Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
Optimizing Chlorogenic Acid Extraction From Spent Coffee Grounds: A Comparative Review of Conventional and Non-Conventional Techniques
- First Published: 27 June 2025
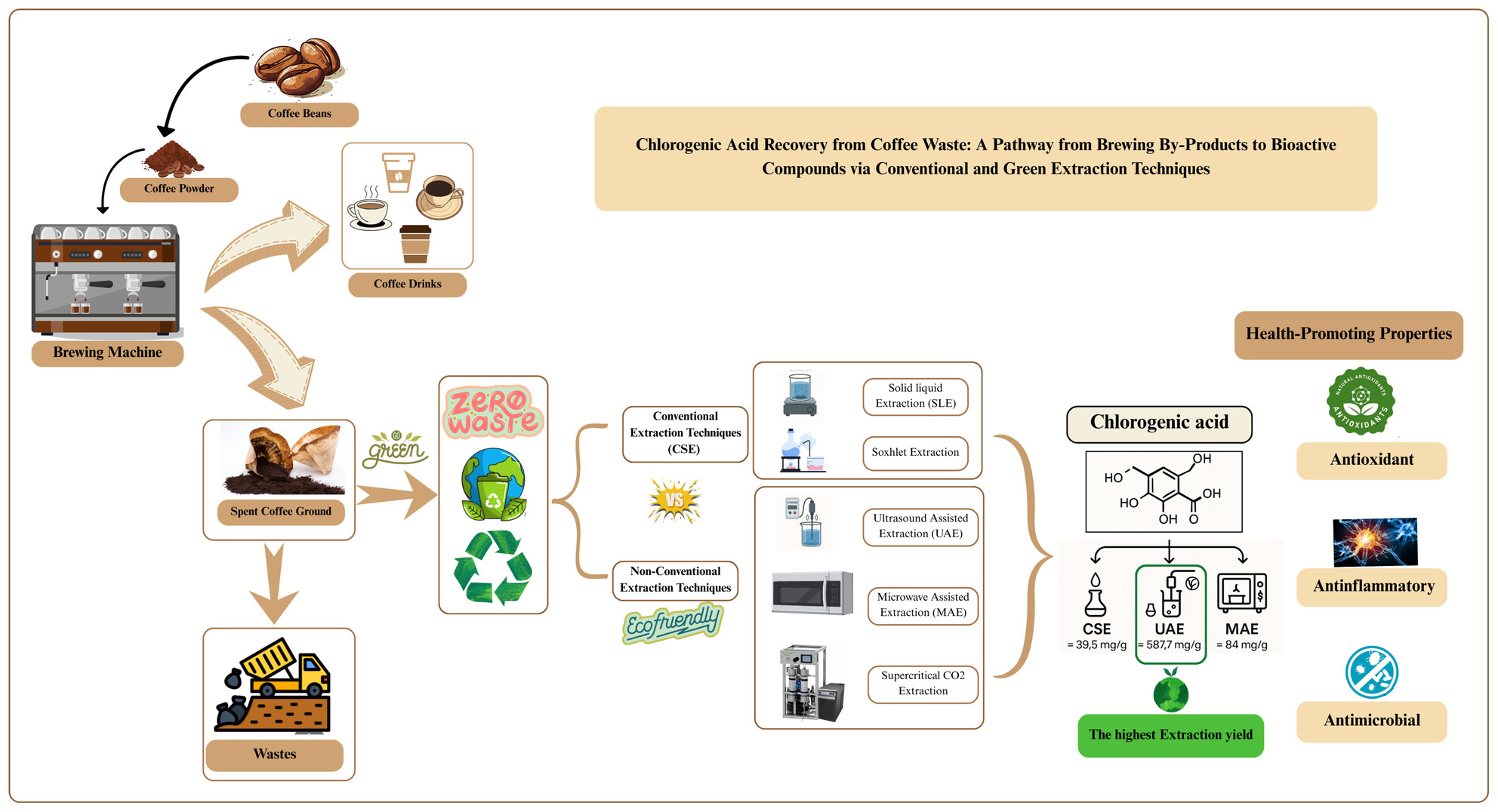
Spent coffee grounds are a rich source of chlorogenic acid, a compound with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. This review conducts a comparative analysis between the conventional and non-conventional extraction techniques based on CGA yield, environmental sustainability, cost, and processing time. Ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) emerged as the most efficient method, providing the highest CGA yield and demonstrating the best environmental performance.
CORRECTION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Tomato Disease Combat and Yield Optimization Using Selenium Nanoparticles: A Sustainable Nano-Agriculture Approach
- First Published: 27 June 2025
Potential Applications of Zingiber officinale, Clitoria ternatea, and Coccinia grandis for Enhancing the Functionality of Set Yogurts
- First Published: 27 June 2025

In this study, aqueous extracts of ginger, blue butterfly pea flower, and ivy leaf were fortified to the yogurts and evaluated the sensorial, physicochemical, and functional characteristics of yogurt along with the protein interactions. Results revealed that the fortification of all the plant extracts had a significant impact on the sensorial, physicochemical, antioxidant, and structural properties of the yogurts.
Yak (Bos grunniens) Meat Peptides: Effects on Immunity, Hypoxia Tolerance, and Antioxidant Capacity in Hypotonic Hypoxia Mice
- First Published: 27 June 2025
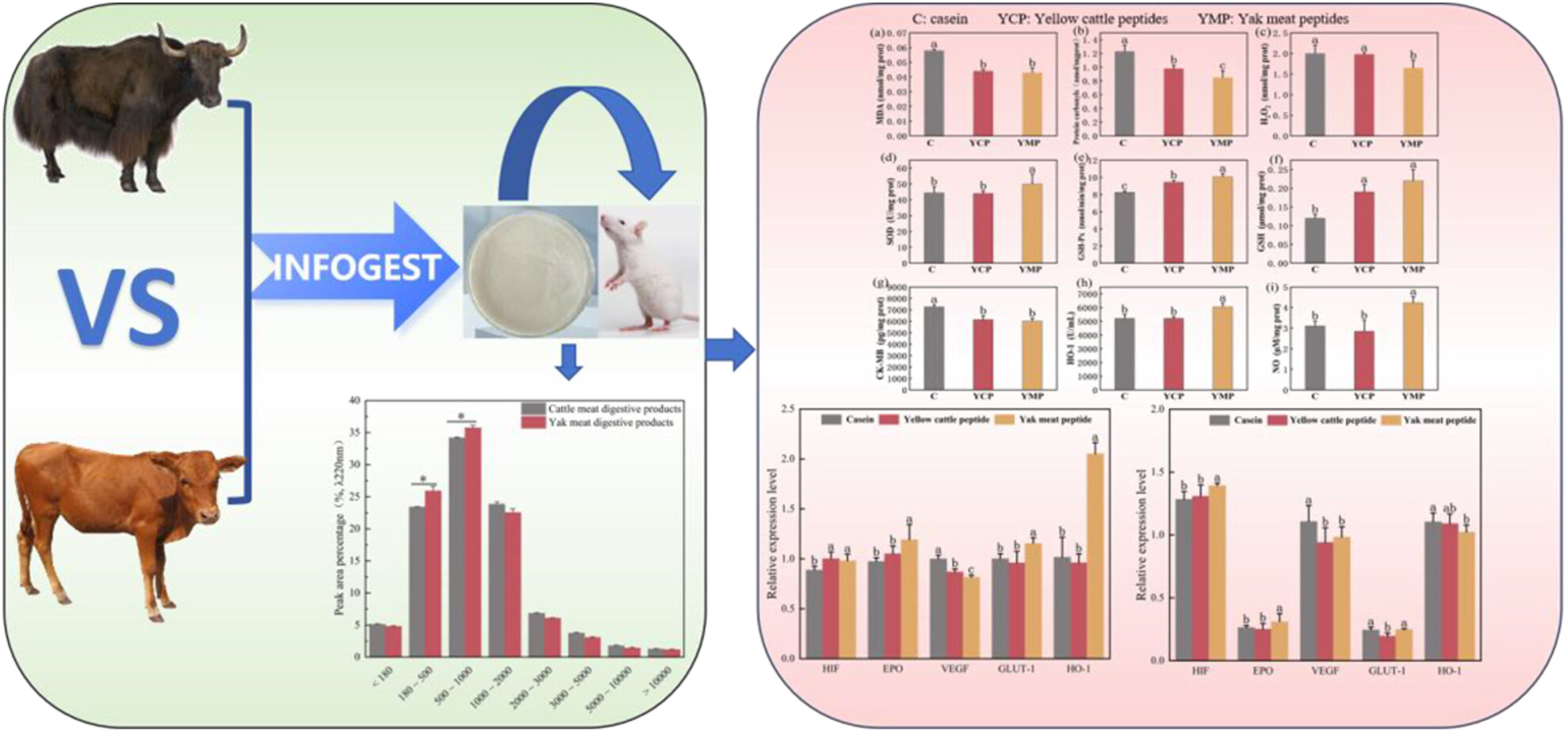
Yak meat peptides can increase immune cell content, oxygen transport capacity, and antioxidant enzyme activities in hypotonic hypoxic mice. Meanwhile, they can reduce oxidative stress, thus enhancing the immunity, antioxidant capacity, and hypoxia tolerance of these mice. They also upregulate hypoxia-related genes HIF and EPO. This study provides a theoretical basis for mitigating oxidative damage and advancing the development of yak-derived bioactive substances.
A Study on the Clustering of Daily Fruit and Vegetable Consumption by Educational Level in European Region Countries
- First Published: 27 June 2025
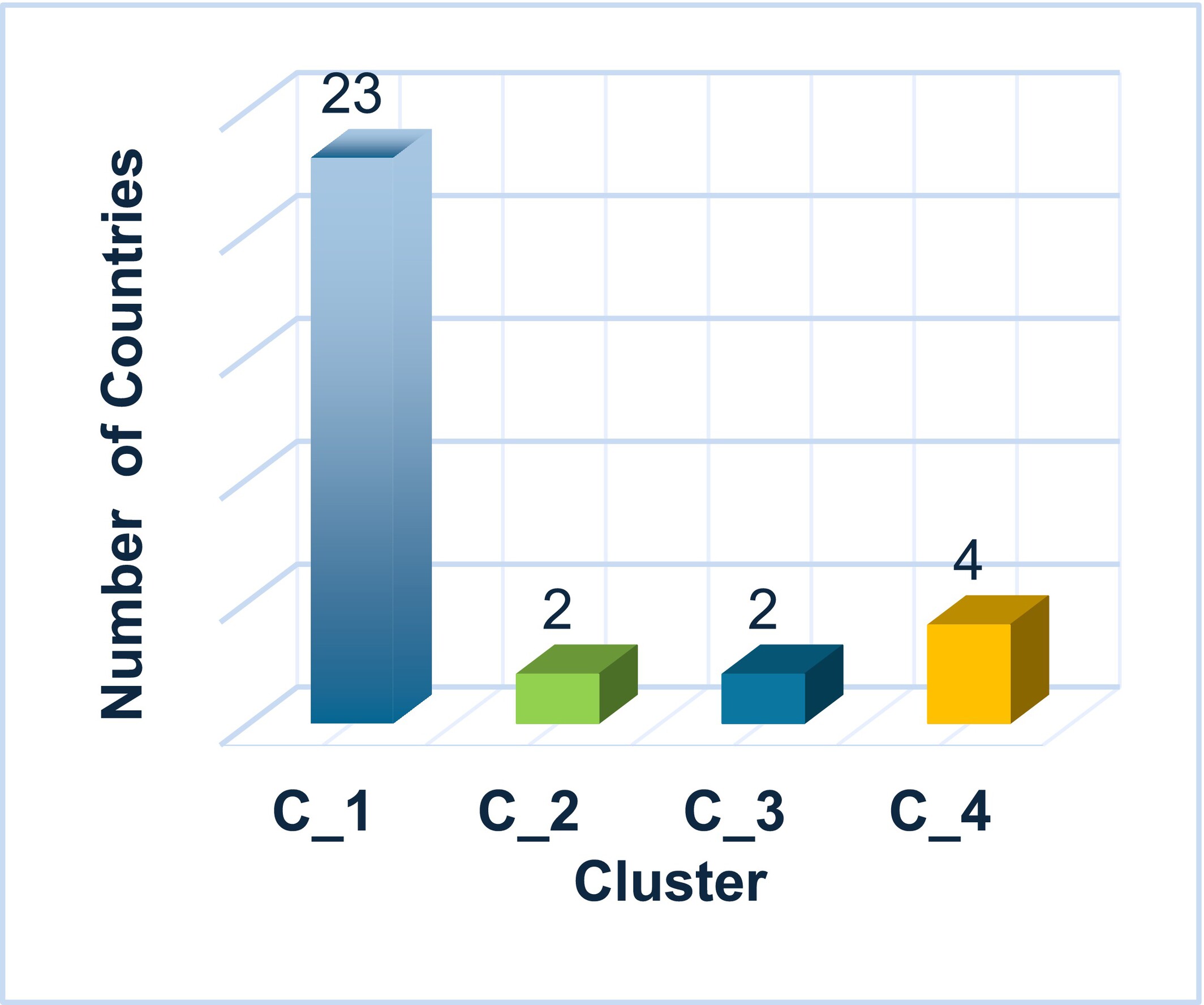
This study used 2022 Eurostat data to cluster 31 European countries by daily fruit and vegetable consumption and educational level. K-means clustering revealed that countries with similar education and socioeconomic status have similar dietary habits. The results highlight the strong association between lower education and low fruit and vegetable intake, emphasizing the role of education in healthy eating patterns across Europe.
Premenstrual Syndrome, Ultra-Processed Food Intake, and Food Cravings: A New Perspective
- First Published: 29 June 2025
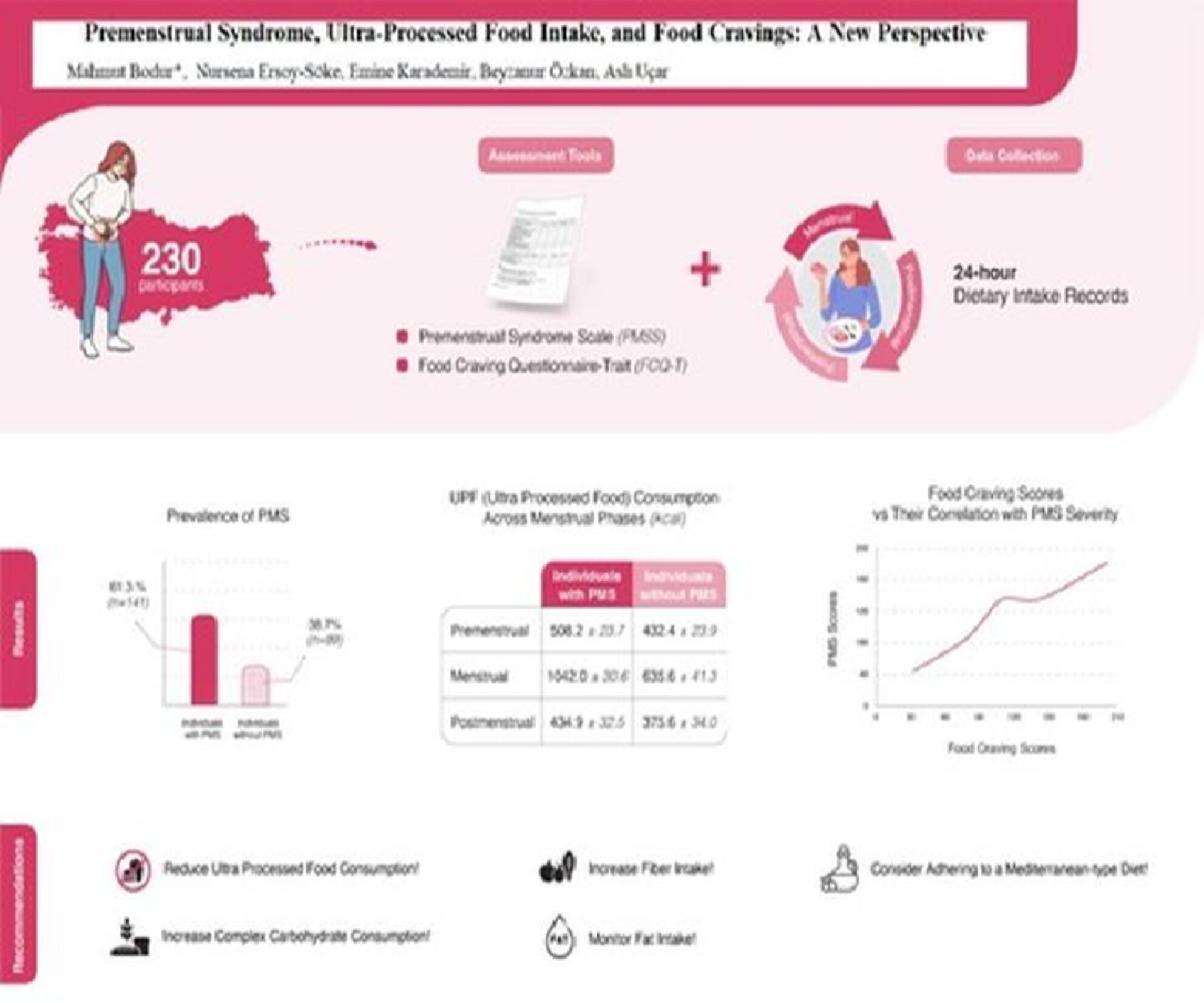
This study examines the association between premenstrual syndrome (PMS), ultra-processed food (UPF) intake, and food cravings in young women. Individuals with PMS reported higher UPF consumption and significantly greater food craving scores across all menstrual phases. The findings highlight the role of dietary patterns in PMS severity and suggest that reducing UPF intake and improving diet quality may support symptom management.
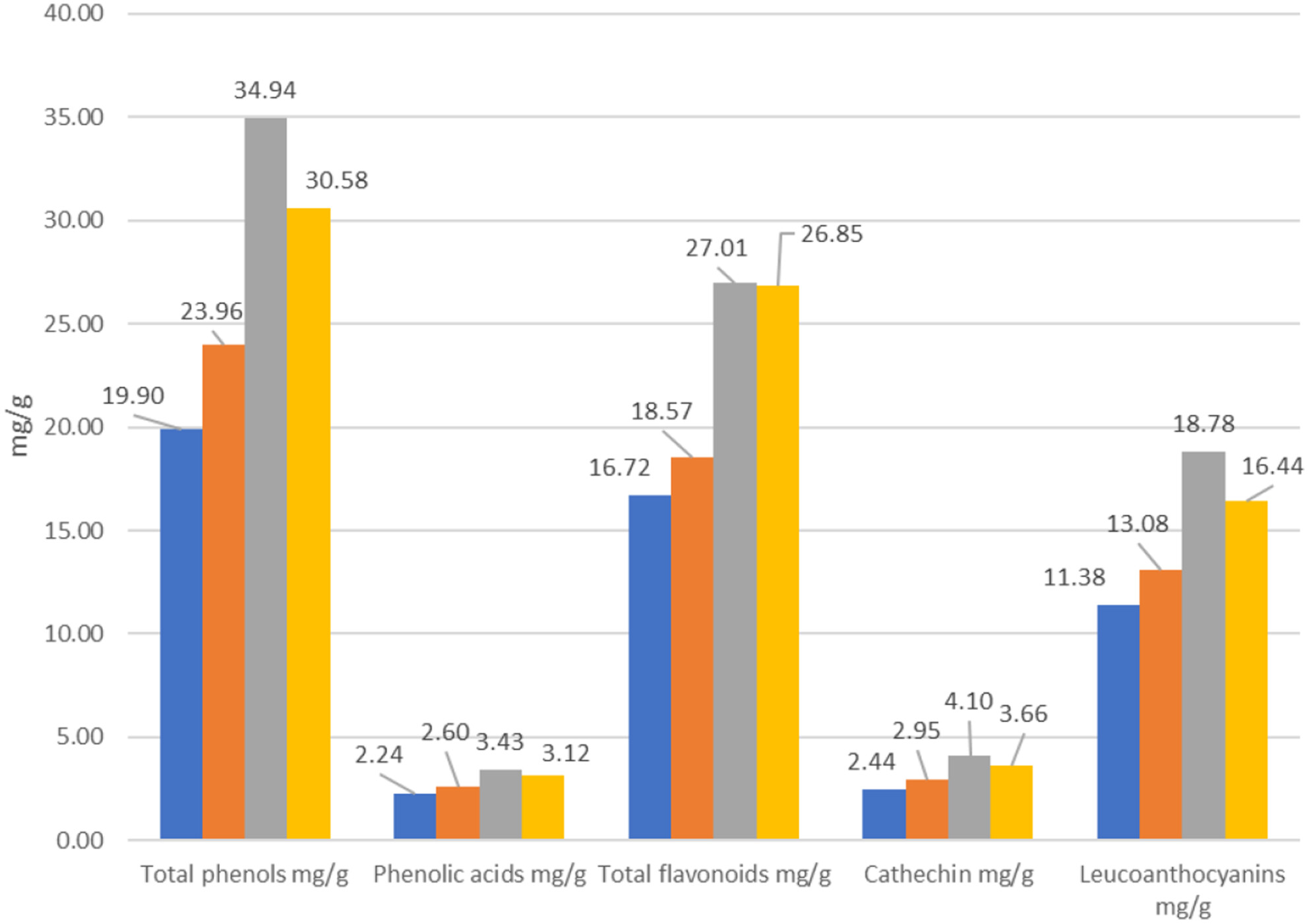
Antioxidant Activity of Different Phenolic-Rich Fractions Obtained From Peels of Turkish Dark Purple Eggplant
- First Published: 27 June 2025

Polyphenol contents of Turkish eggplant peels were extracted by different solvent systems and extraction methods. Liquid–liquid extraction was performed for anthocyanin separation. Qualitative and quantitative differences in phenolic profiles were observed. Soxhlet extraction by absolute ethanol showed the highest total phenolic content and strongest antioxidant activity. Hot water bath extraction with an acidic medium yielded a high extraction of flavonoid compounds.
Enhancement of In Vitro Bioaccessibility of Alpinia officinarum Hance Extract With Dual-Coated Liposomes
- First Published: 01 July 2025
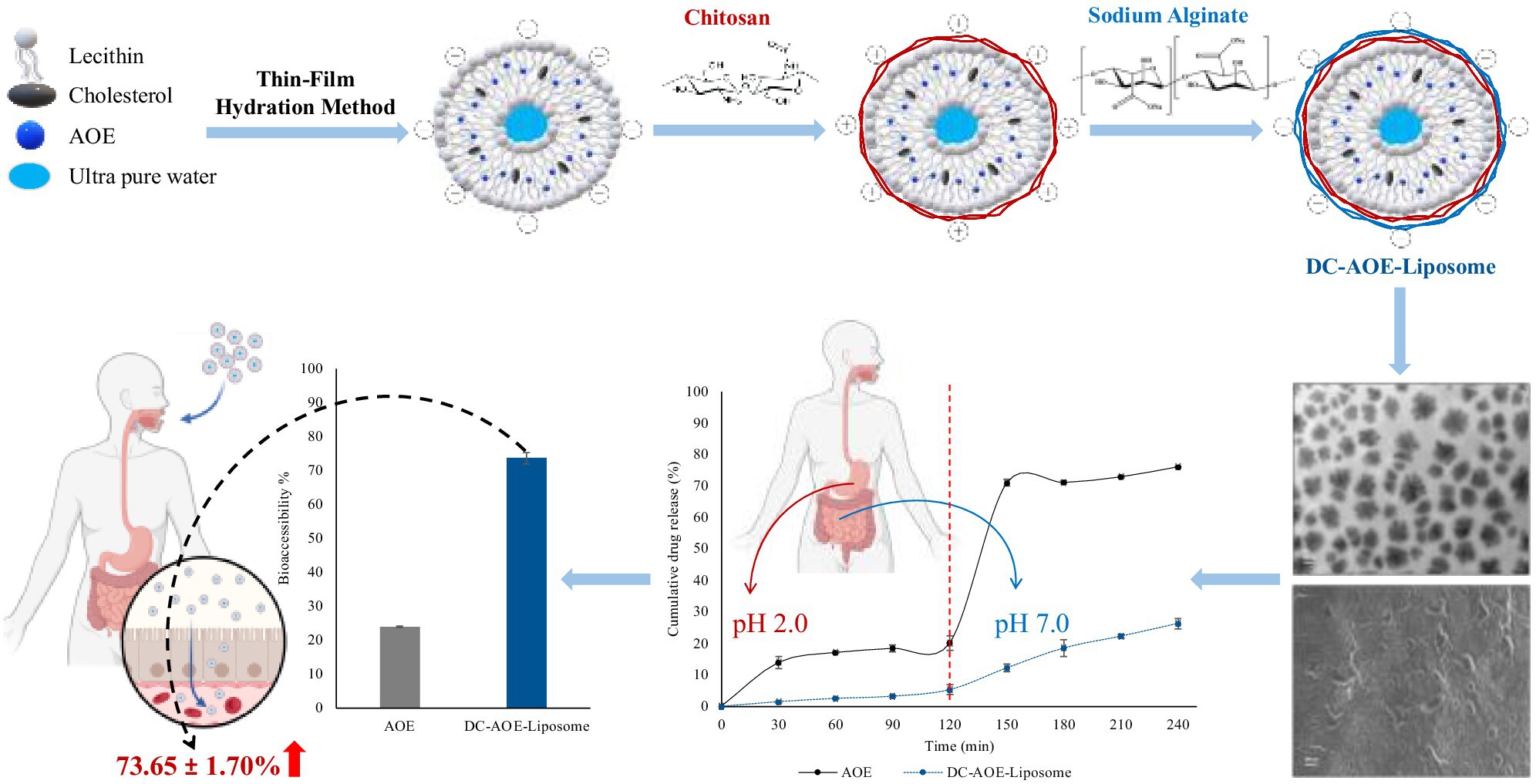
The liposomes were produced with 93.19% ± 0.02% encapsulation efficiency and a size of 155 ± 22.61 nm, zeta potential of −40.97 ± 13.41 mV. The bioaccessibility of galangin in Alpinia officinarum Hance extract was 23.87% ± 0.24%, and in dual-coated liposomes was 73.65% ± 1.70%. By virtue of the developed system, liposomes loaded with Alpinia officinarum Hance extract resisted gastrointestinal tract conditions and increased its bioaccessibility approximately three fold by slowing the release of the extract.
The Effects of a Novel Fortified Dairy Product on Weight Loss, Metabolic Profiles, and Endocrine Hormones in Women With Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial
- First Published: 27 June 2025
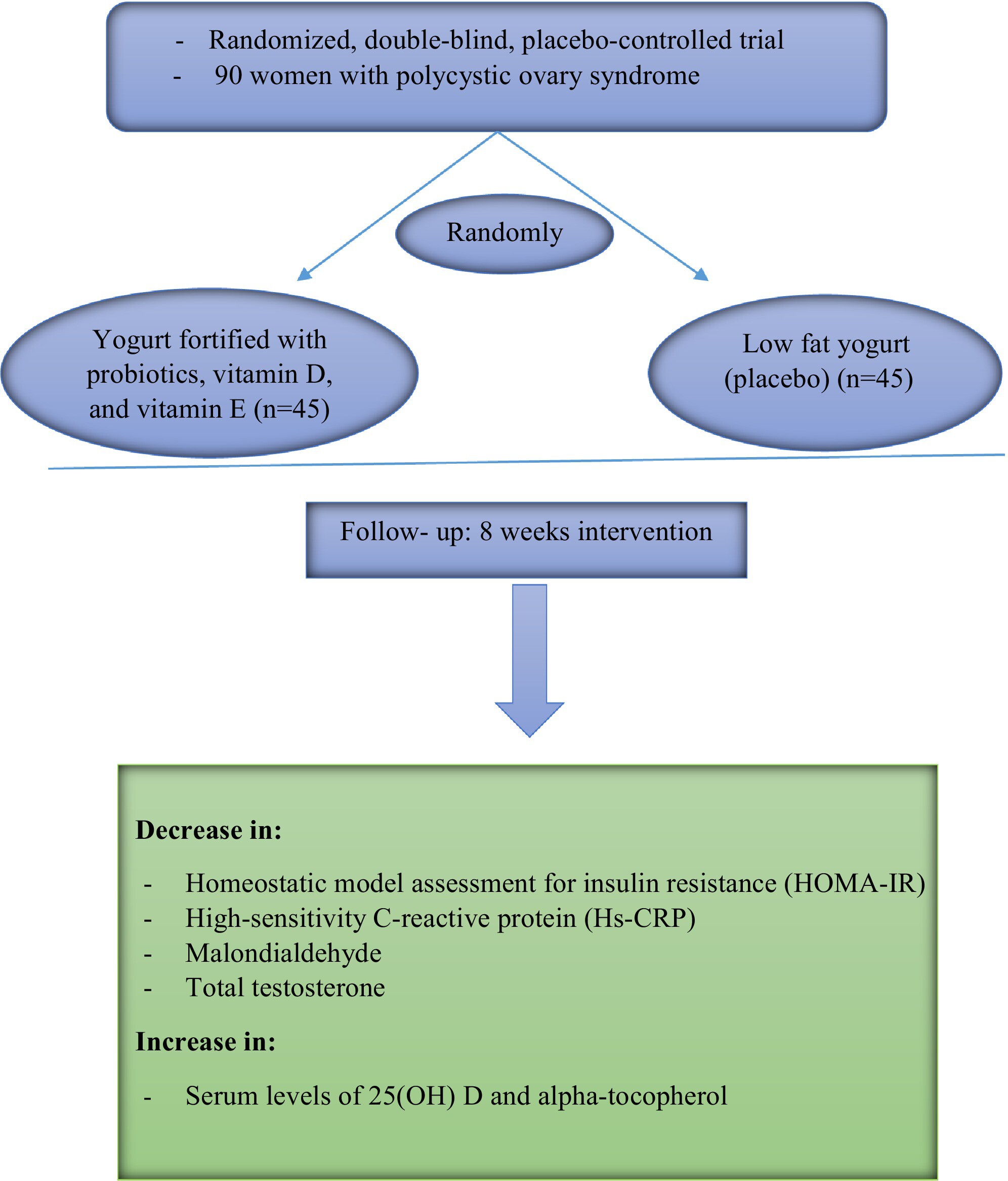
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the leading cause of anovulation worldwide.
- The present randomized controlled clinical trial was conducted on PCOS patients to assess the efficacy of a novel fortified yogurt.
- First trial showing the synergetic effect of probiotics with vitamin D and vitamin E.
- The fortified yogurt as a non-invasive complementary therapy improved PCOS symptoms.
Shedding Light on the Phytochemical and Biological Fingerprints of Fibigia clypeata (L.) Medik Essential Oil as a Pharmacotherapeutic Agent
- First Published: 04 July 2025

This study aims to analyze the phytochemical composition and in silico and in vitro biological activity of Fibigia clypeata (L.) Medik essential oil is a natural pharmaceutical source for the first time in the literature. GC–MS Analysis showed that dimethyl disulfide and dimethyl trisulfide were the main compounds of the plant essential oil. The antifungal properties of plant essential oil are more effective than its antibacterial properties. Anticholinesterase activity was proved and free radical scavenging activity and Cupric ion-reducing capacity were the most promising antioxidant studies.
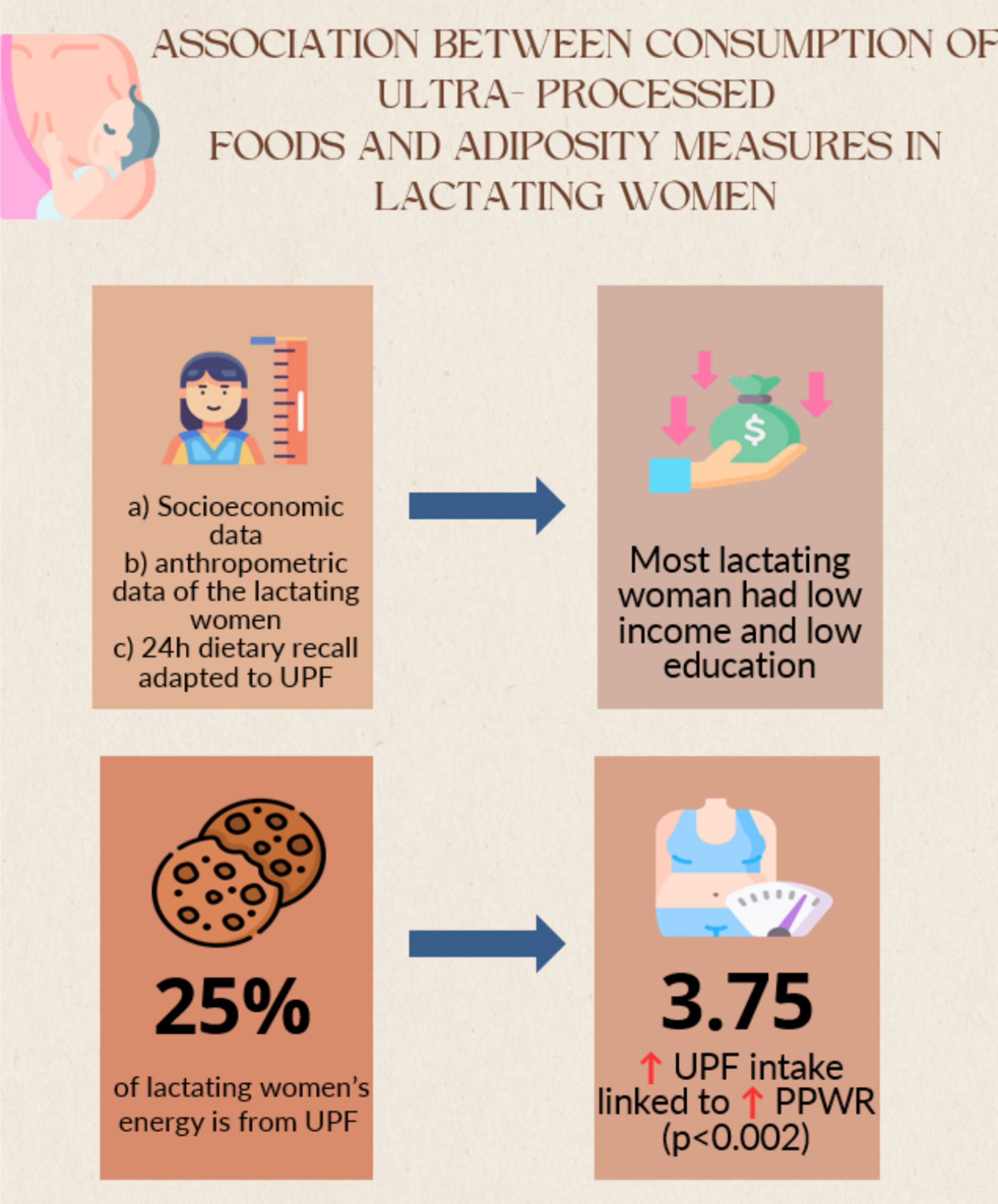
Association Between Consumption of Ultra-Processed Foods and Adiposity Measures in Lactating Women
- First Published: 27 June 2025
Morphological and Pomological Characterizations of Peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] Accessions
- First Published: 27 June 2025
![Morphological and Pomological Characterizations of Peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] Accessions](/cms/asset/fdee7c4c-f531-4dc7-8b99-80dc52cc6443/fsn370501-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Among the studied accessions, the first 15 accessions with the highest scores based on individual quantitative datasets were identified as “Panjebog-19,” “Panjebog-26,” “Rachedr-1,” “Panjebog-20,” “Panjebog-2,” “Panjebog-8,” “Panjebog-24,” “Panjebog-30,” “Panjebog-32,” “Panjebog-10,” “Panjebog-3,” “Panjebog-7,” “Panjebog-33,” “Rachedr-5,” and “Panjebog-27.”
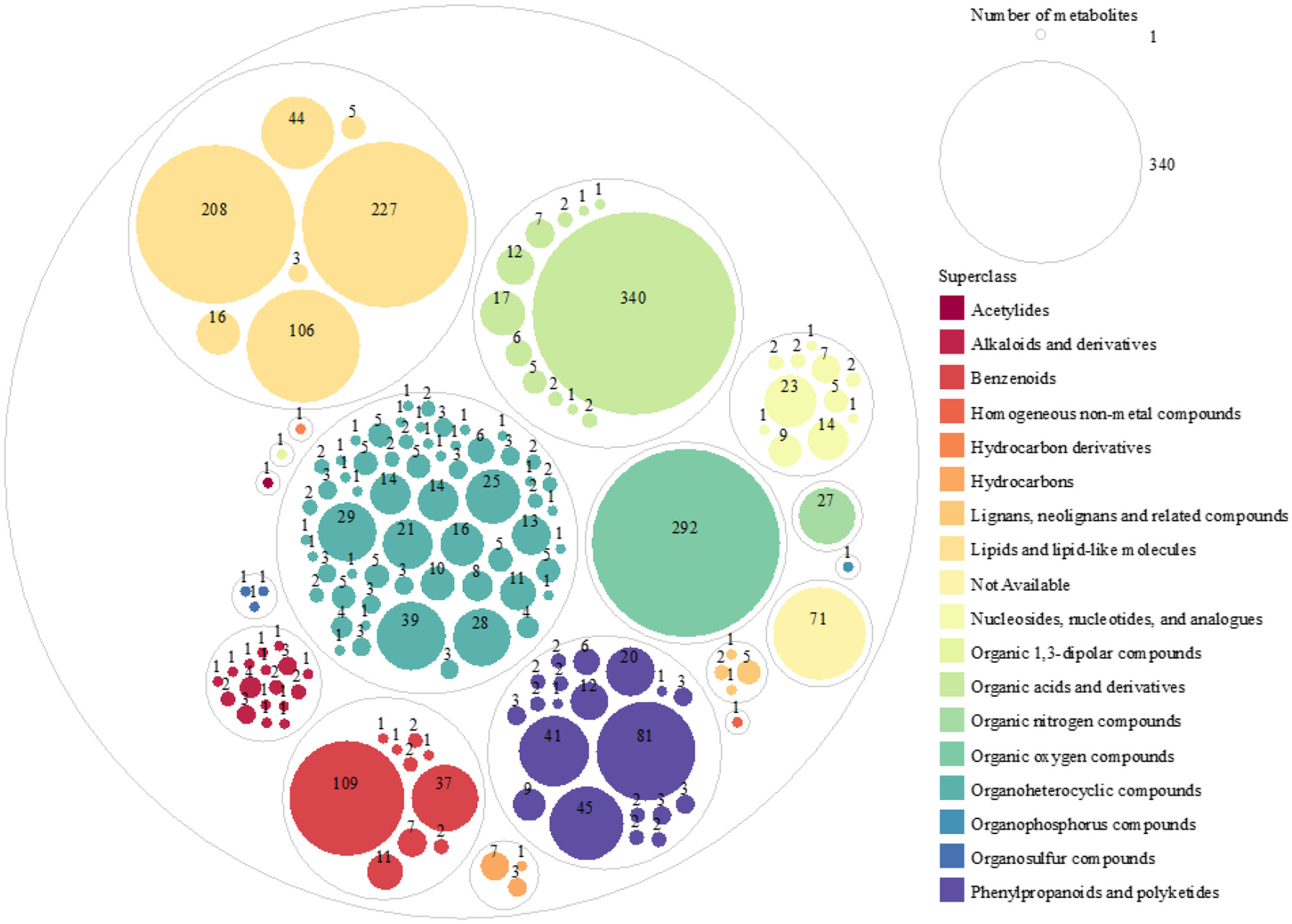
Chemical Composition Analysis of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae) in Georgia and Development of Innovative Valorization Technologies
- First Published: 14 July 2025
Sea buckthorn, widely found as a wild berry in Georgia, is a rich source of natural antioxidants, traditionally used for preparing food additives like sea buckthorn oil, carotenoids, tocopherols, and phospholipids. Despite its longstanding use, this berry's physicochemical properties and potential applications remain underexplored. This study investigates the biologically active compounds in sea buckthorn berries harvested from different climatic and soil regions across Georgia.
Investigating the Ultrasonication-Induced Changes in the Physicochemical, Phytochemical, Microbial, and Sensory Properties of Cantaloupe–Sugarcane Blend Juice
- First Published: 27 June 2025

Sonication at optimum operating conditions is an advancing green processing technology for processing and preservation of fruit juices. This treatment enhanced the juice's phytochemical contents and antioxidant activity, suggesting its potential health advantages. Cantaloupe–sugarcane blend juice sonicated for 6 min has shown higher nutritional, sensory, and phytochemical properties.
Formulation and Characterization of Muffins Enriched With Green Pea Powder: A Physical Study Using Response Surface Methodology
- First Published: 27 June 2025
Relationship Between Flavor and Well-Being
Effect on Arabica Coffee Flavor Quality of Enhanced Fermentation With Pichia membranifaciens Through Change Microbial Communities and Chemical Compounds
- First Published: 28 June 2025
Weissella, Lactococcus, Trichococcus, Leuconostoc, and Massila at the bacterial general level and Pichia, Hanseniaspora, Lachancea, Candida, and Cystofilobasidium at the fungi general level were the predominant microorganisms during the enhanced fermentation of Arabica coffee. Meanwhile, 122 differentially changed nonvolatile compounds (VIP > 1, p < 0.05, FC > 1.5 or FC < 0.65) were found between PE and PB. Furthermore, 26 differentially changed volatile compounds (VIP > 1, p < 0.05, FC > 2.0 or FC < 0.50) were found between PE and PB.
Kinetic Models for the Changes in Moisture, Bioactive Compounds, and Antioxidant Activities During the Storage of Tu Quy Mango Powder (Mangifera indica L.)
- First Published: 27 June 2025

Freeze-dried mango powder retains the characteristics of fresh fruit, offering health benefits, but its quality during storage is influenced by temperature and humidity. This study developed mathematical models to describe moisture absorption, bioactive compound degradation, and antioxidant activity, helping predict the shelf life of mango powder under different storage conditions. The results showed that the Vu model best predicted moisture content, whereas other models effectively described the degradation of bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity, aiding in quality control and shelf life estimation.
Transcription Factors and Regulate Network in Food Plant Stress and Growth Responses
White Light Orchestrates Mycoparasitic and Infection Activities by Regulating Expression of Effectors in Trichothecium roseum
- First Published: 28 June 2025
REVIEW
Health Benefits of Dietary Phytochemicals: Mechanism of Action
Phytochemicals, Extraction Methods, Health Benefits, and Applications of Loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.) and Its By-Products: A Comprehensive Review
- First Published: 01 July 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Dietary Creatine and Hydration Biomarkers in the General Population: NHANES 1999–2023
- First Published: 27 June 2025

