Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
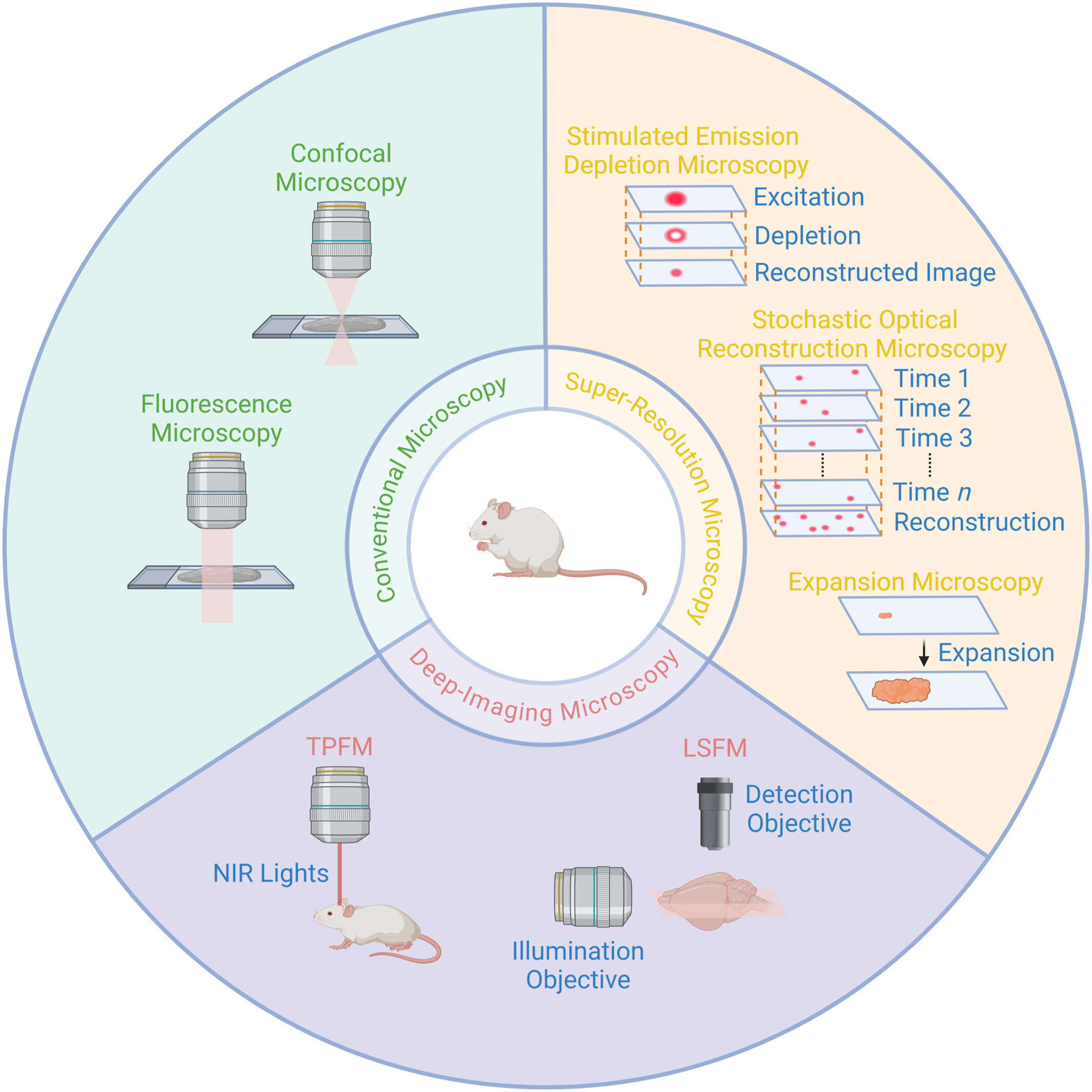
Advanced Optical Microscopic Imaging Techniques for Imaging Amyloid Beta and Deciphering Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis
- Pages: 95-114
- First Published: 06 March 2025
Implications of Artificial Intelligence in Stroke Intervention and Care
- Pages: 115-131
- First Published: 04 April 2025
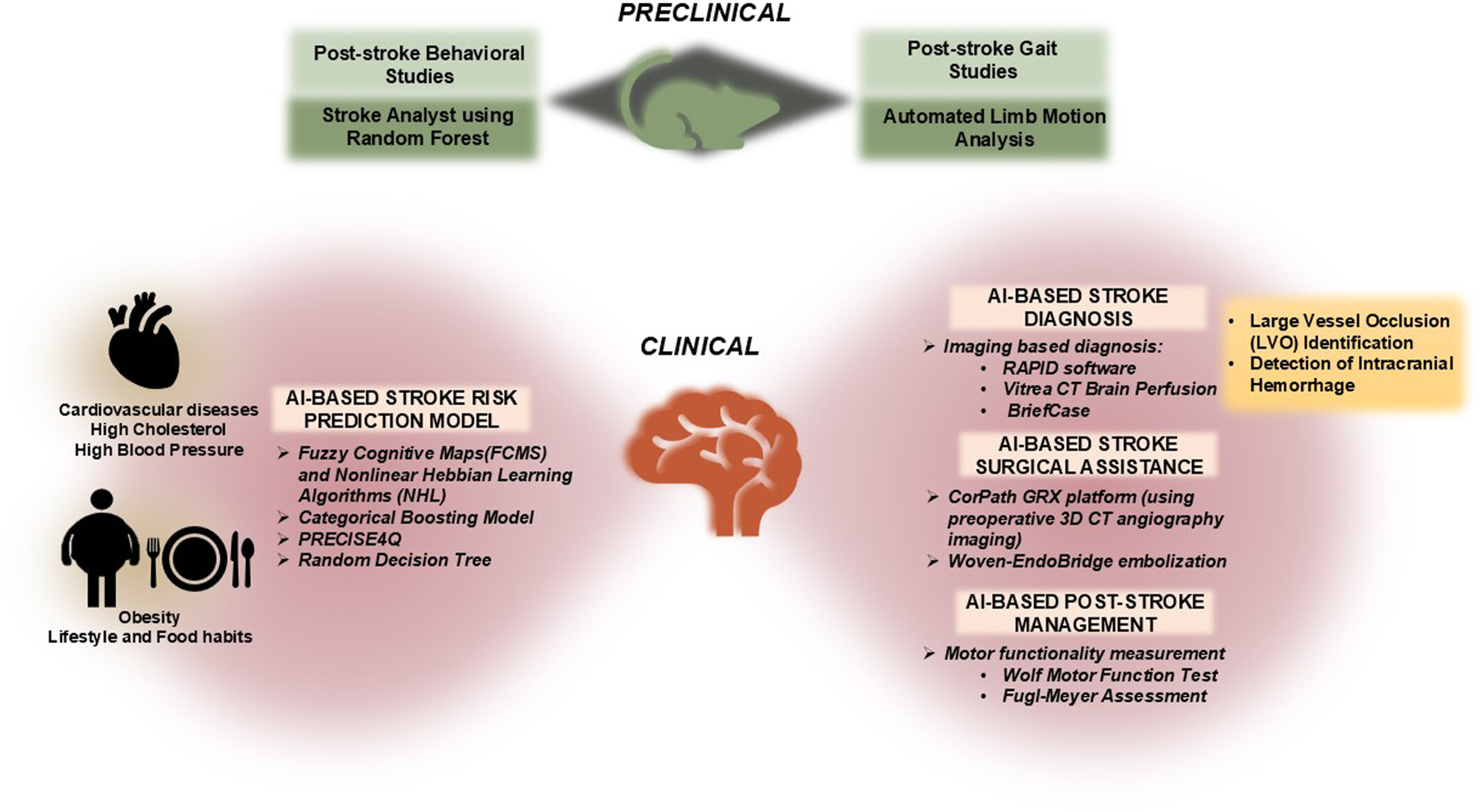
The implication of AI based algorithms in preclinical and clinical stroke studies → Efficiency of post-stroke analysis of animal behavioral and motor function in preclinical models have been improved by AI-based methods. In clinical scenario, population-based risk-prediction as well as post-stroke diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation has been positively influenced by AI-based models.
