Honorary Editor-in-Chief: Haibo Song; Editors-in-Chief: Hualiang Wang & Hengjun Gao
VIEW is an open access journal for interdisciplinary research focused on “biodiagnostics” in the field of biomaterials. Coverage spans from in vitro to in vivo, and from fundamentals to application, with an emphasis on the biomaterials used particularly in biotechnology and medicine.
VIEW aims to turn research into innovation, publishing full-length research articles, communications, reviews and mini-reviews, as well as perspectives, case reports, analysis, and other editorial content of general interest to the field of biomaterials.
Journal Metrics
- 14.5CiteScore
- 8.5Journal Impact Factor
- 34%Acceptance rate
- 30 days Submission to first decision
Why publish in VIEW?
- Open access means your research is available to read, download, and share.
- An opportunity for transforming research excellence to innovation with an aspiring premier journal.
- Dedicated special issues make your work easily discoverable to like-minded scientists.
- Published in partnership with the Professional Community of Experimental Medicine. By partnering directly with the community, we've built up the trust to help drive change faster, together.
VIEW embraces all significant advances in research fields including drug delivery, lab-on-a-chip, microfluidics, bioimaging, biomarkers, omics, biosensors and bioelectronics, computational diagnostics, bioinformatics, and novel diagnostic devices, and more.
Submit your paper here.
Announcement
Hear from our Associate Editor, Prof. Dr. Kun Qian!
On the Cover
Articles
Targeting the SOD1‒MMP‐2‒COLXVII axis: A therapeutic strategy for age‐related tissue degeneration
- 17 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
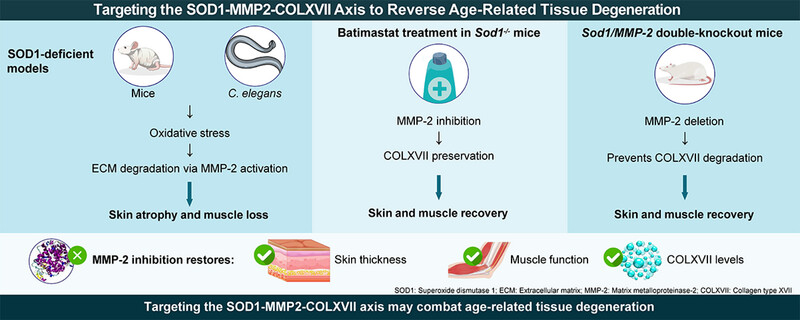
Our work identifies a novel role for MMP-2 in driving senescence-associated skin and muscle degeneration through ECM degradation. We demonstrate that inhibiting MMP-2 activity restores tissue integrity by preserving COLXVII, revealing a new therapeutic pathway for combating oxidative stress-induced tissue aging. Using both mammalian and nematode models, we provide robust evidence that targeting the SOD1‒MMP-2‒COLXVII axis can reverse aging-related structural and functional declines, offering translational potential for clinical intervention in age-related disorders.
Brain metastasis in non‐small cell lung cancer: High‐risk factors and predictive models
- 8 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
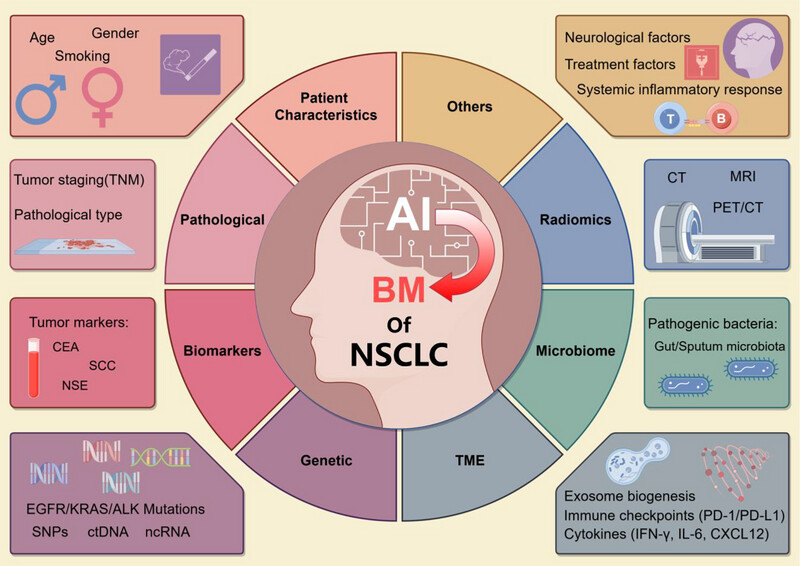
Artificial intelligence (AI) can integrate of data to predict brain metastases (BM) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). AI algorithms are employed to analyze these multifaceted datasets, enabling the identification of complex patterns and correlations that may not be apparent through traditional analytical methods. The data integration process encompasses a wide range of factors, including clinical and pathological characteristics, biological markers, genomic information, radiomic features, microbiome elements, tumor microenvironment dynamics, and historical treatment records.
