vitamin D and its receptor play an integral role in establishing conditions under which atherosclerotic plaques undergo the calcification process.
Regulation of Adipogenesis Through Differential Modulation of ROS and Kinase Signaling Pathways by 3,4′-Dihydroxyflavone Treatment
- Pages: 1065-1077
- First Published: 31 August 2016
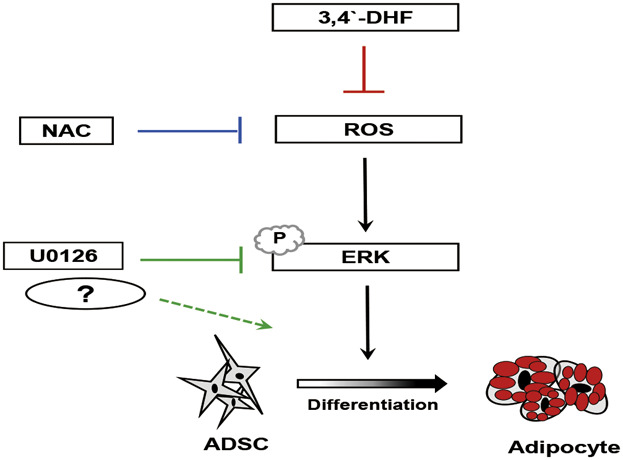
Treatment of the naturally derived flavonoid, 3,4′-dihydroxyflavone (3,4′-DHF) suppressed adipogenesis in murine 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes and equine adipose-derived stromal cells (eADSCs) through differential modulation of ROS and kinase signaling pathways. These results suggest that the flavonoid can be used to regulate adipogenesis in ADSCs, which has potential therapeutic application in regenerative medicine or health care for humans and many sport or companion animals.
In Vivo Characterization of I91T Sod2 Polymorphism of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Pages: 1078-1086
- First Published: 01 September 2016
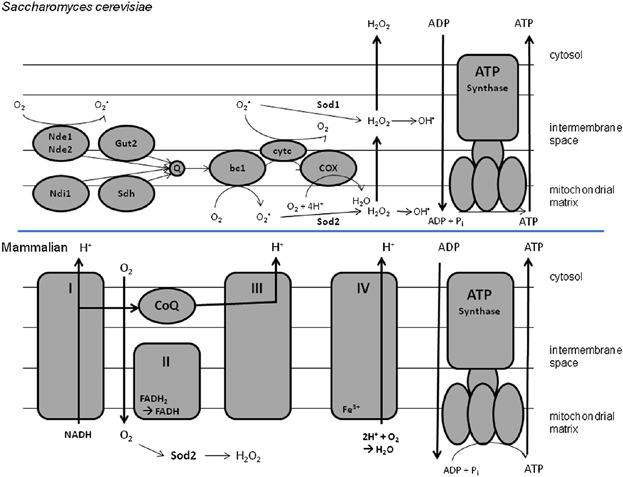
The mitochondrial antioxidant enzyme Mn-Superoxide Dismutase (Sod2) is essential for mammalian survival. Sod2 and the mutant Sod2 I91T, which corresponds to the human mutant Sod2 I82T, were cloned in sod2Δ strain. Although overexpression of Sod2 containing I91T mutation allows higher cell viability, longevity of cells is hampered, showing that in long-term this mutation is not neutral.
