Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURES
Front Cover: Label-free spectroscopic tissue characterization using fluorescence excitation-scanning spectral imaging (J. Biophotonics 2/2020)
- First Published: 03 February 2020

A false-colored and merged image of fresh, ex vivo rat kidney acquired using an excitation-scanning hyperspectral imaging system. The spectral image was acquired using excitation wavelengths from 360 to 550 nm. Colors represent principal components extracted from a spectral image cube featuring no added labels or markers.
Further details can be found in the article by Peter F. Favreau, Joshua A. Deal, Bradley Harris, et al. (e201900183).
Inside Cover: Optical coherence tomography as a noninvasive 3D real time imaging tool for the rapid evaluation of phenotypic variations in insect embryonic development (J. Biophotonics 2/2020)
- First Published: 03 February 2020
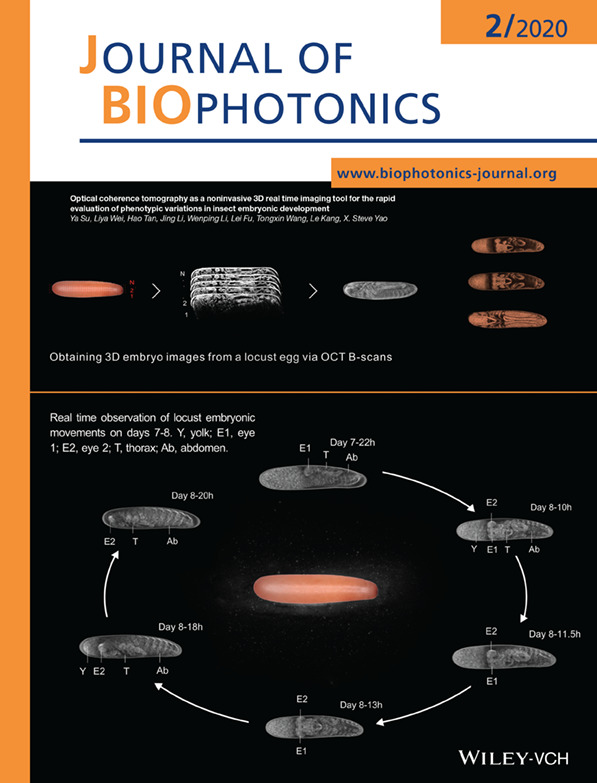
Top: Illustration of how to obtain 3D embryo images from a locust egg using OCT B-scans. The internal structures of the embryo can be clearly identified as it develops.
Bottom: The real time observation of katatrepsis and twist of a lowland locust embryo on days 7-8, as the embryo develops. The embryonic movements can be readily identified by tracking the positions of the embryo's eyes (E1 and E2).
Further details can be found in the article by Ya Su, Liya Wei, Hao Tan, et al. (e201960047).
ISSUE INFORMATION
LETTERS
Phase-sensitive fluorescence detector for parathyroid glands during thyroidectomy: A preliminary report
- First Published: 07 November 2019
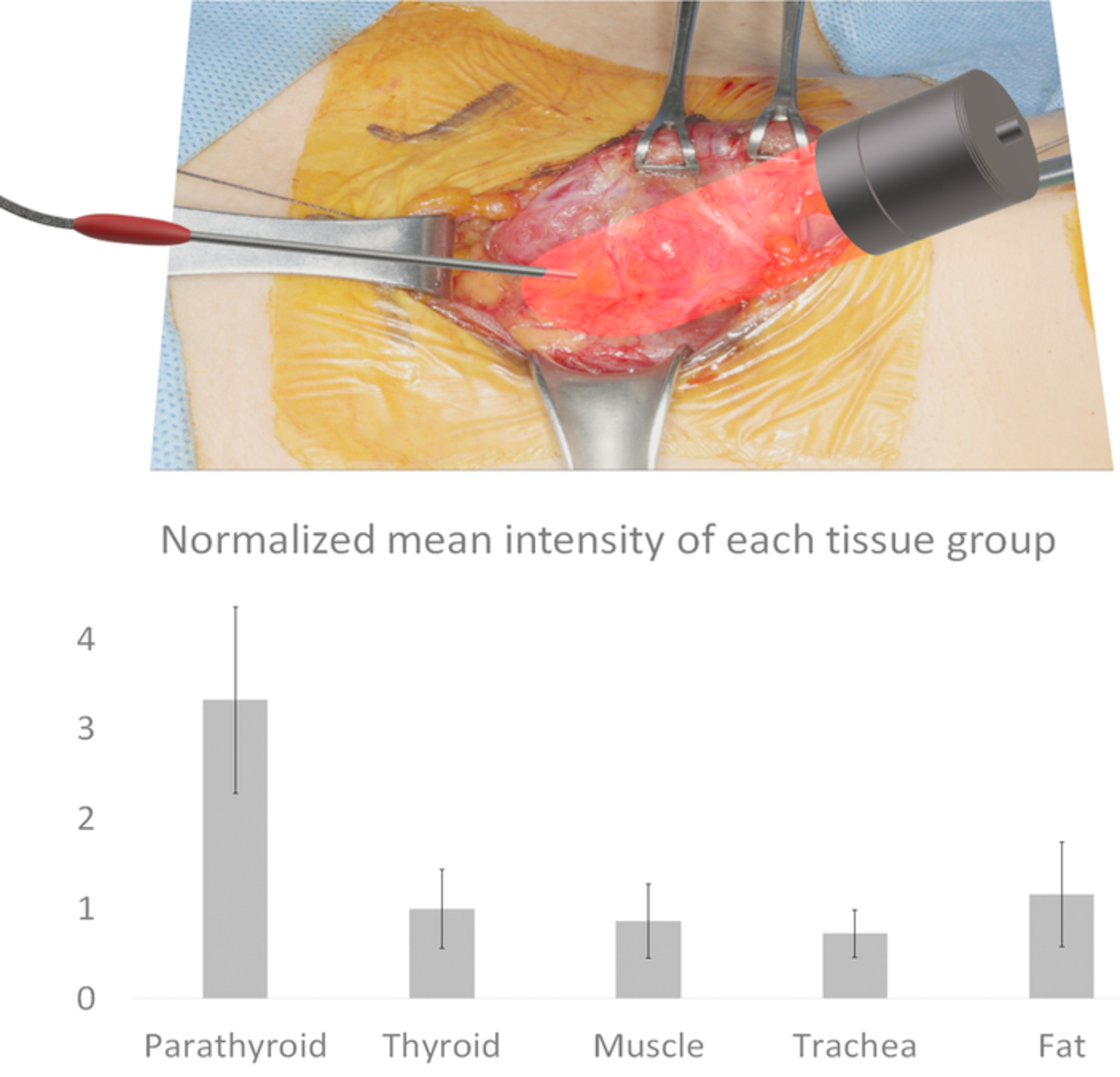
A phase-sensitive autofluorescence detection system was developed to distinguish autofluorescence of parathyroid glands without turning off any surgical lights. Excellent discernment ability was confirmed in vitro experiment with indocyanine green. The parathyroid glands were accurately detected in actual surgery. The feasibility of a phase-sensitive parathyroid autofluorescence detection was verified as a unique system under clinical circumstances.
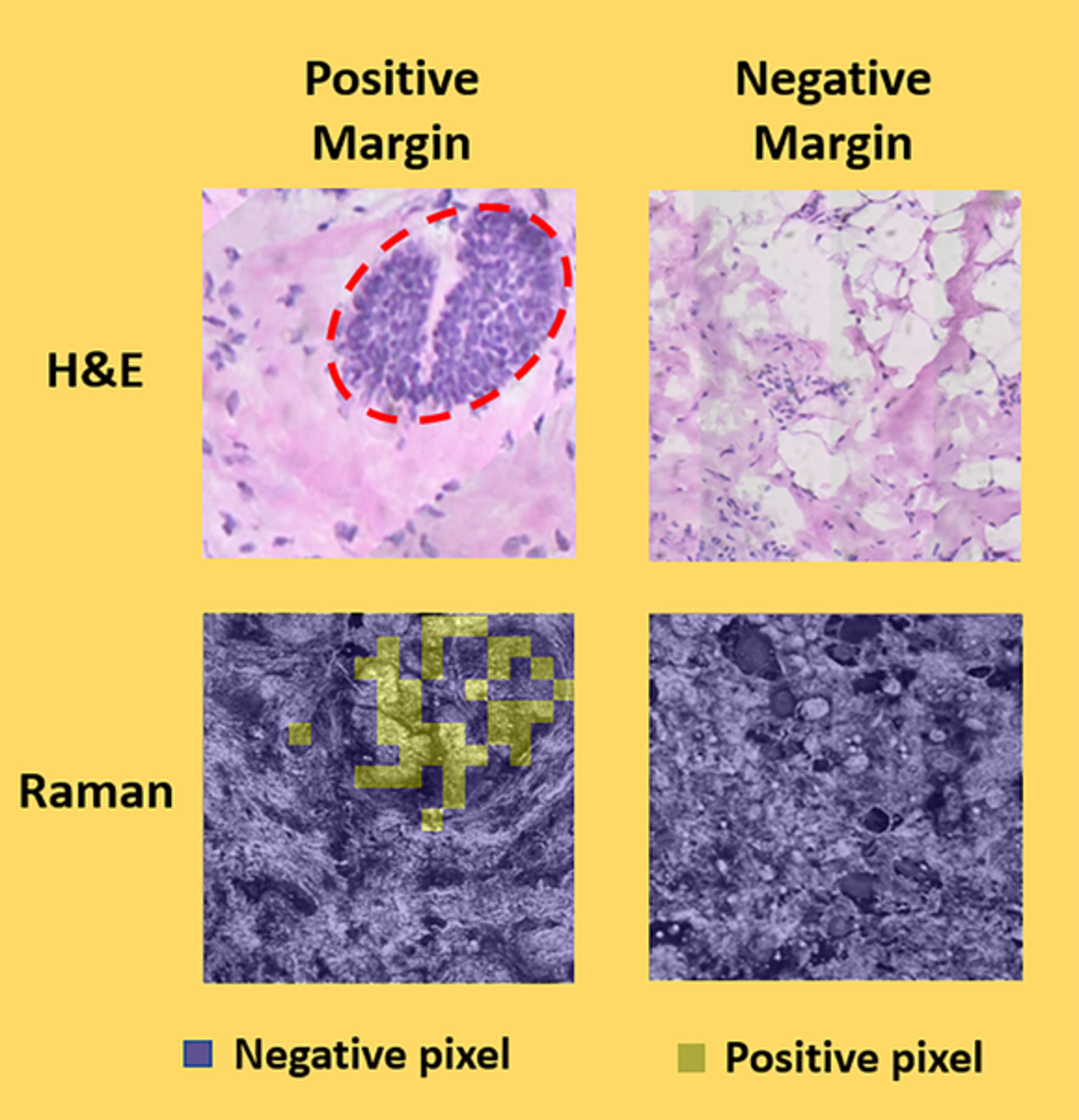
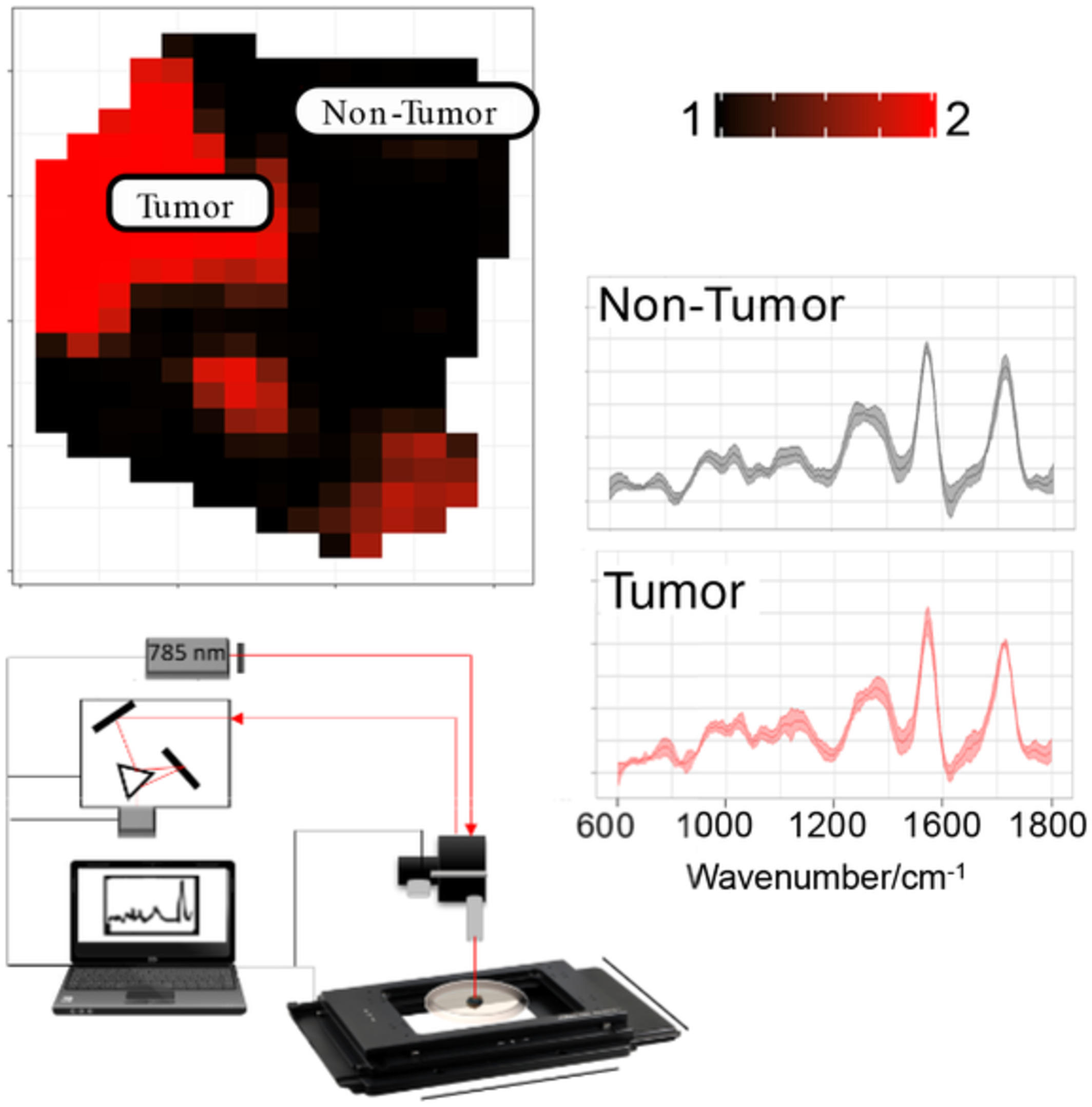
Superpixel Raman spectroscopy for rapid skin cancer margin assessment