Our findings indicate a complex relationship between dietary creatine intake and systemic hydration, with both low and high intake levels are associated with changes in plasma osmolality and hydration markers, whereas moderate intake shows minimal effects. Notably, higher creatine intake is linked to reductions in total body water (TBW), intracellular fluid (ICF), and extracellular fluid (ECF) volumes. These results challenge the traditional view that creatine consistently improves hydration and underscore the need for further investigation into its role in fluid balance.
Chemical Characterization, Antidiabetic and Antioxidant Potential of Allium cepa Peels Silver Nanoparticles Against Alloxan Induced Diabetes in Rabbits
- First Published: 27 June 2025
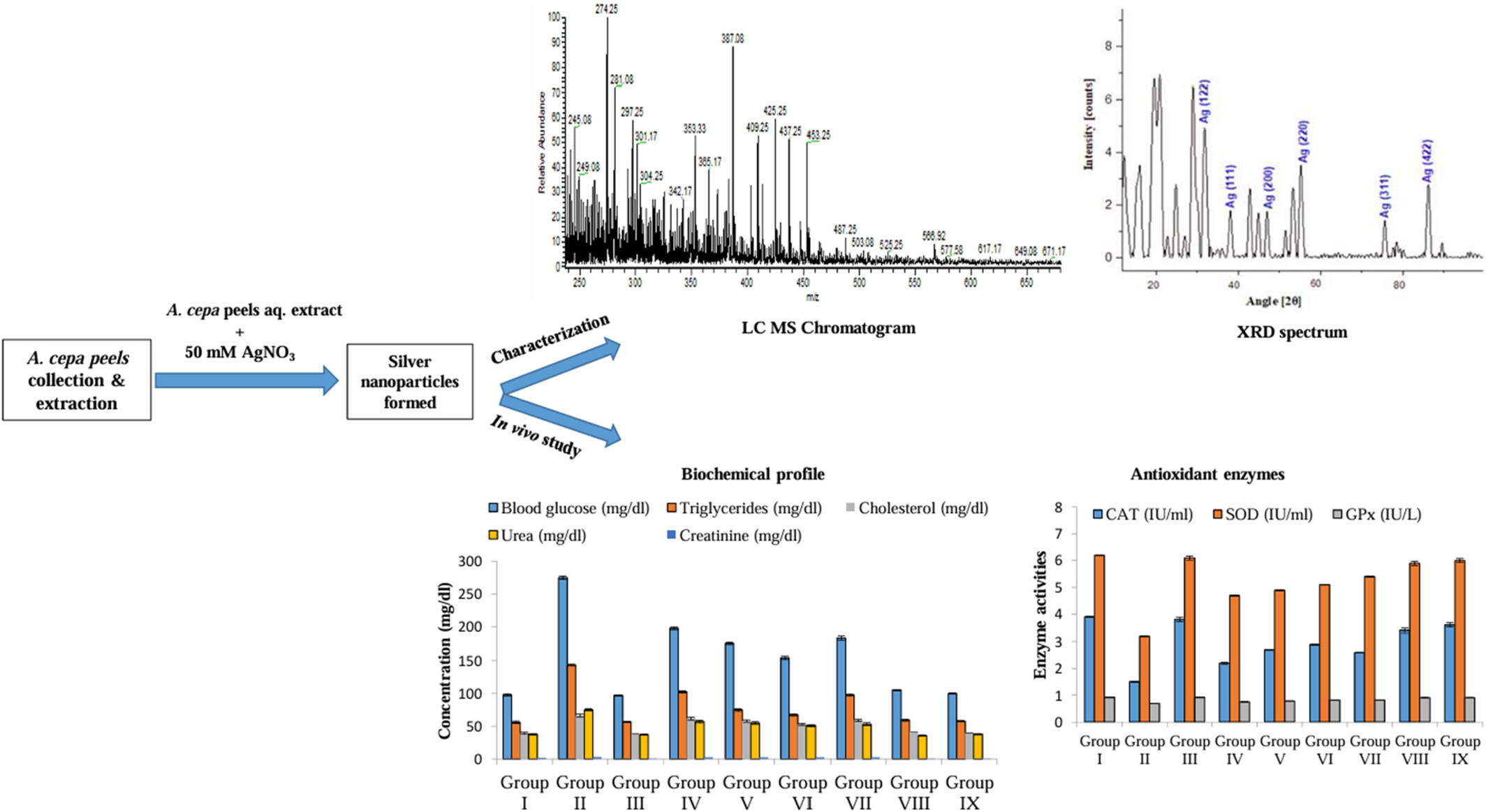
The study demonstrated remarkable antidiabetic potential of A. cepa peels extract and the synthesized silver nanoparticles as evidenced through the lowered glucose, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels while increasing antioxidant enzyme activities in A. cepa extract and synthesized nanoparticle-treated animals. A. cepa peels as a promising competitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus with high therapeutic efficiency and lower side effects.
Nutritional, Anti-Nutritional and Mineral Contents of Selected Wild Edible Plants in Ethiopia: Mussaenda arcuata, Celosia trigyna, and Pteridium aquilinum
- First Published: 27 June 2025
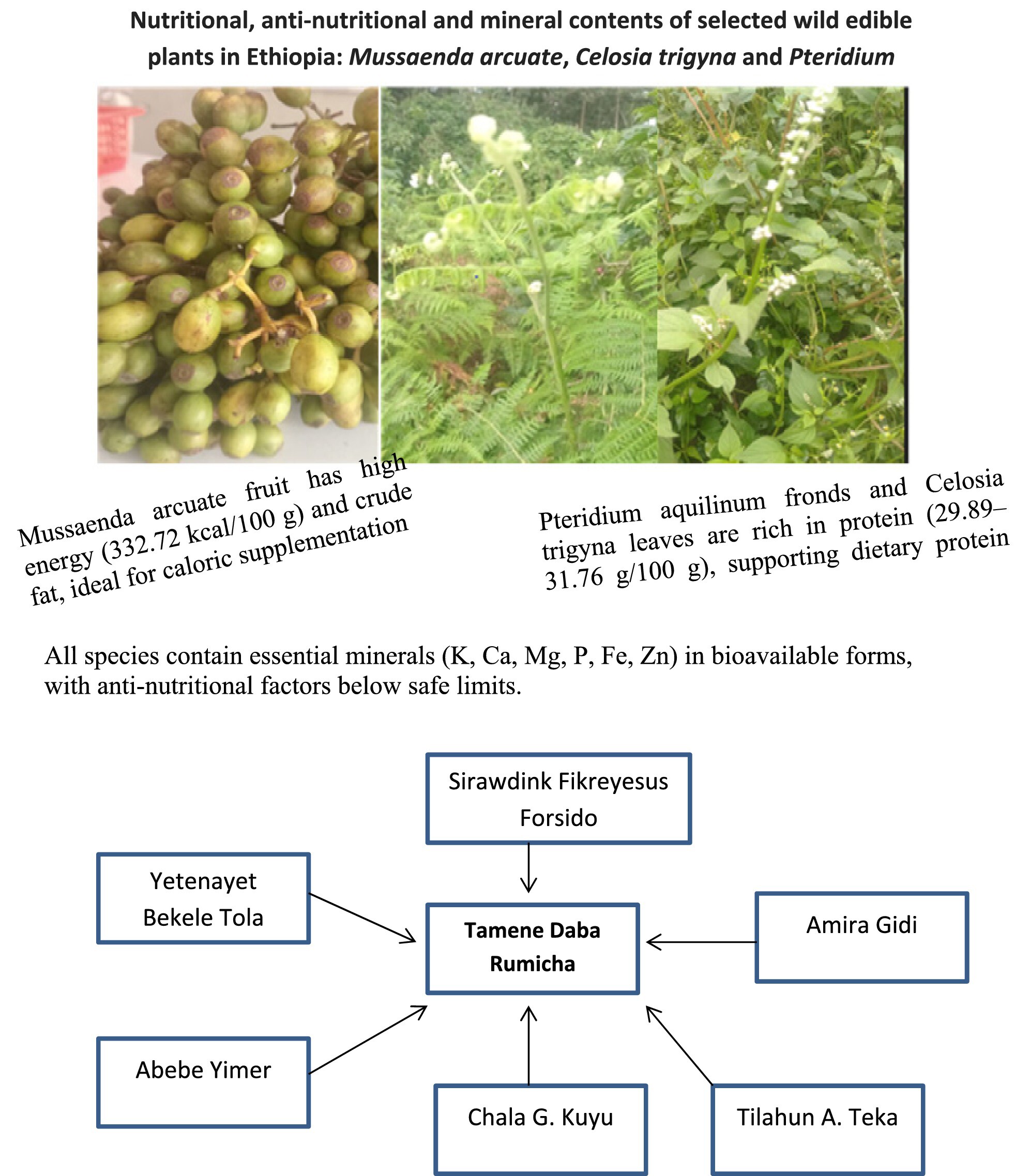
Mussaenda arcuate fruit has high energy (332.72 kcal/100 g) and crude fat, ideal for caloric supplementation. Pteridium aquilinum fronds and Celosia trigyna leaves are rich in protein (29.89–31.76/100 g), supporting dietary protein needs. All species contain essential minerals (K, Ca, Mg, P, Fe, Zn) in bioavailable forms, with anti-nutritional factors below safe limits.
Mendelian Randomization Analysis Reveals Causal Effects of Circulating Metabolites on Hyperaldosteronism
- First Published: 14 July 2025
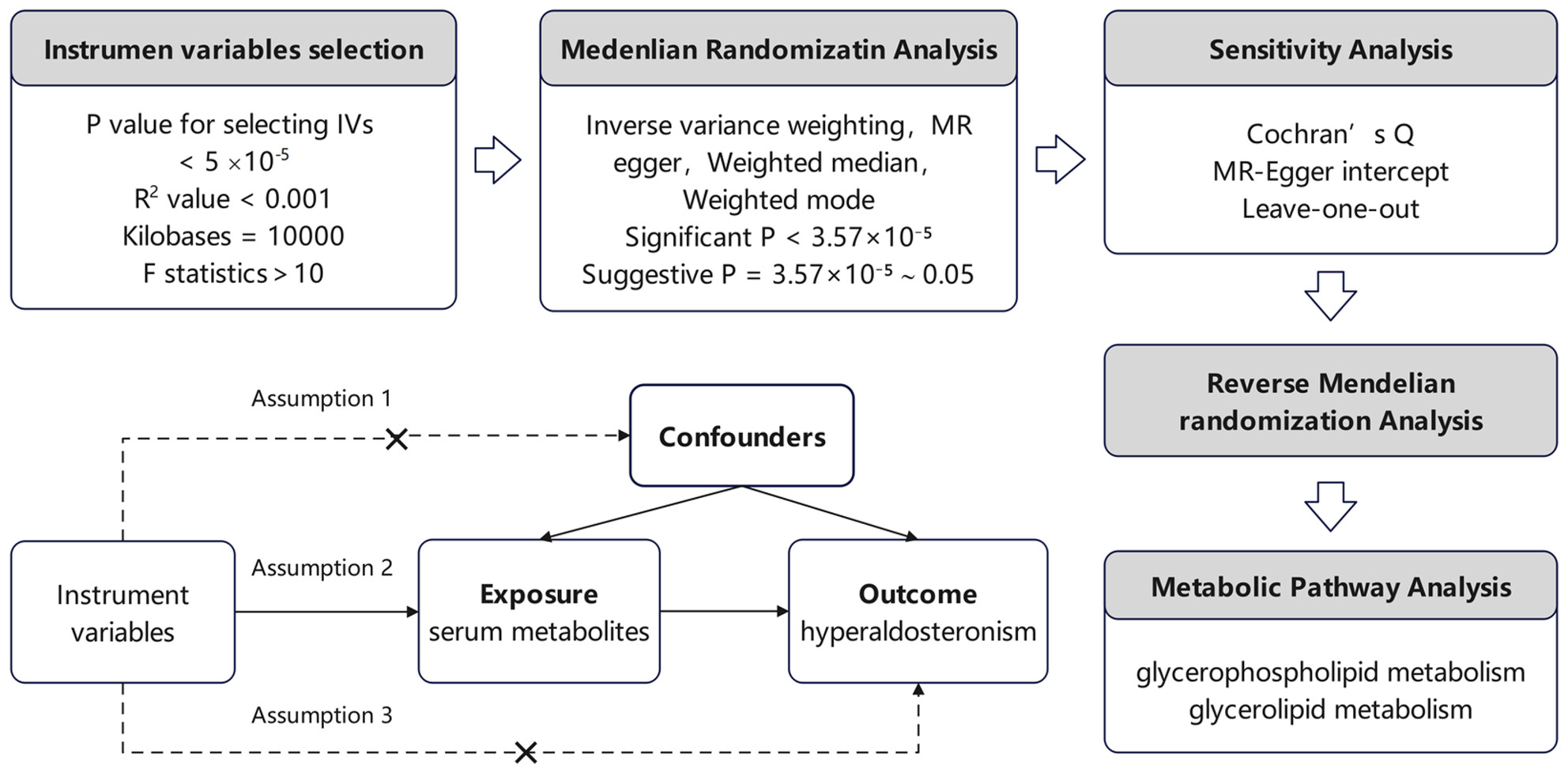
We found 66 metabolites/metabolic ratios nominally associated with hyperaldosteronism using medenlian randomization analysis. Reverse MR analysis indicated no reverse causality between hyperaldosteronism and the 1400 metabolites/metabolite ratios. Metabolomic pathway analysis revealed that two main pathways are involved in the impact of metabolites on hyperaldosteronism.
Enhancement of Bioactive Compounds in “Valencia” Orange Peel Waste During Cold Storage by Melatonin and Arginine Treatments
- First Published: 27 June 2025
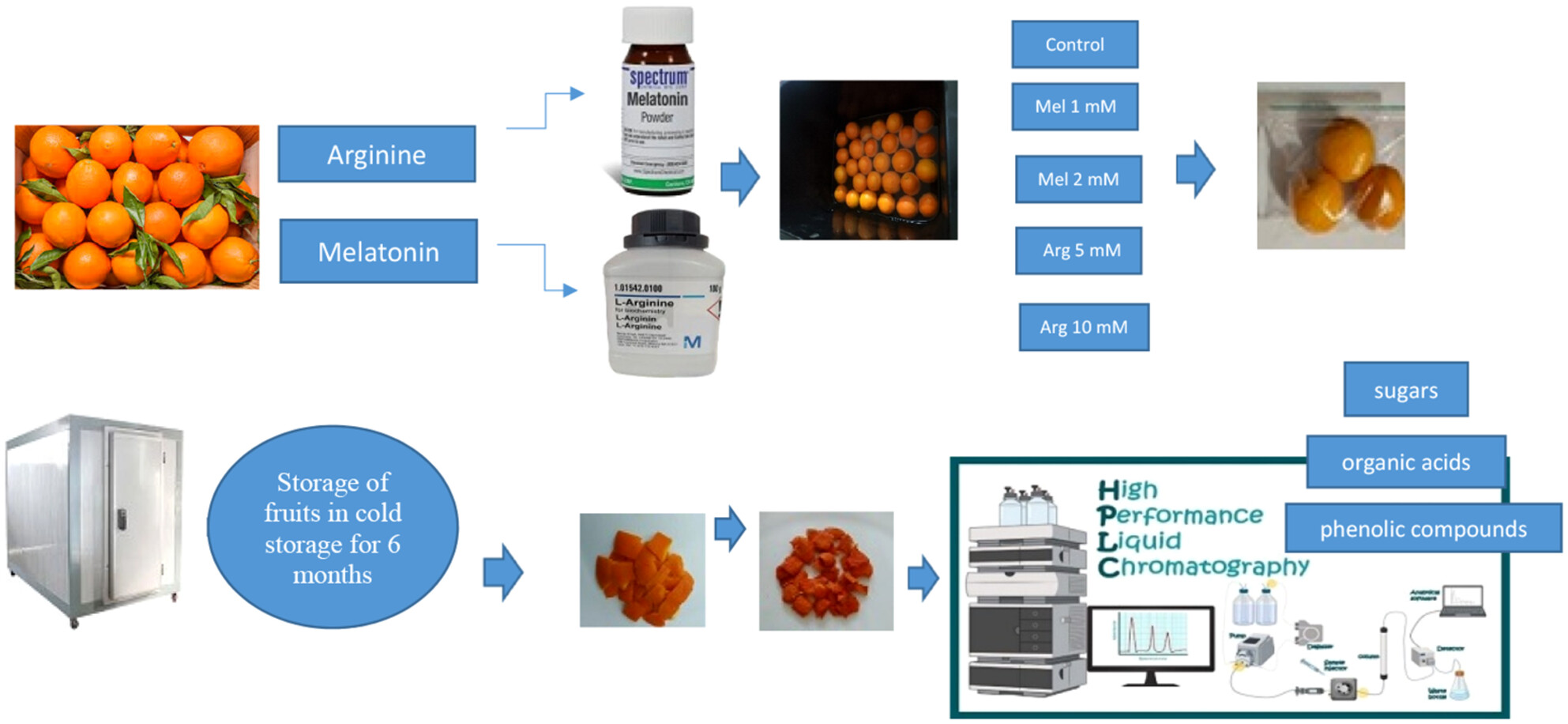
This study evaluated melatonin and arginine effects on bioactive compounds in Valencia orange peel during 6 months of cold storage. Mel (1 mM) enhanced fructose, ascorbic, citric, and chlorogenic acids, whereas Arg (10 mM) increased sucrose, ascorbic acid, and phenolic compounds. Both treatments preserved and enhanced bioactive compounds in orange peel.
REVIEW
Effectiveness of School-Based Nutrition Interventions in Italy: A Scoping Review
- First Published: 15 July 2025

This scoping review aims to examine the literature on the nature and extent of research conducted in school-based nutrition intervention programs in Italy and their effectiveness. Established and emerging programs and practices are reviewed to identify successful strategies in Italy. While Italian schools have implemented diverse and culturally tailored interventions, challenges persist, including variability in program implementation, limited follow-up, and underutilized theoretical frameworks. Regional distribution of school-based nutrition intervention studies in Italy (North, Central, and South).
Molecular Mechanisms, Endurance Athlete, and Synergistic Therapeutic Effects of Marine-Derived Antioxidant Astaxanthin Supplementation and Exercise in Cancer, Metabolic Diseases, and Healthy Individuals
- First Published: 27 June 2025
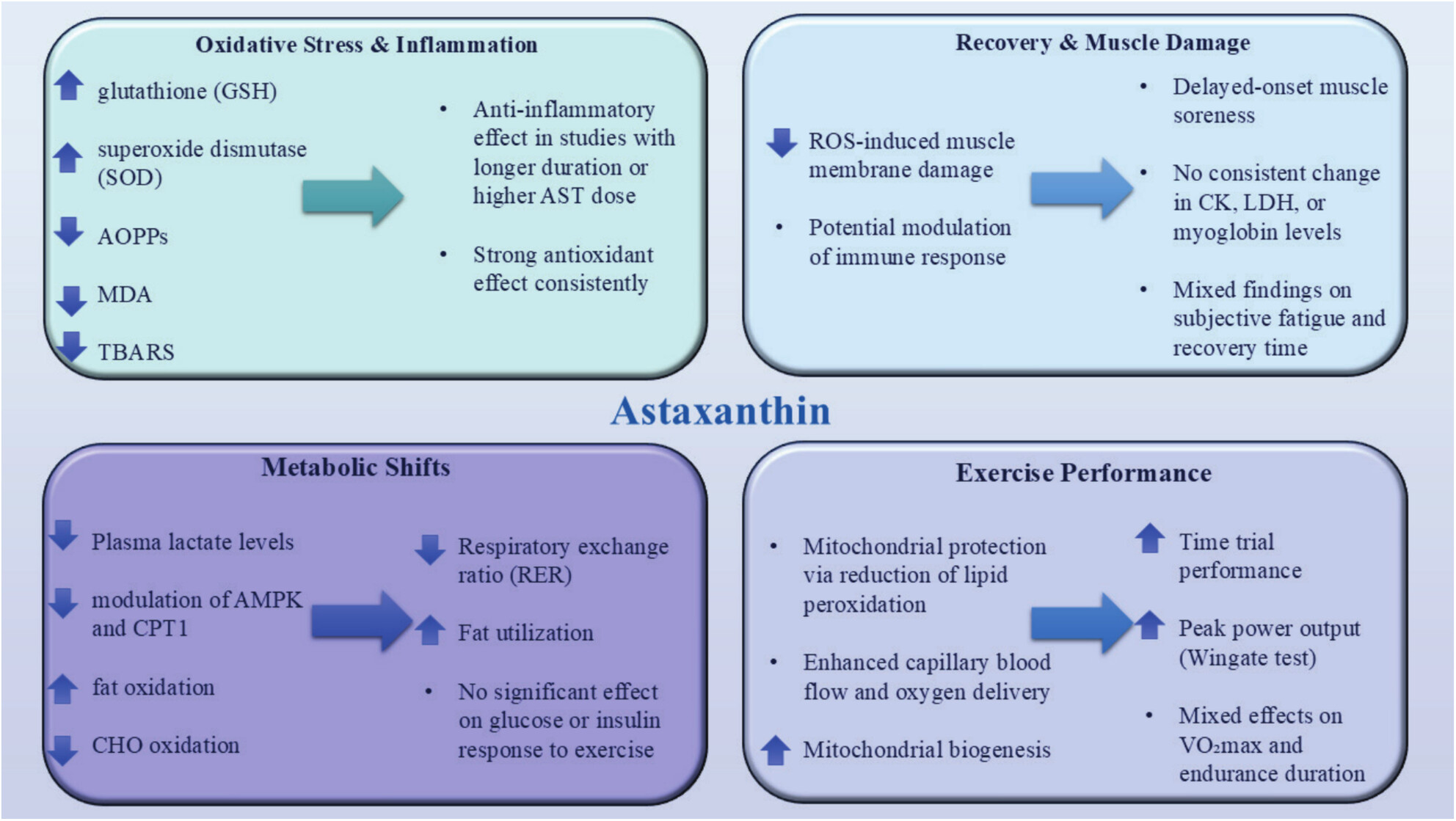
In metabolic disease, astaxanthin reduces lactate and carbohydrate (CHO) oxidation, while increasing fat oxidation, suggesting improved metabolic efficiency. In relation to exercise, astaxanthin enhances mitochondrial protection and biogenesis, boosts capillary blood flow, and improves oxygen delivery, all of which could lead to better endurance and recovery. In cancer, astaxanthin helps lower inflammation and oxidative stress, highlighting its potential role in cancer prevention or therapy support.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Dietary Nutrition, Gut Microbiota, and Health Status Across Geographically Diverse Populations in Mongolia: A Cross-Sectional Study
- First Published: 04 July 2025
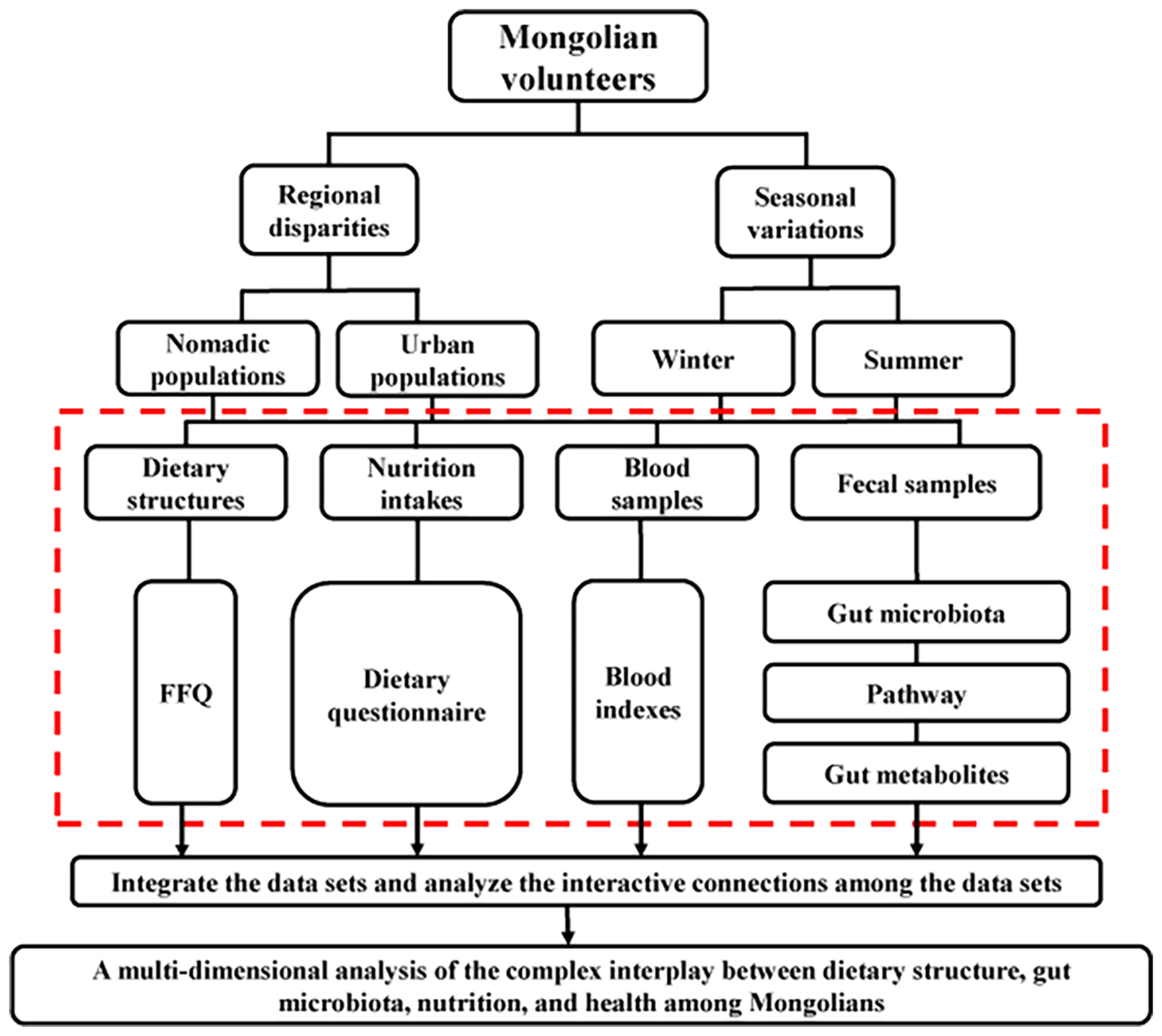
Nomadic nomadism has been the dominant culture in Mongolia. Dietary patterns have evolved to fit this culture and ensure the health of Mongolia populations. The study revealed significant differences in dietary nutrition, gut microbiota, and health status among geographically diverse populations in Mongolia, as well as correlations between microbial species and blood indices. This contributes to a deeper understanding of the complex interplay between gut microbiota, nutrition, and health among Mongolians.
REVIEW
Recent Advances in the Characterization of Food Biomacromolecules: Polysaccharide, Protein, and Lipid
- First Published: 29 June 2025
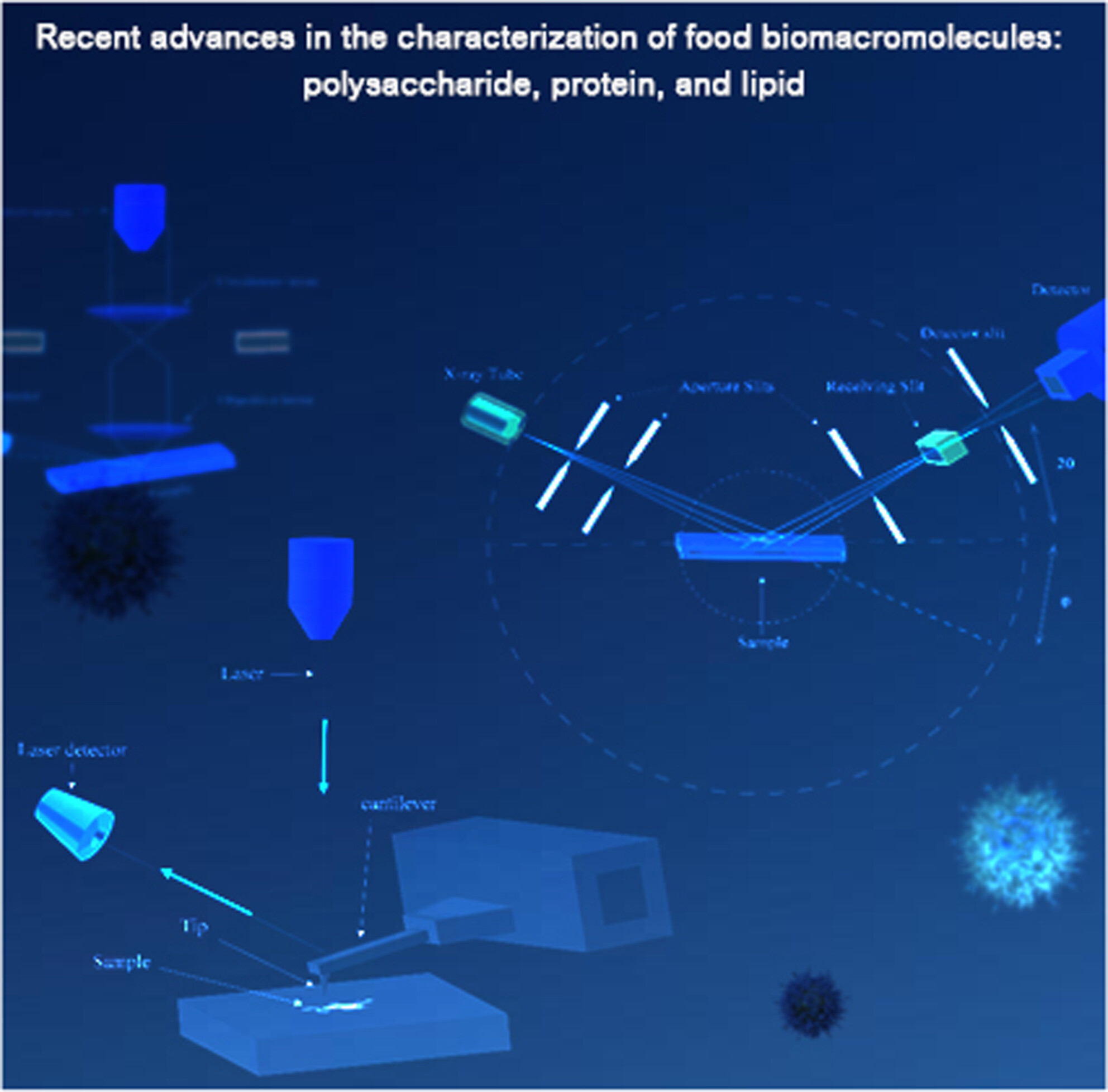
Polysaccharides, proteins, and lipids are key biomacromolecules that determine the structure, function, and nutritional value of food systems. Recent advances in spectroscopic, chromatographic, and imaging techniques have significantly enhanced our ability to characterize their complex structures and dynamic behaviors. This review highlights these analytical breakthroughs and their impact on understanding food macromolecules within diverse and heterogeneous matrices.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Protective Mechanisms of EGCG in Mitigating Oxidative Stress and Liver Toxicity From Cigarette Smoke-Induced Damage
- First Published: 07 July 2025
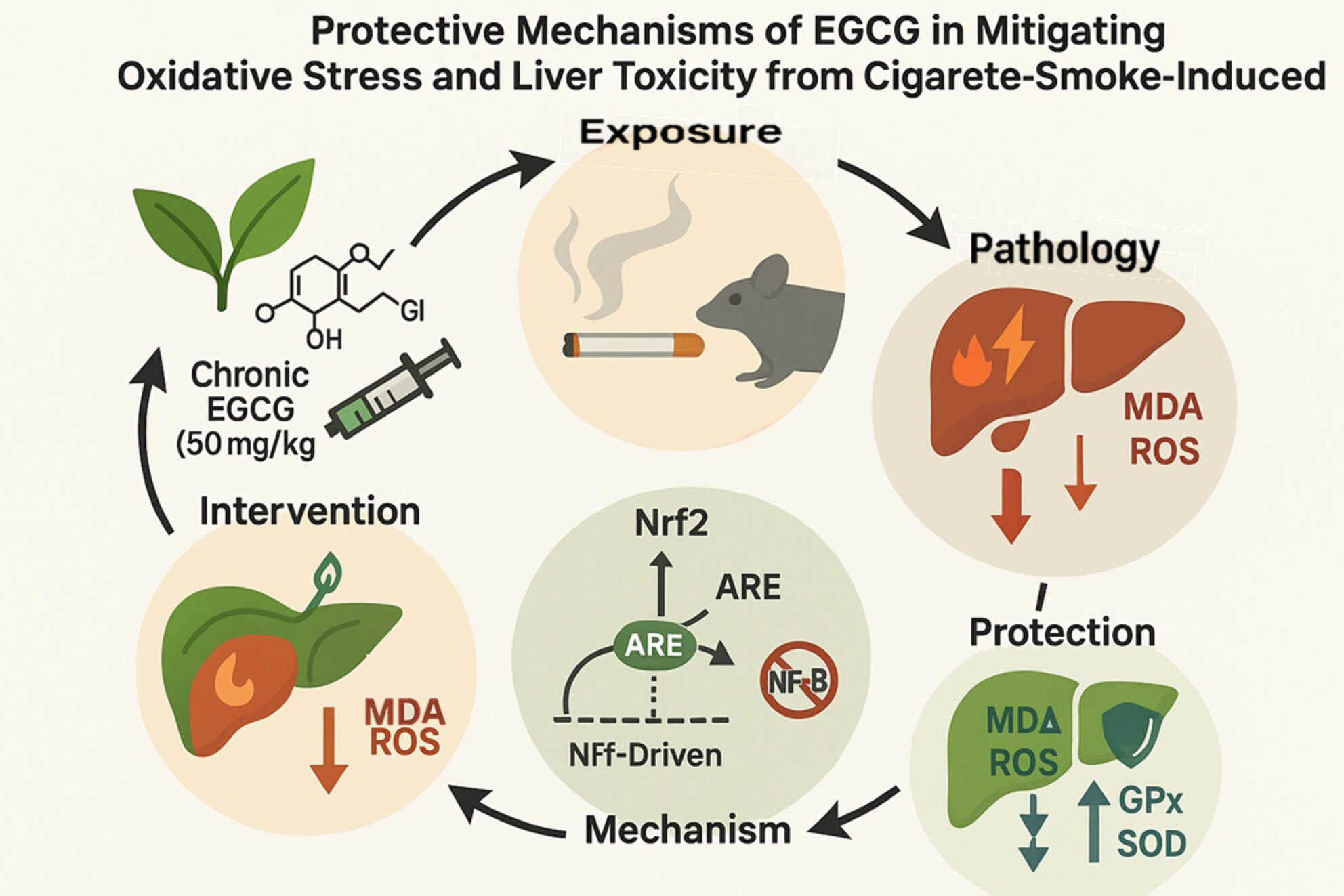
The chronic administration of EGCG has been demonstrated to effectively mitigate the oxidative stress that is induced by chronic exposure to the harmful components in cigarette smoke, thus potentially providing a protective effect. It is essential to acknowledge that the beneficial effects of EGCG administration on the antioxidant defense system require a specific duration of time to manifest fully. The chronic application of EGCG has been shown to result in a significant increase in the levels of the antioxidant enzymes glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) and chronically treated with EGCG, especially at the dose of 50 mg/kg, displayed relatively healthier liver tissue morphology.
In Vivo and In Silico Evaluation of Analgesic and Hypoglycemic Activities of Methanolic Extract of Codariocalyx gyroids
- First Published: 29 June 2025
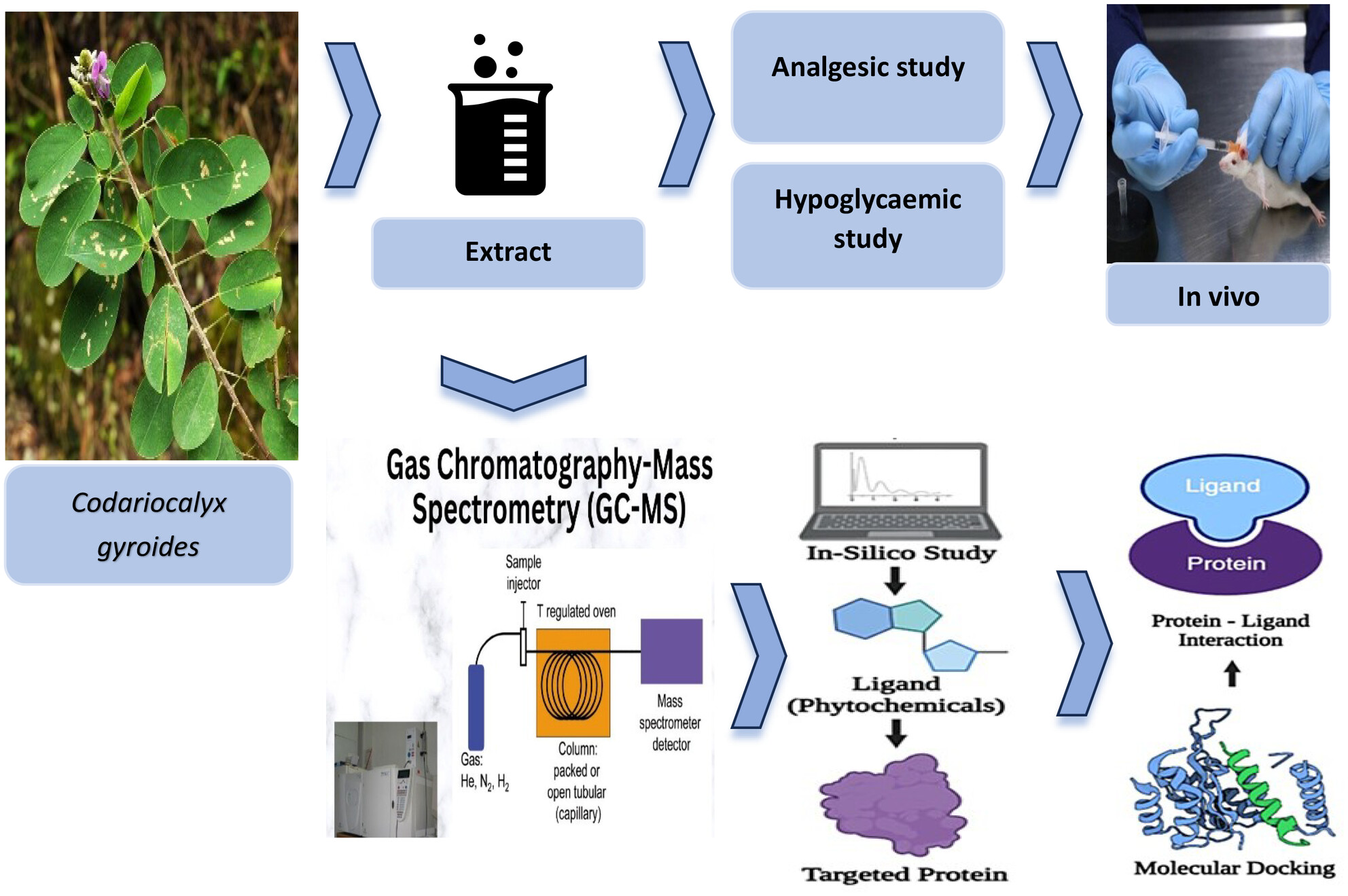
Codariocalyx gyroides (Roxb. ex Link) Hassk has been traditionally valued for its medicinal properties, yet its hypoglycemic and analgesic effects remain underexplored. This study demonstrated that the methanolic extract of Codariocalyx gyroides (MECG) exhibited dose-dependent analgesic efficacy in Swiss albino mice and significantly reduced plasma glucose levels in a Streptozotocin-induced diabetic model. In silico molecular docking identified stigmasterol and lanosterol as key bioactives, providing mechanistic insights into MECG's dual pharmacological potential, highlighting its promise for pain and diabetes management.
Enhanced Maize Leaf Disease Detection and Classification Using an Integrated CNN-ViT Model
- First Published: 30 June 2025
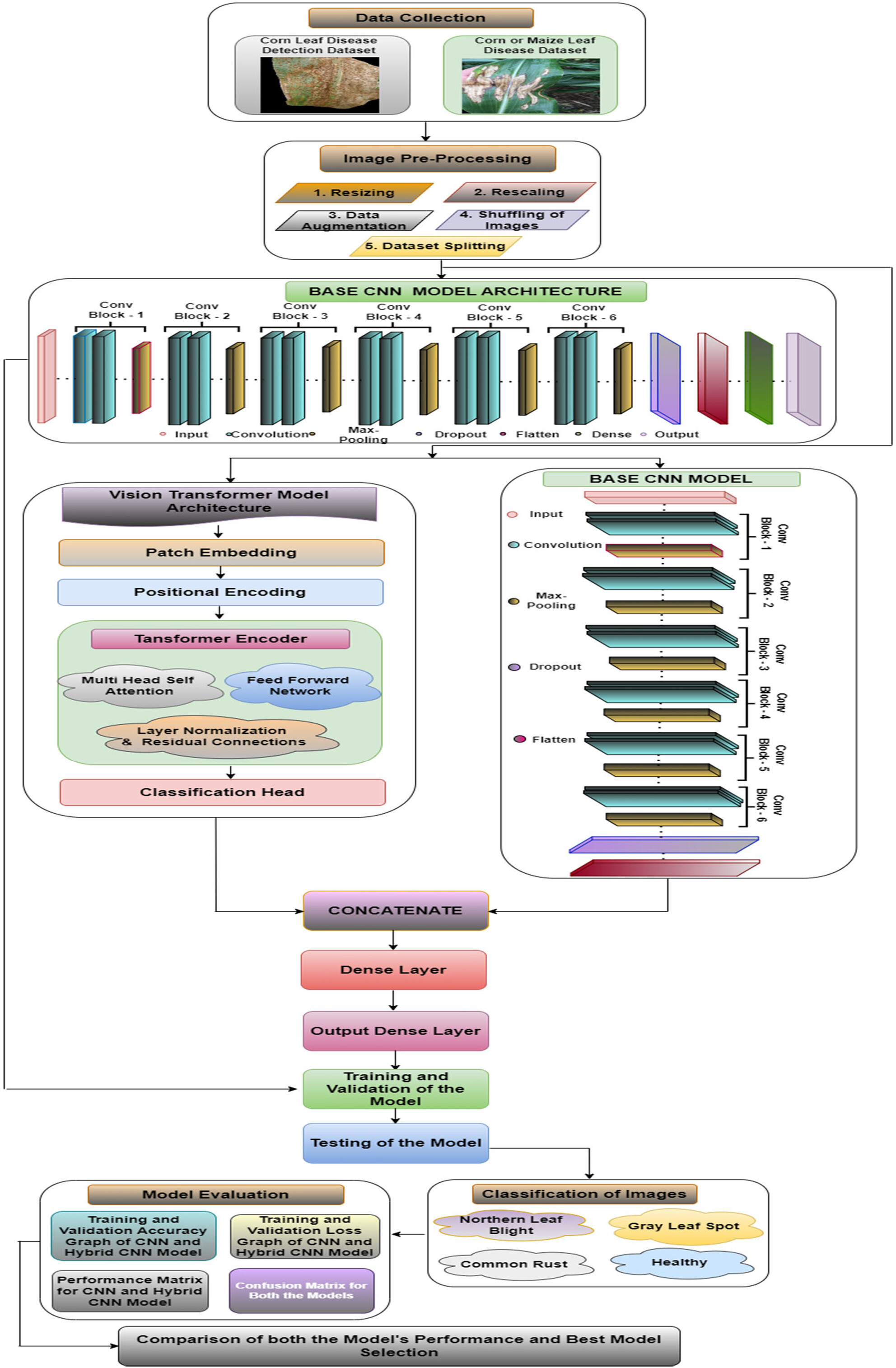
A hybrid CNN-ViT model was proposed to improve maize leaf disease classification by leveraging both local and global image features. The model achieved 99.15% accuracy, with precision, recall, and F1-score all at 99.13%, outperforming standalone CNN and ViT architectures. Cross-validation and testing on external datasets confirmed the model's robustness and potential for real-world agricultural deployment.
Eating Quality of Ribeye Steaks From Young Bulls and Steers Is Comparable: A Study Examining the Effect of Sex, Frame Size, and Feed Time on Palatability Attributes
- First Published: 30 June 2025
Purification, Structural Characterization, Antioxidant Activity, and In Vitro Digestibility of Peach Gum Polysaccharide Extracted Using an Enzymatic Method
- First Published: 29 June 2025
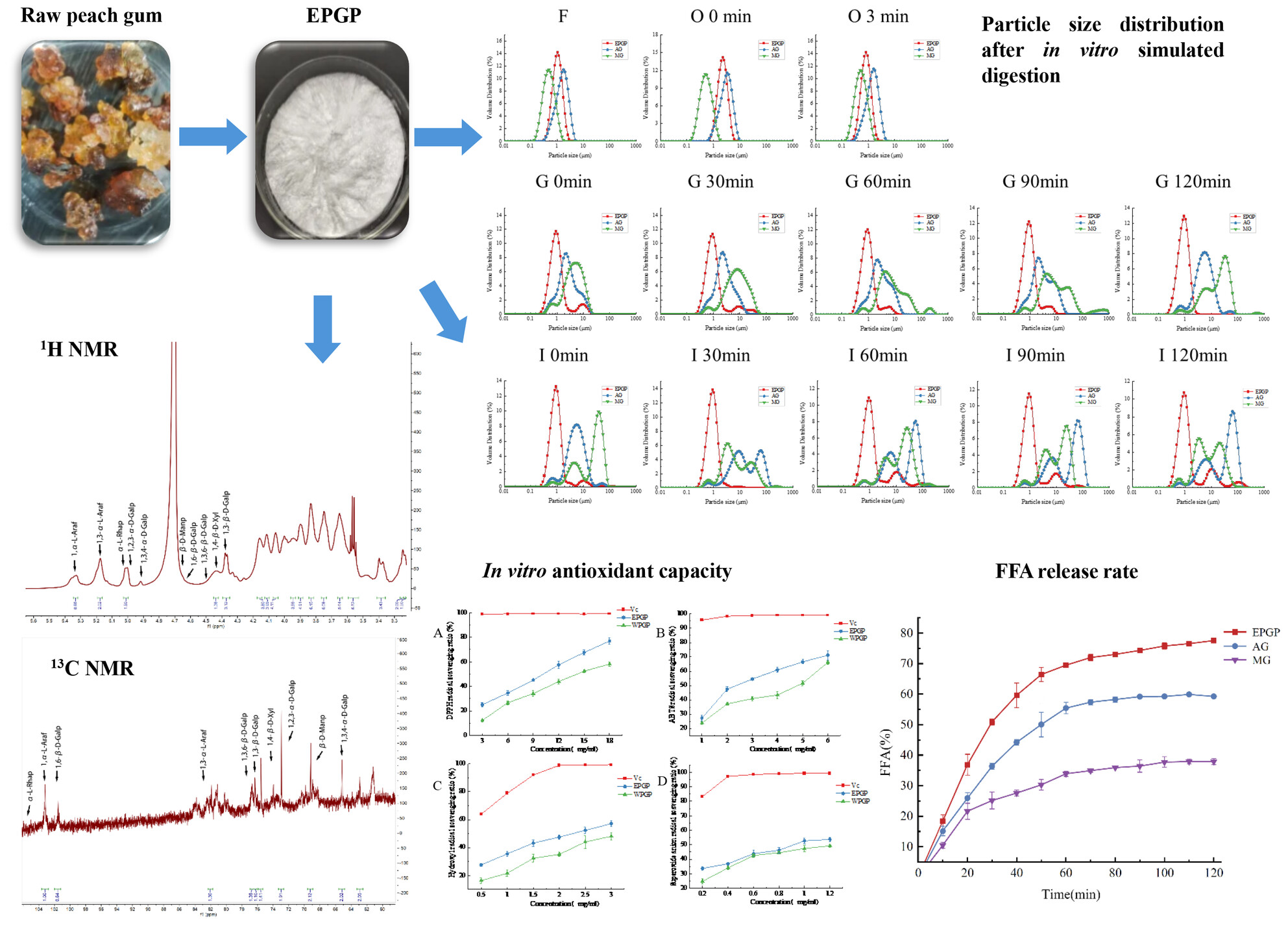
Xylanase was employed for the extraction of peach gum polysaccharide, resulting in the production of a low molecular weight polysaccharide with a molecular weight of 1.3 × 106 Da. Low molecular weight polysaccharides exhibit elevated antioxidant activity. EPGP demonstrates superior emulsification properties compared to AG and MG. EPGP showcases a heightened free fatty acid release rate.
Lactobacillus acidophilus UCLM-104 and Lacticaseibacillus paracasei UCLM-41 Are Promising Candidates to Produce Synbiotic Yogurt
- First Published: 30 June 2025
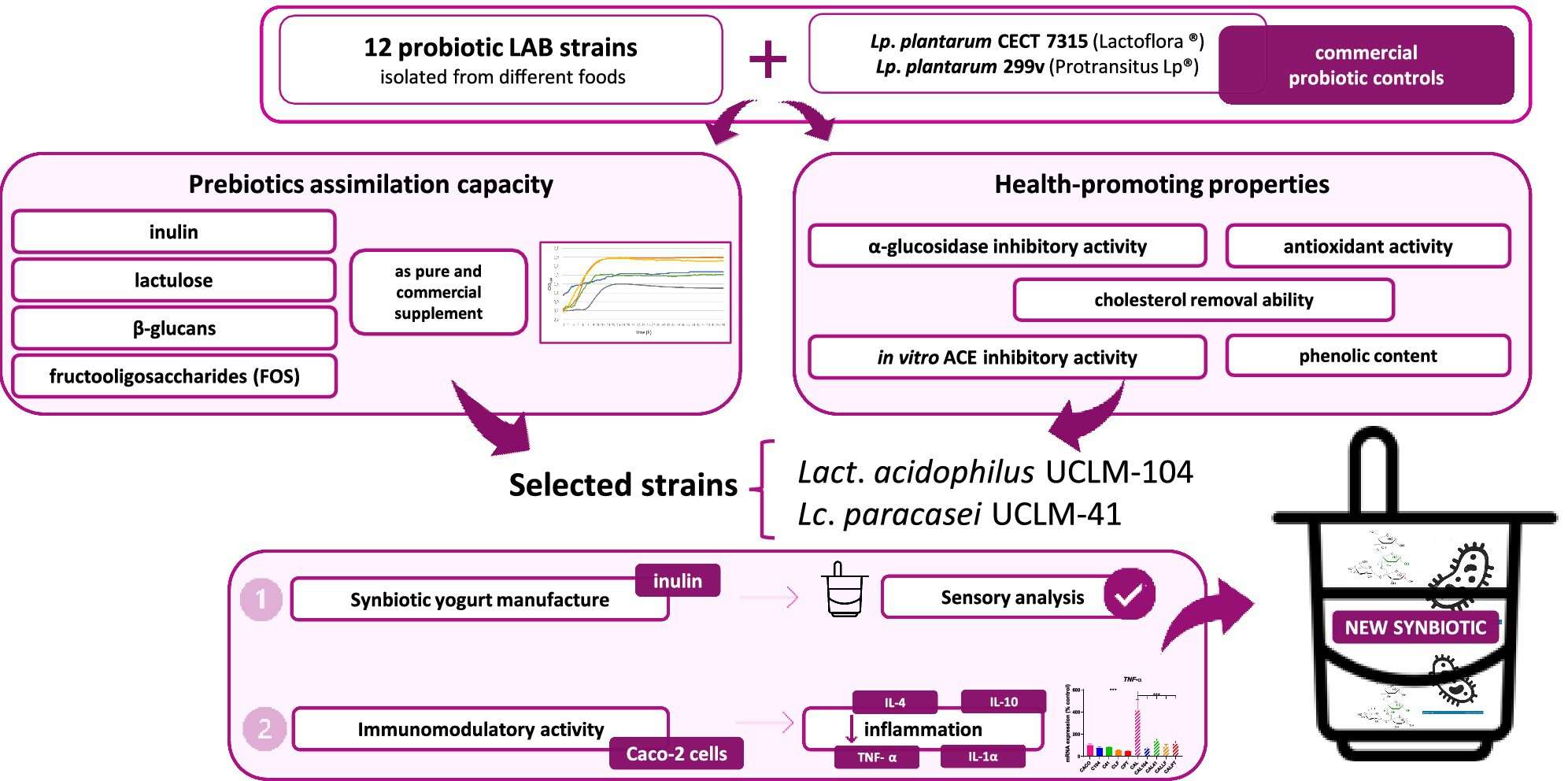
Use of health-promoting lactic acid bacteria in the production of synbiotic yogurt. Lactobacillus acidophilus UCLM-104 and Lacticaseibacillus paracasei UCLM-41 are promising probiotic strains due to their antioxidant, cholesterol removal, phenolic content, ACE-inhibition, α-glucosidase inhibitory activity, and anti-inflammatory potential.
Effect of Low Light Intensity With Supplemental Far-Red Light on Growth, Yield and Quality of Broccoli Microgreens
- First Published: 30 June 2025