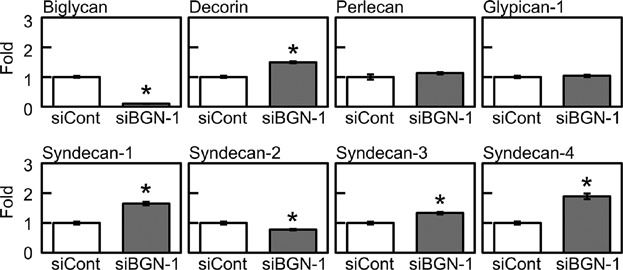
Biglycan Intensifies ALK5–Smad2/3 Signaling by TGF-β1 and Downregulates Syndecan-4 in Cultured Vascular Endothelial Cells
- Pages: 1087-1096
- First Published: 01 September 2016
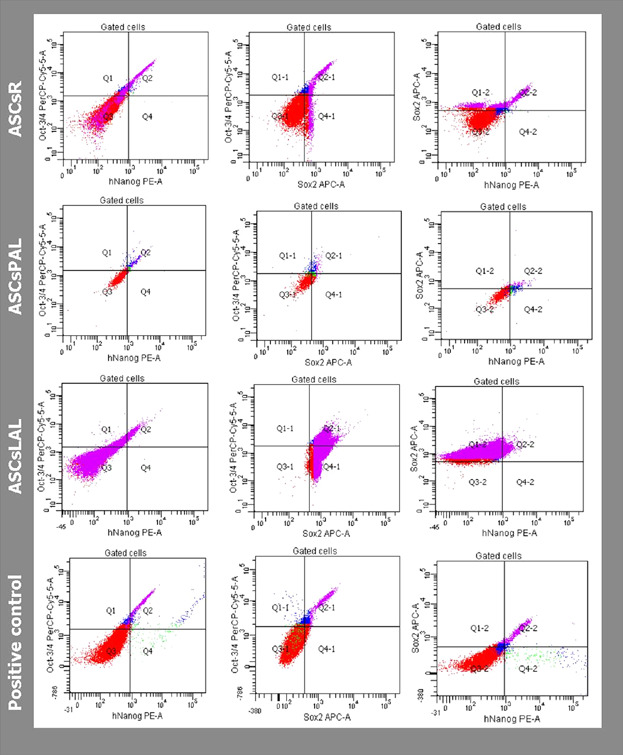
Does the Harvesting Technique Affect the Properties of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells?—The Comparative Biological Characterization
- Pages: 1097-1107
- First Published: 08 September 2016
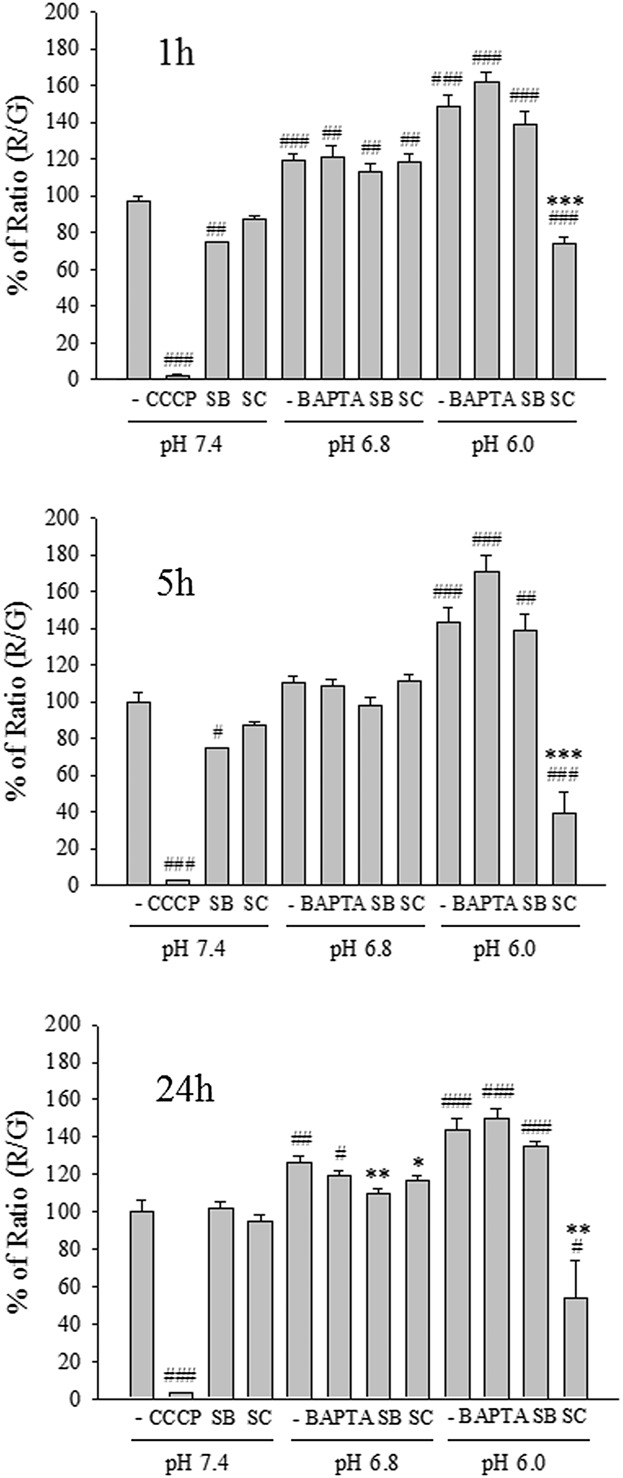
Perturbation of Akt Signaling, Mitochondrial Potential, and ADP/ATP Ratio in Acidosis-Challenged Rat Cortical Astrocytes
- Pages: 1108-1117
- First Published: 08 September 2016
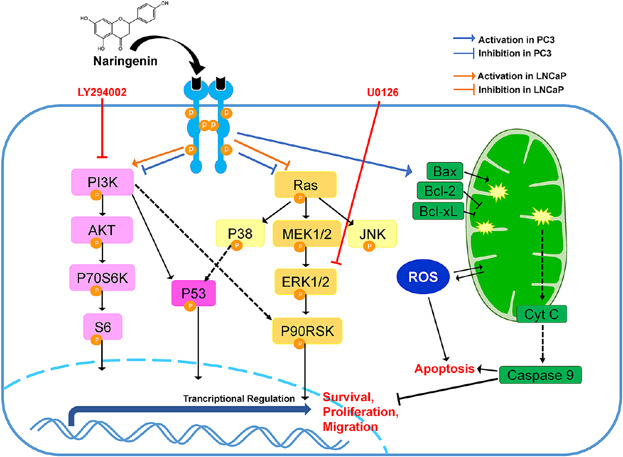
Naringenin-Induced Apoptotic Cell Death in Prostate Cancer Cells Is Mediated via the PI3K/AKT and MAPK Signaling Pathways
- Pages: 1118-1131
- First Published: 08 September 2016
A Novel Peptide Derived From Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator Potently Inhibits Angiogenesis and Corneal Neovascularization
- Pages: 1132-1143
- First Published: 12 September 2016
A novel peptide derived from a beta-sheet motif of the kringle 2 domain of tPA effectively inhibits angiogenesis and it can be used for treatment of corneal neovascularization by targeting VEGF and non-VEGF pathways.
Sulfhydryl-Based Inhibition of δ-ALA-D and Na+, K+-ATPase Activities Depends on the Organoselenium Group Bonded to the Isoquinoline
- Pages: 1144-1150
- First Published: 15 September 2016

Compounds substituted with electron-withdrawing groups at the selenium-bonded aromatic ring inhibited δ-ALA-D and Na+, K+-ATPase; Enzymatic activities were restored by a reducing agent, suggesting the involvement of sulfhydryl residues in the inhibition. 3-Phenyl-4-(phenylseleno) isoquinoline, which has documented pharmacological properties, had no toxicological effects on the parameters evaluated.
