Bacteriochlorin-bis(spermine) conjugate affords an effective photodynamic action to eradicate microorganisms
María B. Ballatore
IDAS-CONICET, Departamento de Química, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Físico-Químicas y Naturales, Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto, Córdoba, Argentina
Search for more papers by this authorMaría E. Milanesio
IDAS-CONICET, Departamento de Química, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Físico-Químicas y Naturales, Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto, Córdoba, Argentina
Search for more papers by this authorHikaru Fujita
Department of Chemistry, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina
Search for more papers by this authorJonathan S. Lindsey
Department of Chemistry, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Edgardo N. Durantini
IDAS-CONICET, Departamento de Química, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Físico-Químicas y Naturales, Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto, Córdoba, Argentina
Correspondence
Edgardo N. Durantini, IDAS-CONICET, Departamento de Química, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Físico-Químicas y Naturales, Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto, Ruta Nacional 36 Km 601, X5804BYA Río Cuarto, Córdoba, Argentina.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorMaría B. Ballatore
IDAS-CONICET, Departamento de Química, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Físico-Químicas y Naturales, Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto, Córdoba, Argentina
Search for more papers by this authorMaría E. Milanesio
IDAS-CONICET, Departamento de Química, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Físico-Químicas y Naturales, Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto, Córdoba, Argentina
Search for more papers by this authorHikaru Fujita
Department of Chemistry, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina
Search for more papers by this authorJonathan S. Lindsey
Department of Chemistry, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Edgardo N. Durantini
IDAS-CONICET, Departamento de Química, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Físico-Químicas y Naturales, Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto, Córdoba, Argentina
Correspondence
Edgardo N. Durantini, IDAS-CONICET, Departamento de Química, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Físico-Químicas y Naturales, Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto, Ruta Nacional 36 Km 601, X5804BYA Río Cuarto, Córdoba, Argentina.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorFunding information: Agencia Córdoba Ciencia, Grant/Award Number: PID 000144/18; Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas, Grant/Award Number: PIP-2015 1122015 0100197 CO; Fondo para la Investigación Científica y Tecnológica, Grant/Award Number: PICT 0667/16; Secretaría de Ciencia y Técnica, Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto, Grant/Award Number: PPI-2016 18/C460
Abstract
A novel bacteriochlorin bearing two spermine units (BCS) was synthesized from 3,13-dibromo-8,8,18,18-tetramethylbacteriochlorin (BC-Br
3,13). The synthesis involved the Suzuki coupling of BC-Br
3,13 to obtain a bacteriochlorin-dibenzaldehyde (BCA), which was subjected to reductive amination with spermine. The resulting bacteriochlorin BCS presents a strong near-infrared absorption band at 747 nm, emits at 750 nm with fluorescence quantum yield of 0.14, and generates singlet molecular oxygen, O2(1Δg), with a quantum yield of 0.27. Photokilling capacities mediated by BCS were evaluated in microbial cells. The viability of Staphylococcus aureus decreased 7 logs when cells were incubated with 1 μM BCS and irradiated for 15 minutes. Comparable photocytotoxic effect was obtained with Escherichia coli, when cells were treated for 30 minutes with visible light. BCS was also an effective photosensitizer to inactivate Candida albicans. In addition, this bacteriochlorin was able to eradicate bacteria at short incubation times. The structure of BCS contains eight basic amino groups that, when protonated in water, increase the binding to the cell envelope. In summary, the readily accessible bacteriochlorin BCS was highly effective at low concentrations as a broad-spectrum antimicrobial photosensitizer.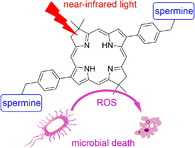
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| jbio201960061-sup-0001-suppinfo.docxWord 2007 document , 230 KB | Figure S1. Absorption spectral changes during the photooxidation of DMA. Figure S2. First-order plots for the photodecomposition of DMA. Appendix S1. General equipment and experimental procedures. |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
REFERENCES
- 1M. N. Ragheb, M. K. Thomason, C. Hsu, P. Nugent, J. Gage, A. N. Samadpour, A. Kariisa, C. N. Merrikh, S. I. Miller, D. R. Sherman, H. Merrikh, Mol. Cell 2019, 73, 157.
