Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine
Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW ARTICLE
Gonadoblastoma in Turner syndrome with puberty delay: A case report and literature review
- First Published: 12 October 2023
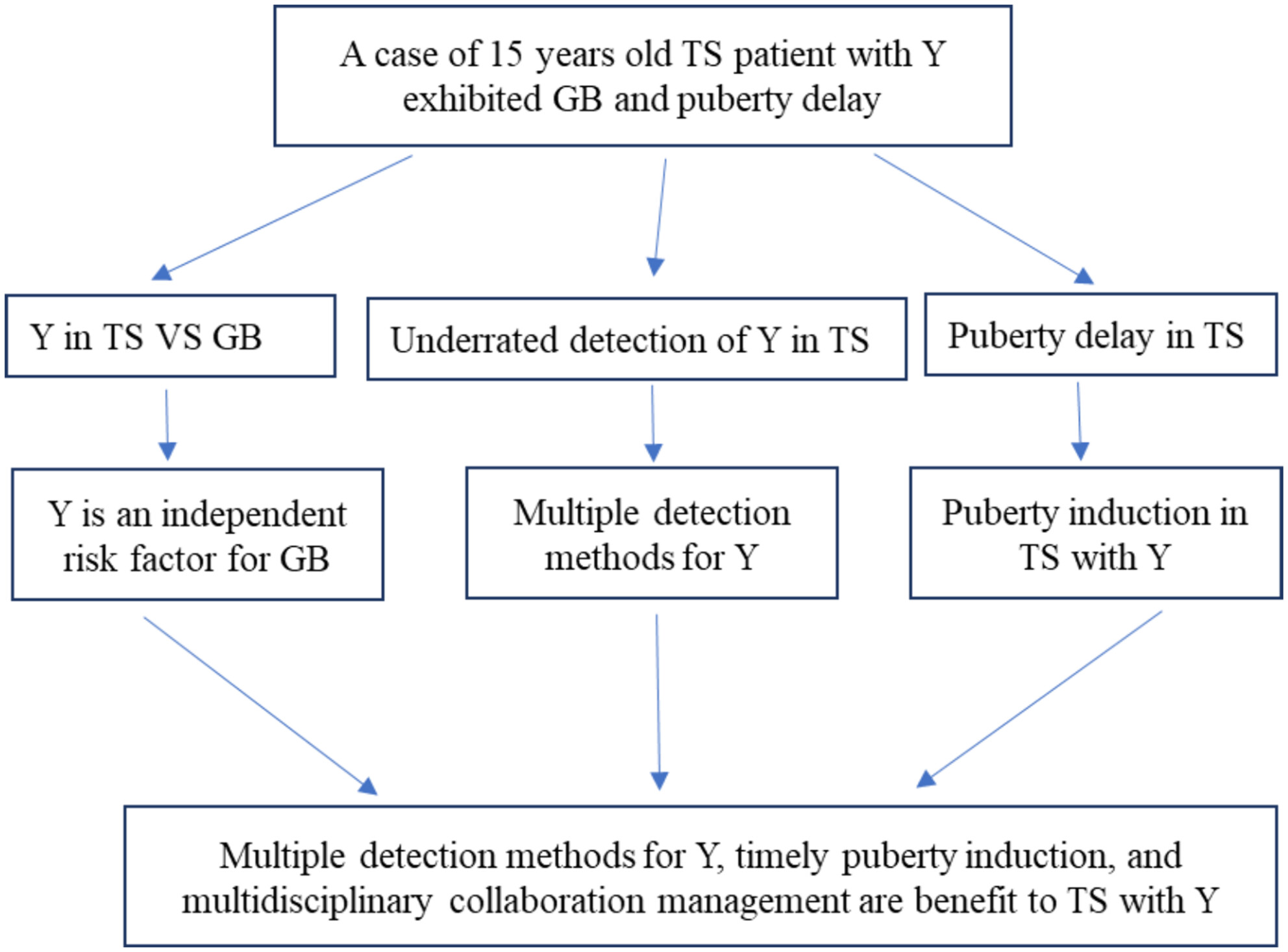
Drawing upon a case report of a TS patient with Y chromosome material and a comprehensive literature review, we underscore the paramount significance of employing multiple Y chromosome material detection techniques, timely initiation of puberty, appropriate oestrogen therapy, and holistic multidisciplinary management in addition to gonadectomy for individuals with TS and Y chromosome material.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Studying carrier frequency of spinal muscular atrophy in the State of Qatar and comparison to other ethnic groups: Pilot study
- First Published: 15 November 2023
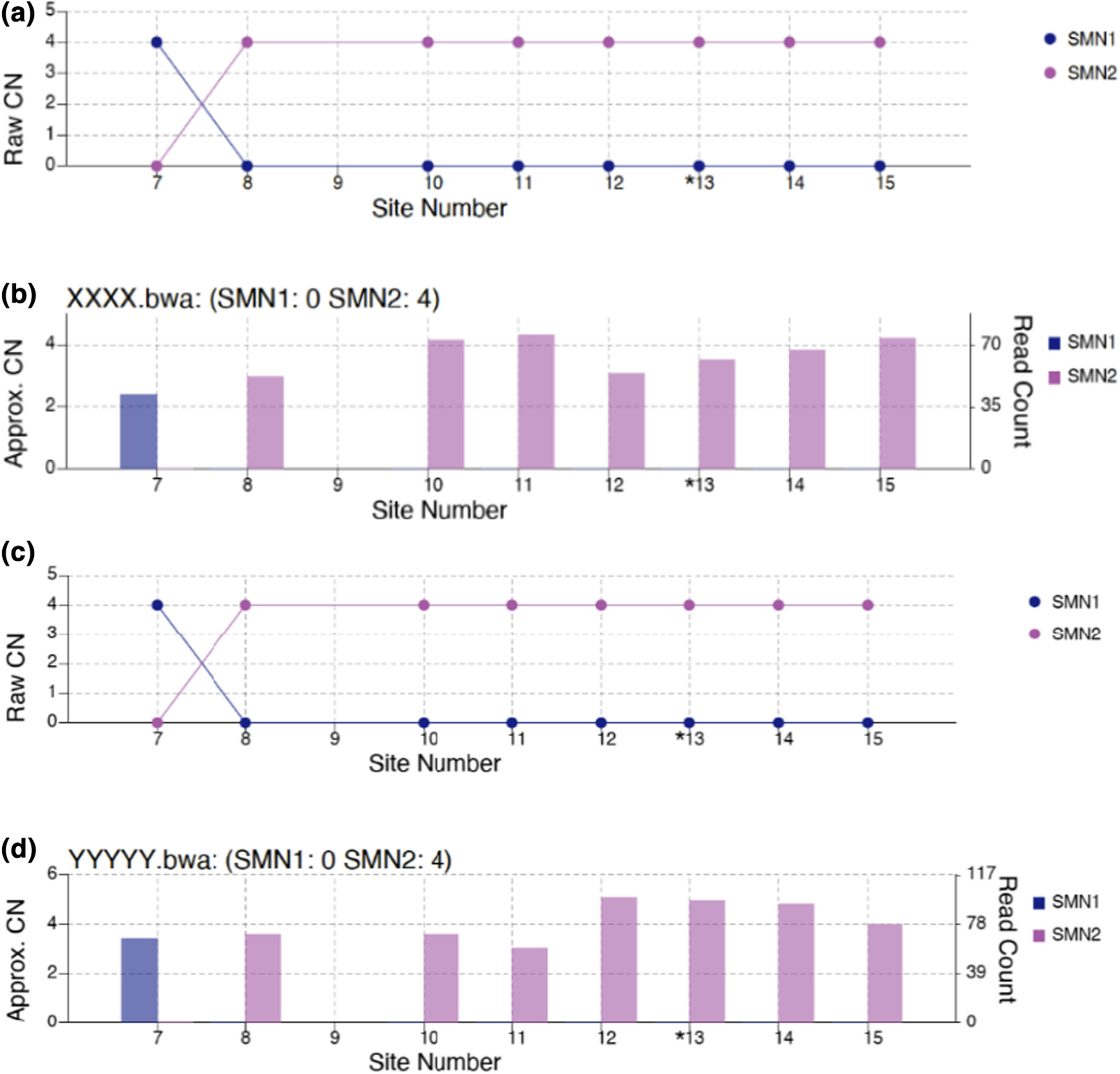
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is an autosomal recessive disease caused by mutations and deletions in SMN1 at exon 7. We examined allelic, genotypic relatedness and copy number (CN) variations and frequencies of SMN1 and SMN2, in 13, 426 samples from Qatar biobank (QBB) to provide a precise estimation of SMA carrier frequency in Qatar in comparison to other populations. The SMA carrier frequency was found to be (2.8%), and the rs143838139 was found in 491/13426 (3.66%) of individuals.
