Epithelium segmentation and automated Gleason grading of prostate cancer via deep learning in label-free multiphoton microscopic images
Qinqin Yang
Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China
Department of Electronic Science, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhexin Xu
Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorChenxi Liao
Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorJianyong Cai
Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorYing Huang
Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorHong Chen
Department of Pathology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorXuan Tao
Department of Pathology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorZheng Huang
Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorJianxin Chen
Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jiyang Dong
Department of Electronic Science, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China
Correspondence
Dr Xiaoqin Zhu, Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou 350007, China.
Email: [email protected]
Dr Jiyang Dong, Department of Electronic Science, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiaoqin Zhu
Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China
Correspondence
Dr Xiaoqin Zhu, Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou 350007, China.
Email: [email protected]
Dr Jiyang Dong, Department of Electronic Science, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorQinqin Yang
Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China
Department of Electronic Science, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhexin Xu
Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorChenxi Liao
Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorJianyong Cai
Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorYing Huang
Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorHong Chen
Department of Pathology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorXuan Tao
Department of Pathology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorZheng Huang
Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorJianxin Chen
Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jiyang Dong
Department of Electronic Science, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China
Correspondence
Dr Xiaoqin Zhu, Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou 350007, China.
Email: [email protected]
Dr Jiyang Dong, Department of Electronic Science, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiaoqin Zhu
Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China
Correspondence
Dr Xiaoqin Zhu, Institute of Laser and Optoelectronics Technology, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Photonics Technology, Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou 350007, China.
Email: [email protected]
Dr Jiyang Dong, Department of Electronic Science, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorFunding information: The National High Technology Research and Development Program of China, Grant/Award Number: 2015AA020508; The National Key Basic Research Program of China, Grant/Award Number: 2015CB352006; The National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant/Award Number: 81871445; The Open Project of Fujian Normal University, Grant/Award Number: JYG1909; The Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University, Grant/Award Number: IRT_15R10; The Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University of Fujian Province, Grant/Award Number: YTR01254
Abstract
In the current clinical care practice, Gleason grading system is one of the most powerful prognostic predictors for prostate cancer (PCa). The grading system is based on the architectural pattern of cancerous epithelium in histological images. However, the standard procedure of histological examination often involves complicated tissue fixation and staining, which are time-consuming and may delay the diagnosis and surgery. In this study, label-free multiphoton microscopy (MPM) was used to acquire subcellular-resolution images of unstained prostate tissues. Then, a deep learning architecture (U-net) was introduced for epithelium segmentation of prostate tissues in MPM images. The obtained segmentation results were then merged with the original MPM images to train a classification network (AlexNet) for automated Gleason grading. The developed method achieved an overall pixel accuracy of 92.3% with a mean F1 score of 0.839 for epithelium segmentation. By merging the segmentation results with the MPM images, the accuracy of Gleason grading was improved from 72.42% to 81.13% in hold-out test set. Our results suggest that MPM in combination with deep learning holds the potential to be used as a fast and powerful clinical tool for PCa diagnosis.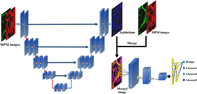
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| jbio201900203-sup-0001-FigureS1.tifTIFF image, 16.1 MB | Figure S1 Three representative multiphoton microscopy image include TPEF signal (red) and SHG signal (green) of PCa tissue from TMA and their corresponding annotation. (a), (b) and (c) represent Gleason pattern 3, 4 and 5, respectively. Large-area images (in yellow square) were sampled from overlapping region of TMA cores. Pathologist 1: blue circle; Pathologist 2: green circle. |
| jbio201900203-sup-0002-FigureS2.tifTIFF image, 7.8 MB | Figure S2 Whisker plot of 5-fold cross validations for Gleason grading of transfer learning and non-transfer learning in MPM-rgb dataset. |
| jbio201900203-sup-0003-FigureS3.tifTIFF image, 20.9 MB | Figure S3 Simulation of under- or over-segmentation in MPM-rgb dataset. (Rows 1–3) Simulated mask, segmented epithelium, and MPM-rgb images with dilating and eroding. 0 represents the original image (mask, segmented or MPM-rgb); −100%, −40% and − 10% represent the eroding rates; +10%, +40% and + 100% represent the dilating rates. |
| jbio201900203-sup-0004-FigureS4.tifTIFF image, 15.5 MB | Figure S4 Whisker plot of 5-fold cross validations for Gleason grading in simulation datasets. |
| jbio201900203-sup-0005-FigureS5.tifTIFF image, 35.3 MB | Figure S5 (Column 1) Representative MPM images include TPEF signal (red) and SHG signal (green) of fresh PCa tissues. (Column 2) The corresponding H&E-stained images. (Column 3) The segmentation results of TPEF and SHG as input. (Column 4) The merged images containing MPM image and segmented result. |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
REFERENCES
- 1R. L. Siegel, K. D. Miller, A. Jemal, CA-Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 7.
