Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Cover Picture: Semaglutide to remodel mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy balance for vascular dementia therapy (View 3/2025)
- First Published: 18 June 2025
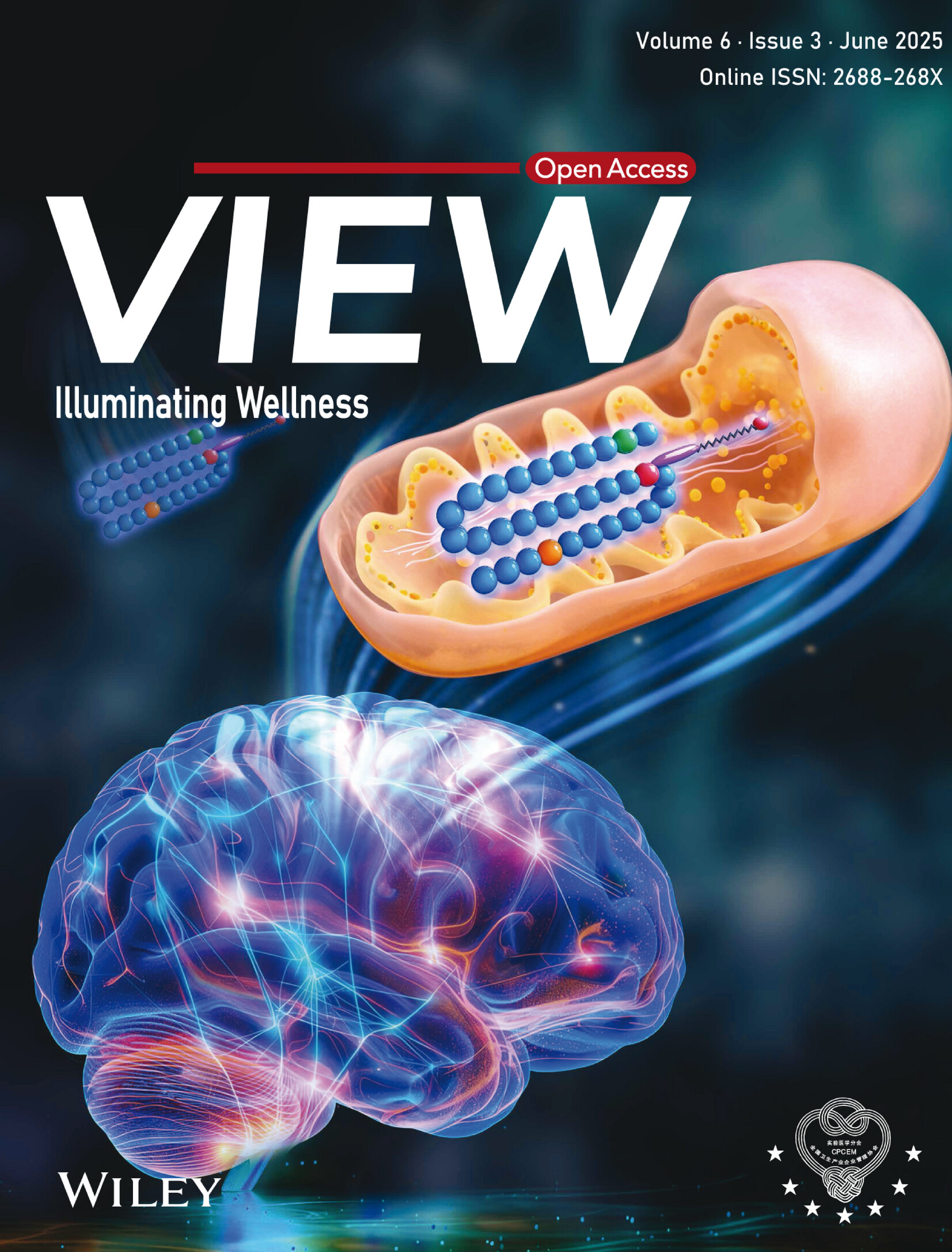
Semaglutide maintained the balance of mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy by improving insulin resistance and passing through GLP-1R/PI3K/Akt pathway, reduced hippocampal neuroinflammation and neuron loss, and thus promoted the recovery of cognitive function in bilateral common carotid artery stenosis (BCAS) mouse model of VaD.
