Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Cover Picture: Antiviral effectiveness and safety of azvudine in hospitalized SARS-CoV-2 patients with pre-existing chronic respiratory diseases: A multicenter, retrospective cohort study (View 2/2025)
- First Published: 23 April 2025
In the cohort of SARS-CoV-2 infected patients with pre-existing chronic respiratory diseases, azvudine can not only relieve disease symptoms by blocking the activity of the viral RNA polymeraseand inhibiting viral replication, but also perform immune-enhancing effect by increasing the number and function of serum lymphocytes, and thus activating the immune system. Accordingly, azvudine achieved a synergistic effect in both treating the symptoms and addressing the underlying causes for the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
INSIDE FRONT COVER
Inside Front Cover: Targeting the integrin beta 1-focal adhesion kinase axis with artemisinin: Biophysical disruption of cell adhesion, migration, and invasion in tongue cancer (View 2/2025)
- First Published: 23 April 2025
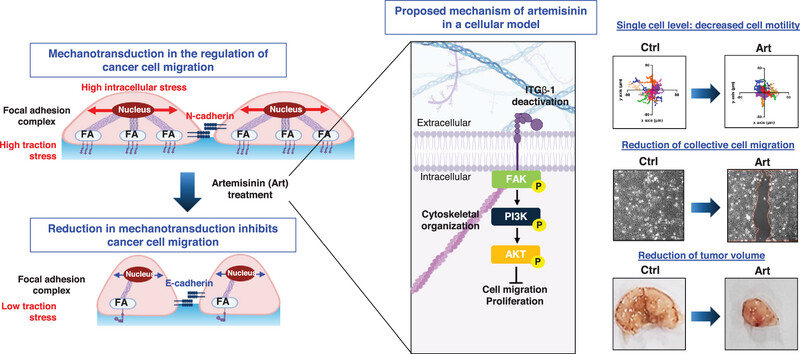
In article Targeting the ITGB1-FAK Axis with Artemisinin: Biophysical Disruption of Cell Adhesion, Migration, and Invasion in Tongue Cancer, Yongsung Hwang, Myung Jin Ban, Sung Sik Hur and co-workers present a novel approach to combat tongue cancer using artemisinin, derived from Artemisia annua. This cover features the plant alongside the molecular structure of artemisinin, emphasizing its potent anti-cancer properties. The cover illustrates a conceptual image of how artemisinin targets and disrupts the integrin-mediated focal adhesion pathway, significantly reducing tumor aggressiveness in the oral cavity. This visual metaphor not only highlights the promising therapeutic potential of artemisinin but also its role in halting the invasive march of cancer cells, as confirmed through rigorous in vitro and in vivo studies.
BACK COVER
Back Cover: Multi-readout thermoplasmonic biosensor for rapid detection of oligonucleotides (View 2/2025)
- First Published: 23 April 2025

A multi-readout thermoplasmonic biosensor for rapid detection of oligonucleotides is presented. It is conceived by incorporating probe oligonucleotides on gold nanorods (AuNRs) random architecture, resulting in a plasmonic DNA microarray. The adopted water-based strategy avoids any probe DNA modification, and the unique morphological properties of the AuNRs array promote DNA hybridization.
The plasmonic microarray's photothermal properties allow monitoring of oligonucleotide hybridization under near-infrared laser irradiation. The plasmonic biosensor detects oligonucleotides by exploiting multiple read-out spectroscopic techniques that enable the quantification of target DNA sequences well below the micromolar detection limit.