- First Published: 22 December 2019
FULL ARTICLES
Label-free spectroscopic tissue characterization using fluorescence excitation-scanning spectral imaging
- First Published: 30 September 2019
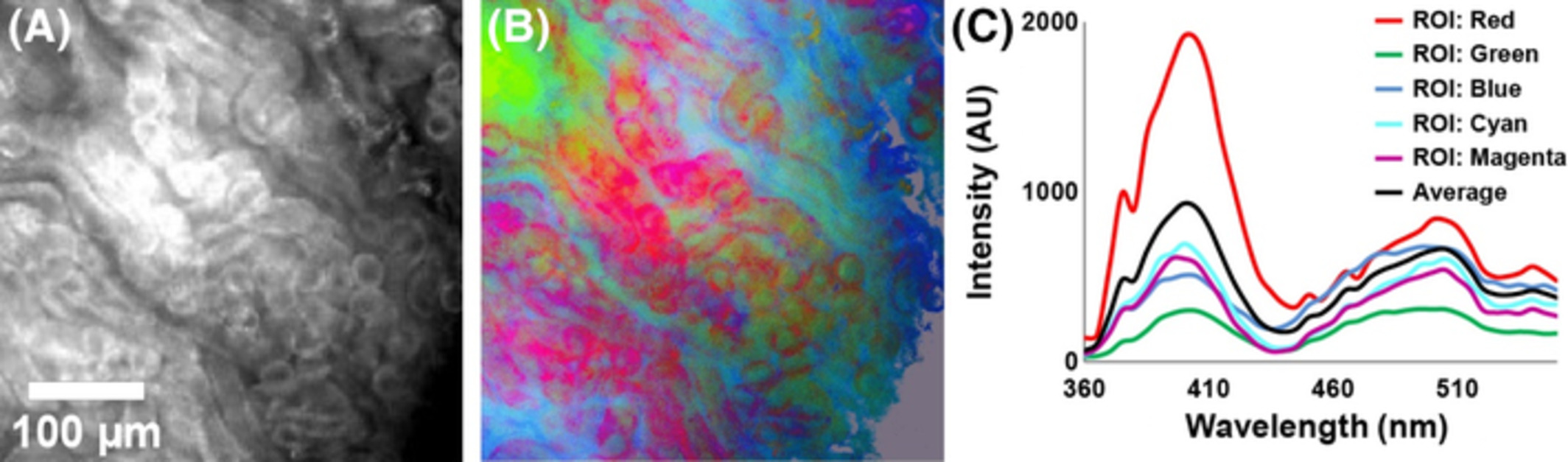
Changes in tissue fluorescence can be a sensitive cancer marker but identifying the molecular origins of these changes remains challenging. This study identified unique tissue spectra corresponding to well-known autofluorescent components using a novel label-free excitation-scanning spectral imaging platform. A suite of four image processing algorithms revealed morphologic contrast generated from autofluorescent components. This approach lays the groundwork for translation of excitation-scanning technologies to clinical imaging platforms.
Optical coherence tomography as a noninvasive 3D real time imaging tool for the rapid evaluation of phenotypic variations in insect embryonic development
- First Published: 04 November 2019
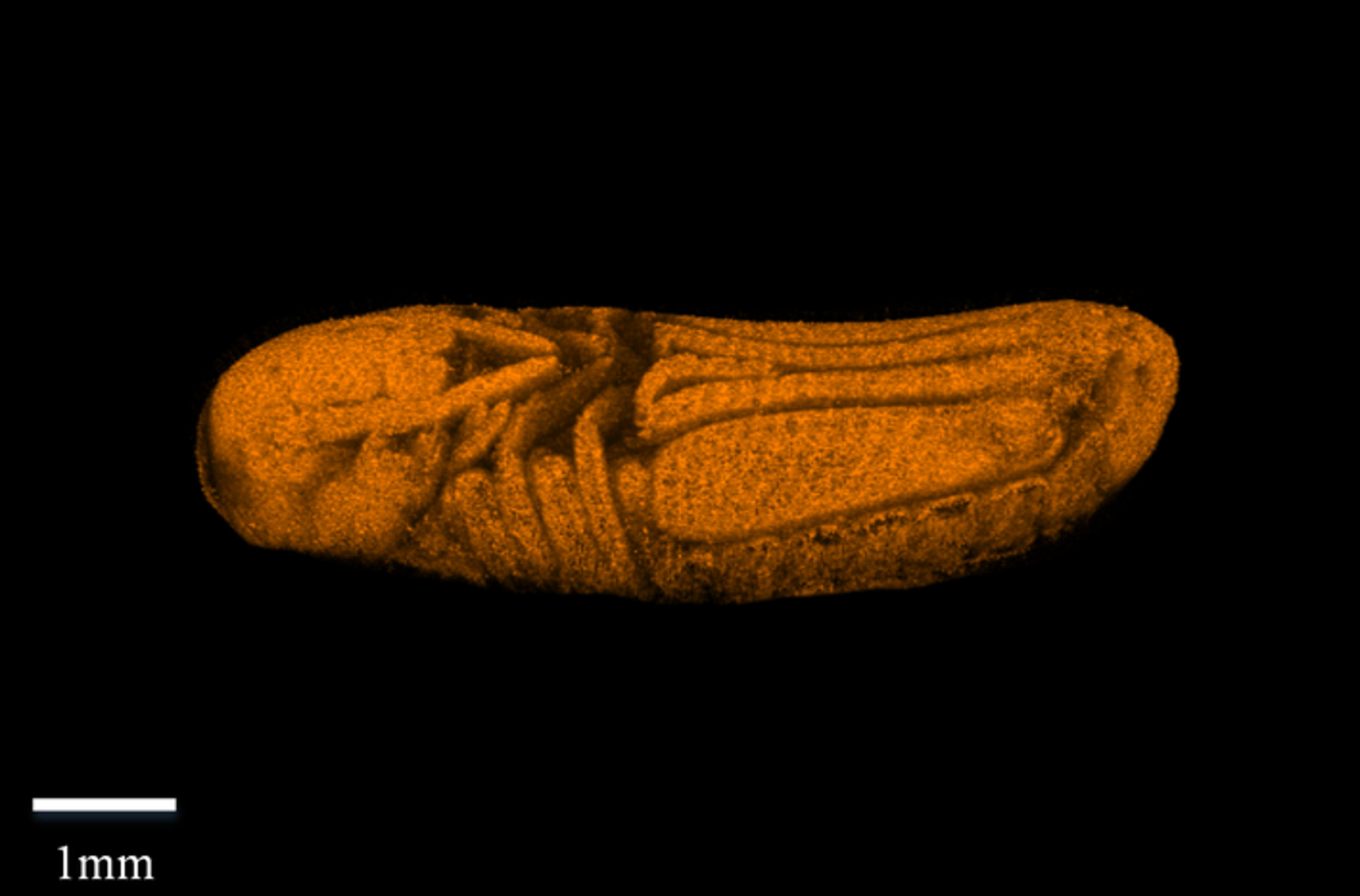
No more dissecting of embryos when studying embryonic development of insects! We demonstrate using optical coherence tomography as a powerful tool to noninvasively exam the detailed embryonic development processes of insects in real time, which not only enables us to capture all the previously known developmental features, but also to discover new ones, and more significantly to effectively detect the early developmental defects of gene-edited embryos with high efficiency.
Full-field swept-source optical coherence tomography and neural tissue classification for deep brain imaging
- First Published: 11 November 2019
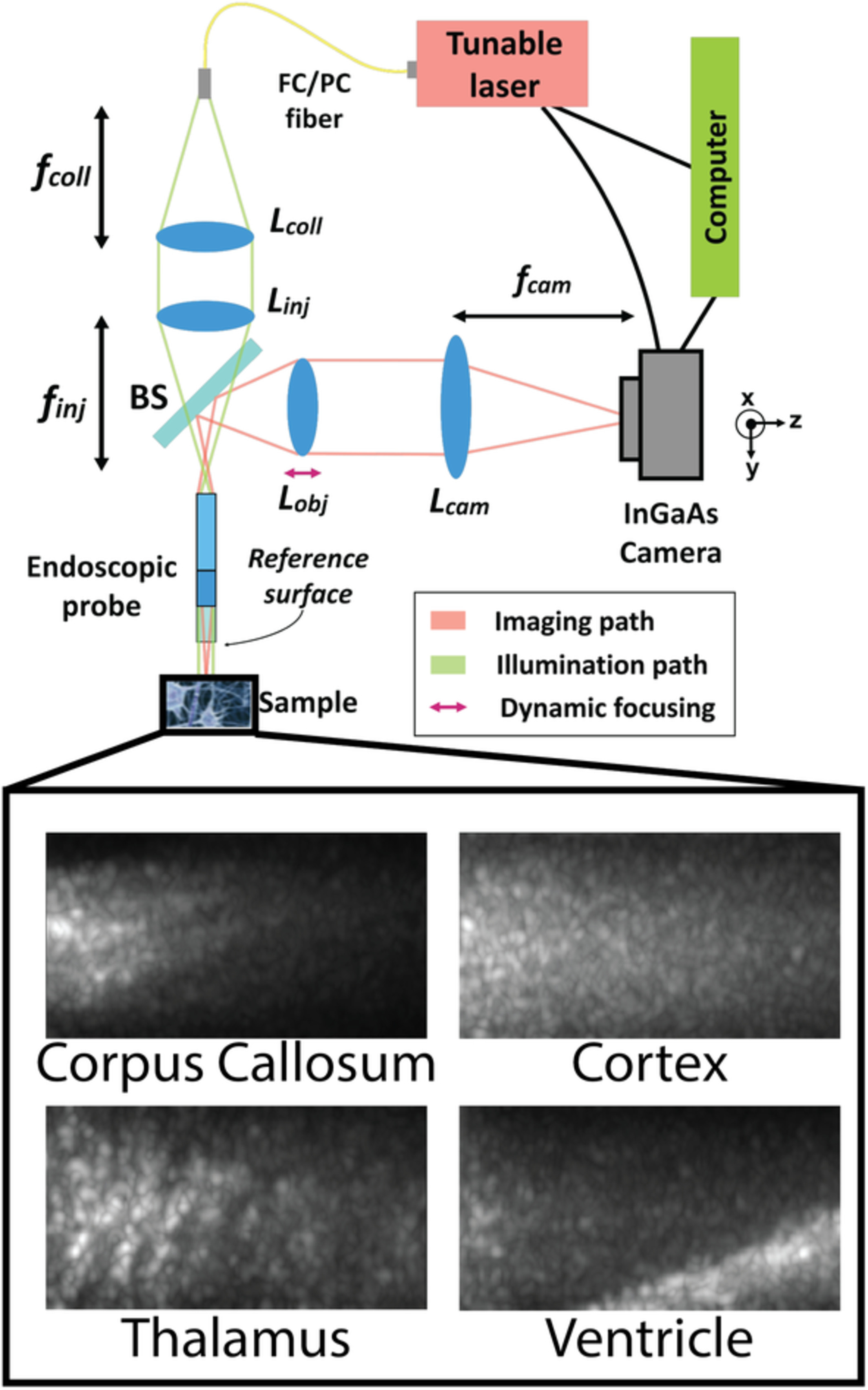
Optical coherence tomography can differentiate brain regions with intrinsic contrast and at a micron scale resolution. We present, to our knowledge, the first full-field swept-source optical coherence tomography system operating near a wavelength of 1310 nm. The proof-of-concept system was integrated with an endoscopic probe tip, which is compatible with deep brain stimulation keyhole neurosurgery. Using classification algorithms involving texture features and optical attenuation, images were successfully classified into three brain tissue types.
