Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
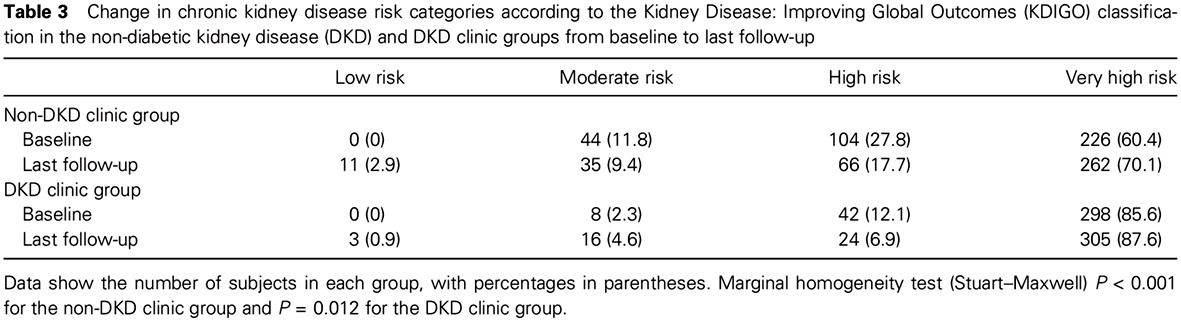
Long-term outcomes of patients with type 2 diabetes attending a multidisciplinary diabetes kidney disease clinic: 在多学科糖尿病肾病诊所就诊的2型糖尿病患者的长期预后
- First Published: 20 November 2017
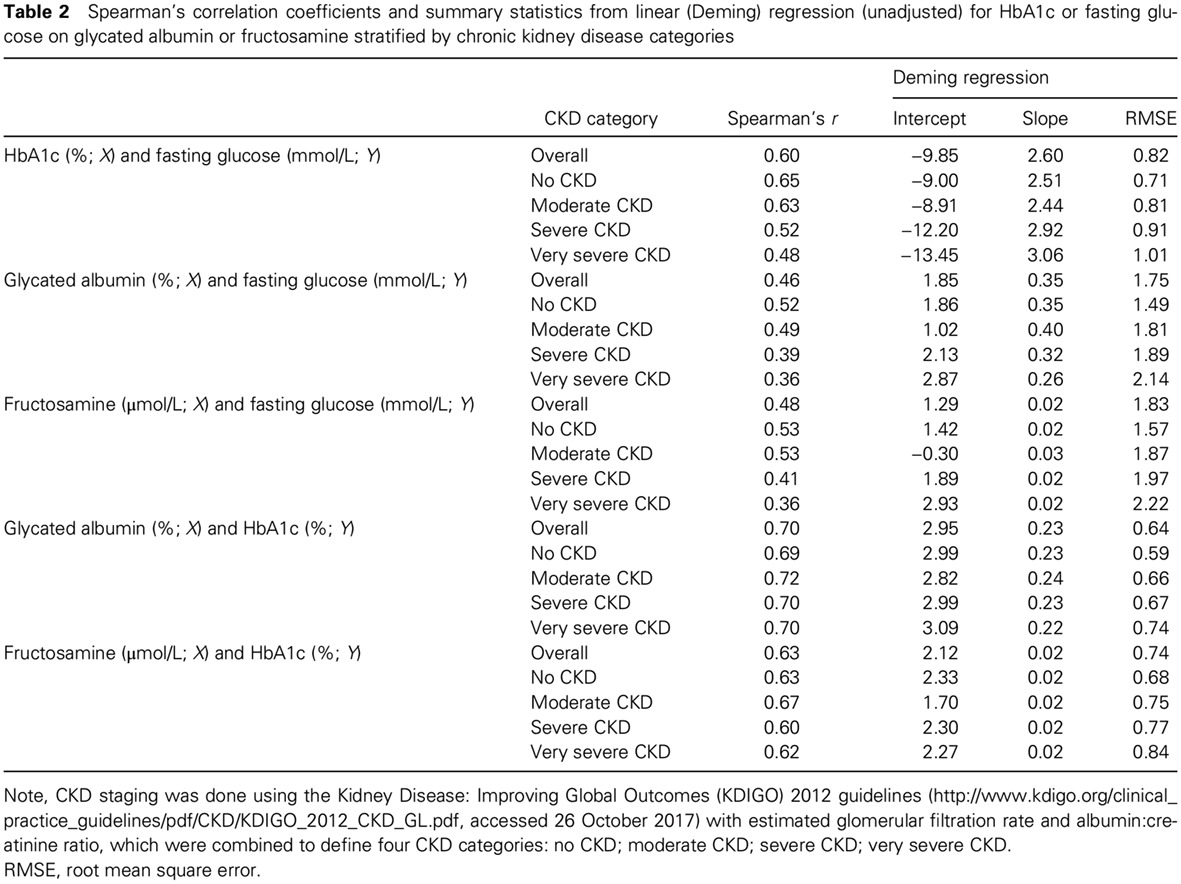
Performance of non-traditional hyperglycemia biomarkers by chronic kidney disease status in older adults with diabetes: Results from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study: 在老年糖尿病患者慢性肾脏疾病状态下非传统高血糖生物标志物的检测效能:来自评估动脉粥样硬化风险社区研究的结果
- First Published: 20 October 2017
Highlights
- Correlations of glycated albumin, fructosamine, and HbA1c with fasting glucose were all lower at more severe stages of chronic kidney disease stages in older adults with diagnosed diabetes.
