Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
April 2023 at a glance: focus on diagnosis and comorbidities
- Pages: 445-447
- First Published: 27 April 2023
VIEWPOINTS
Sex differences in heart failure: the evolving use of biomarkers
- Pages: 448-449
- First Published: 28 February 2023
Time to reconsider the perception and management of hypertensive heart disease
- Pages: 450-453
- First Published: 23 February 2023
Dosing of iron supplementation for iron-deficient patients with heart failure: should we prefer more intensive or less intensive repletion targets?
- Pages: 454-456
- First Published: 28 February 2023
CONSENSUS STATEMENTS
Inotropic therapy in patients with advanced heart failure. A clinical consensus statement from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology
- Pages: 457-468
- First Published: 27 February 2023
European Society of Cardiology quality indicators for the care and outcomes of adults with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology
- Pages: 469-477
- First Published: 16 March 2023
EPIDEMIOLOGY, DIAGNOSIS AND ASSESSMENT
Review
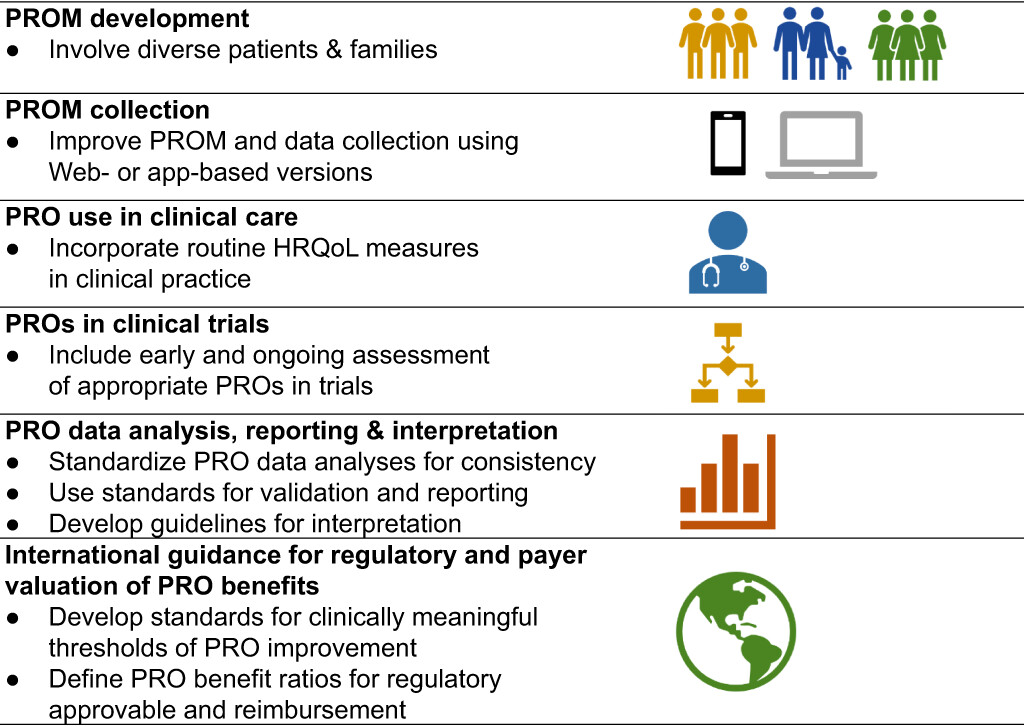
Patient-reported outcome measures and patient engagement in heart failure clinical trials: multi-stakeholder perspectives
- Pages: 478-487
- First Published: 16 March 2023
Research articles
Characteristics and outcomes of patients with a history of cancer recruited to heart failure trials
- Pages: 488-496
- First Published: 15 March 2023
Deep phenotype characterization of hypertensive response to exercise: implications on functional capacity and prognosis across the heart failure spectrum
- Pages: 497-509
- First Published: 29 March 2023