Broccoli microgreens grown under low light intensity (100 μmol/m2 s) displayed increased biomass, ascorbic acid, and total phenolic compounds. Adding far-red light under low light further increased hypocotyl height and microgreen yield. Manipulation of low light intensity and far-red light are effective to increase microgreen yield and quality while reducing the energy cost.
Nutritional Properties and Preventive Potential of Leptadenia hastata (Pers) Decne (Apocynaceae) Against Metabolic Diseases
- First Published: 04 July 2025
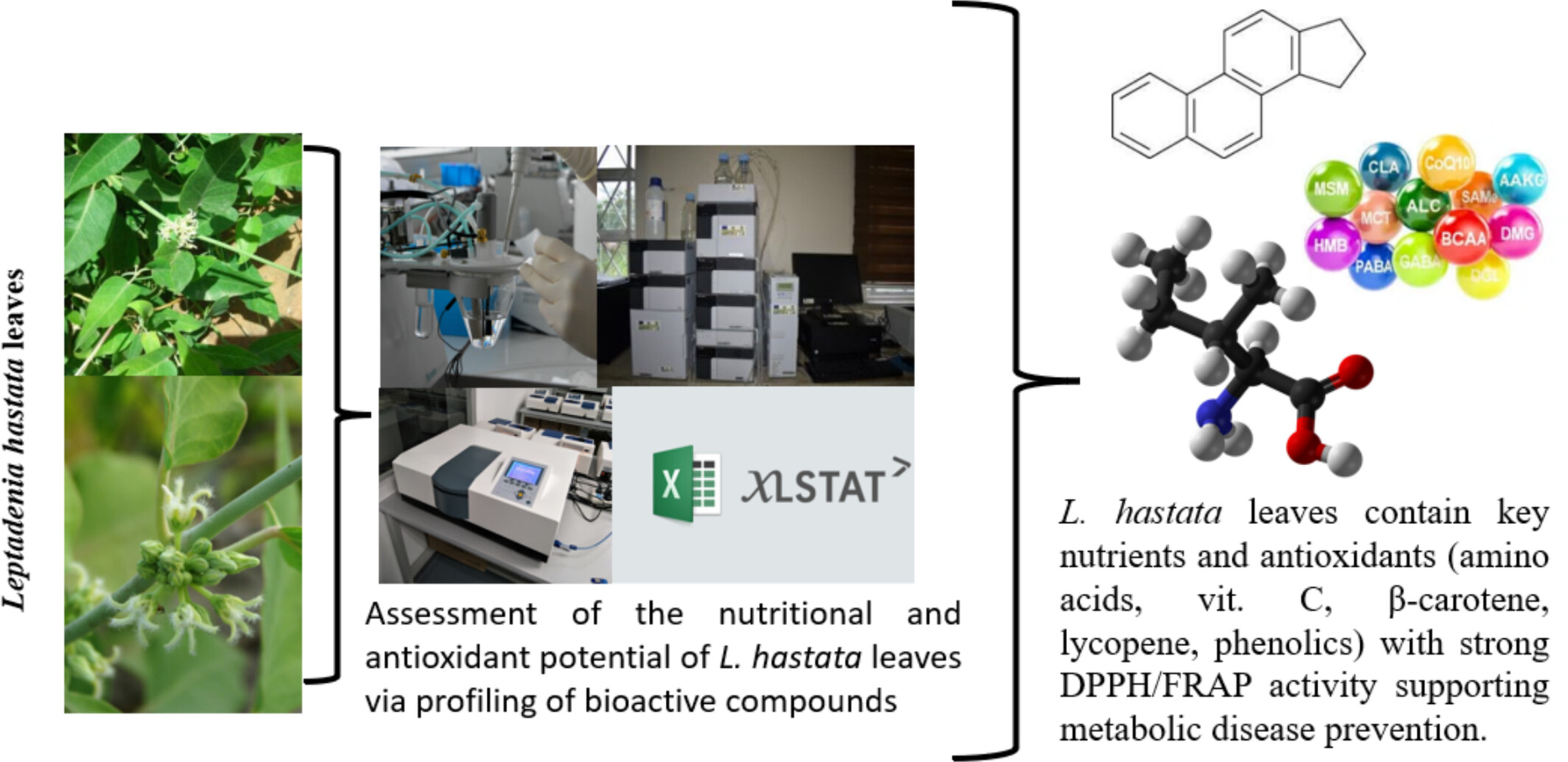
Leptadenia hastata leaves are rich in essential amino acids, vitamin C, β-carotene, and lycopene. The ethyl acetate fraction showed the highest antioxidant activity, with strong DPPH and FRAP values correlated with phenolic content. These results support its potential as a dietary source of natural antioxidants for preventing oxidative stress-related metabolic diseases.
REVIEW
Role of Dietary Carbohydrates in Cognitive Function: A Review
- First Published: 01 July 2025
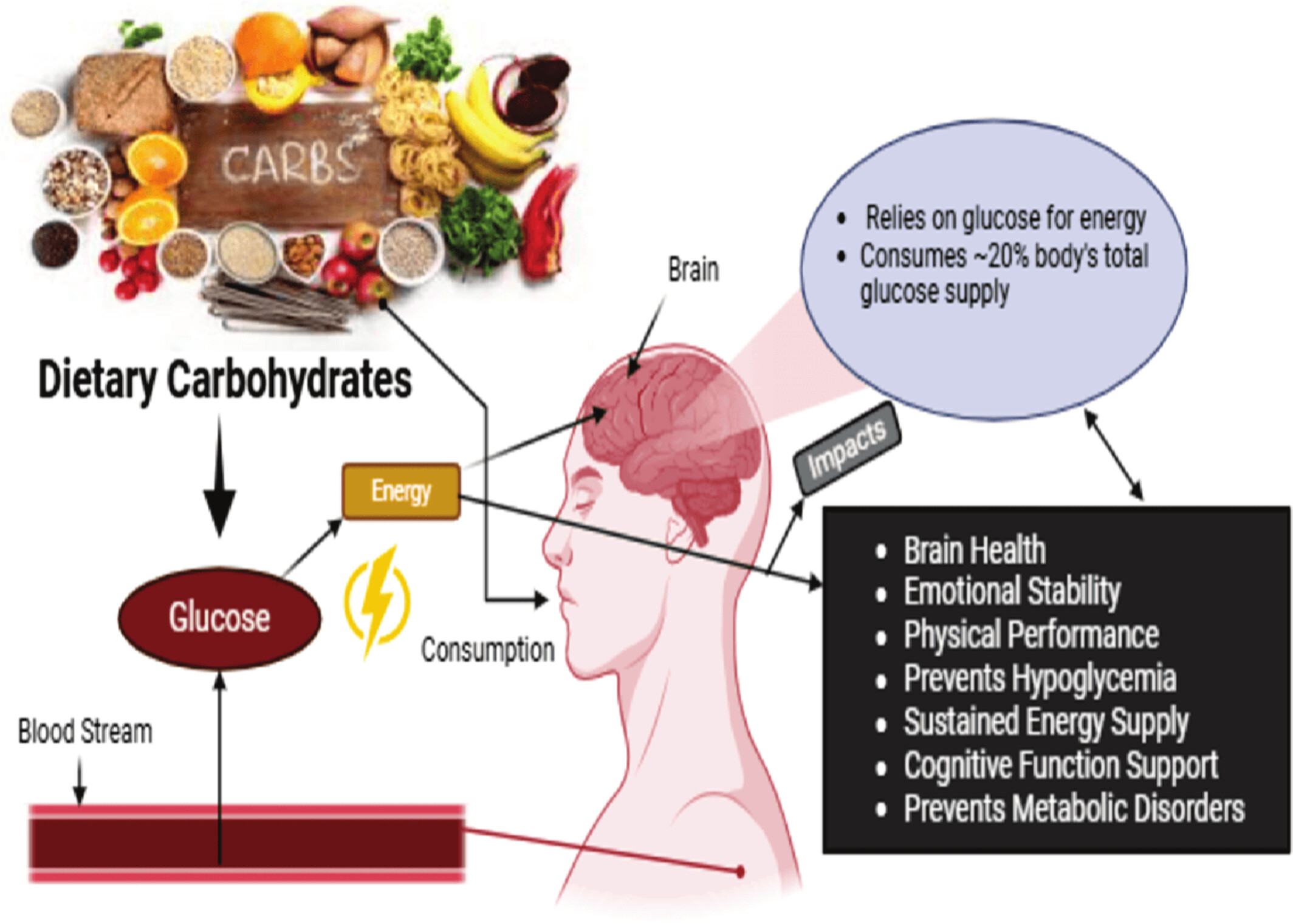
The review will focus on the intricate relationship between brain function and carbohydrate intake, emphasizing how different types of carbohydrates impact mental health and cognitive outcomes. We look at how carbohydrates impact brain energy metabolism, specifically how the brain utilizes glucose as the primary fuel source and how consuming too little carbohydrate affects emotional stability and cognitive functioning.
Exploring the Effects of Plant-Based Ingredients and Phytochemicals on the Formation of Advanced Glycation End Products in Bakery Products: A Systematic Review
- First Published: 30 June 2025

This systematic review highlights the potential activity of plant-based ingredients and phytochemicals to reduce the formation of AGEs and α-dicarbonyl compounds in bakery products. The examined studies demonstrated that various phytochemicals, including flavonoids, phenolic acids, stilbenes, and other polyphenols, as well as various plant extracts and by-products, can effectively reduce the levels of specific AGEs and α-dicarbonyl compounds in breads, cookies, and cakes.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Comprehensive Evaluation of Mathematical Models Used in the Thin-Layer Cold Dried Foods
- First Published: 01 July 2025

This study comprehensively evaluates the statistical criteria applied in mathematical models in thin layer drying of foods. As a functional sensitive food, fish was used in different sample thicknesses with high air velocity and cold drying. It was concluded that only r, R2, χ2 and RMSE equations were sufficient in the evaluation of mathematical models. At the same time, it was determined that some models could be selected as common models in all experimental materials.
Chicory (Cichorium intybus) Leaves Extract: Phenolic Composition, Antibacterial Activity, and Antioxidant Capacity Assessment
- First Published: 30 June 2025

Cichorium intybus, a plant with a long history of medicinal applications, was extracted using three solvents: hexane, ethanol, and ethyl acetate. The extracts were analyzed using chromatographic techniques, resulting in five distinct fractions: Fractions I and II were obtained from the ethyl acetate extract, whereas Fractions III, IV, and V were derived from the ethanol extract. This study investigated the antibacterial activity of the fractions against five aggressive Gram-negative bacteria associated with periodontitis: Neisseria perflava, Eikenella corrodens, Neisseria pharyngis, Morococcus cerebrosus, and Neisseria mucosa.
Male Partner Involvement in Child Feeding and Associated Factors Among Children Aged 6 to 23 Months in Hawassa City, Sidama Region, Southern Ethiopia: A Community Based Cross Sectional Study
- First Published: 01 July 2025
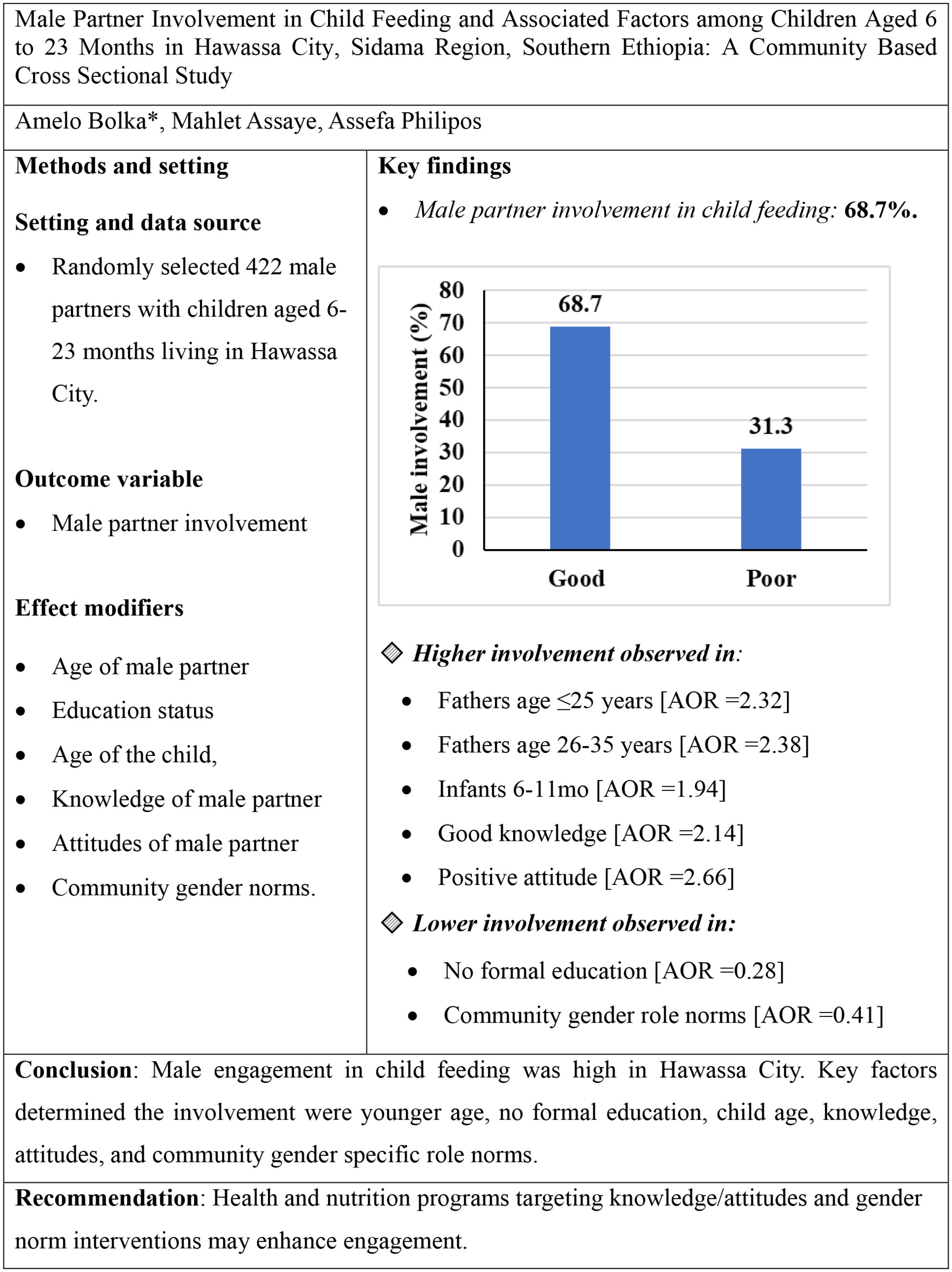
This study assessed male partner involvement in child feeding and associated factors among 422 households in Hawassa City, Ethiopia. Using a community-based cross-sectional design, the study found 68.7% prevalence of good involvement, with significant associations linked to age, education, child age, knowledge, attitudes, and gender norms. Interventions targeting knowledge, attitudes, and gender norms are recommended to enhance male engagement in child feeding practices.
Effect of Marine-Derived Scallop Peptide Hydrolysate on Immune Modulation and Gut Microbiota Restoration in Cyclophosphamide-Induced Immunosuppressed Mice
- First Published: 23 July 2025

Cyclophosphamide (CTX), a chemotherapy agent, can impair immune responses and disrupt gut microbiota, leading to dysbiosis and inflammation. This study evaluated the effects of scallop peptide hydrolysate (SCH) on immune suppression and gut microbiota in BALB/c mice treated with CTX. SCH significantly restored intestinal mucosal integrity, enhanced tight-junction proteins, and improved colon and spleen histology. It increased body weight, immune organ indices, pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, TNF-α), and immunoglobulins (IgM, IgG), while decreasing anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10, IL-4). Additionally, SCH promoted macrophage activity, splenic lymphocyte proliferation, and increased CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes, restoring gut microbiota balance by enhancing beneficial bacteria. These findings suggest that SCH functions as a prebiotic and may provide therapeutic benefits for gastrointestinal disorders and immune regulation.
The Association Between Weight-Adjusted-Waist Index and S-Klotho Levels in Adults: NHANES 2007–2016
- First Published: 17 July 2025

This study investigates the relationship between the weight-adjusted waist index (WWI) and serum Klotho levels in adolescents, highlighting WWI as a potentially more accurate obesity indicator than traditional measures like BMI. The findings reveal a significant negative association between WWI and serum Klotho concentrations, suggesting that WWI may serve as a predictive indicator of serum Klotho levels, with implications for understanding obesity's influence on aging. Further research is needed to explore the underlying mechanisms of this relationship.
Mitigation of Fungal Contamination in Vegetables: Key Factors From a Study in Debre Tabor, Ethiopia
- First Published: 15 July 2025
Phytochemical Profiling and Anti-Bacterial Activity of Red Delicious Apple Pomace With Integrated Hydrolysis to Obtain Fermentable Sugars: A Biorefinery Approach
- First Published: 09 July 2025
Assessment of the Impact of Fruit Vinegars on the Tenderness and Quality Attributes of Spent Hen Meat
- First Published: 01 July 2025

Vinegar addition lowered pH and cooking loss, while the Cp group had the highest moisture and WHC. SEM images revealed that marination with vinegar led to extensive degradation of connective tissues. Meat marinated with pineapple and strawberry vinegar showed significantly lower hardness, WBSF, and WBSE. These results were further supported by sensory analysis, as texture scores aligned with the TPA and SEM findings. Marination with vinegars caused a significant reduction in microbial counts.
Unlocking Resveratrol's Potential: Targeting Ferroptosis in Atherosclerosis Through MAPK1
- First Published: 21 July 2025

Using network pharmacology, bioinformatics, machine learning, and molecular docking, we identified mechanisms and core six key targets (MAPK1, IL1B, RELA, HIF1A, SRC, and PTEN) in RSV-AS-Ferroptosis. Experimental validation was performed using ApoE−/− mouse fed a high-fat diet (HFD) for 12 weeks to establish AS model. RSV treatment reduced aortic lipid plaques, reduced serum GSH, SOD, MDA and iron levels, and significantly downregulated MAPK1 expression in aortic root, which providing a new theoretical framework for AS prevention and treatment.
Cyamopsis tetragonoloba Gum-Based Active Coatings Incorporated With Pycnocycla bashagardiana Essential Oil for Reducing Postharvest Losses of Fresh Pistachio Fruits
- First Published: 07 July 2025
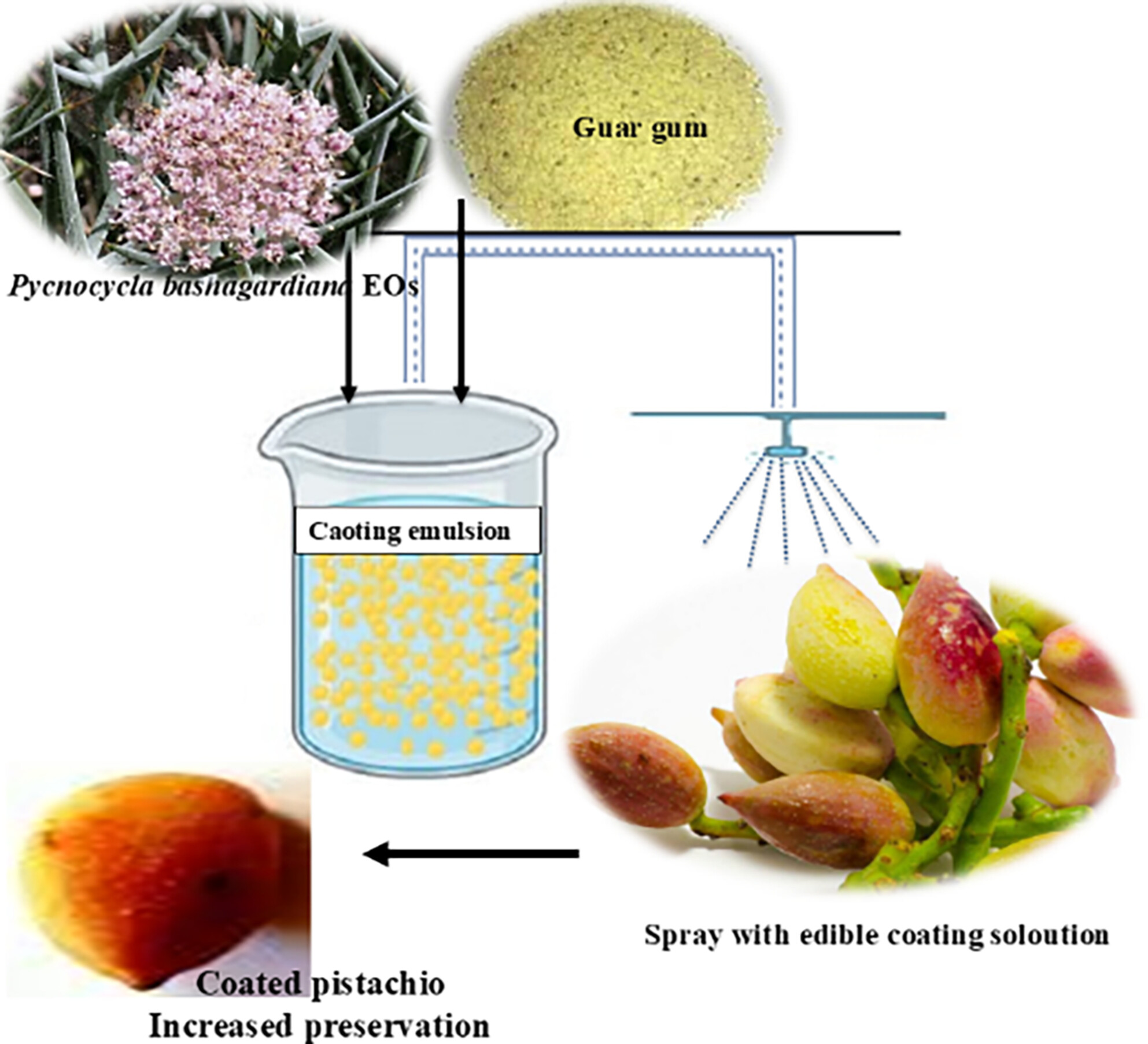
Treated pistachio retained phenolics and total antioxidant capacity. The guar gum-PBEO coating had the best antifungal effects on Penicillium and Aspergillus growth. The guar gum, along with PBEO, elevates the storage period of fresh pistachio up to 60 days.
The Effects of Wuniuzao Green Tea on Mice With High-Fat Diet-Induced Liver Steatosis
- First Published: 03 July 2025
REVIEW
Hyperhomocysteinemia-Driven Ischemic Stroke: Unraveling Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Horizons
- First Published: 03 July 2025
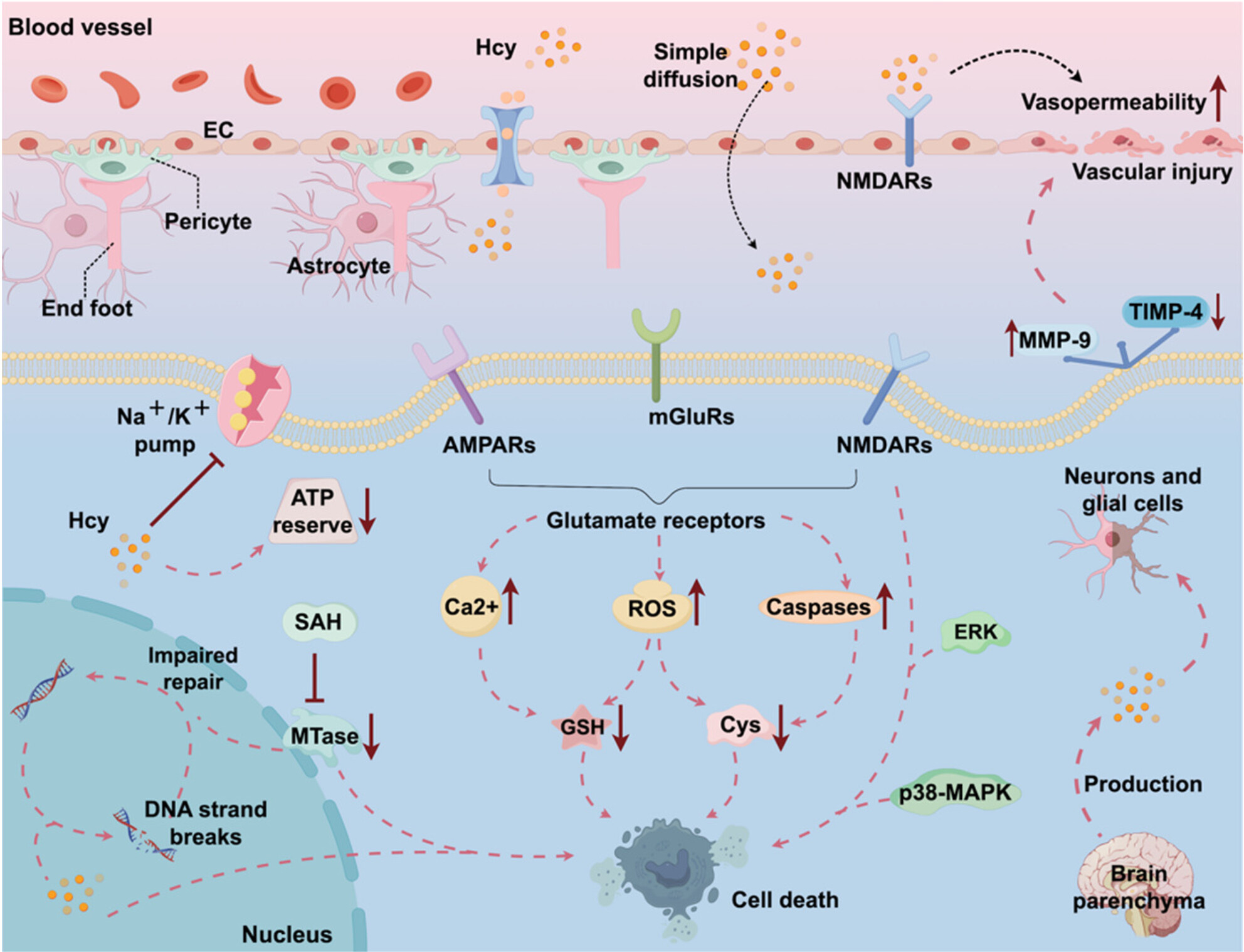
Neurotoxicity of Hcy. (A figure that best represents the scope of the paper.) Homocysteine can reduce the tightness of endothelial cell connections, increase vascular permeability, and damage the blood–brain barrier. Homocysteine activates various glutamate receptors on the surfaces of neurons and glial cells, triggering excitotoxicity, promoting the production of ROS, disrupting the antioxidant system, and leading to DNA damage and cell apoptosis.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Transcriptome and WGCNA Reveal the Key Genes of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi in Regulating Sugarcane Growth and Nutrient Absorption
- First Published: 03 July 2025
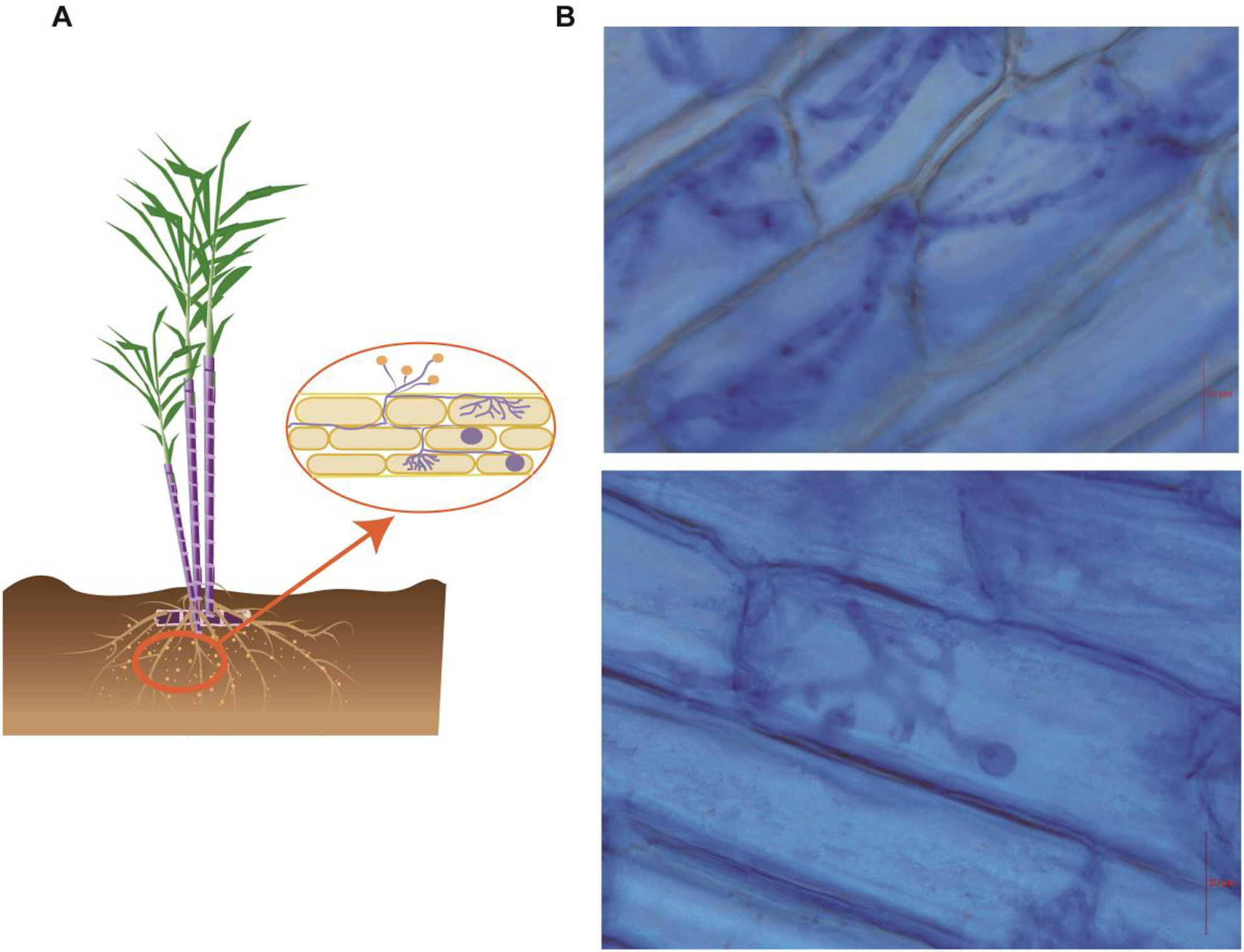
AM fungal inoculation boosted sugarcane biomass and improved rhizosphere soil nutrient levels. RNA-seq and WGCNA revealed gene modules linked to nutrient uptake and growth, differentiating above- and belowground responses. Hub genes (CESA9, ANR, CYCP4, LHA1, SUS4, RPS15AE, CNGC2) were identified as key regulators of sugarcane growth and nutrient cycling.
Isolation, Chemical Structure, and Antagonistic Activity Against Galectin-1 of Water-Soluble Polysaccharides From Plantago asiatica
- First Published: 01 July 2025

Plantago asiatica has been utilized as a dietary supplement in health foods and for medicinal purposes, enjoying a long-standing acceptance throughout history. This study will provide new insights into the relationship between the antagonistic activity against galectin-1 of P.asiatica polysaccharides and their applications in the fields of food and medicine.
REVIEW
Effects of Avocado Products on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Adults: A GRADE-Assessed Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- First Published: 02 July 2025
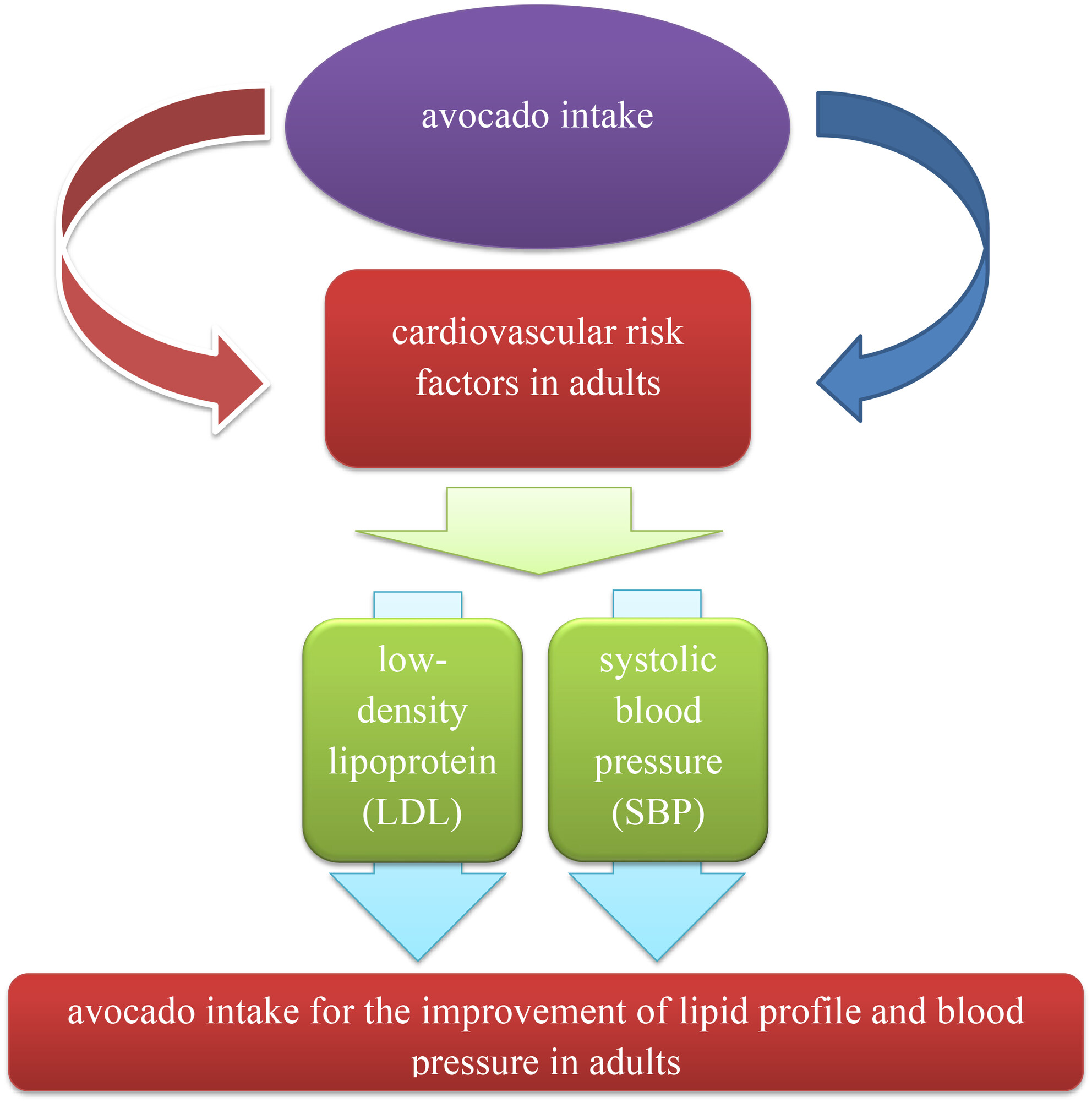
Cardiovascular diseases are a major global health concern, and avocados, rich in monounsaturated fats and bioactive compounds, may help improve heart health by influencing lipid profiles and other risk factors. However, existing studies on avocado consumption and cardiovascular benefits show inconsistent results and no comprehensive meta-analysis has been conducted. This study aims to systematically review and analyze current research to provide a quantitative assessment of avocados' effects on cardiovascular risk factors in adults.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Can Enhanced Nutrition Knowledge Improve Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Among Physically Active Individuals? Evidence From a Cross-Sectional Study
- First Published: 08 July 2025
REVIEW
Sodium Reduction Through Sensory Interactions With NaCl: Strategies and Underlying Mechanisms
- First Published: 04 July 2025

