Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURES
Front Cover: Optical fan for single-cell screening (J. Biophotonics 1/2020)
- First Published: 02 January 2020
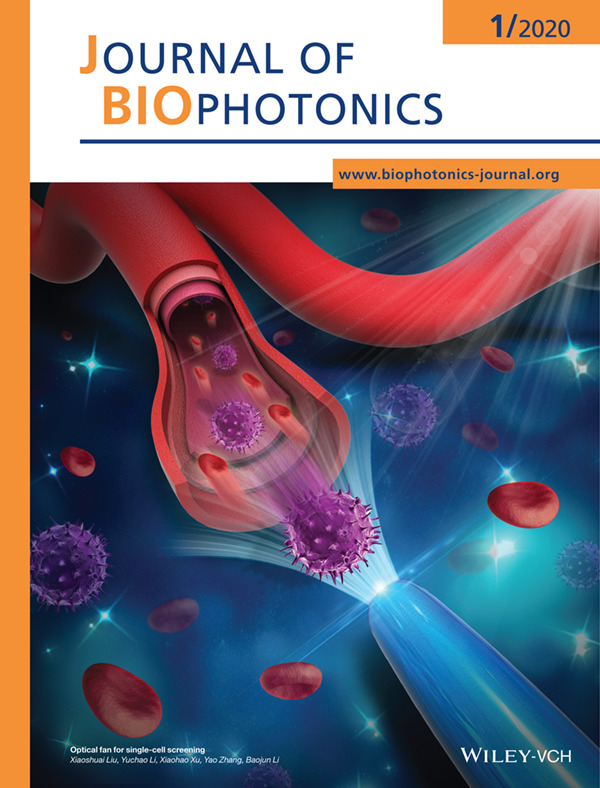
An optical fan was demonstrated to screen leukemia cells from the blood sample at the single-cell level in a noninvasive and noncontact manner.
Further details can be found in the article by Xiaoshuai Liu, Yuchao Li, Xiaohao Xu, Yao Zhang, Baojun Li (e201900155).
Inside Front Cover: Fast and sensitive delineation of brain tumor with clinically compatible moxifloxacin labeling and confocal microscopy (J. Biophotonics 1/2020)
- First Published: 02 January 2020
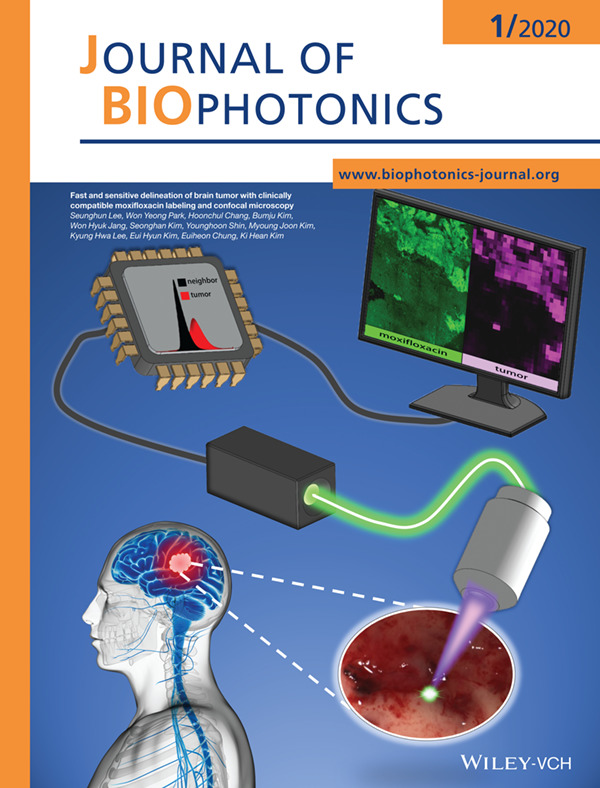
A new high-speed cellular imaging method using clinically applicable moxifloxacin labeling, called as moxifloxacin based confocal microscopy (MBCM), was developed for fast and sensitive tumor detection and delineation. The MBCM demarcated malignant brain tumor from normal brain by visualizing dense and irregular cell distribution in the tumor. An image processing algorithm was developed for automated brain tumor detection.
Further details can be found in the article by Seunghun Lee, Won Yeong Park, Hoonchul Chang, et al. (e201900197).
Inside Front Cover: Neurosurgical brain tumor detection based on intraoperative optical intrinsic signal imaging technique: A case report of glioblastoma (J. Biophotonics 1/2020)
- First Published: 02 January 2020
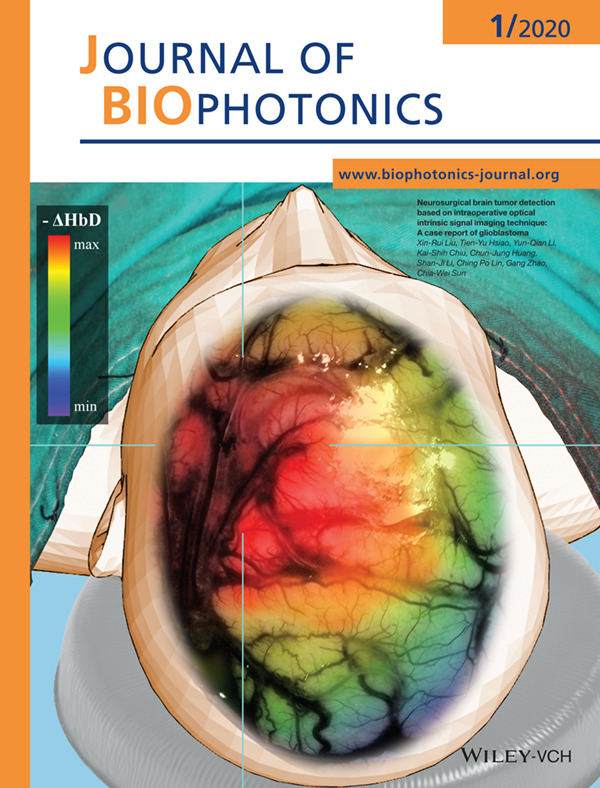
Intraoperative neurosurgical diagnosis of brain tumor determines the success rate of patients' prognoses. We firstly proposed a novel approach based on an optical method to distinguish the site of the tumor functionally. The promoted technique is non-invasive, non-radioactive, dye-free, and potential of real-time monitoring, which is still not available nowadays by using other techniques. The method could be applied to neuroimage guiding system for precision surgery of brain.
Further details can be found in the article by Xin-Rui Liu, Tien-Yu Hsiao, Yun-Qian, et al. (e201900200).
ISSUE INFORMATION
LETTERS
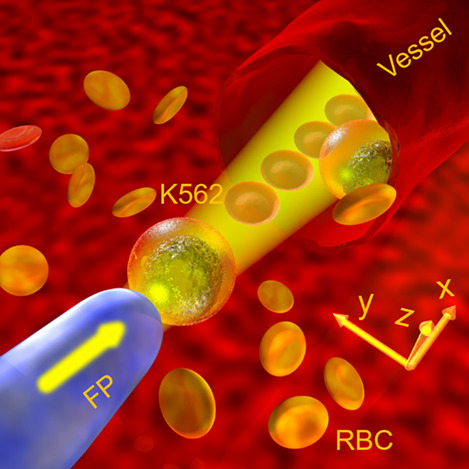
Quadrature demodulation in line-scan focal modulation microscopy for imaging three-dimensional zebrafish neural structure
- First Published: 25 July 2019
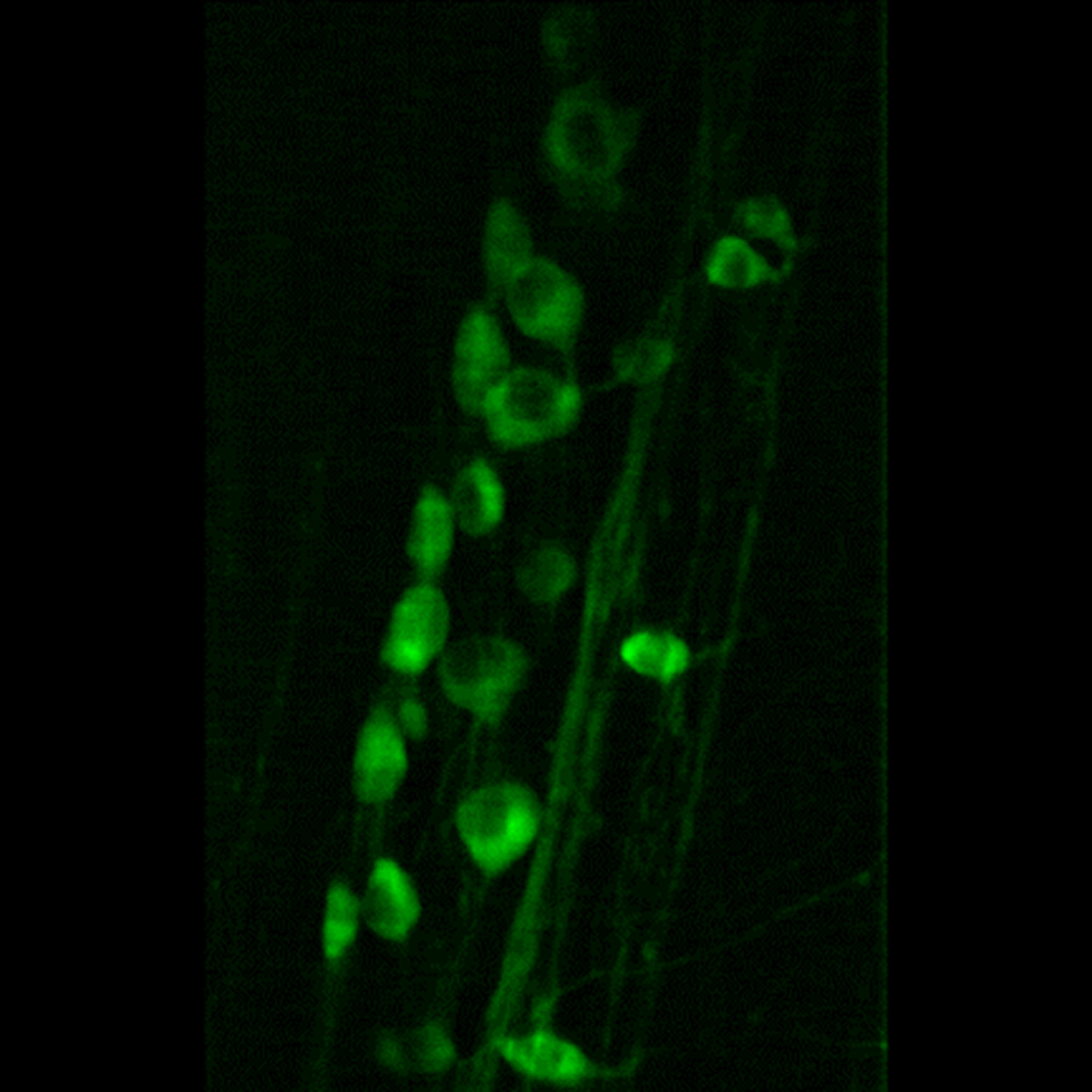
Line-scan focal modulation microscopy enables high speed acquisition and good optical sectioning ability at the same time. To further improve the image quality, this article presents a quadrature demodulation method to extract the focal information with an extended frequency bandwidth and therefore higher spatial resolution. Reduced background, reduced artifacts and more detailed morphological information can be retrieved in the three-dimensional zebrafish neural images, contributing to the neuroscience research.
Pathological crystal imaging with single-shot computational polarized light microscopy
- First Published: 04 September 2019
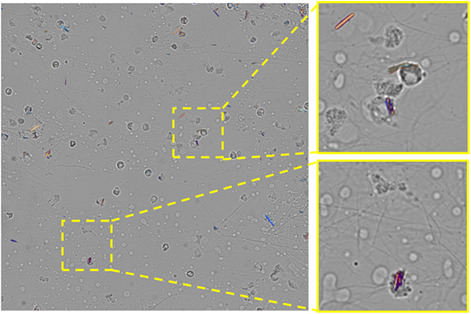
Single-shot computational polarized light microscopy method, termed SCPLM, achieves quantitative polarization imaging of pathological crystals using a standard light microscope and a pixelated polarizer camera. This method is fast, simple-to-operate and compatible with all the existing standard optical microscopes without extensive or costly modifications. This microscopy technique will provide improved sensitivity, specificity and speed, all at low cost, for clinical diagnosis of crystals found in synovial fluid and other bodily fluids.
FULL ARTICLES
Fast and sensitive delineation of brain tumor with clinically compatible moxifloxacin labeling and confocal microscopy
- First Published: 01 August 2019
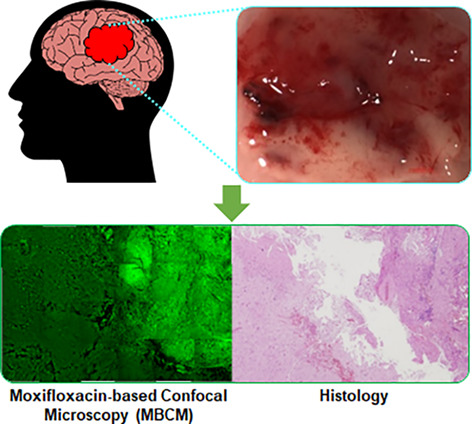
In brain tumor surgery, complete resection of tumor tissue while preserving normal brain tissue is critical to obtain an optimal clinical outcome. A high-speed cellular imaging method using clinically applicable moxifloxacin labeling, called as moxifloxacin based confocal microscopy (MBCM), was developed for fast and sensitive tumor detection and delineation. MBCM distinguished brain tumors from normal brain based on cytoarchitectural difference, and would have potentials as a surgery-guiding method.