Accelerated inactivation of M13 bacteriophage using millijoule femtosecond lasers
- First Published: 25 October 2019
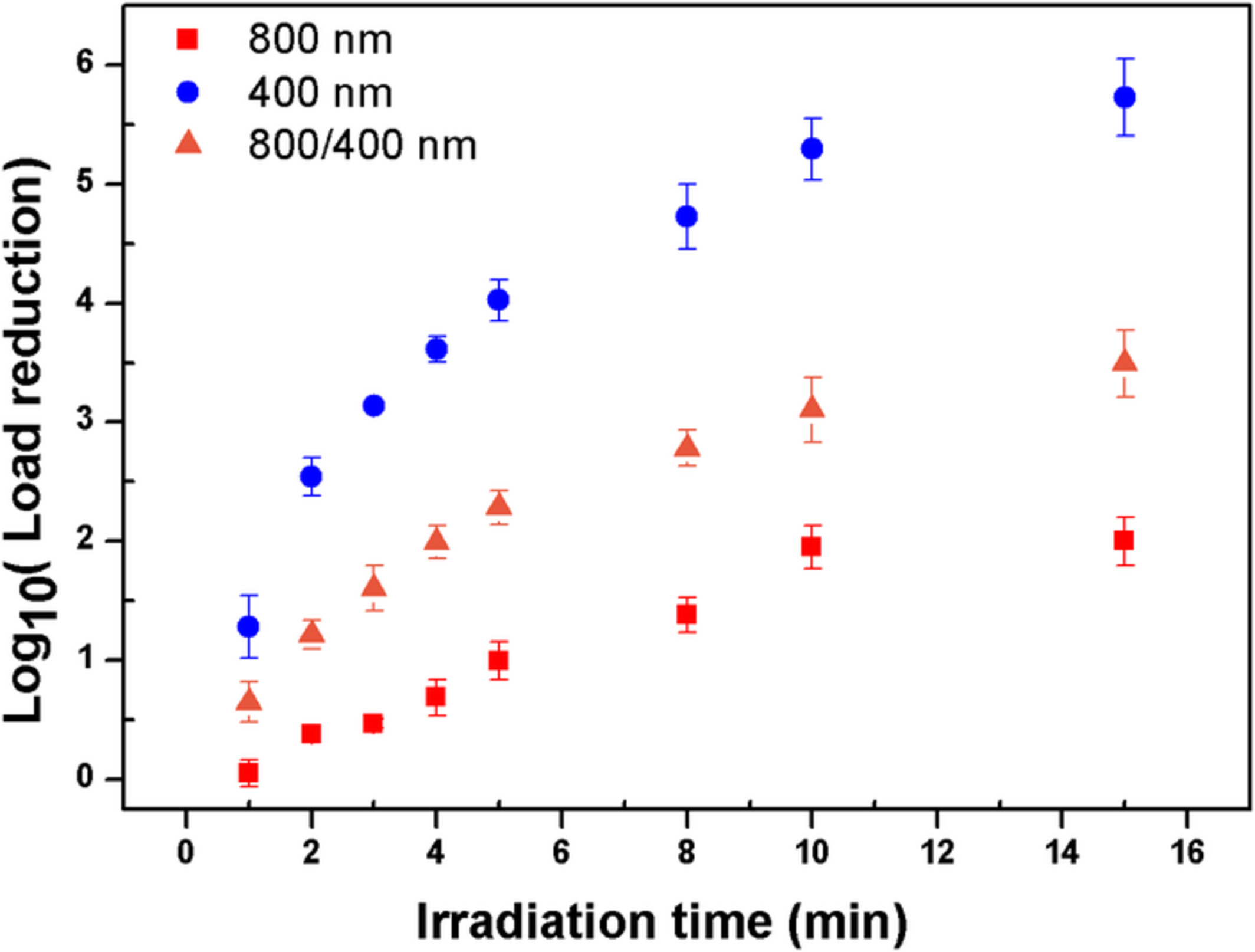
We demonstrate the rapid inactivation of M13 bacteriophages in 1 cc of buffer solution using energetic femtosecond lasers (20 mJ/pulse, 40 fs, 10 Hz, 800 or 400 nm wavelength), with significant load reduction in a matter of minutes. We show that inactivation is much more efficient using the 400 nm laser, increasing rapidly for pulse durations shorter than 200 fs.
Exploration research on the fusion of multimodal spectrum technology to improve performance of rapid diagnosis scheme for thyroid dysfunction
- First Published: 08 October 2019
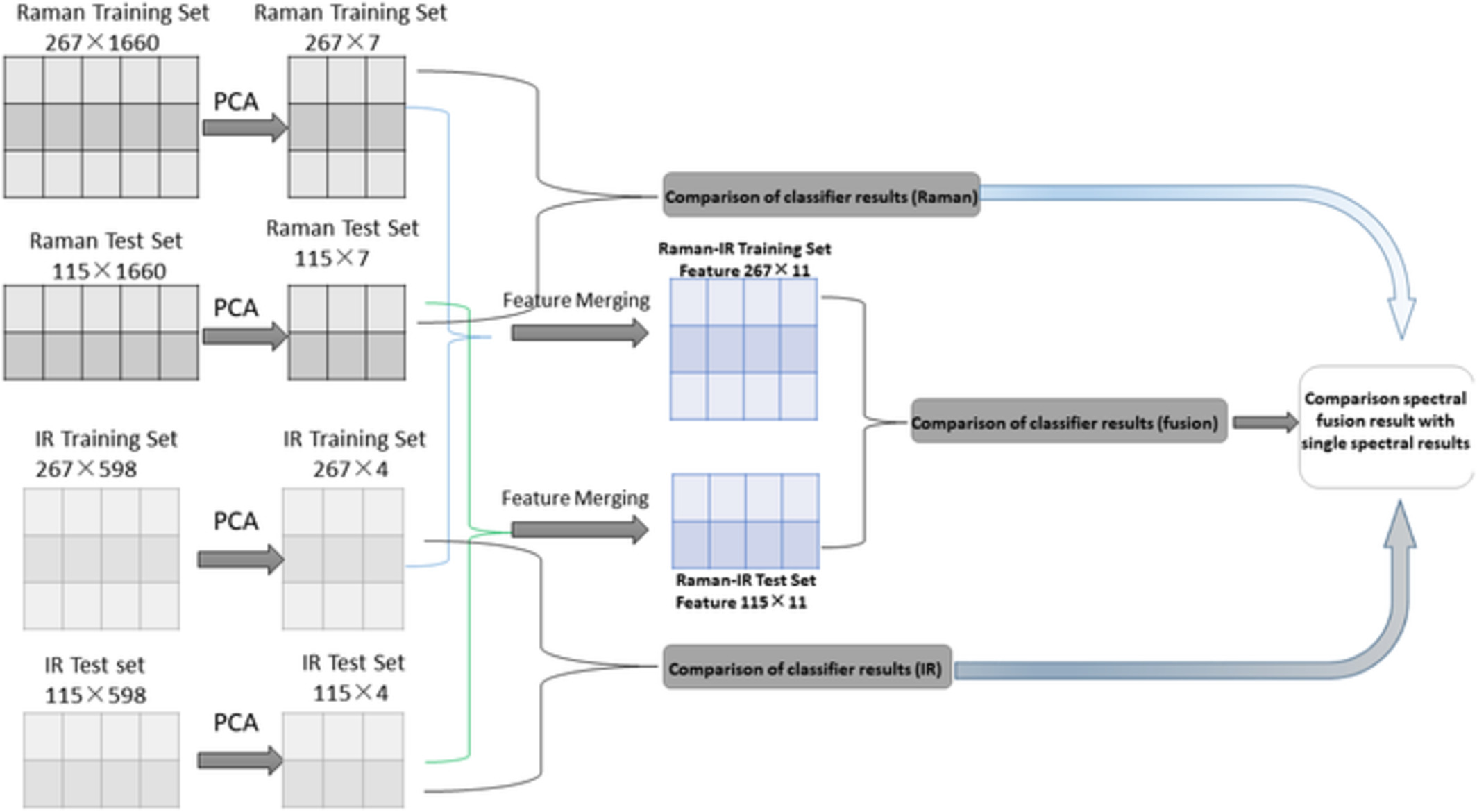
Three hundred eighty-two cases were divided into 267 cases as a training set and 115 cases as a test set. The Raman spectral data and the infrared spectral data of the training set and the test set were separately extracted by PCA, and matrixes of 267 × 7, 115 × 7, 267 × 4 and 115 × 4 were obtained. The two training set matrices were merged into a 267 × 11 matrix, and the two test set matrices were merged into a 115 × 11 matrix. Then, several pattern recognition algorithms were used for classification, and the results of the spectral fusion was compared with the results of the single-spectrum analysis.
The combination of two-dimensional and three-dimensional analysis methods contributes to the understanding of glioblastoma spatial heterogeneity
- First Published: 19 November 2019
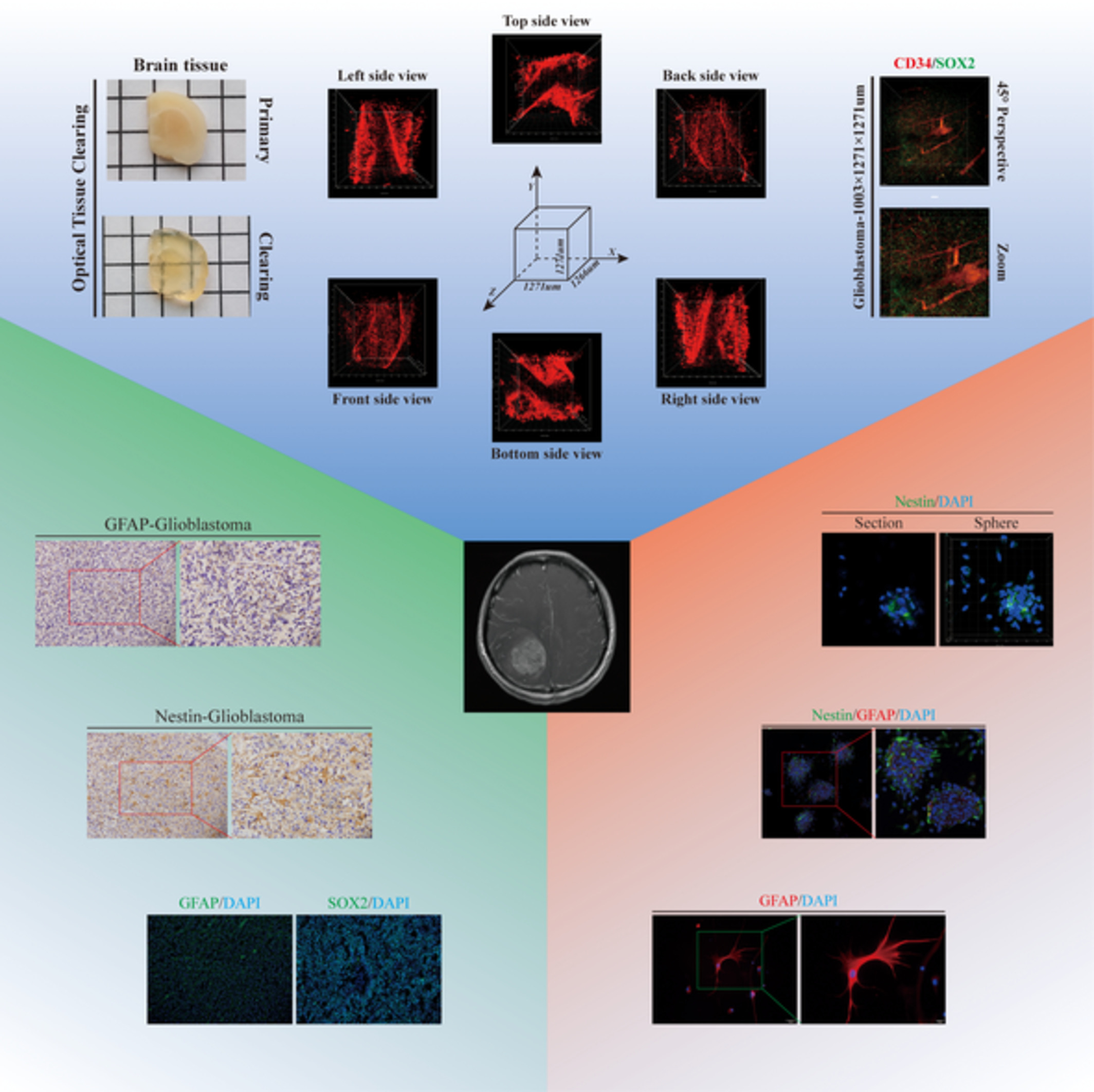
Heterogeneity is regarded as the major factor leading to the poor outcomes of glioblastoma (GBM) patients. This study aimed at developing an effective analysis strategy to increase the understanding of GBM spatial heterogeneity. Two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) analysis methods were compared for the examination of cell morphology, cell distribution and large intact structures, and both types of methods were employed to dissect GBM spatial heterogeneity. 2D assays showed only cross-sections of specimens but provided a full view whereas the 3D analysis showed specimens at a large spatial scale at cell-level resolution and had overwhelming advantages in comparison to the 2D methods. Thus, 2D and 3D analysis methods should be combined to provide much greater detail to increase the understanding of GBM spatial heterogeneity.