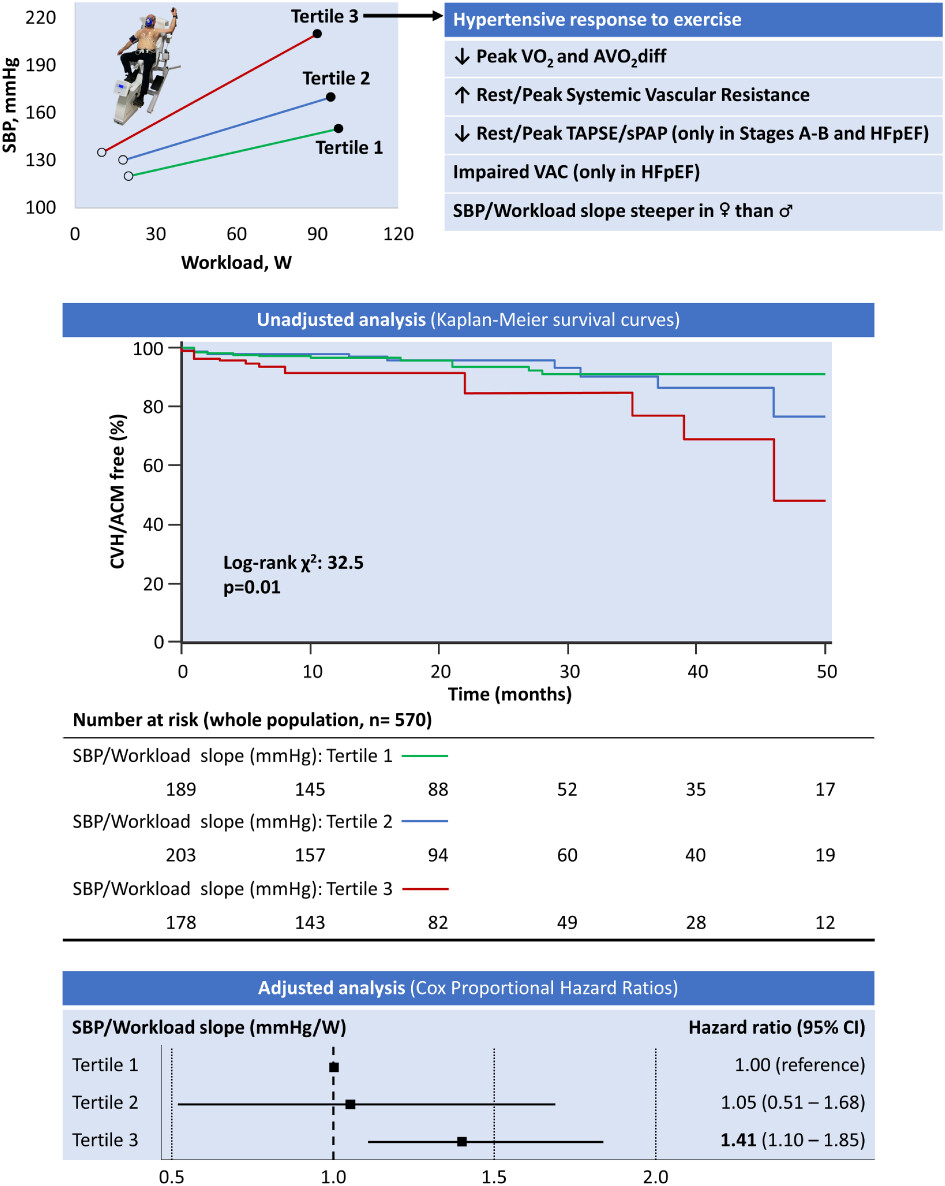
Impact of hypertensive response to exercise on functional capacity and prognosis. Cumulative survival and relative risk of all-cause mortality (ACM) and cardiovascular hospitalizations (CVH) after a median follow-up of 16 months per tertile of systolic blood pressure (SBP)/workload slope. Unadjusted analysis (Kaplan–Meier survival curves) for the primary outcome in the whole patient population. Adjusted analysis (Cox proportional hazard ratios) illustrating higher mortality in the highest tertile of the SBP/workload slope. Hazard ratios are adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, previous myocardial infarction, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, rest and peak SBP, rest and peak cardiac output, rest and peak left ventricular ejection fraction, and medications (beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers). AVO2diff, arterial–venous oxygen content difference; CI, confidence interval; HFpEF, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; sPAP, systolic pulmonary artery pressure; TAPSE, tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion; VAC, ventricular–arterial coupling; VO2, oxygen consumption.
Left ventricular wall thickness and severity of cardiac disease in women and men with transthyretin amyloidosis
- Pages: 510-514
- First Published: 15 March 2023
Prevalence, characteristics and outcomes of older patients with hereditary versus wild-type transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy
- Pages: 515-524
- First Published: 16 January 2023
Invited editorial
Variant and wild type transthyretin amyloidosis: two sides of the same coin or different currencies in different pockets?