BACK COVER
Back Cover: Circulating genomic biomarkers predict chemoradiotherapy resistance and immunotherapy response in locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (View 3/2025)
- First Published: 18 June 2025
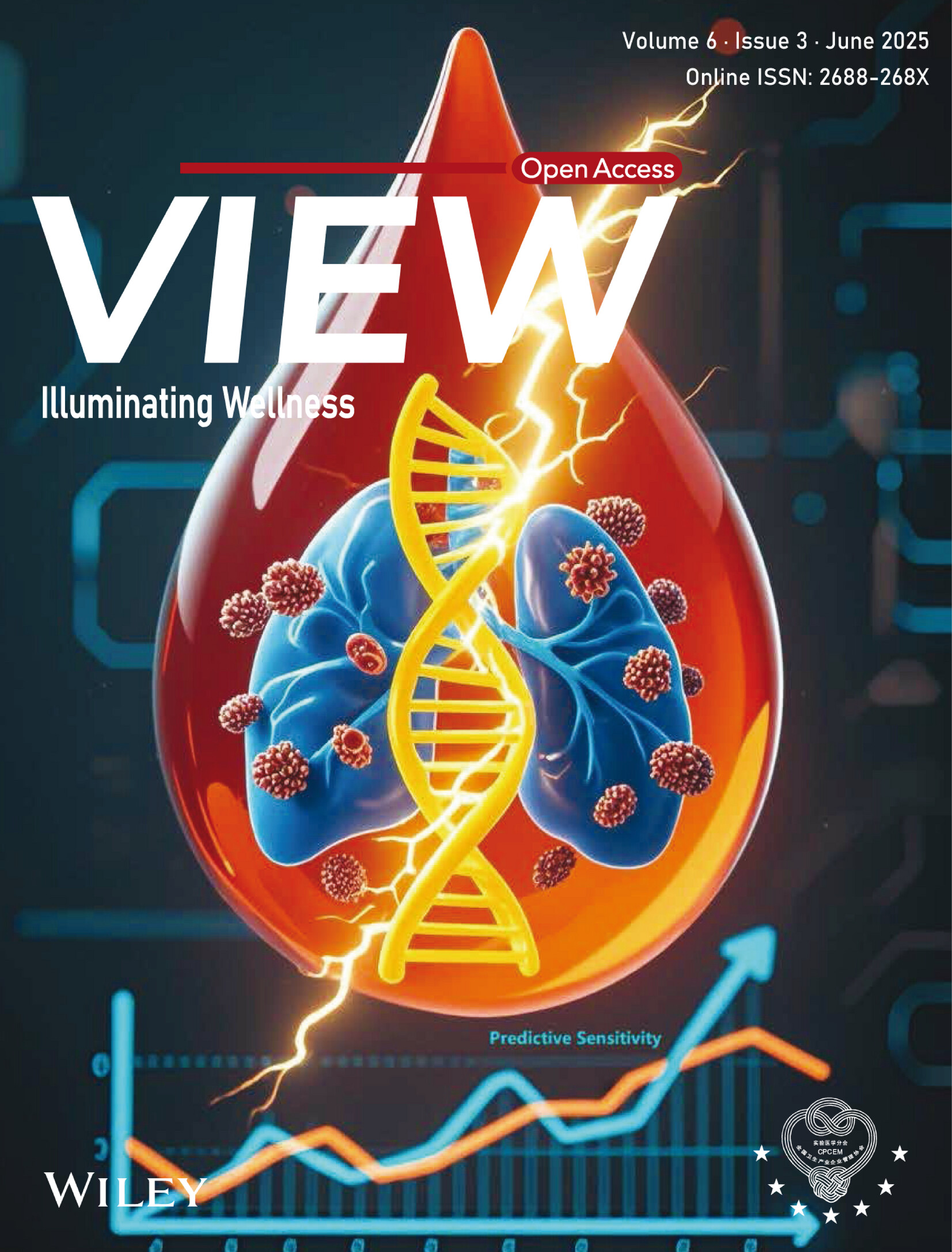
In this article, the authors demonstrate that circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA)-based genomic features can predict efficacy of chemoradiotherapy and immunotherapy in patients with unresectable locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Blood-based STK11/KEAP1 mutations are associated with poor prognosis and resistance to definitive chemoradiotherapy, but suggest benefits from consolidation immunotherapy. This integrative biomarker strategy of combining post-treatment ctDNA molecular residual disease detection with pre-treatment STK11/KEAP1 mutations effectively enhances predictive sensitivity, offering a promising approach for personalized therapeutic decisions.