Rare functional variants in the CRP and G6PC genes modify the relationship between obesity and serum C-reactive protein in white British population
- First Published: 26 July 2023
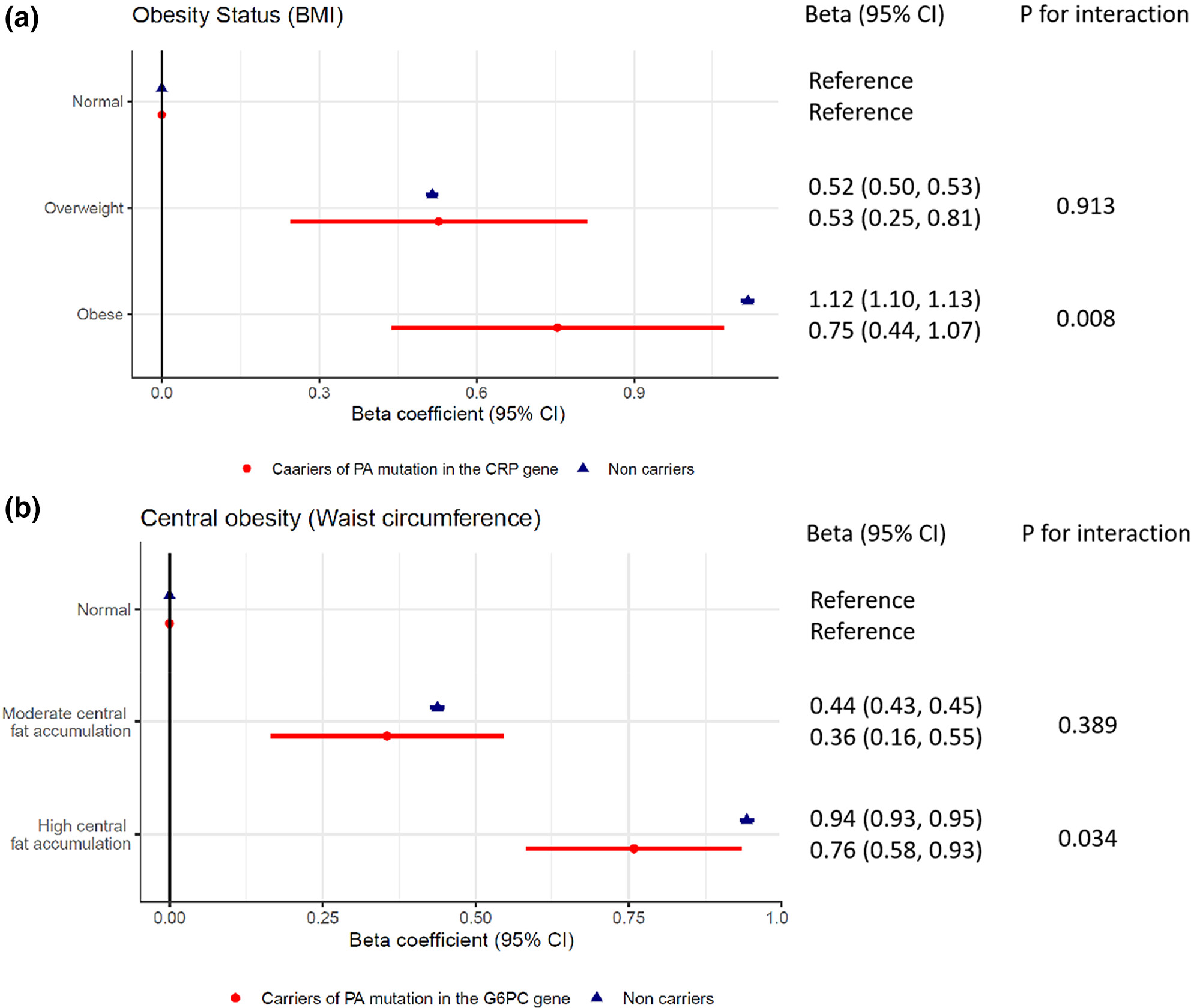
The effects of obesity and central obesity on serum CRP concentration were smaller among the protein-altering mutation carriers in the CRP (pinteraction = 0.008) and G6PC gene (pinteraction = 0.034) compared to the corresponding non-carriers. As serum CRP and obesity are important predictors of cardiovascular risks in clinics, our observations suggest taking rare genetic factors into consideration might improve the delivery of precision medicine.
Expanding the allelic spectrum of ELOVL4-related autosomal recessive neuro-ichthyosis
- First Published: 18 August 2023
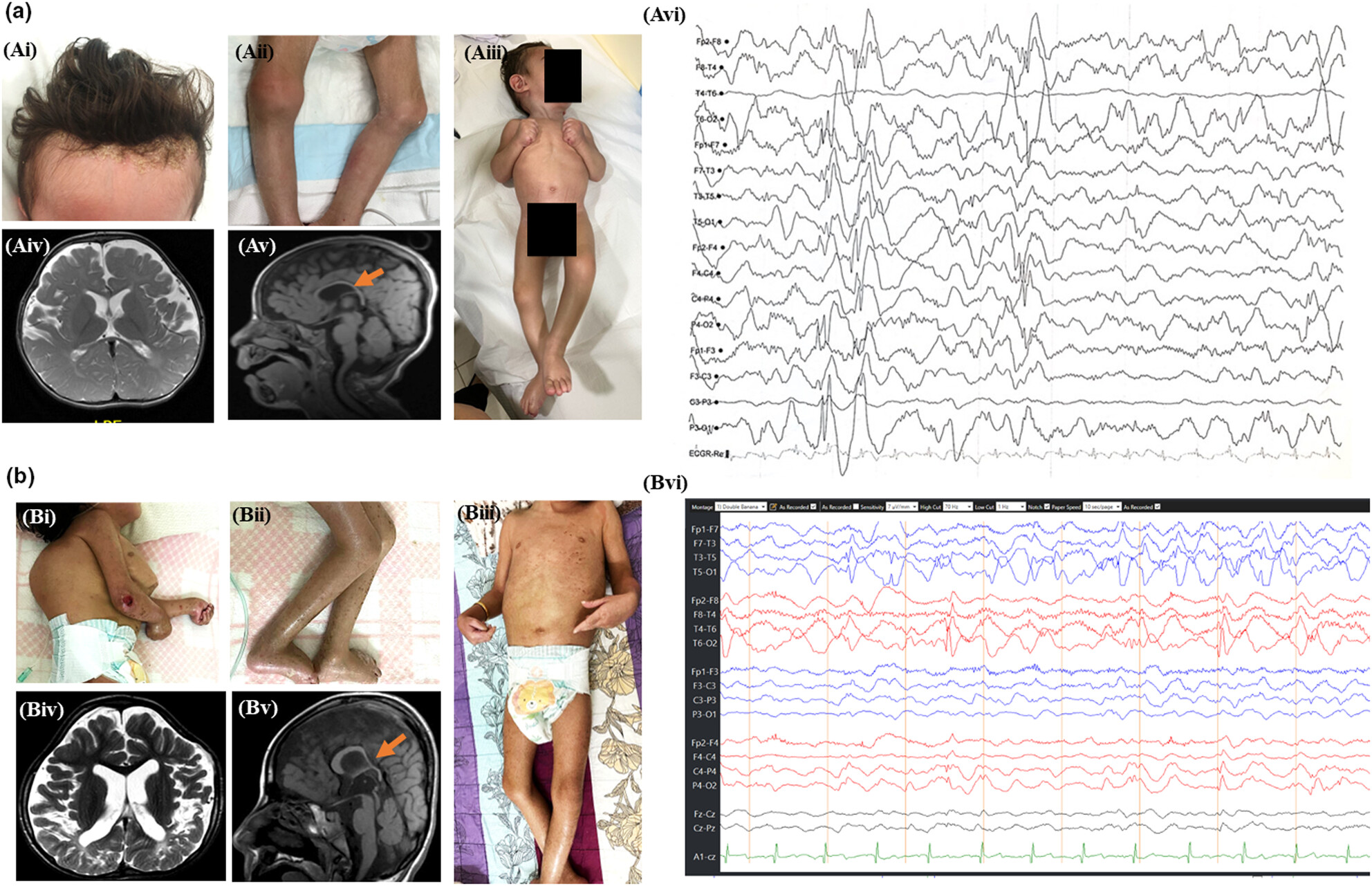
ELOVL4-related ichthyosis, spastic quadriplegia and mental retardation (ISQMR) is a rare autosomal recessive disorders characterized by ichthyosis with neurological features. Only five families with ISQMR with biallelic single-nucleotide variants have been described date and no families with copy number variants (CNVs) have been described. We include four new families with ISQMR, including two that carry a biallelic CNV and originate from the same tribe suggesting a tribal founder variant.