Extracellular Phosphate Induces the Expression of Dentin Matrix Protein 1 Through the FGF Receptor in Osteoblasts
- Pages: 1151-1163
- First Published: 17 September 2016
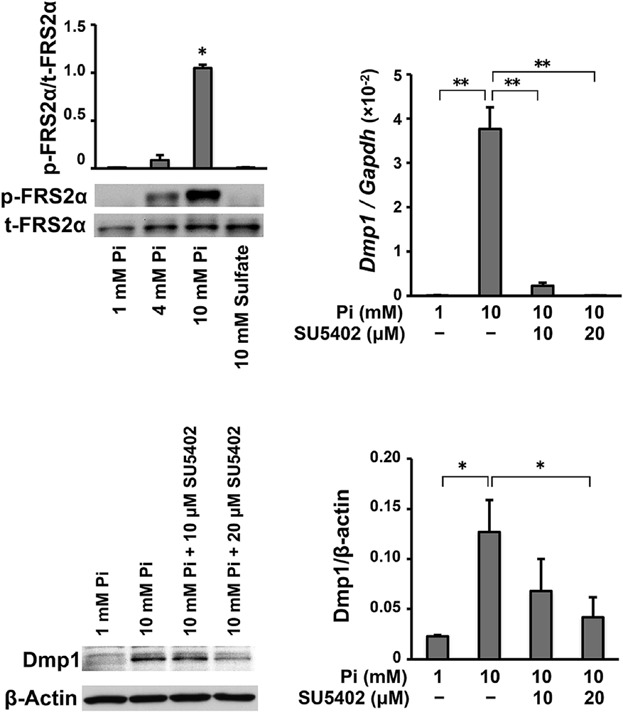
We found that elevated extracellular Pi strongly induced the expression of dentin matrix protein 1 (Dmp1) in osteoblasts and explored its underlying mechanism. Elevated extracellular Pi resulted in the phosphorylation of FRS2α, and an inhibitor against FGFR abolished the up-regulation of Dmp1 induced by elevated Pi. These results suggest the close relationship between the signaling evoked by elevated extracellular Pi and FGF/FGFR signaling.
Proteomic Profiling Reveals the Induction of UPR in Addition to DNA Damage Response in HeLa Cells Treated With the Thiazolo[5,4-b]Quinoline Derivative D3ClP
- Pages: 1164-1173
- First Published: 29 September 2016
Detection of FLT3/TKD and IDH1 Mutations in Pakistani Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients by Denaturing HPLC
- Pages: 1174-1181
- First Published: 13 October 2016
Prediction of B Cell Epitopes Among Hantavirus Strains Causing Hemorragic Fever With Renal Syndrome
- Pages: 1182-1188
- First Published: 17 October 2016
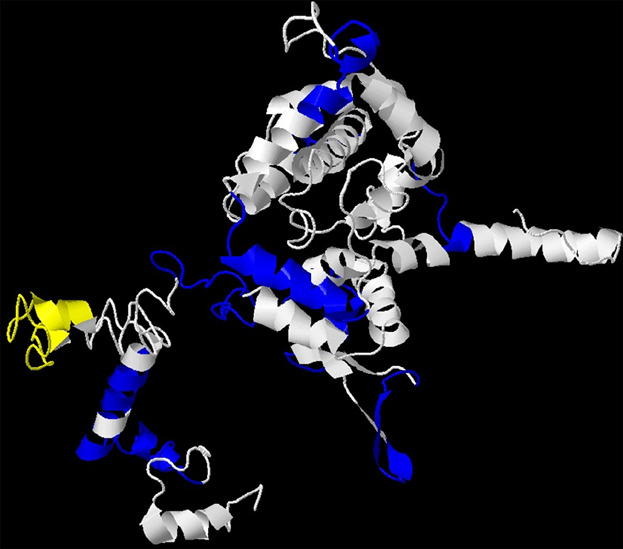
We reported our characterization of the sequence diversity of HFRS strains, 3D structure of Hantaan N protein, and B-cell epitopes on this molecule. We identified 20 amino acid sequence length peptide for development of geographic region-specific immunoassays like EIAs for antibody detection, monoclonal antibody development, and immunoblots (line immunoassay).