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
Development and application of microfluidic sweat detection technology in mental health monitoring
- First Published: 23 April 2025
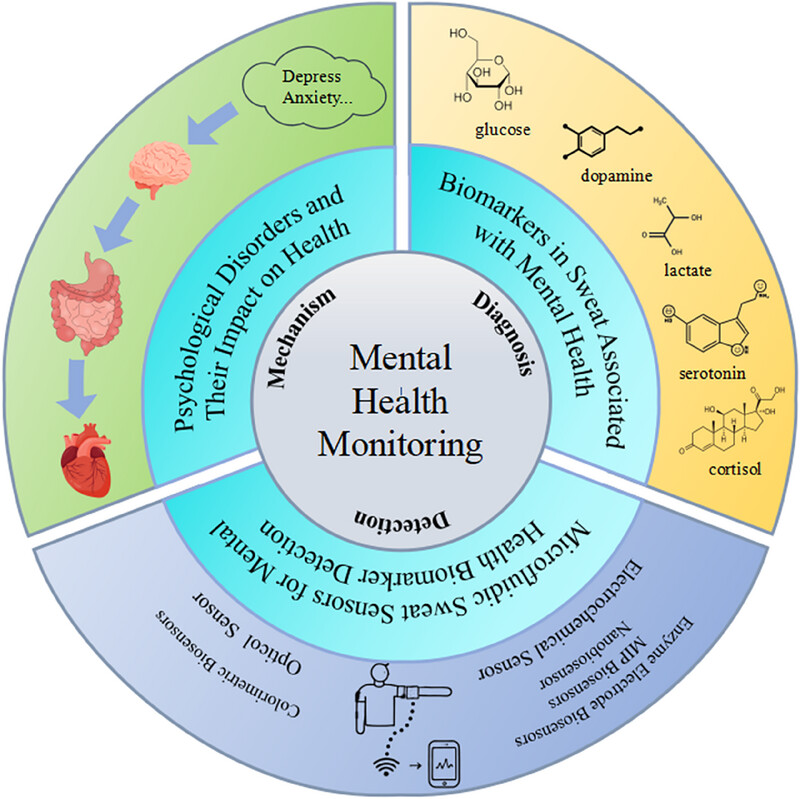
In this review, the authors emphasize the potential of microfluidic sweat detection technology in the field of mental health monitoring. The work explores the intricate relationship between psychological disorders, such as depression and anxiety, and their physiological impact, emphasizing how these conditions can influence systemic health. Furthermore, the study discusses key sweat-associated biomarkers, including serotonin, cortisol, dopamine, glucose and lactate, which have been linked to mental health status. The review also provides an in-depth analysis of advanced microfluidic sensor technologies, such as electrochemical sensors, nanobiosensors, enzyme-based electrodes and colorimetric biosensors, showcasing their application in real-time, non-invasive mental health assessment. Additionally, this study addresses the challenges, opportunities, and future perspectives in integrating sweat biomarker detection into routine mental health diagnostics, filling a critical gap in the current literature.