- Pages: 525-527
- First Published: 23 February 2023
IRON SUPPLEMENTATION
Research article
Intravenous iron in patients with heart failure and iron deficiency: an updated meta-analysis
- Pages: 528-537
- First Published: 23 February 2023
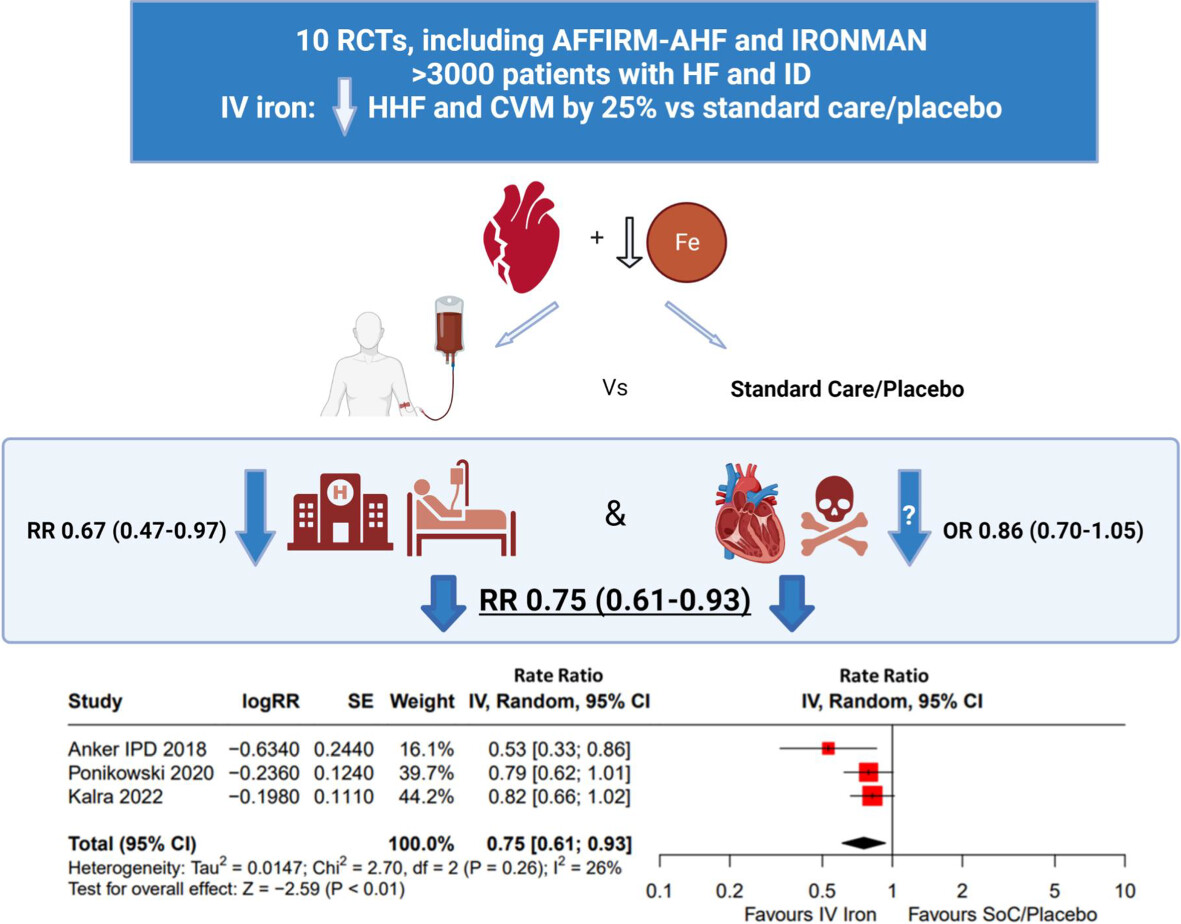
In a meta-analysis of ten randomized controlled trials (RCTs) including AFFIRM-AHF and IRONMAN of over 3000 patients with heart failure (HF) and iron deficiency (ID), compared to standard care/placebo, intravenous (IV) iron reduced the primary outcome of recurrent hospitalisations for heart failure (HHF) and cardiovascular mortality (CVM) by 25%. The effect was mainly driven by a reduction in HHF with the effect on CVM being inconconclusive. Created in BioRender.com. Additional icons provided from http://icon-library.com/icon/heart-disease-icon-3.html.html Heart Disease Icon #293840. CI, confidence interval; CVM, cardiovascular mortality; HF, heart failure; HHF, hospitalization for heart failure; I, iron deficiency; IV, intravenous/interval variable; OR, odds ratio; RCT, randomized controlled trial; RR, risk rate; SE, standard error; SoC, standard of care.