Utilizing Radiomics as Predictive Factor in Brain Metastasis Treated With Stereotactic Radiosurgery: Systematic Review and Radiomic Quality Assessment
- Pages: 132-143
- First Published: 07 April 2025
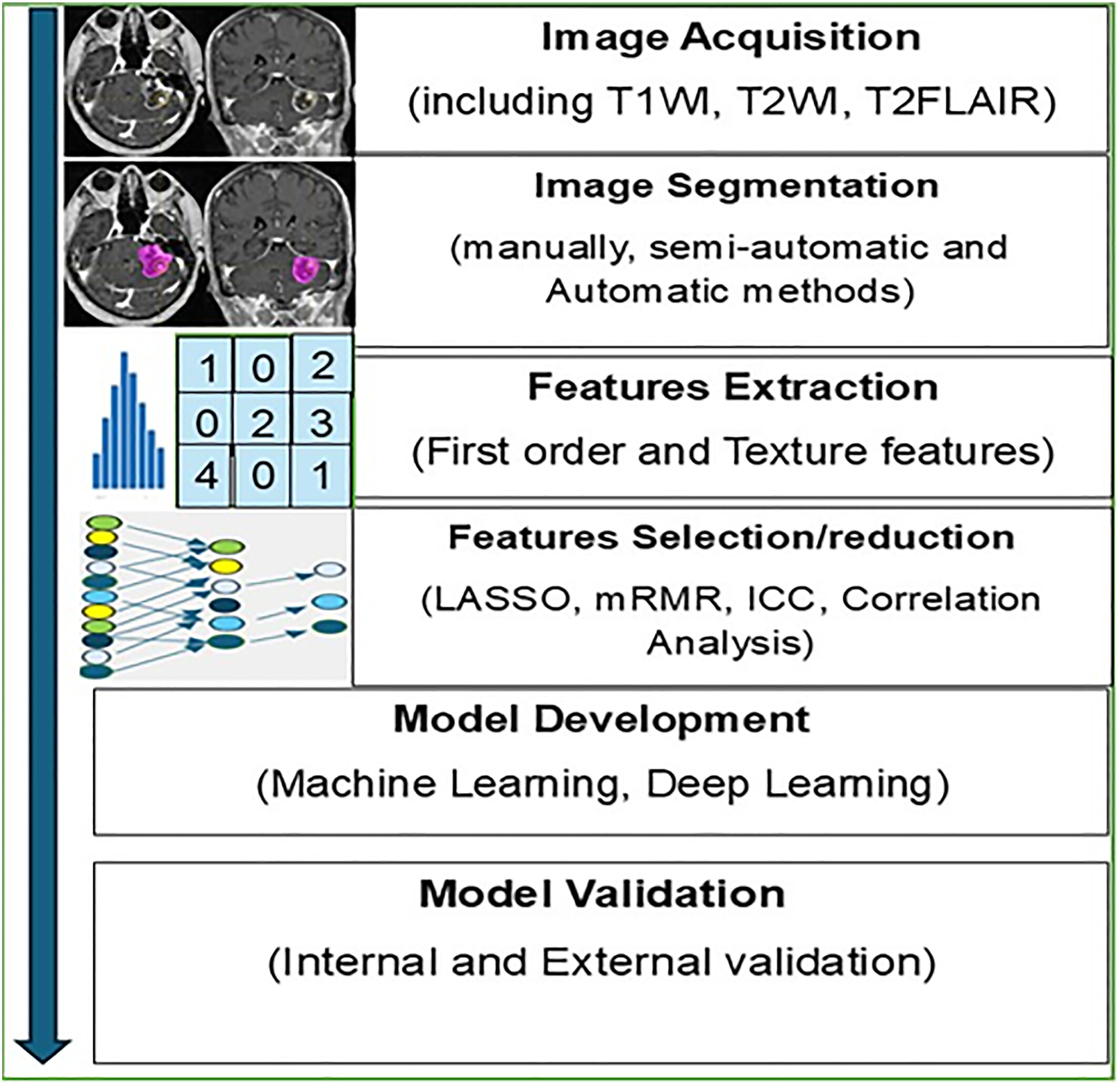
This systematic review assessed radiomics-based studies for predicting treatment response in brain metastases, evaluating their predictive performance and radiomic quality score (RQS) adherence. Radiomic models demonstrated superior predictive performance outperforming the clinical and visual assessment, with further improvement when clinical features were integrated. However, RQS adherence across studies remains moderate to poor. (Images Sourced: HCTM KL, 2023).