Hybrid nanosystems for the treatment of infectious diseases produced by multidrug-resistant bacteria: A systematic review
- First Published: 08 April 2025

This review explores the potential of hybrid nanosystems, nanometer-sized particles composed of a combination of materials such as metals and polymers, in combating antibiotic-resistant bacteria. These advanced delivery systems are designed to target infection sites with greater precision and efficiency. Promising results from both in vitro and in vivo studies highlight their potential as a novel strategy for future treatment of drug-resistant infections.
Deciphering the tumor immune microenvironment: Microscale measurements for precision detection and multidimensional analysis
- First Published: 20 March 2025
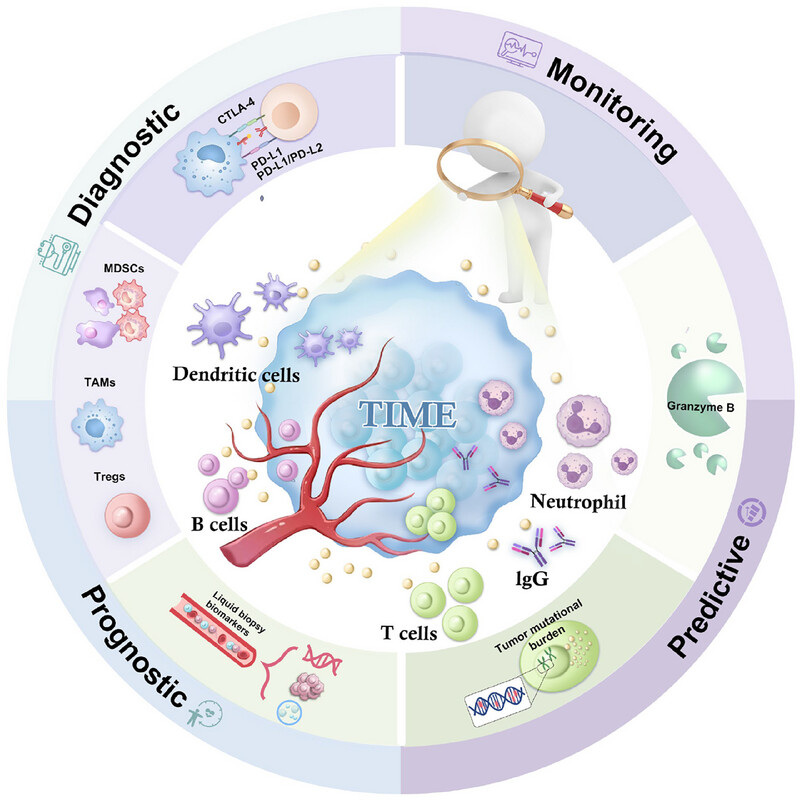
The tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) plays a critical role in cancer progression and treatment response. Advanced tools like nanotechnology-empowered sensors to precisely detect at microscopic scales are introduced. These innovations improve the ability to predict patient responses to immunotherapies and identify new therapeutic targets, paving the way for more personalized and effective cancer treatments.