Invited editorial
Benefits of intravenous iron supplementation in patients with heart failure: mounting evidence and open questions
- Pages: 538-540
- First Published: 01 February 2023
MITRAL REGURGITATION
Research articles
Impact of mitral regurgitation in patients with acute heart failure: insights from the RELAX-AHF-2 trial
- Pages: 541-552
- First Published: 13 March 2023
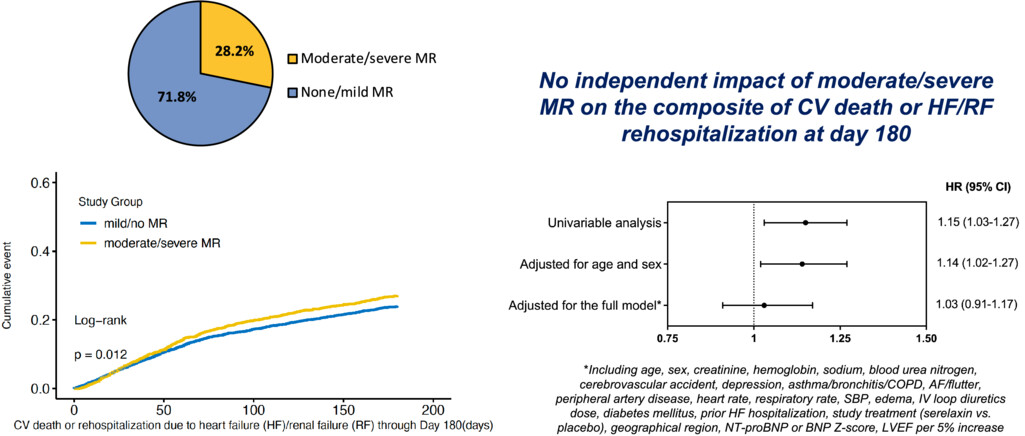
Impact of mitral regurgitation (MR) in patients with acute heart failure (HF): an analysis on 6420 patients from RELAX-AHF-2. AF, atrial fibrillation; BNP, B-type natriuretic peptide; CI, confidence interval; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CV, cardiovascular; HR, hazard ratio; IV, intravenous; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; RF, renal failure; SBP, systolic blood pressure.
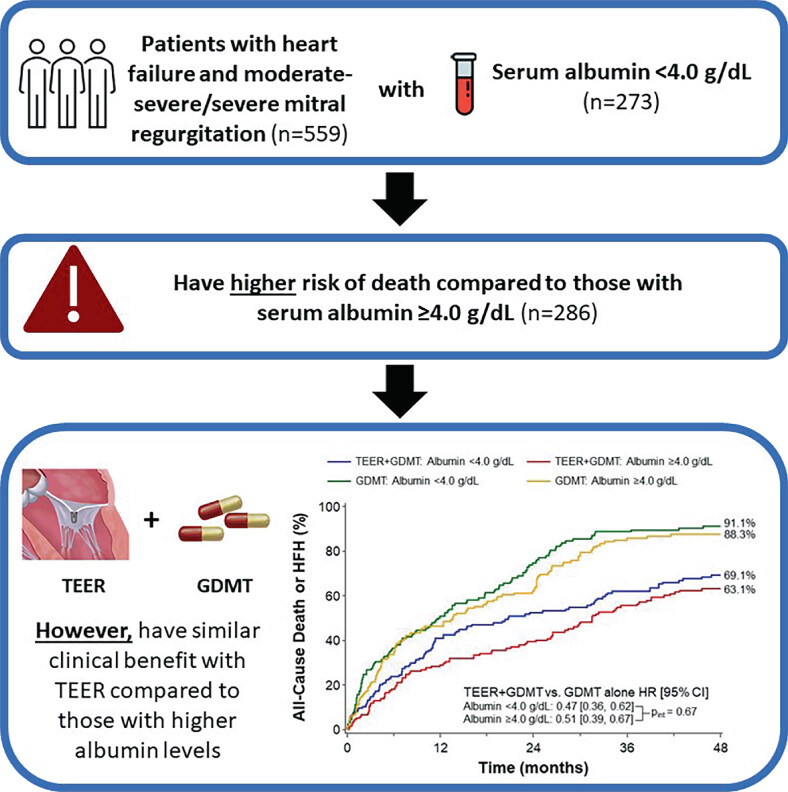
Association between serum albumin and outcomes in heart failure and secondary mitral regurgitation: the COAPT trial
- Pages: 553-561
- First Published: 23 February 2023
MECHANICAL CIRCULATORY SUPPORT
Research article
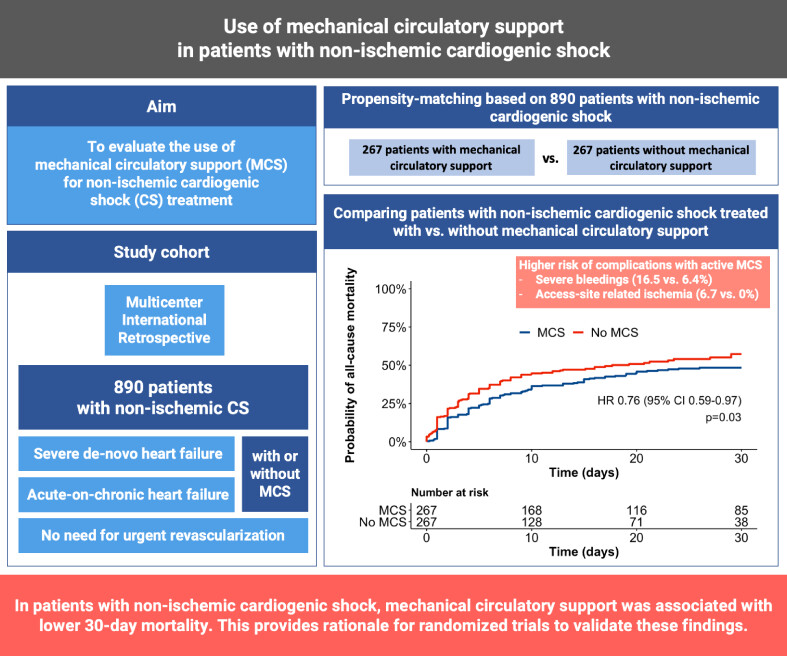
Use of mechanical circulatory support in patients with non-ischaemic cardiogenic shock
- Pages: 562-572
- First Published: 13 February 2023
Invited editorial
For the best management, please ask for assistance!
- Pages: 573-575
- First Published: 16 March 2023
CELL THERAPY
Research article
Effect of allogeneic adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cell treatment in chronic ischaemic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction – the SCIENCE trial
- Pages: 576-587
- First Published: 16 January 2023
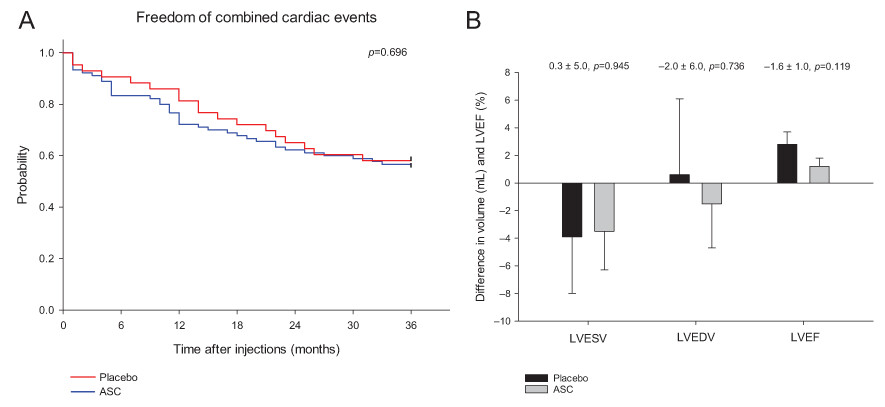