- 2C. Ghosh, P. Sarkar, R. Issa, J. Haldar, Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 323.
- 3M. R. Hamblin, Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 33, 67.
- 4M. Oszajca, M. Brindell, Ł. Orzeł, J. M. Dabrowski, K. Śpiewak, P. Łabuz, M. Pacia, A. Stochel-Gaudyn, W. Macyk, R. van Eldik, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 327, 143.
- 5L. G. Arnaut, M. M. Pereira, J. M. Dąbrowski, E. F. Silva, F. A. Schaberle, A. R. Abreu, L. B. Rocha, M. M. Barsan, K. Urbańska, G. Stochel, Chem. A Eur. J. 2014, 20, 5346.
- 6J. M. Dąbrowski, L. G. Arnaut, M. M. Pereira, K. Urbańska, S. Simões, G. Stochel, L. Cortes, Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 1188.
- 7M. B. Ballatore, M. B. Spesia, M. E. Milanesio, E. N. Durantini, RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 22876.
- 8N. Kashef, M. R. Hamblin, Drug Resist. Updat. 2017, 31, 31.
- 9T. Maisch, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2015, 14, 1518.
- 10E. Alves, M. A. F. Faustino, M. G. P. M. S. Neves, A. Cunha, H. Nadais, A. Almeida, J. Photochem. Photobiol. C: Photochem. Rev. 2015, 22, 34.
- 11N. K. Shrestha, T. G. Fraser, S. M. Gordon, Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 71.
- 12C. Furusawa, T. Horinouchi, T. Maeda, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 54, 45.
- 13K. E. Pristov, M. A. Ghannoum, Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 792.
- 14A. M. Durantini, D. A. Heredia, J. E. Durantini, E. N. Durantini, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 144, 651.
- 15H. Abrahamse, M. R. Hamblin, Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 347.
- 16D. G. Sami, H. H. Heiba, A. Abdellatif, Wound Med. 2019, 24, 8.
10.1016/j.wndm.2018.12.001 Google Scholar
- 17A. Martinez De Pinillos Bayona, P. Mroz, C. Thunshelle, M. R. Hamblin, Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2017, 89, 192.
- 18E. Yang, N. Zhang, M. Krayer, M. Taniguchi, J. R. Diers, C. Kirmaier, J. S. Lindsey, D. F. Bocian, D. Holten, Photochem. Photobiol. 2016, 92, 111.
- 19N. Zhang, J. Jiang, M. Liu, M. Taniguchi, A. K. Mandal, R. B. Evans-Storms, J. B. Pitner, D. F. Bocian, D. Holten, J. S. Lindsey, New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 7750.
- 20M. Q. Mesquita, J. C. J. M. D. S. Menezes, M. G. P. M. S. Neves, A. C. Tomé, J. A. S. Cavaleiro, Â. Cunha, A. Almeida, S. Hackbarth, B. Röder, M. A. F. Faustino, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 808.
- 21L. Huang, Y.-Y. Huang, P. Mroz, G. P. Tegos, T. Zhiyentayev, S. K. Sharma, Z. Lu, T. Balasubramanian, M. Krayer, C. Ruzie, E. Yang, H. L. Kee, C. Kirmaier, J. Diers, D. F. Bocian, D. Holten, J. S. Lindsey, M. R. Hamblin, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3834.
- 22L. Huang, M. Krayer, J. G. S. Roubil, Y.-Y. Huang, D. Holten, J. S. Lindsey, M. R. Hamblin, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol. 2014, 141, 119.
- 23O. Mass, J. S. Lindsey, J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 9478.
- 24K. Utimoto, Y. Wakabayashi, Y. Shishiyama, M. Inoue, H. Nozaki, Tetrahedron Lett. 1981, 22, 4279.
- 25M. Krayer, T. Balasubramanian, C. Ruzié, M. Ptaszek, D. L. Cramer, M. Taniguchi, J. S. Lindsey, J. Porphyrins Phthalocyanines 2009, 13, 1098.
- 26H.-J. Kim, J. S. Lindsey, J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 5475.
- 27M. Taniguchi, D. L. Cramer, A. D. Bhise, H. L. Kee, D. F. Bocian, D. Holten, J. S. Lindsey, New J. Chem. 2008, 32, 947.