We proposed effective sodium-reduction strategies by analyzing the mechanisms of sensory interactions between sodium chloride and flavor stimuli at peripheral and central nervous system levels. The results indicate that top-down regulation by higher neural centers (e.g., insular and orbitofrontal cortex) plays a key role in enhancing saltiness perception.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Capsaicinoid Glucoside Attenuates Lipid Accumulation in HepG2 Cells Through TRPV1/AMPK-Dependent Signaling Pathway
- First Published: 02 July 2025
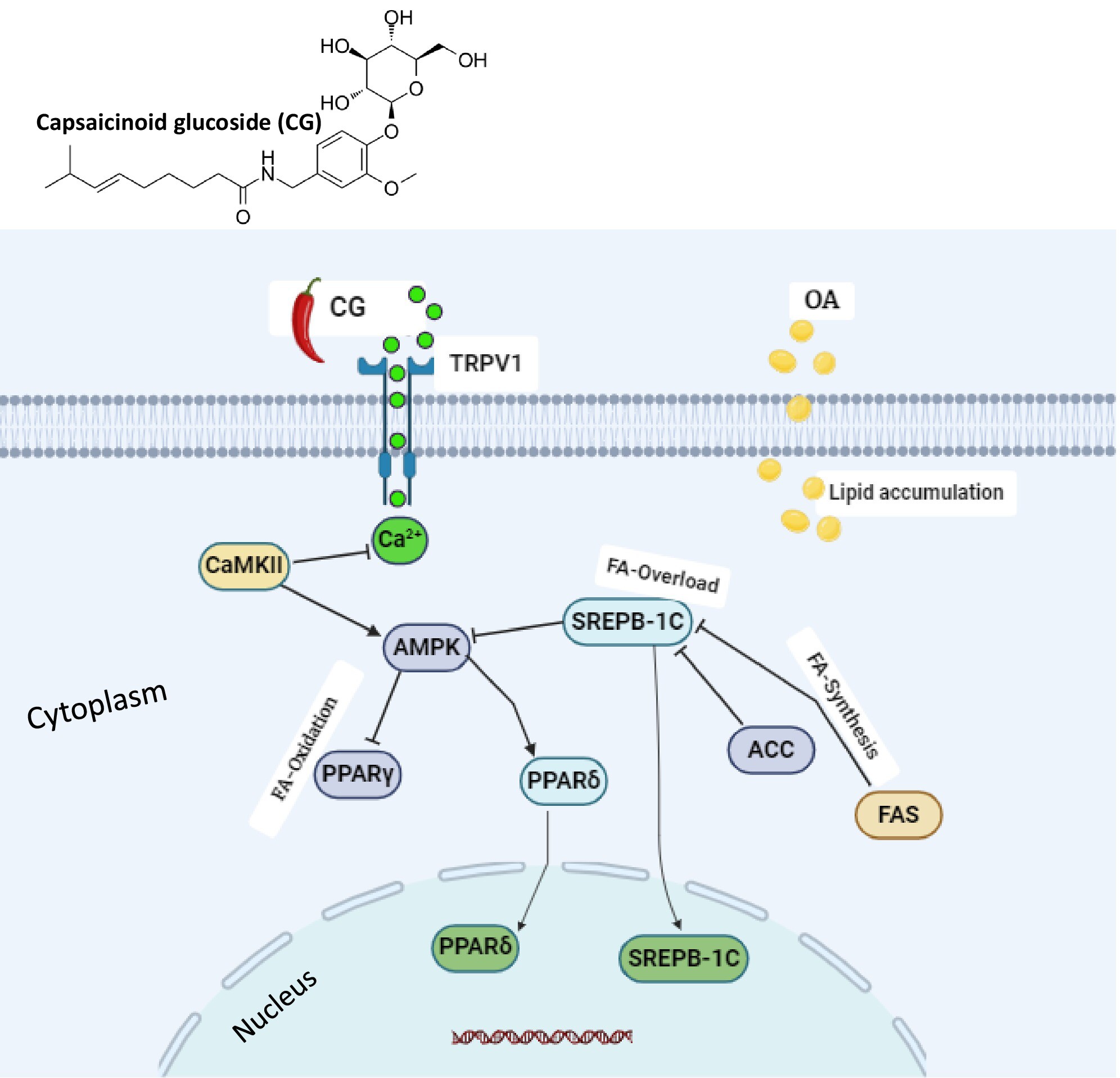
Capsaicinoid glucoside (CG), reduces triglyceride (TG) and total cholesterol (TC) accumulation in OA-treated HepG2 cells. CG alleviates reactive oxygen species (ROS) and enhancing lipid oxidation. CG activates the TRPV1/AMPK pathway, while downregulating the expression of lipogenic genes SREBP-1C and FAS. Molecular docking indicates that CG forms stable complexes with TRPV1 and AMPK, suggesting their involvement in lipid regulation.
Transcription Factors and Regulate Network in Food Plant Stress and Growth Responses
Genome-Wide Analyses of Phosphate Transporters in Wild Rice (Oryza brachyantha) Revealed Their Evolution and Regulatory Roles in Phosphate Homeostasis
- First Published: 02 July 2025

Oryza brachyantha, a wild rice species, was identified as highly efficient in phosphorus (P) uptake. Genome-wide analysis revealed 31 phosphate transporter (ObPT) genes, with several ortholog losses and dynamic expression under Pi starvation. These findings highlight the evolutionary divergence and potential of wild rice in enhancing P use efficiency.
Utilizing Quinoa Flour for Functional Lavash Bread Production
- First Published: 04 July 2025

This study investigated the effects of incorporating 5%–20% quinoa flour into lavash bread. The addition of quinoa improved dough rheology, enhanced protein, fiber, and mineral content, and maintained sensory acceptability. Lavash enriched with 15%–20% quinoa flour showed optimal nutritional and functional qualities.
REVIEW
An Investigation Into Impact of Date Seed Bioactive Compound Addition on the Quality Attributes, Shelf Life, In Vitro Digestibility, and Bioactive Properties of Cottage Cheese
- First Published: 04 July 2025

This study evaluated the incorporation of date seed bioactive compounds (DSBCs) into cottage cheese (CC) as a functional ingredient and natural preservative. Enrichment with DSBCs enhanced the cheese's antioxidant and antimicrobial properties, extended shelf life during 14-day storage, and improved bioaccessibility of bioactives post-digestion. Findings highlight DSBCs as promising functional additives for improving the nutritional quality and stability of dairy products.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Causal Relationship Between Various Vitamins and Different Diabetic Complications: A Mendelian Randomization Study
- First Published: 07 July 2025
REVIEW
Nutritional, Pharmacological and Industrial Applications of Mangosteen and Passion Fruit: A Review
- First Published: 07 July 2025

The objective of this review was to comprehensively discover the pharmacological, industrial, and nutritional solicitations of passion fruit and mangosteen, the importance of their functional foods, and their therapeutic potential. This study investigated their pharmacological activities, including antioxidant, antidiabetic, anticancer, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory activities, by analyzing their dense phytochemical content, which consists of polyphenols, carotenoids, tannins, xanthones, and anthocyanins.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Enhanced YOLOv11n: A Method for Potato Peel Damage Detection
- First Published: 04 July 2025

Potatoes are susceptible to skin damage during harvest and transportation, which impacts storage capabilities, increases the risk of microbial contamination and decay, and diminishes both quality and food safety. Rapid detection of potato peel damage is crucial for the subsequent automatic sorting process. To address this, this paper introduces an enhanced YOLOv11n target detection algorithm for identifying damaged potatoes.
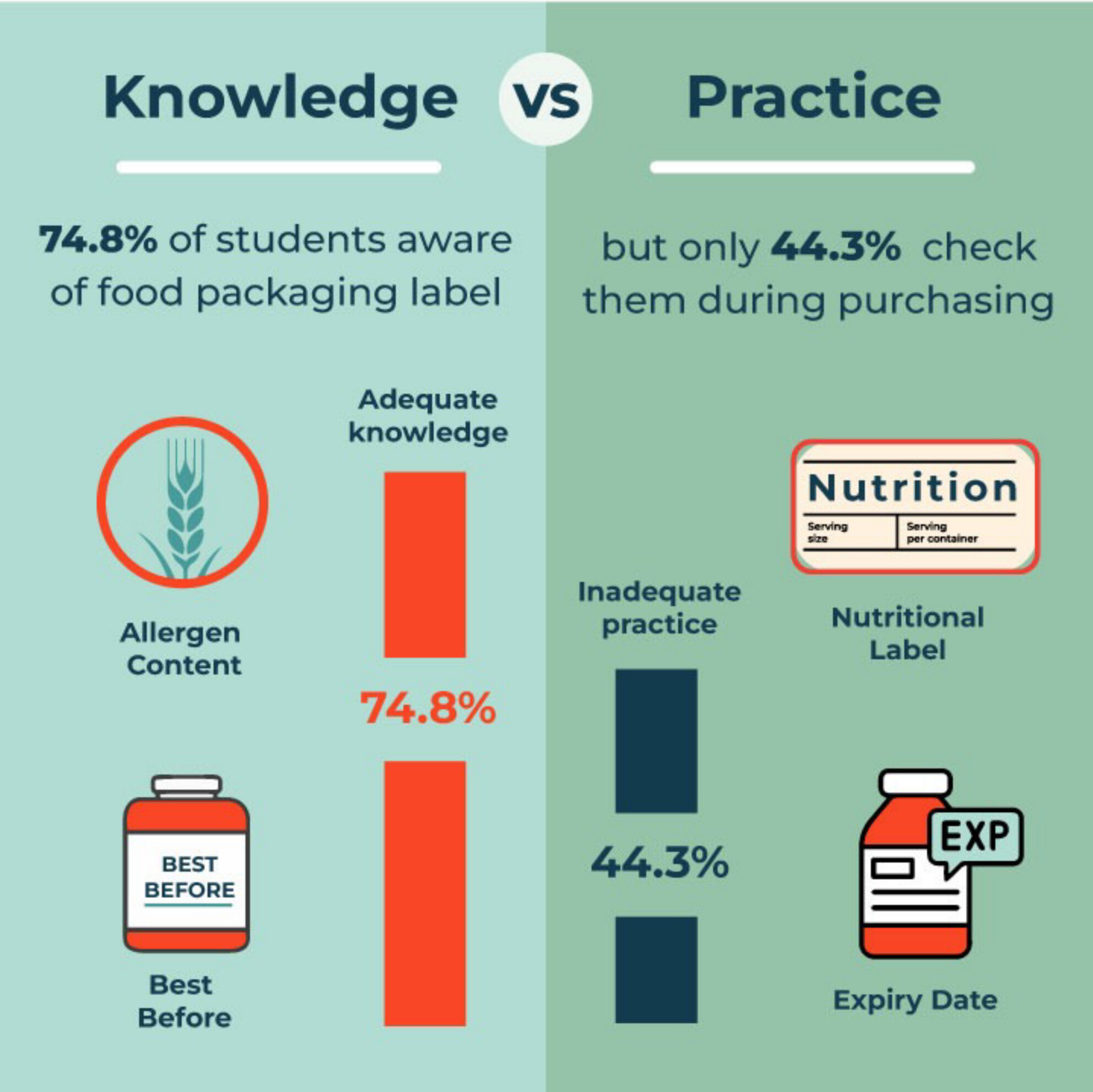
University Student's Knowledge, Practices, and Perceptions of Food Packaging Labels in Bangladesh: A Cross-Sectional Study
- First Published: 04 July 2025
Innovative Utilization of Watermelon By-Product Powders to Enhance Fresh Pasta Quality: Improving Nutritional Value and Functional Properties
- First Published: 04 July 2025

This study investigates the incorporation of watermelon by-product powders (peel, rind, and seed) into fresh pasta to enhance its functional properties. The results indicate that these by-products significantly improve the nutritional composition, antioxidant activity, and texture of the pasta, offering a sustainable approach to food waste utilization. This research underscores the potential of watermelon by-products as valuable, functional ingredients in the fortification of pasta, contributing to both enhanced product quality and sustainability.
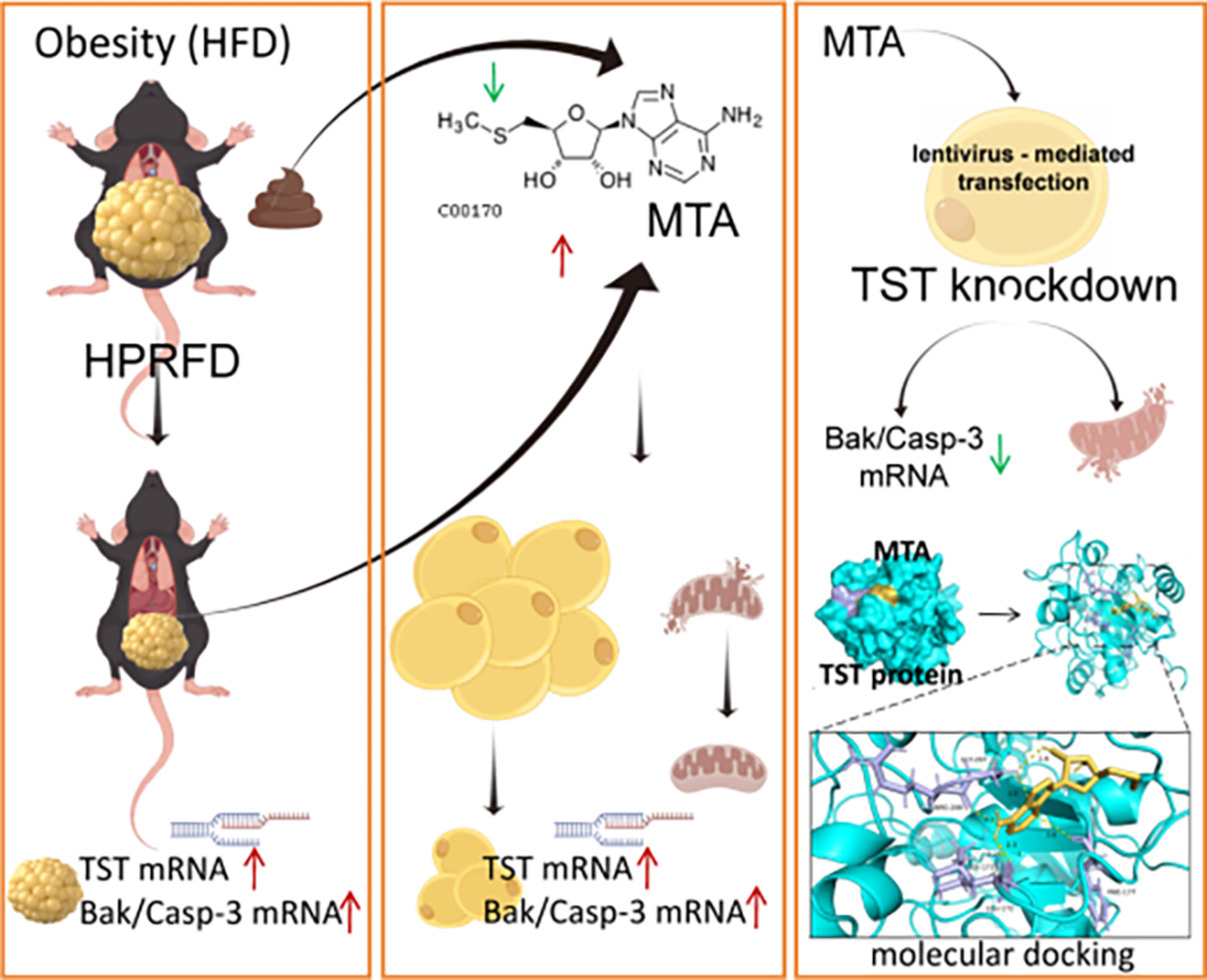
MTA-TST Axis-Mediated Apoptosis Activation: A Multi-Omics Insight Into High-Protein Diet's Anti-Adiposity Effect
- First Published: 09 July 2025
The Hypolipemic Properties of Kaempferol Presented in Microwaved Cooked Broccoli Between Hyperlipidemic Rat Models
- First Published: 07 July 2025
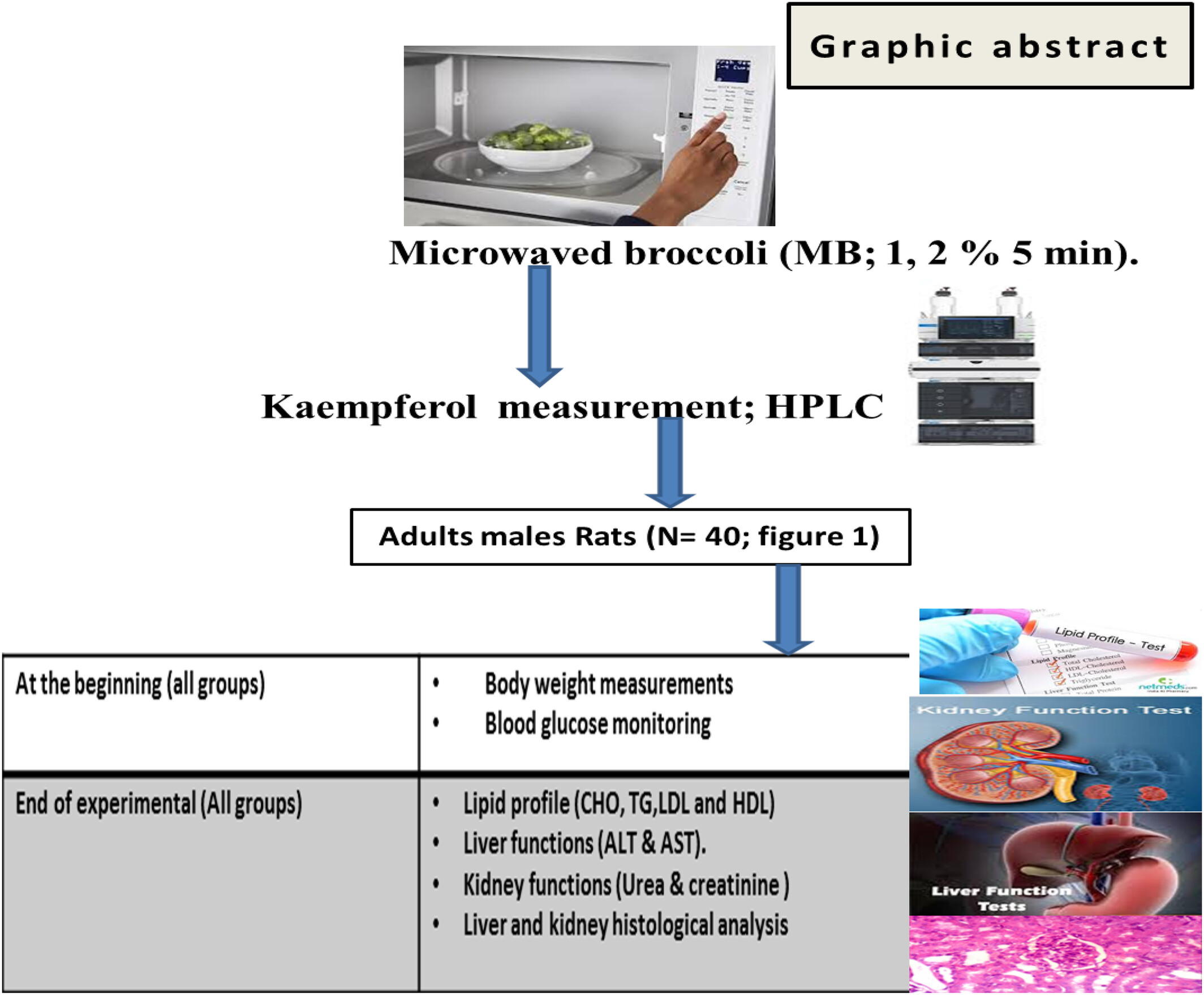
The current study aimed to measure Kaempferol between microwaved broccoli (MB) samples using High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Also, their potential hypo-lipid properties between hyper-lipid rats were investigated. Kaempferol in microwaved broccoli demonstrated potential in modulating levels of BG, lipids, kidney and liver functions between hyper-lipid models thus incorporating microwaved broccoli at 2-5 min influenced the antioxidant levels providing a valuable adjunct as traditional lowering lipid therapy.
CORRECTION
Correction to “Investigation on Anti-Diarrheal and Antipyretic Activities of Citrus maxima Seeds in Swiss Albino Mice Model”
- First Published: 25 July 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Lycopene Alleviates Lipid Dysregulation, Oxidative Stress, and Hypercholesterolemia in Obese Rats Subjected to a High-Fat Diet
- First Published: 07 July 2025
Association Between Fermented Food Consumption and Sleep Quality Under Psychological Stress: Prospective Cohort Study
- First Published: 07 July 2025

A prospective cohort questionnaire-based study was conducted online on a group of 280 Polish medical students under exam stress to assess the association between their fermented food consumption and sleep quality. The association was found to be V-shaped. Both raw and adjusted analyses showed that students whose fermented food consumption was found in the second tercile had lower mean PSQI scores, which indicated higher sleep quality, than students in the first and third terciles.
REVIEW
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Impact of Cornus mas L. on Anthropometric Indices and Body Composition
- First Published: 15 July 2025

Findings indicated no significant differences in cases of body weight (BW), body fat percentage (BF%), fat mass (FM), waist circumference (WC) and hip circumference (HC) after administering Cornus mas L. A modest but significant increase in body mass index (BMI) was observed. According to sub-group analyses, BW, BMI, BF%, FM, WC, and HC were significantly increased in MAPLD patients, > 50 sample size, with lyophilized dried and CM fruit extract forms, < 12 weeks' intervention duration, and ≥ 30 g doses.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Evaluation of Nutraceutical Potential of Carduus marianus: Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effects in Paracetamol-Induced Hepatotoxicity and GC–MS Analysis
- First Published: 18 July 2025
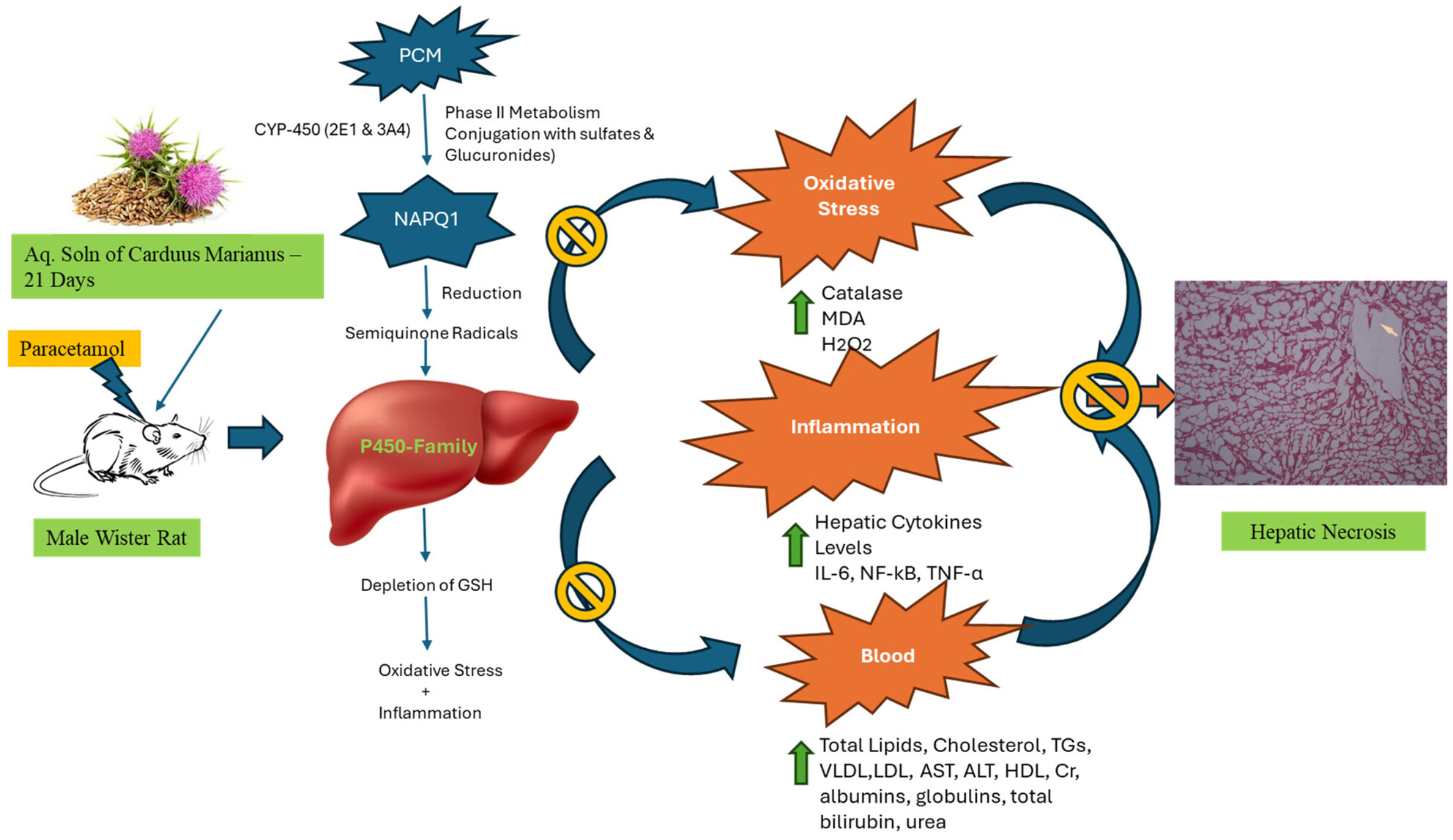
This study evaluates the hepatoprotective potential of Carduus marianus aqueous extract in male Wistar rats subjected to paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity. Paracetamol metabolism via hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes generates NAPQI, triggering oxidative stress, inflammation, and vascular disturbances, culminating in hepatic necrosis. Pre-treatment with C. marianus for 21 days mitigated these effects by inhibiting NAPQI-induced pathways, as evidenced by reduced oxidative and inflammatory markers and preserved hepatic histoarchitecture. These findings suggest C. marianus as a promising natural agent against drug-induced liver injury.
REVIEW
Insect Lipids as Novel Source for Future Applications: Chemical Composition and Industry Applications—A Comprehensive Review
- First Published: 20 July 2025
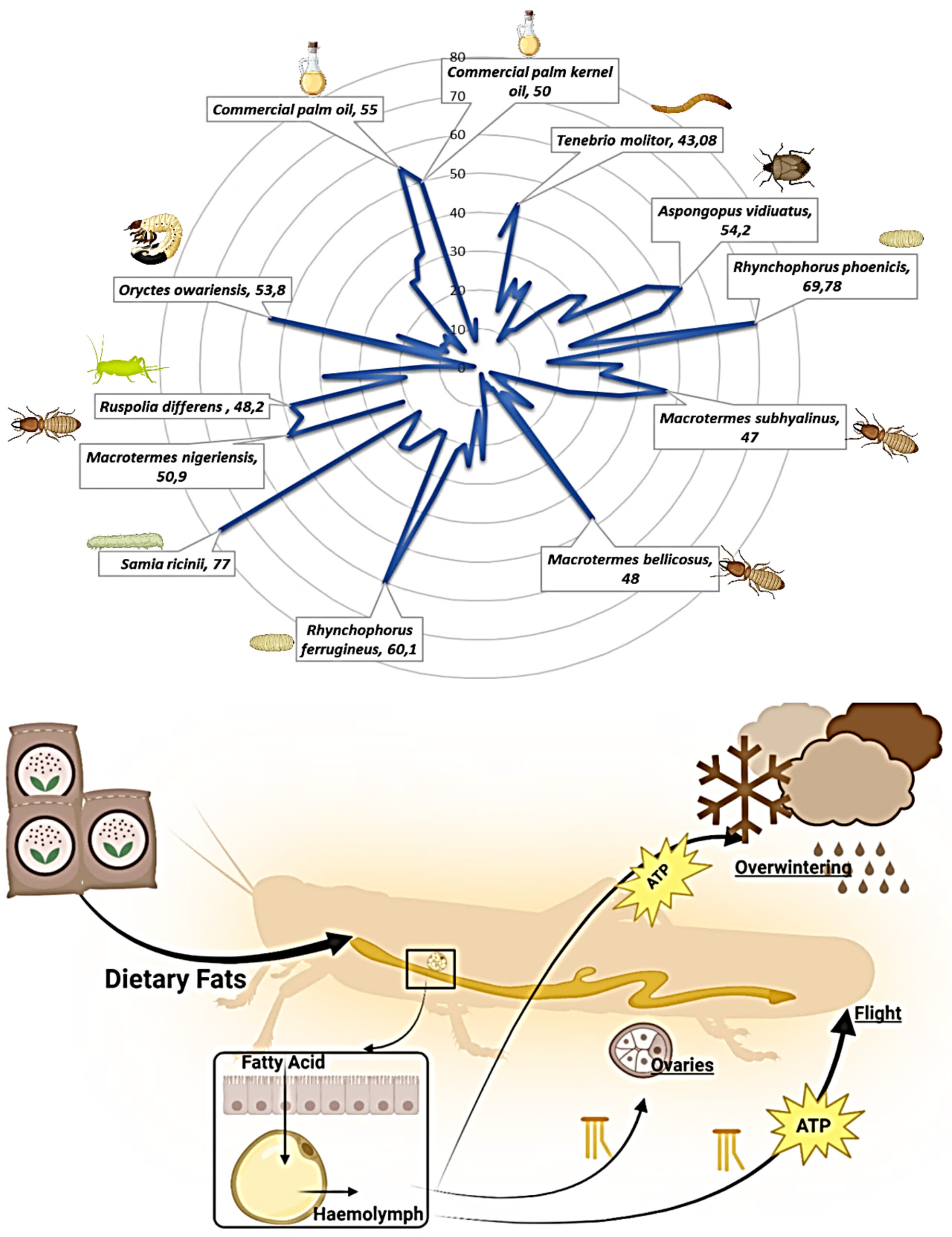
Fat body (FB) acts as a major metabolic center important for the regulation of a variety of physiological processes such as embryogenesis, reproduction, flight, overwintering, protection, and communication. Lipid amounts and fatty acid (FA) composition vary with species, stage of life, and their diet.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Effect of Marination on the Formation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Grilled Vegetables
- First Published: 07 July 2025

The effect of marination on the formation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in charcoal-grilled vegetables was studied. A substantial decrease in PAH4 formation was observed in marinated vegetables. These findings offer valuable insights for reducing PAH levels in grilled vegetables and preventing their formation.
Centaurea lycaonica Extracts Induce Apoptosis in HeLa Human Cervical Cancer Cells via Bax/Bcl-2 Modulation and Caspase Activation: An LC-HRMS-Based Study
- First Published: 15 July 2025

This study highlights the pharmacological mechanisms of dichloromethane (CHD) and methanol (CHM) extracts of Centaurea lycaonica Boiss. & Heldr. herba as the induction of apoptosis on HeLa cells. Apoptotic properties of CHD and CHM are through suppression of Bcl-2 and increase in Bax, caspase 9, and 3 activities on HeLa cells. The dichloromethane extract increases the cytotoxic activity of HeLa cells. The major compounds in active CHD extract were detected as diosmetin.
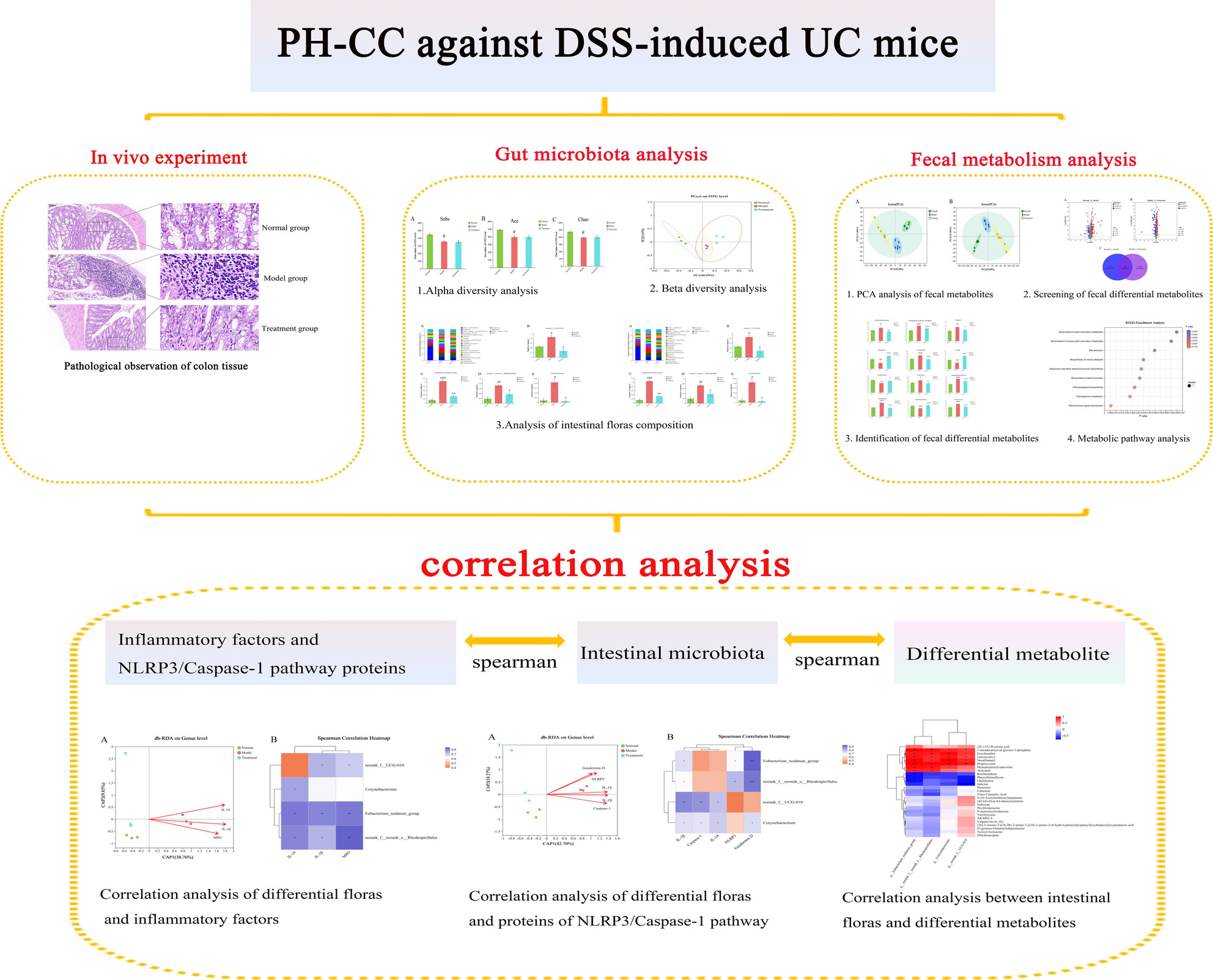
The Herbal Pair Polygonum hydropiper L-Coptis chinensis Franch Attenuate DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis by Modulating Metabolism and Intestinal Flora
- First Published: 08 July 2025
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of TaDES1 Gene Family Responded to Biotic and Abiotic Stress in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- First Published: 08 July 2025

The TaDES1 gene family in wheat consists of 18 genes across 13 chromosomes, categorized into four subfamilies. Evolutionary analysis shows segmental duplication as a key driver of family expansion, with strong purifying selection. TaDES1 members play critical roles in stress response, phytohormone regulation, and plant growth and development, supported by promoter cis-elements, gene ontology (GO) enrichment, transcriptomic data, RT-qPCR, and co-expression network studies. Simple sequence repeats (SSRs) and variation analysis further highlight their potential utility for wheat breeding.
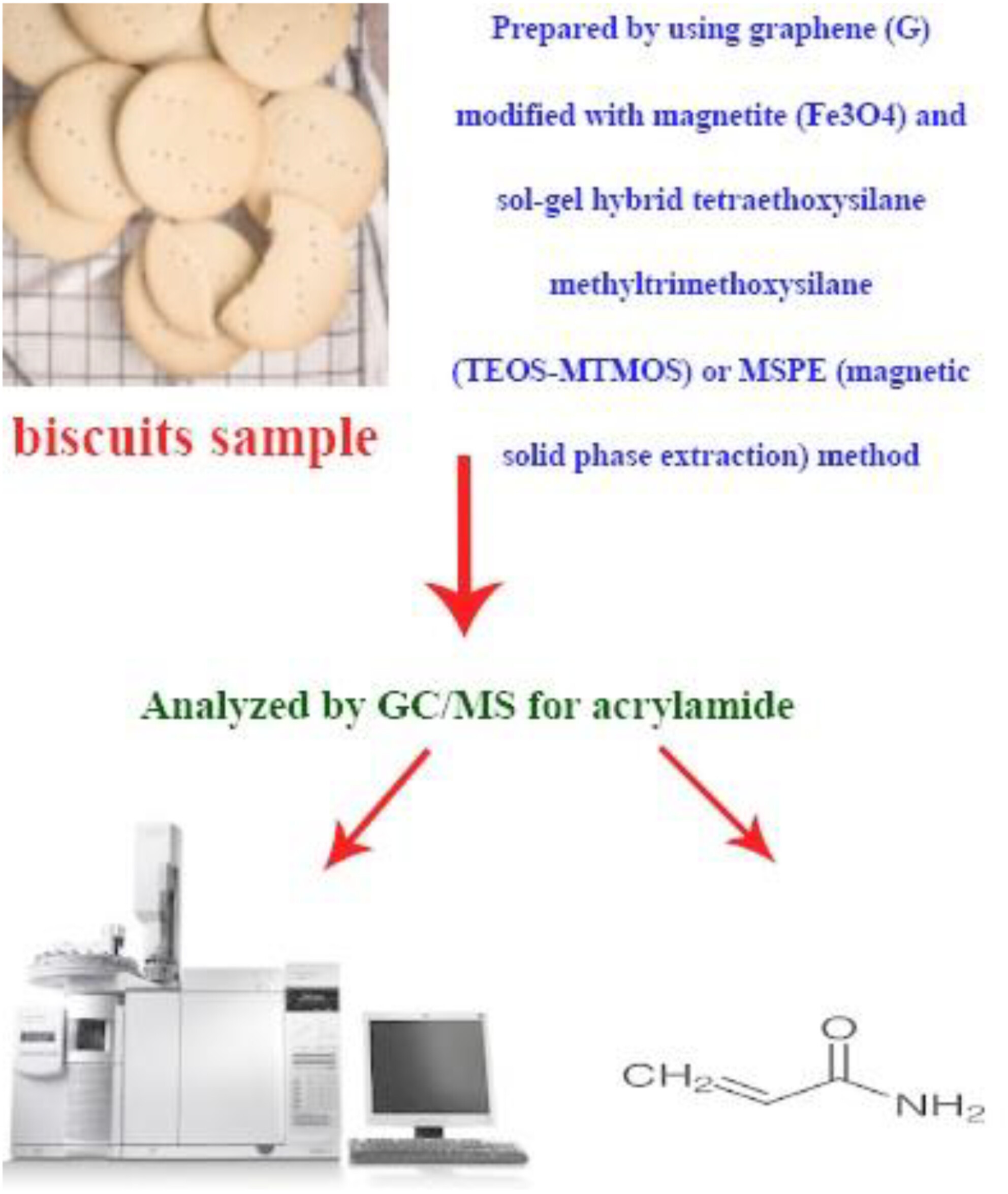
Acrylamide Occurrence in Iranian Biscuits and Its Potential Risk of Exposure
- First Published: 08 July 2025
Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis Using UPLC–MS/MS Reveals Metabolic Changes Associated With Lanmaoa asiatica Poisoning
- First Published: 08 July 2025

Lanmaoa asiatica possesses notable nutritional and pharmacological value, yet its potential to cause neuropsychiatric symptoms remains unclear. This study represents the first application of UPLC-MS/MS non-targeted metabolomics technology to systematically analyze the plasma metabolic profiles of patients with Lanmaoa asiatica poisoning, particularly involving mitochondrial dysfunction and morphine addiction pathways. Key metabolites such as 5-methoxytryptophan and adenosine derivatives may be identified as potential biomarkers. However, the small sample size and limitations of untargeted metabolomics may affect the generalizability and interpretation of the results.
Bibliometric Mapping of Quercetin Research: Analysis of the Most-Cited Articles (2000–2023)
- First Published: 10 July 2025

This study performs a bibliometric analysis of the 200 most-cited articles on quercetin, identifying key research hotspots, topics, leading institutions, and countries, while emphasizing the global and interdisciplinary nature of quercetin research. It also reveals current research trends and challenges in the field, providing a thorough overview of its complexities. Finally, the analysis offers insights into research trends and gaps, guiding the direction of future studies in this crucial area.
Argon Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma-Induced Effects on Glucose
- First Published: 22 July 2025
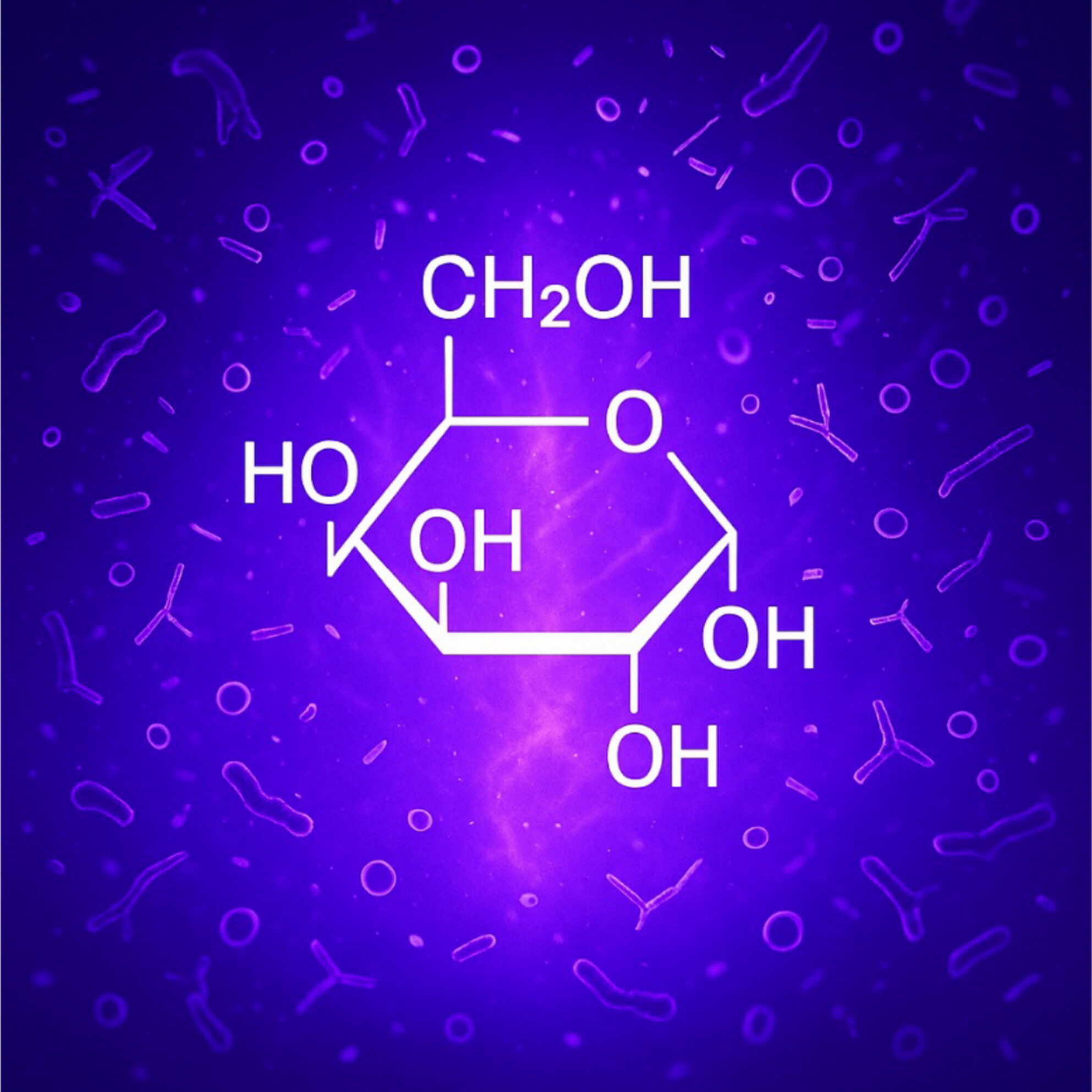
This study describes the effects of cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) on glucose. Samples were treated for up to 16 min using an argon-driven plasma device, revealing chemical modifications such as oxidation processes and ring openings on glucose. The results show that reactive plasma species led to the formation of carbonyl groups and possibly to carbon-nitrogen and carbon–carbon double bonds.
Evaluation of the Clinical Outcomes Associated With the Use of Fatty Acids and Vitamin D in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- First Published: 21 July 2025