Neurosurgical brain tumor detection based on intraoperative optical intrinsic signal imaging technique: A case report of glioblastoma
- First Published: 04 September 2019
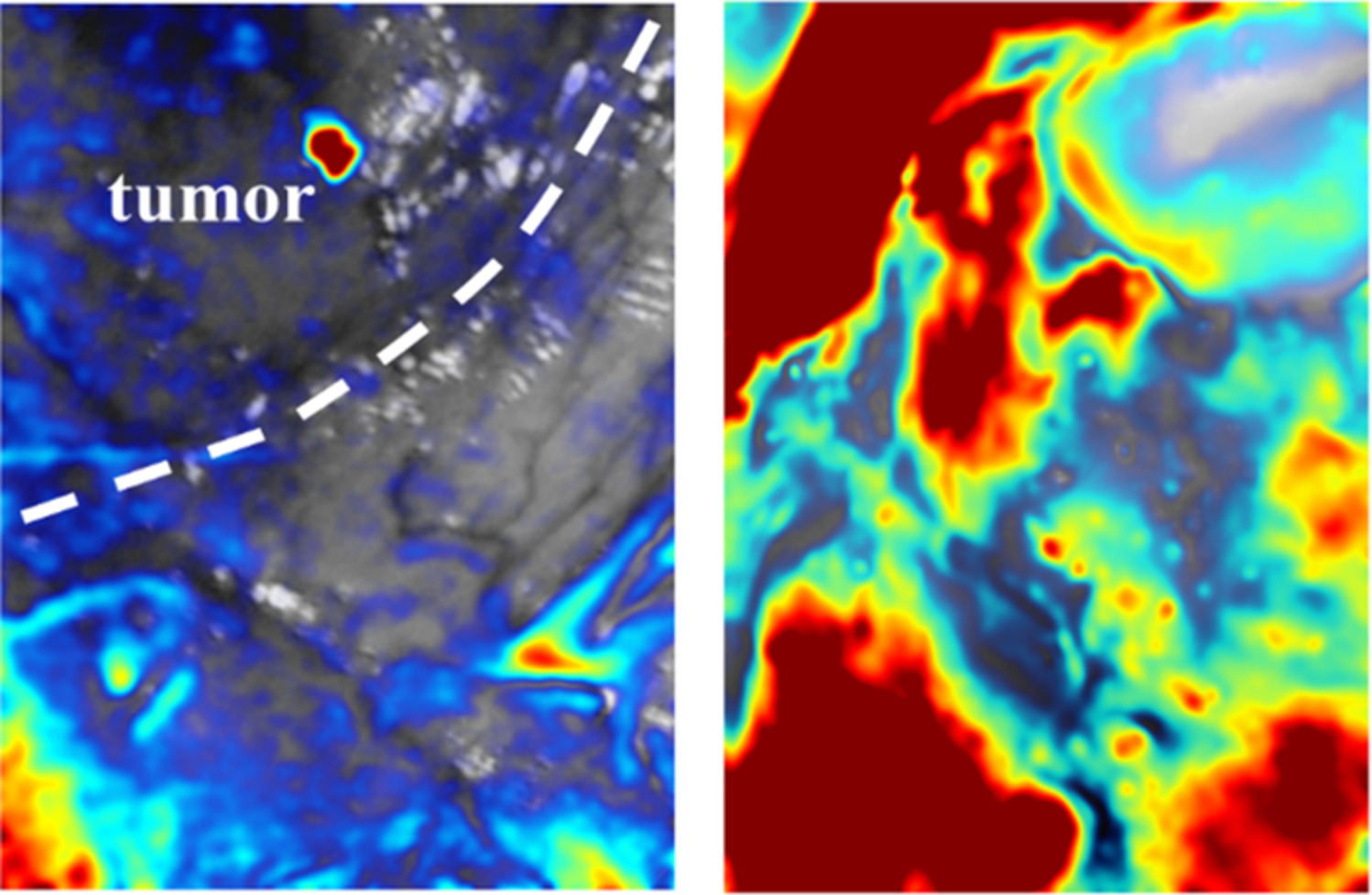
Intraoperative neurosurgical diagnosis of brain tumor determines the success rate of patients' prognoses. We first proposed a novel approach based on optical method to distinguish the site of tumor by functional manner. The promoted technique is noninvasive, nonradioactive, dye-free and potential of real-time monitoring, which is still not available nowadays by using other techniques. We believe that this method can facilitate clinical examination in the future and greatly elongate the patients' longevity.
Optical investigation of three-dimensional human skin equivalents: A pilot study
- First Published: 08 October 2019
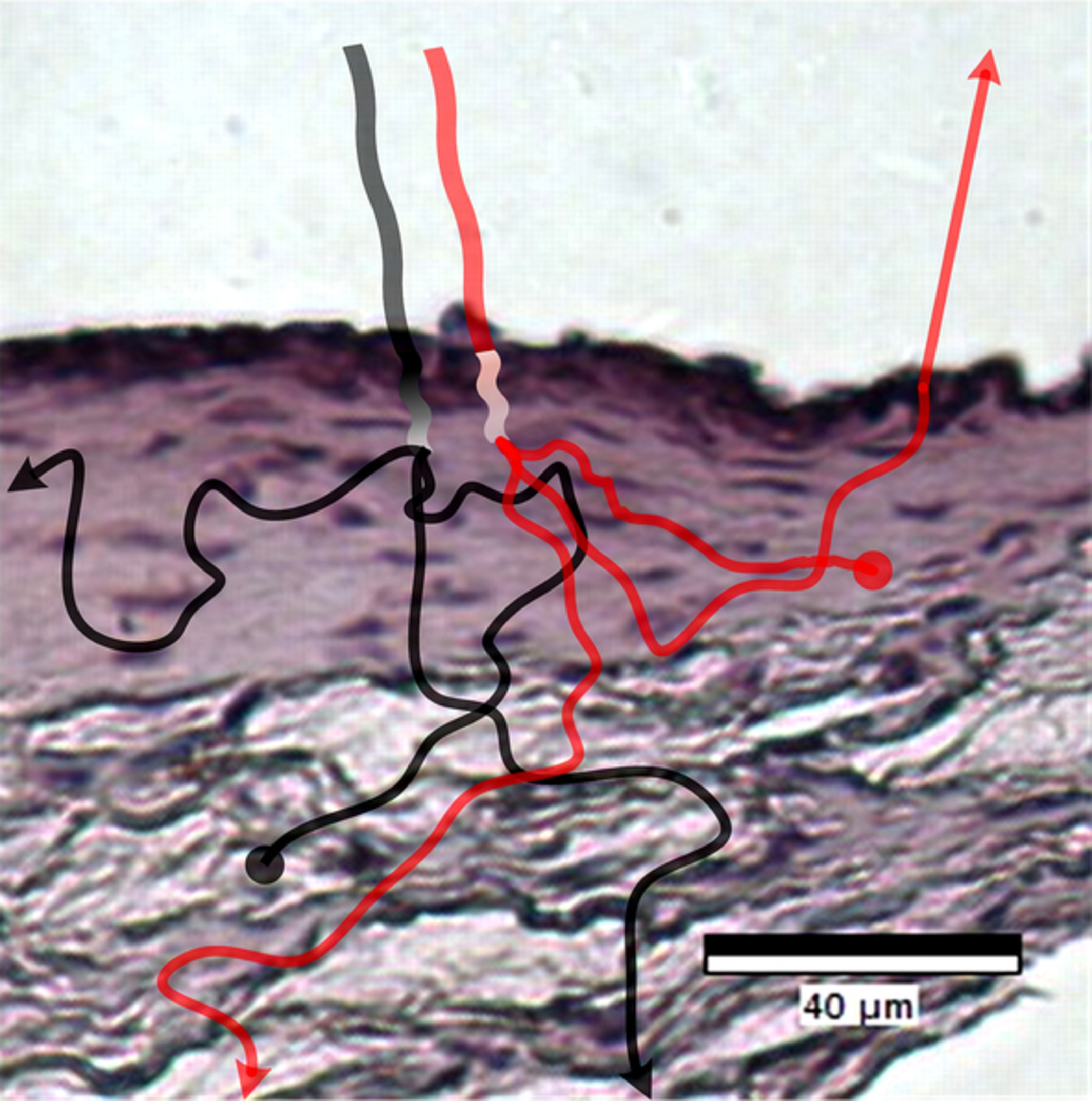
Human skin equivalents are living cultures of skin tissue, grown by seeding fibroblasts and keratinocytes on a scaffold. Although devoid of chromophores, skin models are used to investigate the interactions between the epidermis and dermis, and the morphology of skin layers. This article describes Monte Carlo simulations and experiments involving two-layer skin models. The measurements were comparable to the simulations, but only for samples thinner than 1 mm.
Evaluation of corneal epithelial thickness in glaucomatous patients using anterior-segment optical coherence tomography
- First Published: 08 October 2019
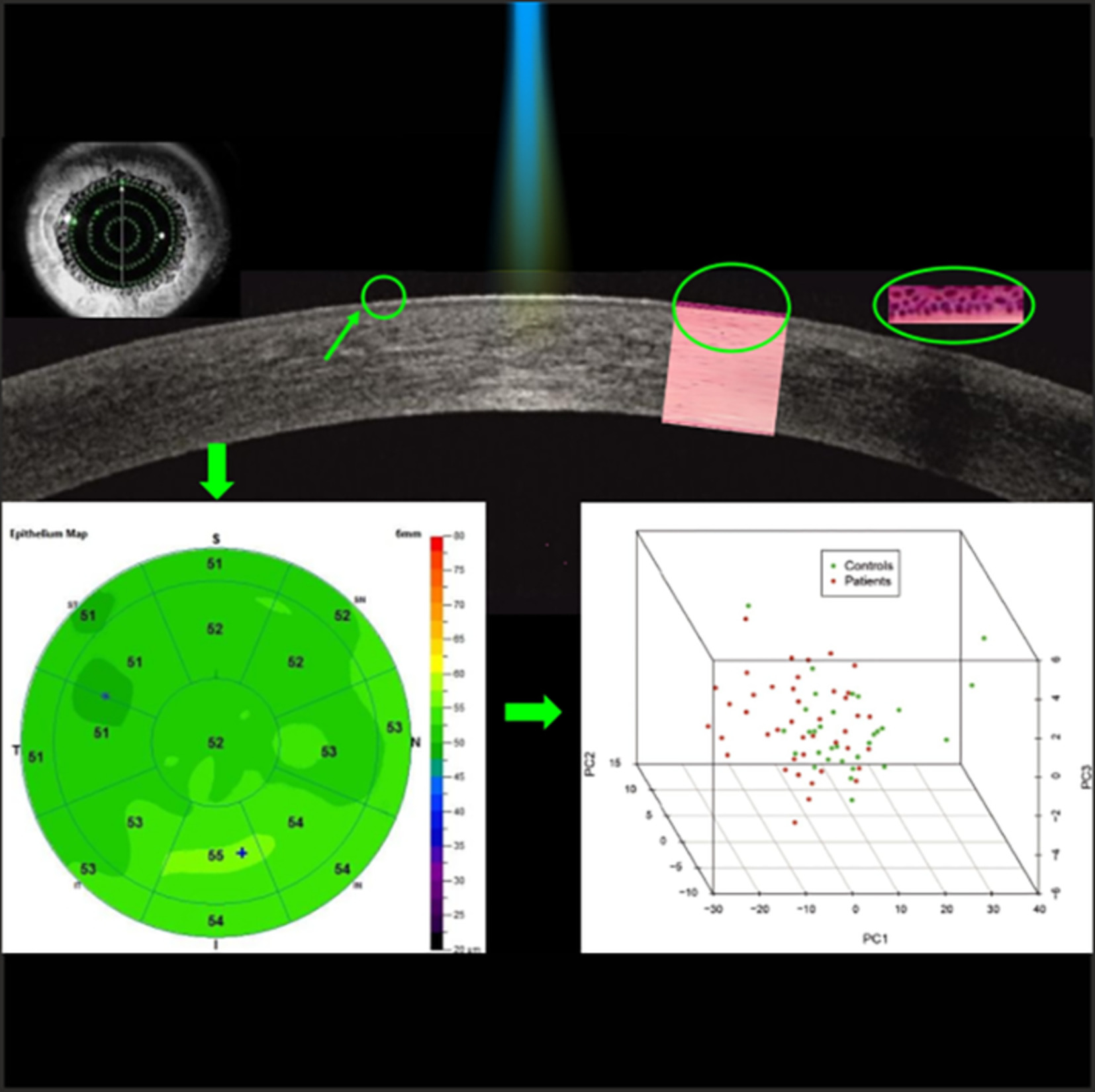
The objective of this study is to gain insights about the changes in corneal epithelium in glaucomatous patients divided according to age, type and duration of therapy using anterior-segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT). The study evaluated patients for whom corneal epithelium thickness (CET) was measured in different sectors of the cornea. The results showed no significant differences in CET among patients divided according to type and duration of treatment, while younger patients showed a thinner CET in comparison with older patients. AS-OCT results demonstrated that the physiological age-related alterations contributed to corneal epithelium changes in patients undergoing chronic antiglaucoma therapy.
Real-time augmented reality for delineation of surgical margins during neurosurgery using autofluorescence lifetime contrast
- First Published: 15 July 2019
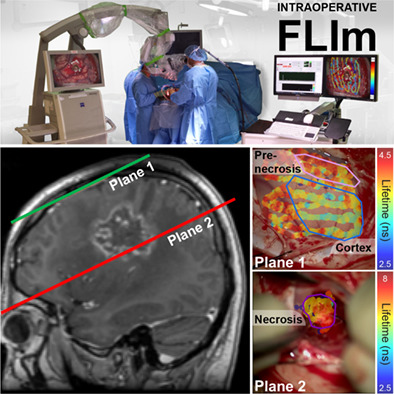
An intraoperative fluorescence lifetime imaging (FLIm) instrument is safely used during human brain surgery to resolve distinct tissue types and pathologies, as reported in three case studies. Autofluorescence lifetime contrast provides label-free biochemical information of distinct brain tissues including cortex, tumors and radiation induced necrosis. The FLIm instrument integrates with surgical microscopes to provide real-time intraoperative augmentation of the surgical field of view with fluorescent-derived parameters encoding diagnostic information.
An automatic diagnostic system of coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease using intravascular optical coherence tomography imaging
- First Published: 18 August 2019
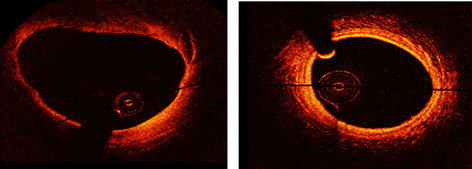
A fully automatic intracoronary diagnostic model is proposed in this study, which contributes to evaluate the structural changes of the arterial wall for each OCT pullback frame and extract all the pathological lesions. The model is designed based on fine-tuning and training a fully convolutional network, which demonstrates the strength of the deep features in describing various coronary artery lesions.