Remote photonic sensing of cerebral hemodynamic changes via temporal spatial analysis of acoustic vibrations
- First Published: 15 August 2019
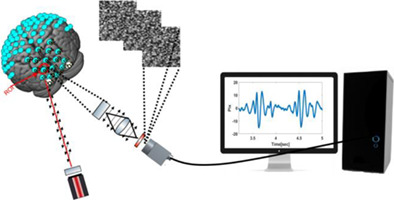
A novel photonic method for remote monitoring of hemodynamic changes in human brain is presented. Physiological processes associated with hemodynamic changes, such as nano-vibrations due to blood flow and tissue oxygenation in the brain, are detected by remote sensing of acoustic vibrations using temporal spatial analysis of defocused self-interference random patterns.
Functional assessment of moisture influenced cadaveric tympanic membrane using phase shift-resolved optical Doppler vibrography
- First Published: 31 October 2019
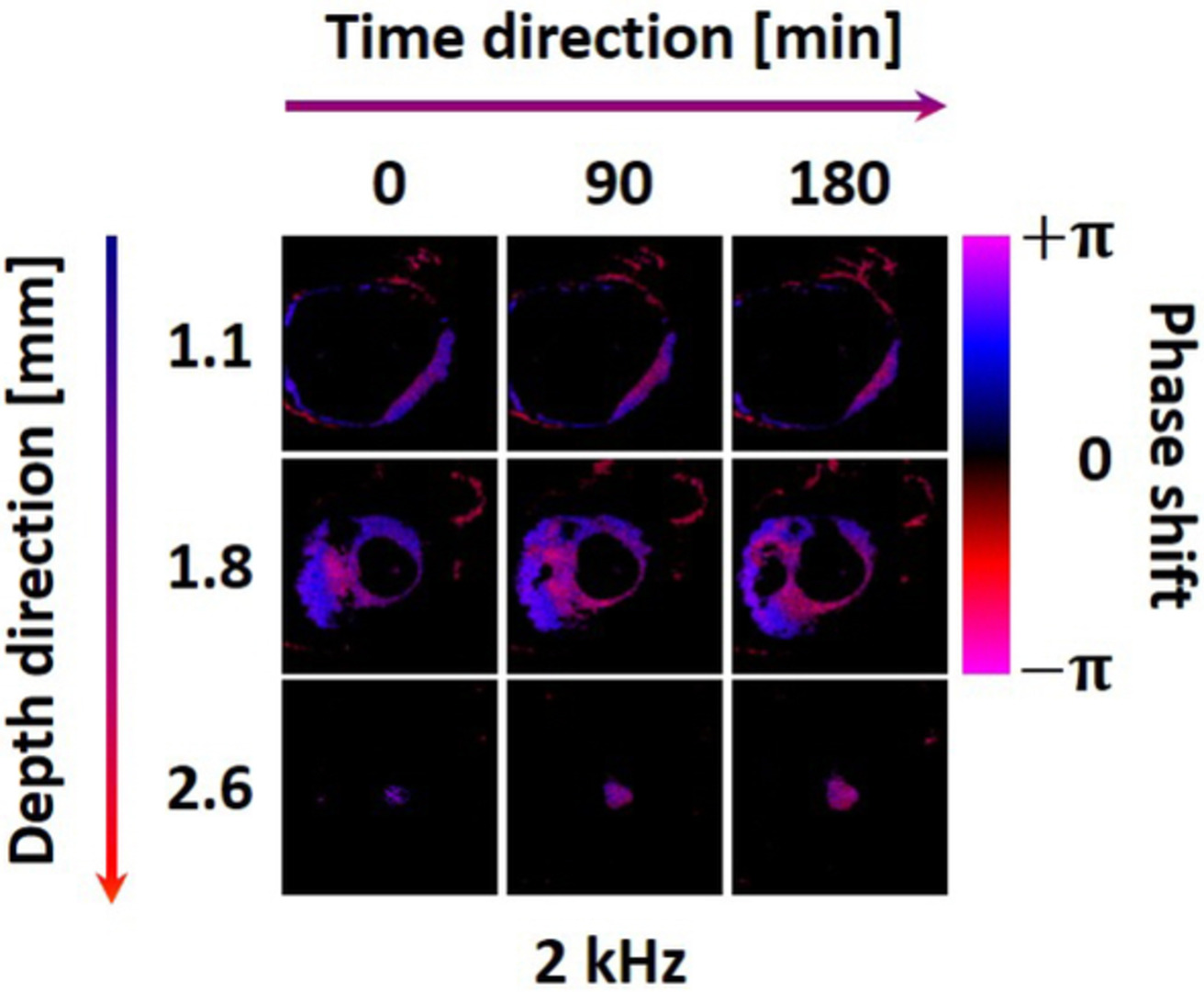
The cadaveric tympanic membrane is soaked in PBS solution for homogenous moisture environment. After that, TM is vibrated by a sound generator that provides multiple frequencies. Optical Doppler vibrography is used to quantitatively analyze the vibration of moisture influenced TM. The quantitative ODV results show a potential for clinical diagnosis of TM diseases.
Epithelium segmentation and automated Gleason grading of prostate cancer via deep learning in label-free multiphoton microscopic images
- First Published: 11 November 2019
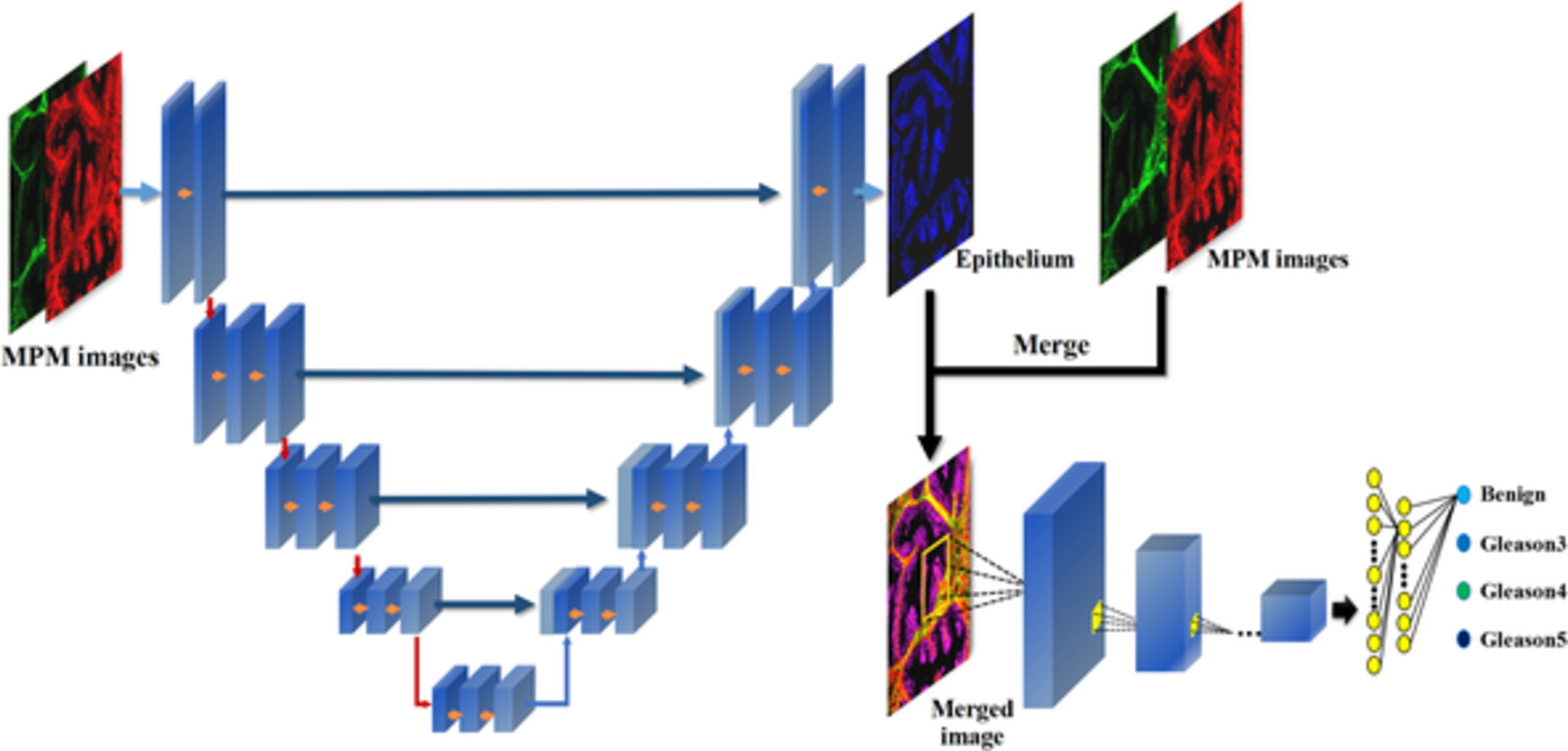
Label-freely multiphoton microscopy (MPM) is employed to produce subcellular-resolution images of the unstained prostate tissues. Then, a cascade deep learning architecture is introduced for epithelium segmentation on the MPM images, and automated Gleason grading based on the architectural pattern of cancerous epithelium with segmented result as a priori. This work suggests that MPM, combined with deep learning method, holds the potential to be a powerful tool in clinical diagnosis for prostate cancers.
Self-assembly of lipid rafts revealed by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy in living breast cancer cells
- First Published: 01 November 2019
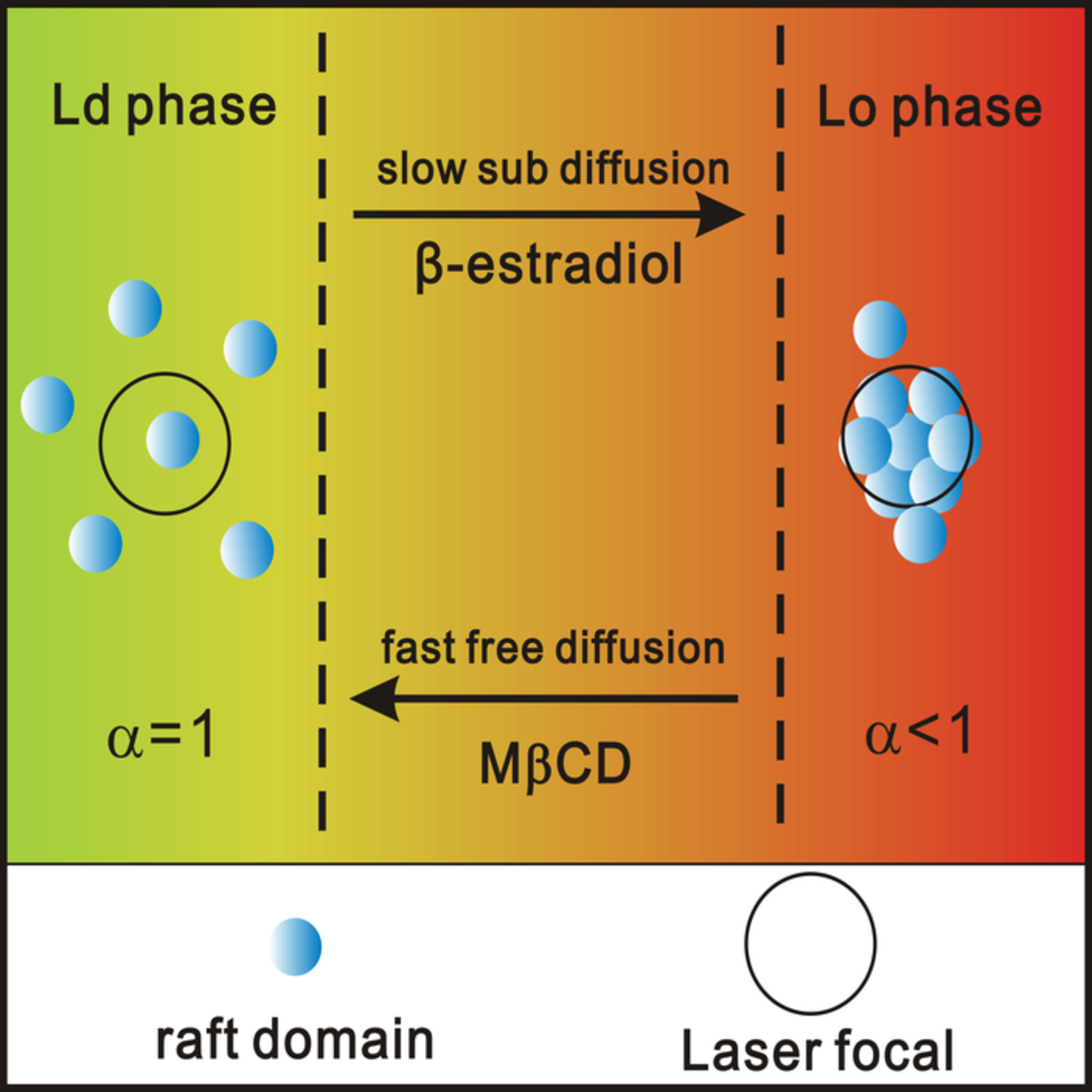
To dissect how the self-assembly of lipids modulates rafts function, the dynamic fingerprints of lipid rafts, such as membrane phase and lipid diffusion, should be integrated into the framework of cellular dynamics to link membrane heterogeneity to cell biological processes. Herein, the self-assembly model of lipid rafts was obtained base on the synchronous response between membrane phase and lipid diffusion to understand the modulation of lipid rafts in pathophysiological processes.