Promoter hypermethylation of RARB and GSTP1 genes in plasma cell-free DNA as breast cancer biomarkers in Peruvian women
- First Published: 07 August 2023
The promoter hypermethylation of RARβ2+GSTP1 is associated with breast cancer, older age, and postmenopausal patients. The PMR of both genes showed a specificity of 86.21% and a sensitivity of 31.03%. Our study accounts for the first evidence of the association of promoter hypermethylation of RARB2 and GSTP1 genes in liquid biopsies (circulating cfDNA) and breast cancer in Peruvian women.
A deleterious frameshift insertion mutation in the ZNF142 gene leads to intellectual developmental disorder with impaired speech in three affected siblings: Clinical features and literature review
- First Published: 26 July 2023
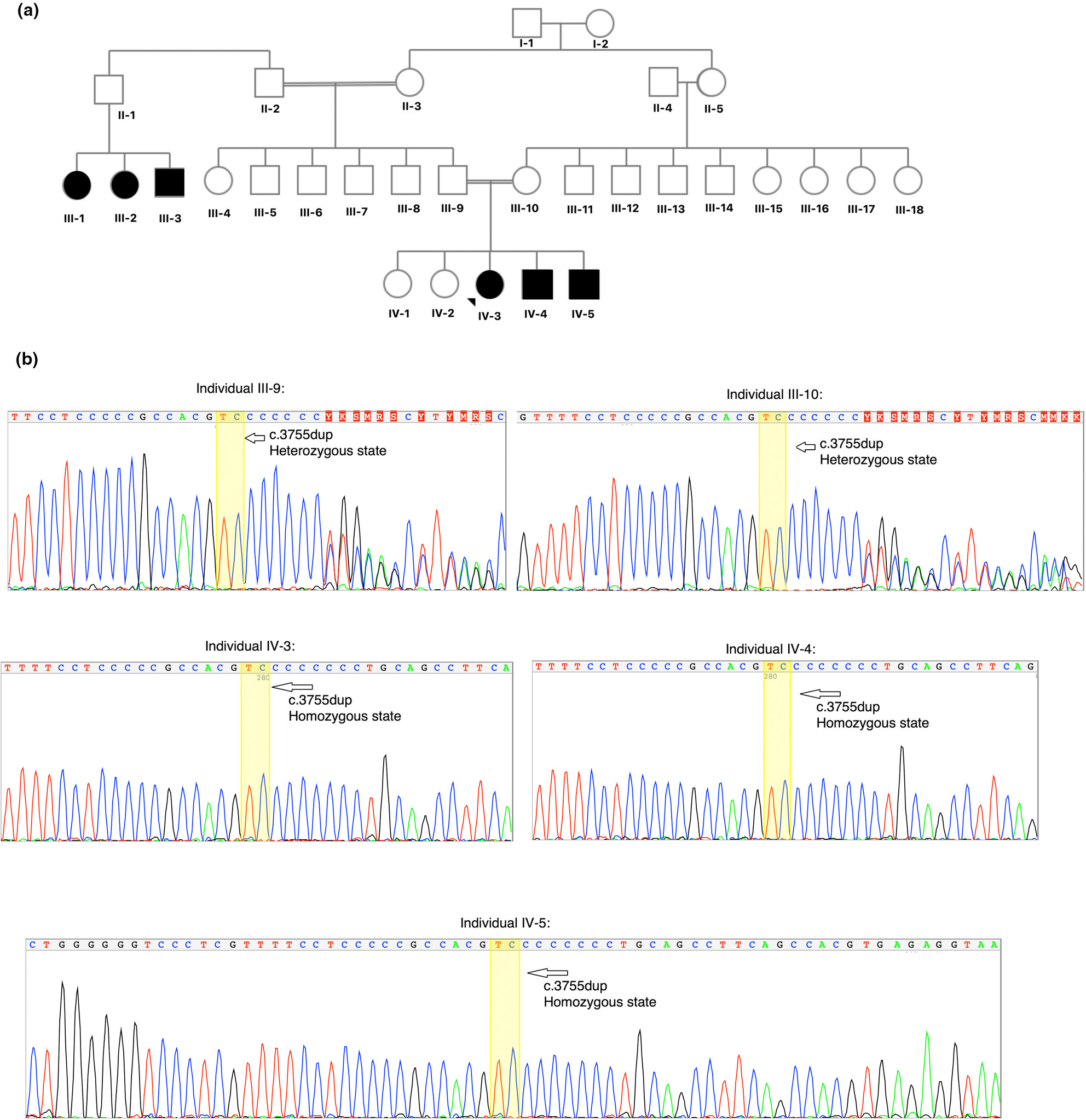
The deleterious recurrent frameshift insertion mutation (NM_001379659.1: c.3755dup) in the ZNF142 gene leads to intellectual developmental disorder with impaired speech in three affected siblings with family history of same condition. The data have implications for genetic diagnosis and counseling in families with the same disorders.