Treatment of chronic ischaemic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) patients with allogeneic adipose tissue-derived stromal cells (ASC) was safe but without any demonstratable restoration of cardiac function or clinical symptoms. (A) Kaplan–Meier plot of freedom of cumulative combined cardiac-related adverse events during a 3-year follow-up period. (B) Differences in baseline to 6-month follow-up in left ventricular end-systolic volume (LVESV), left ventricular end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) in ASC treated compared to placebo patients.
Invited editorial
Cell therapy for heart failure: lessons learned from SCIENCE
- Pages: 588-590
- First Published: 23 February 2023
RESEARCH LETTERS
Efficacy of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitors for heart failure in black patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Pages: 591-593
- First Published: 15 March 2023
Splanchnic nerve block with botulinum toxin for therapy of chronic heart failure – mechanism of action (SPONGE-HF)
- Pages: 594-596
- First Published: 16 March 2023
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Interleukin-6 in acute heart failure: it does work, but how much? Letter regarding the article ‘Quantifying inflammation using interleukin-6 for improved phenotyping and risk stratification in acute heart failure’
- Page: 597
- First Published: 25 January 2023
Reply to ‘Interleukin-6 in acute heart failure: it does work, but how much?’
- Pages: 597-598
- First Published: 15 February 2023
Letter regarding the article ‘Little at a time: trying to understand the battery of benefits of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in heart failure’
- Page: 598
- First Published: 24 January 2023