Towards Raman spectroscopy of urine as screening tool
- First Published: 04 November 2019
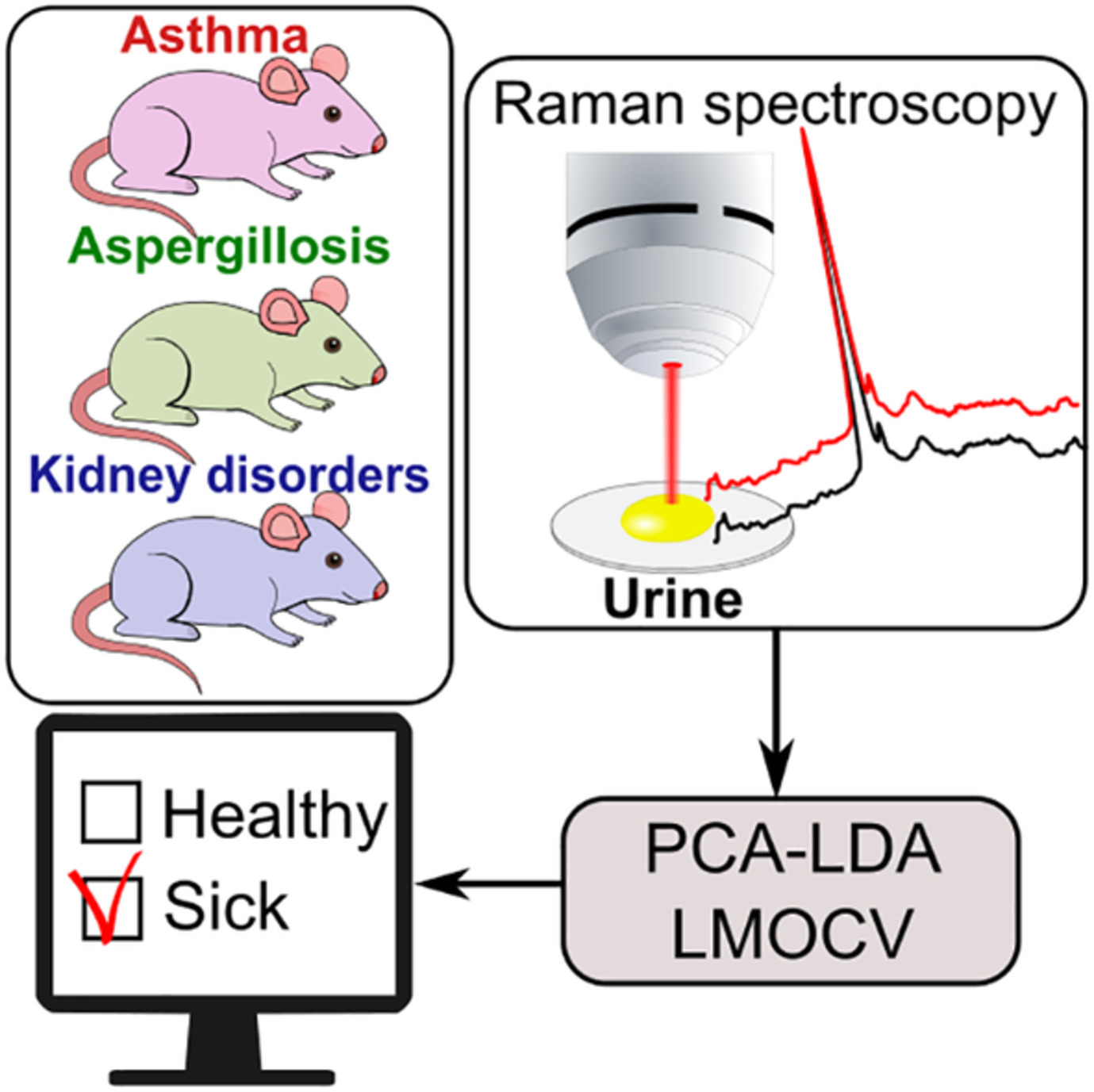
Utilizing mouse models of different diseases the potential of urine based Raman spectroscopy for screening applications was investigated. For the kidney diseases, which have direct influence on urine composition, the diagnostic accuracy of 100% was achieved. Considering respiratory tract diseases the diagnostic value of urine was noticeably lower, but still for both, asthma and aspergillosis, the discrimination accuracy between healthy and sick mice exceeded 77%.
Quantification of collagen structural changes during chick corneal development
- First Published: 29 August 2019
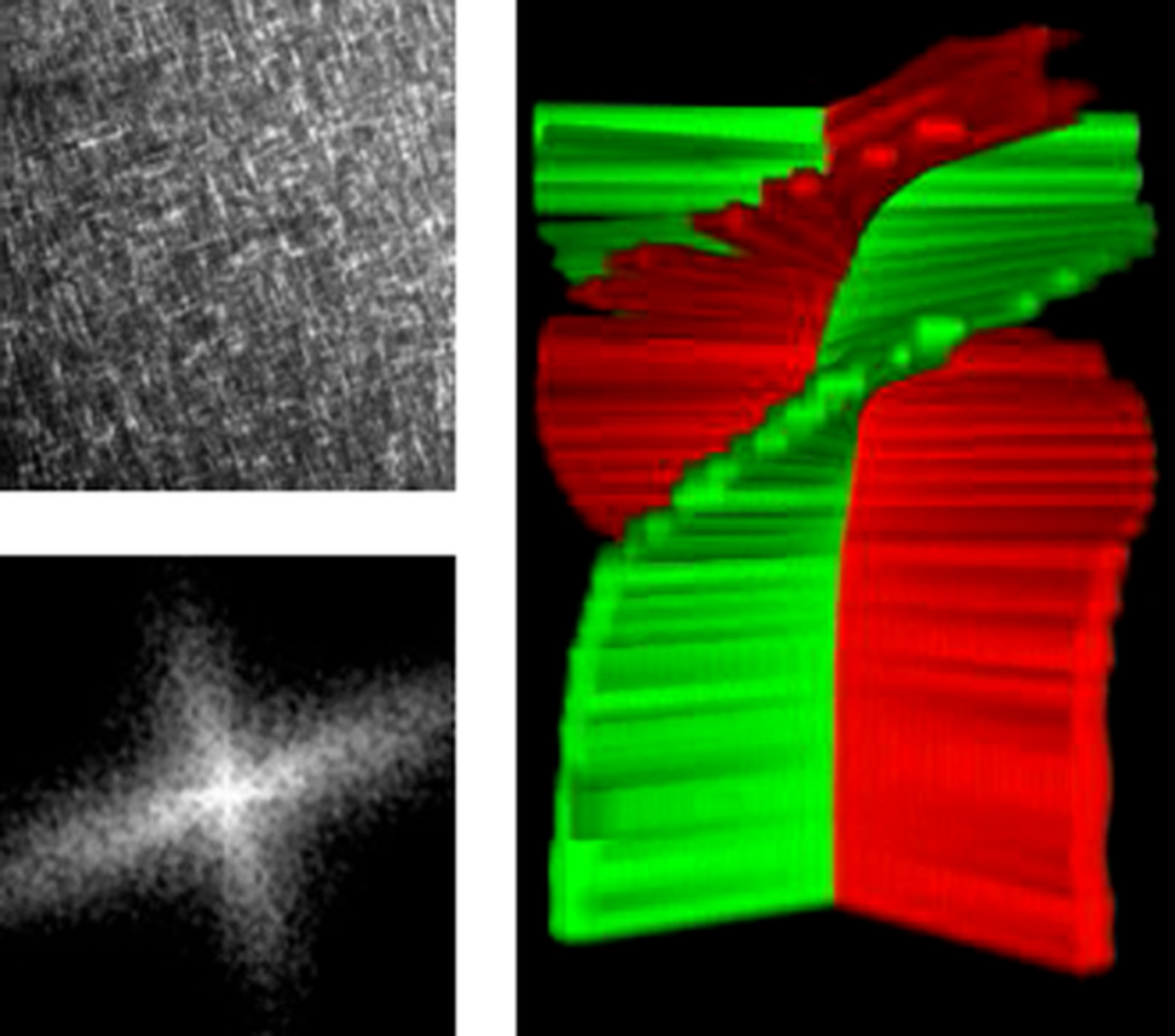
Abnormal cornea development can lead to conditions such as agenesis, megalocornea, microcornea, and cornea plana. Therefore, understanding the mechanisms of collagen assembly during development may contribute to the prevention or treatment of corneal diseases. The current study enhances our understanding of corneal development in a significant way making use of an established, yet state of the art nonlinear imaging method combined with a suitable analysis method.
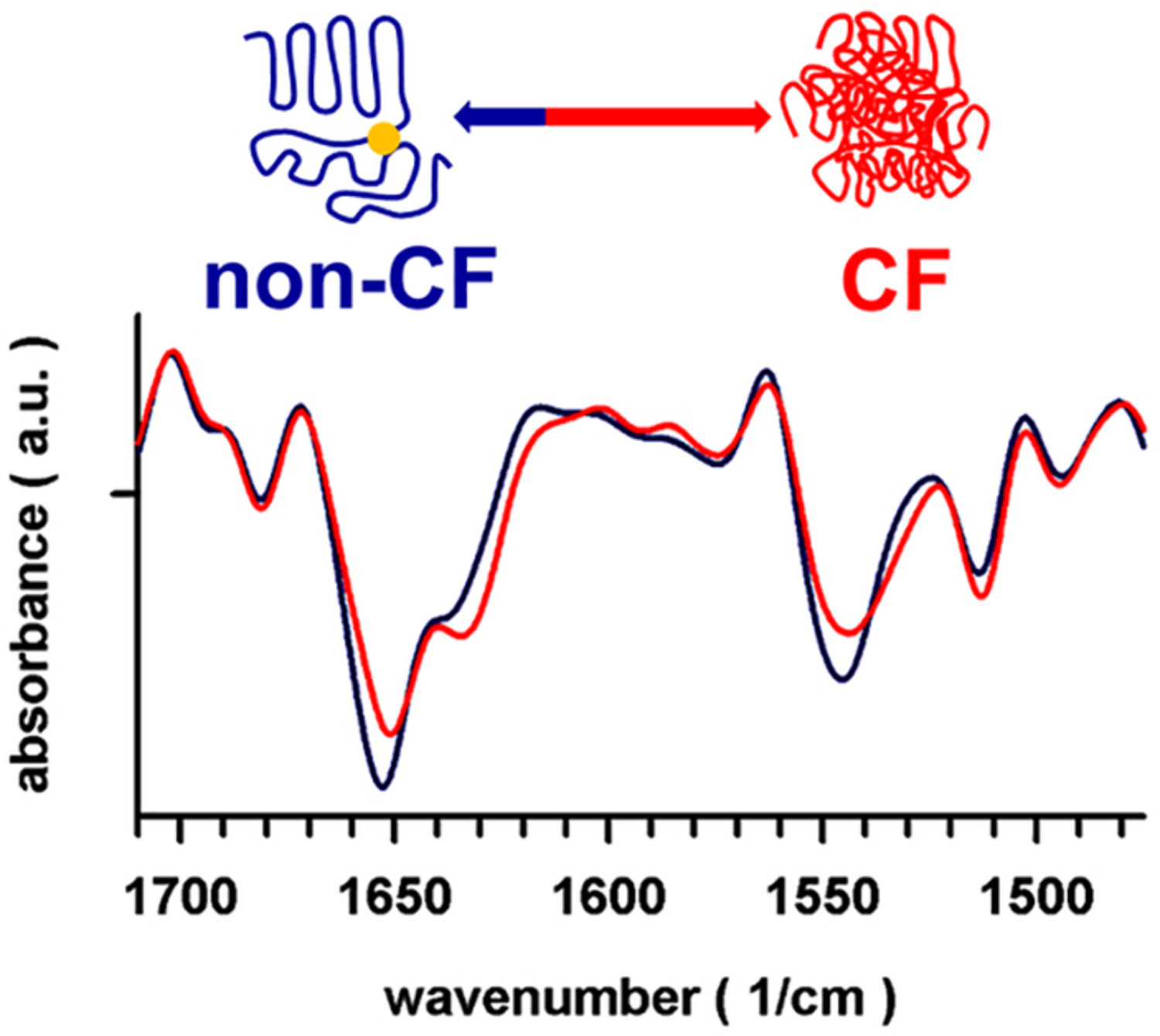
Infrared biomarkers of impaired cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator protein biogenesis
- First Published: 26 October 2019
In vivo longitudinal imaging of RNA interference-induced endocrine therapy resistance in breast cancer
- First Published: 03 September 2019
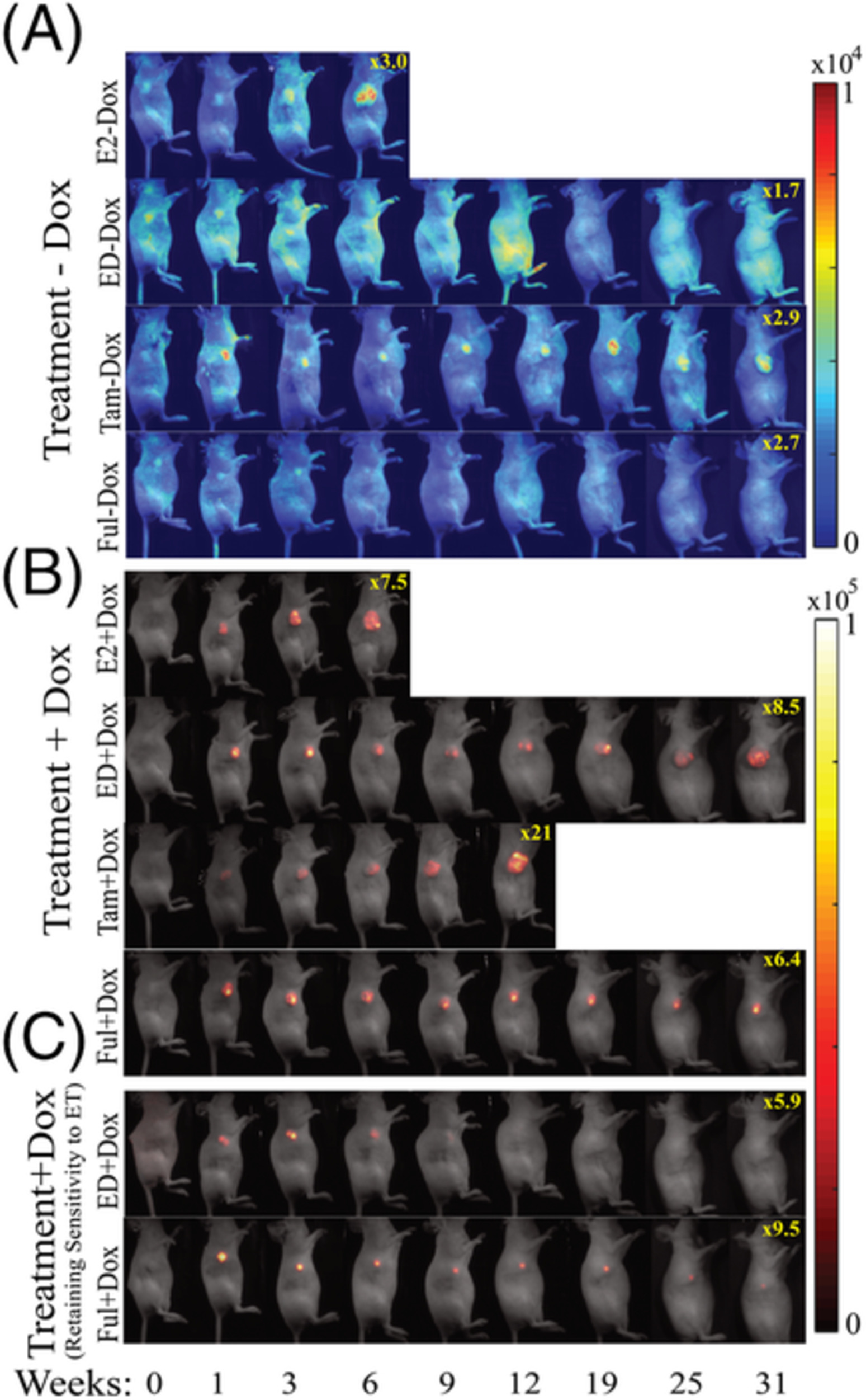
In vivo images of GFP and RFP channels for treatment with (A) −Dox and (B) +Dox in mice. C, The tumor exhibiting resistance to endocrine therapy has been demonstrated with typical images from ED + Dox and Ful + Dox. Dox, doxycycline; ED, estrogen deprivation; Ful, fulvestrant; GFP, green fluorescent protein; RFP, red fluorescent protein.