Nectin4-targeted molecular imaging in solid tumors: Current status and future perspectives
- First Published: 16 April 2025
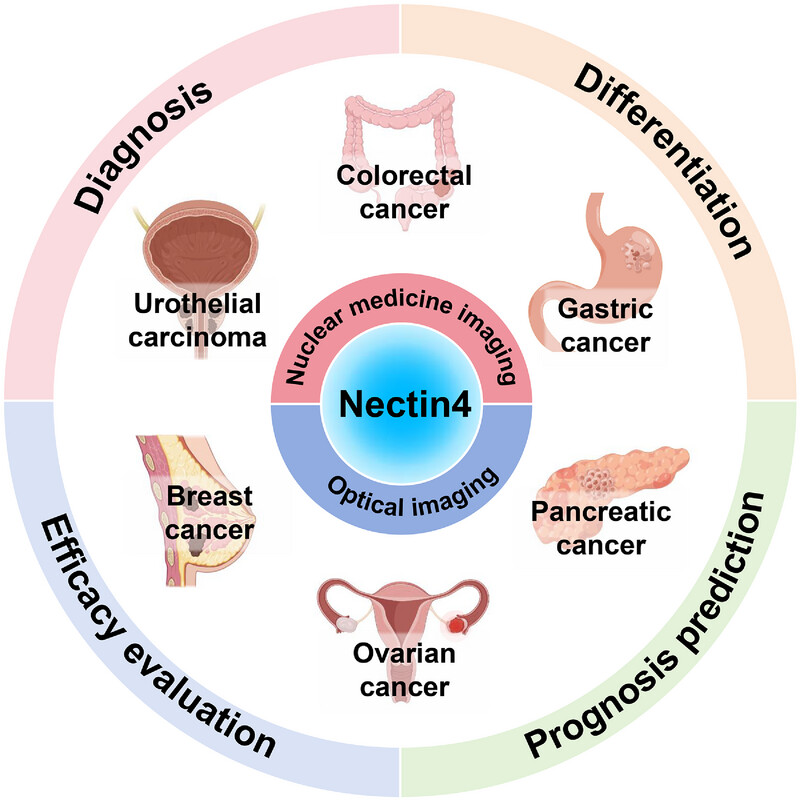
In this review, we provide a concise overview of the mechanisms by which Nectin4 contributes to the pathogenesis of various malignancies and detail the classes of Nectin4-targeted molecular probes. We then delve into the significant advancements in Nectin4-targeted molecular imaging techniques, encompassing both nuclear medicine and optical imaging modalities, as applied in the theranostic context for breast, urothelial, gastric, pancreatic, ovarian, colorectal, and other solid tumors. Specifically, we critically evaluate the application, diagnostic accuracy, prognostic value, therapeutic efficacy assessment, as well as the limitations and challenges associated with molecular imaging in these tumor types.
Unveiling the complex extra-oral colonization pathways and pathogenic mechanisms of Fusobacterium nucleatum, a heterogeneous oral pathogen
- First Published: 15 April 2025
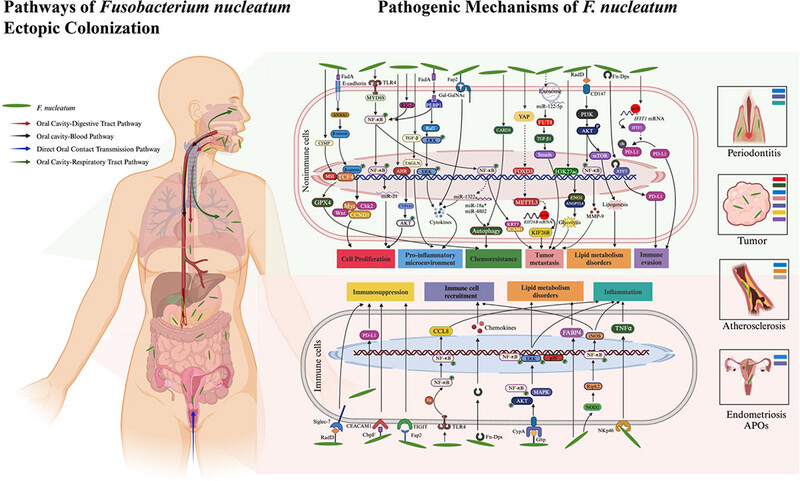
We summarize the taxonomic characteristics, capabilities to adhere to and invade host cells, extra-oral ectopic colonization pathways, and major pathogenic mechanisms of Fusobacterium nucleatum, and explore the regulation of F. nucleatum’s pathogenesis, aiming to provide references and assistance for the development of clinical interventions and future research.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