- 28M. B. Ballatore, M. B. Spesia, M. E. Milanesio, E. N. Durantini, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 83, 685.
- 29L. Roitman, B. Ehrenberg, N. Kobayashi, J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 1994, 77, 23.
- 30D. D. Ferreyra, E. Reynoso, P. Cordero, M. B. Spesia, M. G. Alvarez, M. E. Milanesio, E. N. Durantini, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol. 2016, 158, 243.
- 31E. Reynoso, E. D. Quiroga, M. L. Agazzi, M. B. Ballatore, S. G. Bertolotti, E. N. Durantini, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2017, 16, 1524.
- 32A. C. Scanone, N. S. Gsponer, M. G. Alvarez, E. N. Durantini, Photodiag. Photodyn. Ther. 2018, 24, 220.
- 33M. Krayer, M. Ptaszek, H.-J. Kim, K. R. Meneely, D. Fan, K. Secor, J. S. Lindsey, J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 1016.
- 34C. Ruzié, M. Krayer, T. Balasubramanian, J. S. Lindsey, J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 5806.
- 35D. Fan, M. Taniguchi, J. S. Lindsey, J. Org. Chem. 2007, 70, 5350.
- 36A. F. Abdel-Magid, S. J. Mehrman, Org. Process Res. Dev. 2006, 10, 971.
- 37A. F. Mironov, M. A. Grin, A. G. Tsiprovskii, R. A. Titeev, E. A. Nizhnik, I. S. Lonin, Mendeleev Commun. 2004, 14, 204.
- 38J. Jiang, E. Yang, K. R. Reddy, D. M. Niedzwiedzki, C. Kirmaier, D. F. Bocian, D. Holten, J. S. Lindsey, New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 5694.
- 39C. Frassineti, S. Ghelli, P. Gans, A. Sabatini, M. S. Moruzzi, A. Vacca, Anal. Biochem. 1995, 231, 374.
- 40E. D. Quiroga, S. J. Mora, M. G. Alvarez, E. N. Durantini, Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2016, 13, 334.
- 41S. Zhang, H.-J. Kim, Q. Tang, E. Yang, D. F. Bocian, D. Holten, J. S. Lindsey, New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 5942.
- 42N. S. Gsponer, M. B. Spesia, E. N. Durantini, Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2015, 12, 67.
- 43M. Novaira, M. P. Cormick, E. N. Durantini, J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 2012, 246, 67.
- 44T. Y. Wang, J. R. Chen, J. S. Ma, Dyes Pig. 2002, 52, 199.
- 45A. Gomes, E. Fernandes, J. L. F. C. Lima, J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2005, 65, 45.
- 46W. Zhu, Y.-H. Gao, P.-Y. Liao, D.-Y. Chen, N.-N. Sun, P. A. N. Thi, Y.-J. Yan, X.-F. Wu, Z.-L. Chem, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 160, 146.
- 47N. Drogat, C. Gady, R. Granet, V. Sol, Dyes Pigm. 2013, 98, 609.
- 48D. Rakesh, Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 2013, 60, 1063.
- 49R. J. Melander, C. Melander, Infect. Dis. 2017, 3, 559.
- 50S. K. Sharma, M. Krayer, F. F. Sperandio, L. Huang, Y. Y. Huang, D. Holten, J. S. Lindsey, M. R. Hamblin, J. Porphyrins Phthalocyanines 2013, 17, 73.
- 51S. S. Puentes, M. Dunstan, Crit. Care Nurs. Clin. North Am. 2018, 30(1), 149.
- 52A. Mirhoseini, J. Amani, S. Nazarian, Microb. Pathog. 2018, 117, 162.
- 53Y. Chong, S. Shimoda, N. Shimono, Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 61, 185.
- 54E. Alves, A. C. Esteves, A. Correia, Â. Cunha, M. A. F. Faustino, M. G. P. M. S. Neves, A. Almeida, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2015, 14, 1169.
- 55D. Liu, L. Li, J. Chen, Z. Chen, L. Jiang, C. Yuan, M. Huang, J. Porphyrins Phthalocyanines 2018, 22, 925.
- 56T. Daia, Y.-Y. Huanga, M. R. Hamblin, Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2009, 6, 170.