- Our data suggest that the limitations of HbA1c may not be overcome by glycated albumin or fructosamine in the setting of chronic kidney disease.
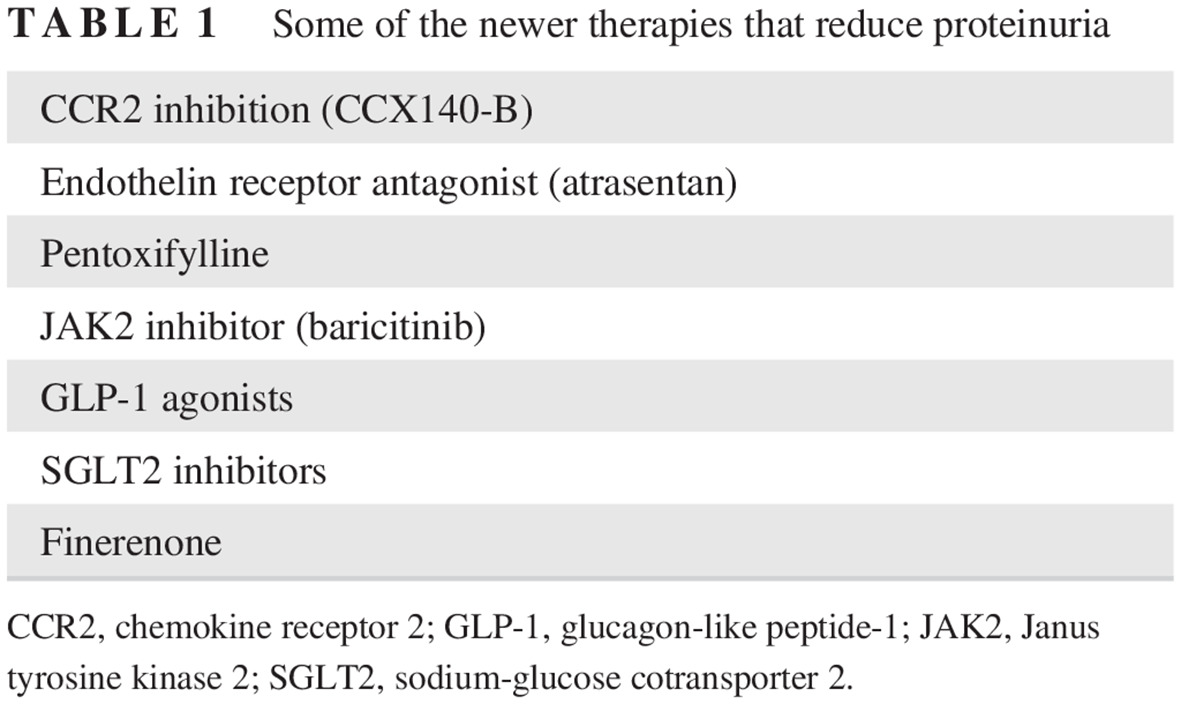
Review of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease and Their Renal Effects
- First Published: 18 July 2019
The kidney and cardiovascular outcome trials: 肾脏与心血管结局试验
- First Published: 14 October 2017
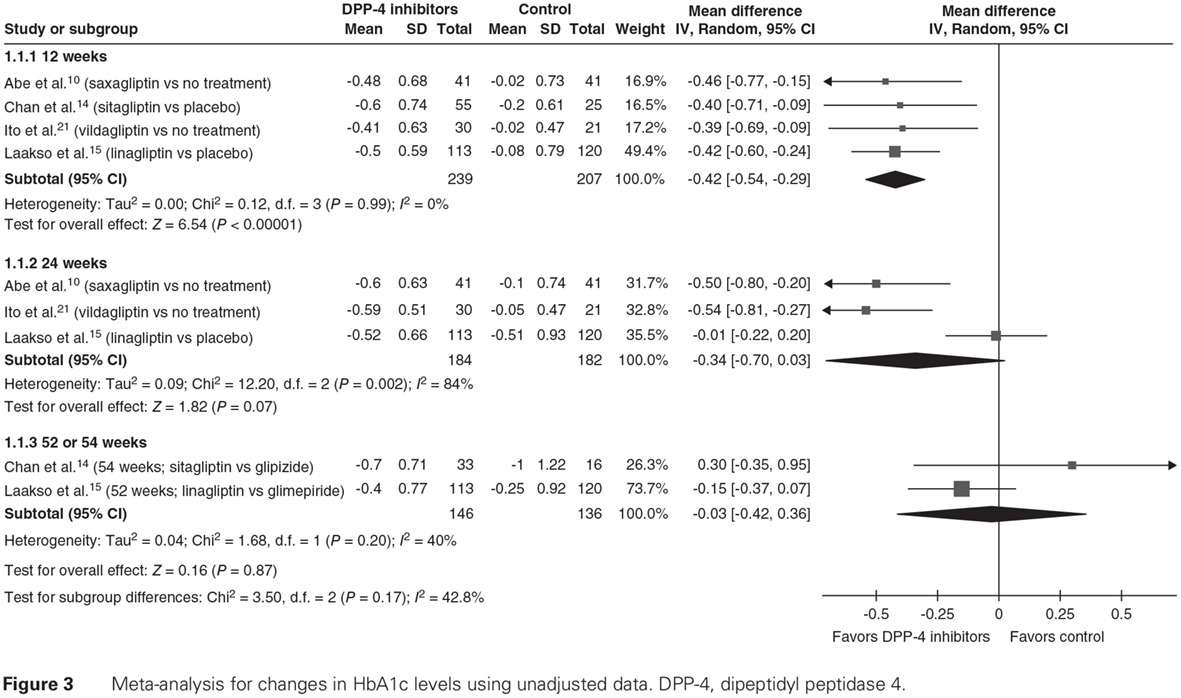
Effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes patients with moderate to severe chronic kidney disease: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials using unadjusted data: DPP-4抑制剂在2型糖尿病伴中至重度慢性肾脏病患者中的作用:利用随机对照研究中未校正数据的meta分析
- First Published: 07 March 2017
Highlights
- Dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitors significantly improved HbA1c levels at 12 weeks in both non-dialysis and dialysis patients, compared with 24 weeks in dialysis patients.