From clinical observations to molecular insights: Decoding immune checkpoint inhibitors-induced prostatitis
- First Published: 10 April 2025
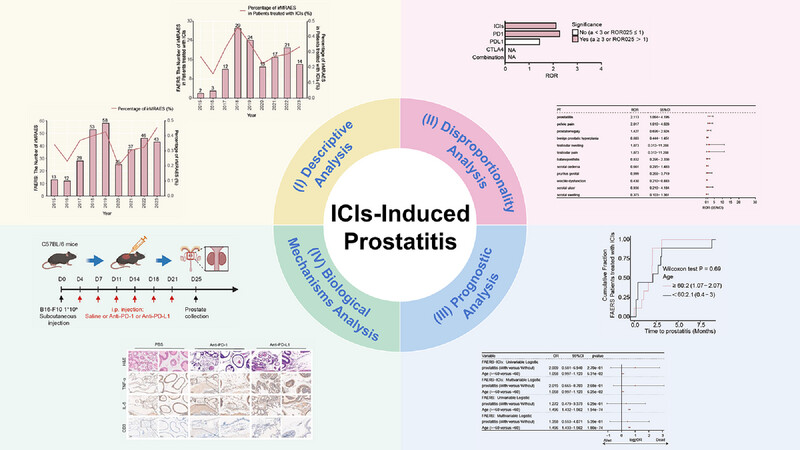
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), an innovative class of cancer therapeutics, may elevate the risk of prostate inflammation (prostatitis) in a subset of male patients. Our investigation demonstrated that ICIs can induce inflammatory responses in prostate tissue; however, selectively targeting specific inflammatory pathways may potentially mitigate these adverse effects. This research provides insights into potential strategies for preventing and treating ICI-associated prostatitis in cancer patients undergoing immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
Semaglutide to remodel mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy balance for vascular dementia therapy
- First Published: 07 April 2025
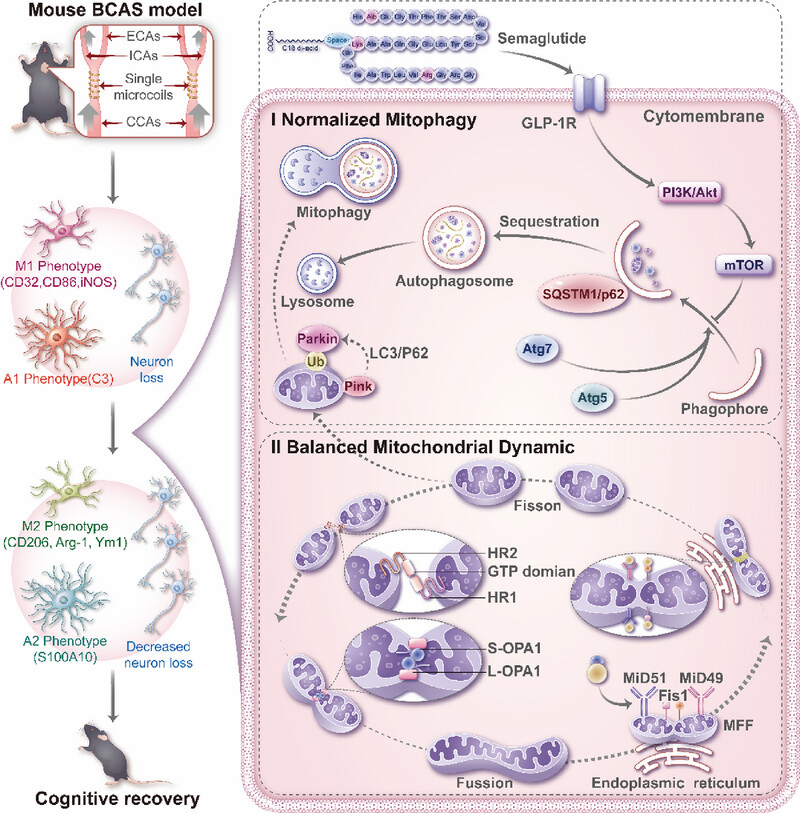
The effects of semaglutide on IR, mitochondrial dynamics, and mitophagy in the hippocampus of BCAS mice after CCH. It was shown that semaglutide maintained the balance of mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy by improving IR and passing through GLP-1R/PI3K/Akt pathway, reduced hippocampal neuroinflammation and neuron loss, and thus promoted the recovery of cognitive function in BCAS mice.