Fluorescence fingerprints of oral bacteria
- First Published: 25 October 2019

We visualized seven oral bacteria based on their auto-fluorescence and distinguished by combining excitation emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy data and PCA analysis. It offers a fundamental proof of reasoning to develop the auto-fluorescence imaging for rapidly detection and identifying of bacteria. These methods can be expanded and implemented in clinical applications.
Interplay of temperature, thermal-stresses and strains in laser-assisted modification of collagenous tissues: Speckle-contrast and OCT-based studies
- First Published: 30 September 2019
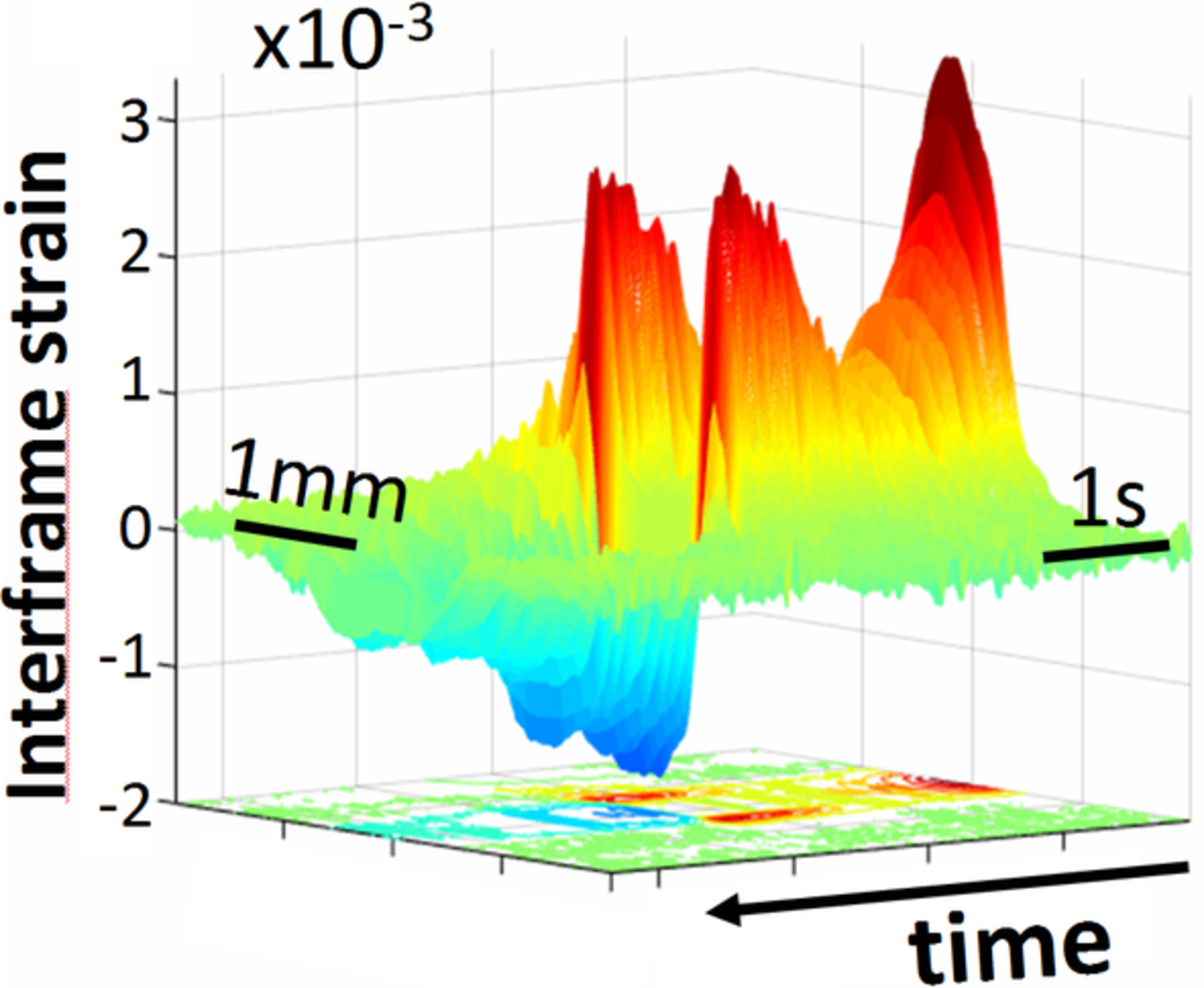
Moderate short-time heating of cartilage and cornea by infrared-laser irradiation can produce biologically nondestructive tissue reshaping, which can be used for fabrication of cartilaginous implants and cornea-refraction correction. We show that thermal stresses can help to produce efficient reshaping at lower temperature outside the temperature maximum. OCT-based visualization demonstrates how the strain-rate maximum arising in the heating-beam center gradually splits and drifts towards the temperature-profile slopes, where maximal thermal stresses are located.
Photobiomodulation therapy in knee osteoarthritis reduces oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines in rats
- First Published: 30 September 2019
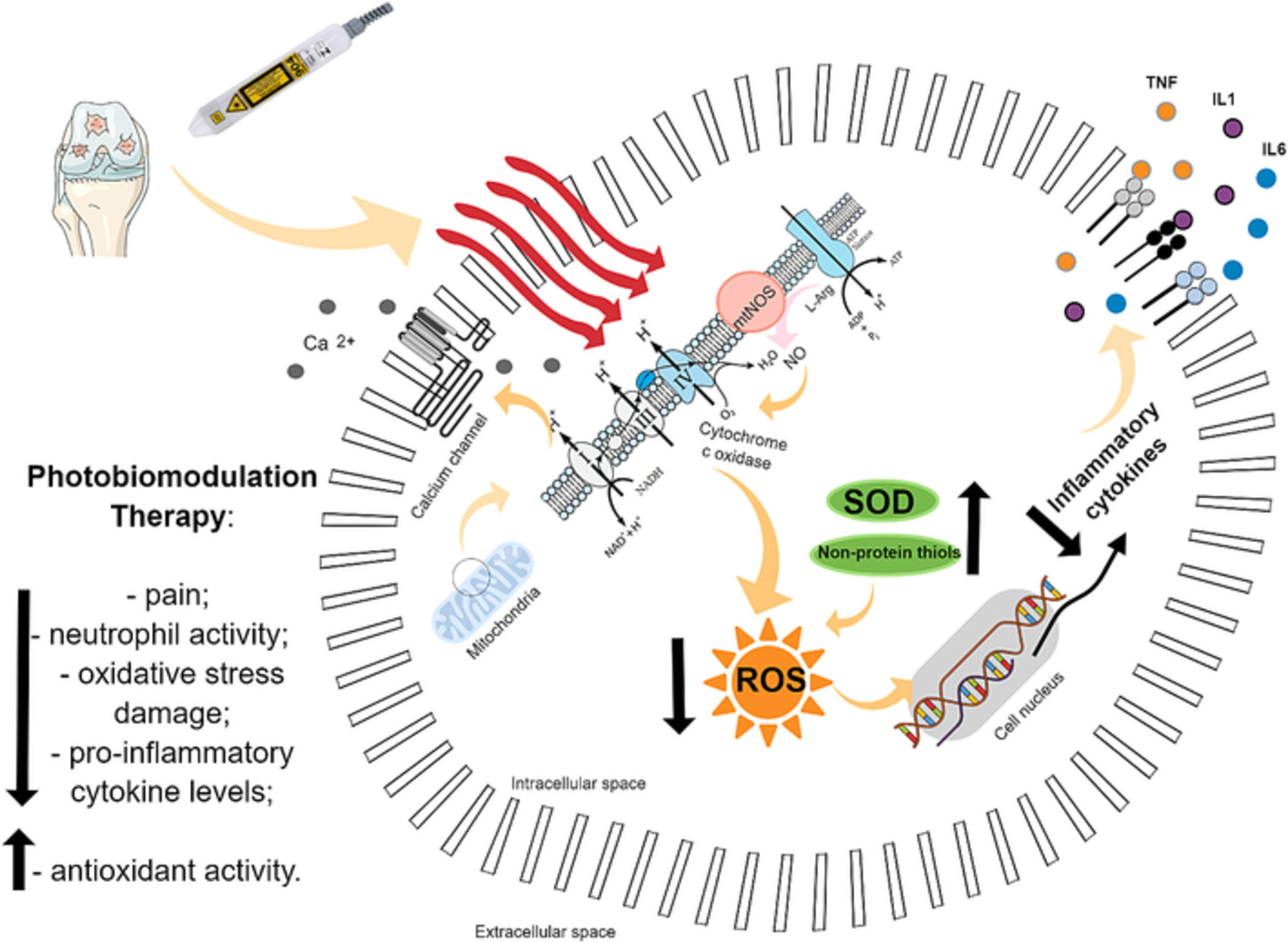
The photobiomodulation therapy, using low intensity laser therapy, is a promising alternative for the osteoarthritis treatment. We studied the effects of photobiomodulation therapy in an animal model of knee osteoarthritis. Our results suggest that photobiomodulation therapy reduced the articular damage related to oxidative stress and elevated the antioxidant reaction, as well as it reduced the inflammatory progress through the cascade of cytokines.
Analysis of relation between skin elasticity and the entropy of skin image using near-infrared and visible light sources
- First Published: 04 September 2019
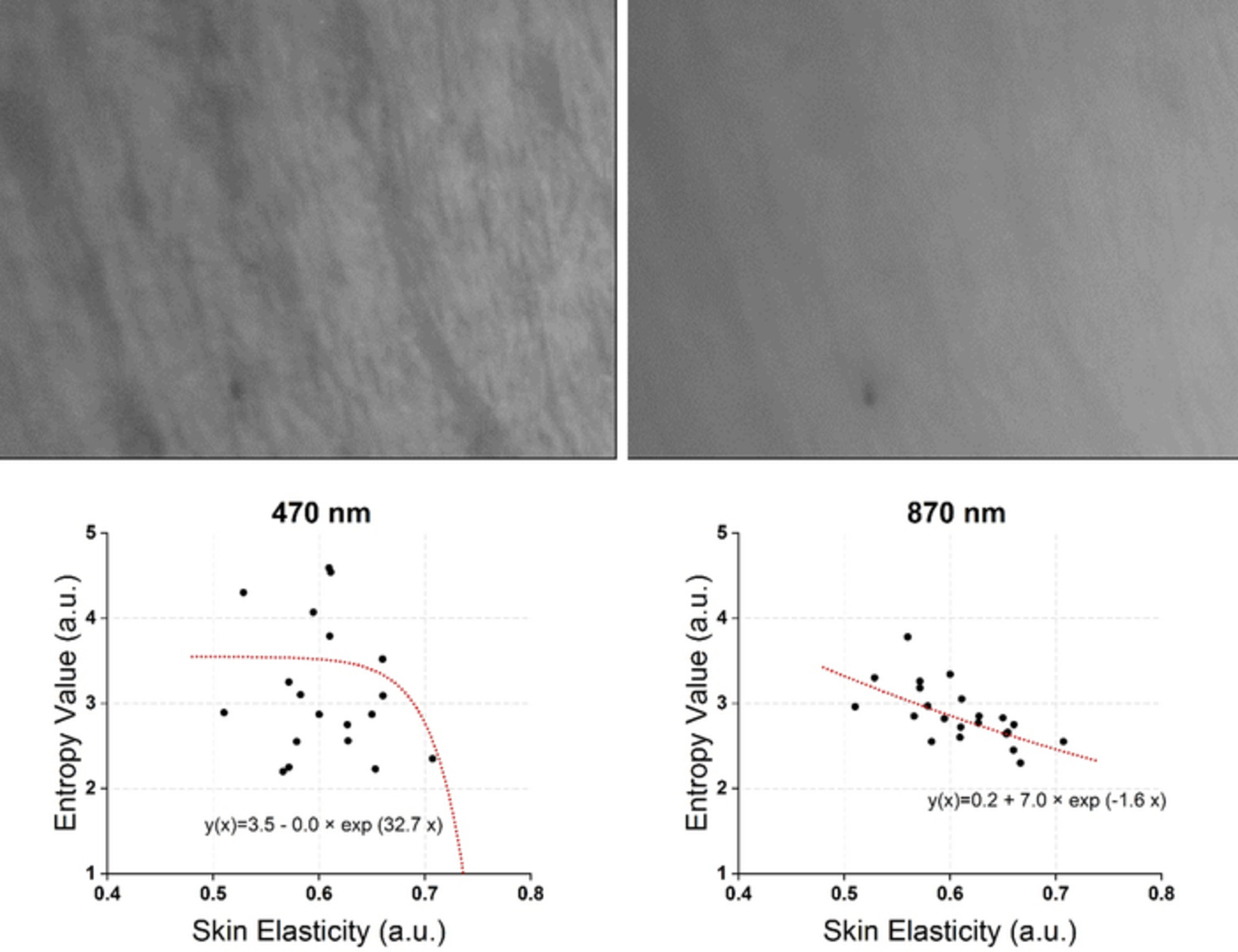
As a first step to develop new methods for measuring skin elasticity, the relation between skin elasticity and the entropy of skin image with near-infrared and visible light sources are analyzed. Wrinkles increases the randomness of frequency components and it is quantified by entropy. In the results, the root mean square error of each wavelength is “0.27” (870 nm), “0.49” (broadband light) and “1.42” (470 nm).