Photoacoustic integrated multimodal imaging for breast cancer diagnosis: A review
- 8 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
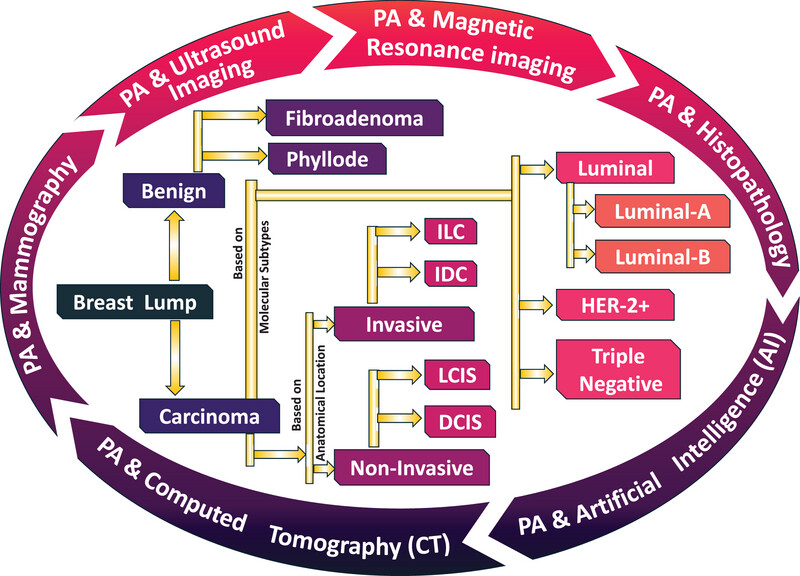
Breast cancer is a complex and challenging to diagnose. This study highlights how combining photoacoustic imaging with traditional techniques like mammography, histopathology, ultrasound, MRI, CT, and artificial intelligence can improve diagnosis, tumor classification, and managing. The integration promises more precise, and noninvasive diagnosis with better disease management and patient outcomes.
A paper‐based bi‐enzymatic sensor for chemiresistive glucose detection
- 3 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
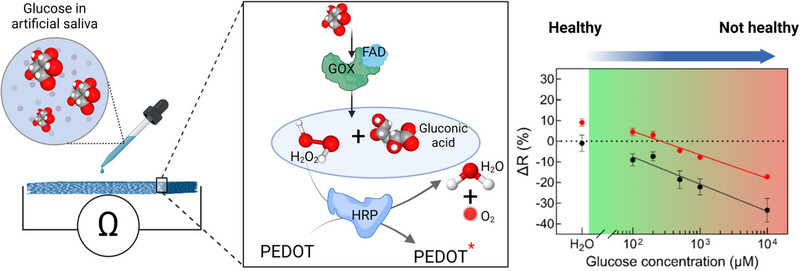
This paper presents the development of a paper-based glucose sensor utilizing poly(3,4-ethylene-dioxythiophene) polystyrene sulfonate (PEDOT:PSS) and a bi-enzymatic system with Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) and Glucose Oxidase (GOx). The chemiresistive sensor is optimized for detecting glucose in biofluids such as saliva, requiring only 40 µL of sample volume and exhibiting a detection limit of 1.1 µM with a linear range of 102–104 µM.