Application of Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging: Current Status and Future Directions
- Pages: 144-151
- First Published: 09 April 2025
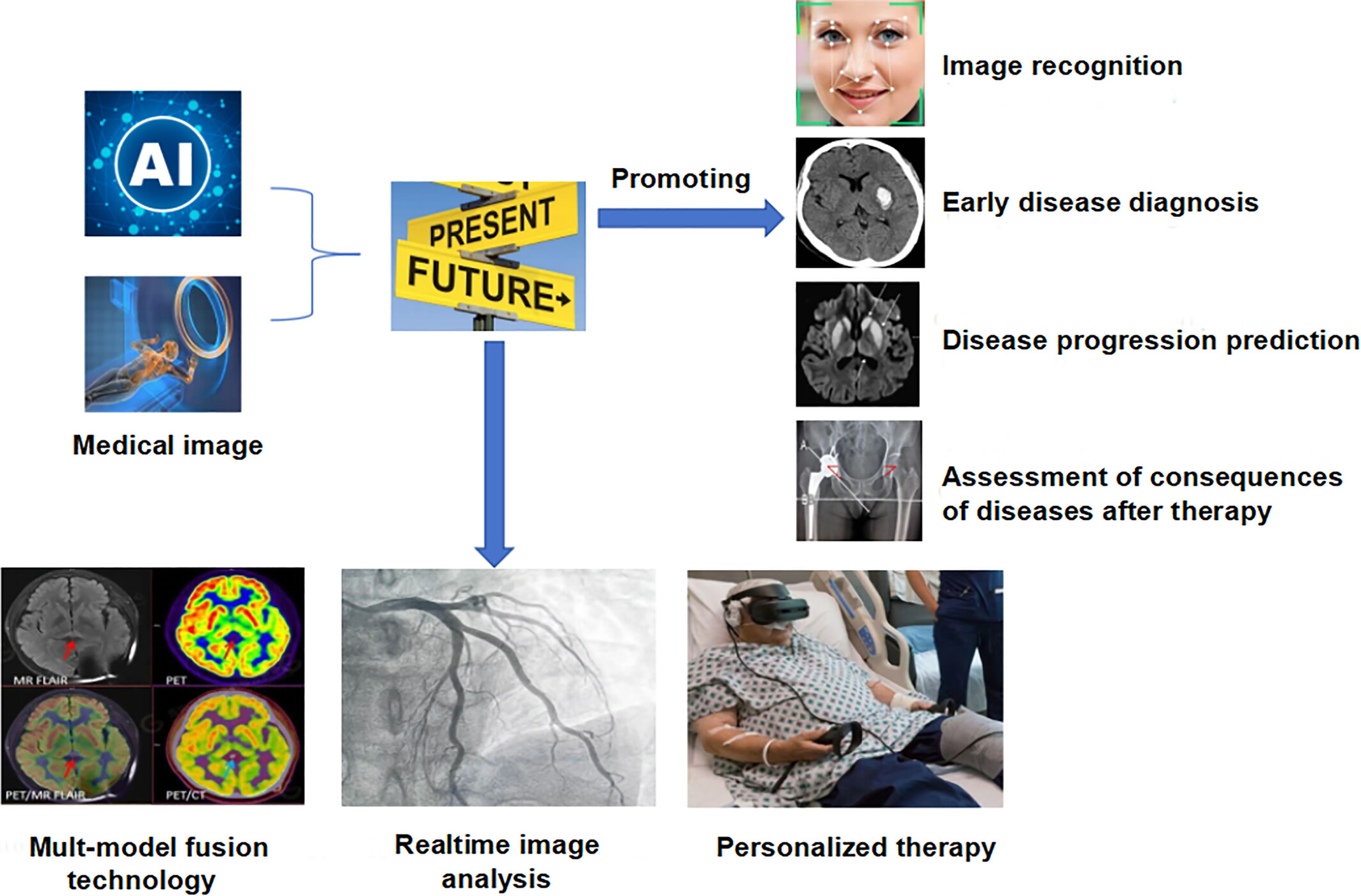
The application of AI in medical imaging is driving a transformation from image recognition to disease management. Current advancements include accurate image diagnosis, encompassing lesion detection, and identification as well as disease-based early diagnosis, progression prediction, and therapeutic efficacy assessment. Future directions are focused on multimodal data fusion, real-time image