Evaluation of breast carcinoma regression after preoperative chemotherapy by label-free multiphoton imaging and image analysis
- First Published: 06 October 2019
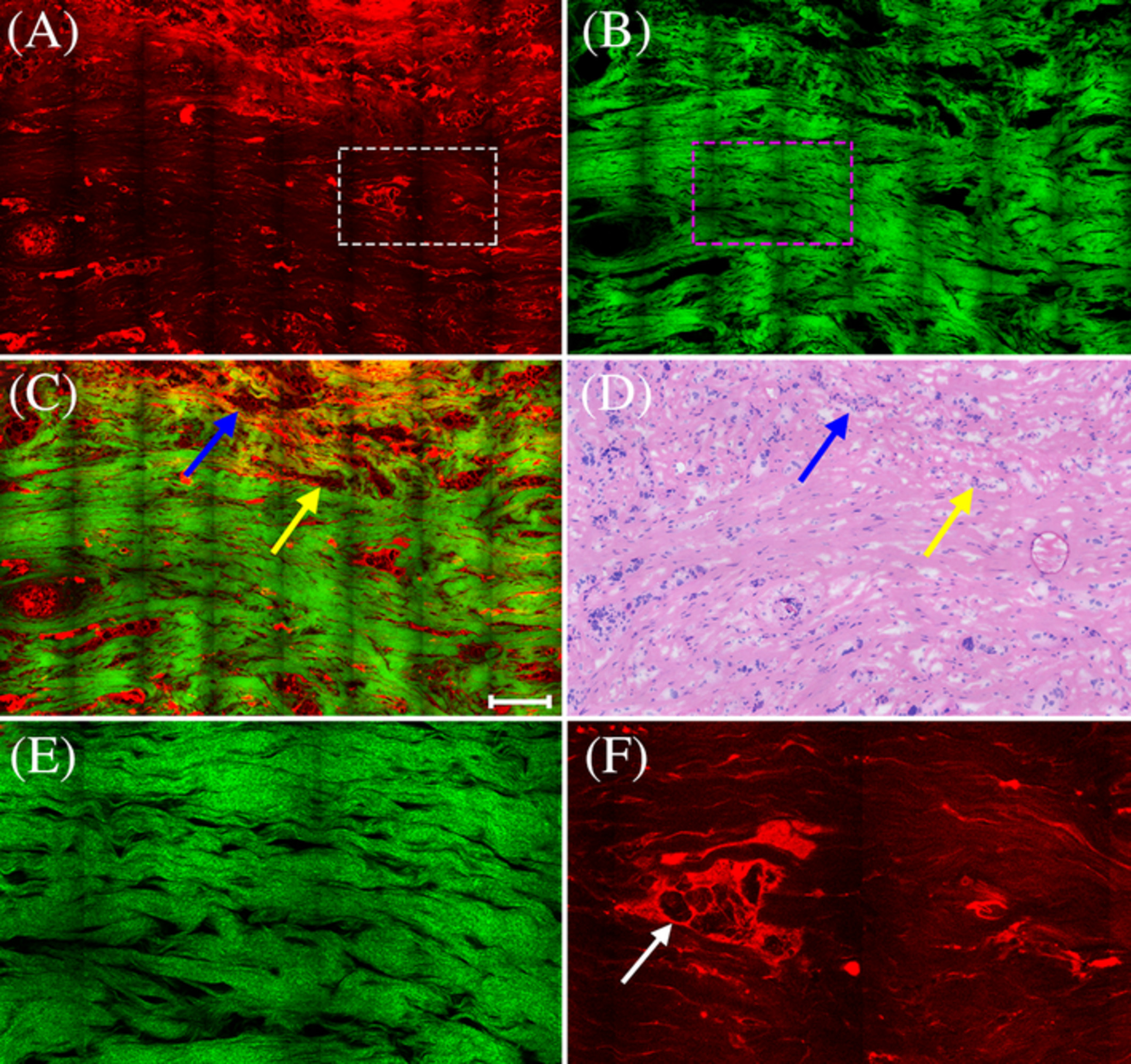
Multimodal multiphoton imaging including two-photon excitation fluorescence and second-harmonic generation was used to identify different degrees of tumor response such as a slight, significant, or complete response and can detect morphological alteration associated with extracellular matrix during the progression of breast carcinoma following preoperative chemotherapy. These results may offer a basic framework for using multiphoton microscopy as a helpful diagnostic tool for assessing breast carcinoma response after neoadjuvant treatment.
Multimodal imaging for tumour characterization from micro- to macroscopic level using a newly developed dorsal chamber designed for long-term follow-up
- First Published: 08 October 2019
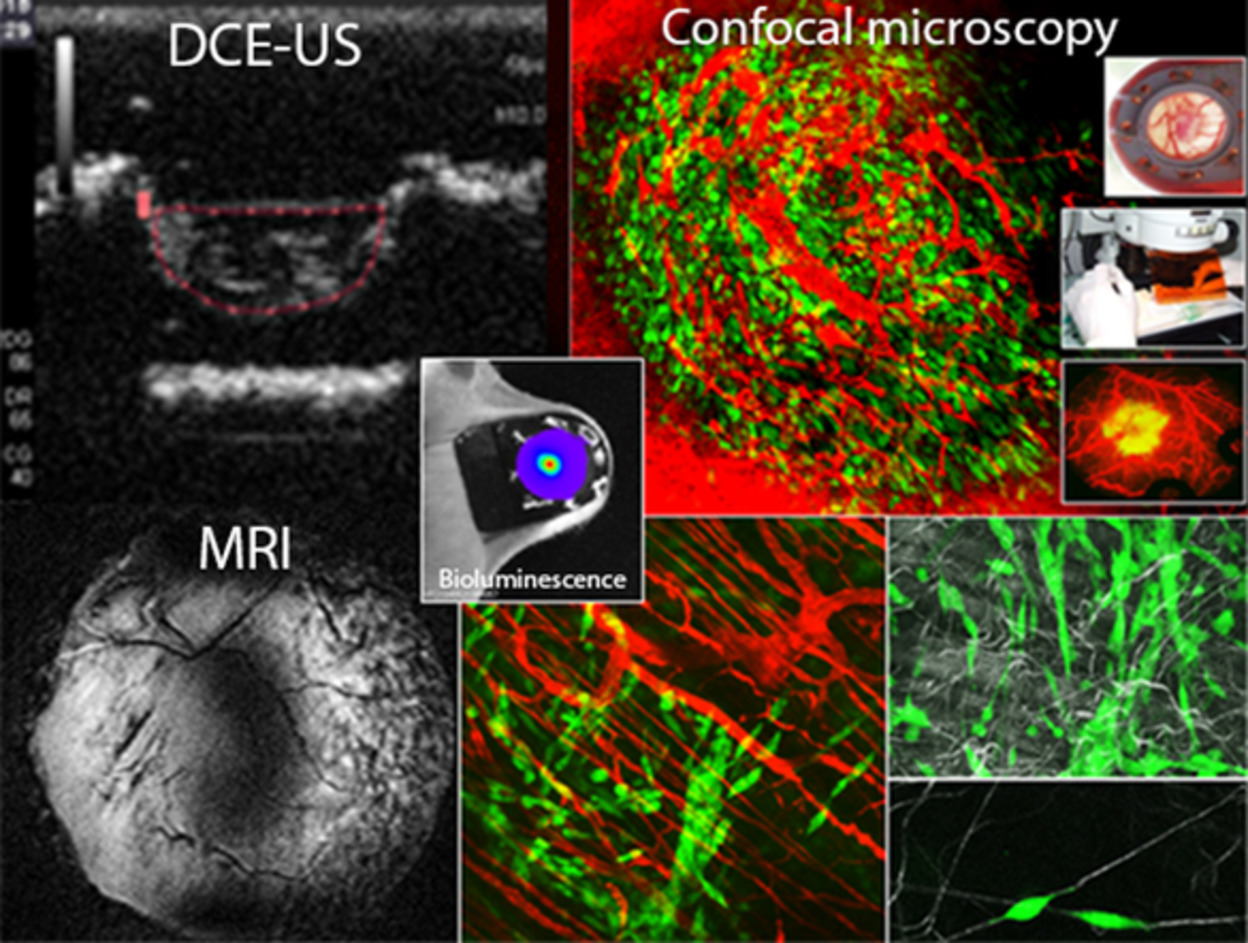
Preclinical in vivo study of molecular and cell interactions dynamics can be achieved in photon imaging thanks to implantable chambers, allowing the multiscale observation from isolated cell to whole organ. We developed a new dorsal chamber very well tolerated by the mice model, making then possible dynamic and long-term imaging without side effects. Designed for multimodality imaging, the tool is also compatible with sonography, X-ray and magnetic resonance imaging for multiparametric characterization.
Spectral characteristics of caries autofluorescence obtained from different locations and caries severities
- First Published: 30 September 2019
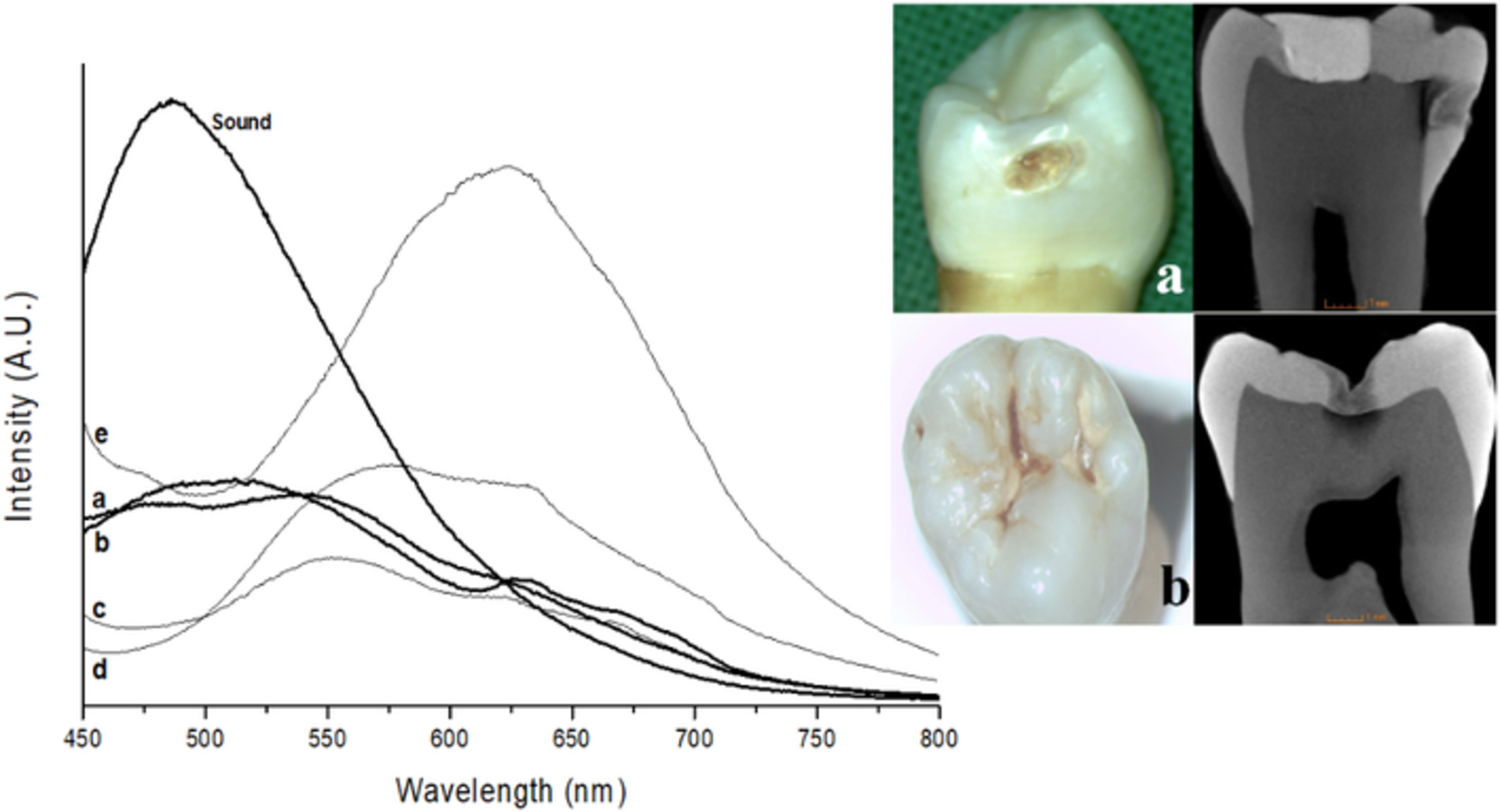
Representative autofluorescence spectra and optical microscope (and micro-CT) images of specimens obtained from sound and stage IV caries (sound, a, b) surfaces (interproximal and occlusal surfaces). However, some specimens had different spectral slope despite similar discolorations on interproximal surfaces compared to specimens a and b. Stained thick layers on grooves (d) and ground powder (e) of that layer were spectrally not different.
OptCAM: An ultra-fast all-optical architecture for DNA variant discovery
- First Published: 09 August 2019
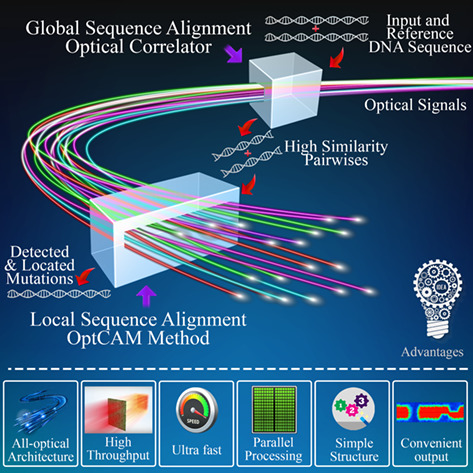
In order to overcome the limitation of current DNA variant discovery methods due to the accelerated expansion of genetic data, a novel optical approach for local sequence alignment, named as OptCAM method, and its corresponding optical architecture are proposed to accurately locate mutations. Exploiting high-speed processing and operational parallelism, inherently exist in optics, and avoiding various limitations of electrical implementations make the OptCAM method significantly faster than its electrical counterparts.