Rapid diagnosis of infection etiology in febrile pediatric oncology patients using infrared spectroscopy of leukocytes
- First Published: 30 September 2019
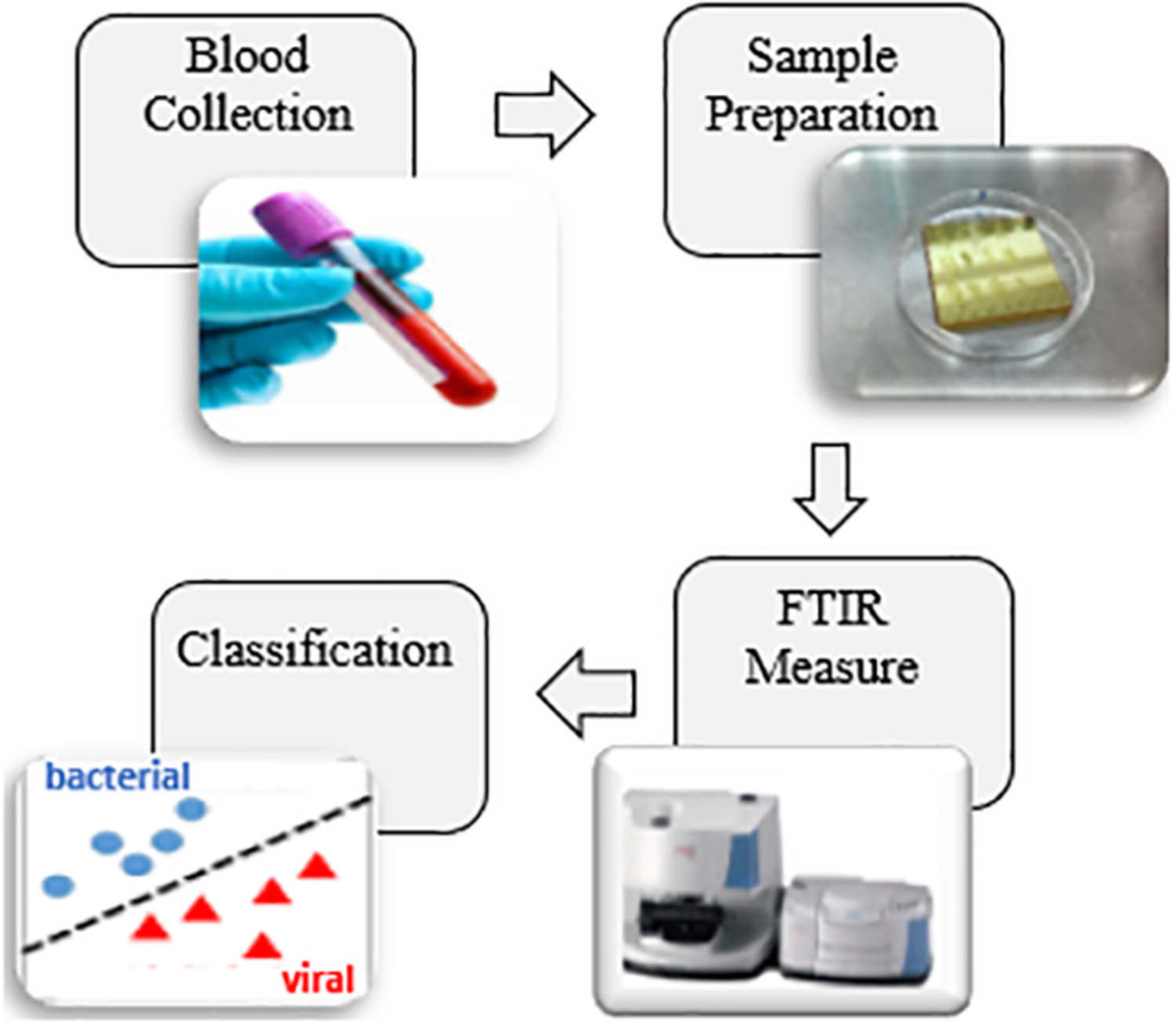
Bacterial and viral infections are responsible for major part of infectious diseases. Both infections have many common symptoms; thus, it is difficult to diagnose the type of infection based on these symptoms. Rapid diagnosis of the etiology of infection as bacterial or viral is highly important for the effective treatment of infected patients. Midinfrared spectroscopy in tandem with different machine learning classifiers was used successfully for this purpose.
A quantitative evaluation of the use of medical lasers in German hospitals
- First Published: 21 October 2019
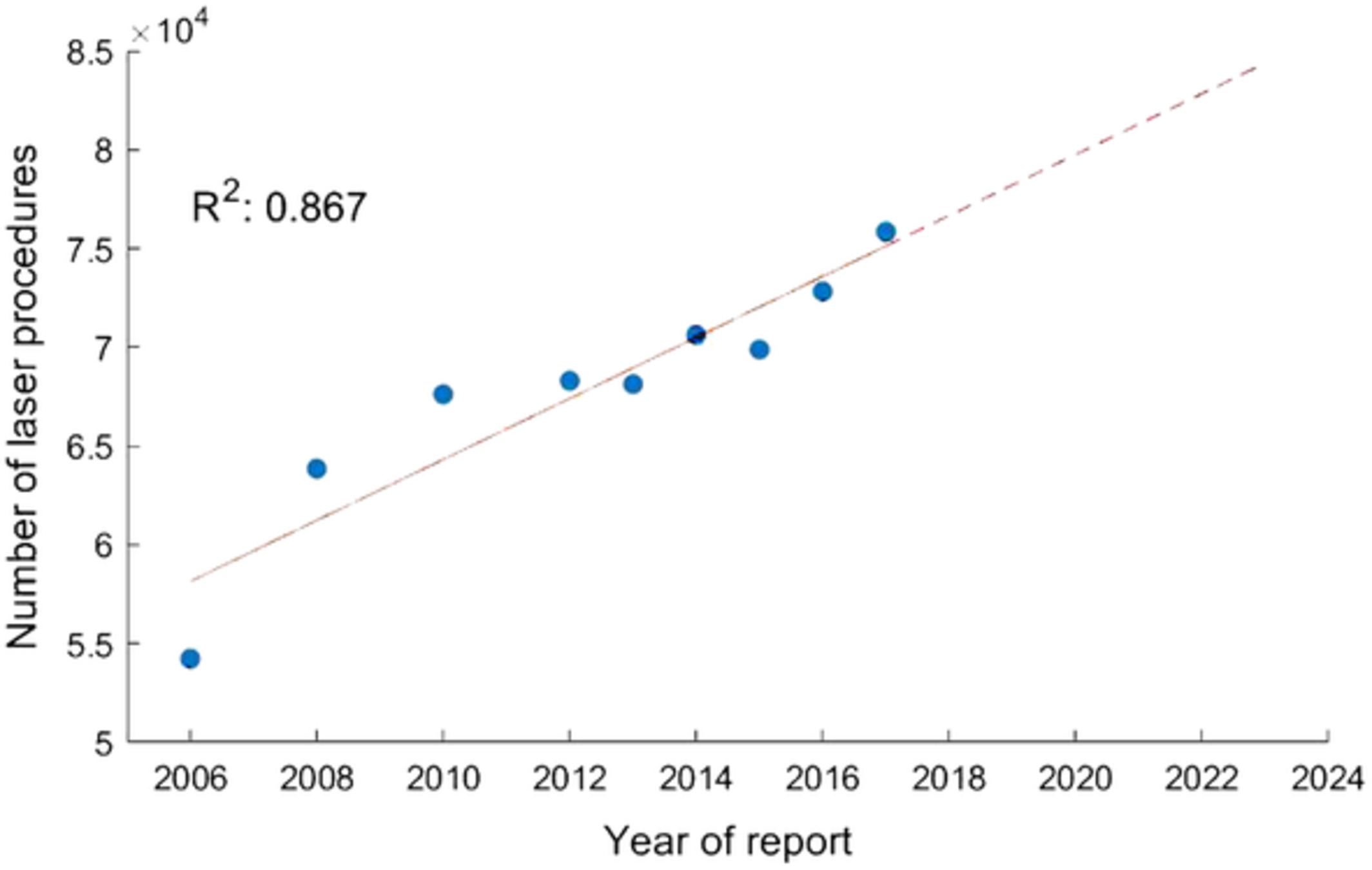
The laser has become an integral part of modern medicine. To gain knowledge about the detailed quantitative development of laser use for medical interventions in hospitals, the present study analyses the raw data of the quality report of German hospitals. Over the 9 years of report, a steady increase in the cumulative number of cases is evident. The present study is able to confirm and substantiate the importance of the laser for medical purposes.
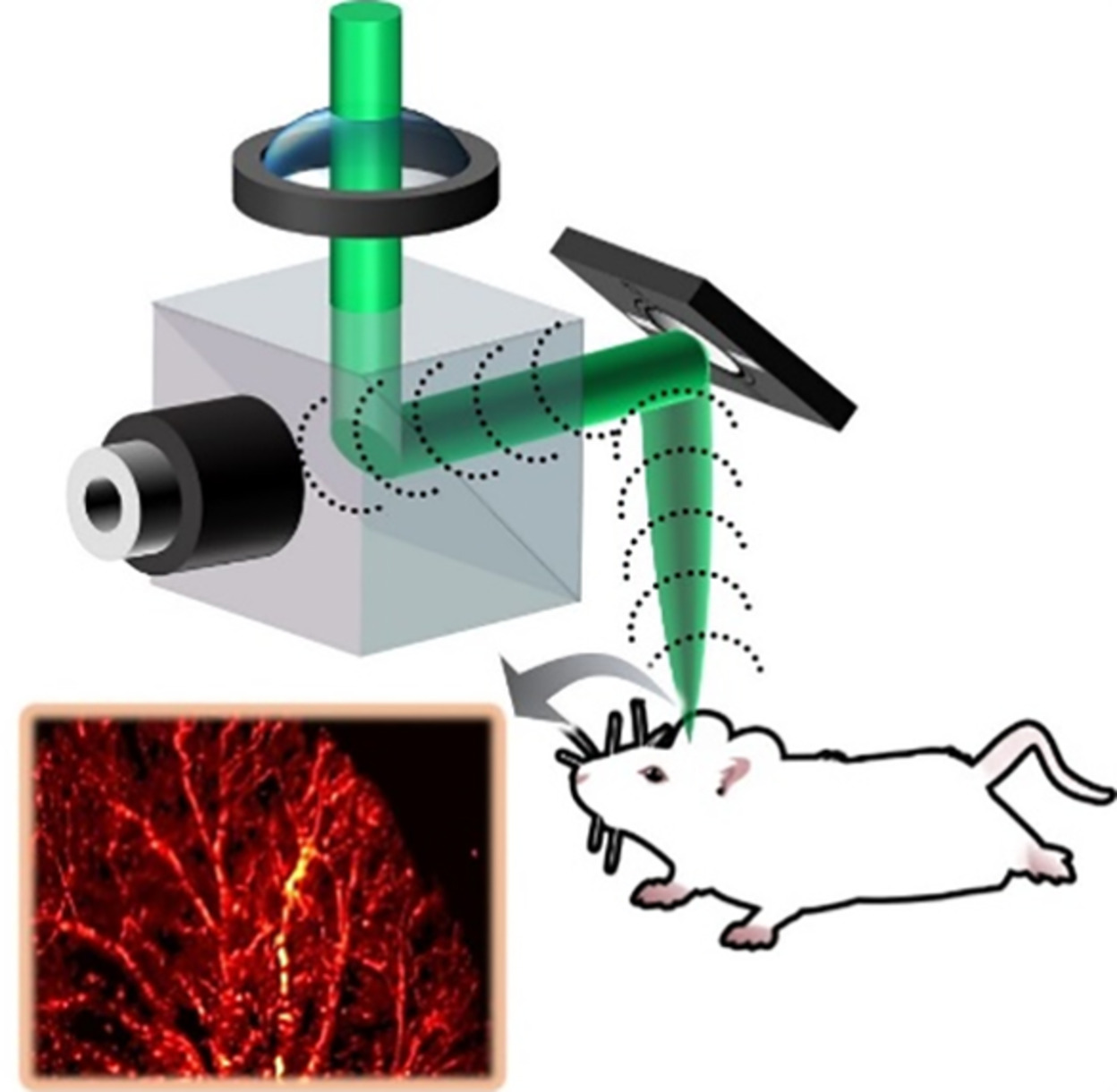
Morphological and functional characteristics of aging kidneys based on two-photon microscopy in vivo
- First Published: 05 November 2019
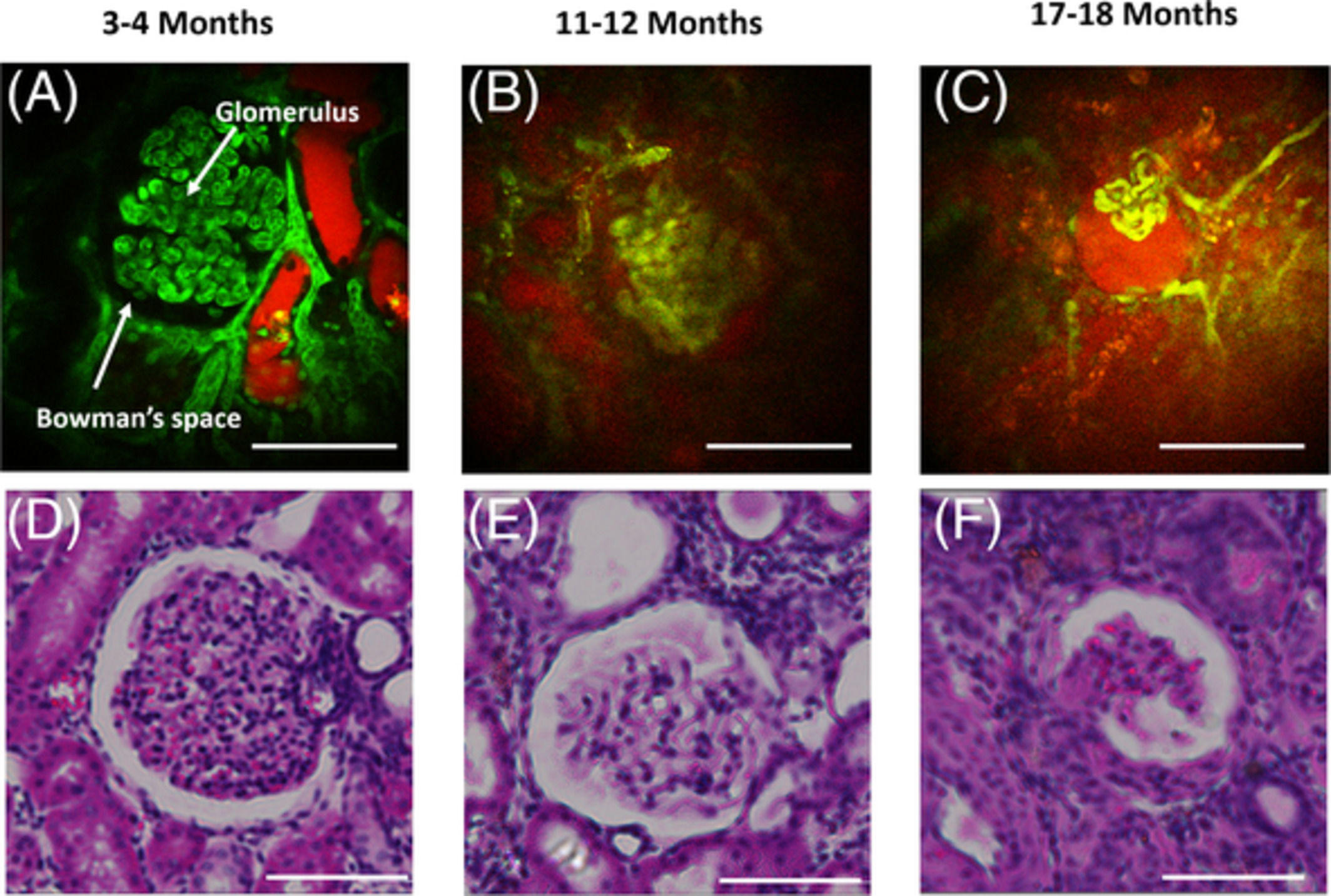
Age-related kidney disease, which is chronic and naturally occurring, is a general term for a set of heterogeneous disorders affecting kidney structures and characterized by a decline in renal function. In our study, the morphological and functional characteristics of rat kidneys with different ages were studied in vivo using two-photon microscopy.
