Morphological and functional characteristics of aging kidneys based on two-photon microscopy in vivo
Shulian Wu
Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Photonic Technology, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Science and Technology for Medicine, College of Photonic and Electronic Engineering, Fujian Normal University, Ministry of Education, Fuzhou, China
Fischell Department of Bioengineering, University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland
Search for more papers by this authorHengchang Guo
Fischell Department of Bioengineering, University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland
Search for more papers by this authorHannah Horng
Fischell Department of Bioengineering, University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland
Search for more papers by this authorYi Liu
Fischell Department of Bioengineering, University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland
Search for more papers by this authorHui Li
Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Photonic Technology, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Science and Technology for Medicine, College of Photonic and Electronic Engineering, Fujian Normal University, Ministry of Education, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorParnaz Daneshpajouhnejad
Department of Pathology, Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, Baltimore, Maryland
Search for more papers by this authorAvi Rosenberg
Department of Pathology, Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, Baltimore, Maryland
Search for more papers by this authorChristopher Albanese
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular & Cellular Biology, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, DC
Search for more papers by this authorSuman Ranjit
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular & Cellular Biology, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, DC
Search for more papers by this authorPeter M. Andrews
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular & Cellular Biology, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, DC
Search for more papers by this authorMoshe Levi
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular & Cellular Biology, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, DC
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Qinggong Tang
Fischell Department of Bioengineering, University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland
Stephenson School of Biomedical Engineering, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Oklahoma
Correspondence
Yu Chen, Fischell Department of Bioengineering, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742.
Email: [email protected]
Qinggong Tang, Stephenson School of Biomedical Engineering, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK 73019.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yu Chen
Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Photonic Technology, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Science and Technology for Medicine, College of Photonic and Electronic Engineering, Fujian Normal University, Ministry of Education, Fuzhou, China
Fischell Department of Bioengineering, University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland
Correspondence
Yu Chen, Fischell Department of Bioengineering, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742.
Email: [email protected]
Qinggong Tang, Stephenson School of Biomedical Engineering, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK 73019.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorShulian Wu
Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Photonic Technology, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Science and Technology for Medicine, College of Photonic and Electronic Engineering, Fujian Normal University, Ministry of Education, Fuzhou, China
Fischell Department of Bioengineering, University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland
Search for more papers by this authorHengchang Guo
Fischell Department of Bioengineering, University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland
Search for more papers by this authorHannah Horng
Fischell Department of Bioengineering, University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland
Search for more papers by this authorYi Liu
Fischell Department of Bioengineering, University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland
Search for more papers by this authorHui Li
Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Photonic Technology, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Science and Technology for Medicine, College of Photonic and Electronic Engineering, Fujian Normal University, Ministry of Education, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorParnaz Daneshpajouhnejad
Department of Pathology, Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, Baltimore, Maryland
Search for more papers by this authorAvi Rosenberg
Department of Pathology, Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, Baltimore, Maryland
Search for more papers by this authorChristopher Albanese
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular & Cellular Biology, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, DC
Search for more papers by this authorSuman Ranjit
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular & Cellular Biology, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, DC
Search for more papers by this authorPeter M. Andrews
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular & Cellular Biology, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, DC
Search for more papers by this authorMoshe Levi
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular & Cellular Biology, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, DC
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Qinggong Tang
Fischell Department of Bioengineering, University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland
Stephenson School of Biomedical Engineering, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Oklahoma
Correspondence
Yu Chen, Fischell Department of Bioengineering, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742.
Email: [email protected]
Qinggong Tang, Stephenson School of Biomedical Engineering, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK 73019.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yu Chen
Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Photonic Technology, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Science and Technology for Medicine, College of Photonic and Electronic Engineering, Fujian Normal University, Ministry of Education, Fuzhou, China
Fischell Department of Bioengineering, University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland
Correspondence
Yu Chen, Fischell Department of Bioengineering, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742.