- Mean HbA1c changes induced by DPP-4 inhibitors were equivalent to those induced by sulfonylureas at 52 or 54 weeks.
- However, DPP-4 inhibitors induced fewer symptomatic hypoglycemic events than sulfonylureas at 52 or 54 weeks.
Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of kidney function decline among individuals with diabetes and prediabetes: A 3-year follow-up study
中性粒细胞-淋巴细胞比值作为糖尿病和糖尿病前期个体肾功能下降的预测因子:一项3年的随访研究
- First Published: 13 January 2019
Highlights
This study is the first study to confirm that the neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is an independent predictive factor for kidney function decline among individuals with diabetes and prediabetes.
Calculating the NLR is easy and inexpensive, so we believe that with more research support the NLR will be used as an effective indicator in the clinical management of individuals with diabetes and prediabetes.
National Kidney Foundation Spring Clinical Meetings 2018
- First Published: 22 May 2018
Effect of liraglutide on the Janus kinase/signal transducer and transcription activator (JAK/STAT) pathway in diabetic kidney disease in db/db mice and in cultured endothelial cells
在合并糖尿病肾病的db/db小鼠以及培养的内皮细胞中,利拉鲁肽对Janus激酶/信号转导与转录激活因子(JAK/STAT)通路的影响
- First Published: 21 December 2018
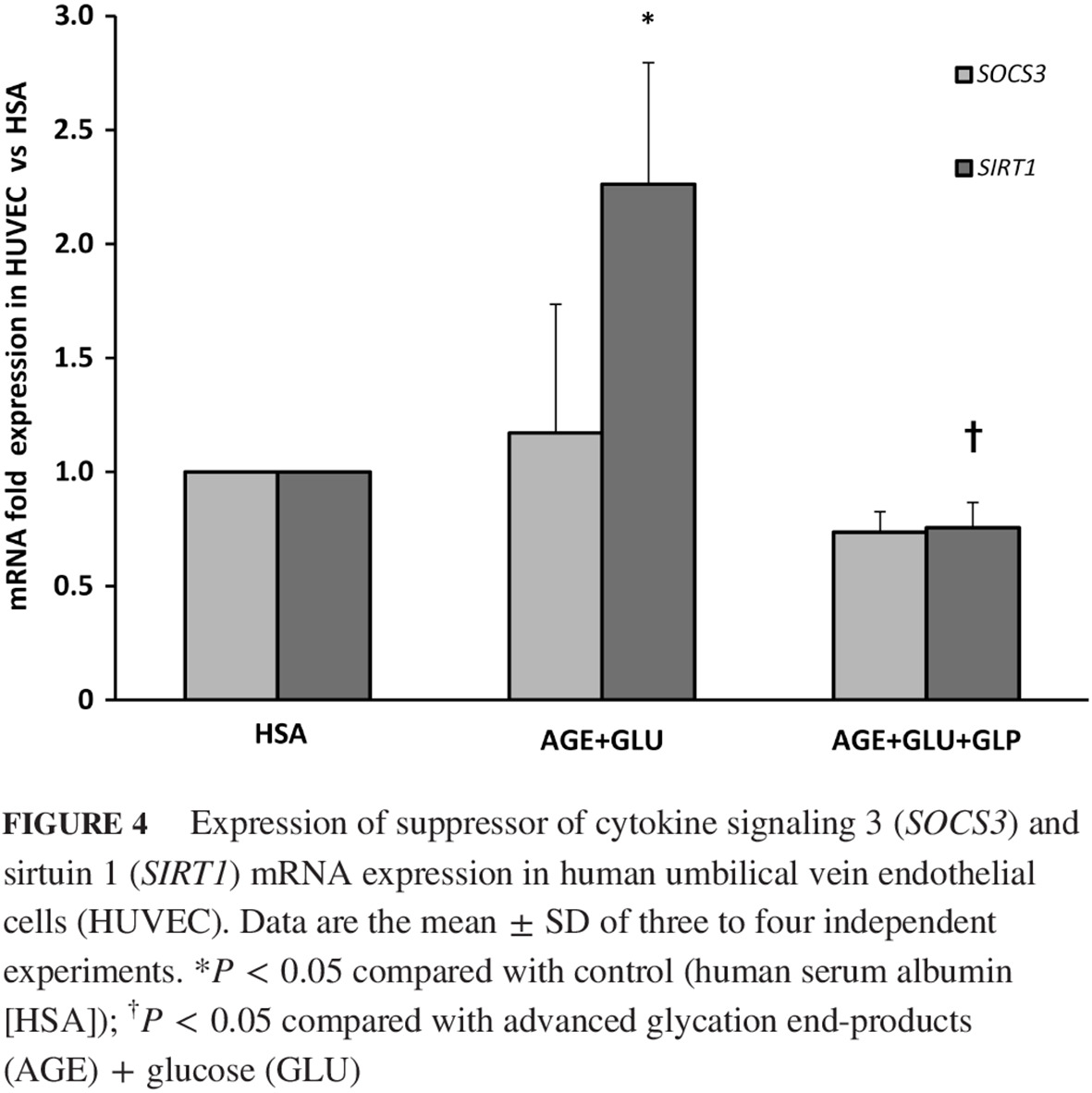
Highlights
- Diabetic conditions elevated expression of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3 and Janus tyrosine kinase (JAK) 2.