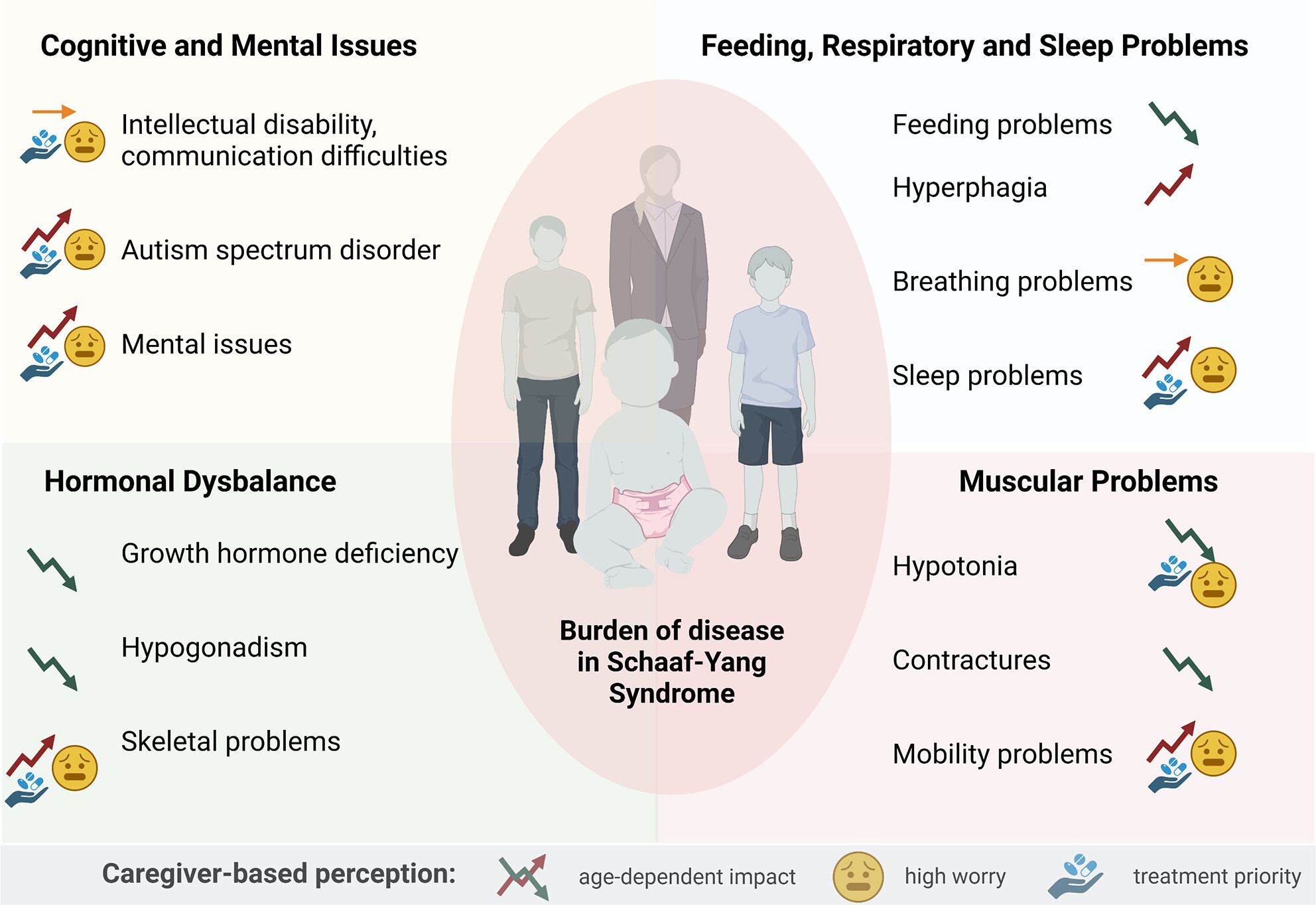
Caregiver-based perception of disease burden in Schaaf-Yang syndrome
- First Published: 03 August 2023
In silico validation revealed the role of SCN5A mutations and their genotype–phenotype correlations in Brugada syndrome
- First Published: 07 August 2023
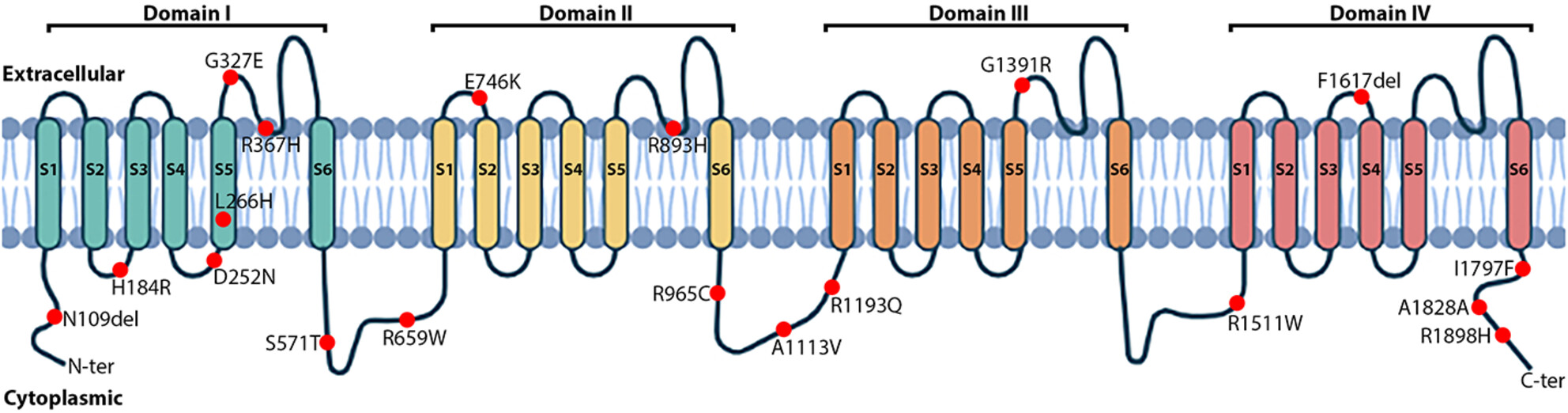
This study aims to identify SCN5A variants and evaluate the genotype-phenotype correlation of Brugada syndrome on 117 Vietnamese probands. Multiple bioinformatic tools were carried out to classify SCN5A variants as benign and disease-causing. In addition, the genotype-phenotype correlation was also revealed.
First-time application of droplet digital PCR for methylation testing of the 11p15.5 imprinting regions
- First Published: 31 July 2023
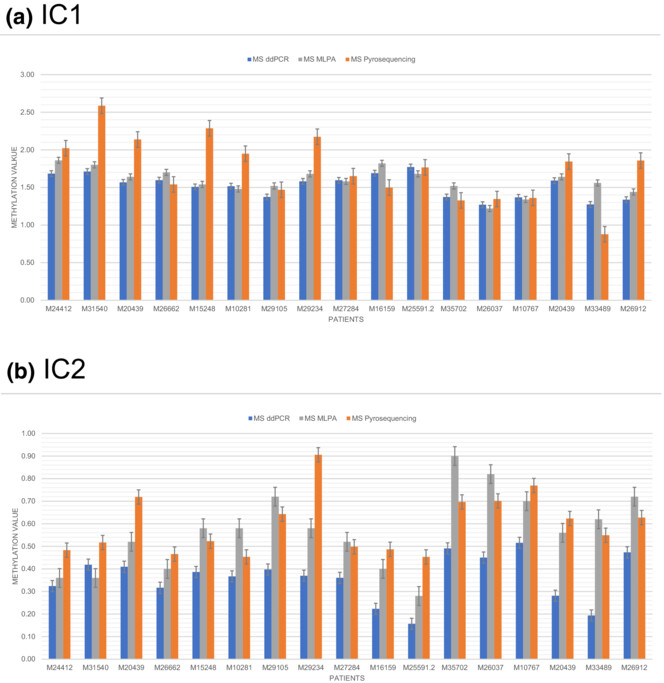
We describe for the first time the application of droplet digital PCR to identify aberrant methylation in imprinting disorders. As a proof of principle of the diagnostic suitability of the method to detect aberrant epigenetic patterns, we have chosen DNA samples with specific aberrant imprinting patterns. We could show the reliability of the technique by comparing it with two other well established methods (MS-MLPA, MS-pyrosequencing).