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Antiviral effectiveness and safety of azvudine in hospitalized SARS-CoV-2 patients with pre-existing chronic respiratory diseases: A multicenter, retrospective cohort study
- First Published: 05 February 2025
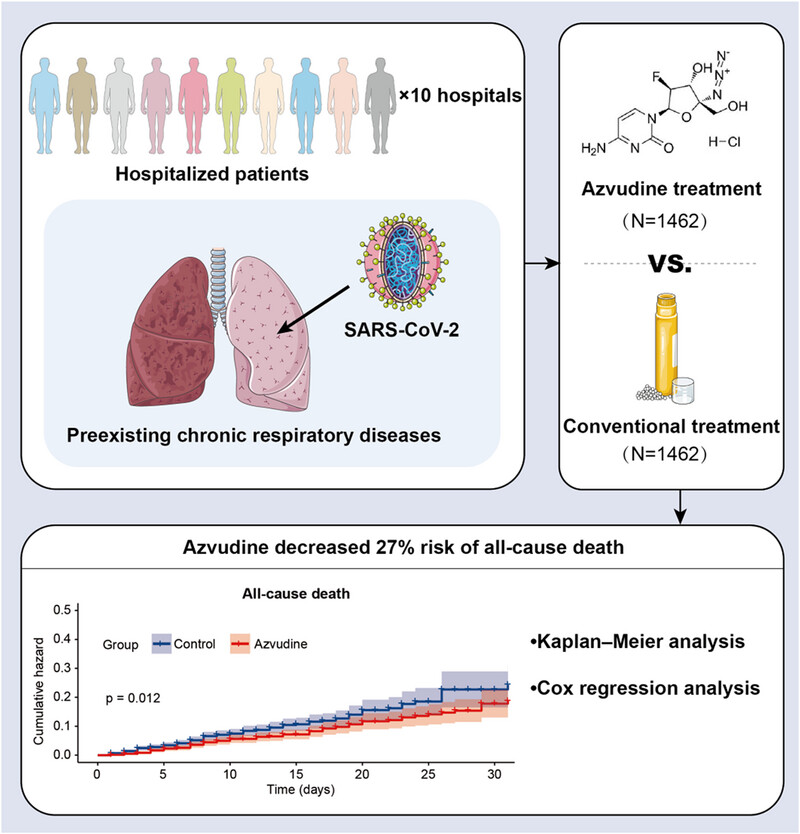
A retrospective, multicenter cohort study involving 10 hospitals in Henan Province was performed to assess the efficacy and safety of azvudine for inpatients with COVID-19 and chronic respiratory diseases. By using Kaplan‒Meier and multivariate Cox regression analyses, azvudine was found to be potentially effective in reducing all-cause death. Additional safety analysis observed acceptable adverse events with azvudine treatment. A nomogram for predicting the survival of inpatients with COVID-19 and chronic respiratory diseases was then further successfully constructed based on 18 clinical features. This study confirmed the effectiveness of azvudine, which provides robust evidence for widespread use of local anti-COVID-19 agents in China.
Single local delivery of 5′-(N-ethylcarboxamido)adenosine depots ameliorates myocardial infarction-induced cardiac dysfunction via the enhancement of mitostasis
- First Published: 13 March 2025
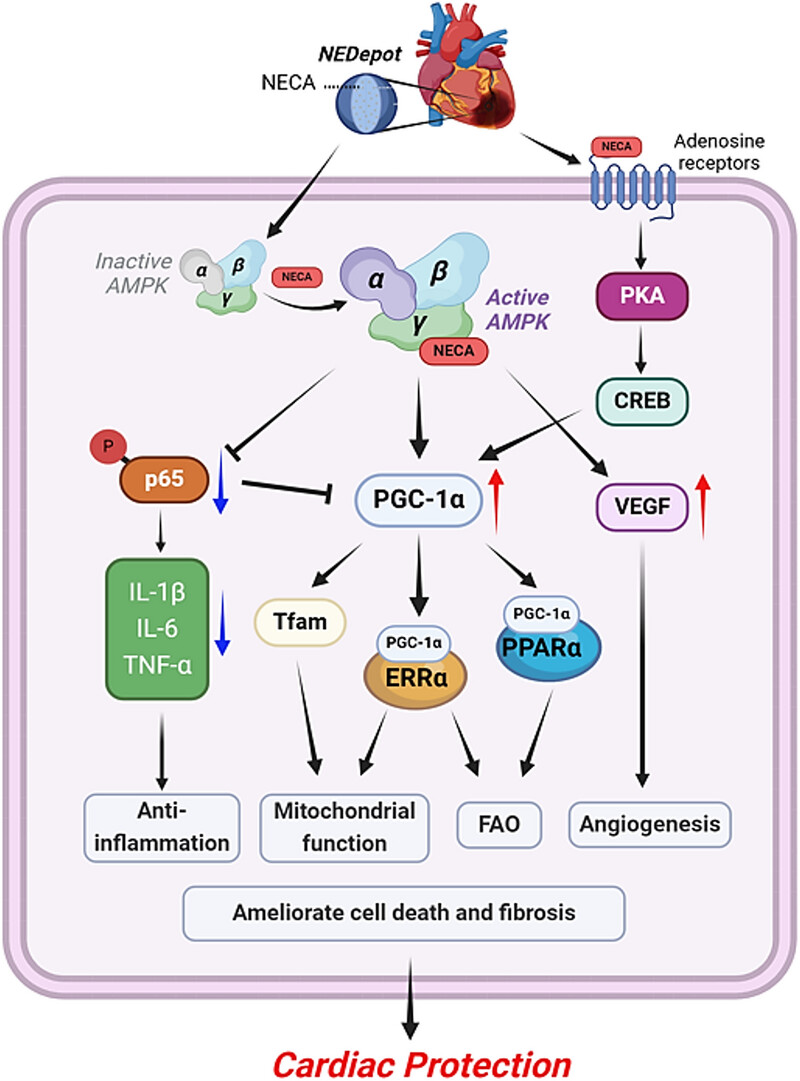