Understanding the effects of culture conditions in bacterial growth: A biochemical perspective using Raman microscopy
- First Published: 24 August 2019
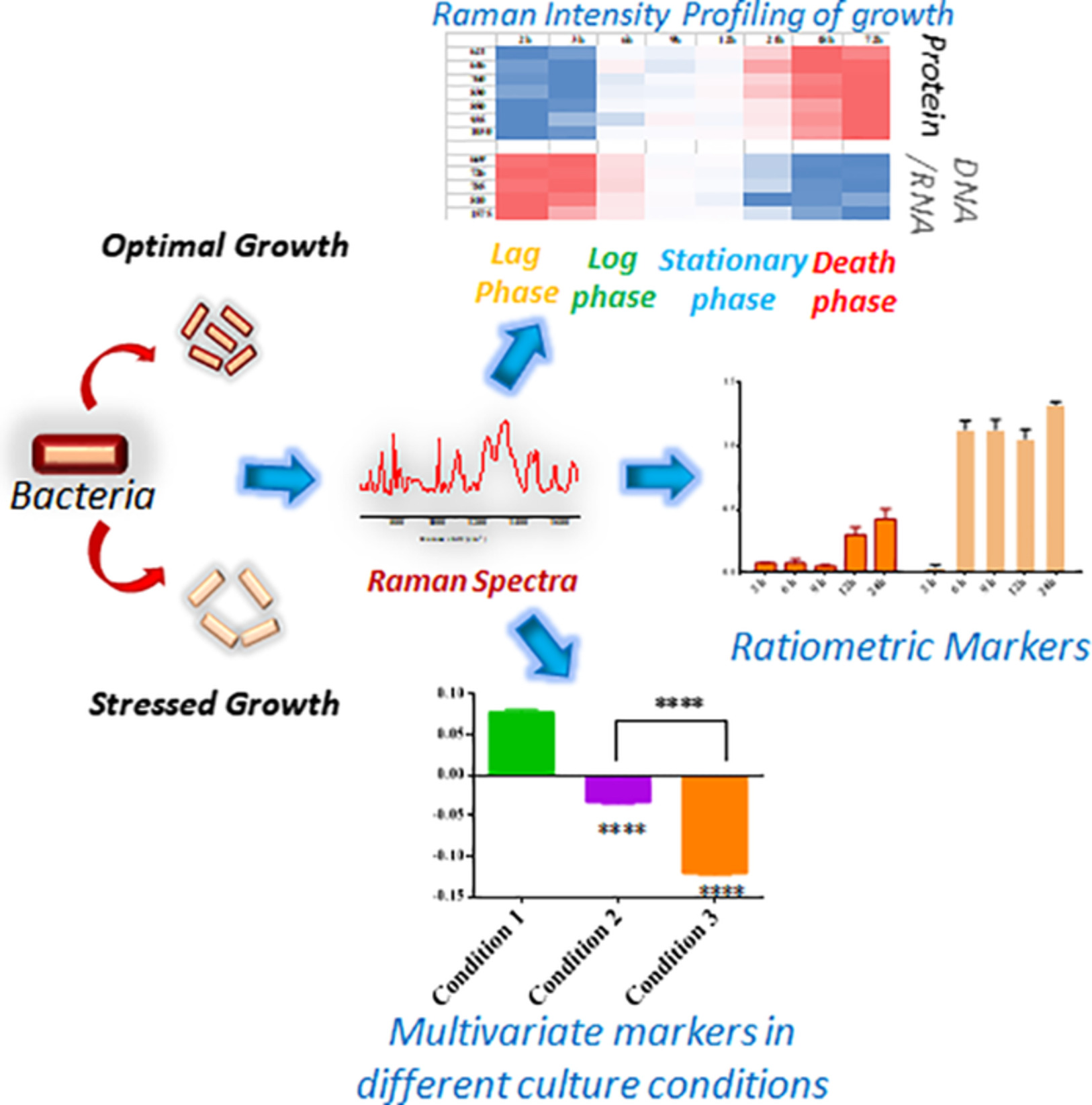
Escherichia coli has been grown in different conditions and corresponding biochemical signatures in each metabolic stage have been obtained using Raman micro-spectroscopy. A detailed spectral analysis has been performed to identify minuscule spectral changes depending on culture condition. A library of such Raman markers at various growth conditions can be a great tool for understanding bacterial mechanism for adapting adverse conditions.
Autofluorescence excitation-emission matrices as a quantitative tool for the assessment of meat quality
- First Published: 06 October 2019

Grading of the commercially produced meat quality currently relies on partly subjective, time-consuming and costly methods. Here, we demonstrate a new method allowing evaluation of meat grade by measuring and analysis of autofluorescence properties in small samples extracted by 8 mm punch probe. This approach paves the way for more sustainable and objective meat quality discrimination.
Improving the limit of detection in portable luminescent assay readers through smart optical design
- First Published: 10 October 2019

Portable, low-cost optical systems such as cell phones are attracting increasing interest as assay readers for point-of-care testing. However, little attention has been paid to the optical design of such systems. We demonstrate that a single number—the source-normalized image intensity—determines how the optical system affects the limit of detection (LOD). By optimizing this number, we design a system that achieves a 10-fold improved LOD compared to prior designs.
Reliability of wavefront shaping based on coherent optical adaptive technique in deep tissue focusing
- First Published: 17 October 2019
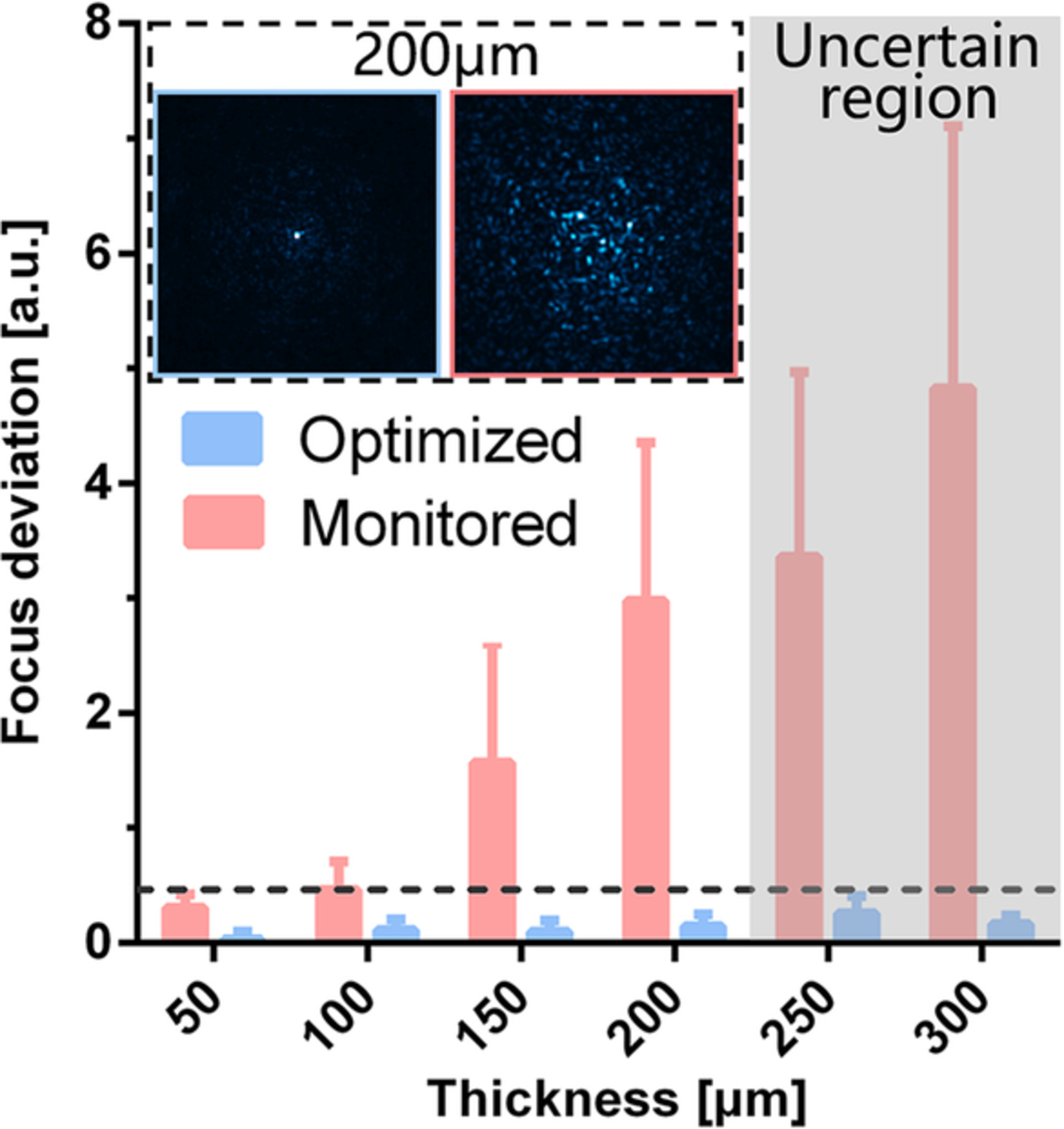
The reliability of wavefront shaping in mouse brain tissue focusing is investigated by using backscattered light as feedback. Statistical results show that when the penetration depth of 488 nm laser reaches 200 μm, the focus on the epi-detection plane is optimized but no effective focusing is reconstructed in the illumination focal plane, which is of importance to improve the epi-detection based wavefront shaping methods in biological applications.
Phase dual-slopes in frequency-domain near-infrared spectroscopy for enhanced sensitivity to brain tissue: First applications to human subjects
- First Published: 03 September 2019
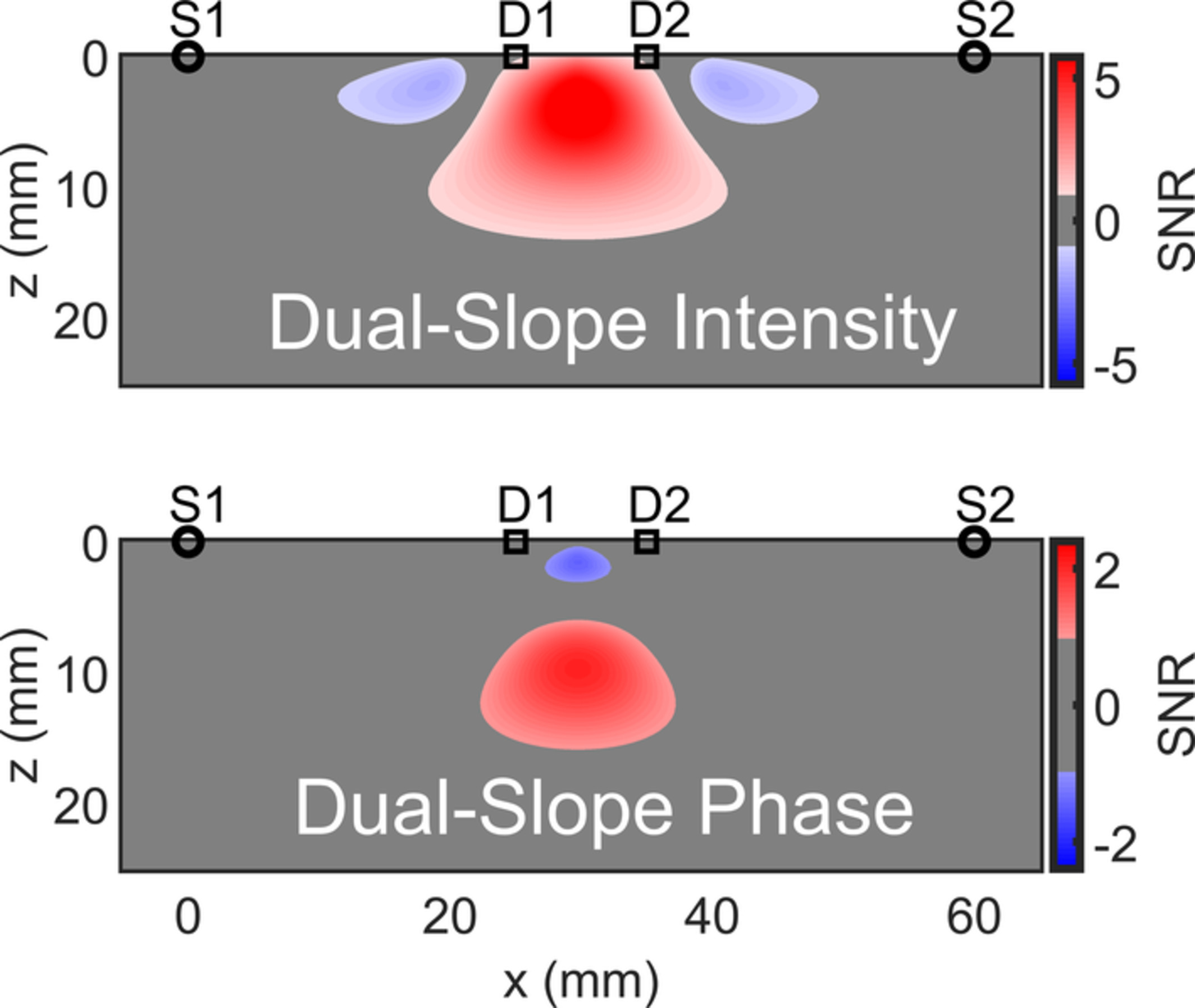
We report simulations and first measurements on the human brain with a new frequency-domain near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) technique based on phase dual-slopes (DSϕ). The DSϕ technique requires two light sources and two optical detectors placed on the tissue surface in a special configuration, and a dedicated data analysis scheme. Our results indicate the deeper region of sensitivity of DSϕ measurements compared with existing NIRS measurement approaches, with a maximal sensitivity at a depth of about 11 mm.