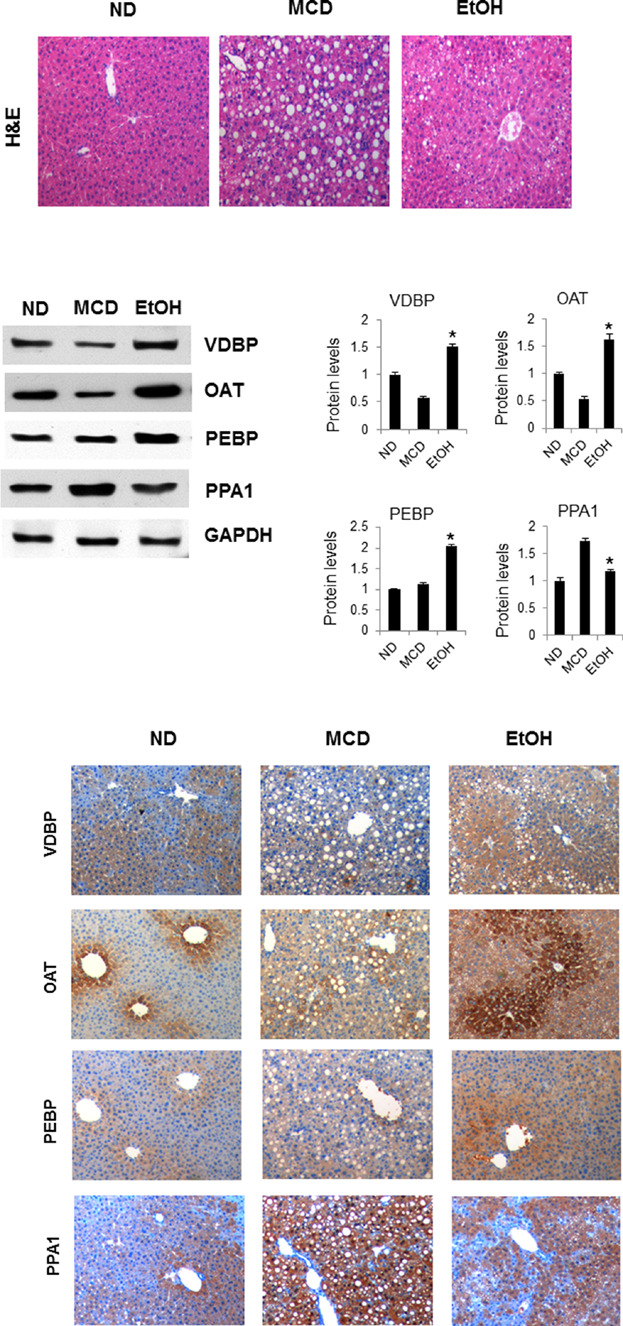
New Potential Biomarker Proteins for Alcoholic Liver Disease Identified by a Comparative Proteomics Approach
- Pages: 1189-1200
- First Published: 20 October 2016
Generation of Immortalized Equine Chondrocytes With Inducible Sox9 Expression Allows Control of Hypertrophic Differentiation
- Pages: 1201-1215
- First Published: 27 October 2016
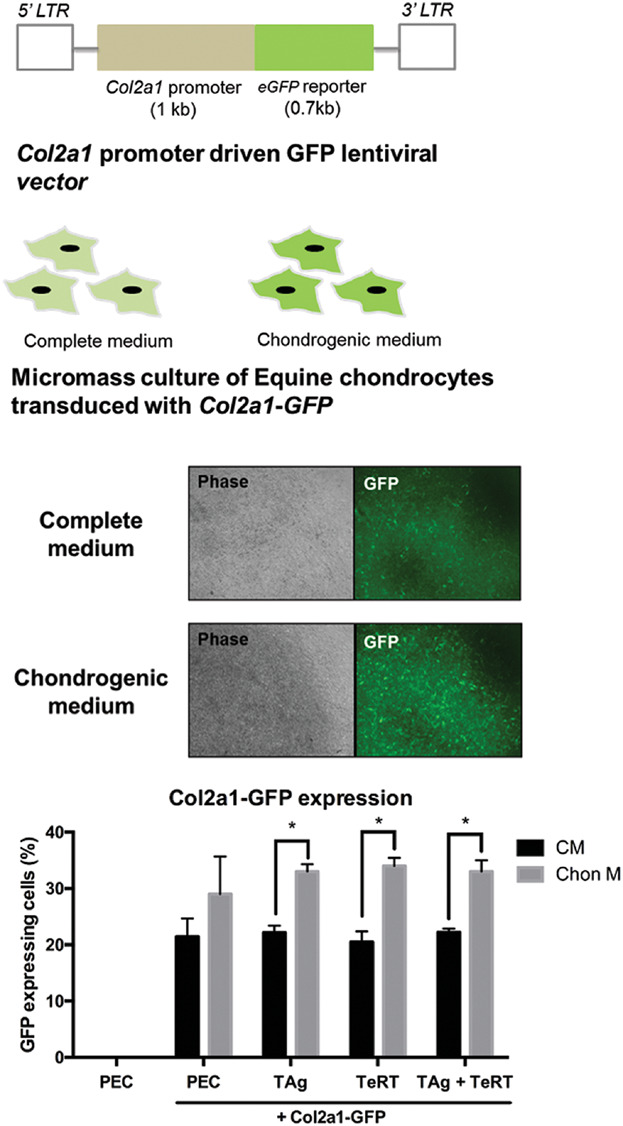
In this study, the SV40 large T antigen and human telomerase reverse transcriptase were employed to immortalize pooled equine chondrocytes through lentiviral vector mediated transduction either singly or on combination. Transformed chondrocytes proliferated stably over multiple passages, but resulted in significantly lower expression of chondrocyte specific collagen II mRNA (P < 0.0001) and up regulation of the hypertrophic marker collagen X (P < 0.0001) in three dimensional cultures whilst modulation of sox9 expression enabled control of hypetrophic characteristics.
Phosphofructokinase-P Modulates P44/42 MAPK Levels in HeLa Cells
- Pages: 1216-1226
- First Published: 28 October 2016