To overcome the limitations of exogenous adenosine in myocardial ischemia treatment, an adenosine derivative 5′-(N-ethylcarboxamido) adenosine (NECA)-loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) micro-depots was fabricated for myocardial infarction (MI) therapy. Single localized NECA delivery via intramyocardial injection of NECA-depots displayed advanced improvement in cardiac function and prevention of myocardial damage in the early phase post-MI, mechanically via the enhancement of mitostasis by triggering AMP-activated protein kinase α phosphorylation.
Targeting the integrin beta 1-focal adhesion kinase axis with artemisinin: Biophysical disruption of cell adhesion, migration, and invasion in tongue cancer
- First Published: 01 April 2025
layman's summary:
Tongue cancer is aggressive and often detected late, making treatment challenging. This study shows that artemisinin inhibits cancer cell migration by disrupting cell–matrix and cell–cell interactions through the ITGβ1-FAK pathway, highlighting its potential as a novel treatment strategy for tongue cancer.
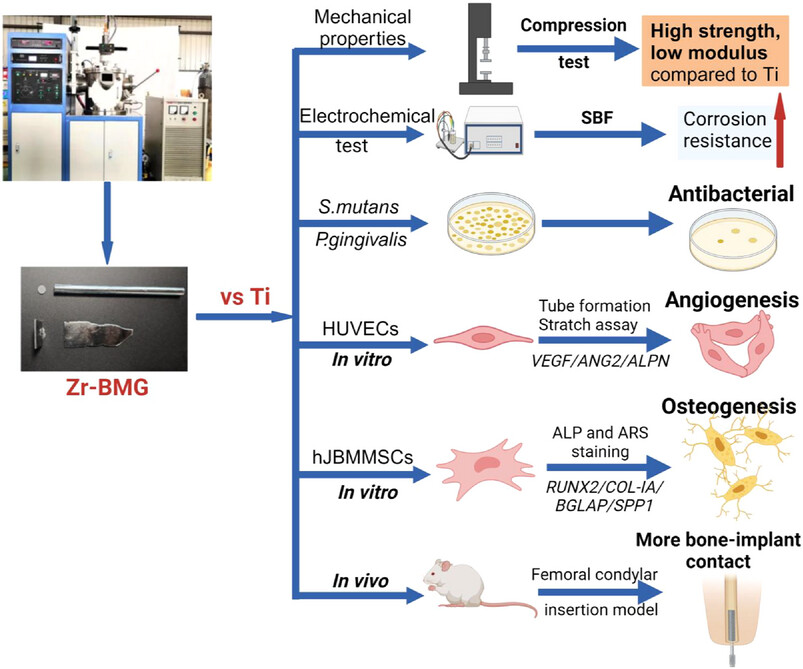
A lasting antibacterial, pro-angiogenic, and pro-osteogenic zirconium-based bulk metallic glass for dental implants
- First Published: 16 March 2025
Multi-readout thermoplasmonic biosensor for rapid detection of oligonucleotides