Bladder tissue characterization using probe-based Raman spectroscopy: Evaluation of tissue heterogeneity and influence on the model prediction
- First Published: 16 October 2019
In vivo study of metabolic dynamics and heterogeneity in brown and beige fat by label-free multiphoton redox and fluorescence lifetime microscopy
- First Published: 18 October 2019
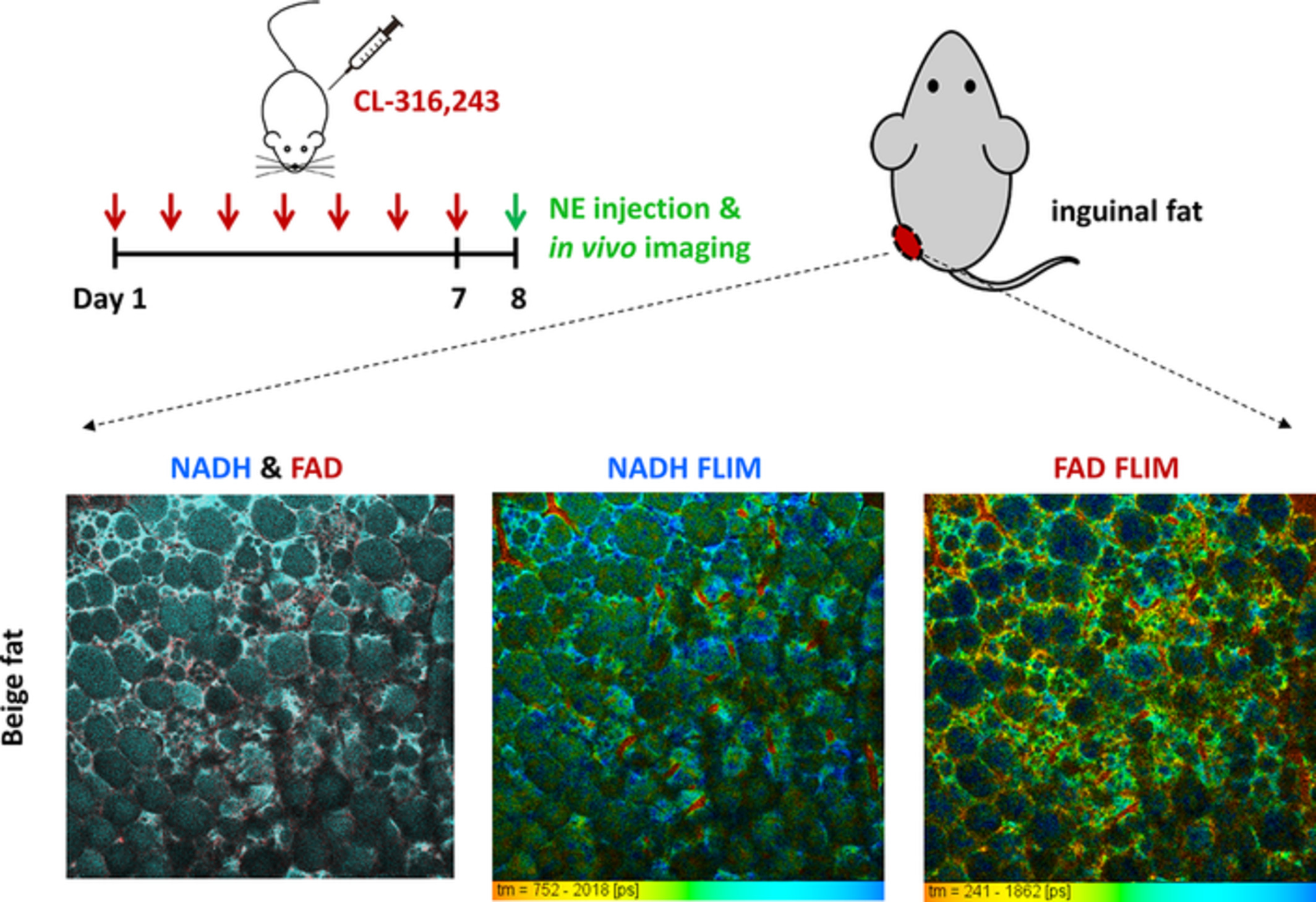
Metabolic characterization of thermogenic adipocytes provides remarkable insight into the mechanism of obesity-related diseases. This paper presents a label-free method to assess the metabolism and thermogenesis of mouse adipose tissues in vivo. The optical redox ratio and fluorescence lifetime are used as biomarkers to determine the thermogenic response of brown, beige and white adipose tissues to different physiological stimulations. This technique may be used to study the recruitment and activation of thermogenic adipocytes.
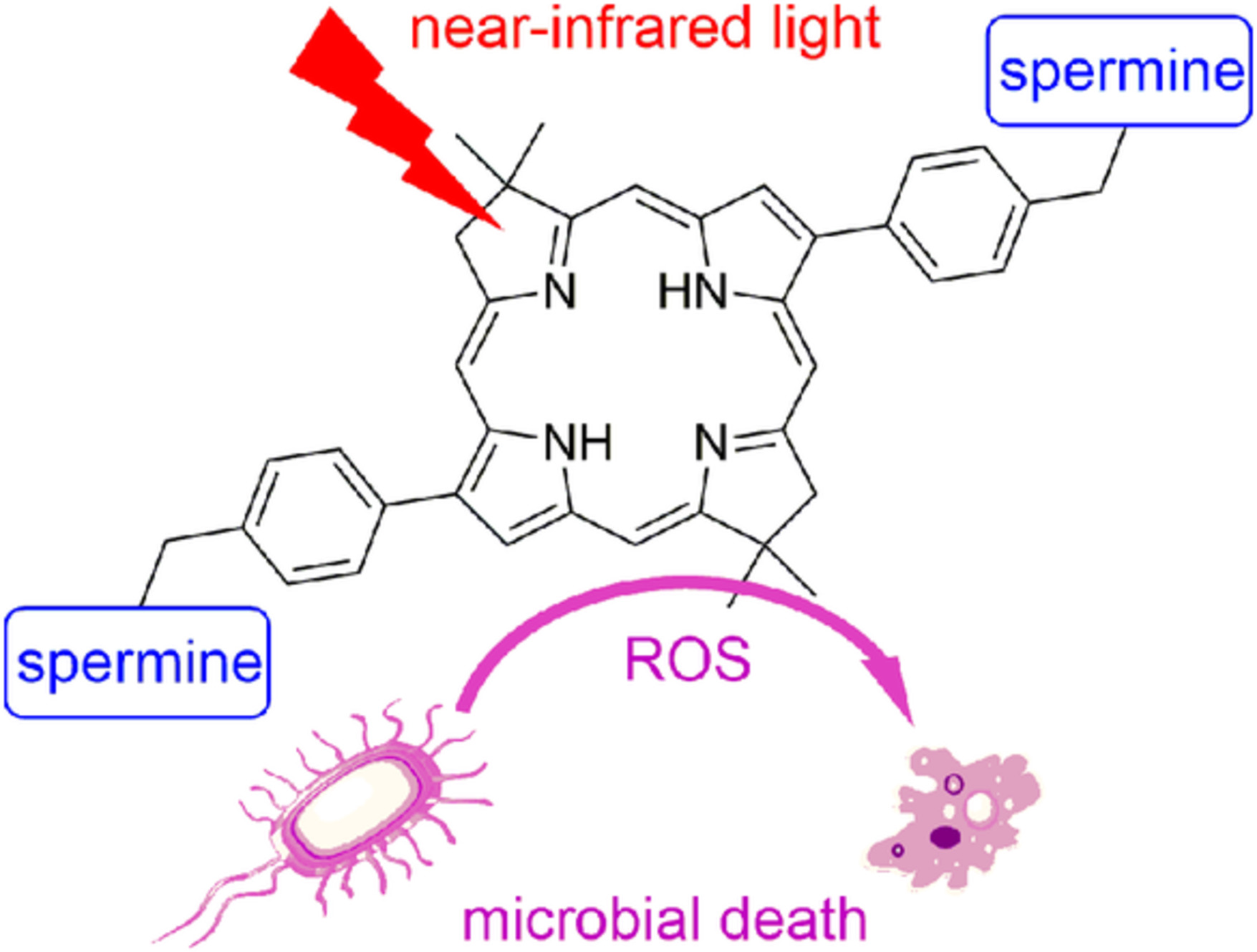
Bacteriochlorin-bis(spermine) conjugate affords an effective photodynamic action to eradicate microorganisms
- First Published: 11 October 2019
Phase unwrapping for Doppler spectral domain optical coherence tomography flow measurement
- First Published: 31 October 2019
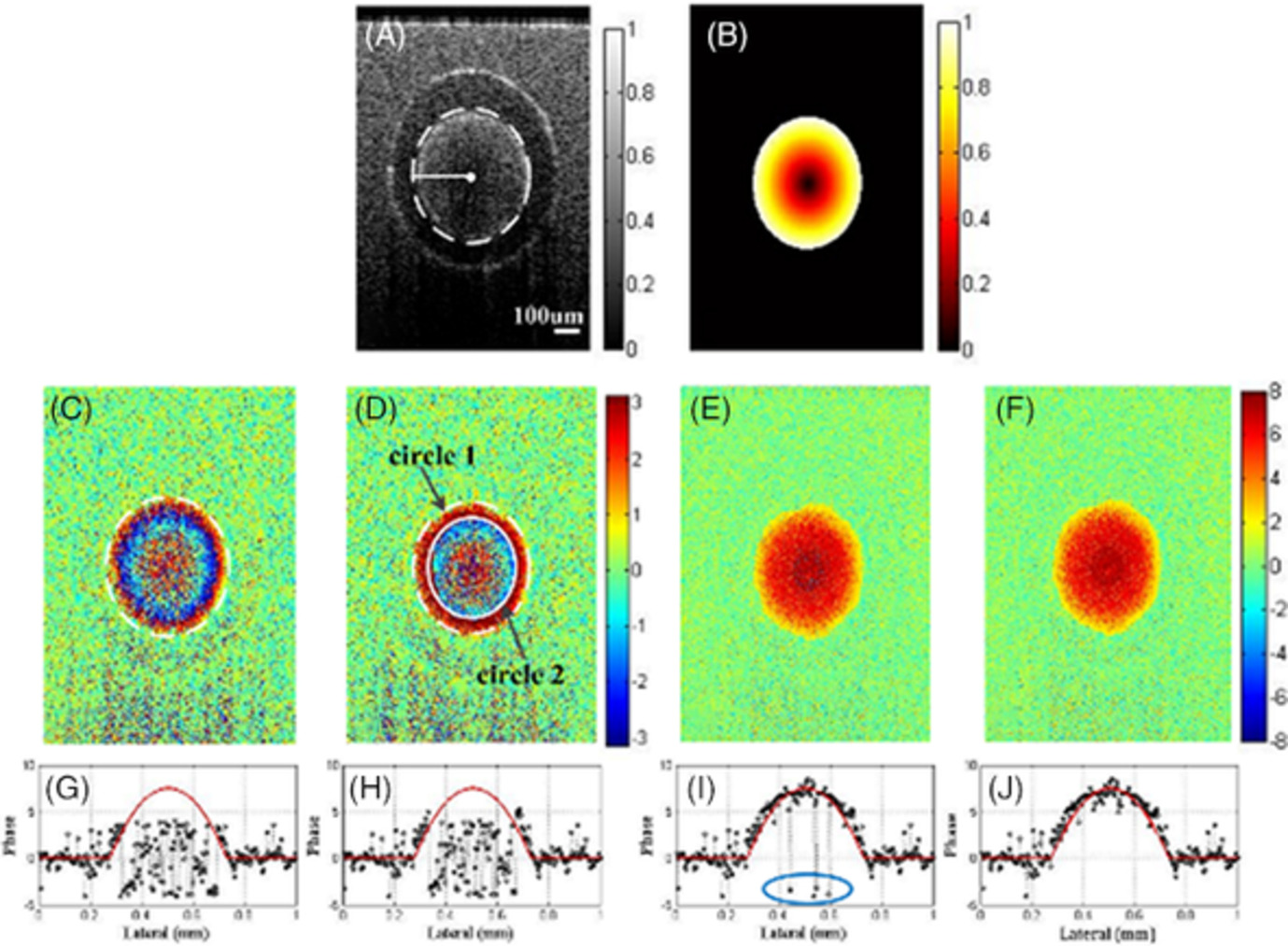
We propose a phase unwrapping method to correct the wrapping phase in Doppler optical coherence tomography image. Points in flow region are divided into groups according to the radial distance. For each point group, signal points are selected and corrected with phase unwrapping algorithm, while noise points are replaced with the mean value of the corrected points. The method is validated with flow in capillary tube and in vivo blood vessels.