analysis, and the development of personalized treatment plans, aiming to enhance diagnostic accuracy, optimize treatment strategies, and achieve precision medicine through comprehensive analysis.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Low-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Ameliorates Cisplatin-Induced Cognitive Impairment by Attenuating Hippocampal Neuroinflammation and Enhancing Synaptic Plasticity in Rats
- Pages: 152-167
- First Published: 10 March 2025
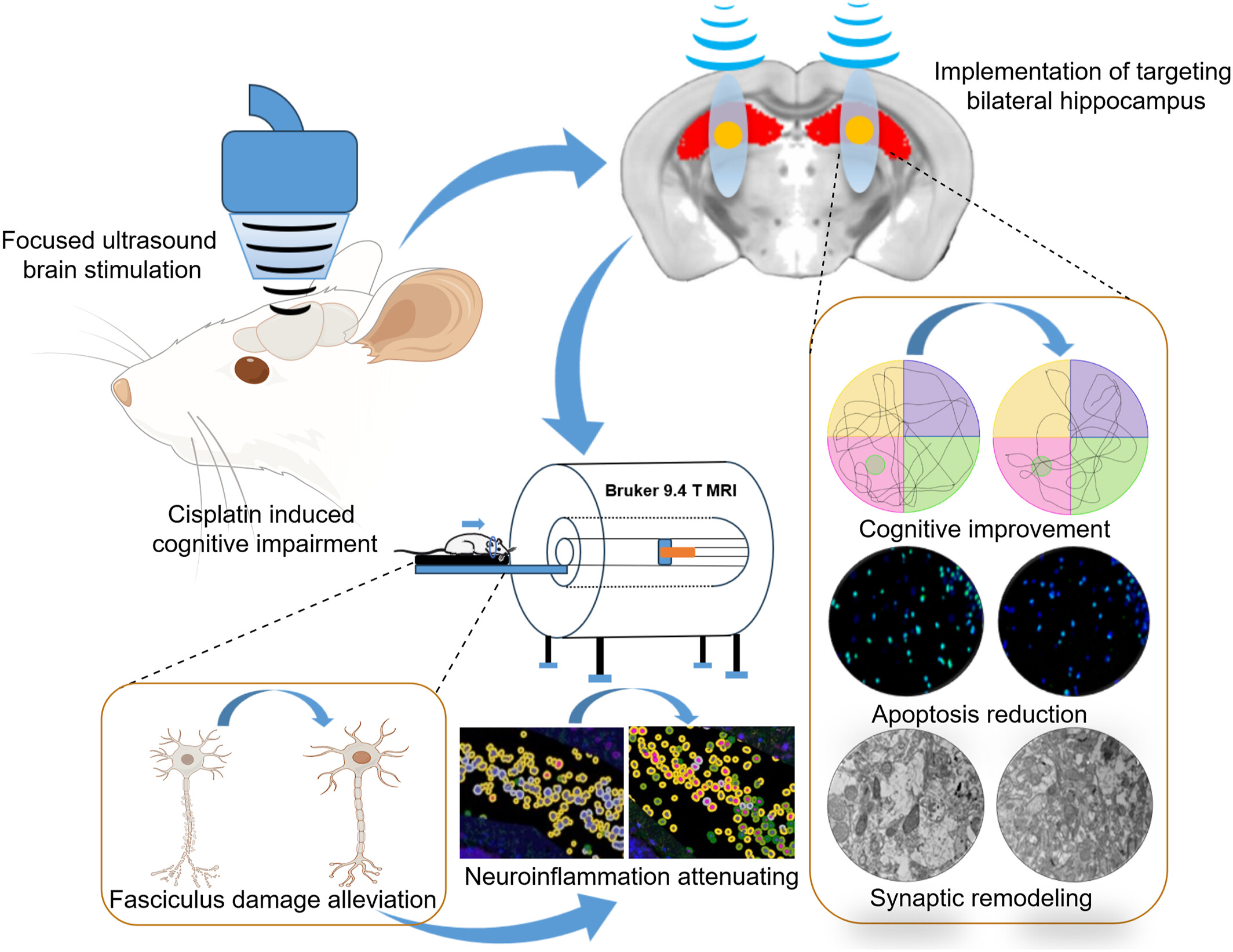
The study evaluates the application of low-intensity focused ultrasound (LIFUS) in alleviating cisplatin-induced cognitive impairment in rats and explores the associated neural mechanisms. Through behavioral assessments and 9.4-T small animal magnetic resonance imaging, results show that LIFUS improved cognitive function in rats, with significant changes in diffusion tensor imaging indices. Histopathology revealed increased dendritic spine density, reduced myelin loss, fewer apoptotic cells, increased synapses, and decreased mitochondrial autophagy, indicating a neurorepair effect of LIFUS. Additionally, microscopic and molecular immunofluorescence analyses showed that LIFUS enhanced synaptic plasticity in hippocampal neurons and mitigated neuroinflammation.