- Diabetic conditions elevated expression of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 and sirtuin 1 (SIRT1).
- The glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analog, liraglutide, is an inhibited STAT3/JAK2 expression, possibly through SIRT1 signaling.
Effects of preoperative hepatitis B virus infection, hepatitis C virus infection, and coinfection on the development of new-onset diabetes after kidney transplantation
肾移植术前乙肝病毒感染、丙肝病毒感染及其共感染对移植后新发糖尿病发病的影响
- First Published: 11 September 2018
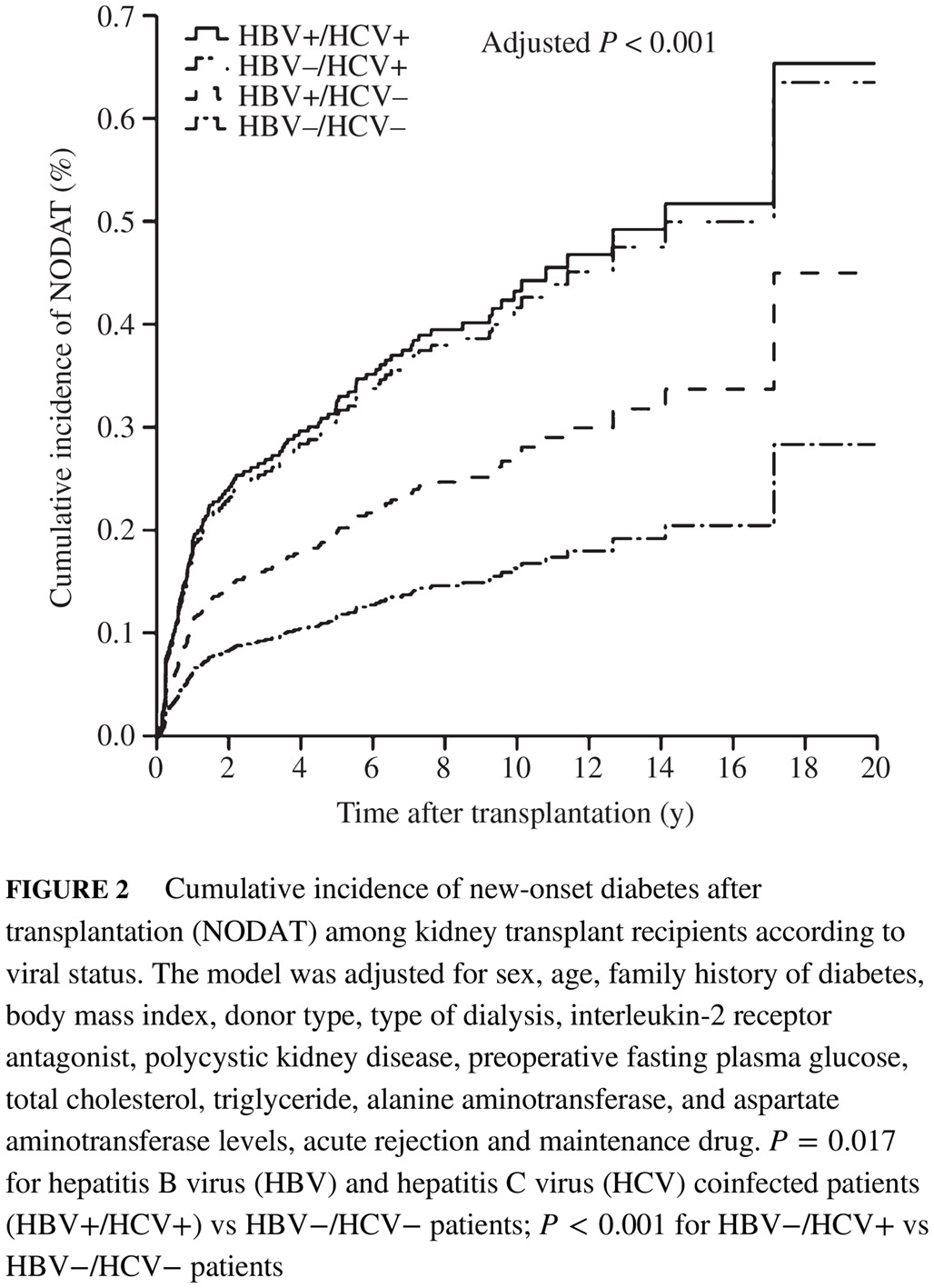
Highlights
- A retrospective cohort study of preoperative hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, and HBV and HCV coinfection was conducted to determine their effects on new-onset diabetes after transplantation (NODAT) among Chinese kidney transplant recipients (KTRs).