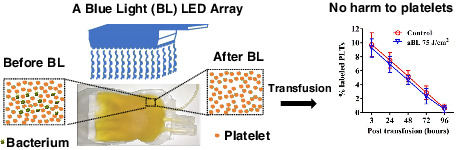
Antimicrobial blue light for decontamination of platelets during storage
- First Published: 12 August 2019
Automated label-free detection of injured neuron with deep learning by two-photon microscopy
- First Published: 11 October 2019
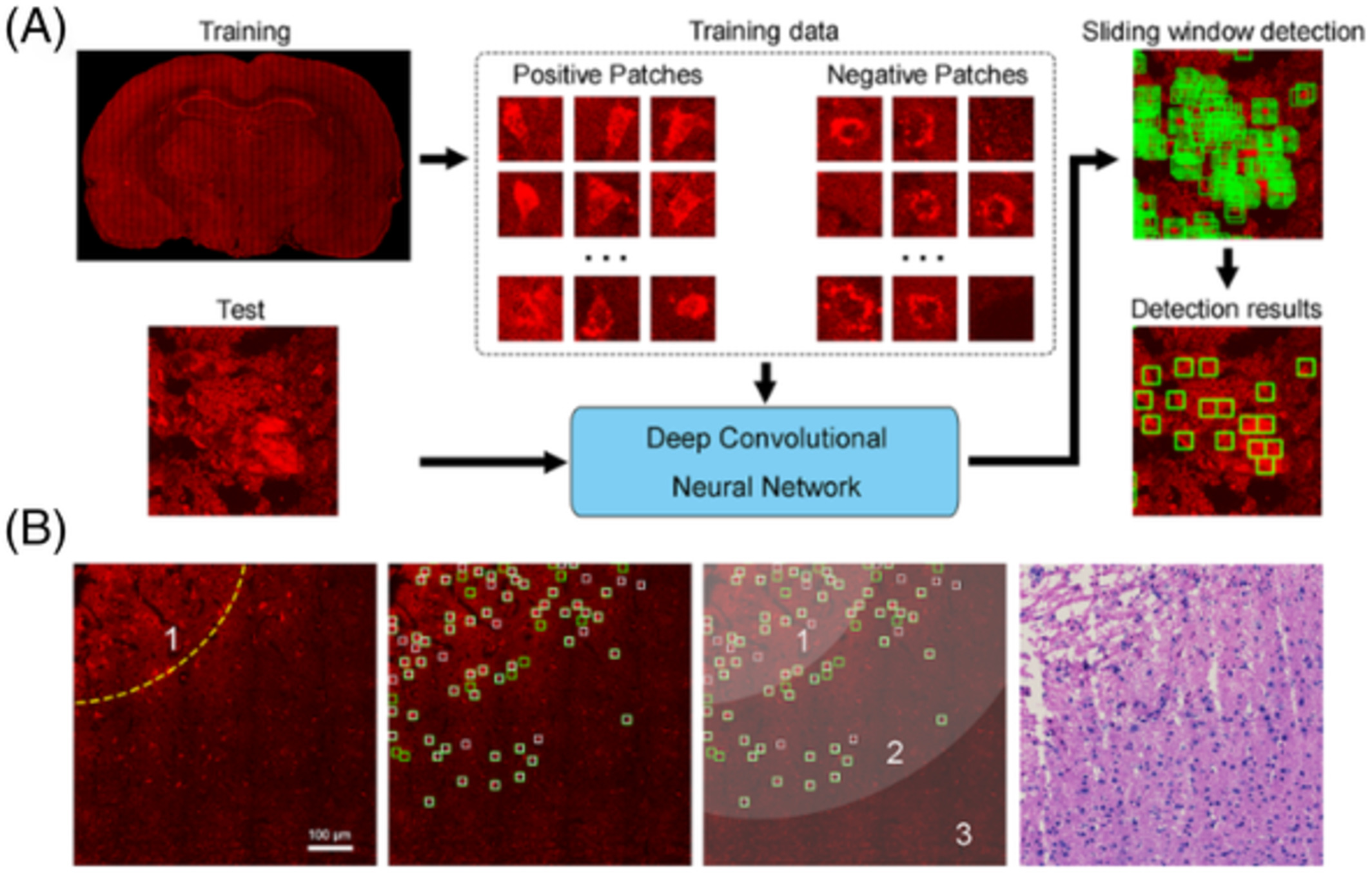
In this study, we investigated the capability of two-photon microscopy (TPM) to label-freely identify injured neurons on unstained thin section and fresh tissue of rat cerebral ischemia-reperfusion model. Moreover, a deep learning model based on convolutional neural network was developed to automatically detect the location of injured neurons. Finally, combining TPM with deep learning, we presented an automated and label-free approach to evaluate the ischemic regions, which could improve diagnostic accuracy compared with standard histology.
Contamination detection by optical measurements in a real-life environment: A hospital case study
- First Published: 15 October 2019
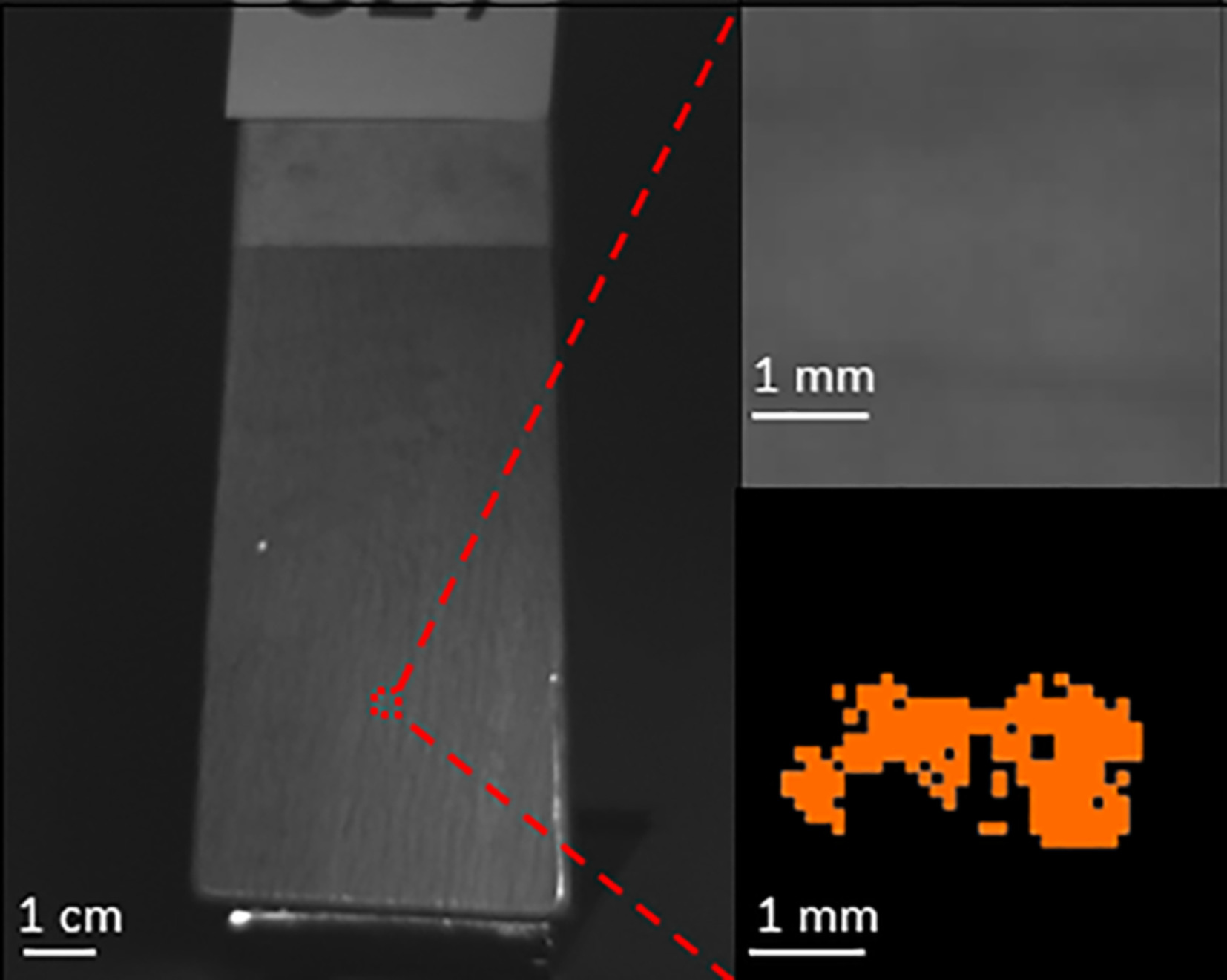
Touch surface cleanliness monitoring by optical imaging was studied in a real-life hospital environment using both manual and automatic hyperspectral scanning algorithms. As the highlight, a human eye invisible stain from a dirty chair armrest was revealed. Thus, the optical imaging system in the safe visible light area shows a promising method for touch surface cleanliness evaluation in real-life environments.
Assessment of corneal viscoelasticity using elastic wave optical coherence elastography
- First Published: 18 October 2019
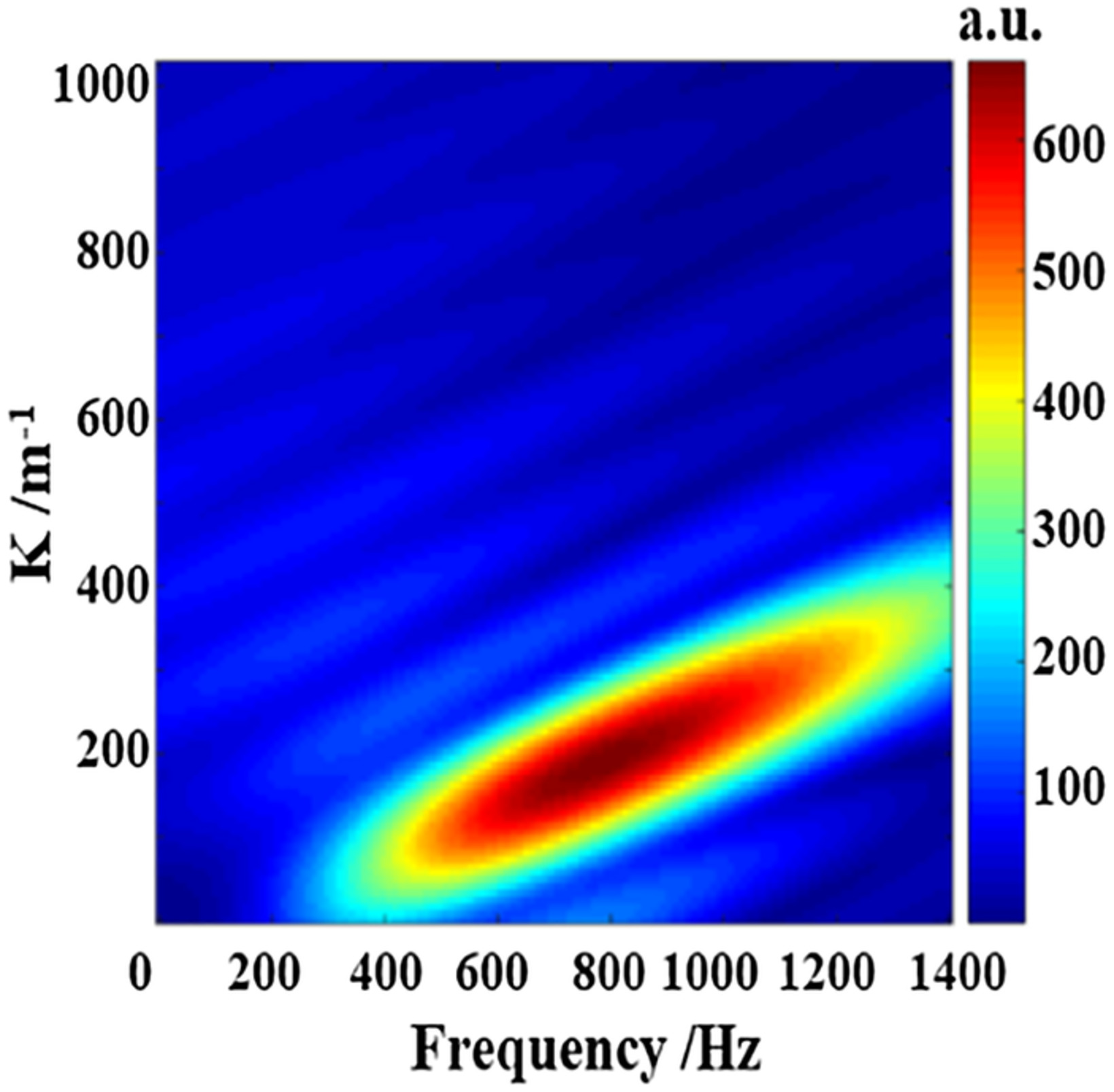
An analysis method utilizing the elastic wave velocity, frequency and energy attenuation to assess the corneal viscoelasticity is presented. Based on the spatial-temporal displacement imaged by optical coherence tomography, the wavenumber-frequency domain map is derived to obtain the phase velocity dispersion curve and center frequency. The energy attenuation coefficient is estimated by curve fitting of the normalized energy distribution curve obtained by transforming the spatial-temporal displacement into the spatial-frequency domain.
Effect of novel porphyrazine photosensitizers on normal and tumor brain cells
- First Published: 08 October 2019
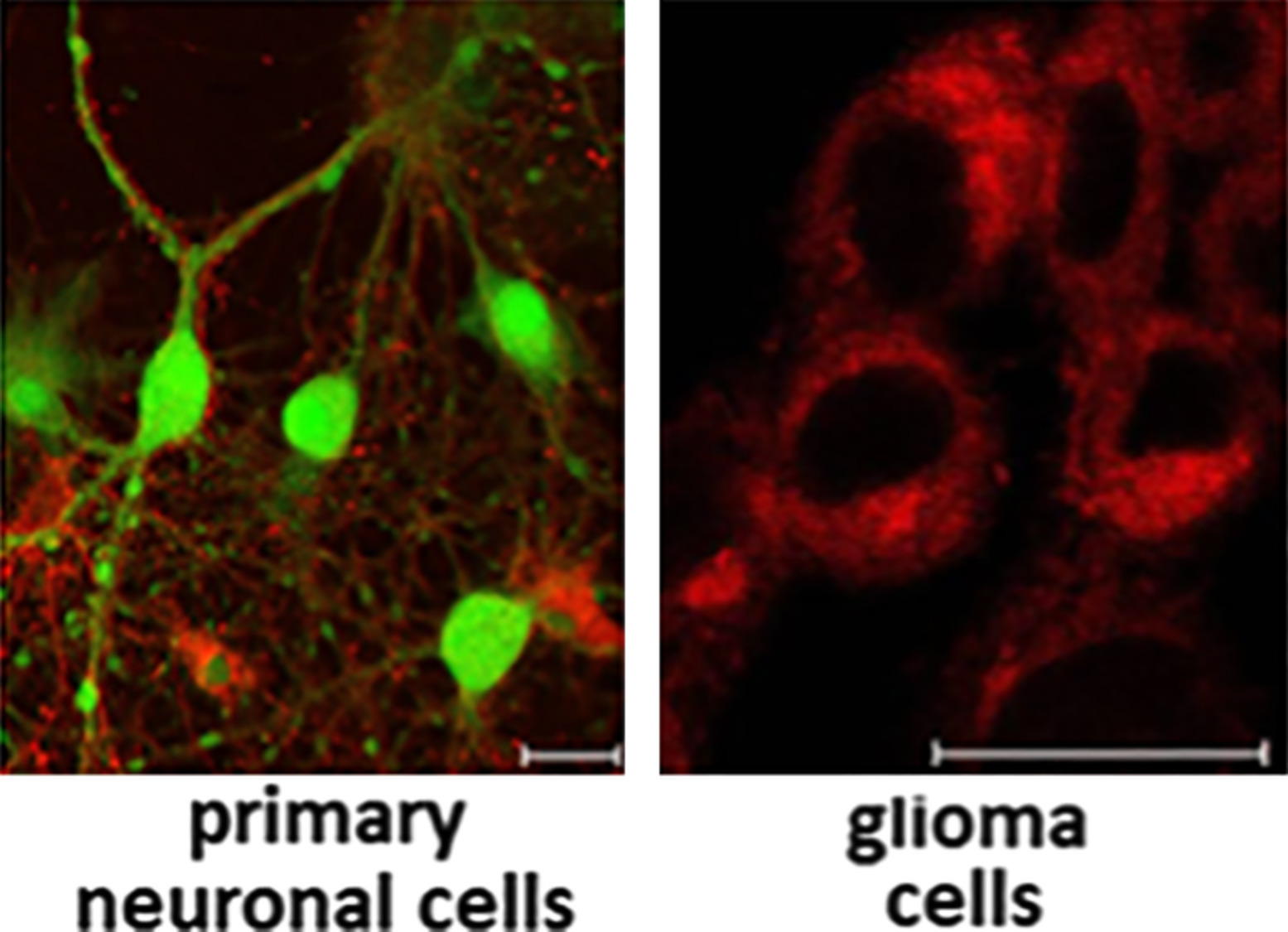
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a clinically approved procedure, which is widely used in research and clinics. Incubation of primary neuronal and glioma cells with pz I-IV resulted in the different rates of internalization, subcellular localization and dark toxicity. Pz II was the most promising photosensitizer, which efficiently killed glioma, while remaining nontoxic to primary neuronal cells. This opens up the possibility of evaluating pz II for experimental PDT for glioma.