Non-pharmacological therapies, including dietary interventions, fatty acids, and vitamin supplementation, as well as physical modifications, are gaining recognition as complementary approaches in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D play a significant role in modulating inflammatory pathways and reducing the production of inflammatory mediators, thereby exerting a positive influence on the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. The meta-analysis integrated findings from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and examined the impact of fatty acid and vitamin D supplementation on clinical outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This meta-analysis shows that fatty acids and vitamin D can reduce pain, improve quality of life, and reduce arthritic symptoms. Fatty acids enhance inflammation outcomes such joint soreness and edema and increase patient function. Outcome measures showed moderate vitamin D supplementation effectiveness.
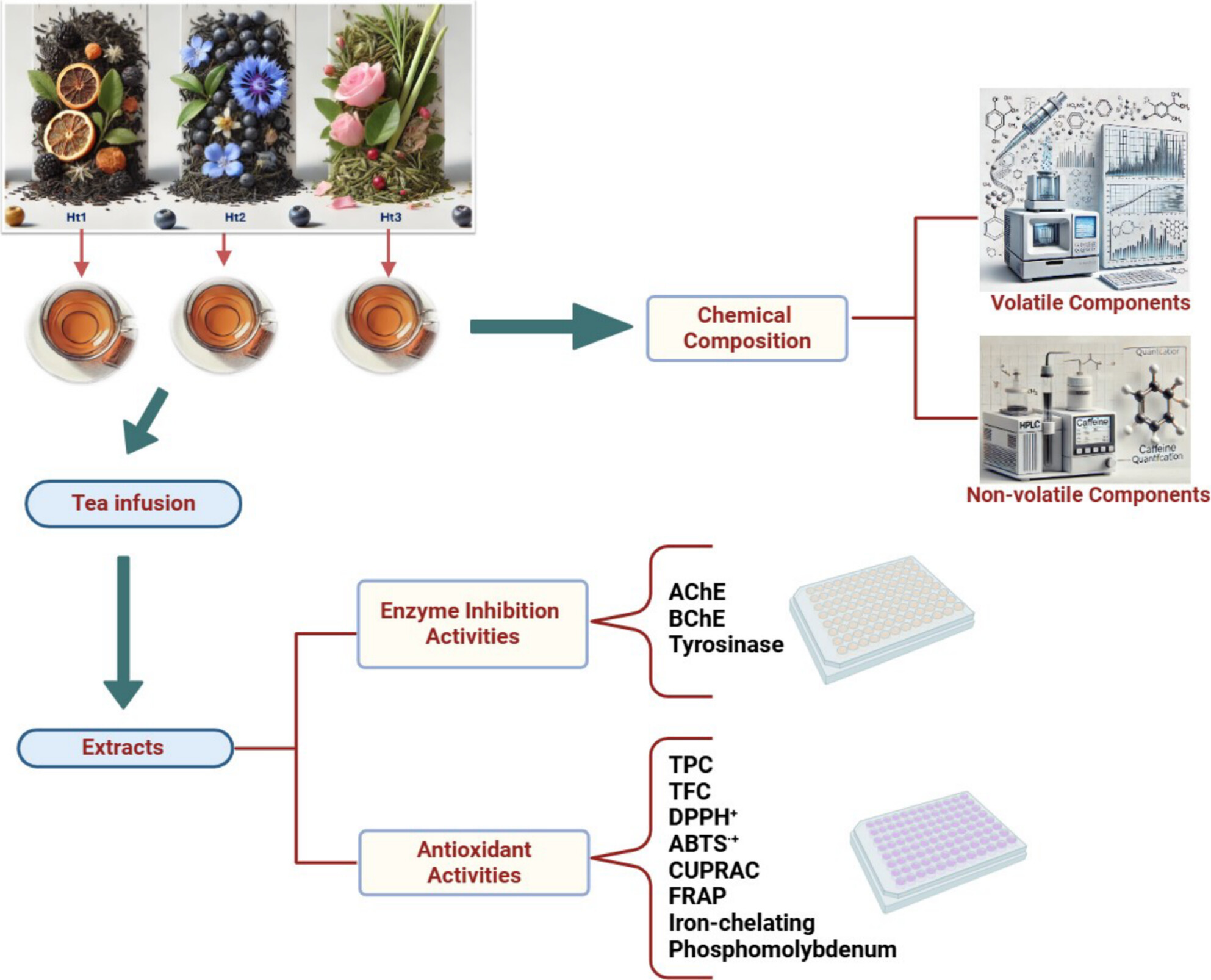
A Multi-Analytical Exploration of Flavored Black Teas: Profiling Volatile Compounds, Caffeine Content, and Biological Effects
- First Published: 09 July 2025
Fermentation Kinetics and Changes in Levels of Antinutrients in Pearl Millet and Pearl Millet-Maize Composite Dough Recipes Used to Prepare Injera
- First Published: 09 July 2025
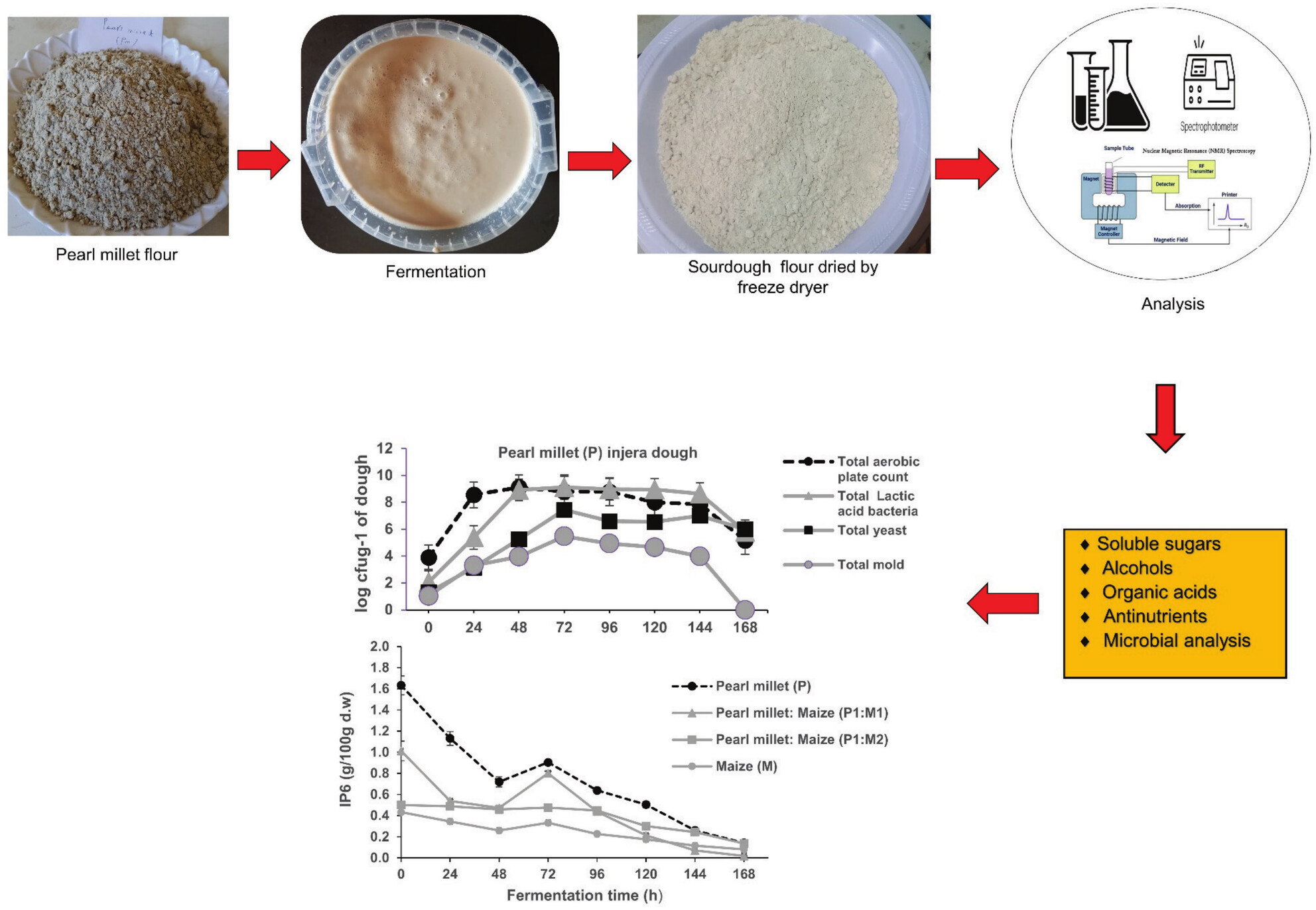
Fermentation time influenced the pH, metabolite profiles, and microbial counts of pearl millet-based injera sourdough. This process facilitates the degradation of antinutrients, specifically phytate and α-galactosides (raffinose). Notably, phytate degradation was higher in pearl millet sourdough compared to other recipes, which has direct implications for the bioavailability of minerals, protein, and starch. Additionally, fermentation changes the monosaccharide, disaccharide, and organic acid profiles during fermentation.
Vitamin D Knowledge, Attitudes, Practices and Serum Concentration Among Pregnant Women Attending a Malaysian Tertiary Hospital
- First Published: 09 July 2025

This hospital-based cross-sectional study assessed knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP), and serum vitamin D concentration among pregnant women in Klang Valley, Malaysia. The majority of the participants demonstrated good knowledge, negative attitudes, inconsistent practices, and a high prevalence of vitamin D deficiency. Findings highlight the need for policies and culturally acceptable strategies to address vitamin D deficiency in pregnancy.
Synbiotic Administration of d-Tagatose and Lacticaseibacillus casei ATCC 393 Improves Hyperlipidemia in BALB/c Mice by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Parameters
- First Published: 10 July 2025

In this study, hyperlipidemia was experimentally induced in BALB/C mice through a high-fat, high-cholesterol diet, followed by administration of a probiotic (Lacticaseibacillus casei ATCC 393), a prebiotic (d-tagatose), and their synbiotic combination. The synbiotic treatment significantly reduced serum glucose, total cholesterol, triglyceride, and HDL levels without impairing liver function, while also alleviating hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammation. Moreover, it selectively modulated the gut microbiota by enriching beneficial genera such as Coprococcus, Parabacteroides, and Bacteroides, indicating its potential as a biotherapeutic agent for hyperlipidemia.
Anti-Inflammatory Activity and Mechanism of Stearic Acid Extract From Purslane
- First Published: 10 July 2025
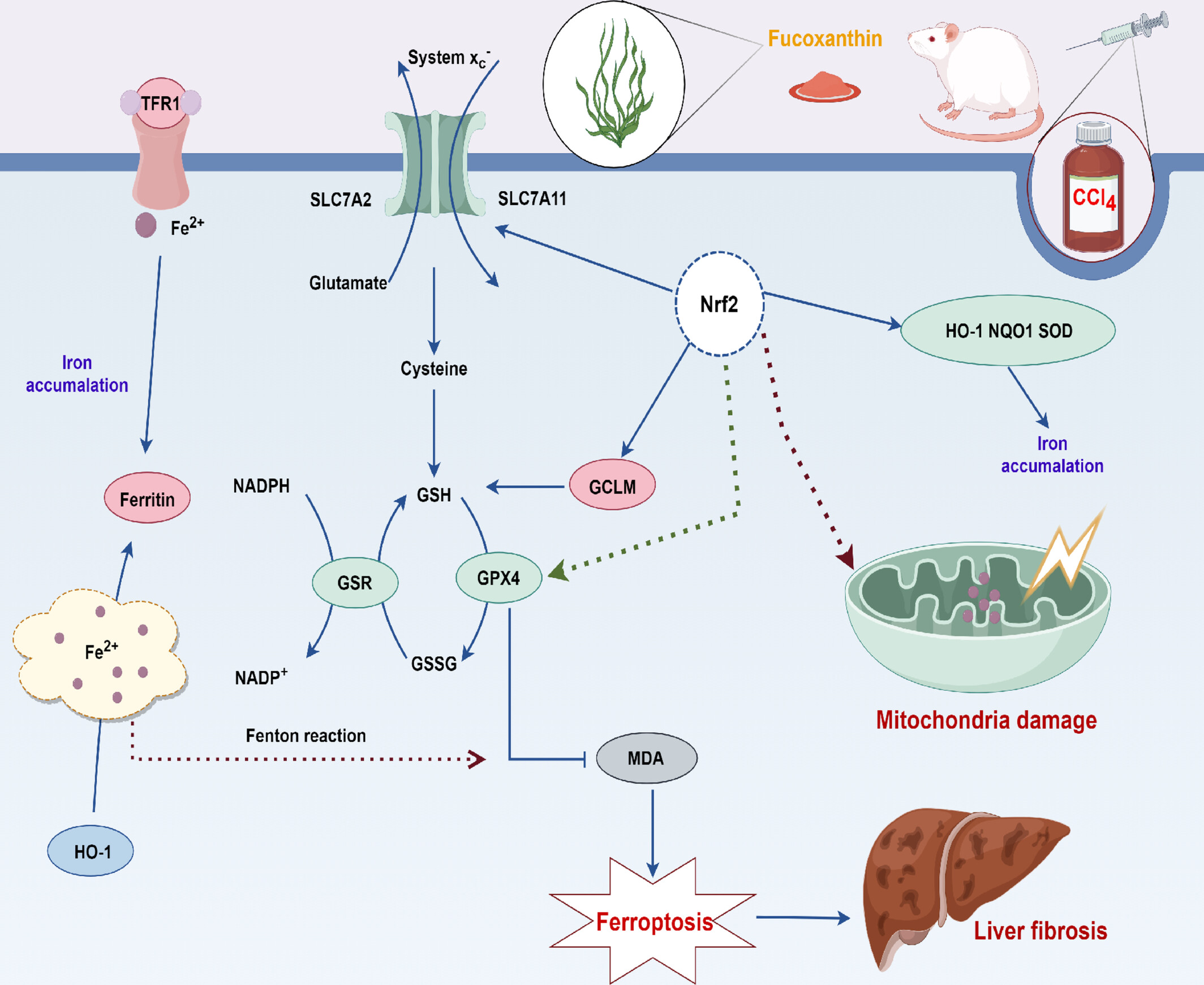
Fucoxanthin Ameliorates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Mice via Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4-Mediated Ferroptosis Pathway
- First Published: 10 July 2025
REVIEW
The Beneficial Effects of Resveratrol on Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Modulation of Apoptosis, Autophagy, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress
- First Published: 24 July 2025

Resveratrol protects against NAFLD and HCC by modulating apoptosis, autophagy, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Resveratrol activates key signaling pathways like PI3K/AKT/mTOR and SIRT1 to promote autophagy and reduce pro-apoptotic and inflammatory responses. In advanced HCC, resveratrol's anti-apoptotic effects may support tumor growth, emphasizing the need to tailor its use to disease stage and context.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
ALA Alleviates Liver Damage in Septic Mice Through PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway
- First Published: 10 July 2025
A Multiplex Real-Time PCR for Qualitative Detection of Mutton, Pork, Chicken, and Duck in Processed Meat Products
- First Published: 14 July 2025
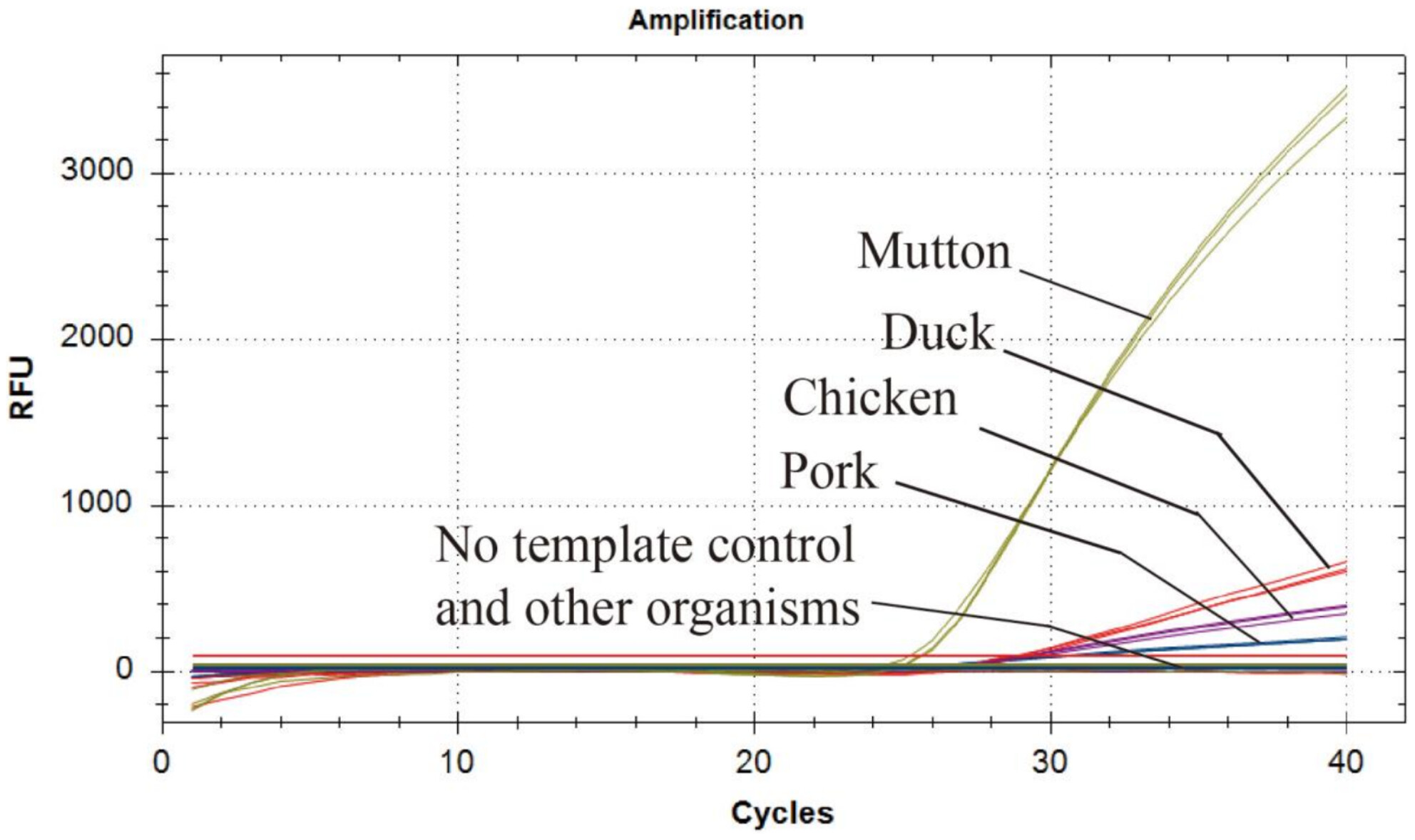
This study aimed to develop a multiplex real-time PCR method for the qualitative detection of pork, chicken, and duck adulteration in mutton products. The method exhibited high specificity, accuracy, and sensitivity through method validation. To evaluate its applicability, we analyzed 35 commercial processed meat products, and the results confirmed the assay's robustness and reliability for meat authenticity testing.
Fabrication and Characterization of Olive Leaf Polyphenols Loaded Sweet Almond Gum/Gelatin Electrospun Nanofiber
- First Published: 14 July 2025
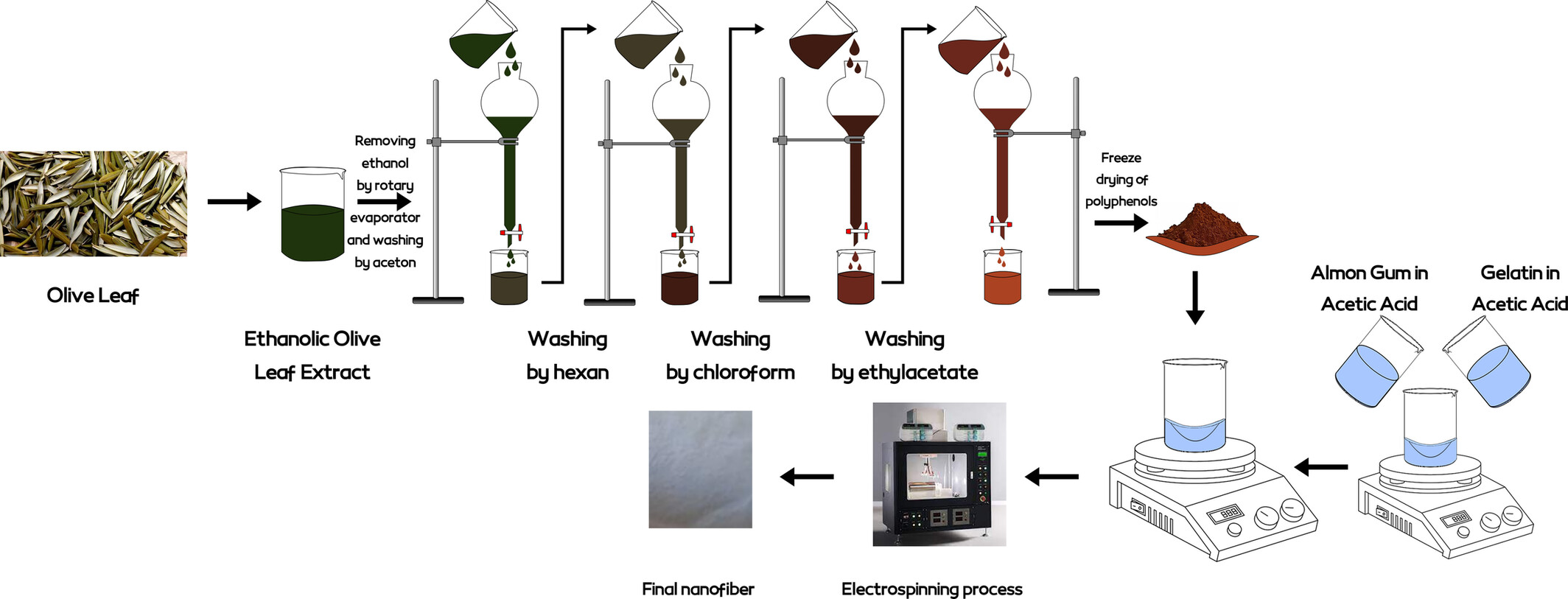
This research was done with the aim of encapsulating olive leaf polyphenol in electrospun nano fibers of almond gum/gelatin. For this purpose, after extraction, polyphenol was loaded in different concentrations (0%, 5%, 10%, and 20%) in almond gum/gelatin electrospun nanofibers. This research showed that electrospun nanofibers of sweet almond gum and gelatin loaded with olive leaf polyphenol can be used in food and medicine.
Association Between the Dietary Index for Gut Microbiota and Frailty: Mediating Role of Body Mass Index
- First Published: 14 July 2025
Genetic Evidence on the Role of Blood Phytosterols in Frailty: A Mendelian Randomization Study
- First Published: 14 July 2025

This Mendelian randomization study found genetically elevated blood sitosterol levels modestly increased Frailty Index risk (OR = 1.035, p = 0.008), with non-HDL-C and ApoB mediating ~50% of this effect. No association was observed with Fried Frailty Score, suggesting specificity to cardiometabolic deficits captured by the Frailty Index. Results imply phytosterols may influence frailty through lipid pathways, warranting caution in their therapeutic use for aging populations.
Valorization of Avocado Leaf as a By-Product of the Avocado Fruit: Nutritional, Textural, and Sensory Properties of Gluten-Free Erişte (Turkish Noodles)
- First Published: 14 July 2025
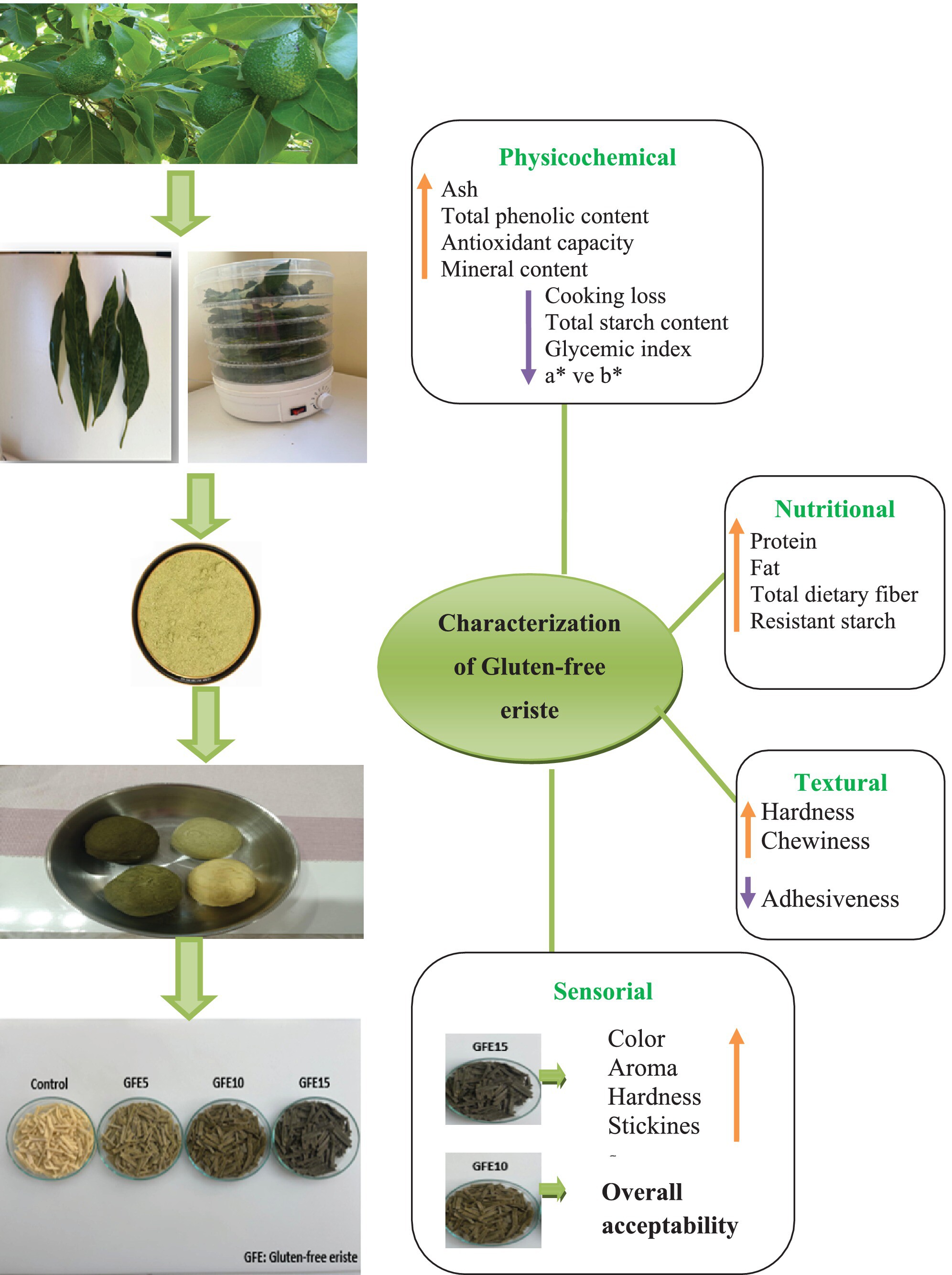
This study explores the incorporation of ALP, a food waste by-product, into gluten-free extrudate (GFE) formulations and evaluates its effects on nutritional, textural, and sensory properties. ALP enrichment significantly enhanced protein, fiber, phenolic content, and antioxidant activity while reducing glycemic index. The GFE10 sample showed the highest overall sensory acceptance, highlighting ALP's potential as a functional ingredient in gluten-free food development.
Improving Quality Management of ‘Ready-To-Eat’ Pomegranate Arils Using Aloe Ferox-Based Edible Coating Enriched With Encapsulated Raspberry Pomace
- First Published: 14 July 2025

This study evaluated an Aloe ferox-based edible coating enriched with encapsulated raspberry pomace powder (ERPP) to preserve the quality and extend the shelf life of ready-to-eat pomegranate arils during cold storage. The AF + 0.3% ERPP treatment was most effective in reducing weight loss and respiration rate while maintaining texture, TSS, and TPC, demonstrating its potential for commercial application as a natural preservation solution.
Pomological and Biochemical Properties of Blackberry (Rubus fruticocus) Genotypes
- First Published: 14 July 2025

In this study, blackberry genotypes naturally grown in Tunceli were examined, and those with superior characteristics were identified. The results showed significant differences among the genotypes in terms of fruit weight, length, width, color values, total soluble solids (TSS), titratable acidity, vitamin C, antioxidant activity, organic acids, and individual phenolic compounds. While the G9 genotype had the largest fruits, the G6 genotype stood out with its high phenolic, flavonoid, and anthocyanin content. The G2 genotype was distinguished by its high color values and acidity content. The levels of phenolic compounds in different blackberry genotypes show great variation; for example, G1, G2, and G6 genotypes have high levels of phenolic compounds, while G4 and G5 genotypes have low levels. In particular, G2 and G1 are rich in hydroxybenzoic acid, caffeic acid, and ferulic acid, while some genotypes such as G4 and G5 have low levels of phenolic compounds. The G7 genotype has the highest oxalic acid level, while G8 has the lowest level. In terms of other acids, G1 is the richest genotype in malic acid, G6 has the highest value in ascorbic acid, and citric acid is at the lowest level in G6. As a result of the study, the G9 genotype had the largest fruits, while the G6 genotype stood out with its high phenolic, flavonoid, and anthocyanin content; also, G2 attracted attention with its high color values and acidity content, and G1 with its richness in malic acid.
Bioactivity of Encapsulated Lemon Peel Phenolics as Affected by Maltodextrin and Foam Mat Drying
- First Published: 14 July 2025

Lemon peel phenolic extract with antihypertensive and antidiabetic bioactivity was encapsulated with WPC and maltodextrin by foam mat drying. Foam mat drying can be preferred as a practical method with low equipment and energy cost and short processing time. The wall materials also contributed to the measured bioactivities besides the lemon peel extract.
Optimization of Ethanol Extraction Conditions From Sun-Dried Apricot and Prediction of Antioxidant, Phenolic, and Flavonoid Contents and Their Effects on HCT116 Cells Using Artificial Neural Networks
- First Published: 17 July 2025

This study optimized ethanol extraction conditions for dried apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) using response surface methodology (RSM), achieving optimal yields at 60°C, 34 W, 46 min, and a 4 g/mL solid–liquid ratio. The extract showed high phenolic (4.20 mg GAE/g) and flavonoid (7.09 mg QE/g) content, strong antioxidant capacity, and dose-dependent cytotoxicity against HCT116 colon cancer cells.
Enhanced Cassava Flour Quality to Improve the Cassava Bread by Attibutes Yeast Fermentation
- First Published: 14 July 2025

- Yeast fermentation enhances cassava flour's nutrition, increasing protein from 0.89 ± 0.08 to 3.86 ± 0.12 g/100 g, reducing hydrocyanic acid from 32.64 ± 0.67 to 7.40 ± 0.22 mg/kg, and boosting flavor compounds.
- It modifies physicochemical properties: smaller particle size, lower paste viscosity, more ordered crystal structure, and improved processing stability.
- Bread with 20% fermented cassava flour has better texture, higher sensory scores, and is close to wheat bread.
Chrysoeriol Chemosensitized Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) Cell Lines to Trigger TRAIL Induced Apoptosis In Vitro by Up-Regulating Pro-Apoptotic and Down-Regulating Anti-Apoptotic Genetic Factors
- First Published: 16 July 2025
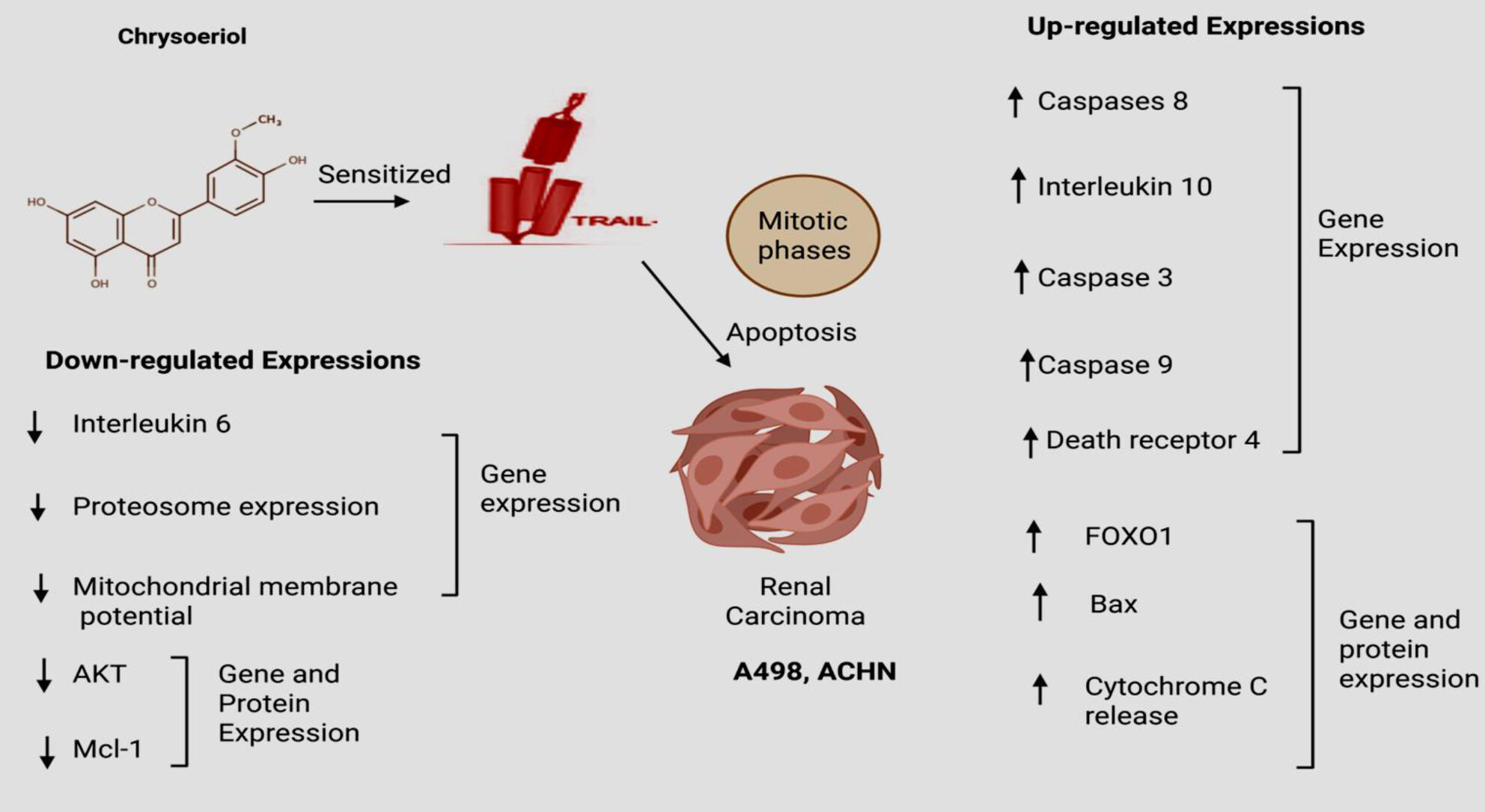
Recently, a synergistic approach has emerged in clinical settings to sensitize cancer cells towards TRAIL treatment by combining it with some natural antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds for providing chemo-sensitizing effects. Hence, this study has used the chemo-sensitizing effect of chrysoeriol for the very first time to sensitize renal carcinoma cell lines for treatment with TRAIL by a synergistic treatment approach, in vitro.
REVIEW
Effects of Curcuminoids Plus Piperine Co-Supplementation on Liver Enzymes and Inflammation in Adults: A GRADE-Assessed Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- First Published: 14 July 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Enhanced Leaf Disease Segmentation Using U-Net Architecture for Precision Agriculture: A Deep Learning Approach
- First Published: 14 July 2025
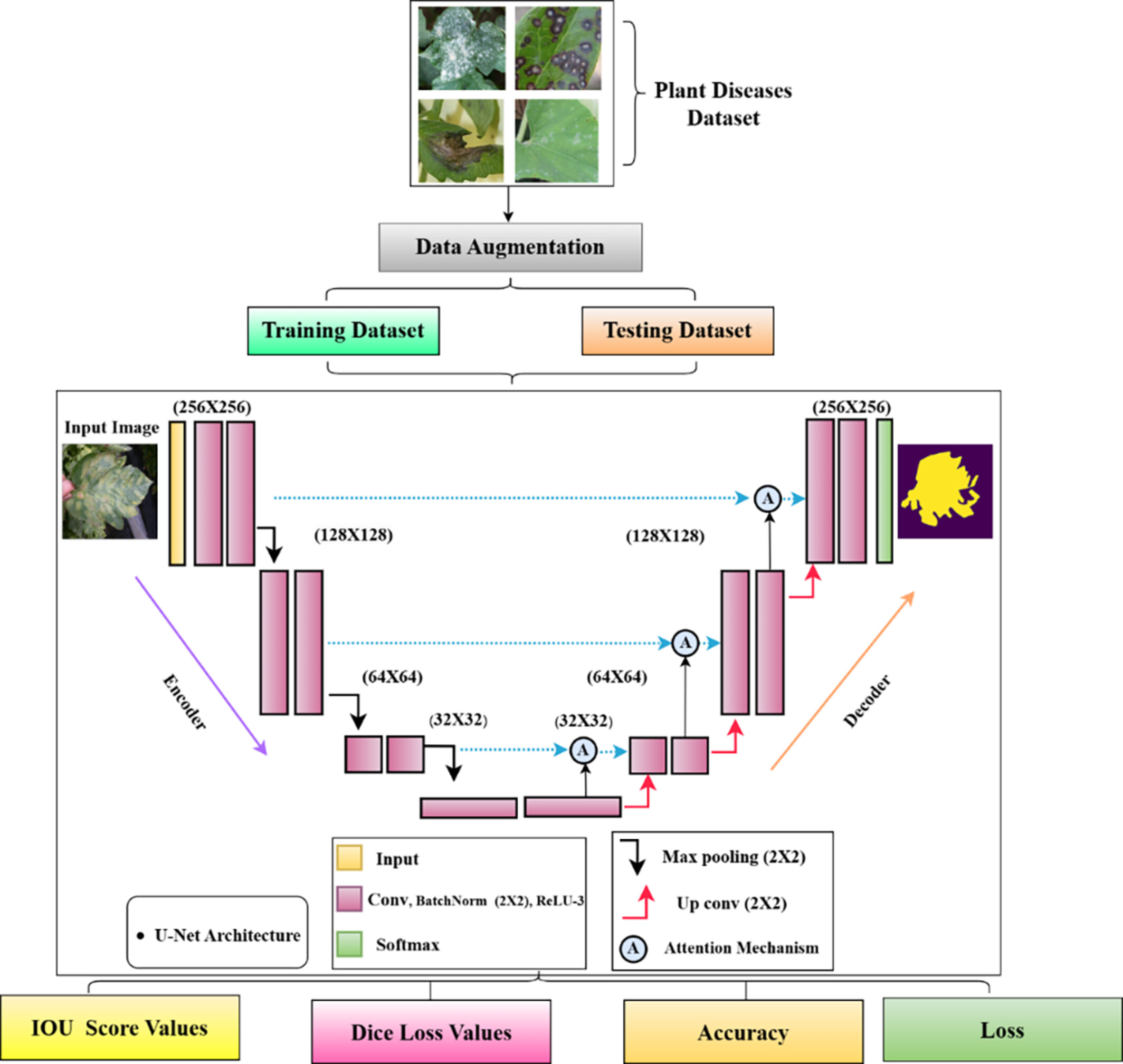
This study proposes a deep learning-based approach for leaf disease identification using the U-Net architecture for precise segmentation. By training on a dataset of 7056 annotated leaf images, the model effectively distinguishes between healthy and diseased regions, achieving 99.70% training accuracy and 98.99% validation accuracy in 40 epochs. The results demonstrate the model's robustness and potential for real-world precision agriculture applications.
ChatGPT-4o for Weight Management: Comparison of Different Diet Models
- First Published: 16 July 2025

Our results revealed the effects of diet plans created by AI in weight management. As technology improves, further research into the application of AI in nutritional therapy is warranted. The graphical abstract is created by the authors via BioRender (https://www.biorender.com/).
Utilization of Fruit Juice Processing Wastes as Prebiotic Ingredients in Probiotic Yogurt: Effects on Microbial Short Chain Fatty Acid Production
- First Published: 14 July 2025