- Preoperative HCV infection was significantly correlated with the risk of NODAT.
- Preoperative HBV and HBV plus HCV coinfection did not independently increase the risk of NODAT.
Predicting, preventing, and managing cardiovascular and chronic kidney disease progression in people with type 2 diabetes: How to improve on traditional strategies
预测、预防与管理2型糖尿病患者的心血管疾病以及慢性肾病的进展:如何改进传统治疗策略
- First Published: 07 May 2019
Regional evidence and international recommendations to guide lipid management in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes with special reference to renal dysfunction: 对亚洲2型糖尿病患者特别是有肾功能障碍患者的血脂管理的地区实证和国际建议
- First Published: 28 September 2017
Highlights
- Despite the proven effectiveness of lipid management in reducing diabetes-related complications, there are major treatment gaps, especially in Asian patients with young-onset diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD).
- Given the propensity of Asian patients with diabetes to develop CKD and the amplifying effect of CKD on atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease, the timely use of statins in Asian patients is particularly important.
- There is an urgent need for Asian countries to review and align their lipid-lowering treatment guidelines to reduce the burden of diabetes in Asia.
Renoprotective effects of brown adipose tissue activation in diabetic mice
- First Published: 24 April 2019
- This study demonstrates that of brown adipose tissue (BAT) with CL316,243 attenuates the progress of diabetic kidney disease (DKD).
- Mechanistically, the activation of BAT improved concentrations of circulating adipokines and microRNAs, which further affected the diabetic kidney and reactivated the AMP-activated protein kinase/sirtuin 1/peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α signaling pathway.
- The data suggest that BAT activation could be a novel therapeutic approach in the treatment of DKD.
Gain in adiposity over 3 years is associated with progressive renal decline in multi-ethnic South-east Asians with type 2 diabetes
在多民族的东南亚2型糖尿病患者中超过3年的肥胖可导致肾功能逐渐下降
- First Published: 03 September 2018
Highlights
- This analysis of multiethnic South-east Asians with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) showed that longitudinal gain in adiposity, albeit relatively modest, was sufficient to be associated with annual estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) decline, but only in men.
- Increased adiposity also predicted rapid eGFR decline and progression of albuminuria.
- The findings suggest that increased adiposity over time adversely affects renal outcomes, highlighting the importance of carefully designing weight-neutral or -loss antidiabetic treatment regimes when managing T2DM in the clinic to ameliorate progressive kidney disease.
Effect of diabetes mellitus on the recovery of changes in renal functions and glomerular permeability following reversible 24-hour unilateral ureteral obstruction
糖尿病对可逆性单侧输尿管梗阻24小时后肾功能以及肾小球通透性变化恢复的影响
- First Published: 28 December 2018
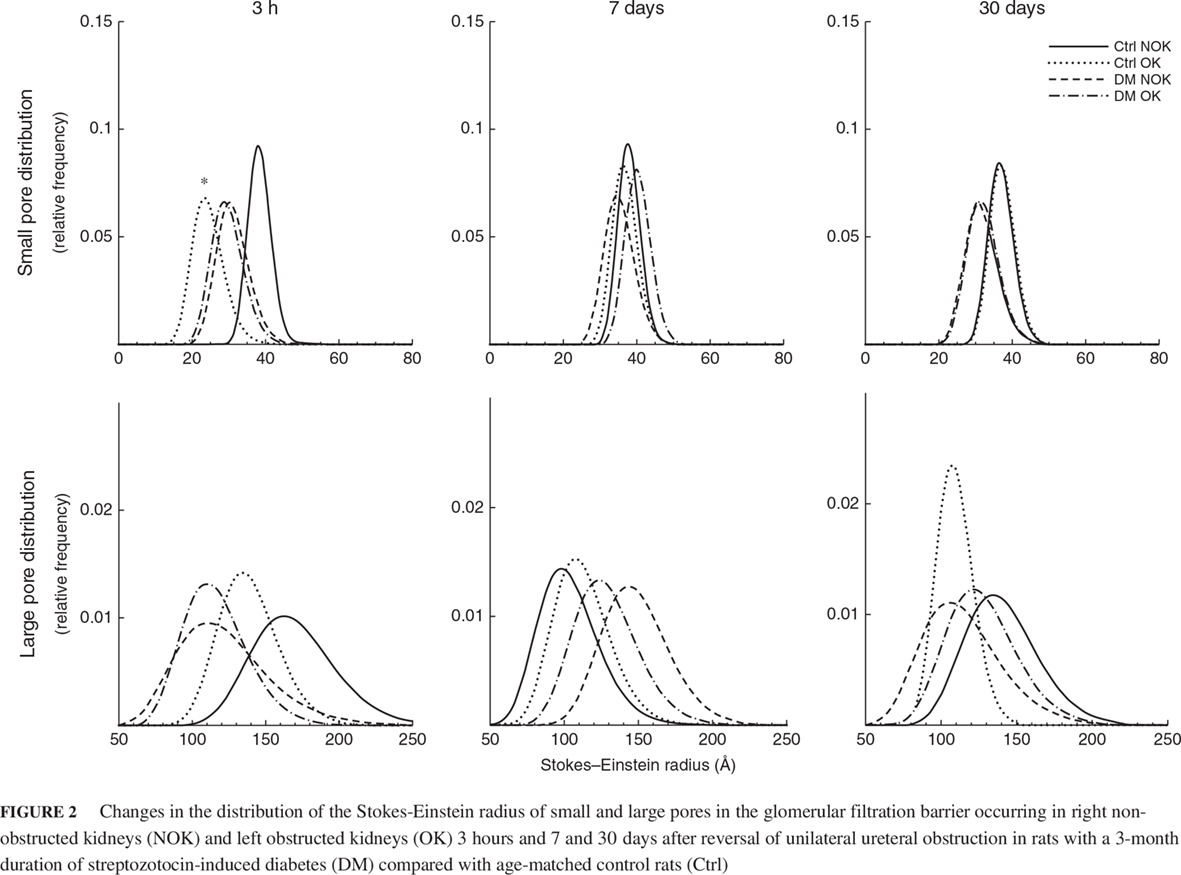
Highlights
- Following reversal of ureteral obstruction, diabetes mellitus results in exaggerated early alterations in glomerular hemodynamic and tubular function, as well as in size selectivity dysfunction of both small and large pores of the glomerular filtration barrier.