Induction and measurement of the early stage of a host-parasite interaction using a combined optical trapping and Raman microspectroscopy system
- First Published: 11 November 2019
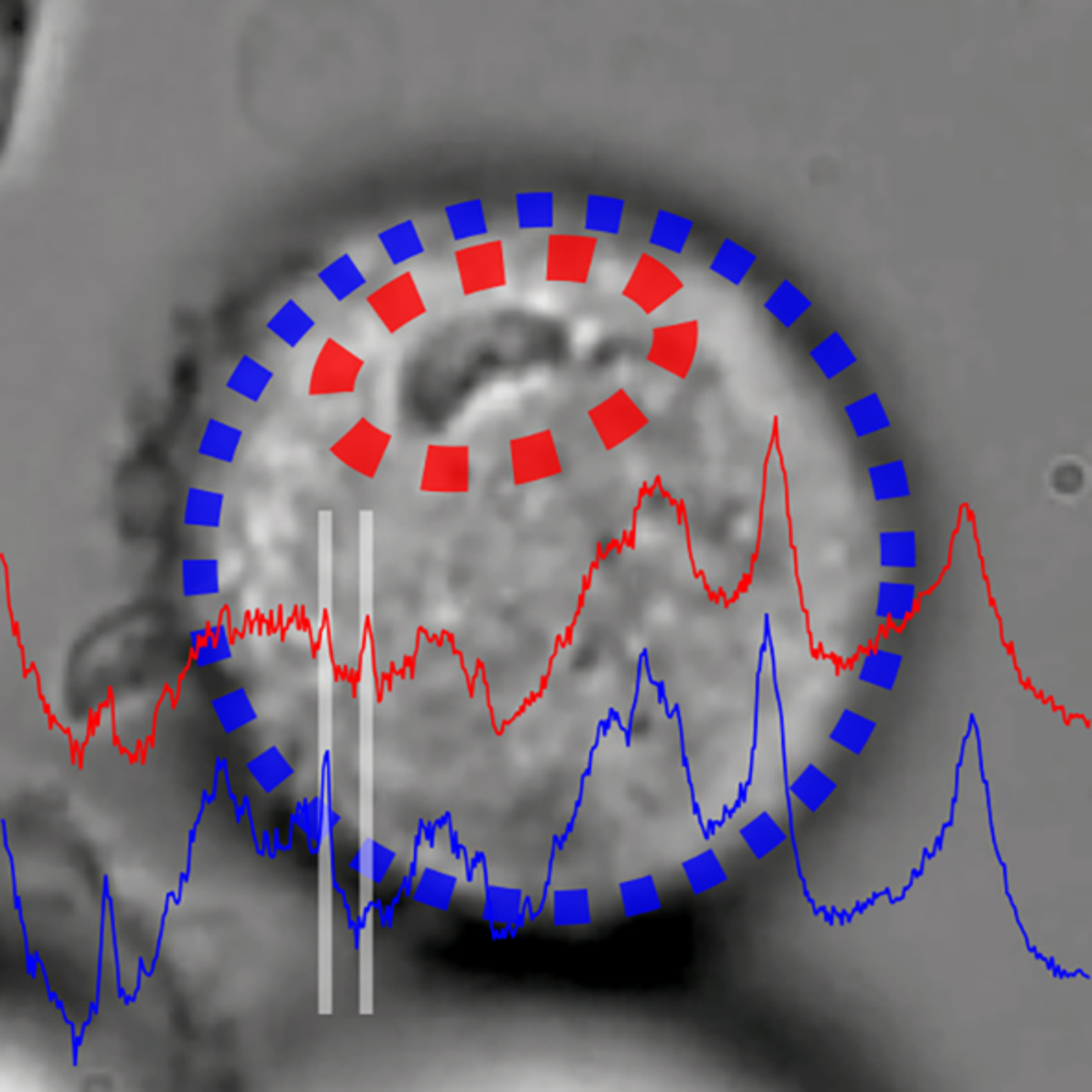
Understanding and quantifying the temporal acquisition of host cell molecules by intracellular pathogens is fundamentally important in biology. In this study, a recently developed holographic optical trapping (HOT)-based Raman microspectroscopy (RMS) instrument is applied to detect, characterize and monitor in real time the molecular trafficking of a specific molecular species at the single cell level. This approach enables simultaneous measurement of the chemical composition of human cerebrovascular endothelial cells and the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii in isolation at the very start of the infection process.
Optimal stimulation frequency for vibrational optical coherence elastography
- First Published: 11 October 2019
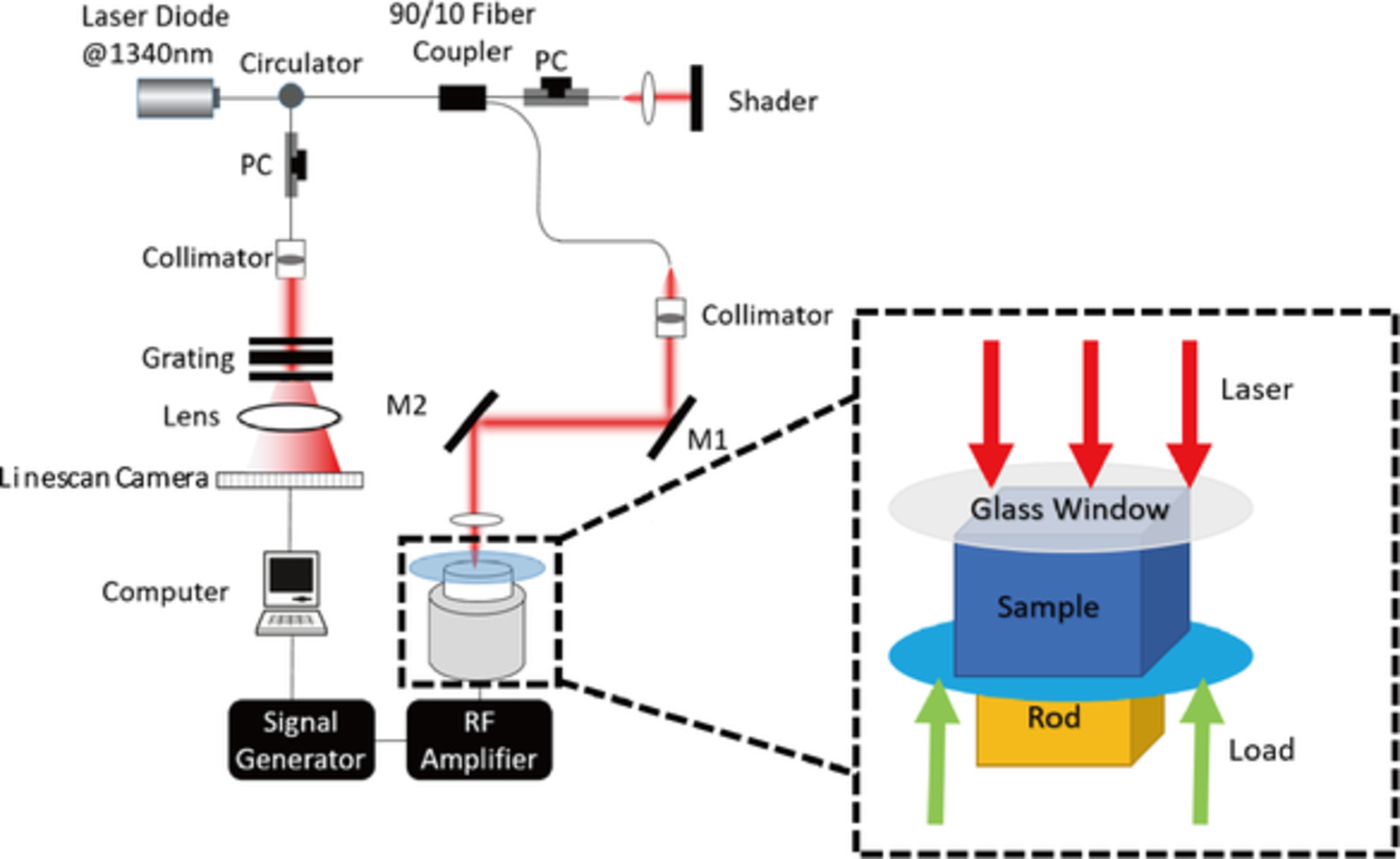
This article first proposes an optimal frequency for vibrational optical coherence elastography, before which no consensus has been approached. Vibration within the optimal frequency range of tested object tends to possess homogeneously distributed stress filed, by which accurate stiffness mapping can be revealed. Cross-validation is accomplished by finite element simulation where stress field distribution at varying frequencies is verified.