Extracellular vesicles derived from silicate‐stimulated antler reserve mesenchymal cells alleviate kidney damage in diabetic nephropathy through inhibiting abnormal angiogenesis and apoptosis
- 2 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
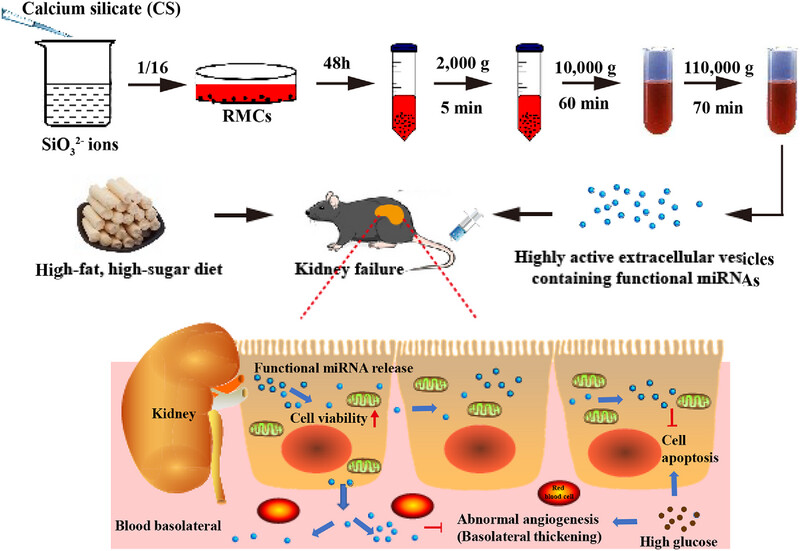
A novel bioengineering platform was invented to harness simple silicate ions to command highly regenerative deer antler cells, transforming them into super-factories that massively produce customized extracellular vesicles (Si-RM-EVs) rich in therapeutic miR-148a-3p, dwarfing natural EV output and payload. These precisionally engineered Si-RM-EVs achieved striking reversal of diabetic kidney damage in mice via simultaneously inhibiting abnormal angiogenesis and apoptosis, proving a promising cell-free therapeutic strategy with vast potential to regenerate damaged organs beside kidney.
The following is a list of the most cited articles based on citations published in the last three years, according to CrossRef.
Biosensors and sensors for dopamine detection
- 13 September 2020
Graphical Abstract
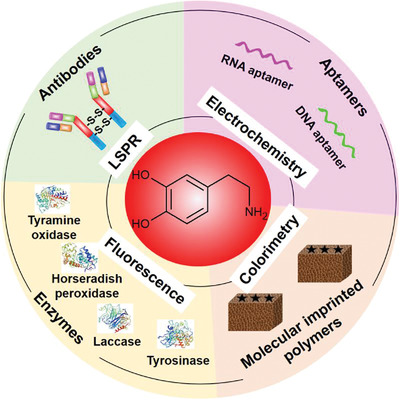
Enzymes, aptamers, antibodies, and molecularly imprinted polymers have been developed to detect dopamine using electrochemical and optical signaling methods to address the analytical needs of fast, selective, sensitive, and in situ analysis of dopamine. On this topic, potential artifacts for sensor design are also critically evaluated.
