Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Highlights from the Editors 2023
The effect of older population on public health spending: Evidence from Spain
- First Published: 12 October 2023
This study analyses the effect of older people, and their health and personal characteristics, on public health spending. The results show us that the main factors that explain the consumption of both health services and health technology, above age, are related to the so-called need factors: self-reported health status, presence of chronic diseases, and disability. The findings may be of special interest for the design of efficient public health policies.
China's aging population: A review of living arrangement, intergenerational support, and wellbeing
- First Published: 09 October 2023
Inception of the Indian Digital Health Mission: Connecting…the…Dots
- First Published: 09 October 2023
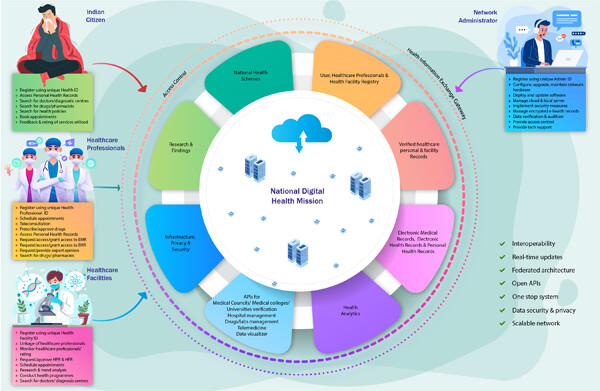
The purpose of the National Digital Health Mission (or more precisely, the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission) is to promote and facilitate the evolution of the National Digital Health Ecosystem in India. The Health Facility Registry, the Healthcare Professionals Registry, and the Unified Health Interface are the major components of the proposed system—which is intended to be a co-operative federated architecture with optimal interoperability provision coupled with authorized access.
Large language models in health care: Development, applications, and challenges
- First Published: 24 July 2023

The advancement of large language models (LLMs) promises to bring significant changes in health care, with extensive applications spanning pre-consultation, diagnostic, and management phases. Moreover, LLMs hold potential utility in medical education and medical writing. Concurrently, it is imperative to recognize the limitations of LLMs, strengthen review measures and enhance supervision system, thereby facilitating more effective collaboration between related personnel and LLMs.
Predicting venous thromboembolism (VTE) risk in cancer patients using machine learning
- First Published: 13 July 2023
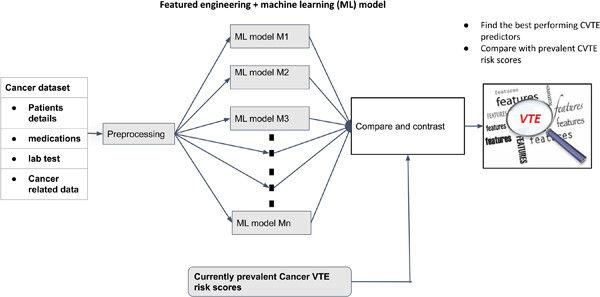
In this study, we examined the utility of using machine learning (ML) to predict venous thromboembolism (VTE) in cancer patients. It allowed us to draw insight into our feature pool and identify the features that could have the most utility in the context of developing an efficient ML classifier. Our ML-based prediction model achieved an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.778 ± 0.006 when trained on a set of 15 features. Our result surpasses the most validated clinical scoring system for VTE risk assessment in cancer patients by 16.1%. We additionally found cancer stage information to be a useful predictor after all performed feature selection processes despite not being used in existing score-based approaches.
Evolution and major changes of the diagnosis and treatment protocol for COVID-19 patients in China 2020–2023
- First Published: 17 May 2023
Lessons learned from the hospital to home community care program in Singapore and the supporting AI multiple readmissions prediction model
- First Published: 10 May 2023
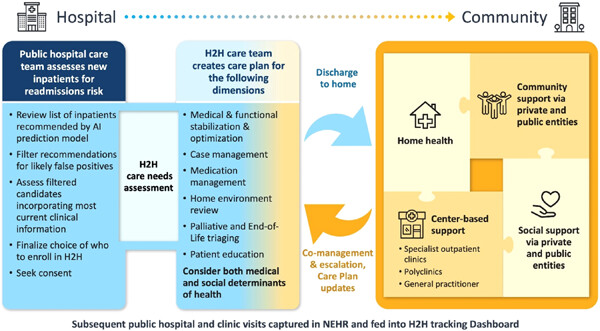
This article elaborates on Singapore's Hospital to Home program and care model, and its supporting AI model for multiple readmission prediction, in the following ways: by providing updates on supporting information systems, by reporting on customer engagement and related service delivery outcomes, by sharing three categories of lessons learned, by highlighting how this effort supported broader Covid-19 response efforts, and by commenting on how the experiences from running this program since 2017 are expected to contribute to the next wave of Singapore's public healthcare efforts from 2023 onwards.
Chinese academic community speaks out on He Jiankui again: Consensus statement on the challenges and responses of science and technology ethics governance
- First Published: 10 April 2023
Retrospective matched cohort study of incidence rates and excess length of hospital stay owing to pressure injuries in an Asian setting
- First Published: 13 March 2023
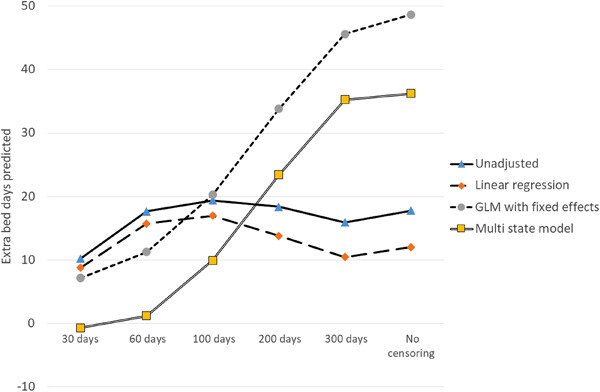
- a.
Stage 1 and 2 health care acquired pressure injuries are common and increase costs by prolonging the length of stay.
- b.
Thus, there is economic value investing in prevention programs.
- c.
Multiple methods are used to attribute excess stay to pressure injury: unadjusted comparison; linear regression; generalized linear regression with a gamma distribution; and, state-based models.
- d.
State based models with appropriate censoring for very long stays provide unbiased estimates.
- e.
Using biased estimates of excess length of stay will overstate the potential value of prevention.
Diagnosis and treatment protocol for COVID-19 patients (Tentative 10th Version)
- First Published: 23 February 2023
Transfer or tailor? Implementing a technology-supported intervention for noncommunicable diseases across contexts
- First Published: 07 November 2022