Automated label-free detection of injured neuron with deep learning by two-photon microscopy
Funding information: the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University, Grant/Award Number: IRT_15R10; National High Technology Research and Development Program of China, Grant/Award Number: 2015AA020508; National Key Basic Research Program of China, Grant/Award Number: 2015CB352006; National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant/Award Numbers: 61972187, 81671730; Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China, Grant/Award Number: 2019J01761; Program for Undergraduate Education and Teaching Reform in University of Fujian Province of China, Grant/Award Number: FBJG20190230; the Joint Funds of Fujian Provincial Health and Education Research, Grant/Award Number: WKJ2016-2-28; the Special Funds of the Central Government Guiding Local Science and Technology Development, Grant/Award Number: 2017L3009
Abstract
Stroke is a significant cause of morbidity and long-term disability globally. Detection of injured neuron is a prerequisite for defining the degree of focal ischemic brain injury, which can be used to guide further therapy. Here, we demonstrate the capability of two-photon microscopy (TPM) to label-freely identify injured neurons on unstained thin section and fresh tissue of rat cerebral ischemia-reperfusion model, revealing definite diagnostic features compared with conventional staining images. Moreover, a deep learning model based on convolutional neural network is developed to automatically detect the location of injured neurons on TPM images. We then apply deep learning-assisted TPM to evaluate the ischemic regions based on tissue edema, two-photon excited fluorescence signal intensity, as well as neuronal injury, presenting a novel manner for identifying the infarct core, peri-infarct area, and remote area. These results propose an automated and label-free method that could provide supplementary information to augment the diagnostic accuracy, as well as hold the potential to be used as an intravital diagnostic tool for evaluating the effectiveness of drug interventions and predicting potential therapeutics.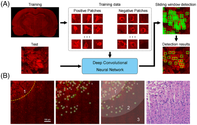
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.