Recent development of nanomedicine for the treatment of bacterial biofilm infections
- 14 October 2020
Graphical Abstract
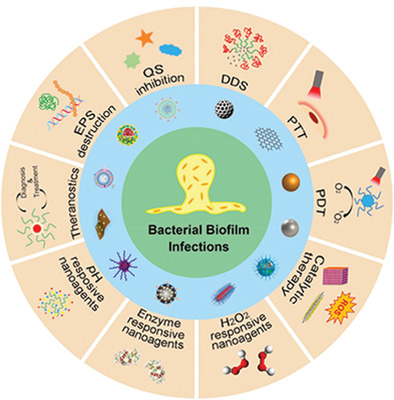
Bacterial biofilm related infections are ever growing threats for global medical community. However, traditional antibiotic therapy is usually ineffective for eradicating bacterial biofilms. In this review, recent development of nanomedicine to treat bacterial biofilm infections is introduced, and typical therapeutic strategies based on nanotechnology are summarized and discussed herein.
Stimuli‐responsive hydrogels: Fabrication and biomedical applications
- 27 August 2021
Graphical Abstract
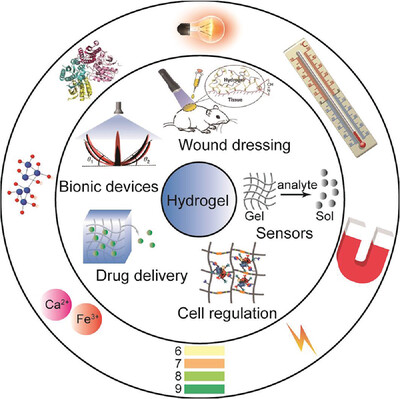
In this review, the authors aim to provide guidelines for researchers to design stimuli-responsive hydrogels of their own interest. Different kinds of construction mode including supramolecular assembly, radical polymerization, chemical reaction and so on are introduced. Different hydrogels response to contact and non-contact, synthetic and natural, and endogenous and exogenous signal are discussed. Various applications developed and will be developed in the future are evaluated, especially in the field of tissue engineering and regeneration medicine, which are still at its primary stage and in an urgent need of development. The growing of stimuli-responsive hydrogels is expected to contribute to this field and provide promising perspectives.
Type I AIE photosensitizers: Mechanism and application
- 13 July 2021
Graphical Abstract
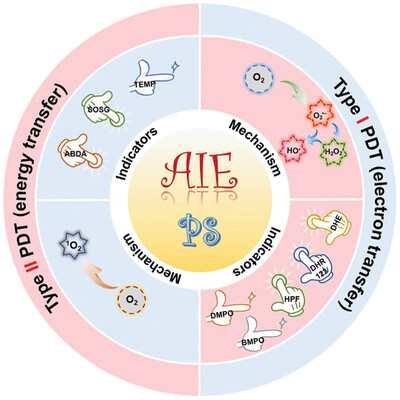
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is emerging as a promising cancer therapeutic treatment and receiving increasing interests. Focusing on this specific theme, this review presents a detailed introduction on the PDT mechanism, summarizes the detection methods for the nature of reactive oxygen species, and discusses the superiority of Type I photosensitizers with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) property. At last, the latest advances on Type I AIE photosensitizers are reviewed.
Bionanoparticles in cancer imaging, diagnosis, and treatment
- 15 March 2022
Graphical Abstract
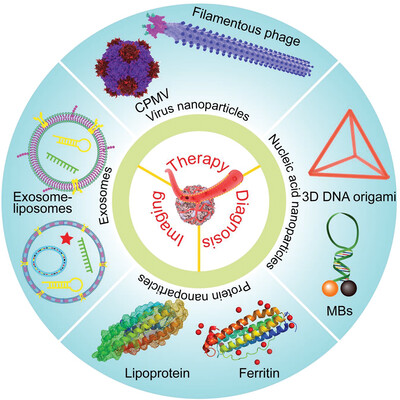
The natural and artificial biological molecules, such as the DNA, proteins, and lipids, could be assembled into bionanoparticles such as bacterial viruses (i.e., bacteriophages or phages), plant viruses, DNA origami, protein nanoparticles, and exosomes. Here, we review their applications in cancer imaging, diagnosis, and treatment and highlight their distinct properties.
Recent issues
- Volume 6, Issue 3June 2025
- Volume 6, Issue 2April 2025
- Volume 6, Issue 1February 2025
- Volume 5, Issue 6December 2024