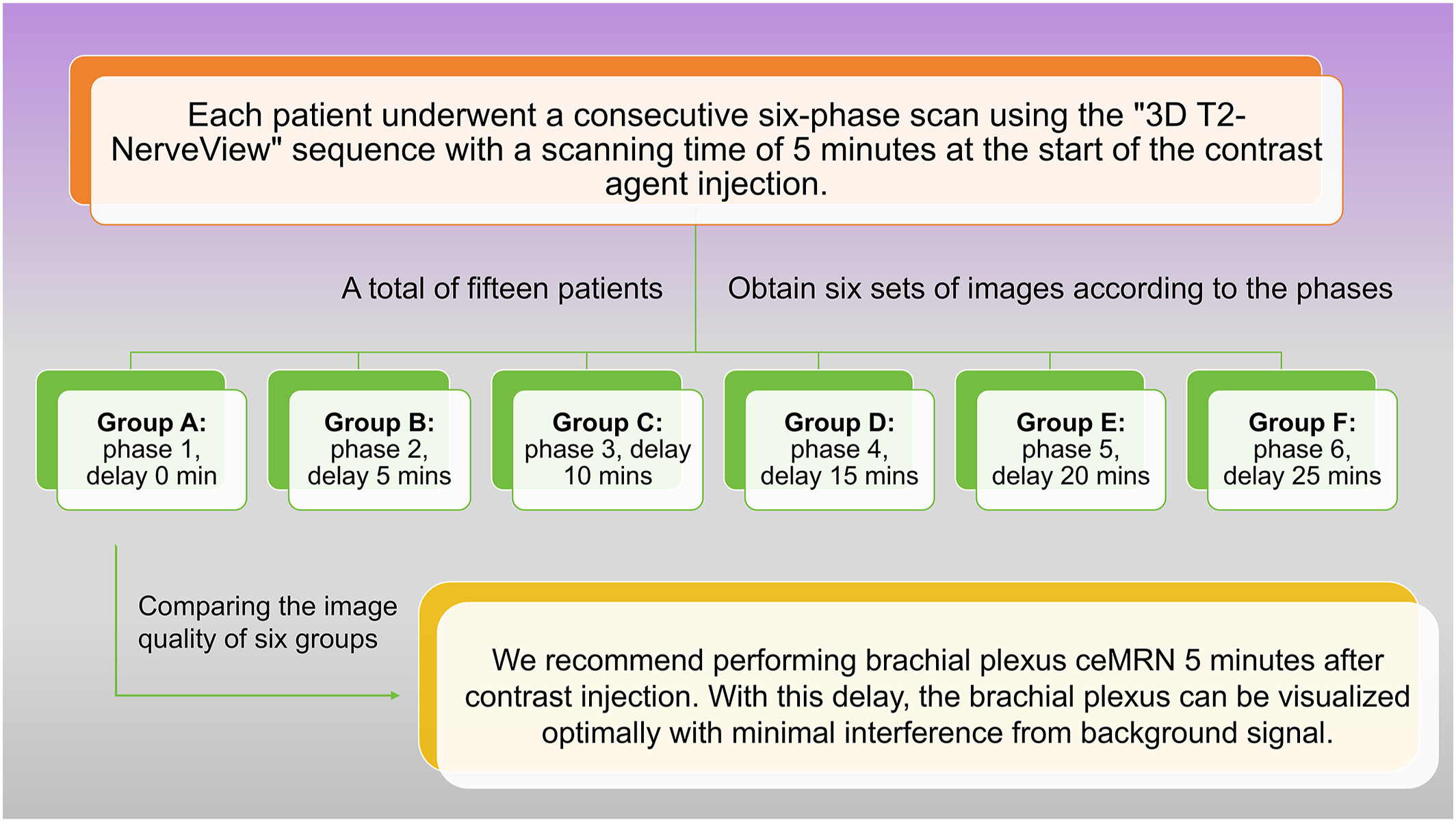
Optimizing Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Neurography of the Brachial Plexus With Delayed Scanning
- Pages: 168-175
- First Published: 17 February 2025
CASE IMAGE
Imaging Features of Rare Ovarian Adenomyoma
- Pages: 176-177
- First Published: 10 February 2025
Biphasic Synovial Sarcoma in the Abdominal Cavity
- Pages: 178-179
- First Published: 16 February 2025
SHORT COMMUNICATION
Aorta–Right Atrial Tunnel in Conjunction With Patent Ductus Arteriosus and Atrial Septal Defect
- Pages: 180-182
- First Published: 05 March 2025