- This was accompanied by a more severe residual dysfunction of large pores, indicating a more ominous outcome in diabetic kidneys following ureteral obstruction.
Regular mailing of personalized feedback reports improves glycemic control in diabetes: A randomized controlled trial: 定期邮寄个体化的反馈报告可以改善糖尿病患者的血糖控制:一项随机对照试验
- First Published: 12 January 2017
- Patients with diabetes who underwent structured complication assessment and received a personalized report through a web-based portal showed significant improvement in glycemic and lipid control after 1 year.
- Under comprehensive care, those who received additional follow-up reports had further reduction in HbA1c.
- In a post-hoc analysis, patients with chronic kidney disease who received additional follow-up reports were less likely to be hospitalized and had shorter length of stay.
Interleukin-2 receptor antagonists: Protective factors against new-onset diabetes after renal transplantation: 白细胞介素2受体拮抗剂:肾移植后新发糖尿病的保护因素
- First Published: 25 March 2018
Highlights
- Previous findings regarding the relationship between interleukin-2 receptor antagonists (IL-2Ra) and new-onset diabetes after transplantation (NODAT) are controversial.
- This study reveals that the use of IL-2Ra protects against the development of NODAT in renal transplant recipients.
Assessment of factors determining an HbA1c concentration ≤7.5% in patients with type 1 diabetes: 评估决定1型糖尿病患者HbA1c≤7.5%的因素
- First Published: 22 May 2017
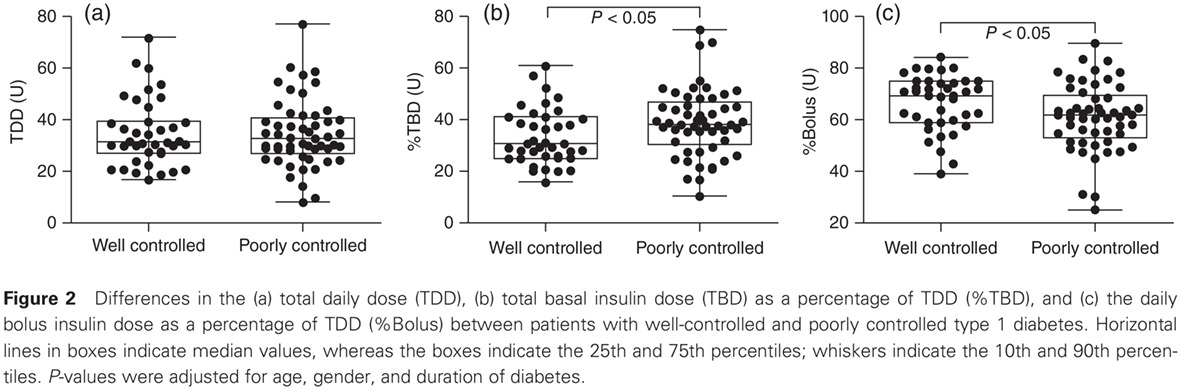
Highlights
- Appropriate insulin dose required for maintaining good glycemic control were assessed in patients with type 1 diabetes.
- Glycemic control did not depend on the total daily insulin dose; rather, the ratio of basal: bolus insulin is important.
- To achieve an HbA1c concentration ≤7.5%, the total daily insulin dose (TDD) should be based on body weight, and the total basal insulin dose as a percentage of TDD should be set at 30% in the Japanese population.