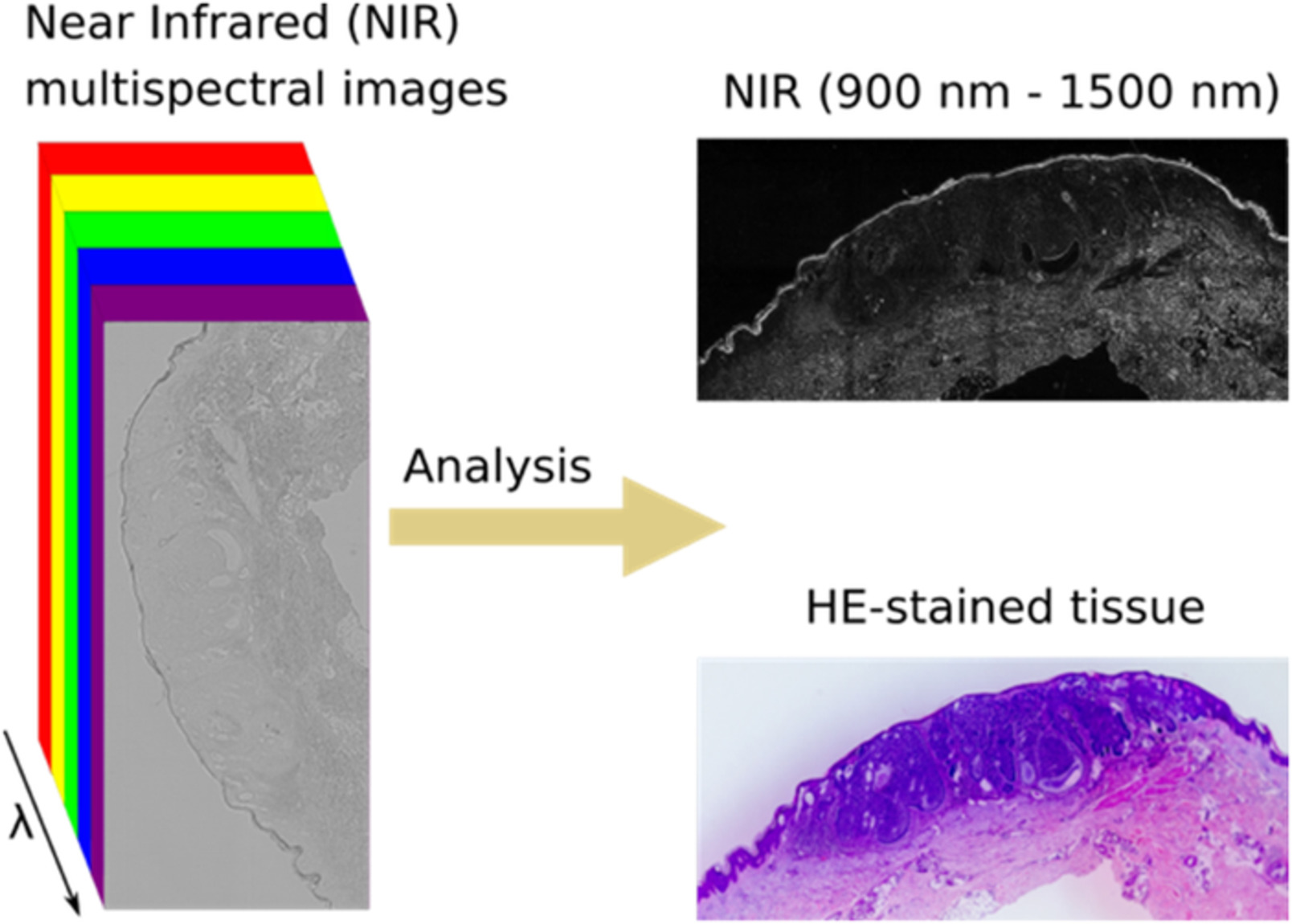
Multispectral near infrared absorption imaging for histology of skin cancer
- First Published: 11 October 2019
Determination of inclusion depth in ex vivo animal tissues using surface enhanced deep Raman spectroscopy
- First Published: 08 October 2019
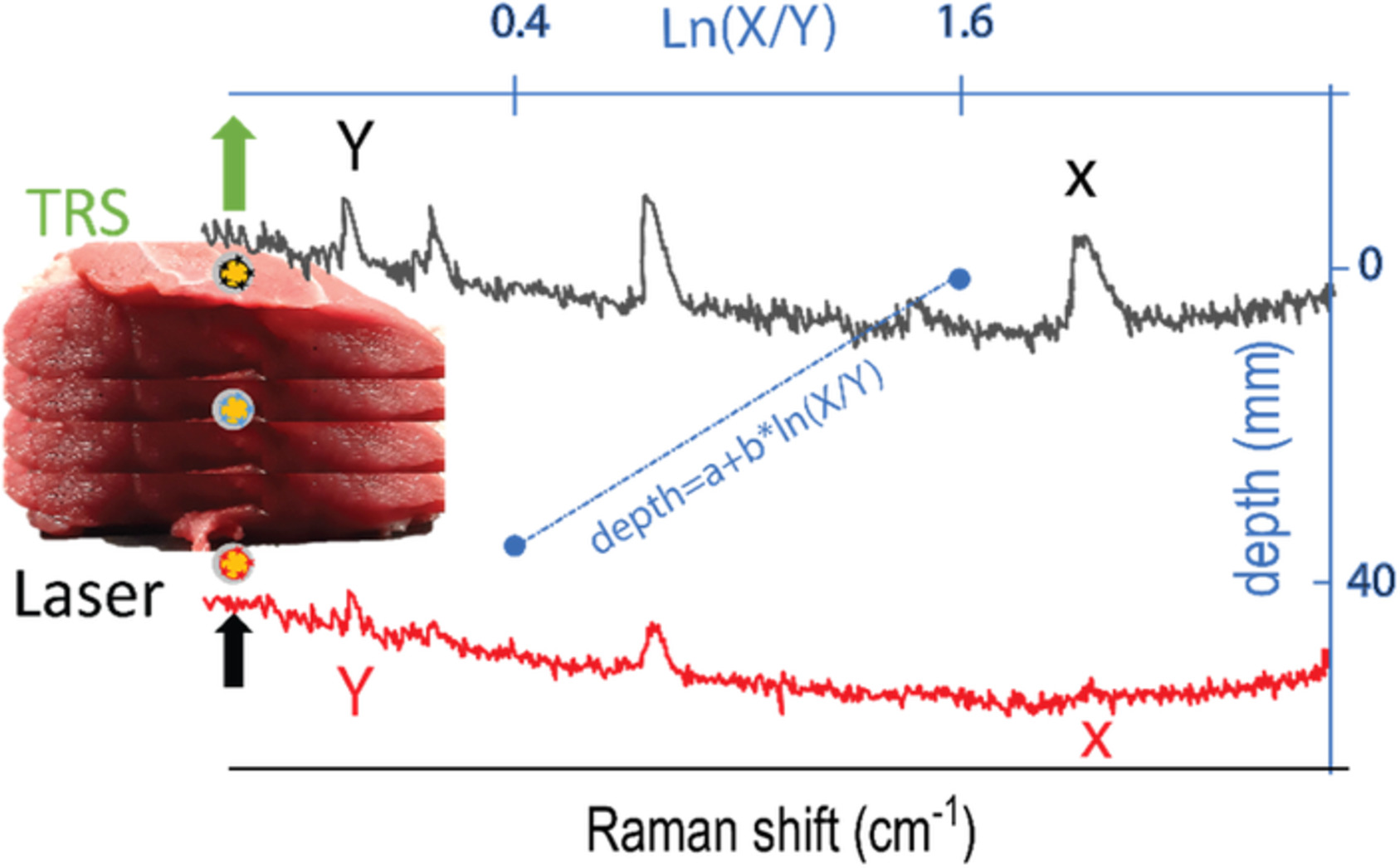
This work demonstrates the use of spatially offset and transmission Raman spectroscopy for noninvasive detection and depth prediction of an inclusion buried inside biological tissues. The concept exploits the differential attenuation of two Raman bands of the inclusion due to the different tissues absorption to retrieve depth information. The results pave the way for future noninvasive deep Raman spectroscopy in vivo enabling to localise cancer biomarkers for an early disease diagnosis.
A modification for the calculation of water depth profiles in oil-treated skin by in vivo confocal Raman microscopy
- First Published: 11 October 2019
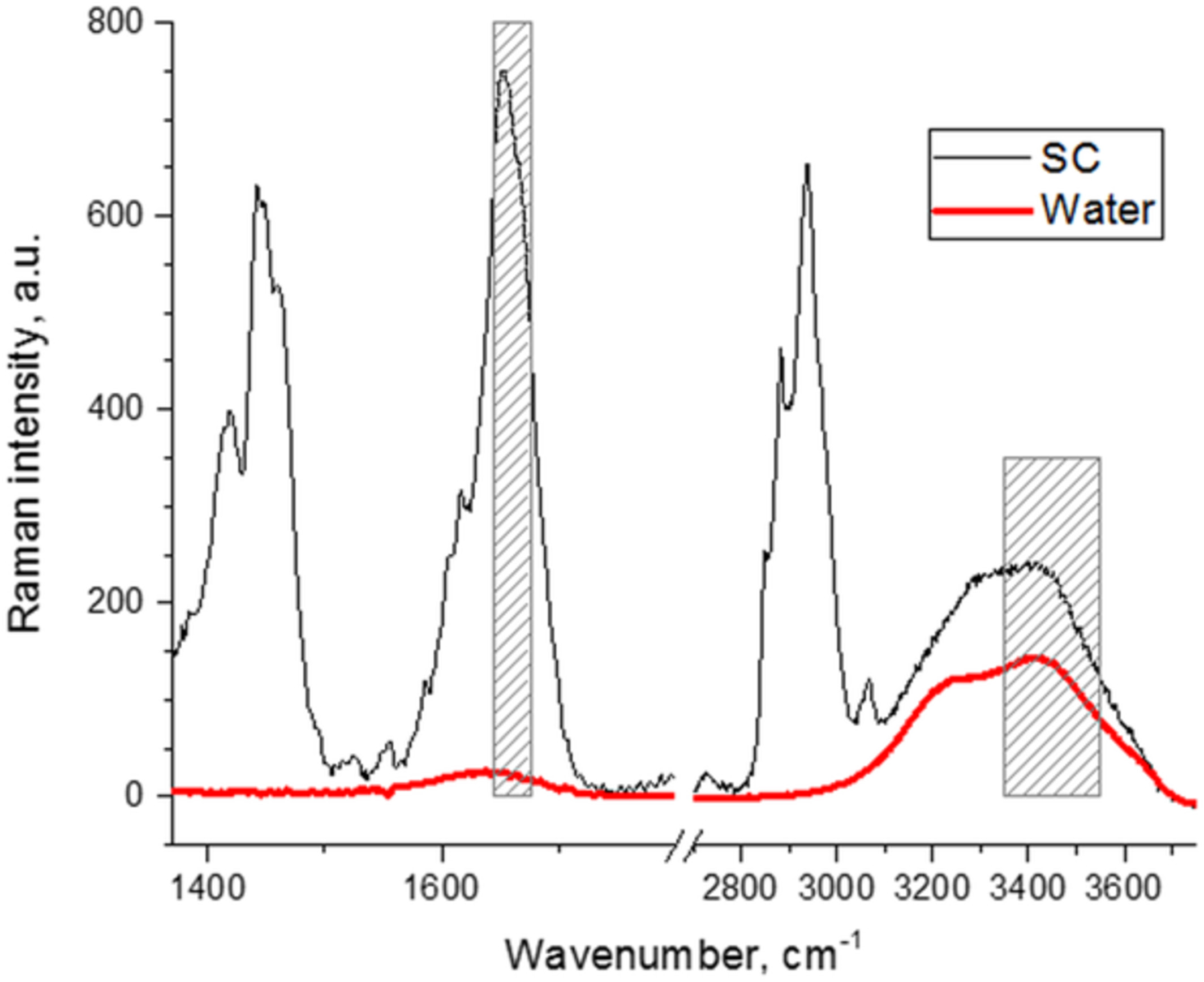
In this study, an extended calculation method for the determination of the water profiles in oil-treated skin is proposed, which is based on the calculation of the ratio between the Raman band intensities of water (3350-3550 cm−1) and keratin Amide I at 1650 cm−1. The proposed extended method shows no artifacts and has the potential to determine the water depth profiles after topical application of formulations on the skin.
CORRIGENDUM
Corrigendum: Origin of improved depth penetration in dual-axis optical coherence tomography: a Monte Carlo study
- First Published: 04 December 2019