Clinical heterogeneity of polish patients with KAT6B–related disorder
- First Published: 01 September 2023
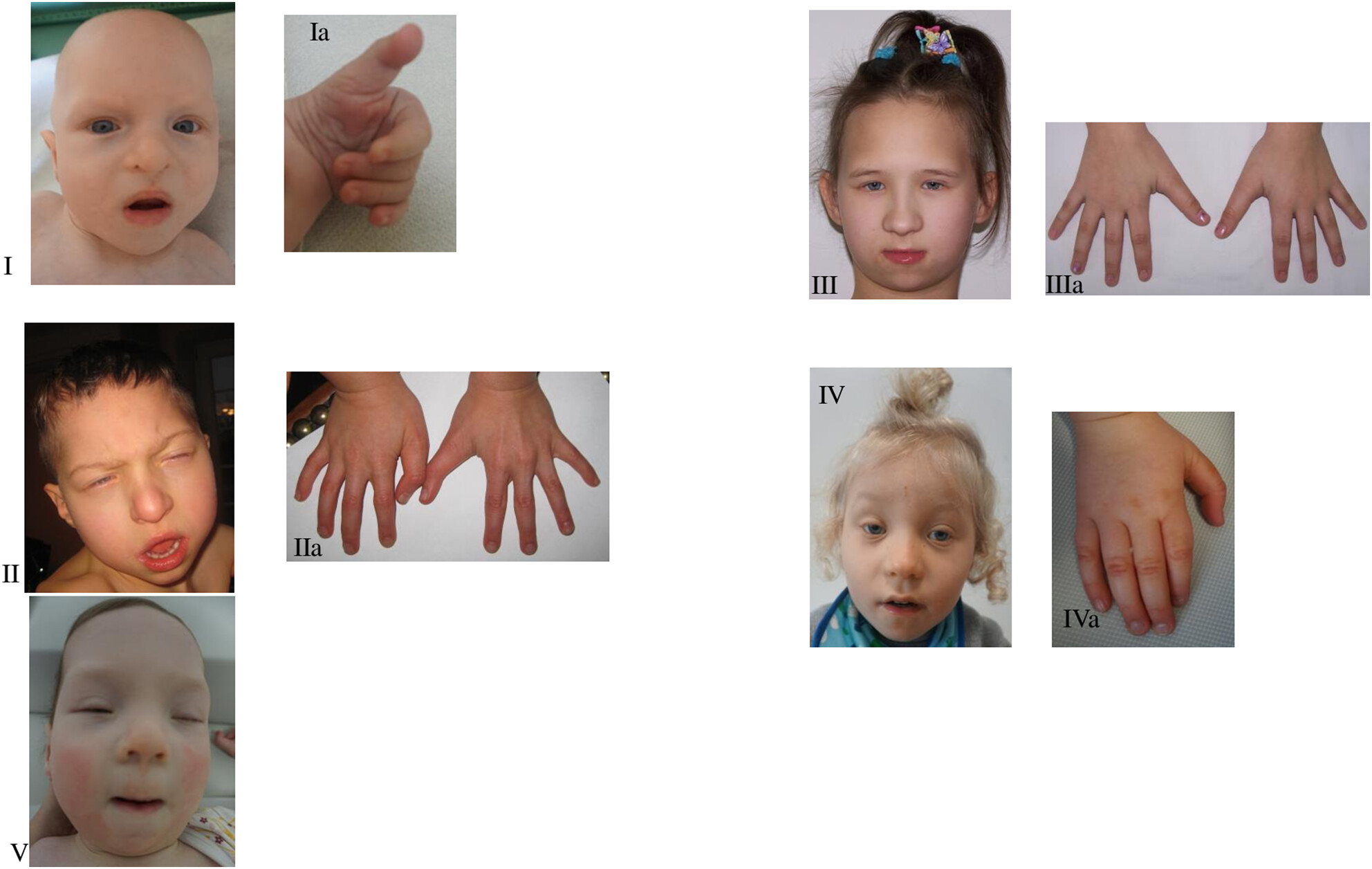
We present a detailed phenotypic analysis of six individuals with KAT6B-related disorders, in whom a heterozygous pathogenic variant in KAT6B gene was found. We report six SBBYS syndrome patients with the same dysmorphic features but a different course of the disease. One known and five novel KATB6 pathogenic variants were identified by molecular diagnostics using Next Generation Sequencing (NGS). While most of the anomalies found in our patients comply with SBBYSS criteria, phenotypic differences in our probands support a broader spectrum of the disease phenotype. To establish the range of this spectrum, a detailed analysis of clinical variability among patients with SBBYSS requires further investigation.
Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome in Chinese population: Analysis of three new cases and review of the literature
- First Published: 15 September 2023
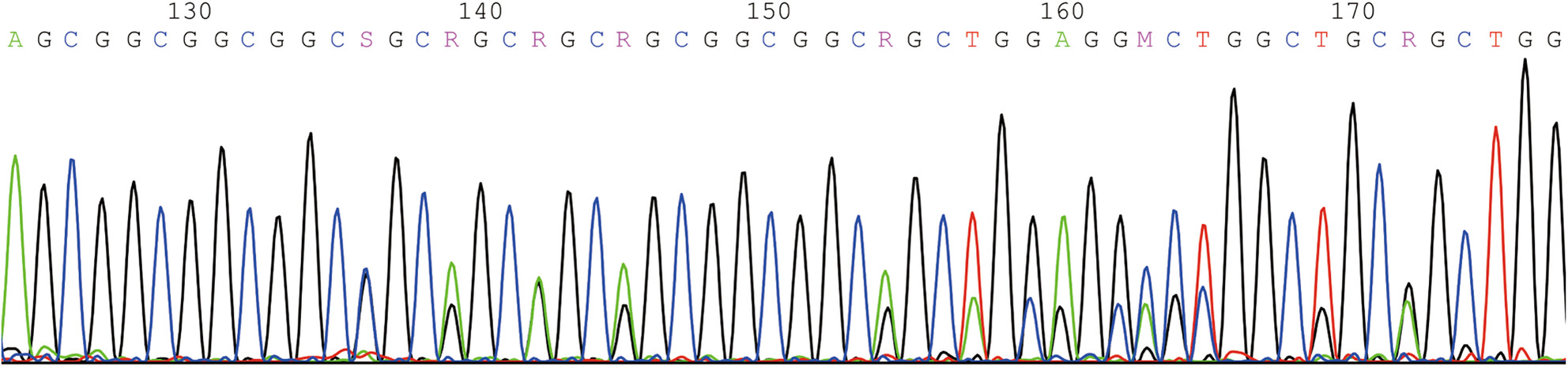
The purpose of this study is to analyze the clinical data and mutations of three new cases, and to summarize the clinical and genetic characteristics of CCHS patients in the Chinese population from our study and previous literature. Our study not only expands the mutation spectrum of PHOX2B, but also improves our understanding of this disease CCHS.
Clinical report and genetic analysis of a Chinese neonate with craniofacial microsomia caused by a splicing variant of the splicing factor 3b subunit 2 gene
- First Published: 09 August 2023
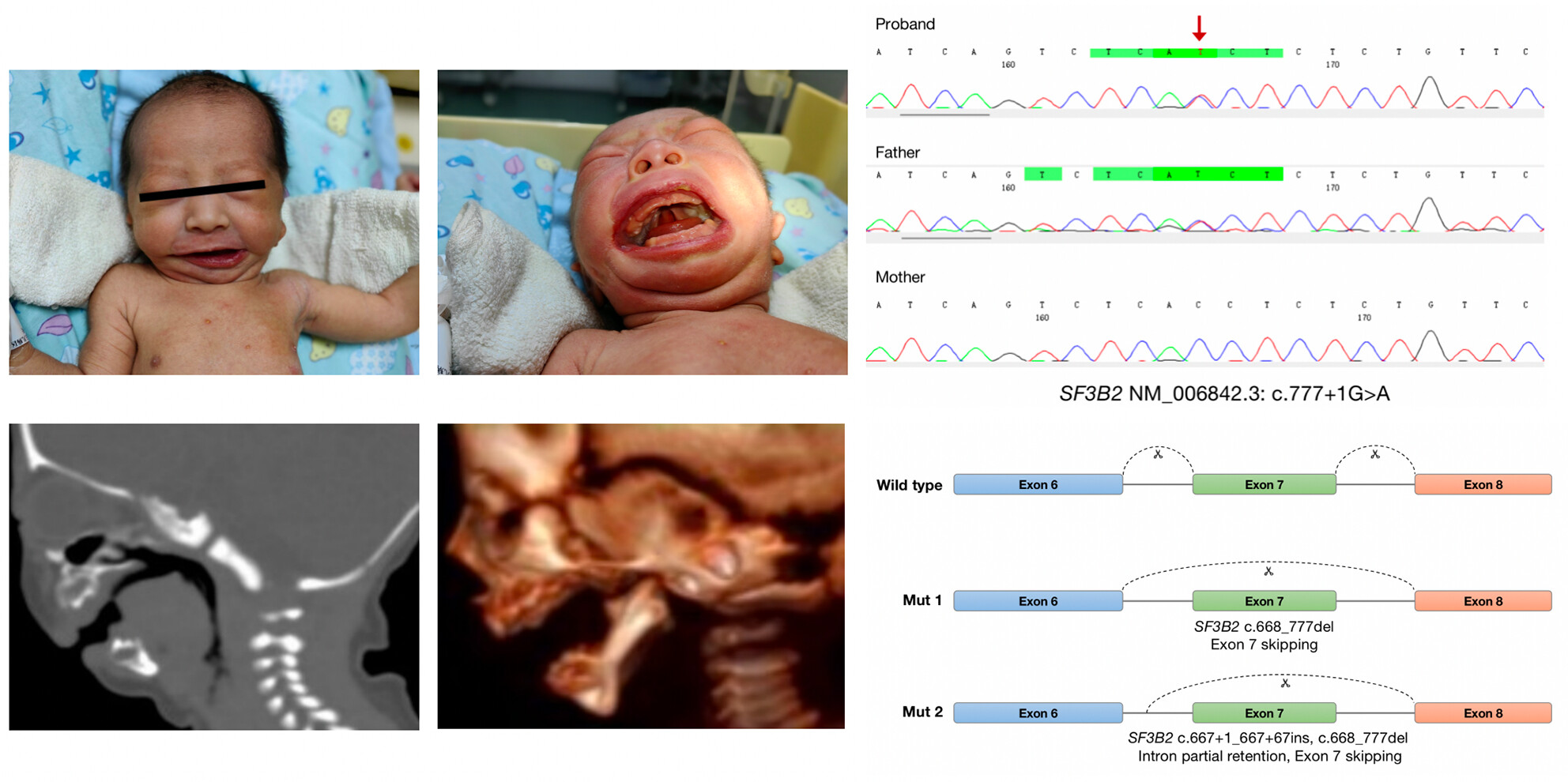
This study presents the clinical phenotype and genetic variant data of a family with craniofacial microsomia. The proband was a neonate with facial abnormalities and a rare feature of airway obstruction. Genetic analyses indicated a heterozygous SF3B2 variant, which was inherited from the father. A Minigene assay revealed that two mRNA products were produced, leading to a premature termination codon.