Plasma lipids affect dabigatran etexilate anticoagulation in rats with unbalanced diabetes mellitus: 在失衡的糖尿病大鼠中血脂可以影响达比加群酯的抗凝作用
- First Published: 03 July 2017
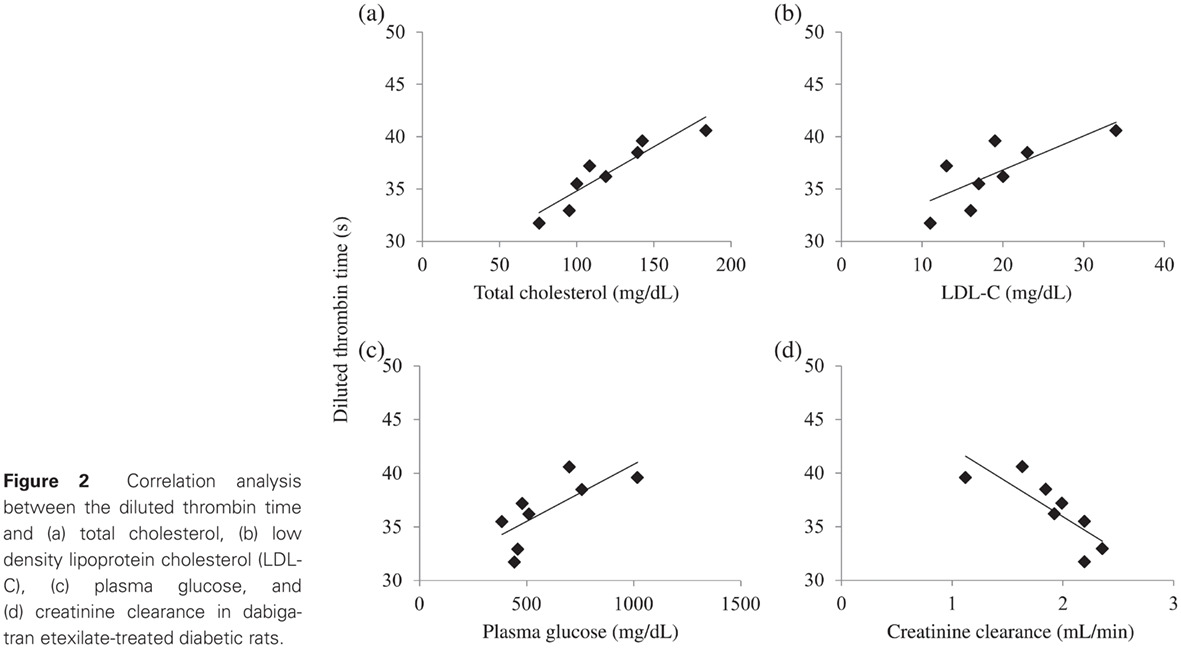
Highlights
- Diabetic rats exhibit significantly more intense dabigatran-induced anticoagulation that does not seem to be solely related to altered kidney function.
- Plasma cholesterol significantly affects dabigatran-induced anticoagulation in this setting.
- These findings could explain the similar benefits of dabigatran in reducing ischemic stroke compared with warfarin in patients with and without diabetes mellitus, despite the significantly higher intrinsic thrombotic risk in the former, as well as the lack of benefit of reducing major bleeding in diabetic patients.
Retracted: Evaluation of antidiabetic activity of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles using Pouteria sapota in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: 在链脲霉素-诱导的糖尿病大鼠中评估使用山榄果生物合成的银纳米粒子的降糖活性
- First Published: 21 March 2017
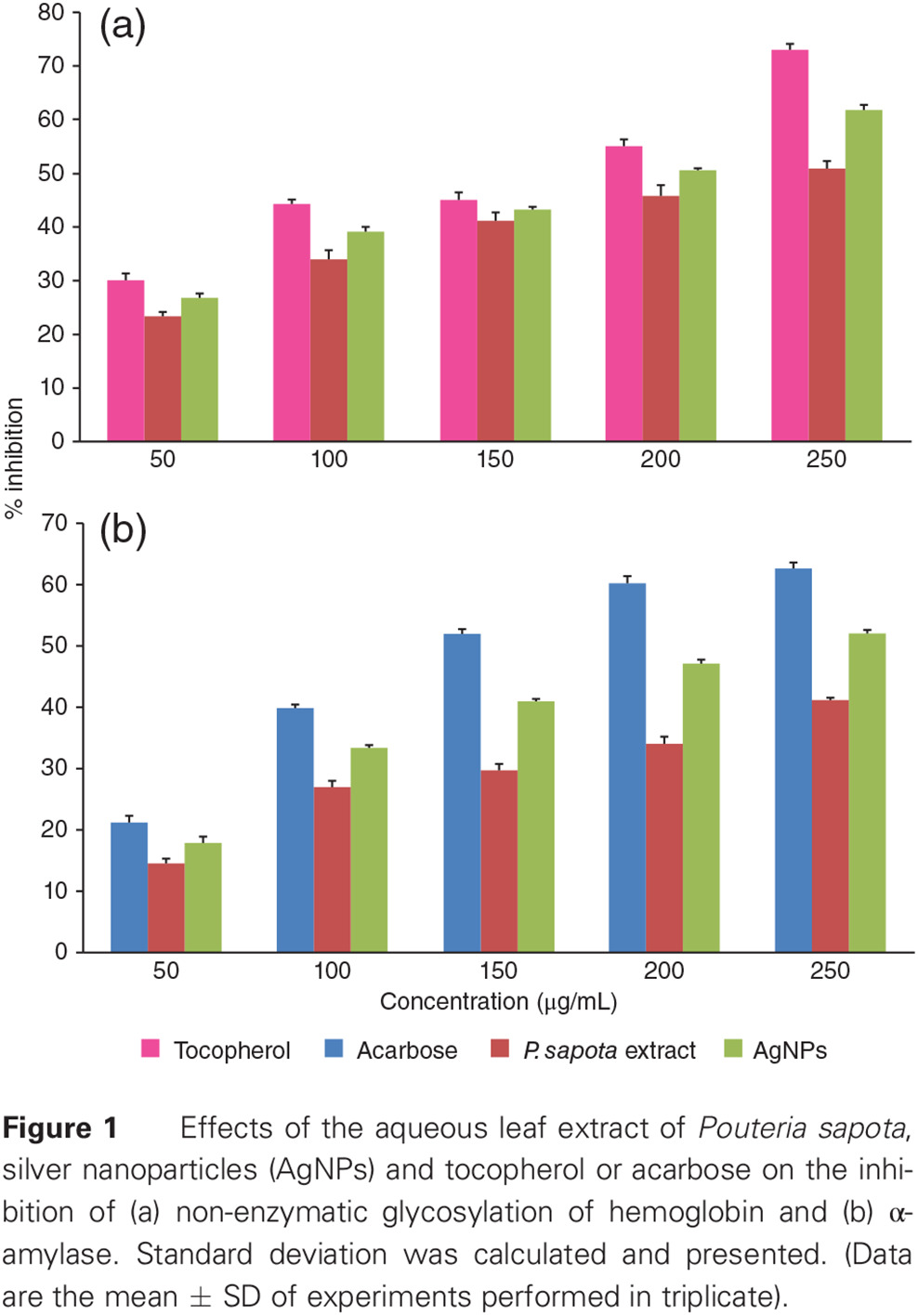
Highlights
- The aqueous leaf extract of P. sapota and biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles play an important role in regulating glucose metabolism.