Modeling fire-related smoke inhalation injury using the human lung-on-a-chip and organoid platform: Pathogenesis insights and therapeutic evaluation
- First Published: 20 March 2025
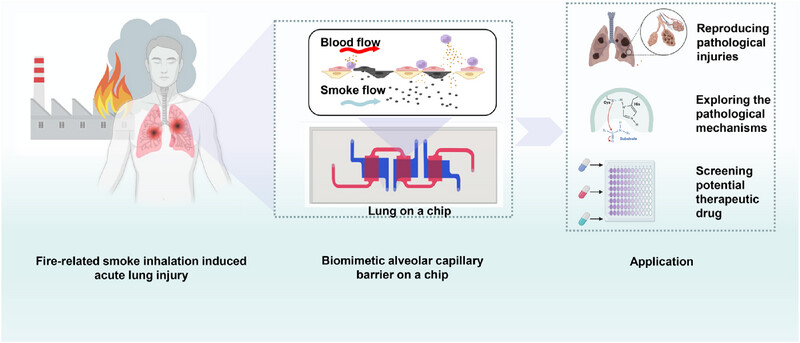
Fire-related smoke inhalation-induced acute lung injury (SI-ALI) poses a significant public health risk, yet effective treatments are limited due to the lack of suitable models. This study developed a more realistic model of SI-ALI using organ-on-a-chip and organoid technologies, identified key molecules such as catechol-O-methyltransferase and potential therapeutic drugs such as Bimatoprost through proteomics and molecular docking, and validated the combined treatment of intravenous vitamin C and nebulized budesonide. The findings provide a powerful tool for understanding SI-ALI mechanisms and advancing drug development.
Glycopattern comparison of sperm and exosomes from conventional in vitro fertilization and rescue intracytoplasmic sperm injection: Enhancing sperm motility through exosome-mediated glycan modulation
- First Published: 09 April 2025
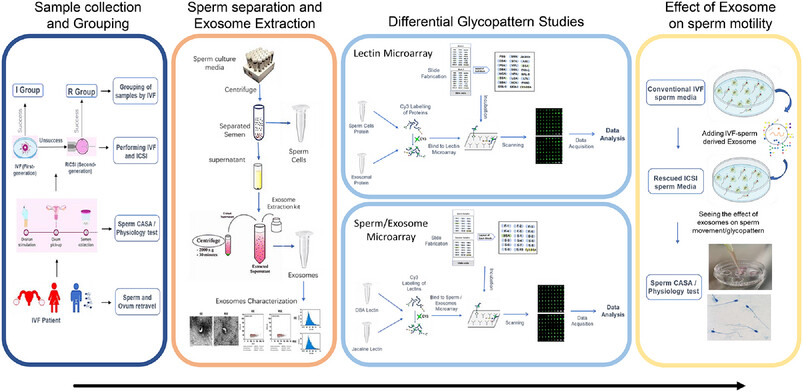
Infertility is a global concern, with male factors contributing to nearly half of cases. This study compared glycopatterns of sperm and sperm-derived exosomes from conventional IVF and rescue ICSI (RICSI) patients, revealing key differences in glycan expression. IVF-derived exosomes enhanced RICSI sperm motility by upregulating specific glycans, offering insights into potential biomarkers and exosome-based therapies to improve fertility outcomes.