Enhancement of Muramyl Dipeptide-Dependent NOD2 Activity by a Self-Derived Peptide
- Pages: 1227-1238
- First Published: 28 October 2016
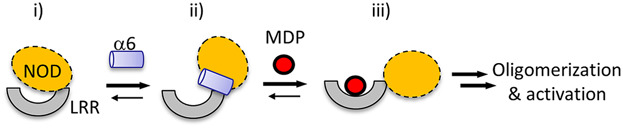
The Crohn's disease-associated mutation, R702W, in NOD2 lowers the activity the molecule by an unknown mechanism. We show that a NOD2 derived peptide containing the amino acid binds the ligand binding, regulatory domain, suggesting the residue is involved in autoinhibition. A synthetic peptide that competes with the interaction increases ligand-dependent NOD2 activity, showing that the receptor activity may be modulated using an allosteric regulator.
P-Glycoprotein Inhibition Sensitizes Human Breast Cancer Cells to Proteasome Inhibitors
- Pages: 1239-1248
- First Published: 04 November 2016
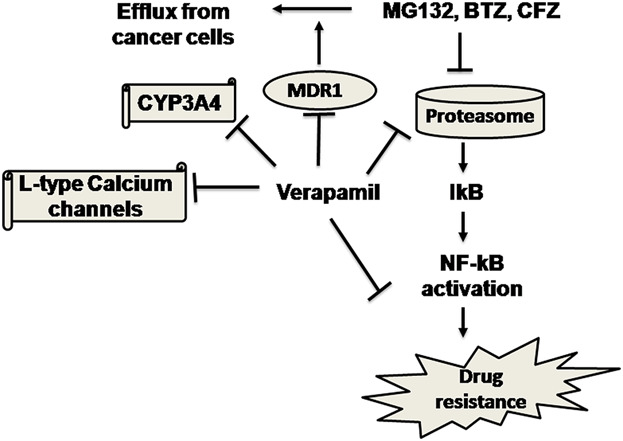
FDA approved proteasome inibitors such as bortezomib and carfilzomib have limited potency in triple negative breast cancer. Here we show that P-glygoprotein inhibitors such as verapamil and nicardipine can enhance the cytotoxic effects of proteasome inhibitors when used in combination to treat triple negative breast cancer cells.