- Determining the role of P. sapota leaf extract in regulating glucose metabolism will provide new insights into the treatment of diabetes, as well as the role of silver nanoparticles in curbing the disease.
Effect of glycemic control on the Diabetes Complications Severity Index score and development of complications in people with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: 在新诊断的2型糖尿病患者中血糖控制情况对糖尿病并发症严重程度指数评分以及并发症进展的影响
- First Published: 04 October 2017
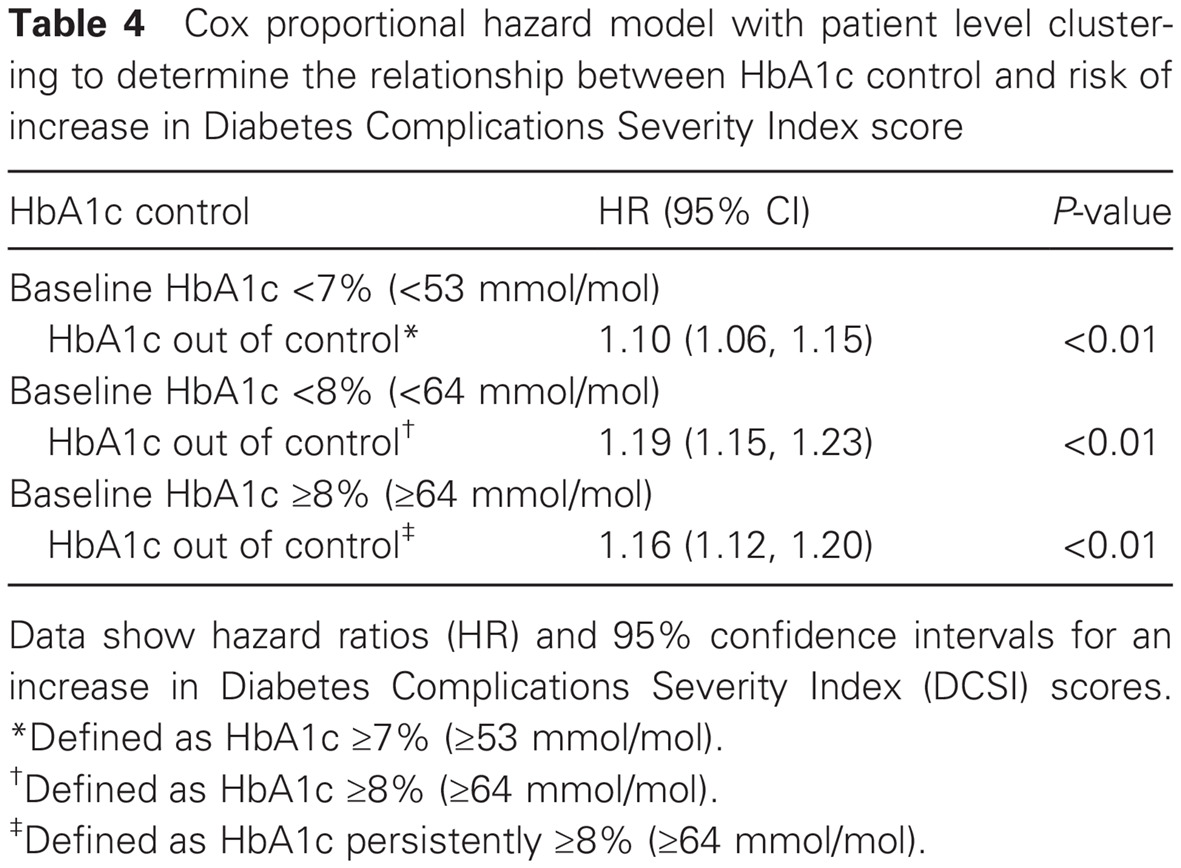
Highlights
- There is a lack of published real-world evidence regarding longitudinal changes in Diabetes Complications Severity Index (DCSI) scores among people with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes (T2D), including how the level of glycemic control at the time of diagnosis may affect DCSI score progression.
- This study evaluated such outcomes over an 11-year period in a very large cohort of patients with newly diagnosed T2D (n = 32 174), with data drawn from electronic health records from a large US integrated healthcare system.
- These are the first known data to demonstrate that worsening or persistently poor glycemic control, but not baseline glycemic control, is associated with increasing DCSI score over time.