Simultaneous detection of cerebral blood perfusion and cerebral edema using swept-source optical coherence tomography
- First Published: 08 November 2019
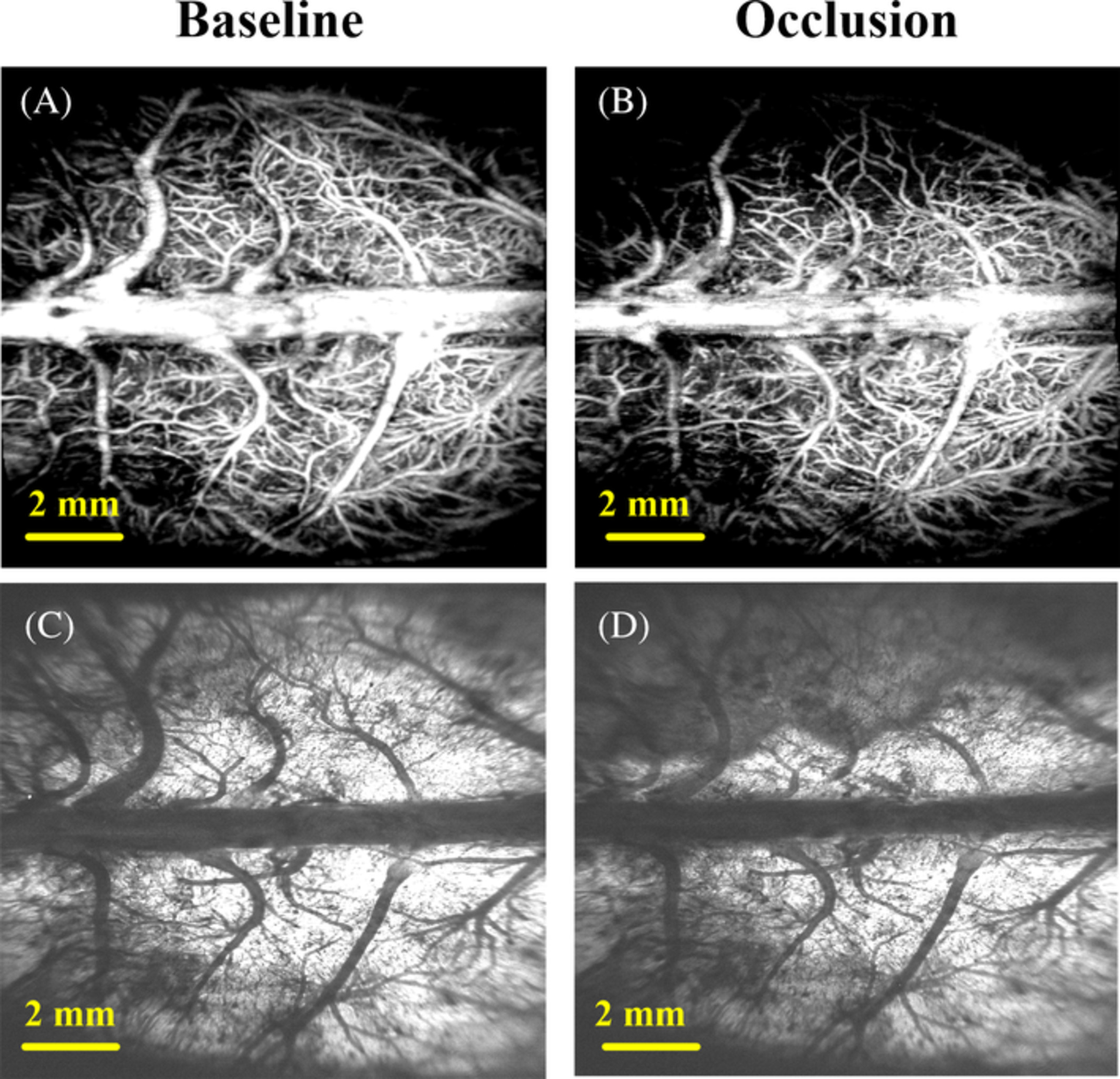
In this article, a wide field of view swept-source optical coherence tomography system was used to detect cerebral edema status and cerebral blood perfusion levels simultaneously in middle cerebral artery occlusion rats. Images reflecting these two physiological states can be reconstructed with only one C-scan. We quantify these two physiological states into four parameters, which contain two vascular parameters and two edema parameters. The association between the two vascular parameters and the two edema parameters was analyzed. The results show that there is a strong linear relationship between blood flow parameters and edema parameters.
Lightsheet fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy with wide-field time-correlated single photon counting
- First Published: 29 October 2019
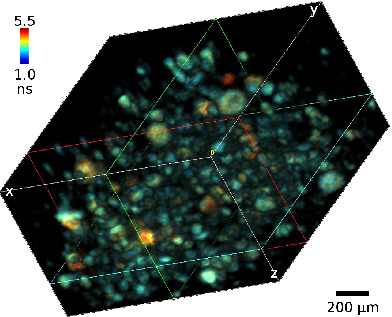
We combine fluorescence lifetime imaging (FLIM) with lightsheet illumination microscopy for 3D imaging of human cancer cell spheroids and living C. elegans. The wide-field TCSPC method used for FLIM detection has many advantages including extremely low illumination intensity, good signal-to-noise ratio and insensitivity to intensity fluctuations and photobleaching, while lightsheet illumination provides optical sectioning, making this technique ideal for 3D FLIM imaging of living organelles.
Fan-shaped scanning approach for miniaturized photoacoustic tomography
- First Published: 30 October 2019
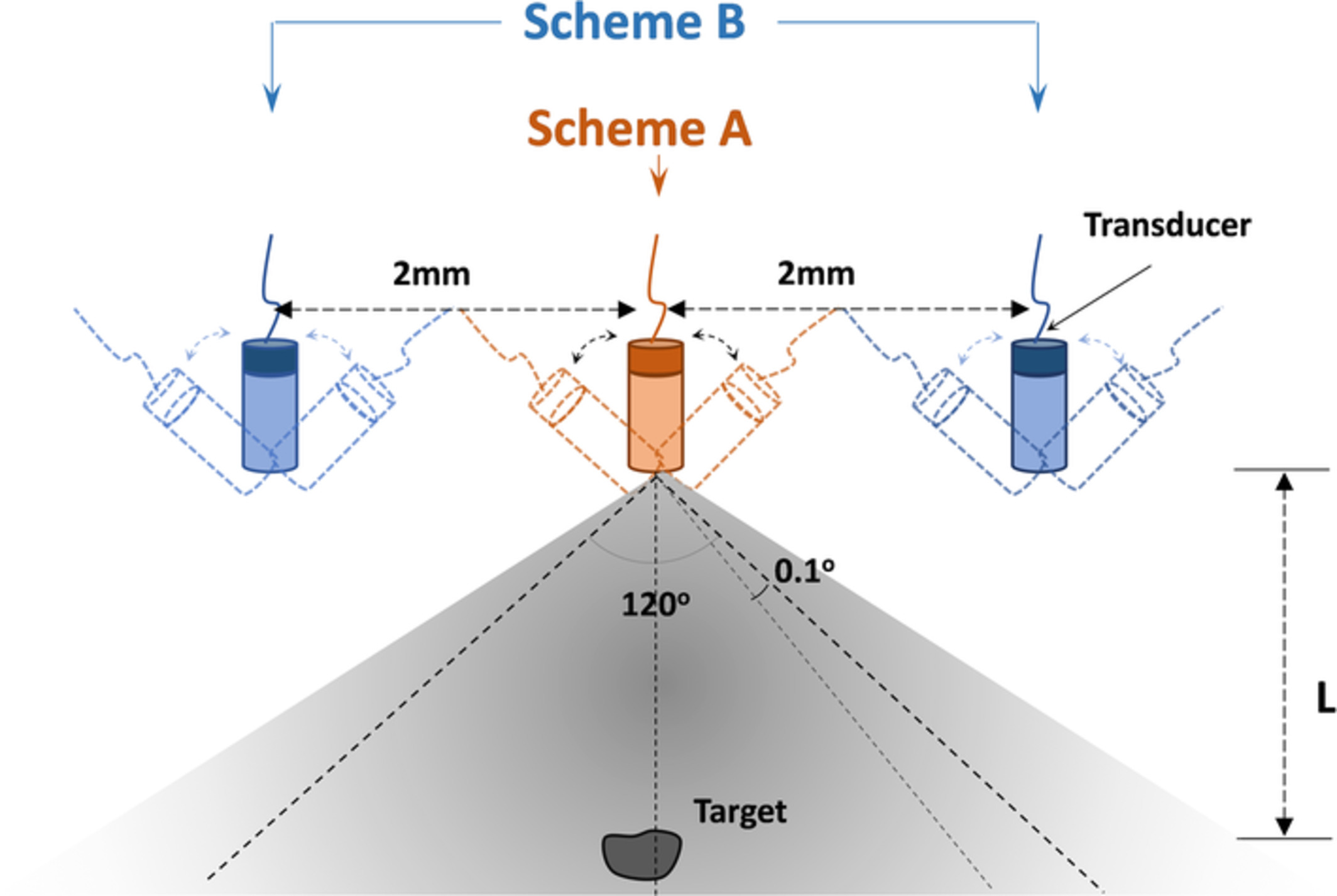
We have described and explored a novel fan-shaped scanning approach to realize miniaturized photoacoustic tomography (PAT) along with a virtual signal reconstruction algorithm. Both the phantom and animal experiments results obtained show that this new scanning approach provides high image quality in the configuration of miniaturized handheld or endoscopic PAT with improved effective field of view and penetration depth.
Photobiomodulation therapy for repeated closed head injury in rats
- First Published: 28 October 2019
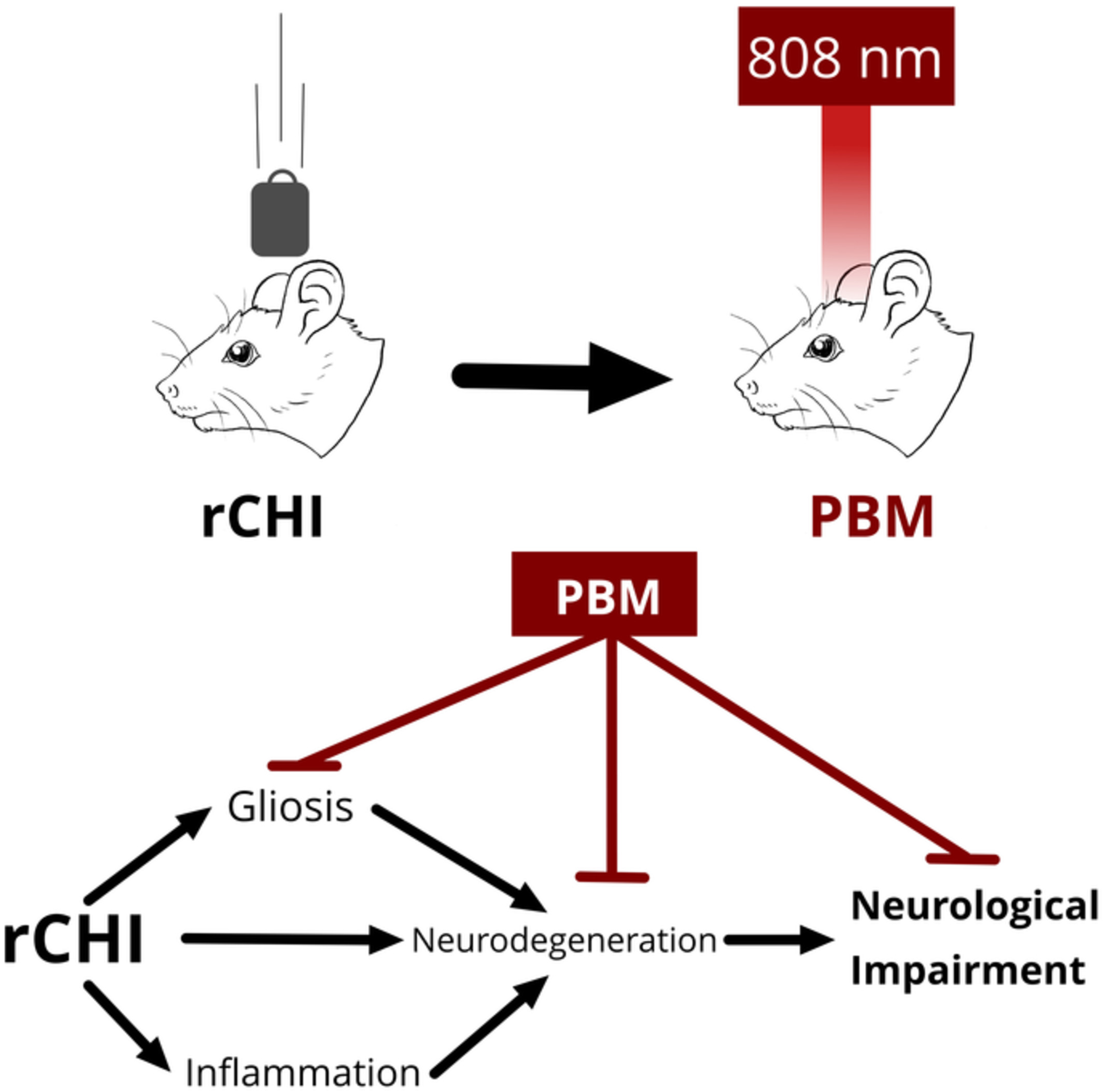
Repeated closed head injury (rCHI) causes progressive neuronal pathology and neurological impairments. Transcranial photobiomodulation, a non-invasive application of near-infrared light to the brain reduced gliosis, inflammation, neurodegeneration, and neurological impairments when applied to rats undergoing an rCHI model. This suggests that photobiomodulation may be an effective therapy for rCHI, and could be of particular interest for career athletes.
Acoustic resolution photoacoustic microscopy based on microelectromechanical systems scanner
- First Published: 04 November 2019
Here, we demonstrate the use of a high-speed microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) scanner for AR-PAM imaging. A 2 × 2.5 mm2 area was imaged in 3 seconds. We also have studied the effect of transducer frequency on the resolution characteristics and imaging depth using the proposed system. The capability of achieving acoustic resolution images using the MEMS scanner is beneficial for the development of miniaturized systems for deep microscopic imaging at high speed.