This study evaluated fruit juice processing wastes (apricot, peach, apple, and grape pomace) as prebiotic sources in probiotic yogurt. The addition of these pomaces led to significant increases (p < 0.05) in short-chain fatty acids (acetate, butyrate, propionate), benefiting gut microbiota. Monosaccharide analysis identified glucose as the primary sugar. Microbiological analysis showed stable probiotic bacteria counts, with Lactobacillus acidophilus utilizing peach and apricot pomace effectively. Sensory evaluation favored 1% apple, apricot, and peach pomace. The findings support fruit pomace as a functional food ingredient.
Nutritional Composition and Acceptability of Egg Powder-Fortified Tom Brown Among School-Aged Children in the Wa Municipality
- First Published: 14 July 2025
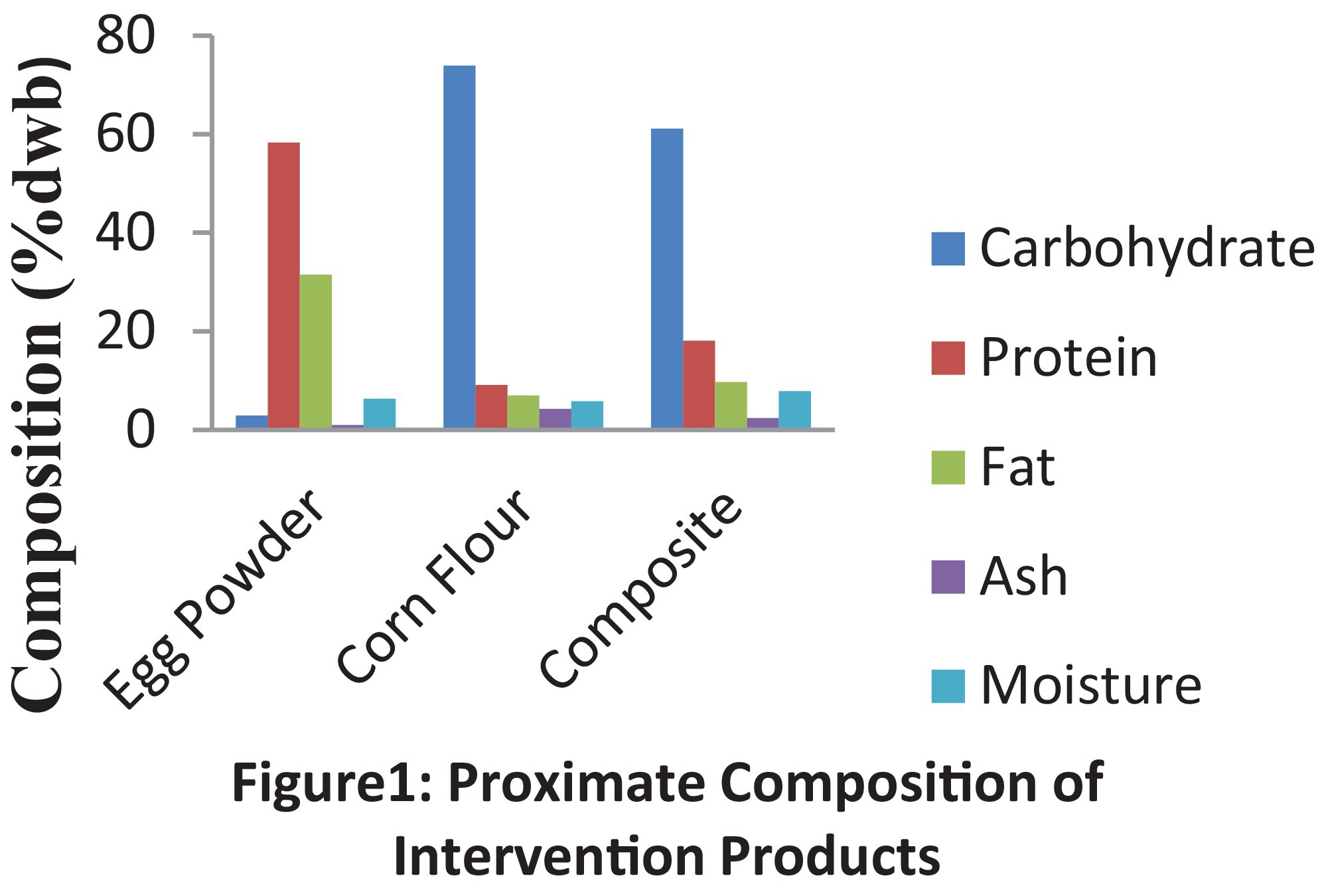
The study evaluated nutritional and functional properties of corn flour-egg powder composite to create a nutrient-dense meal for children. The composite had enhanced protein (18.09%) and carbohydrates (61.99%), with improved iron, zinc, magnesium, vitamin A, and folate levels. Functional properties showed good viscosity (168 RVU) and stability (12-month shelf life). Sensory evaluation favored the 100:20 egg powder-to-corn flour ratio for taste and acceptability. These findings highlight its potential as a fortified intervention food to improve children's nutrition and hemoglobin levels.
Impact of Fatty Acid Carbon Chain Length and Protein Composition on Physicochemical and Digestive Properties of MFGM Contained Emulsions
- First Published: 07 July 2025

Emulsions prepared by OPO (long-chain fatty acids) exhibited the largest average particle size and greater stability compared to those with medium-chain fat (coconut oil) and ultra-long-chain fat (DHA algae oil). When whey protein and casein were added in a 6:4 ratio, the effect of fatty acid carbon chain length on the average particle and the emulsification characteristics of the lipid droplet interface were significantly reduced. Emulsions composed of fat globules with a core of short-chain fatty acids or low surface protein content had higher lipolysis rates.
Four Dairy Products Mitigates Sarcopenia in Mice by Modulating Muscle Inflammation, Autophagy, and Protein Degradation
- First Published: 14 July 2025

Dairy consumption, particularly goat fortified vitamin D and calcium low-fat milk, could improve muscle mass and reduce fat weight in sarcopenic mice. Dairy consumption has the potential to improve muscle mass and prevent sarcopenia by modulating autophagy, reducing inflammation, and regulating gut microbiota. The interaction between dairy intake, gut microbiota, and circulating metabolites indicates a potential mechanism for the beneficial effects of dairy in preventing sarcopenia.
Proteostasis Disruption by Proteasome Inhibitor MG132 and Propolin G Induces ER Stress- and Autophagy-Mediated Apoptosis in Breast Cancer
- First Published: 13 July 2025

- Combination treatment with MG132 and propolin G, a c-prenylflavanone from Taiwanese propolis, synergistically suppressed proteasome activity, leading to proteotoxic stress-mediated apoptosis in breast cancer.
- This combination treatment triggers apoptosis by activating the PERK-mediated unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway.
- Autophagy-mediated cell death is a key mechanism contributing to apoptosis induction by this combination treatment.
METHOD
Preparation and Characterization of Superfine Longan Powder Rich in Polysaccharides: Optimization of Processing Conditions and Functional Properties
- First Published: 13 July 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Characterization of Microencapsulated Thymus schimperi Essential Oil Prepared by Spray and Freeze-Drying Using Gum Arabic as Carrier Material
- First Published: 13 July 2025

This study investigated gum Arabic's impact as a coating on Thymus schimperi essential oil microcapsules using spray and freeze-drying. The research examined various physicochemical properties, including water content, density, and solubility. Spray drying yielded higher encapsulation efficiency (71.05%) than freeze drying (68.89%) and better solubility. Spray-dried microcapsules were also more spherical, demonstrating significant differences in properties compared to freeze-dried ones.
REVIEW
A Comprehensive Review on the Molecular Mechanism of Lycopene in Cancer Therapy
- First Published: 13 July 2025

This review highlights the molecular mechanism by which lycopene imparts its anticancerous role, focusing on clinical and animal trials to validate its effectiveness. The antioxidant profile of lycopene promotes anticancerous properties that reduce cancer prevalence by activating cell signaling pathways and gene expression (involved in cancer cell proliferation). Lycopene's anti-inflammatory properties suppresses the tumor growth and development-promoting pathways, such as the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. The anticancer property of lycopene is also evidenced by its inhibitory potential of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway that is involved in cancer cell modulation and propagation.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Mechanism of Anti-Cancer in Breast Cancer Cells With HER2 Overexpression by Dietary Supplement of Five Edible Plants
- First Published: 14 July 2025

Mylife/Mylife100, a Thai a dietary supplement, composed of five types of edible plants (Sesamum indicum L., Psidium guajava L., Centella asiatica (L.) Urb., Glycine max (L.) Merr., and Garcinia mangostana L.) was evaluated for their anti-cancer effect on drug resistant breast cancer cells with HER2 overexpression (SK-BR-3 cell line). The supplement showed cytotoxic activity against SK-BR-3 cells growth in a dose-dependent manner. These findings indicated that Mylife/Mylife100 supplement suppresses cell growth and induces apoptosis via activation of the intrinsic pathway and regulation of the PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways against SK-BR-3 cells.
REVIEW
Nutritional Influences on Brown and Beige Adipocyte: Unraveling the Molecular Mechanisms and Metabolic Implications
- First Published: 15 July 2025
Mushroom Bioactive Molecules as Anticancerous Agents: An Overview
- First Published: 14 July 2025
This review discusses the molecular mechanisms through which these compounds inhibit cancer progression, including the induction of reactive oxygen species, inhibition of mitotic kinase and angiogenesis, and suppression of topoisomerase activity. By providing the latest insights on these anti-tumor agents and their pharmacological actions, our review aims to contribute valuable information to the field of cancer research and support the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Nutritional Composition, Mineral Profile, Bioactive Phytochemicals, and Antioxidant Activities of Selected Edible Weeds: A Comprehensive Analysis
- First Published: 15 July 2025
Edible weeds from Bangladesh have been evaluated and found to contain significant amounts of nutrients, bioactive phytochemicals, and antioxidants, supporting their potential as valuable alternative sources of functional foods. However, some species exhibit elevated levels of trace metals, posing health risks. Overall, these weeds offer valuable nutraceutical prospects but require safety assessments to ensure contaminated element levels are within permissible limits for safe consumption.
REVIEW
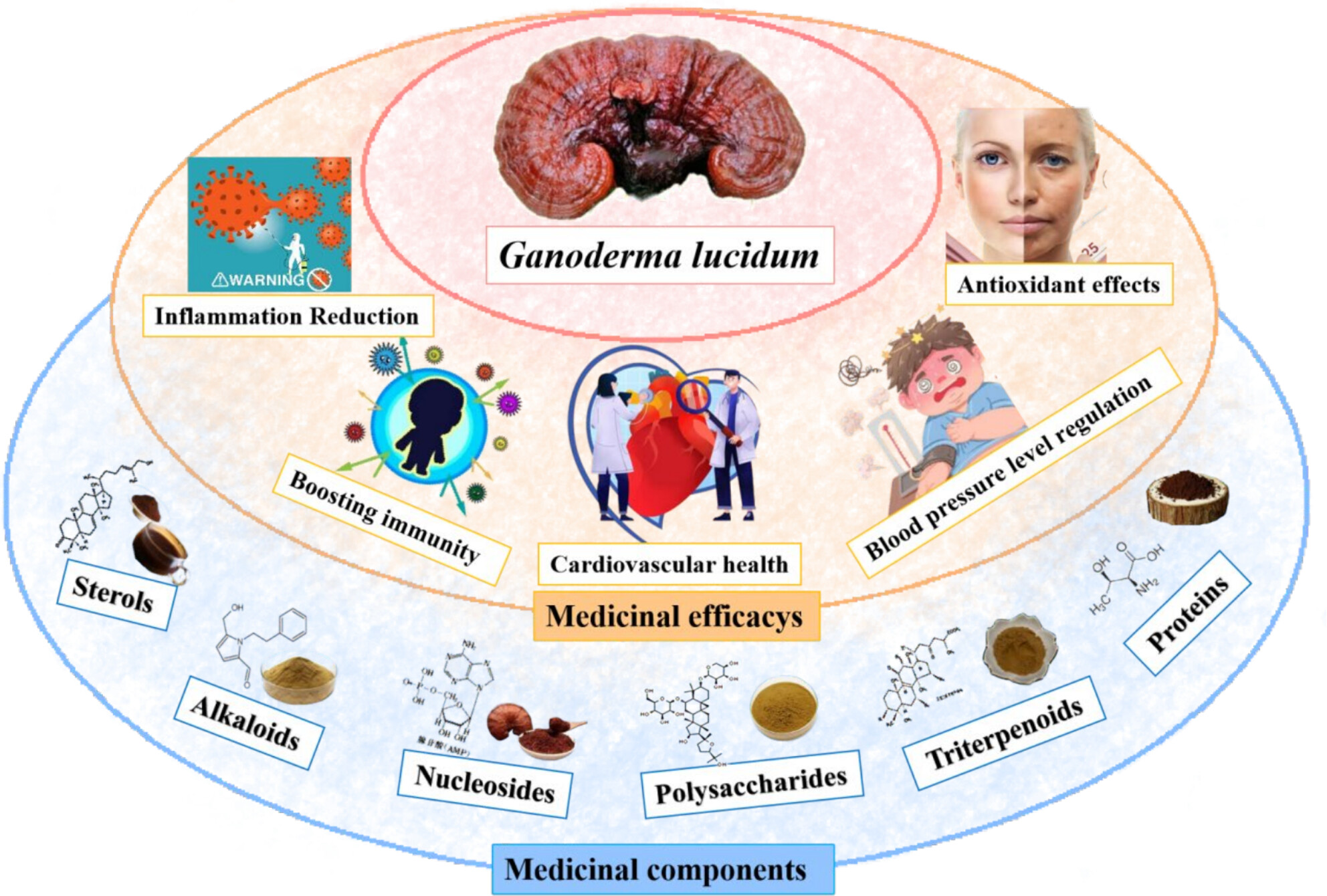
A Review of Bioactive Components and Pharmacological Effects of Ganoderma lucidum
- First Published: 13 July 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Luteolin Protects Against Acrylamide-Induced Cellular Toxicity in Mouse Leydig Cells
- First Published: 14 July 2025
Proteomic and Amino Acid Dynamics During Jujube Blackening: Structural Transformations and Maillard Reaction Linkages
- First Published: 25 July 2025
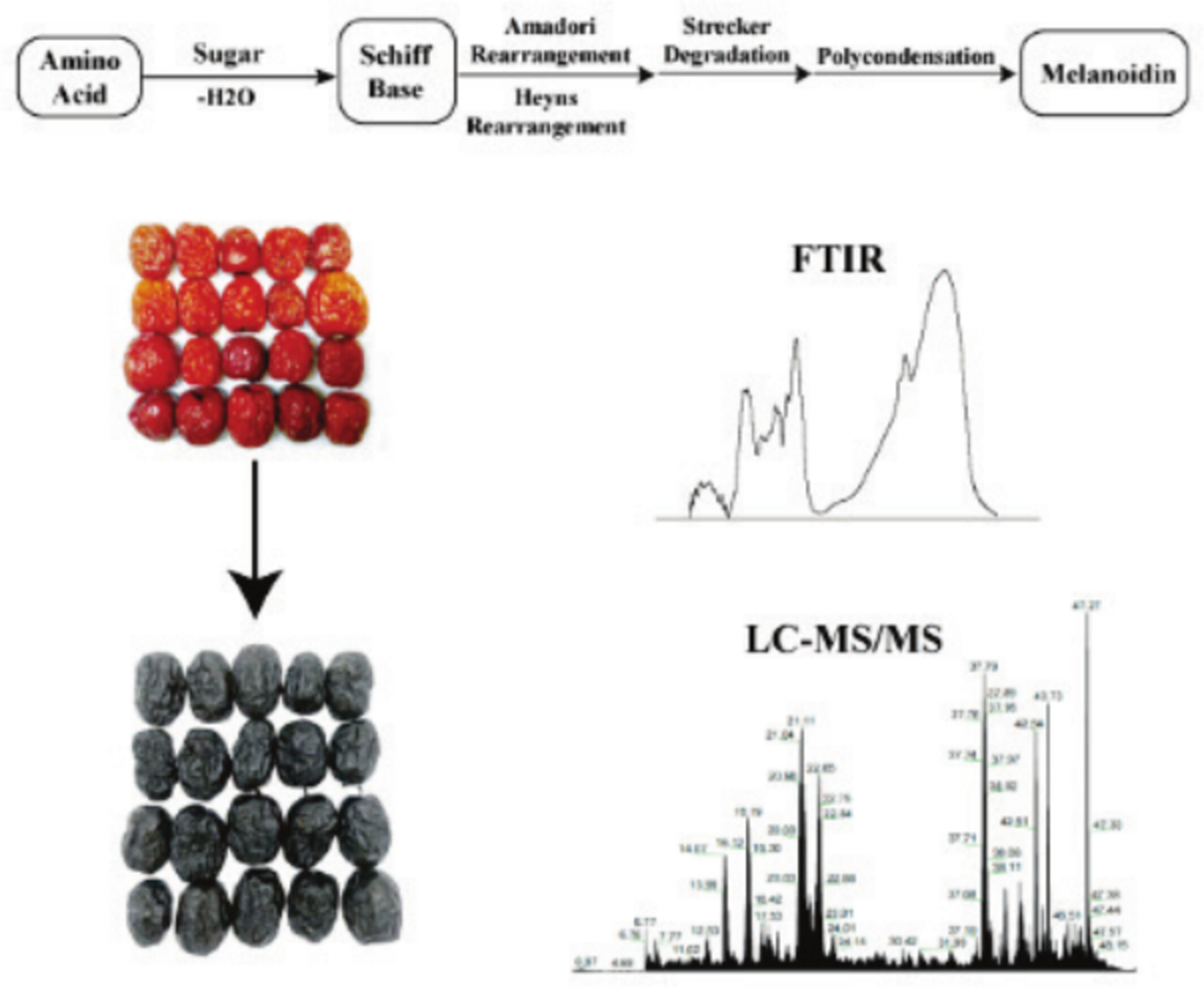
This study characterized the protein structure and amino acid content changes in jujube during the blackening process, which is likely linked to the Maillard reaction. The reaction caused protein covalent bond disruption, aggregation, and significant structural changes after 6 h, with blackened jujube showing higher levels of pyruvate dehydrogenase and hydrophobic amino acids. Essential amino acids, particularly valine (68.69%), and non-essential amino acids, especially cysteine (13.38%), were found to be the most abundant after the blackening, providing insights into the Maillard reaction's impact on jujube proteins and amino acids.
Research on the Effects of Extruded Okara on Improving Gluten Protein Stability and Dough Processing Properties
- First Published: 15 July 2025
Exploring the Chemical Profile, Antioxidants, and Anti-Diabetic Properties of Coffee Beans From Selected East African Countries: A Comparative In Vitro and Computational Study
- First Published: 14 July 2025

Burundian coffee showed the strongest antioxidant activity (DPPH/FRAP), Ugandan coffee excelled in nitric oxide scavenging, while Tanzanian coffee led in α-glucosidase/α-amylase inhibition. LC–MS revealed that phenolic acids dominated in Burundian/Tanzanian beans, whereas Ugandan coffee had the highest caffeine content. Computational studies confirmed the relationship between phytochemical-enzyme binding and their region-specific antioxidant/antidiabetic effects, supporting East African coffees as functional foods for metabolic disorders.
Nutrient-Synbiotic Complex Ameliorates LPS-Induced Depressive-Like Behavior via Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Tryptophan Metabolism in Mice
- First Published: 15 July 2025
REVIEW
Vitamin A and Its Related Diseases
- First Published: 15 July 2025
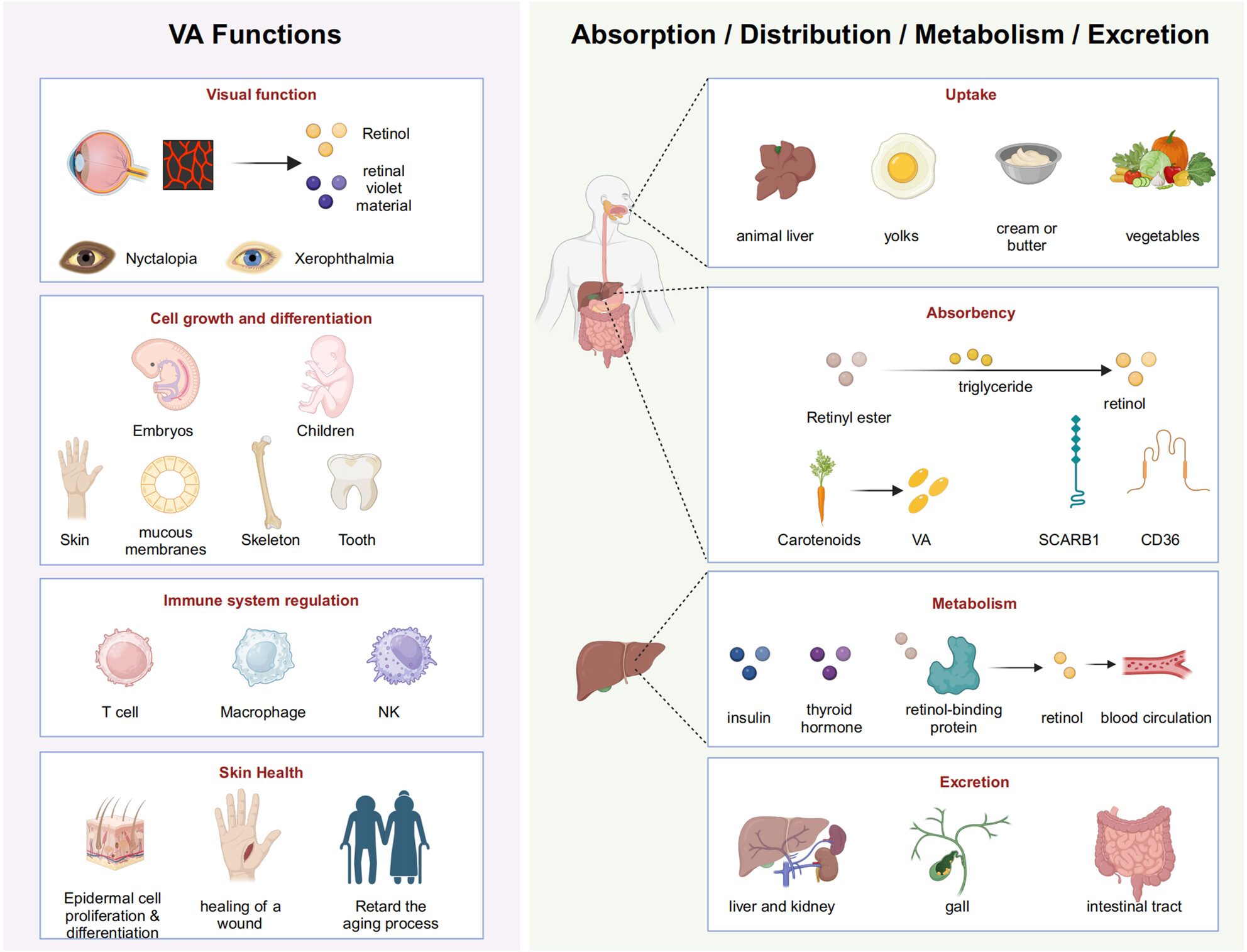
Vitamin, an essential micronutrient, is pivotal in human growth, development, immune function, and vision. Deficiency in VA disrupts growth and development in children and increases susceptibility to infectious diseases, such as respiratory and gastrointestinal infections. A comprehensive understanding of VA's involvement in clinical diseases is vital for effective disease prevention and treatment, providing a theoretical basis for interventions to improve VA nutritional status, thereby reducing disease incidence and enhancing patient outcomes.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
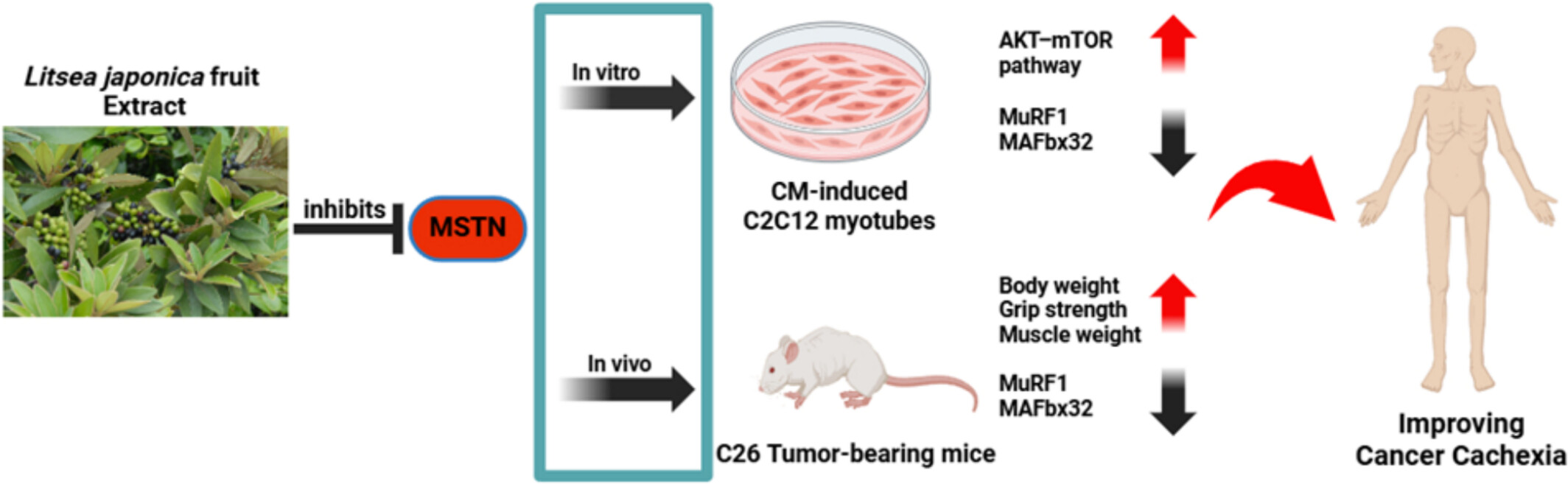
Extract of Litsea japonica (Thunba.) Jussieu Fruit Reduces Muscle Atrophy in Cancer Cachexia
- First Published: 16 July 2025
Effect of Encapsulation on the Viability of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus and Lacticaseibacillus paracasei During In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion and Storage Conditions
- First Published: 16 July 2025

This study explores the encapsulation of L. rhamnosus and L. paracasei using carob flour via an emulsion method. The encapsulated probiotics demonstrated significantly improved survival under gastrointestinal and storage stress conditions. The optimized process was evaluated through physicochemical, FTIR, and SEM analysis, revealing successful structural integration and stability enhancement.
Household Food Insecurity and Women's Dietary Diversity in Seqota Declaration Pilot Woredas Across the Tekeze River Basin of Amhara and Tigray Regions
- First Published: 18 July 2025

In the Seqota Declaration pilot woredas, over half of households faced moderate to severe food insecurity, with only 7%–10% of pregnant and lactating women meeting minimum dietary diversity requirements. Older household heads and those with lower wealth status were at a higher risk of food insecurity. In contrast, increased livestock ownership, improved land and water management, and greater production diversity reduced these risks. Larger land size and higher wealth status significantly improved Women's Dietary Diversity Score.
Climatic Determinants of Physicochemical Traits and Probiotic Composition in Dwarf Honeybee (Apis florea) Honey
- First Published: 16 July 2025
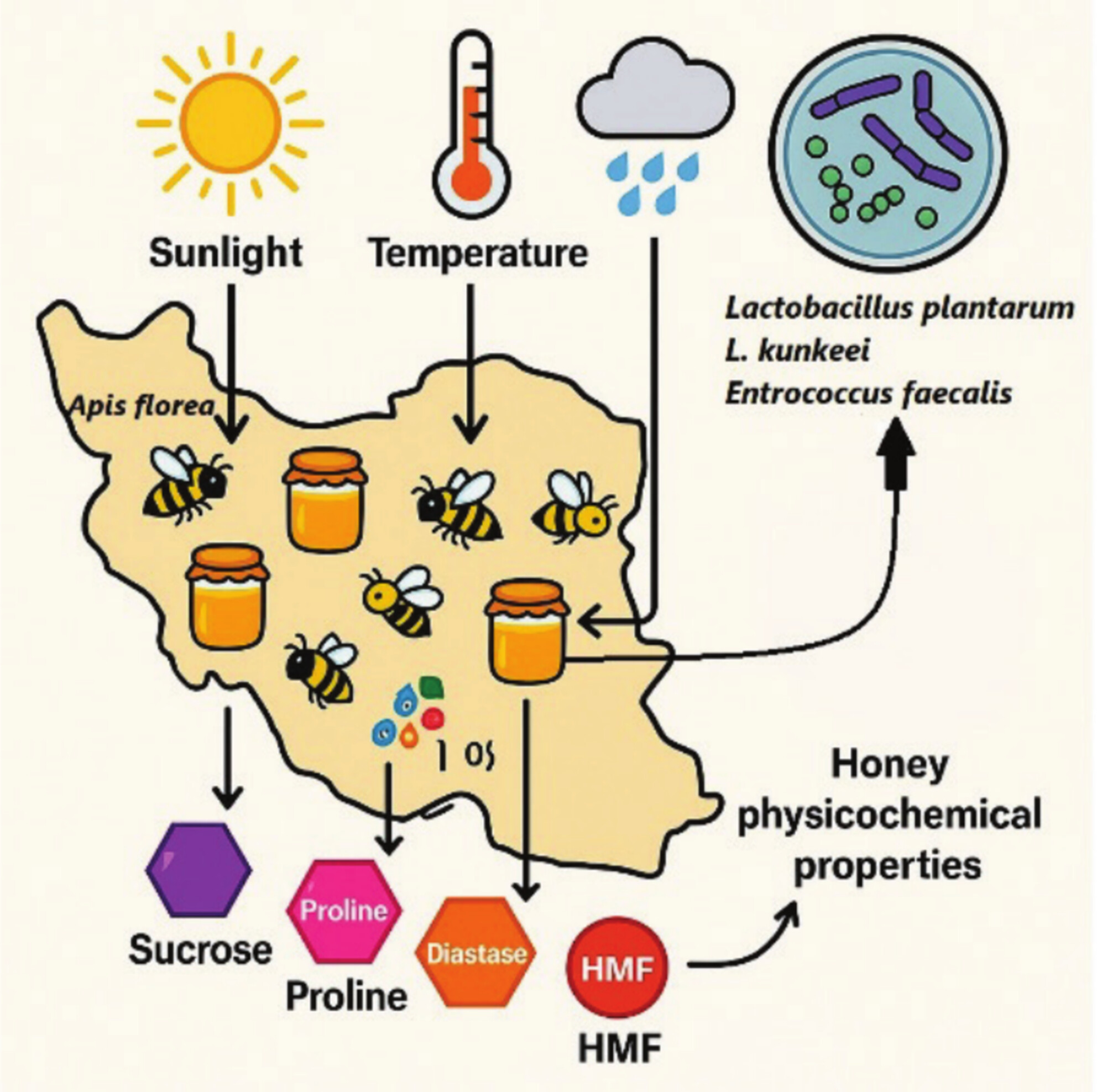
This study investigates the relationship between climatic variables and honey's physicochemical and microbiological properties from various regions. It highlights how environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, influence honey quality, composition, and microbial communities. The findings provide insights into regional differences and contribute to quality assessment and honey authentication.
Evaluation of Antioxidant and Enzyme Inhibition Properties of Siran Propolis: Correlations With Phenolic Content Determined by LC–MS/MS
- First Published: 21 July 2025
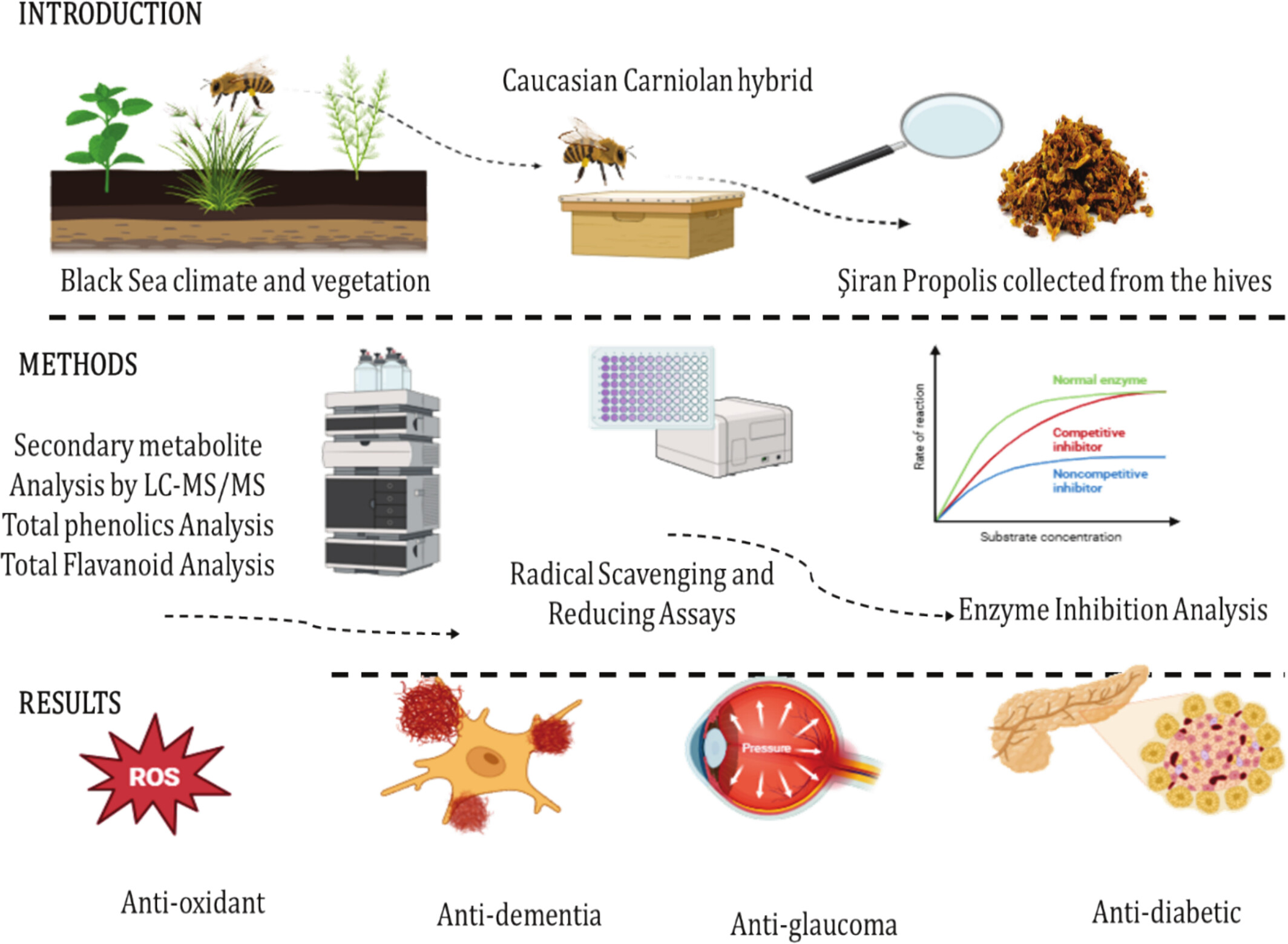
The ethanolic extract of Şiran propolis exhibited strong antioxidant activity and inhibited α-glycosidase, AChE, and human carbonic anhydrase isozymes I and II. High levels of phenolic acids, especially p-coumaric and ferulic acids, correlated with its bioactivity. These results suggest Şiran propolis as a potential natural source for therapeutic and functional food applications.
REVIEW
Harnessing the Nutritional Value, Therapeutic Applications, and Environmental Impact of Mushrooms
- First Published: 15 July 2025

Mushrooms are highly nutritious, packed with vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, essential amino acids, and bioactive compounds. They offer various health benefits, including boosting immunity, reducing inflammation, and supporting gut and cardiovascular health. Rich in carbohydrates, quality protein, essential fatty acids, and both soluble and insoluble fibers, they are versatile for culinary use. Furthermore, mushrooms and their byproducts show promise in food enhancement, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and as a sustainable animal feed.
An Updated Review of the Anticancer Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential of Naringenin
- First Published: 15 July 2025
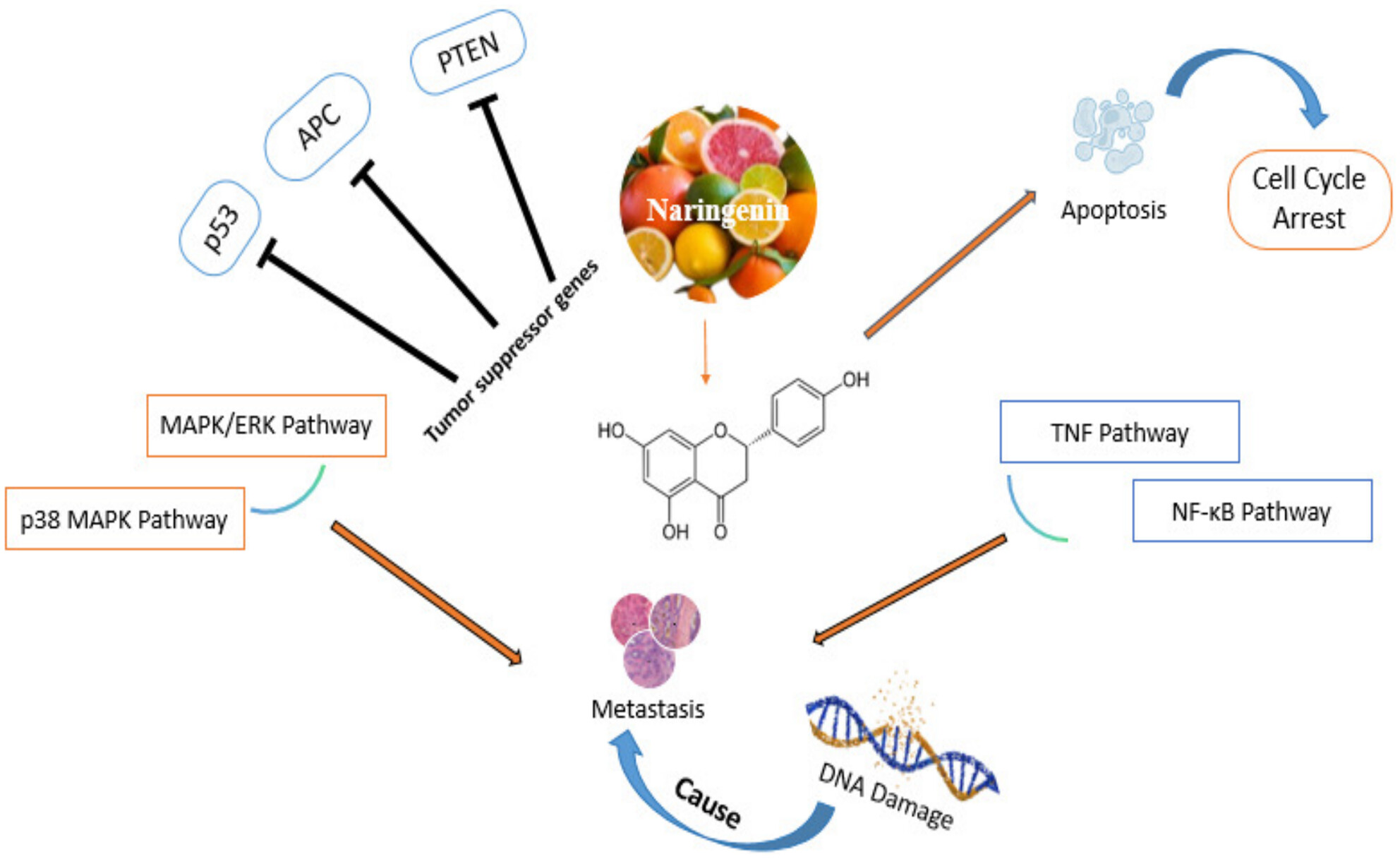
Naringenin is a bioactive compound widely distributed in the citrus family, belonging to polyphenols known for several health-promoting properties, including anticancer activity. Several evidence-based reports have proved that Naringenin can reduce tumorigenesis via inhibiting NRF2, TNF, NF-κB, NR3C1, P13K/AKT, TGF-β1/Smad3, and Bcl-2 expression. Moreover, Naringenin's anticancer potential is due to its ability to regulate growth factors like IGF, EGF, FGF, and tumor suppressor genes (TSGs) such as p53, PTEN, and Caspase-9 and Caspase-3 enzymes activity. The current review focuses on the bioavailability, antioxidant, and anticancer potential of Naringenin through possible mechanisms.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
The Association Between Dietary Fiber Intake and Depression Among US Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study Based on NHANES Data From 2005 to 2020
- First Published: 16 July 2025
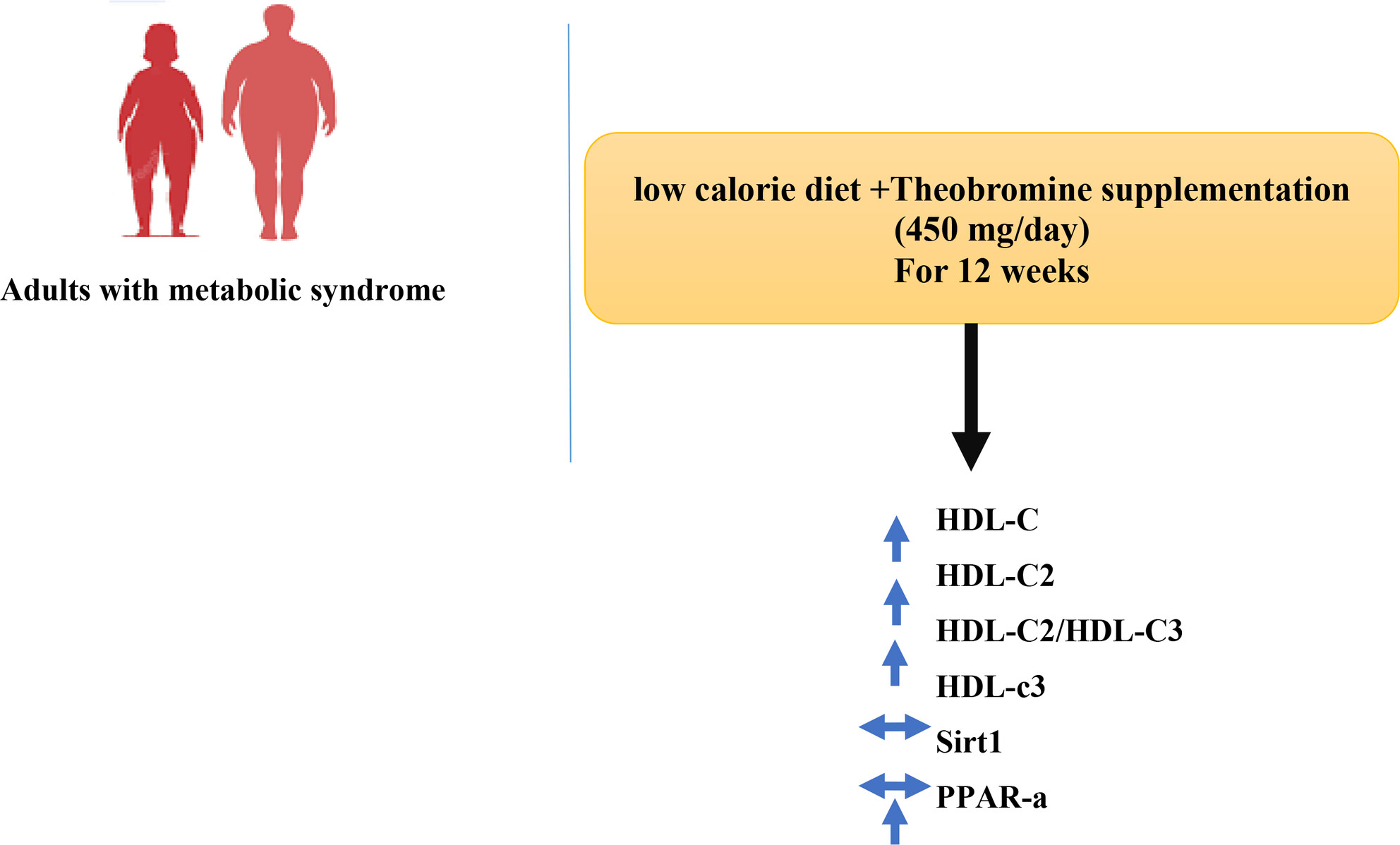
The Effect of Theobromine Supplementation on HDL-c Subclasses (HDL-c2, HDL-c3), HDL-c2/HDL-c3 Ratio, and Gene Expression of PPAR-α and Sirt1 in Subjects With Metabolic Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
- First Published: 16 July 2025
Assessment of Preclinical Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Cornus macrophylla Wall. Bark
- First Published: 16 July 2025
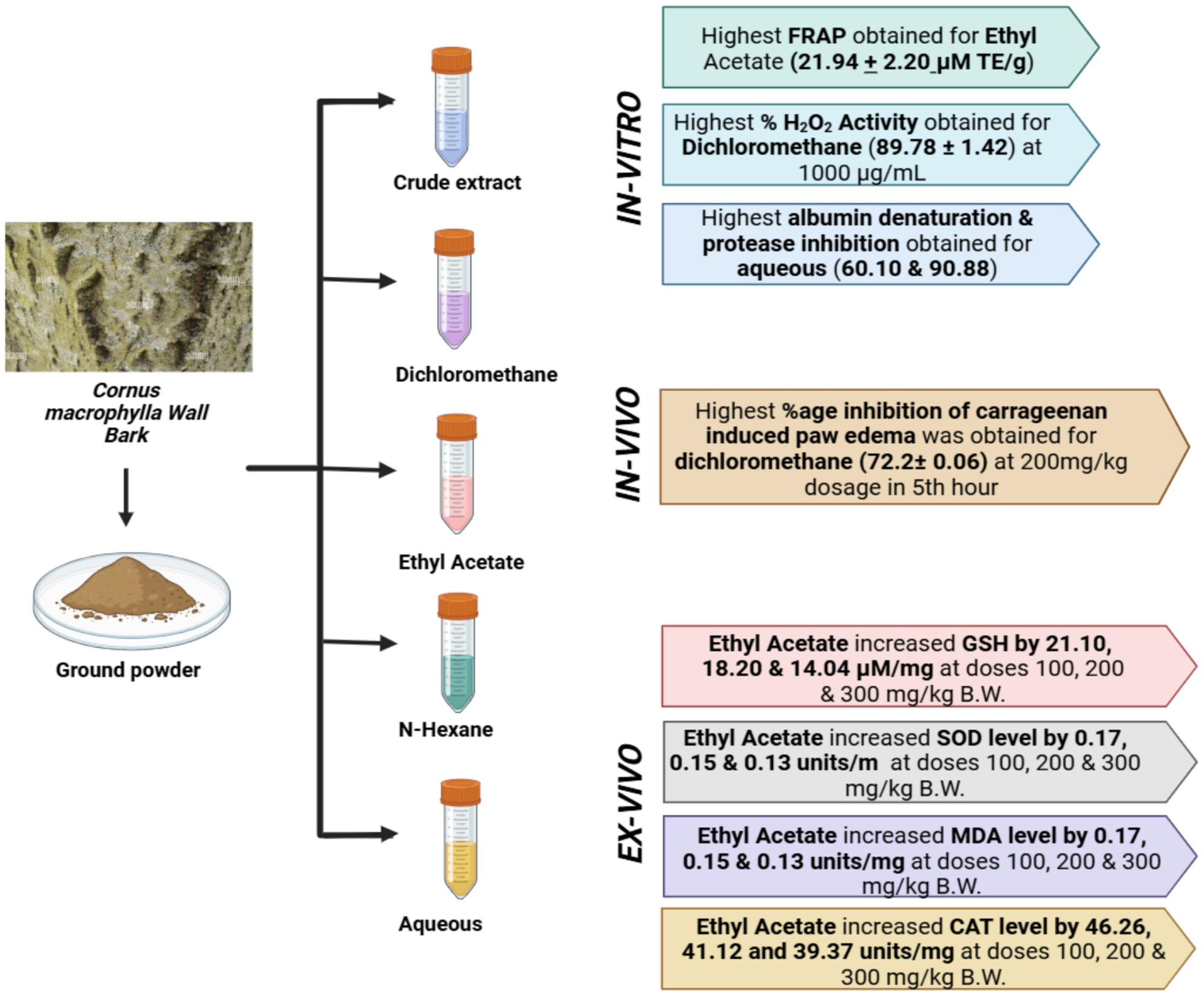
C. macrophylla, belonging to the Cornaceae family, exhibits significant anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. The ethyl acetate fraction showed the highest efficacy in reducing oxidative stress, restoring antioxidant levels (GSH, SOD, TBARS, and CAT), and improving locomotor activity in LPS-treated mice, validating its therapeutic potential.
Effect of Infant Formula Made With Milk Free of A1-Type β-Casein on Growth and Comfort: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- First Published: 15 July 2025