Phenotypic and genetic characteristics of 24 cases of early infantile epileptic encephalopathy in East China, including a rare case of biallelic UGDH mutations
- First Published: 18 August 2023
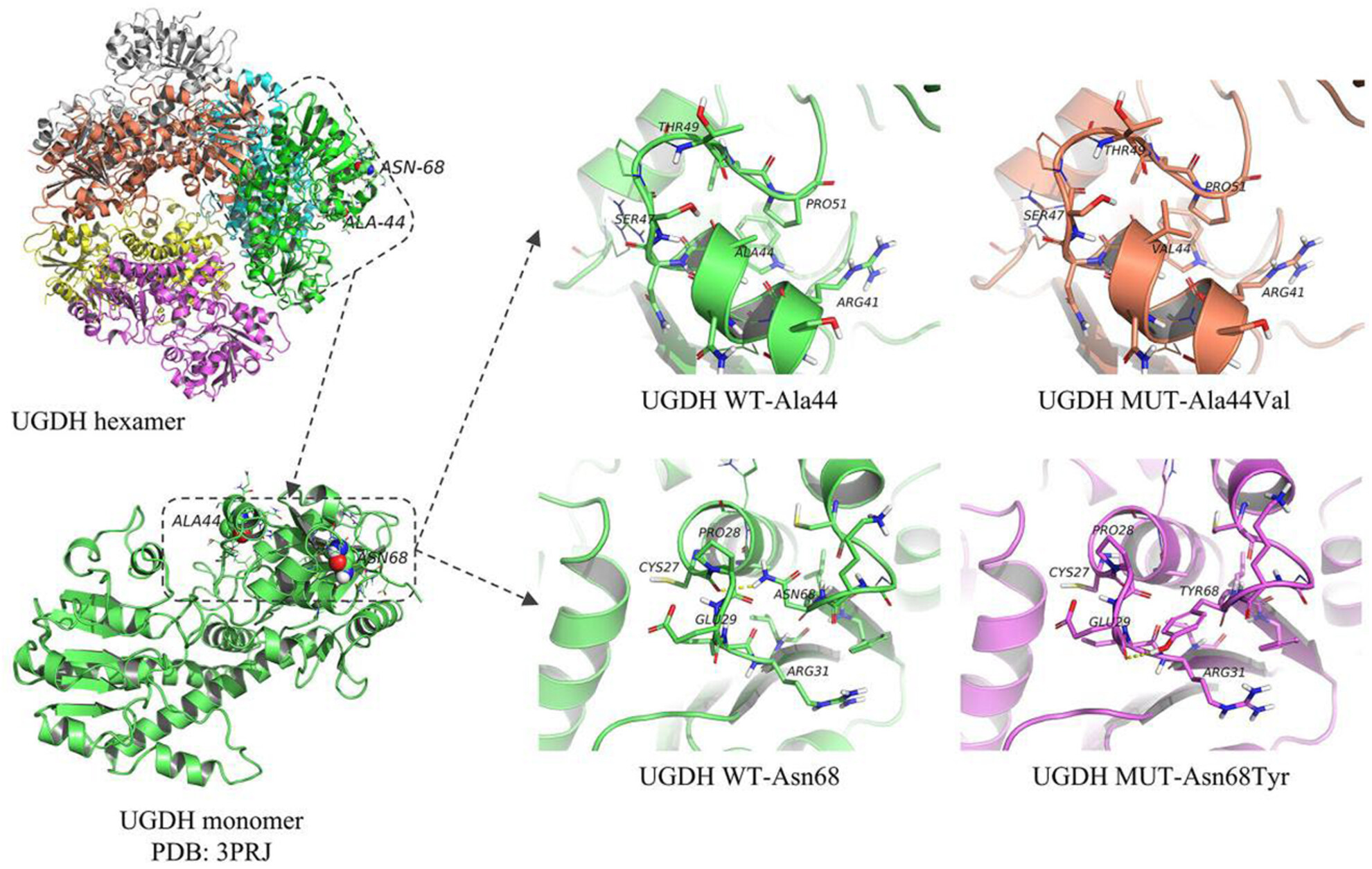
We conducted a retrospective study of 24 cases in a hospital in eastern China and found variants in several genes. Of note, we found a compound heterozygous mutation in UGDH. One of the mutations in the second exon has not been described previously. We performed a protein analysis of the structure and proposed that the mutated protein may be unstable. Our results add to the growing list of mutations that affect this gene. Since the condition responds poorly to antiepileptic therapy, increased single-gene mutations may aid in more targeted therapy.