The effectiveness and safety of azvudine treatment in COVID-19 patients with kidney disease based on a multicenter retrospective cohort study
- First Published: 09 April 2025
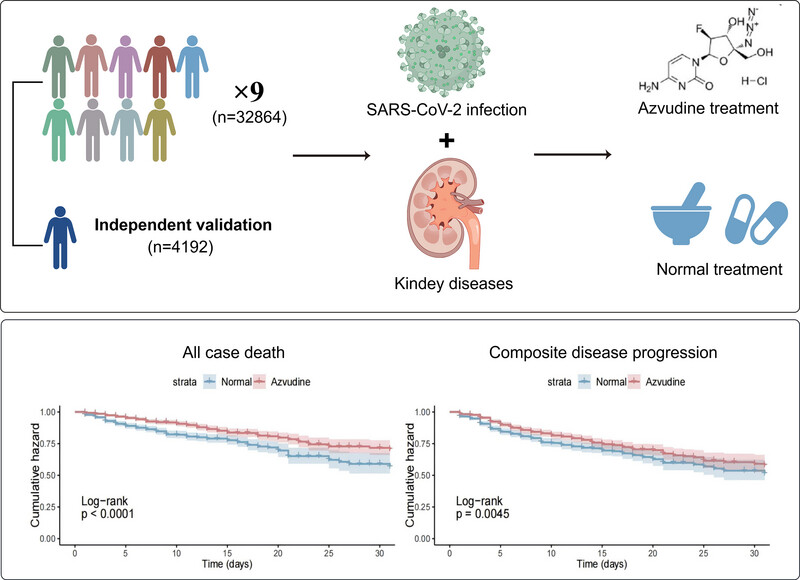
A retrospective, multicenter cohort study was conducted across nine hospitals in Henan Province, aiming to evaluate the efficacy and safety of azvudine in hospitalized COVID-19 patients with kidney disease. Through the application of Kaplan‒Meier and multivariate Cox regression analyses, it was found that azvudine may have potential effects in reducing all-cause mortality and composite disease progression. Additional safety analyses observed adverse events that could be caused by azvudine treatment. The findings were further validated through various sensitivity analyses. This study confirms the effectiveness of azvudine, providing robust evidence for the widespread use of local anti-COVID-19 drugs in China.
Circulating genomic biomarkers predict chemoradiotherapy resistance and immunotherapy response in locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
- First Published: 14 May 2025
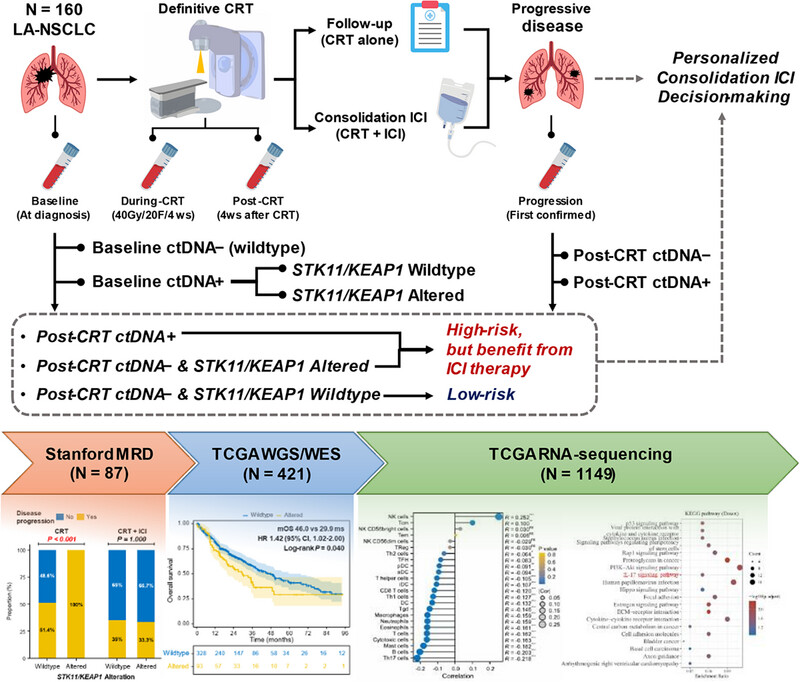
The insufficient sensitivity of single circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA)-molecular residual disease (MRD) prediction remains unresolved and hinders the clinical implementation of ctDNA. Through prospective cohort study, independent validations, and mechanism exploration from peripheral blood and tumor tissue, we demonstrate that ctDNA-based STK11/KEAP1 mutations predict resistance to chemoradiotherapy and efficacy of consolidation immunotherapy. Combining baseline circulating genomic features with ctDNA-MRD can improve predictive sensitivity and facilitate more personalized clinical decisions.