- First Published: 24 March 2025
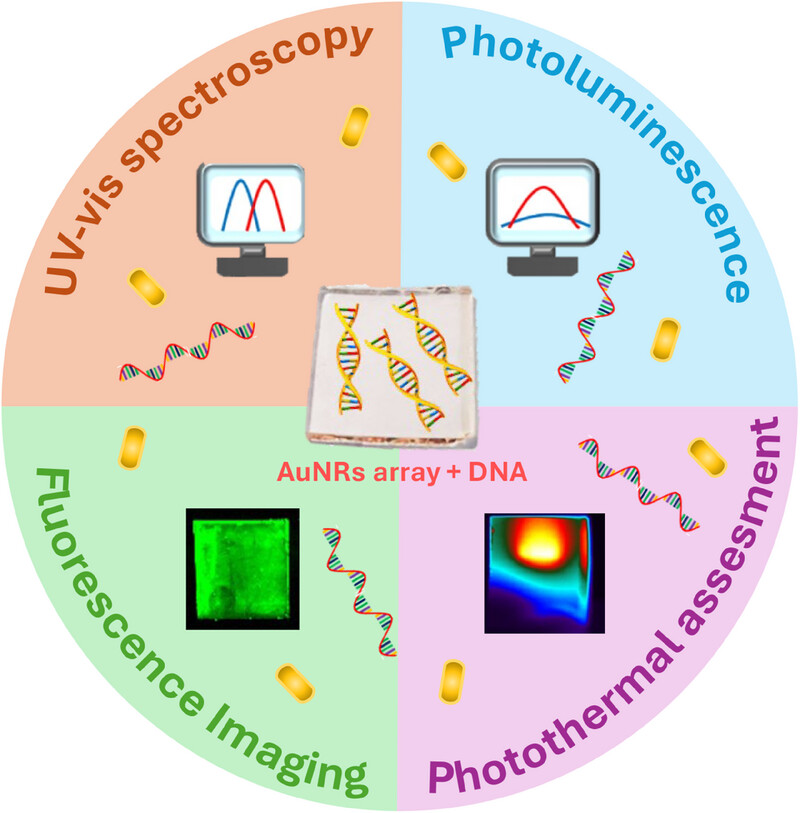
An innovative thermoplasmonic biosensor is developed exploiting an array of functionalized gold nanorods. This biosensor can qualitatively detect DNA hybridization using various readout techniques, including UV–visible absorption spectroscopy and laser scanning fluorescence imaging. It also allows for the quantitative analysis of DNA hybridization through photoluminescence assessment. The thermoplasmonic properties of this biosensor are crucial for creating next-generation devices with reusability capabilities.
Predicting the pathological subdiagnosis of benign prostatic hyperplasia with MRI radiomics: A noninvasive approach
- First Published: 16 March 2025
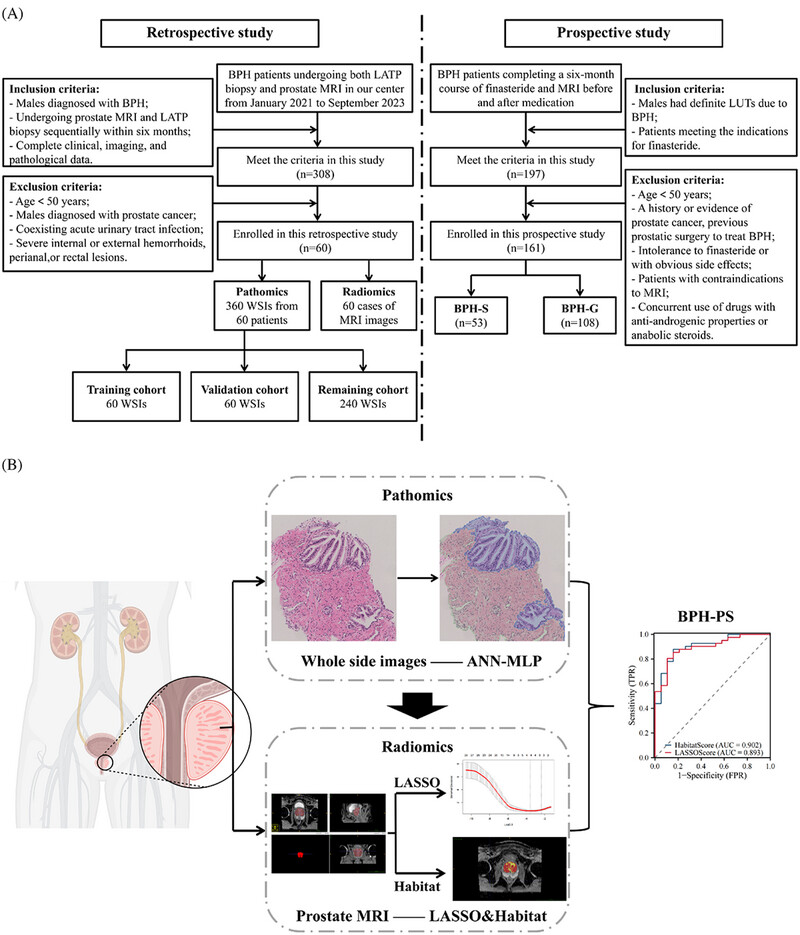
To predict the pathological subdiagnosis of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH-PS) with the overarching aim of mitigating finasteride overtreatment, we conducted a study integrating clinical, pathological, and radiomic data from BPH patients at our center. The study revealed that the ADC value was associated with the gland ratio and could be utilized to predict BPH-PS. Furthermore, the findings suggested that the therapeutic efficacy of finasteride could be anticipated by diagnosing BPH-PS.