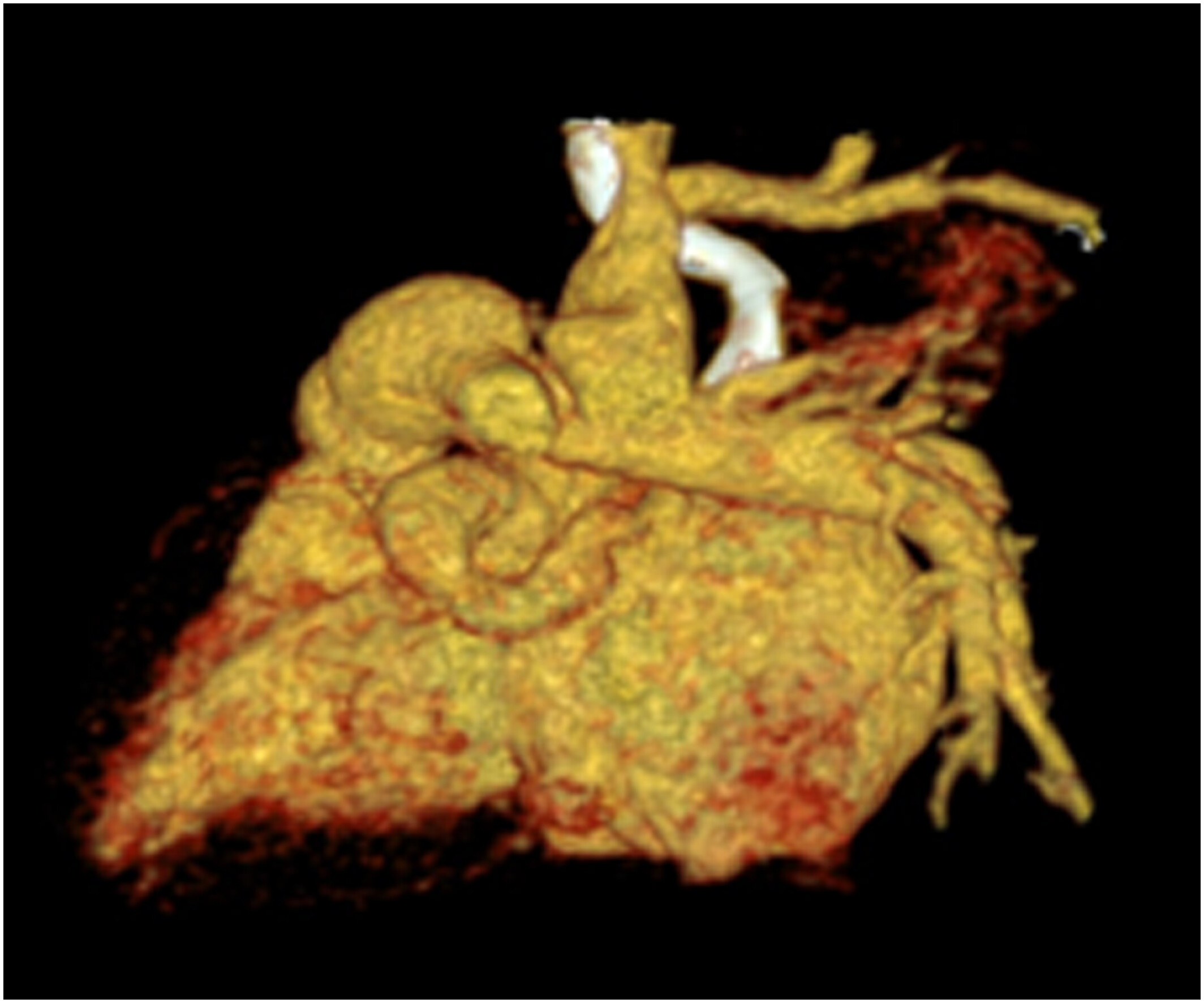
Congenital aorta–right atrial tunnel (ARAT) is a rare congenital cardiovascular malformation characterized by an abnormal tunnel-like connection between the aorta and the right atrium. Patients with ARAT frequently have other congenital heart malformations and require diagnosis through a variety of imaging examinations. We report a 1-month-old female infant with multiple congenital cardiac malformations who was diagnosed with ARAT using low-dose multislice spiral computed tomography because echocardiography was unclear.