A new line method; A direct test in spinal muscular atrophy screening for DBS
- First Published: 23 August 2023
A case report of a novel HIST1H1E mutation and a review of the bibliography to evaluate the genotype–phenotype correlations
- First Published: 21 August 2023
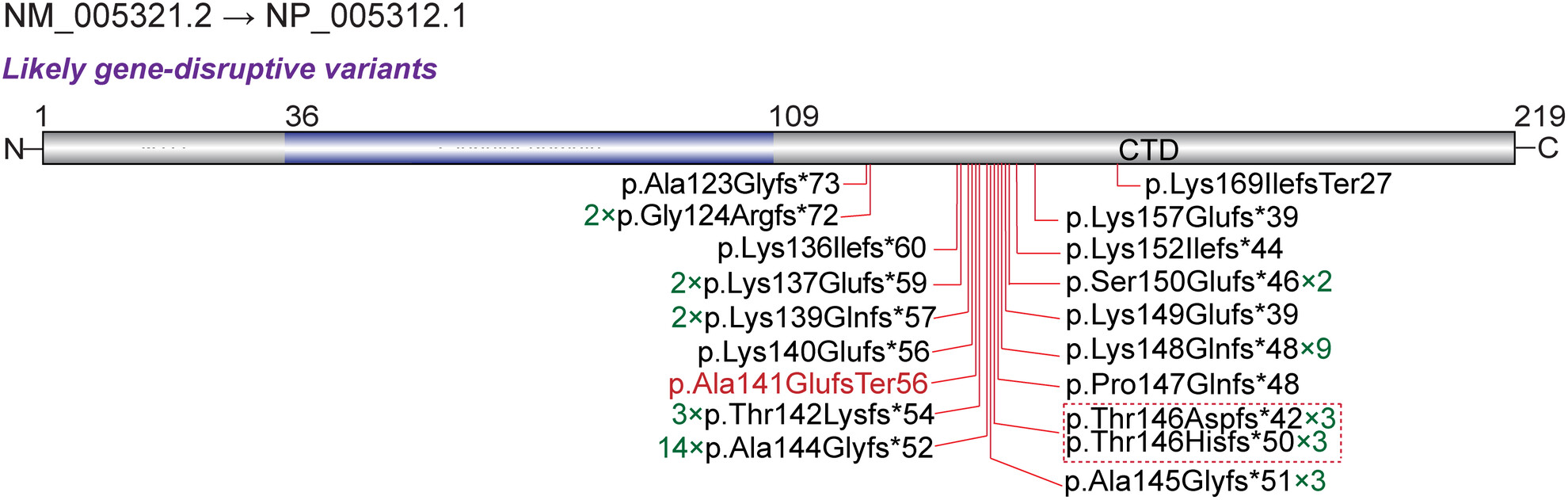
We reported a new de novo frameshift mutation in HIST1H1E (NM_005321.2, c.416_419dupAGAA, p.Ala141GlufsTer56) in an individual with Rahman syndrome. we comprehensively curated and summarized 23 variants and the clinical features from 52 patients. Our findings revealed that likely gene-disrupting variants in HIST1H1E contribute to a wide range of neurodevelopmental phenotypes.
CLINICAL REPORTS
A novel pathogenic variant located just upstream of the C-terminal Ser423-X-Ser425 phosphorylation motif in SMAD3 causing Loeys–Dietz syndrome
- First Published: 20 October 2023
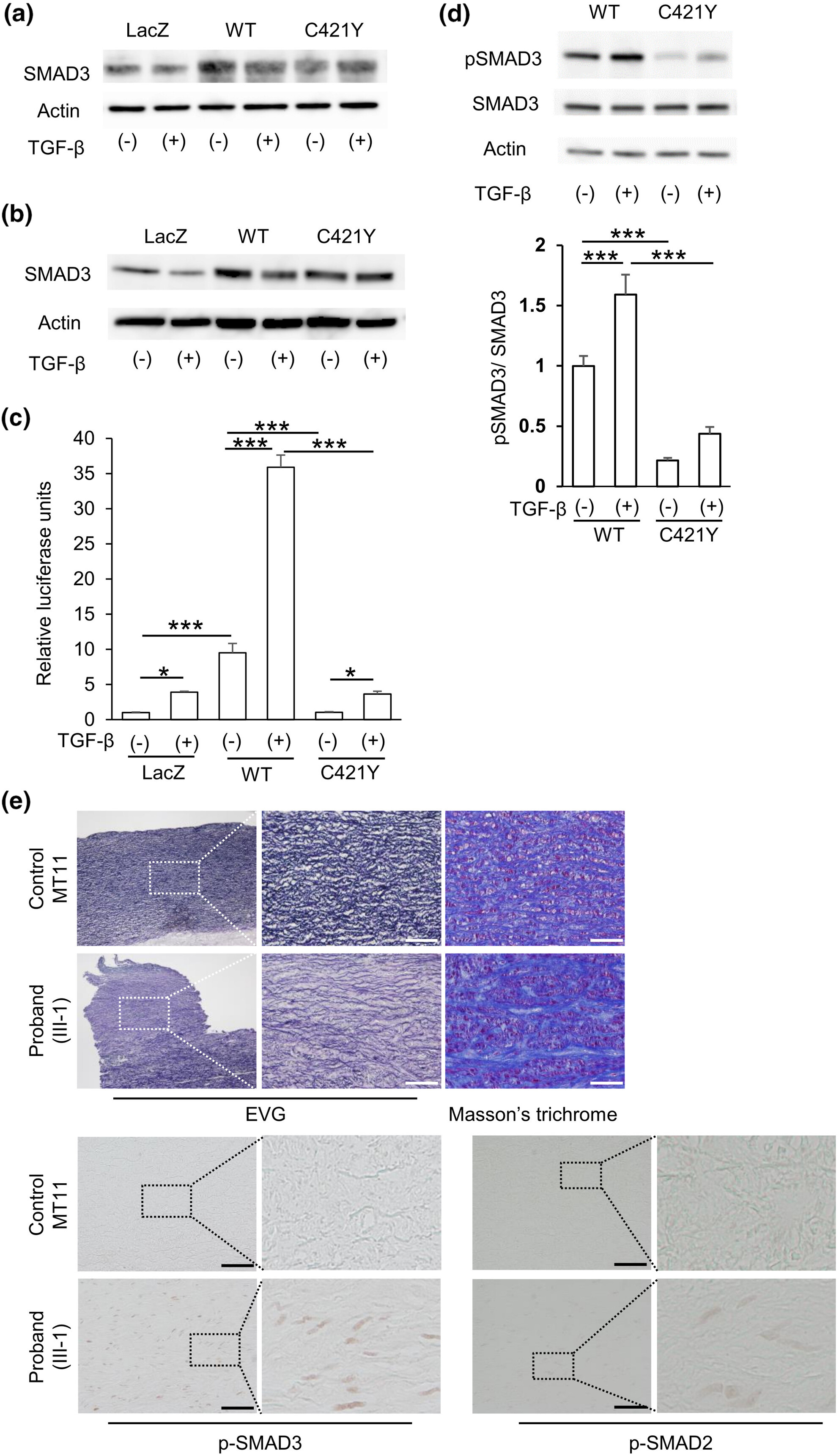
The novel heterozygous missense variant of SMAD3 [c.1262G>A, p.(Cys421Tyr)], which was present just upstream of the C-terminal Ser423-X-Ser425 phosphorylation motif, was found in this Japanese family instance of Loeys–Dietz syndrome (LDS) type 3. This variant led to reduced phospho-SMAD3 (Ser423/Ser425) levels and transcription activity in vitro; however, a paradoxical upregulation of TGF-ß signaling was evident in the aortic wall. Further research is warranted to clarify the influence of the SMAD3 variant type and location on the LDS3 phenotype as well as the molecular mechanism of TGF-ß paradox in LDS3 aortopathy.