- 2T. A. Ozkan, A. T. Eruyar, O. O. Cebeci, O. Memik, L. Ozcan, I. Kuskonmaz, Scand. J. Urol. 2016, 50, 420.
- 3J. I. Epstein, L. Egevad, M. B. Amin, B. Delahunt, J. R. Srigley, P. A. Humphrey, C. Grading, Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 244.
- 4J. I. Epstein, J. Urol. 2010, 183, 433.
- 5M. Varma, B. Jasani, Histopathology 2005, 47, 1.
- 6H. H. Tu, Y. Liu, D. Turchinovich, M. Marjanovic, J. K. Lyngso, J. Laegsgaard, E. J. Chaney, Y. B. Zhao, S. X. You, W. L. Wilson, B. W. Xu, M. Dantus, S. A. Boppart, Nat. Photon. 2016, 10, 534.
- 7J. X. Chen, J. Xu, D. Y. Kang, M. F. Xu, S. M. Zhuo, X. Q. Zhu, X. S. Jiang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 5.
- 8K. Larson, H. H. Ho, P. L. Anumolu, T. M. S. Chen, Dermatol. Surg. 2011, 37, 1089.
- 9W. R. Zipfel, R. M. Williams, R. Christie, A. Y. Nikitin, B. T. Hyman, W. W. Webb, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2003, 100, 7075.
- 10N. D. Kirkpatrick, M. A. Brewer, U. Utzinger, Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2007, 16, 2048.
- 11A. Zoumi, A. Yeh, B. J. Tromberg, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2002, 99, 11014.
- 12O. Nadiarnykh, R. B. LaComb, M. A. Brewer, P. J. Campagnola, BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 14.
- 13P. Campagnola, Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 3224.
- 14W. Y. Hu, G. Zhao, C. Y. Wang, J. G. Zhang, L. Fu, PLoS One. 2012, 7, 8.
- 15R. Cicchi, D. Kapsokalyvas, M. Troiano, P. Campolmi, C. Morini, D. Massi, G. Cannarozzo, T. Lotti, F. S. Pavone, J. Biophotonics 2014, 7, 914.
- 16R. M. Williams, A. Flesken-Nikitin, L. H. Ellenson, D. C. Connolly, T. C. Hamilton, A. Y. Nikitin, W. R. Zipfel, Transl. Oncol. 2010, 3, 181.
- 17N. Fang, Z. Y. Wu, S. S. Cai, Y. P. Chen, Y. X. Lin, X. Y. Zheng, H. H. Tu, L. D. Qiu, X. Y. Liu, F. Wang, Y. Chen, L. H. Li, X. F. Wang, J. X. Chen, Laser Phys. Lett. 2019, 16, 015603.
- 18M. B. Ji, S. Lewis, S. Camelo-Piragua, S. H. Ramkissoon, M. Snuderl, S. Venneti, A. Fisher-Hubbard, M. Garrard, D. Fu, A. C. Wang, J. A. Heth, C. O. Maher, N. Sanai, T. D. Johnson, C. W. Freudiger, O. Sagher, X. S. Xie, D. A. Orringer, Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 309ra163.
- 19Z. Q. Zhang, J. C. de Munck, N. Verburg, A. J. Rozemuller, W. Vreuls, P. Cakmak, L. M. G. van Huizen, S. Idema, E. Aronica, P. C. D. Hamer, P. Wesseling, M. L. Groot, Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 11.
- 20Z. Han, L. Li, D. Kang, Z. Zhan, H. Tu, C. Wang, J. Chen, Lasers Med. Sci. 2019, 34, 1595.
- 21W. Lee, M. M. Kabir, R. Emmadi, K. C. Toussaint, J. Microsc. 2016, 264, 175.
- 22L. M. G. van Huizen, N. V. Kuzmin, E. Barbe, S. van der Velde, E. A. te Velde, M. L. Groot, J. Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201800297.
- 23J. X. Chen, S. M. Zhuo, R. Chen, X. S. Jiang, S. S. Xie, Q. L. Zou, New J. Phys. 2007, 9, 212.
- 24A. K. Tewari, M. M. Shevchuk, J. Sterling, S. Grover, M. Herman, R. Yadav, K. Mudalair, A. Srivastava, M. A. Rubin, W. R. Zipfel, F. R. Maxfield, C. Xu, W. W. Webb, S. Mukherjee, BJU Int. 2011, 108, 1421.
- 25Y. T. Ling, C. H. Li, K. R. Feng, S. Palmer, P. L. Appleton, S. Lang, D. McGloin, Z. H. Huang, G. Nabi, J. Biophotonics 2017, 10, 911.