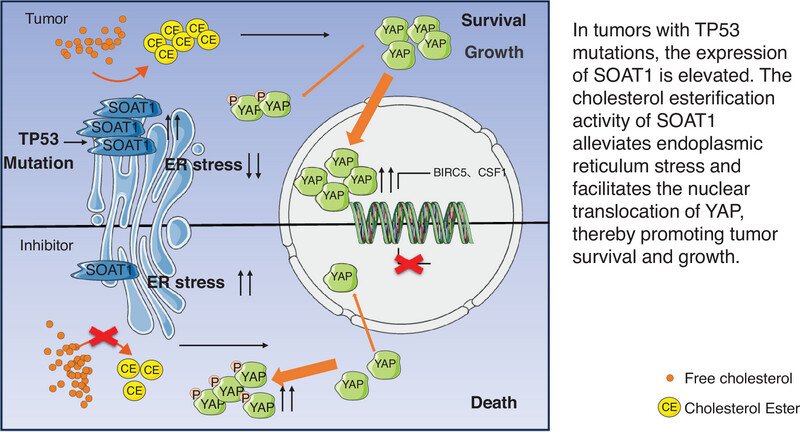
SOAT1 exacerbates tumor progression by promoting YAP signaling activation and attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress
- First Published: 23 March 2025
Multifunctional Z-scheme NaGdF4:Yb,Tm@ZnO/Ag3PO4 nanoheterojunction photocatalysts for water purification and antibacterial wound healing
- First Published: 16 March 2025
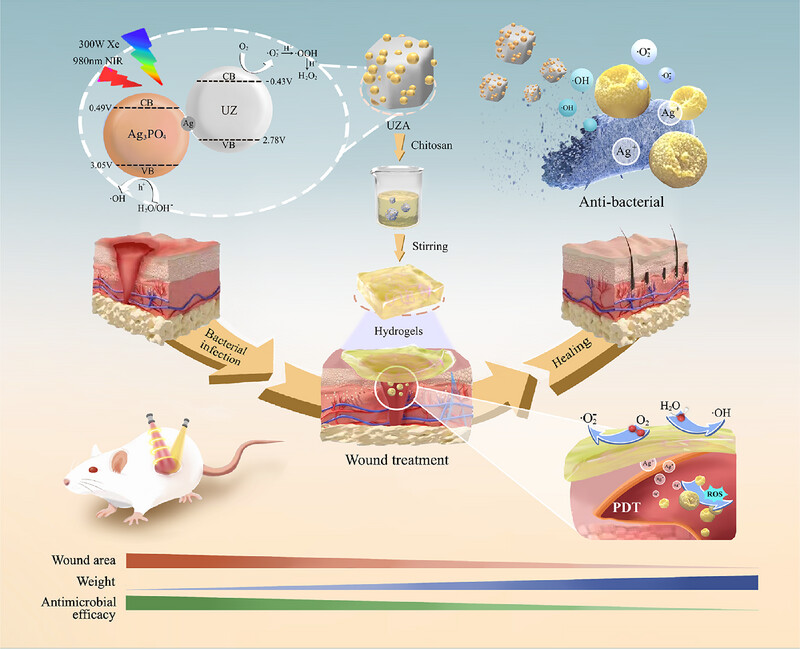
UZA exhibits enhanced antibacterial properties and accelerates wound healing. When combined with chitosan hydrogel, it ensures the uniform distribution of UZA, optimizing its effectiveness in wound recovery. Additionally, UZA demonstrates the ability to degrade organic pollutants and combat pathogenic bacteria, further contributing to its therapeutic potential.