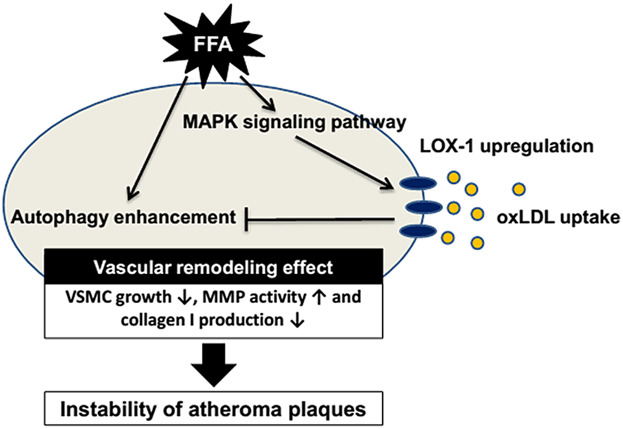
Free Fatty Acids Induce Autophagy and LOX-1 Upregulation in Cultured Aortic Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
- Pages: 1249-1261
- First Published: 05 November 2016
Fasttrack
Histone H4 Methyltransferase Suv420h2 Maintains Fidelity of Osteoblast Differentiation
- Pages: 1262-1272
- First Published: 09 November 2016
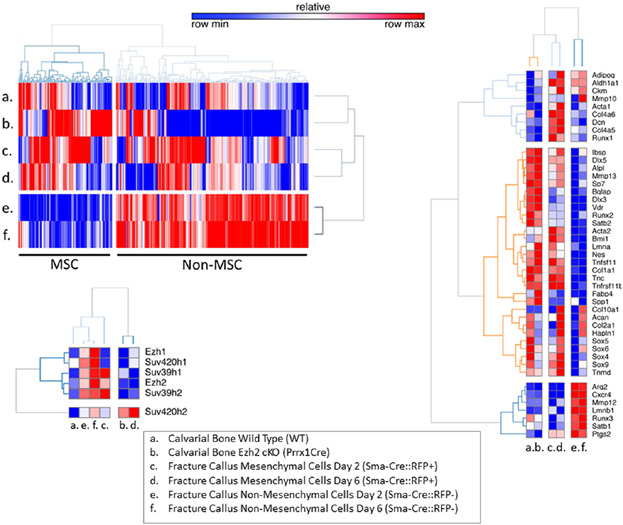
Cells with increased osteogenic potential have higher levels of the H4K20 methyl transferase Suv420h2 compared to other methyl transferases. Loss of function analysis of Suv420h2 shows loss of H4K20 methylation and decreased expression of bone biomarkers and osteogenic transcription factors as well as decreased matrix mineralization during osteoblast differentiation. We conclude that Suv420h2 controls the H4K20 methylome of osteoblasts and is critical for normal progression of osteoblastogenesis.
Erratum
Caveolin-1 Mediates Inflammatory Breast Cancer Cell Invasion via the Akt1 Pathway and RhoC GTPase
- Page: 1273
- First Published: 19 March 2017



![Proteomic Profiling Reveals the Induction of UPR in Addition to DNA Damage Response in HeLa Cells Treated With the Thiazolo[5,4-b]Quinoline Derivative D3ClP](/cms/asset/636e18f0-aefc-4915-ab76-5678976e75dd/jcb25753-blkfxd-0001-m.jpg)