A somatic splice-site variant in PIK3R1 in a patient with vascular overgrowth and low immunoglobulin levels: A case report
- First Published: 28 August 2023
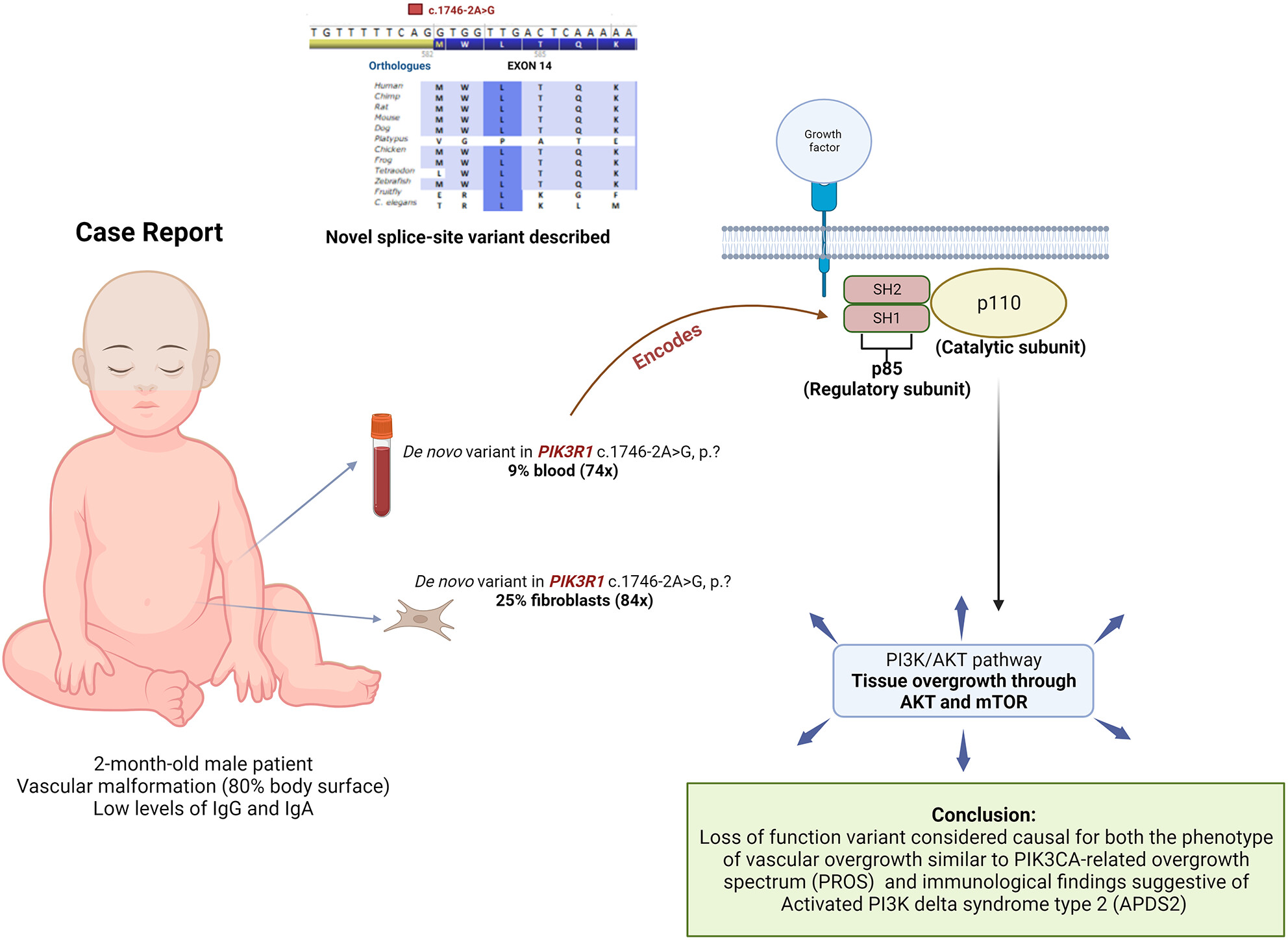
The PI3K/AKT pathway is important in regulating cell metabolism, differentiation, and proliferation, and is studied in cancer. Variants in the PIK3R1 gene have been associated with vascular lesions and Activated PI3K delta syndrome type 2 (APDS2). This case report describes an infant boy with vascular malformations and syndactyly, along with low levels of IgA and IgG, due to a de novo variant in PIK3R1.
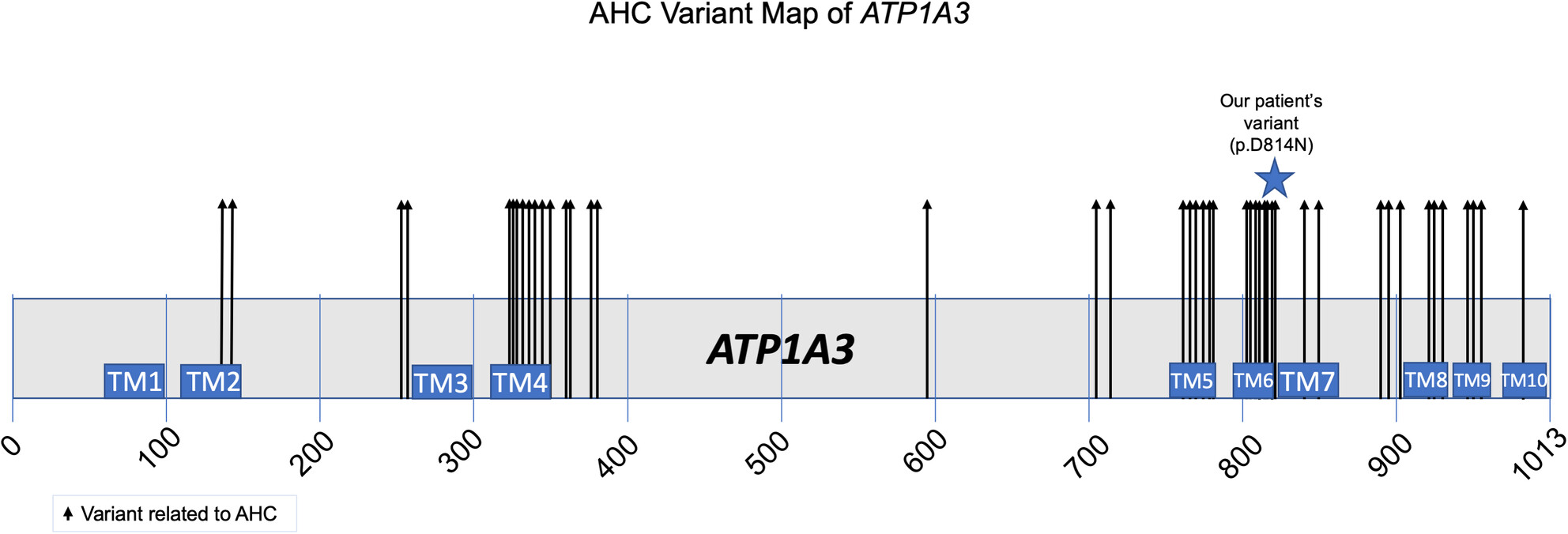
Precision therapy for a medically actionable ATP1A3 variant from a genomic medicine program in an underserved population
- First Published: 23 August 2023
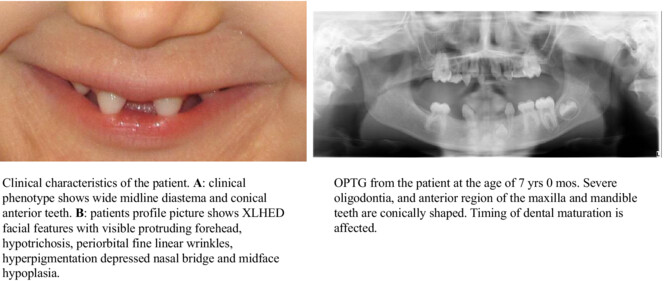
New observation of severe tooth malformation in a female patient with ectodermal dysplasia due to the EDA splice acceptor variant c.742-2A>G
- First Published: 04 September 2023
Fahr's disease linked to a novel mutation in MYORG variants manifesting as paroxysmal limb stiffness and dysarthria: Case report and literature review
- First Published: 07 September 2023
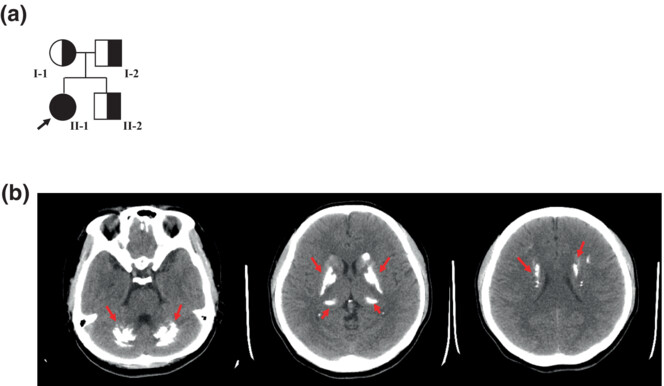
This study described a young patient with a primary familial brain calcification harboring a novel homozygous MYORG mutation (c.743delG: p.G248Afs*32), and reviewed all reported cases of PFBC with biallelic MYORG mutations. Our study makes a significant contribution to the literature because it is important to screen for MYORG mutations in patients with primary brain calcification, especially younger patients without a family history.