We compared growth, gastrointestinal tolerance, and crying frequency/duration in healthy Chinese infants aged 3–4 months who consumed both breastmilk and formula free of A1-type β-casein (A1PF) or conventional infant formula (CON). At Weeks 2 and 4, the A1PF group had significantly lower mean daily total Infant Gastrointestinal Symptom Questionnaire (IGSQ) scores; lower mean stooling, spitting up/vomiting, crying, and fussiness domain scores; and lower mean number of daily crying periods than the CON group (p < 0.05). Both formulas were generally well tolerated, but infants who consumed A1PF infant formula had improved comfort as measured by relieved gastrointestinal symptoms and fewer crying periods.
Bioprotective and Functional Activities of Postbiotics From Lactic Acid Bacteria Derived From Artisanal Dairy Products
- First Published: 16 July 2025

Postbiotics derived from 10 native LAB species were evaluated for their in vitro functional properties and their biopreservative effects in a model product of pasteurized milk. Postbiotics belonging to E. faecalis, Lc. lactis, L. plantarum, and L. paraplantarum were accepted as potential candidates in terms of in vitro functional properties. As to biopreservation capacity, E. faecium, Lc. lactis, and Lb. brevis was chosen as the best strain. The preferred microbial source can be selected based on the intended purpose of the product, such as enhancing antimicrobial or antioxidant activity, or increasing phenolic and/or organic acid content.
Unveiling the Synergistic Effects of Melatonin, Arginine, and Nano-Chelated Zn-Fe on Enhancing Fruit Quality in Apricot (Prunus armeniaca)
- First Published: 22 July 2025

Highest levels of mineral materials and vitamins were observed in arginine (150 ppm) + melatonin (400 μmol/L) + Nano-chelated Zn-Fe at either 2 or 3 g/L. T27 and T28 resulted in the highest fruit yield, total soluble solids, fruit set, and firmness, along with reduced acidity. 150 ppm + 400 μmol/L + 2 g/L and 150 ppm + 400 μmol/L + 3 g/L are recommended as the most effective for enhancing yield and fruit quality.
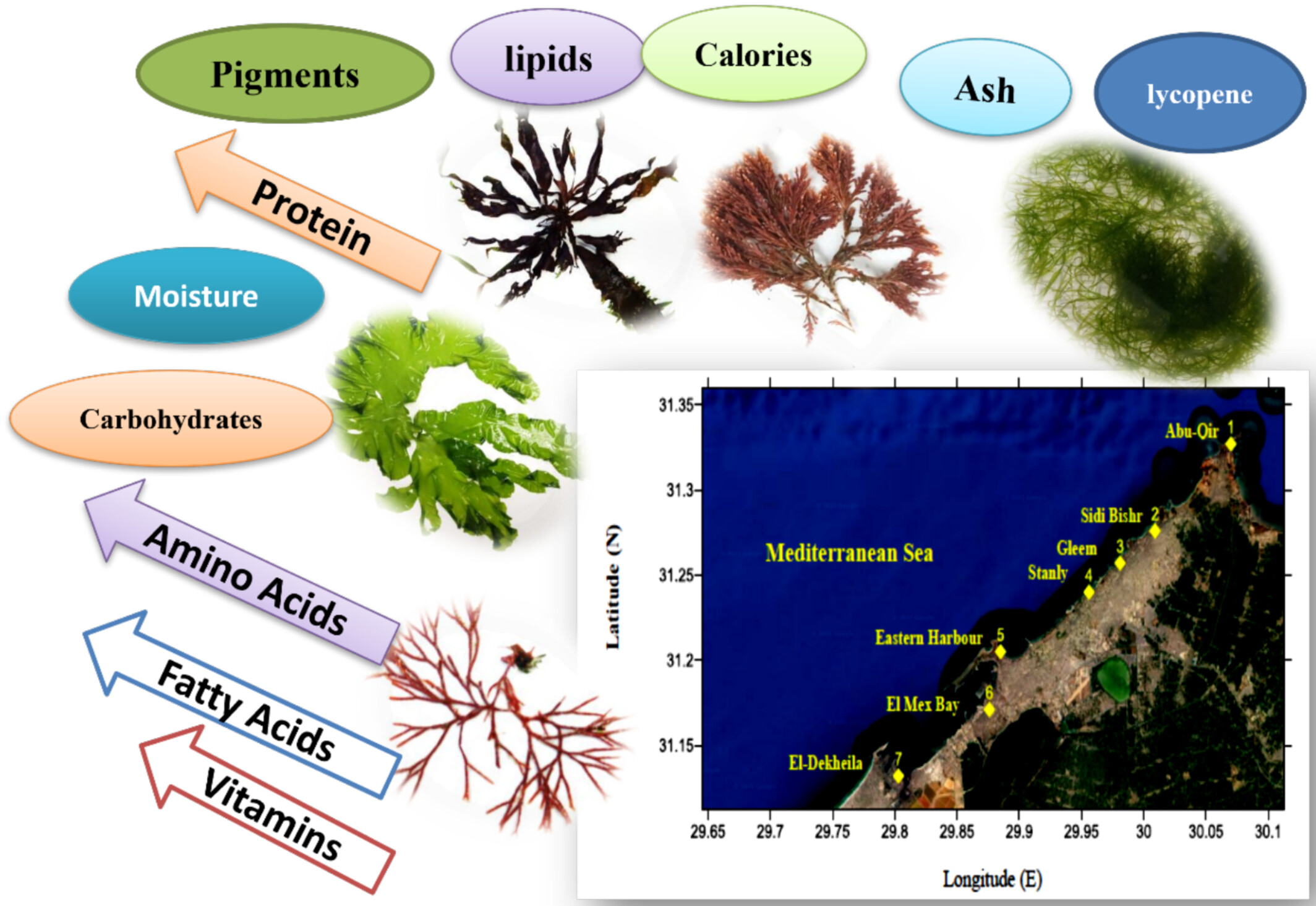
Evaluation of the Spatial Variations in the Biochemical Composition of Seaweed Species Along the Coast of Alexandria, With a Focus on Fatty Acids and Total Amino Acids of the Prevalent Edible Species
- First Published: 16 July 2025
The Burden of Nonmalignant Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in the Western Pacific Region: A Systematic Analysis From 1990 to 2021
- First Published: 16 July 2025

The overall GBD descriptions of non-malignant MASLD in the western pacific region. (A) Estimated annual percentage changes (EAPCs) in age standardized rates of incidence for non-malignant MASLD by country, for the period 1990–2021. (B) EAPCs in age standardized rates of prevalence for non-malignant MASLD by country, for the period 1990–2021. (C) EAPCs in age standardized rates of deaths for non-malignant MASLD by country, for the period 1990–2021. (D) EAPCs in age standardized rates of disability adjusted life years (DALYs) for non-malignant MASLD by country, for the period 1990–2021. (E) EAPCs in age standardized rates of years of healthy life lost due to disability (YLDs) for non-malignant MASLD by country, for the period 1990–2021. (F) EAPCs in age standardized rates of years of life lost (YLLs) for non-malignant MASLD by country, for the period 1990–2021.
The Impact of Free and Nanoencapsulated Banana and Apple Peels Extracts on the Physicochemical, Oxidative Stability, Microbial and Sensory Properties of Whipped Cream
- First Published: 16 July 2025

Apple and banana peel extract contain bioactive phenolic compounds exhibiting antioxidant and antibacterial activity. Free and nanoencapsulated extracts increased the shelf life of whipped cream during cold storage. Nanoencapsulated extract improved the pH, apparent viscosity, hardness, overrun, oxidative stability, and foam stability and also significantly reduced the acidity, drainage, and microbial load of whipped cream samples during the cold storage period. It can be a good alternative to synthetic preservatives. pH, apparent viscosity, overrun, drainage, color indexes, peroxide value, thiobarbituric acid, total microbial count, and sensory characteristics of WC were examined.
Vinegar-Processed Black Soybean Promotes Hair Growth and Prevents Alopecia via Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway
- First Published: 16 July 2025

Vinegar-processed black soybean (VPBS) and its aqueous extract (VPBS-AE) dose-dependently accelerated hair growth, stimulated anagen phase entry, and attenuated cyclophosphamide-induced alopecia. VPBS-AE promoted follicular repair, delayed alopecia, and preserved follicle integrity. These effects may be mediated through activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
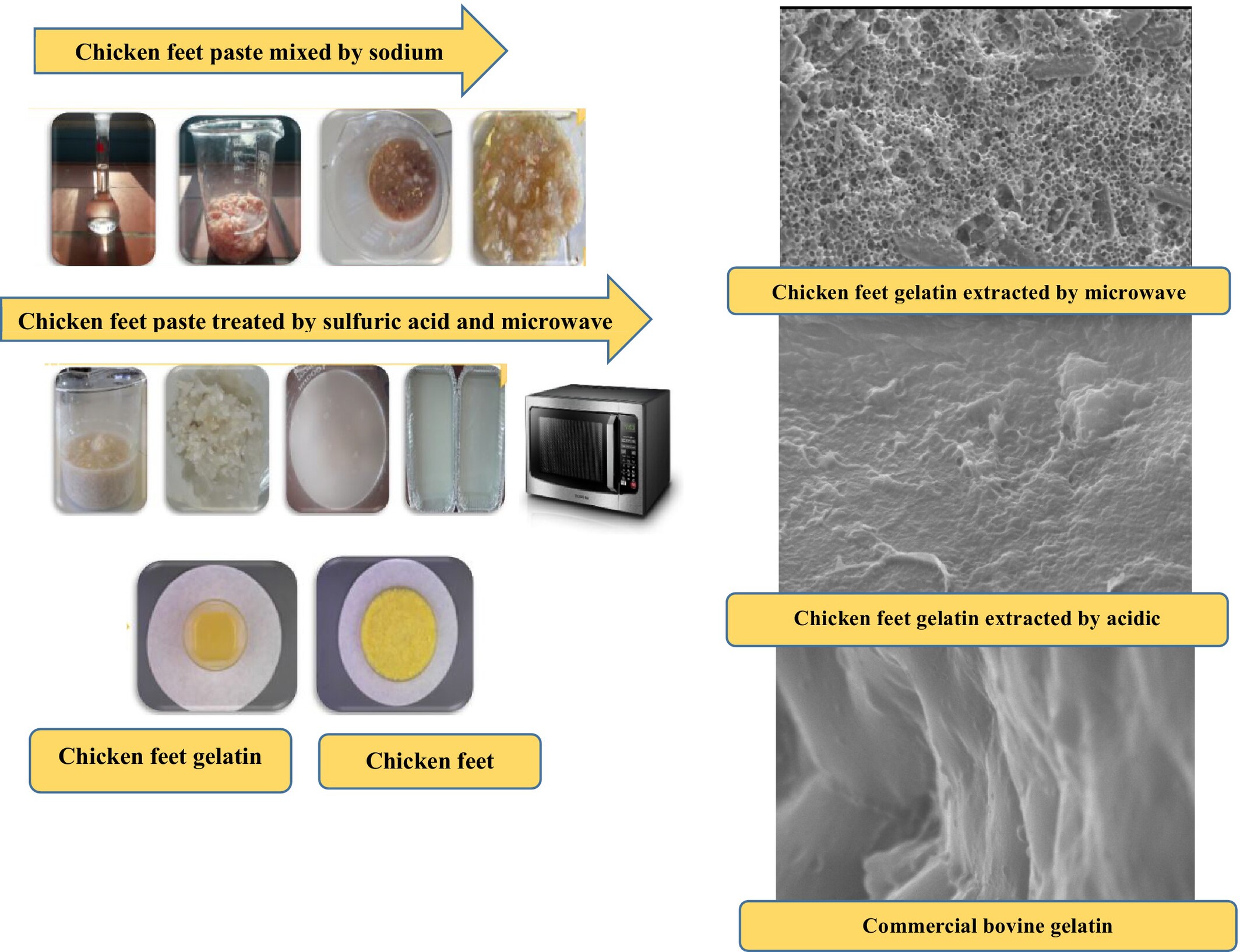
Comparison of the Physicochemical, Rheological and Functional Properties of Chicken Feet Gelatin Extracted by Acidic and Microwave Methods and Commercial Bovine Gelatin
- First Published: 18 July 2025
Royal Jelly Supplementation Improves Endurance and Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Athletes: A Crossover Trial
- First Published: 16 July 2025
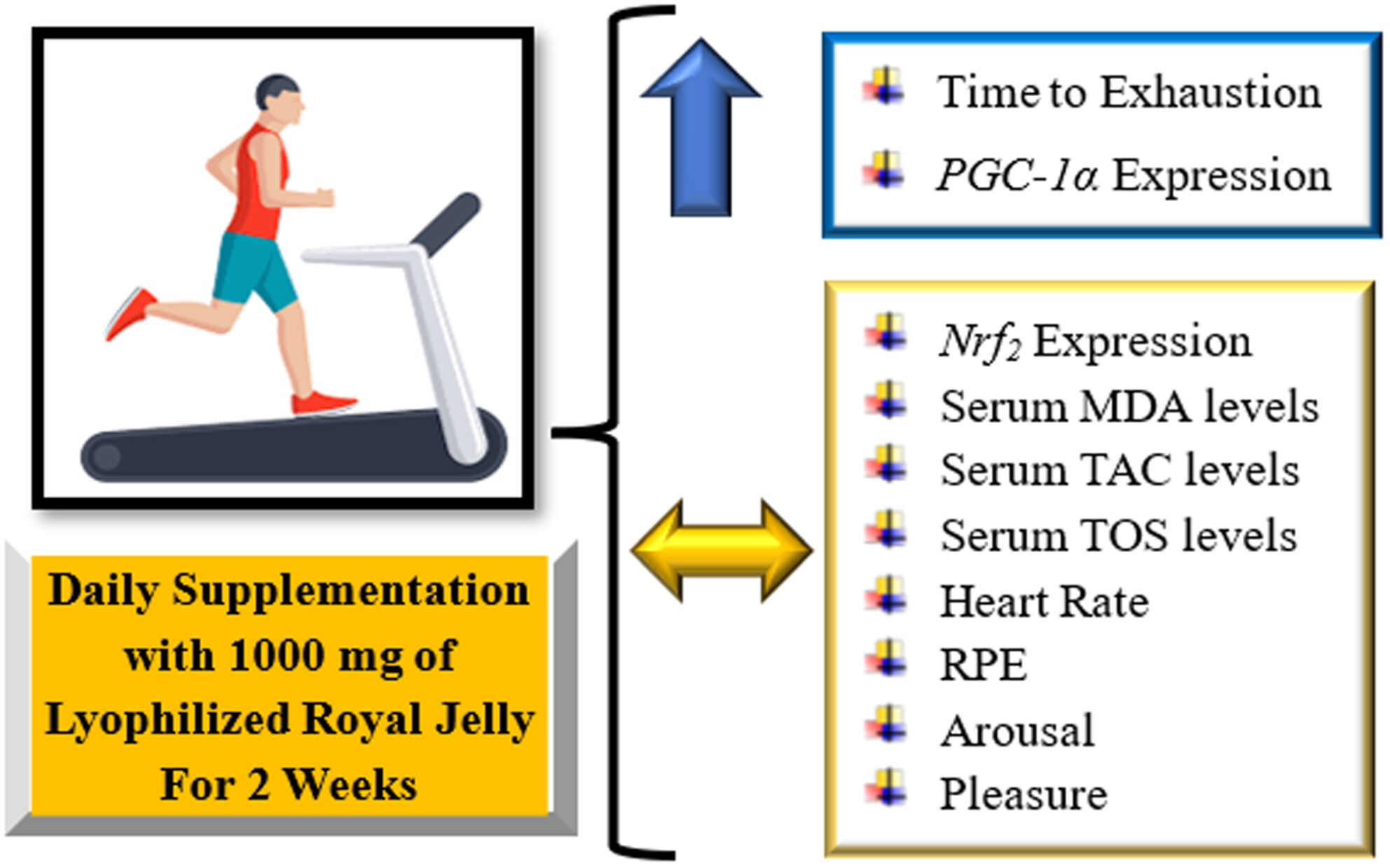
This clinical trial showed that royal jelly supplementation significantly improved athletic performance by increasing the time to exhaustion and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α) gene expression during the exhaustive endurance-running test. However, its supplementation had no significant effects on nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) gene expression, malondialdehyde (MDA), total antioxidant capacity (TAC), total oxidant status (TOS), heart rate, rate of perceived exertion (RPE), arousal, and pleasure to exercise [Up Arrow (Increase); Double-sided Arrow (Without Change)].
Piperine Enhances Mitochondrial Biogenesis to Mitigate Stress in SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells
- First Published: 16 July 2025
Nutritional Profile and Functional Characteristics of Various Types of Traditionally Produced PEKMEZ—Part I
- First Published: 16 July 2025
This study examines the nutritional profile and functional characteristics of eight traditionally produced pekmez varieties, focusing on essential amino acids, vitamin content, and bioactive compounds. The results highlight the high arginine and vitamin C content, suggesting potential health benefits. Additionally, Principal Component Analysis (PCA) reveals key factors contributing to the variability among pekmez samples.
REVIEW
The Dual Role of Conjugated Linoleic Acid in Obesity and Metabolic Disorders
- First Published: 22 July 2025

Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) modulates lipid metabolism, adipogenesis, energy expenditure, and inflammation, showing anti-obesity effects in animal models. However, human studies reveal inconsistent outcomes due to dosage, isomer type, and individual variability. Personalized supplementation strategies are essential to maximize CLA's benefits while minimizing metabolic risks.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Protective Effects of Gallic Acid Against Lead Acetate- Induced Toxicity in Mice Ovary: Focus on Apoptosis, Inflammation, and Folliculogenesis
- First Published: 16 July 2025
Enhancing the Quality and Nutritional Properties of Gluten-Free Pancakes Using Sprouted Quinoa Flour Treated With Magnetic Fields, Ultrasound, and Infrared Drying
- First Published: 18 July 2025

The incorporation of sprouted quinoa flour in pancake formulation enhanced nutritional and quality attributes, resulting in increased phenolic content and antioxidant capacity. This pancake also exhibited the lowest values for baking loss, density, and hardness. Sensory analysis indicated the highest overall acceptance, highlighting its potential as a valuable ingredient in gluten-free products.
EAT-Lancet Diet Adherence in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study
- First Published: 18 July 2025
In a sample of 385 adults with type 2 diabetes, higher EAT-Lancet Diet Index scores correlated with increased dietary fiber intake and reduced total energy, protein, and fat consumption. Improved adherence was also associated with significantly lower fasting blood glucose and HbA1c levels. These results suggest that promoting a sustainable, plant-forward dietary pattern may enhance glycemic control and overall metabolic health in this population.
Evaluation of Lacticaseibacillus casei 39 Paraprobiotic in Modulating Inflammatory and Oxidative Pathways in Acetic Acid Induced Ulcerative Colitis
- First Published: 18 July 2025
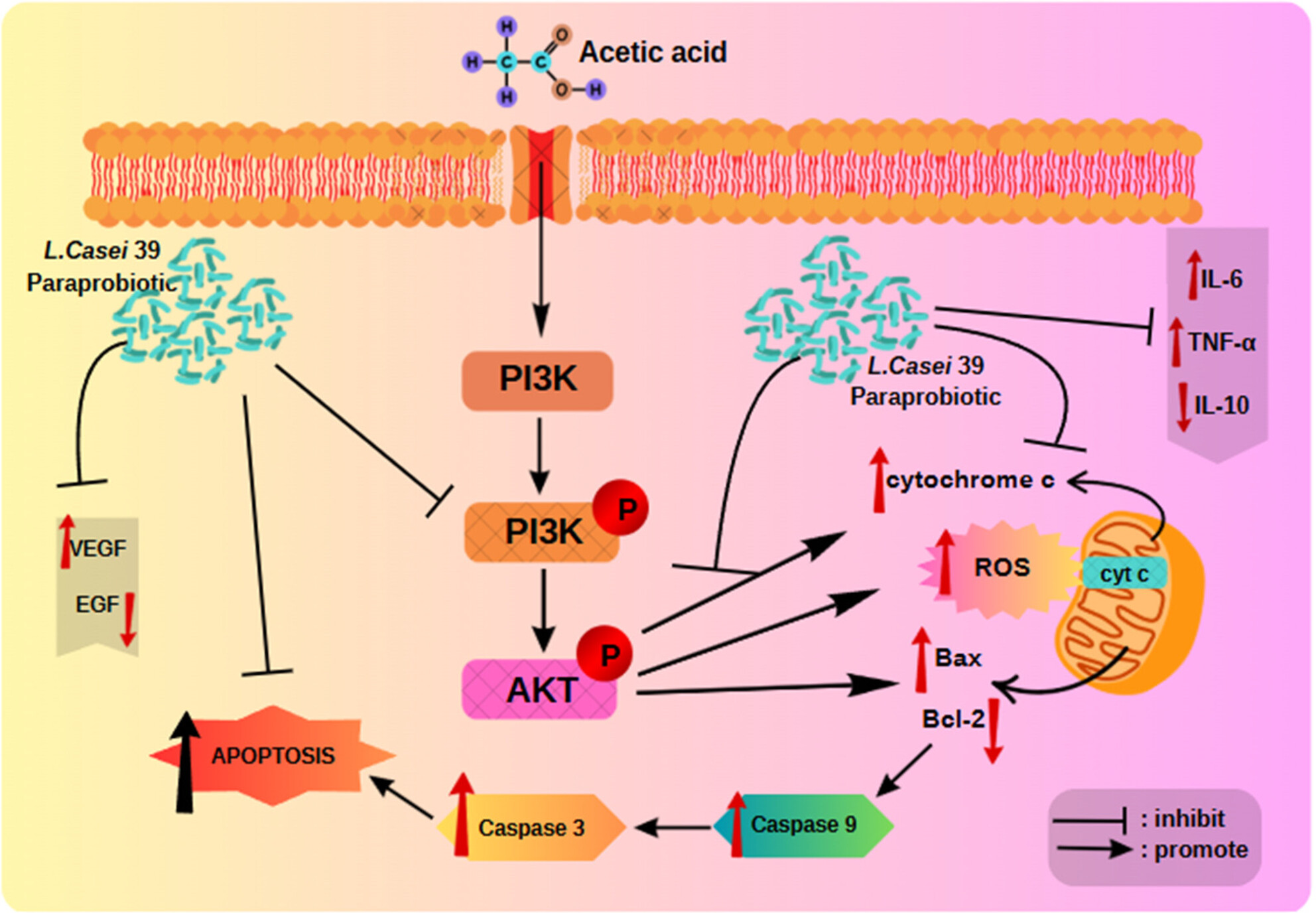
UV-C inactivated Lacticaseibacillus casei 39 paraprobiotic suppressed inflammation (↓TNF-α, IL-6; ↑IL-10), oxidative stress (↓TOC, ↑TAC) and apoptosis (↓Bax/Bcl-2, ↓Caspase-3/9, ↓cyt c) in an acetic acid-induced colitis model. It promoted healing by regulating VEGF/EGF expression. It showed a multi-targeted protective effect by inhibiting PI3K/AKT pathway activation. These findings suggest that L. casei 39 paraprobiotic is a promising anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic agent in the treatment of ulcerative colitis.
Impact of Fertilization on Antioxidant Activity, Microbiological Quality, and Sensory Attributes of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Cultivated in Ethiopia's Central Rift Valley
- First Published: 18 July 2025

Compost fertilization significantly increased vitamin C, flavonoids, total phenolics, DPPH radical scavenging activity, and FRAP antioxidant capacity. However, chemical fertilization enhanced beta-carotene and lycopene content across both growing seasons. Both organic and conventional farming practices pose no significant microbiological risks. Overall, this finding suggests that compost fertilization can enhance the production of bioactive compounds and improve the antioxidant activity of tomatoes, particularly in the Gelilema and Galilea varieties.
Assessing Environmental Hotspots and Sustainable Development Goal Alignment in Food Production in India
- First Published: 18 July 2025

This study evaluates the environmental impacts of 18 commonly consumed food items in India using a production-based LCA, highlighting key hotspots in greenhouse gas emissions, land and water use, and biodiversity loss. It aligns findings with SDGs 3, 6, 13, 14, and 15, and proposes dietary shifts, especially toward millets and sorghum, that could reduce impacts by up to 79%. The results emphasize the importance of sustainable diets and agricultural practices for environmental and nutritional gains.
REVIEW
Effect of Low-Carbohydrate Diets on C-Reactive Protein Level in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- First Published: 18 July 2025
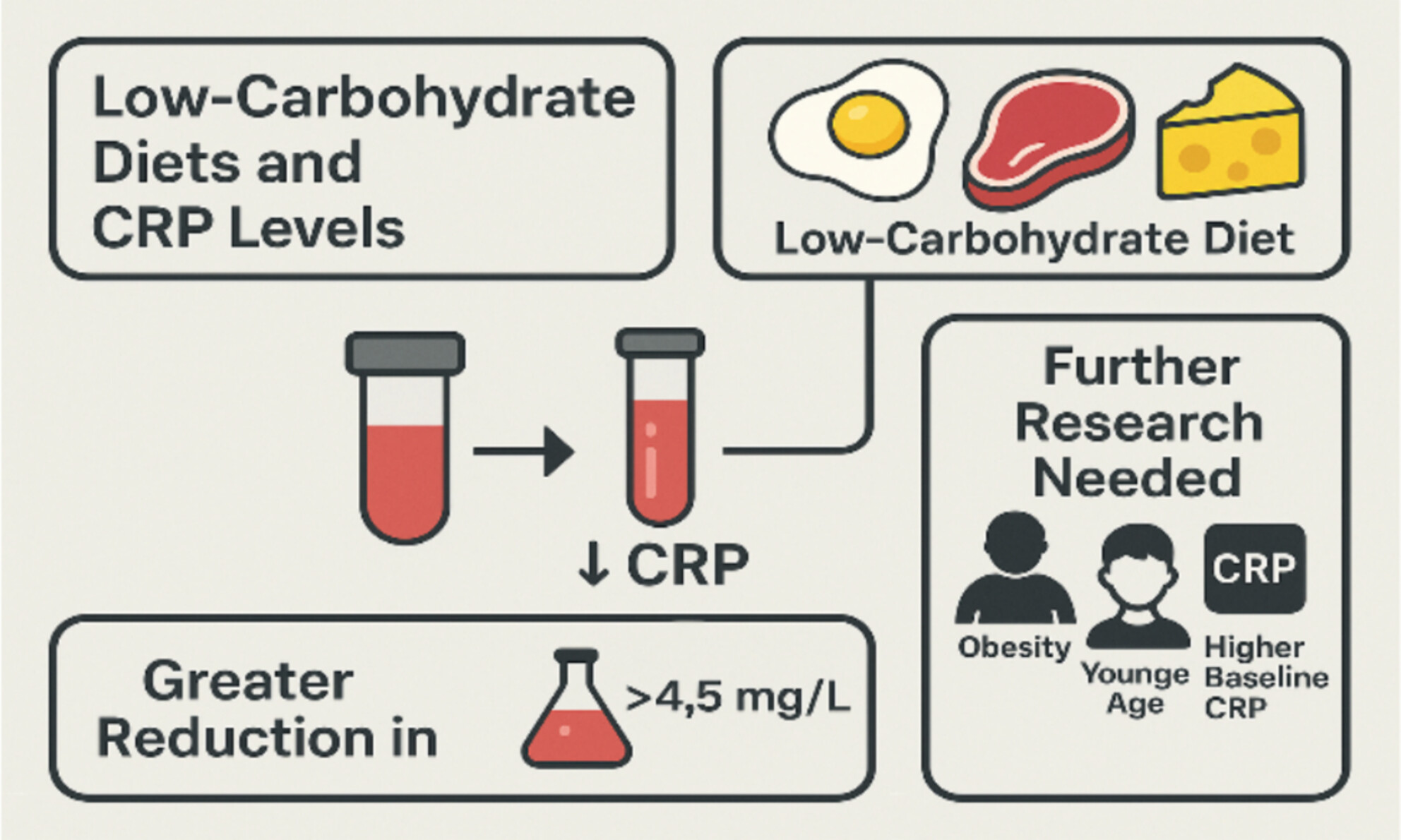
Chronic low-grade inflammation is a probable mediator between quantity of carbohydrate intake and health outcomes. The results of the present systematic review and meta-analysis showed that low carbohydrate diets are an effective dietary strategy for improving CRP levels especially among obese adults with baseline CRP concentration more than 4.5 mg/L.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Impact of Free and Nanoencapsulated Echinophora platyloba Essential Oil on the Physicochemical, Microbial, and Sensory Properties of Siahmazgi Cheese
- First Published: 18 July 2025

This study evaluated the impact of free and nanoencapsulated Echinophora platyloba essential oil on the physicochemical, microbial, and sensory properties of Siahmazgi cheese. Nanoemulsions showed spherical morphology and stable zeta potentials. The 0.3% nanoencapsulated treatment improved microbial safety, reduced molds and bacteria, and maintained favorable texture and flavor during 90 days. These findings highlight the potential of nanoencapsulated EPEO as a natural preservative to enhance traditional dairy products.
Preservative Effects of Gracilaria sp. Extract in Maintaining the Quality and Shelf Life of Refrigerated Pangas (Pangasius hypophthalmus) Fillets
- First Published: 20 July 2025

This study intended to investigate the preservative effects of Gracilaria sp. extracts on the quality and shelf life of pangas fillets during refrigerated storage. Results revealed that 2% Gracilaria sp. extracts had a significant impact on the physio-chemical, microbial, and sensory attributes of fish fillets and enhanced the shelf life by 6 days more than the control fillets under refrigerated conditions.
Gallic Acid Improves Muscular Function Through Enhanced Myoblast Myogenesis in Mice
- First Published: 18 July 2025

Gallic acid treatment enhances myogenesis in primary myoblasts, with particularly strong effects under growth conditions. Dietary supplementation with gallic acid increases soleus muscle mass and improves exercise performance in mice. These findings suggest gallic acid promotes muscle synthesis and could serve as a natural supplement for improving muscle function.
REVIEW
Exploring the Multifaceted Potential of Elaeagnus angustifolia L.: A Comprehensive Review of Its Nutritional, Pharmacological, and Environmental Significance
- First Published: 04 July 2025

Elaeagnus angustifolia is a resilient, multi-purpose plant valued for its roles in food, medicine, fuel, and environmental protection. This review highlights its rich biochemical composition and therapeutic properties, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and wound-healing effects. It emphasizes the plant's potential in developing nutraceuticals, pharmaceuticals, and eco-friendly applications.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Polygonati Rhizoma Polysaccharides Ameliorated Diabetic Kidney Disease in db/db Mice via Inhibiting TGFβ/Smad2 Signaling Pathway
- First Published: 18 July 2025
Setaria viridis Ethanol Extract Attenuates Muscle Loss and Body Fat Reduction in Sarcopenic Obesity by Regulating AMPK in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice
- First Published: 18 July 2025
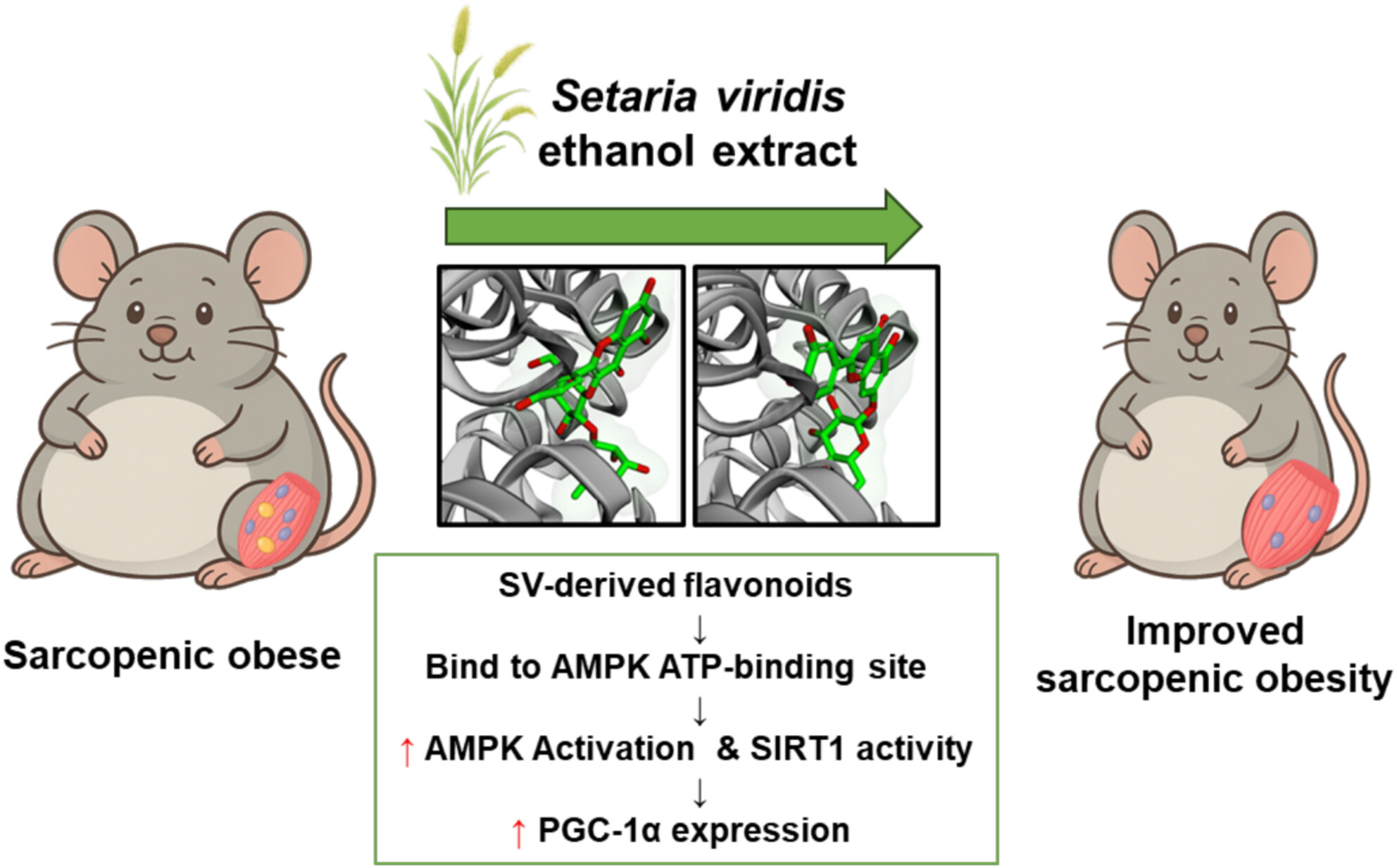
Setaria viridis (SV)-derived flavonoids activate AMPK by binding to its ATP-binding site, leading to enhanced SIRT1 activity and PGC-1α expression. In high-fat diet-induced obese mice, SV supplementation increased muscle protein synthesis, reduced fat mass, and suppressed inflammation. These findings suggest AMPK as a key therapeutic target of SV in managing sarcopenic obesity.
Safety and Nutritional Profile of Traditional Turkish Cheeses: A Comprehensive Study on Their Mineral Content, Heavy Metal Contamination, and Health Risks of Aho, Golot, and Telli
- First Published: 20 July 2025
REVIEW
Exploring the Frontiers of Food Science: A Comprehensive Review of Advanced Magnetic Resonance Applications in Food Analysis, Quality Analysis, and Safety Assessment
- First Published: 20 July 2025
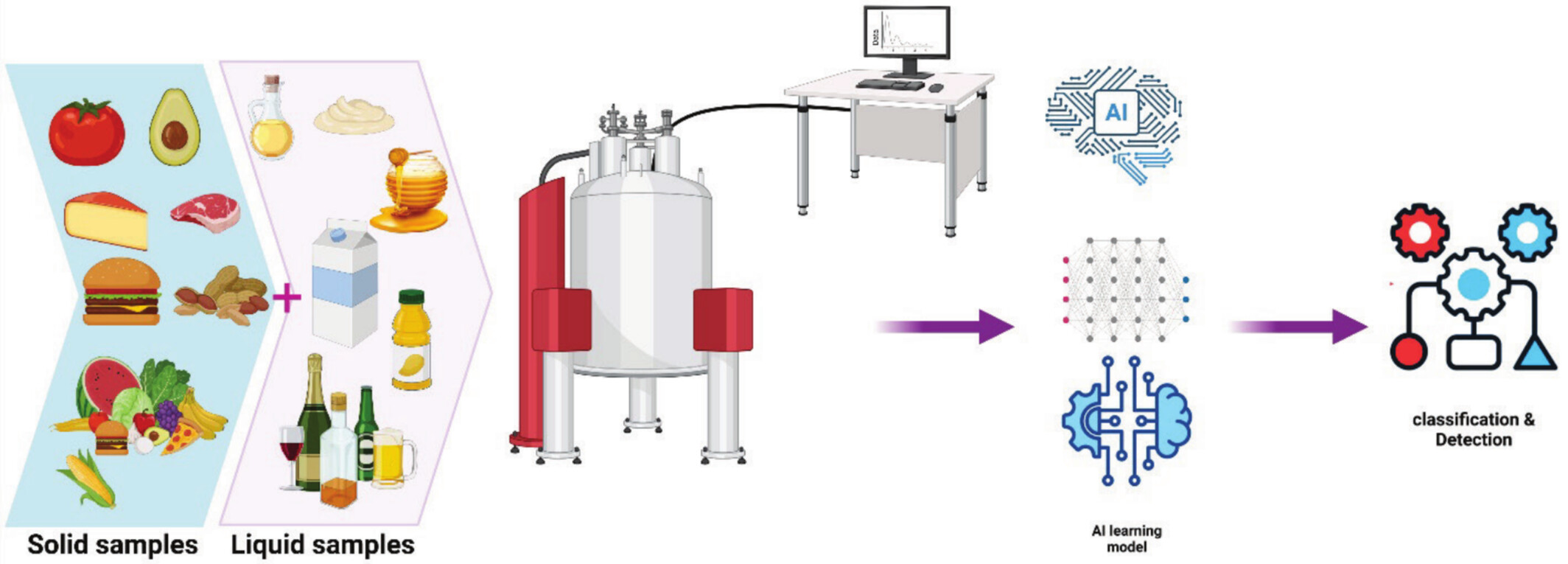
The paper reviews advanced magnetic resonance (MR) technologies—NMR, MRI, ESR, and MRS—for food analysis, quality, and safety. MR techniques enable non-invasive detection of adulteration, compositional profiling, and monitoring of food processing and storage. Integrating MR with AI enhances real-time diagnostics, predictive modeling, and food authenticity, supporting innovation and sustainability.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Volatilomic Analysis in Peel, Pulp and Seed of Hass Avocado (Persea americana Mill.) From the Northern Subregion of Caldas by Gas Chromatography With Mass Spectrometry
- First Published: 07 July 2025