- 26G. Litjens, T. Kooi, B. E. Bejnordi, A. A. A. Setio, F. Ciompi, M. Ghafoorian, J. van der Laak, B. van Ginneken, C. I. Sanchez, Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60.
- 27A. Janowczyk, A. Madabhushi, J. Pathol. Inform. 2016, 7, 29.
- 28S. E. A. Raza, L. Cheung, M. Shaban, S. Graham, D. Epstein, S. Pelengaris, M. Khan, N. M. Rajpoot, Med. Image Anal. 2019, 52, 160.
- 29S. Graham, H. Chen, J. Gamper, Q. Dou, P. A. Heng, D. Snead, Y. W. Tsang, N. Rajpoot, Med. Image Anal. 2019, 52, 199.
- 30H. Chen, X. J. Qi, L. Q. Yu, Q. Dou, J. Qin, P. A. Heng, Med. Image Anal. 2017, 36, 135.
- 31G. Nir, S. Hor, D. Karimi, L. Fazli, B. F. Skinnider, P. Tavassoli, D. Turbin, C. F. Villamil, G. Wang, R. S. Wilson, K. A. Iczkowski, M. S. Lucia, P. C. Black, P. Abolmaesumi, S. L. Goldenberg, S. E. Salcudean, Med. Image Anal. 2018, 50, 167.
- 32E. Arvaniti, K. S. Fricker, M. Moret, N. Rupp, T. Hermanns, C. Fankhauser, N. Wey, P. J. Wild, J. H. Ruschoff, M. Claassen, Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12054.
- 33G. Litjens, C. I. Sanchez, N. Timofeeva, M. Hermsen, I. Nagtegaal, I. Kovacs, C. Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, P. Bult, B. van Ginneken, J. van der Laak, Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26286.
- 34H. Källén, J. Molin, A. Heyden, C. Lundström, K. Åström, IEEE Int. Symp. Biomed. Imag. 2016, 1163.
- 35W. Bulten, P. Bandi, J. Hoven, R. van de Loo, J. Lotz, N. Weiss, J. van der Laak, B. van Ginneken, C. Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, G. Litjens, Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 864.
- 36W. Li, J. Li, K. V. Sarma, K. C. Ho, S. Shen, B. S. Knudsen, A. Gertych, C. W. Arnold, IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 38, 945.
- 37S. M. Zhuo, J. X. Chen, T. S. Luo, D. S. Zou, J. J. Zhao, Opt. Express 2006, 14, 7810.
- 38O. Ronneberger, P. Fischer, T. Brox, arXiv 2015, 1505, 04597.
- 39A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, G. E. Hinton, Commun. ACM. 2017, 60, 84.
- 40D. Kingma, J. Ba, arXiv 2014, 1412, 6980.
- 41K. Simonyan, A. J. C. S. Zisserman, arXiv 2014, 1409, 1556.
- 42C. Szegedy, L. Wei, J. Yangqing, P. Sermanet, S. Reed, D. Anguelov, D. Erhan, V. Vanhoucke, A. Rabinovich, arXiv 2014, 1409, 4842.
- 43K. M. He, X. Y. Zhang, S. Q. Ren, J. Sun, arXiv 2015, 1512, 03385.
- 44N. Tajbakhsh, J. Y. Shin, S. R. Gurudu, R. T. Hurst, C. B. Kendall, M. B. Gotway, J. M. Liang, IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1299.
- 45H. C. Shin, H. R. Roth, M. C. Gao, L. Lu, Z. Y. Xu, I. Nogues, J. H. Yao, D. Mollura, R. M. Summers, IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1285.
- 46J. Deng, W. Dong, R. Socher, L. J. Li, K. Li, F. F. Li, IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, NY: IEEE; 2009, p. 248.
- 47H. H. Chang, A. H. Zhuang, D. J. Valentino, W. C. Chu, Neuroimage 2009, 47, 122.
- 48A. Lopez-Beltran, G. Mikuz, R. Luque, R. Mazzucchelli, R. Montironi, Virchows Arch. 2006, 448, 111.
- 49L. Gailhouste, Y. Le Grand, C. Odin, D. Guyader, B. Turlin, F. Ezan, Y. Desille, T. Guilbert, A. Bessard, C. Fremin, N. Theret, G. Baffet, J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 398.
- 50R. G. Koch, A. Tsamis, A. D'Amore, W. R. Wagner, S. C. Watkins, T. G. Gleason, D. A. Vorp, J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 935.
- 51M. J. Huttunen, A. Hassan, C. W. McCloskey, S. Fasih, J. Upham, B. C. Vanderhyden, R. W. Boyd, S. Murugkar, J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 066002.