The volatilome of Hass avocado peel, pulp, and seed was characterized using HS-SPME-GC–MS, revealing 87 VOCs with tissue-specific profiles. Terpenes dominated the seed, while esters and aldehydes were more abundant in the pulp, and oxygenated terpenes were prominent in the peel. Metabolic enrichment analysis highlighted key biosynthetic pathways including sesquiterpenoid/triterpenoid biosynthesis, glycolysis, and fatty acid metabolism, reflecting distinct biochemical roles across fruit tissues.
The Association between Ultra-Processed Foods and Depression, Anxiety and Sleep in Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study in Iran
- First Published: 20 July 2025
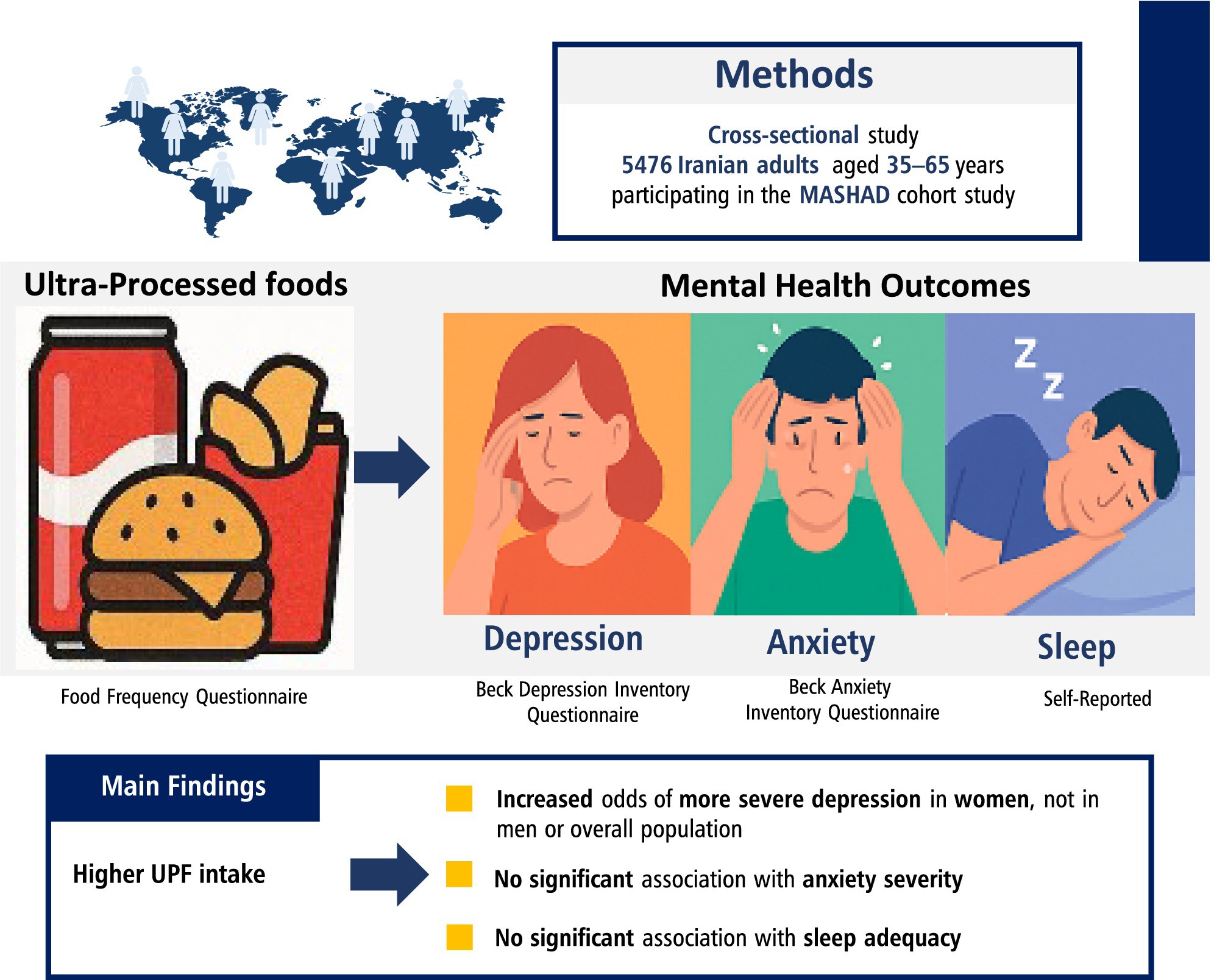
This cross-sectional study examined the link between ultra-processed food (UPF) consumption and mental health indicators in 5476 Iranian adults. Higher UPF intake was associated with increased odds of severe depression, particularly in females, while no significant associations were found for anxiety or sleep adequacy. These findings highlight the potential impact of diet on mental well-being, warranting further research into underlying mechanisms.
Investigating Exogenous Tyrosine Supplements on the Responses of the Kale Plant to Salinity Stress
- First Published: 20 July 2025
DBA-DeepLab: Dual-Backbone Attention-Enhanced DeepLab V3+ Model for Plant Disease Segmentation
- First Published: 21 July 2025
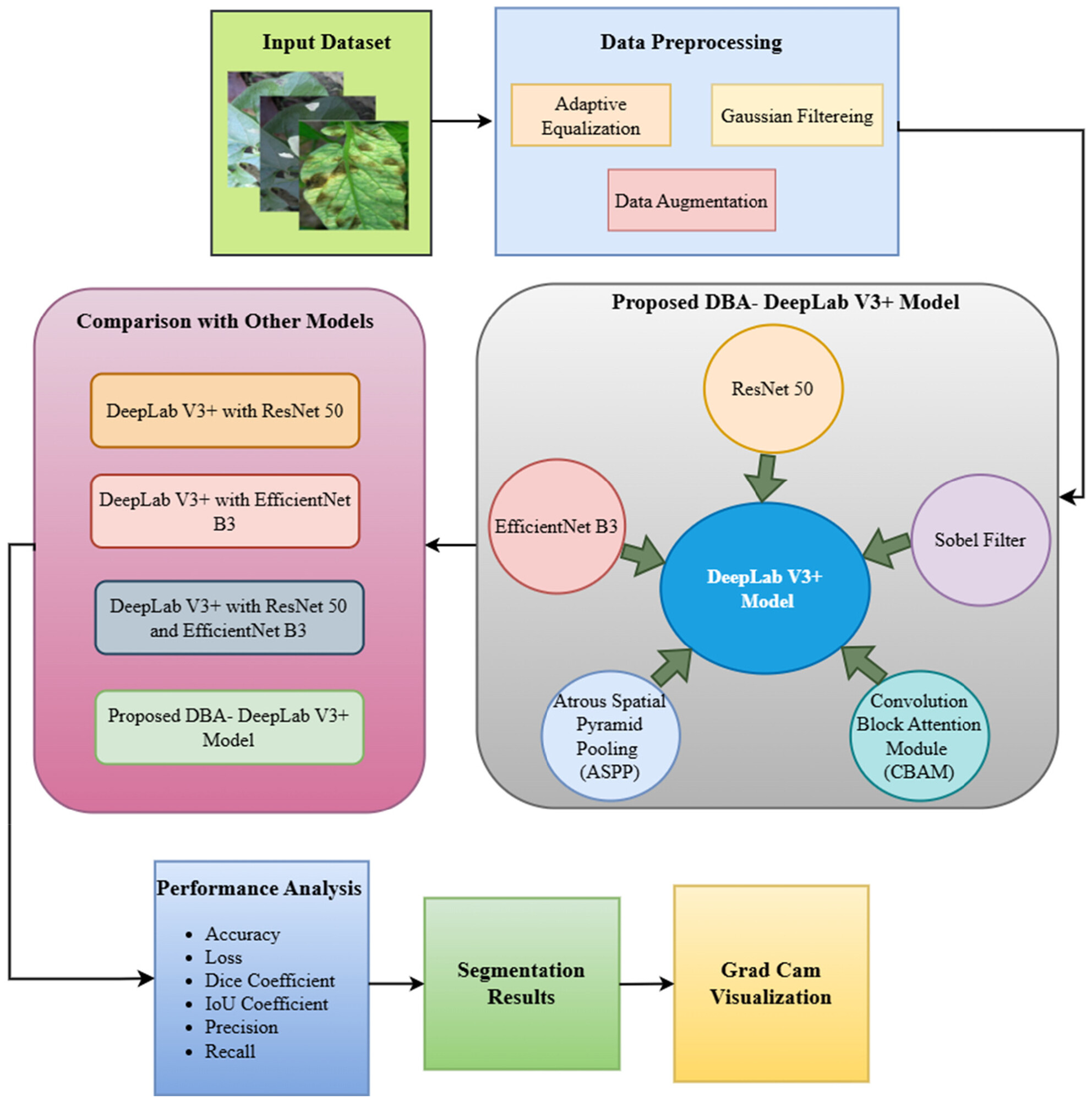
This study introduces DBA-DeepLab, a novel plant disease segmentation model that integrates dual backbones—ResNet-50 and EfficientNet-B3—with a Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) and Sobel filtering for enhanced accuracy. Trained on the PlantDoc dataset, the model achieves superior performance metrics, including 99.35% accuracy and 100% recall, making it highly effective for precision agriculture and automated disease detection.
Dietary Vitamin D Supplementation Improves Hair Follicle Development and Affects Fatty Acid Metabolism in Rex Rabbits
- First Published: 21 July 2025
Transcription Factors and Regulate Network in Food Plant Stress and Growth Responses
Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Role of Trehalose in Response to Polyethylene Terephthalate Nanoplastics Treatment in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica) Seedlings
- First Published: 21 July 2025

Transcriptome sequencing of seedlings treated with 1 g/L PET nanoplastics (3 and 7 days) revealed genes associated with trehalose biosynthesis (SiTPS/SiTPP) and degradation (SiTRE) were dynamically regulated, suggesting trehalose homeostasis as a critical stress-response mechanism. (2) Exogenous trehalose application effectively alleviated ROS damage under nanoplastic treatment, corroborating its protective role. (3) Further WGCNA analysis indicated the potential involvement of ABA signal transduction and the MAPK signaling pathway in foxtail millet's response to PET nanoplastic stress.
Overdose Toxicological Effect of Methanol Extract of Popular Edible Colocasia esculenta Linn. Flowers: Biochemical, Hematological, and Behavioral Study on Swiss Albino Mice
- First Published: 23 July 2025

Colocasia esculenta Linn., an annual herbaceous plant from the Araceae family, has long been utilized in traditional medicine throughout tropical and subtropical regions for the treatment of diverse health conditions. This study investigated the effects of the methanolic extract of C. esculenta flowers (CEF-ME) on mice, focusing on physiological, biochemical, hematological, and behavioral parameters.
VGG-EffAttnNet: Hybrid Deep Learning Model for Automated Chili Plant Disease Classification Using VGG16 and EfficientNetB0 With Attention Mechanism
- First Published: 24 July 2025
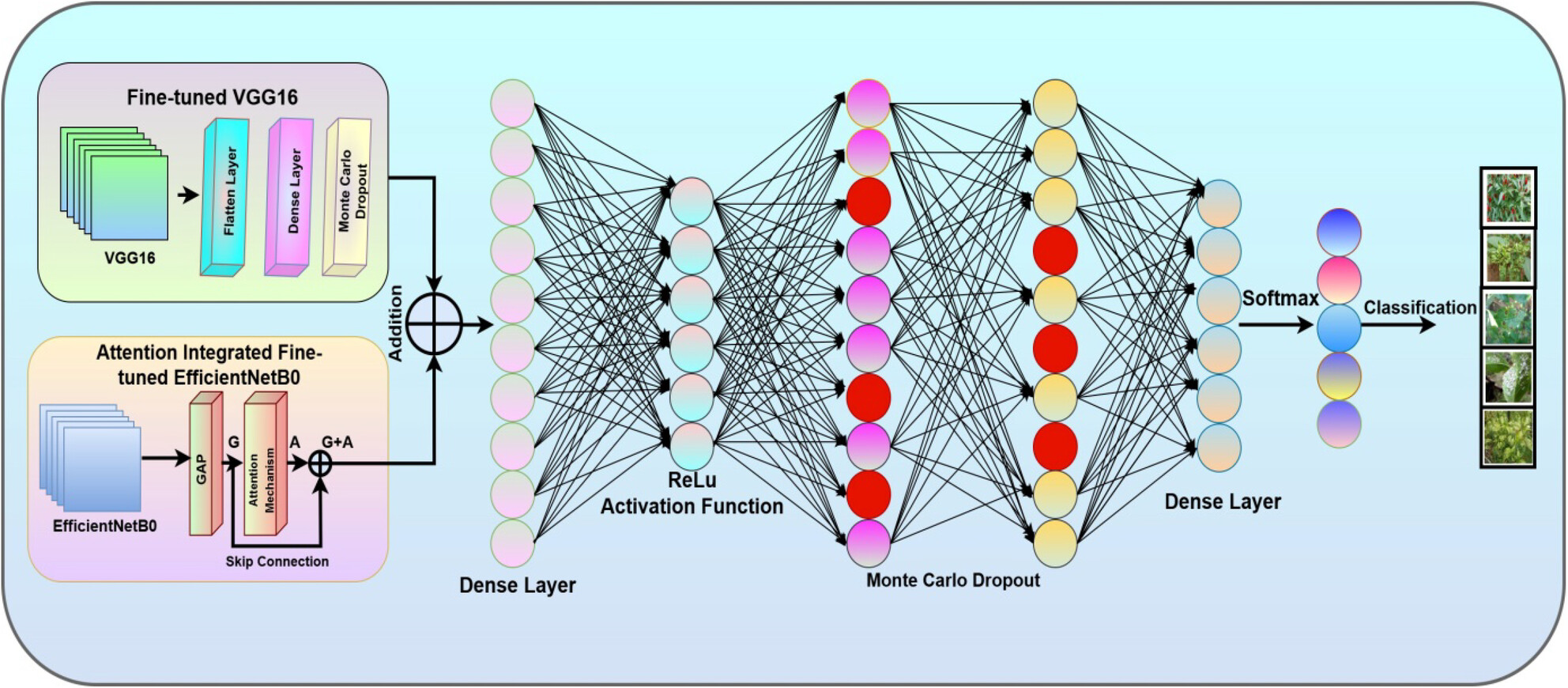
Introduced VGG-EffAttnNet, a hybrid deep learning model combining VGG16 and EfficientNetB0 with an attention mechanism and Monte Carlo Dropout. Achieved 99% accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score across five chili plant disease classes. Outperformed individual models and state-of-the-art methods, demonstrating superior robustness, generalization, and suitability for real-time precision agriculture.
Comprehensive Analysis of 50 Edible Flowers From Yunnan Province: Active Components, Antioxidant Capacity, Tyrosinase Inhibition, and Antimicrobial Activity
- First Published: 21 July 2025
Functional Food Ge-Zhi Soup Ameliorates Acute Liver Injury Through the AKT/GSK3β/PPARα Pathway
- First Published: 21 July 2025
Explainable AI for Cotton Leaf Disease Classification: A Metaheuristic-Optimized Deep Learning Approach
- First Published: 22 July 2025

A hybrid deep learning (DL) model combining EfficientNetB3 and InceptionResNetV2 achieved 98% accuracy in classifying six types of cotton leaf diseases. Genetic Algorithm (GA) optimization improved model generalization, while LIME and SHAP provided interpretable visual and feature-based explanations, enhancing trust among users. The model is lightweight, deployable on mobile devices, and shows high performance even on visually similar disease categories, supporting real-time precision agriculture.
Food Price Changes, Household Food and Nutrition Security in Ethiopia: Evidence From Household Level Analysis Through a Gender Lens
- First Published: 23 July 2025

The study reveals that rising food prices disproportionately impact vulnerable groups, notably female-headed and low-income households, by increasing food expenditure shares and reducing dietary diversity. Households aged 26–49 experience notable declines in diet quality, influenced by income, size, and resource access. Targeted policy interventions that empower women and address gender-based inequalities in resource access and decision-making are essential for improving food security and nutrition outcomes, particularly for female-headed households.
Incorporation of Pomegranate (Punica granatum) Extract Enhanced the Concentration of Bioactive Compounds and Shelf Life of Bread
- First Published: 24 July 2025
Bidirectional Causal Associations Between Endogenous/Exogenous Antioxidant Levels and Risks of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Three Complications
- First Published: 24 July 2025
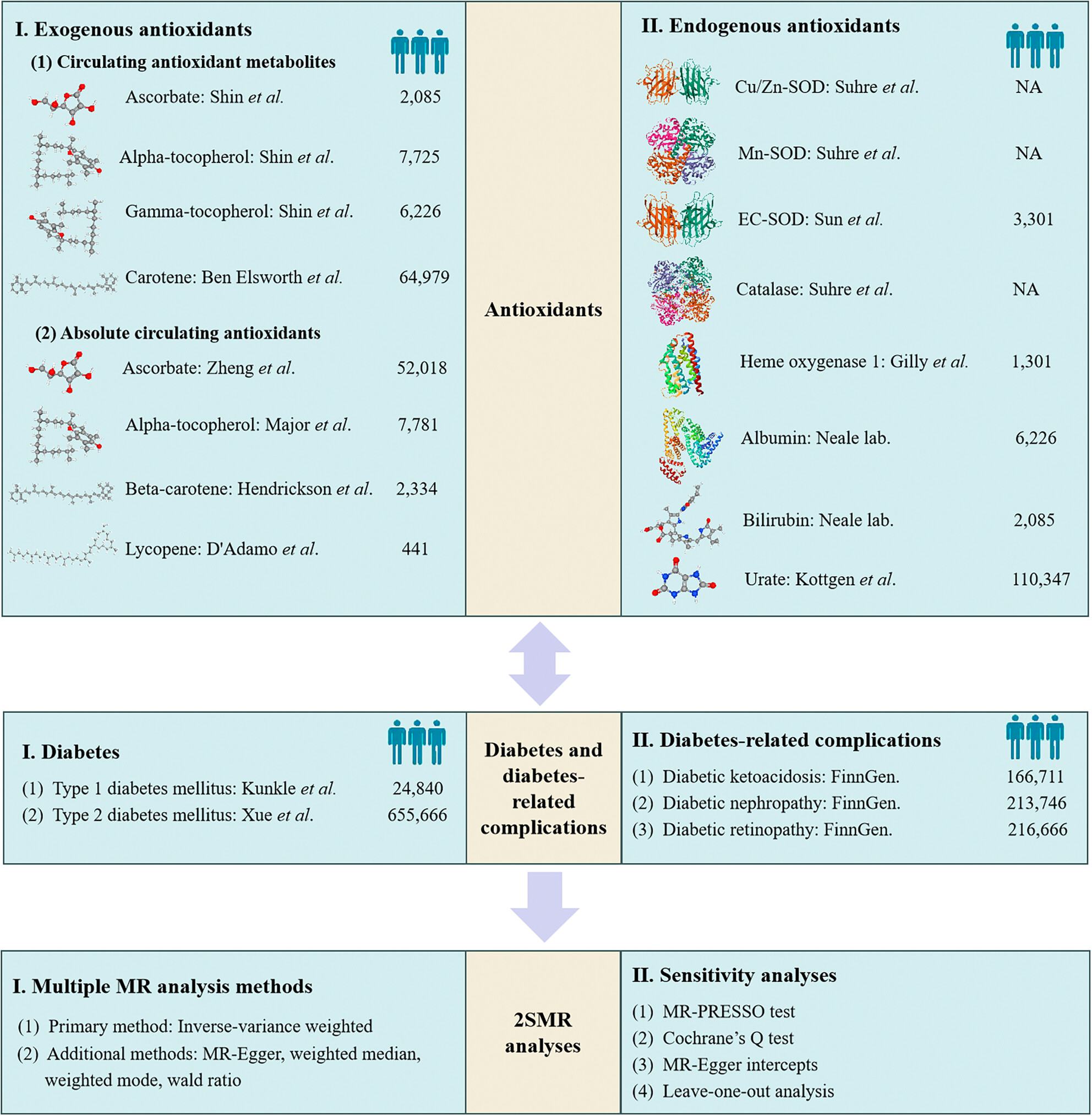
The bidirectional causal associations between levels of a series of endogenous and exogenous antioxidants and risks of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), as well as three complications, diabetic ketoacidosis, diabetic nephropathy, and diabetic retinopathy, were investigated by Mendelian randomization analyses.
Analysis of the Aerial Parts of Millettia speciosa Champ. and Mechanistic Study of Its Active Ingredient Formononetin in Improving Metabolic Syndrome
- First Published: 24 July 2025

Millettia speciosa Champ. is a traditional medicinal and edible plant. Its aerial parts are often discarded, leading to resource waste. HPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS analysis identified a total of 41 chemical compounds in the stems, branches, and leaves of M. speciosa. Network pharmacology screening identified Formononetin (FMN) as a key compound of M. speciosa. FMN could downregulate the expression of Iba-1 and GFAP in the hypothalamus of metabolic syndrome mice and alleviate neuronal damage in the hypothalamus. It may also improve glycolipid metabolism disorders by inhibiting the central NF-κB signaling pathway. In this study, we preliminarily demonstrated that the aerial parts of M. speciosa have significant medicinal value, providing theoretical guidance for the effective utilization of M. speciosa resources.
Black Tea Aqueous Extract Extends Yeast Longevity via Antioxidant Gene Activation: Transcriptomic Analysis of Anti-Aging Mechanisms
- First Published: 24 July 2025
Protective Effects of Calligonum comosum as a Natural Remedy to Counteract Pregabalin-Induced Toxicity: Insights From Chemical Profiling, In Vivo, and In Silico Analyses
- First Published: 25 July 2025
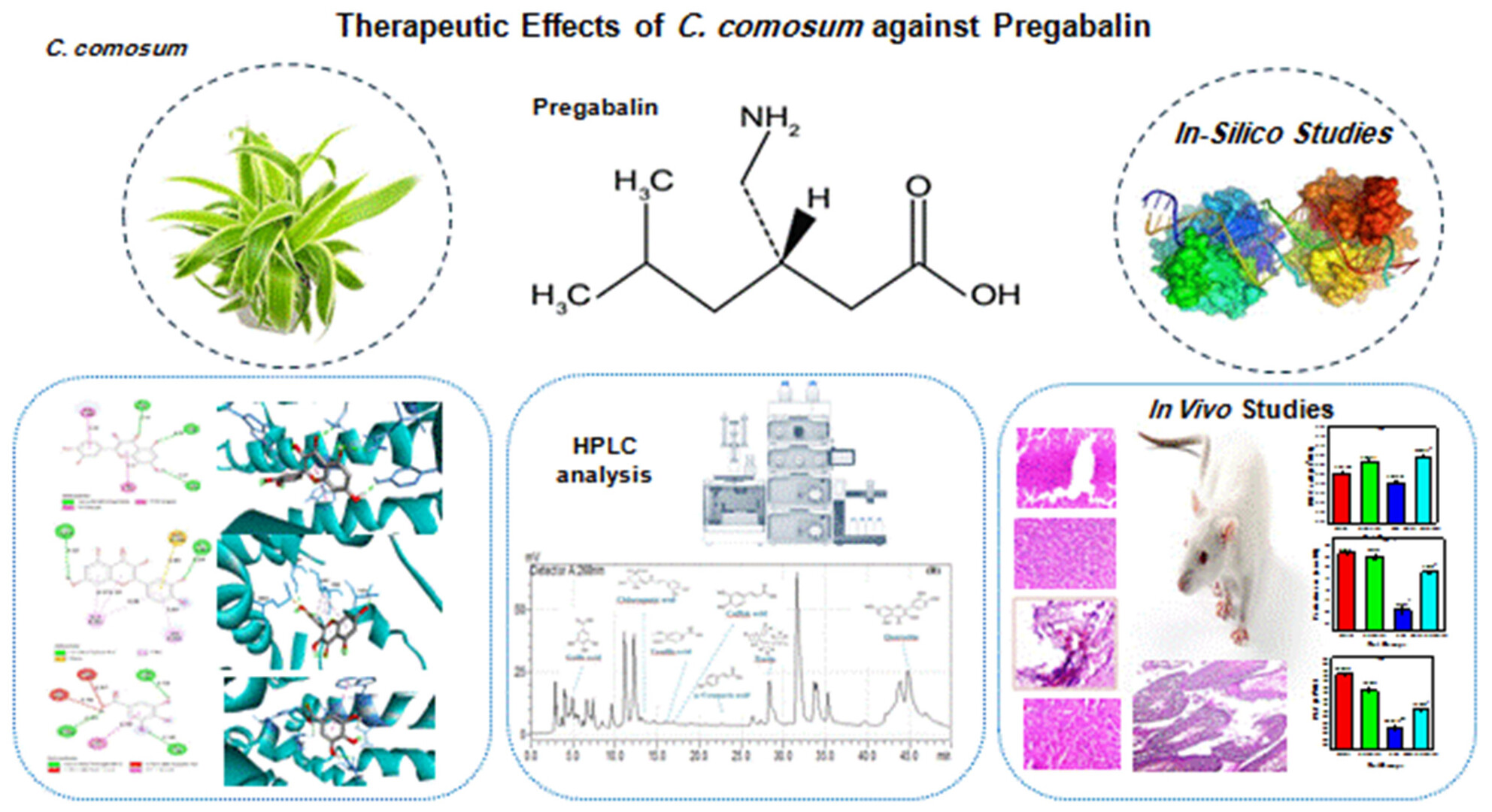
This study highlights the significant therapeutic effects of C. comosum extract in counteracting PGB-induced toxicity in the liver, kidneys, and testes. Furthermore, in silico analysis offered insights into the protective molecular mechanisms of C. comosum phytochemicals against PGB-induced toxicity. The integration of these computational and experimental findings underscores the potential of C. comosum as a natural remedy for PGB-induced toxicity, providing a strong basis for future studies on natural therapeutic alternatives to mitigate drug-related adverse effects.
Examining the Relationship Between Dietary Glycemic Load (GL), Glycemic Index (GI), and the Odds of Diminished Ovarian Reserve: A Case–Control Study
- First Published: 24 July 2025

The higher dietary glycemic index (GI) and glycemic load (GL) were significantly associated with indicators of diminished ovarian reserve (DOR), including reduced antral follicle count (AFC) and increased odds of DOR. These associations persisted even after controlling for key confounding variables such as physical activity, energy intake, fat mass (FM), and BMI.
REVIEW
Gut-Brain Axis in Obesity: How Dietary Patterns Influence Psychological Well-Being and Metabolic Health?
- First Published: 24 July 2025
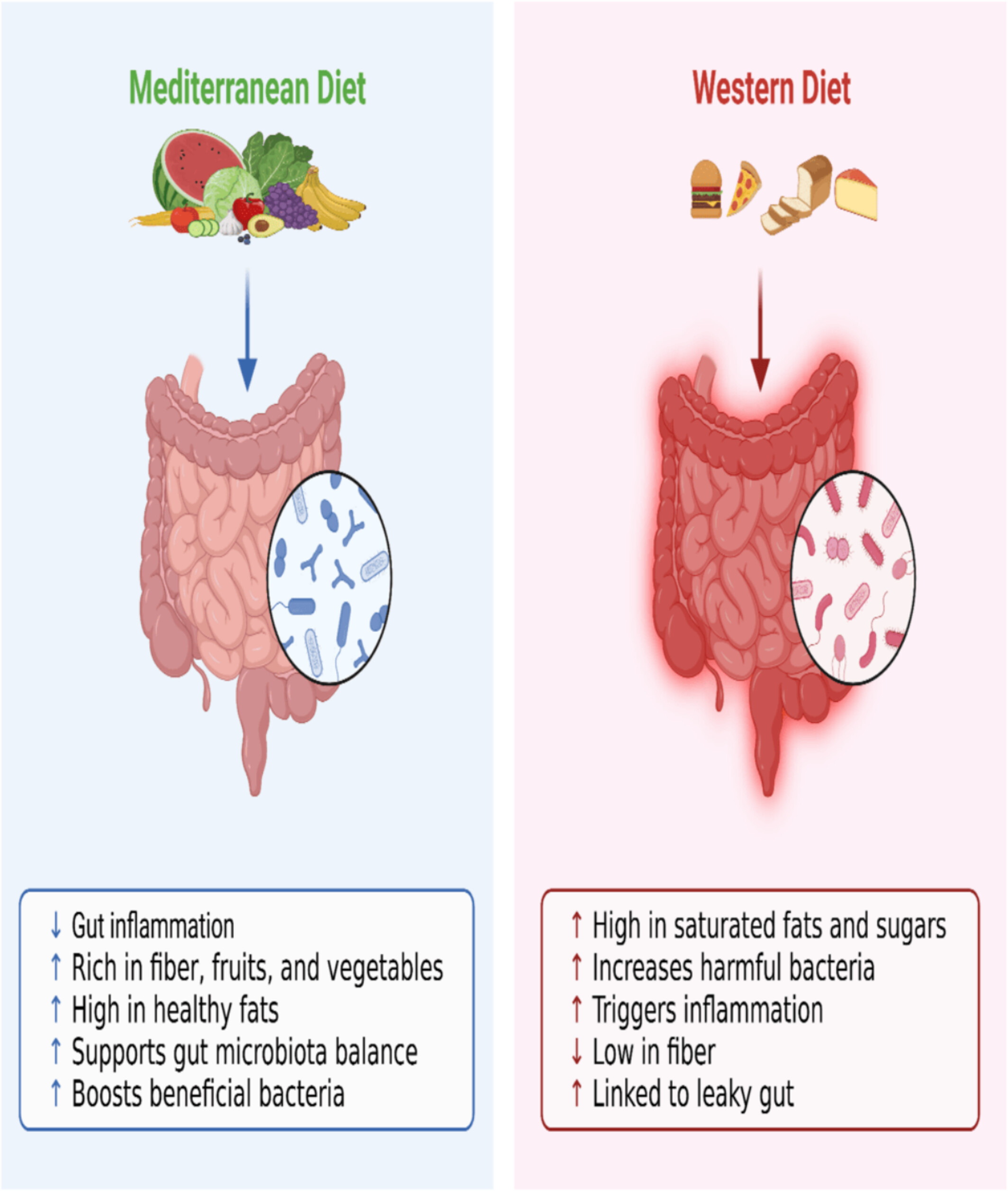
Therapeutic diets that can influence metabolic and psychological outcomes, such as prebiotics, probiotics, and fiber-rich nutrition, are examined. Individualized nutrition through microbiome profiling and integrative treatment models that combine dietary intervention, psychological treatment, and medical management are among the future directions covered in this paper. This review discusses the gut-brain axis as a viable approach to obesity management by integrating the disciplines of psychology, microbiology, and nutrition science.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Apteranthes tuberculata's Antidiabetic Potential: Exploring Phytochemicals, Screening Antioxidant Activity, and Validating DPP-4 Inhibition Using In Vitro and In Silico Approaches
- First Published: 24 July 2025

Metabolomics revealed 24 major compounds, mainly glycosides, flavonoids, and triterpenes. Antidiabetic compounds Kaempferol-7-O-rutinoside and Kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside-7-O-glucoside show maximum inhibiting activity for DPP4 protein (in vitro and in silico). Out of 24 compounds, 5 demonstrate no PAINS and break alerts.
The Effect of Non-Nutritive Sweeteners' Consumption on Body Weight: A Randomized-Controlled Trial
- First Published: 24 July 2025
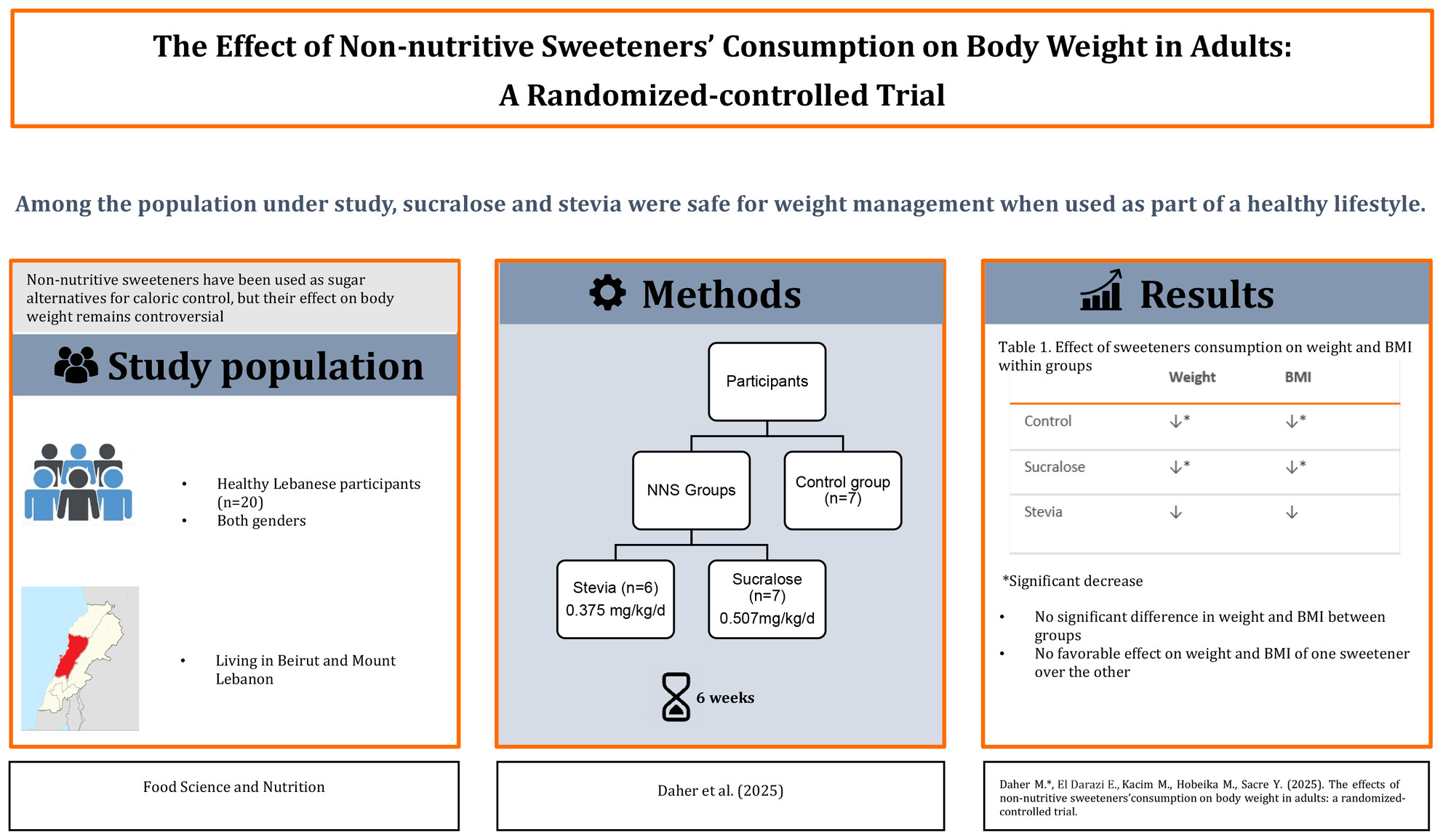
Non-nutritive sweeteners have been used as sugar alternatives for caloric control, but their effect on body weight remains controversial. A randomized-controlled trial was conducted on a final number of 20 healthy Lebanese participants over a period of 6 weeks, with an initial screening session and two follow-up sessions. Among the population under study, sucralose and stevia were safe for weight management when used as part of a healthy lifestyle.
Integrated Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Profiling Identifies Candidate Genes and Pathways Associated With Pedicel Abscission Susceptibility in Capsicum annuum
- First Published: 24 July 2025
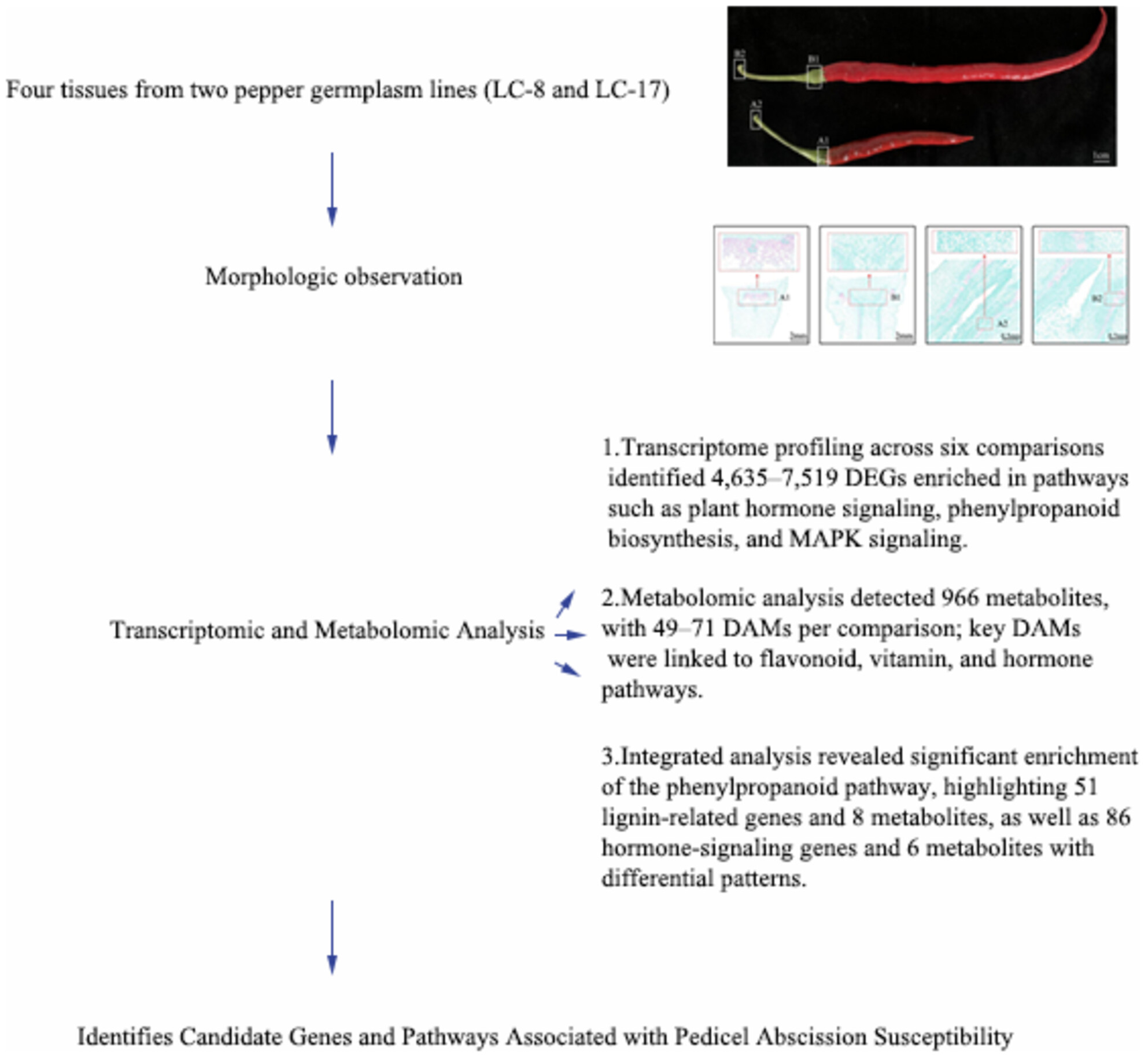
Capsicum germplasm lines with distinct pedicel abscission behaviors were analyzed via integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics. Differential lignification patterns, hormone signaling, and flavonoid biosynthesis were linked to abscission susceptibility. Key regulators of lignin and phytohormone pathways underpin structural and metabolic control of the abscission zone.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Burdekin Plum During Fruit Development
- First Published: 25 July 2025
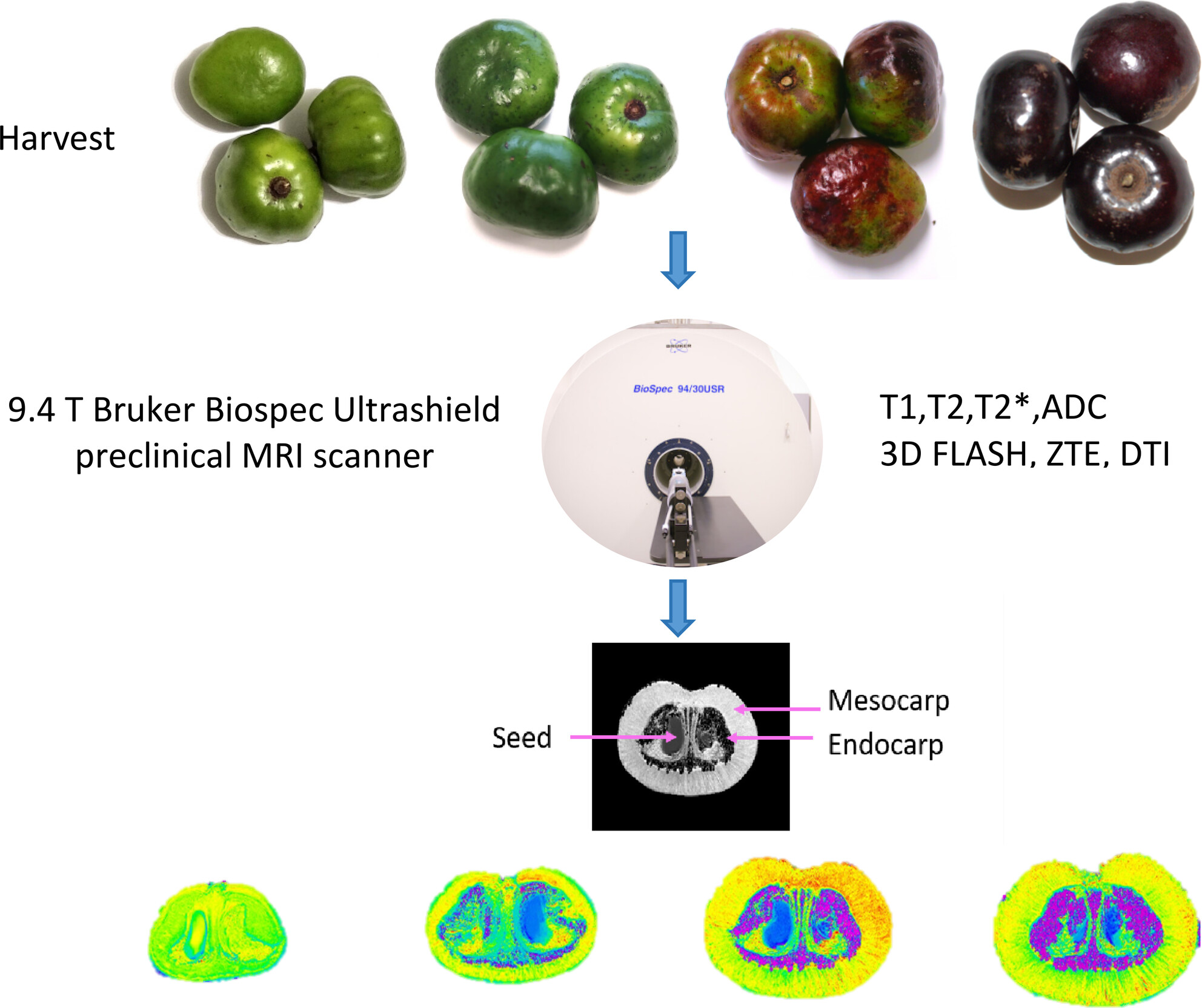
MRI was used to distinguish major tissues in Burderkin plums, including mesocarp, endocarp, and seeds. Quantitative T1, T2, T2*, and ADC of these tissues changed during fruit development, with the most notable changes happening from stage 1 to stage 2. Diffusion MRI tractography was used to visualize the fruit water transportation pathways.
Geraniin Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis in ApoE−/− Mice
- First Published: 25 July 2025

GE treatment significantly reduced serum concentrations of lipids, oxidative stress damage, lipid deposition, and atherosclerotic plaque lesions in the ApoE−/− mice. A network pharmacology analysis indicated that the beneficial effect of GE treatment on atherosclerosis is closely related to its effect on oxidative stress, cell apoptosis, and inflammatory responses. GE promoted the release of NO, increased the activity of antioxidant enzymes, reduced endothelial cell apoptosis, reduced the production of inflammatory cytokines IL1β, IL6, and TNFα, and activated the Akt/eNOS/NO and GSK-3β/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways in H2O2-treated HUVEC cells.
Impact of Applying Magnetic Fields on the Development of Postbiotic Metabolites and Probiotic Microorganisms in Kombucha Tea
- First Published: 25 July 2025
In Vitro Antioxidant Potential of Various Plant Extracts and Application of the Extracts With the Highest Antioxidant Activity in Ground Beef for Enhancing the Quality and Shelf Life
- First Published: 25 July 2025

This study aimed to assess in vitro antioxidant activity of P, AR, CR, CA and L extracts, and then select those with the highest antioxidant activity (P and CA) and evaluate their influence on lipid oxidation, physico-chemical and microbiological features in cooked ground beef. The findings indicated that CA or P extract incorporation in the ground beef exhibited capability for lipid oxidation inhibition and thus can be utilized to enhance quality and shelf life of the meat products.
Sex-Specific Associations Between Prebiotic Supplement Intake and Sarcopenia Risk: Evidence From NHANES
- First Published: 25 July 2025

The study found that prebiotic intake is significantly associated with a reduced risk of sarcopenia in adult women but not in men, based on data from NHANES 2011–2014 using FNIH criteria. After adjusting for multiple confounders, female prebiotic consumers had lower odds of sarcopenia, while no significant association was observed in males. These results suggest potential sex-specific benefits of prebiotic consumption for muscle health and highlight the need for further research on underlying mechanisms.