Email: [email protected]
Qinggong Tang, Stephenson School of Biomedical Engineering, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK 73019.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorFunding information: Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Grant/Award Number: R21 AG042700; Special Funds of the Central Government Guiding Local Science and Technology Development, Grant/Award Number: 2017L3009
Abstract
Age-related kidney disease, which is chronic and naturally occurring, is a general term for a set of heterogeneous disorders affecting kidney structures and characterized by a decline in renal function. Age-related renal insufficiency has important implications with regard to body homeostasis, drug toxicity and renal transplantation. In our study, two-photon microscopy was used to image kidney morphological and functional characteristics in an age-related rat model in vivo. The changes in morphology are analyzed based on autofluorescence and Hoechst 33342 labeling in rats with different ages. Structural parameters including renal tubular diameter, cell nuclei density, size and shape are studied and compared with Hematoxylin and Eosin histological analysis. Functional characteristics, such as blood flow, and glomerular filtration rate are studied with high-molecular weight (MW) 500-kDa dextran-fluorescein and low-MW 10-kDa dextran-rhodamine. Results indicate that morphology changes significantly and functional characteristics deteriorate with age. These parameters are potential indicators for evaluating age-related renal morphology and function changes. Combined analyses of these parameters could provide a quantitative, novel method for monitoring kidney diseases and/or therapeutic effects of kidney drugs.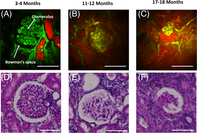
REFERENCES
- 1R. Saran, B. Robinson, K. C. Abbott, L. Y. C. Agodoa, J. Bragg-Gresham, R. Balkrishnan, D. Xue, A. Eckard, P. W. Eggers, A. Gaipov, Am J Kidney Dis 2018, 71, A7.
- 2D. Bolignano, F. Mattace-Raso, E. J. Sijbrands, C. Zoccali, Ageing Res Rev 2014, 14, 65.
- 3M. Gekle, Exp Gerontol 2017, 87, 153.
- 4D. F. Gudbjartsson, H. Holm, O. S. Indridason, G. Thorleifsson, V. Edvardsson, P. Sulem, F. D. Vegt, F. C. H. D'Ancona, M. D. Heijer, L. Franzson, PLoS Genet 2010, 6, e1001039.
- 5X. J. Zhou, D. Rakheja, X. Yu, R. Saxena, N. D. Vaziri, F. G. Silva, Kidney Int 2008, 74, 710.
- 6R. Schmitt, A. Melk, Am J Transplant 2012, 12, 2892.
- 7A. Hart, J. M. Smith, M. A. Skeans, S. K. Gustafson, A. R. Wilk, A. Robinson, J. L. Wainright, C. R. Haynes, J. J. Snyder, B. L. Kasiske, Am J Transplant 2018, 18, 18.
- 8M. Cirillo, J Nephrol 2010, 23, 125.
- 9X. Tang, E. J. Bergstralh, R. A. Mehta, T. J. Vrtiska, D. S. Milliner, J. C. Lieske, Kidney Int 2015, 87, 623.
- 10S. Kai, E. Braig, K. Willer, M. Willner, A. A. Fingerle, M. Chabior, J. Herzen, M. Eiber, B. Haller, M. Straub, Sci Rep 2015, 5, 9527.
- 11K. Jiang, H. Tang, P. K. Mishra, S. I. Macura, L. O. Lerman, Magn Reson Med 2018, 79, 2935.
- 12S. Clotet, M. J. Soler, M. Riera, J. Pascual, F. Fang, J. Zhou, I. Batruch, S. K. Vasiliou, A. Dimitromanolakis, C. Barrios, Mol Cell Proteom 2017, 16, 368.
- 13H. Bhutani, V. Smith, F. Rahbarioskoui, A. Mittal, J. J. Grantham, V. E. Torres, M. Mrug, K. T. Bae, Z. Wu, Y. Ge, Kidney Int 2015, 88, 146.
- 14O. N. Gofrit, M. Orevi, J Urol 2016, 196, 648.
- 15K. Shimizu, N. Kosaka, Y. Fujiwara, T. Matsuda, T. Yamamoto, T. Tsuchida, K. Tsuchiyama, N. Oyama, H. Kimura, Magn Reson Med Sci 2017, 16, 38.
- 16J. A. Hokamp, R. E. Cianciolo, M. Boggess, G. E. Lees, S. L. Benali, M. Kovarsky, M. B. Nabity, J Vet Intern Med 2016, 30, 591.
- 17P. M. Andrews, H.-W. Wang, J. Wierwille, W. Gong, J. Verbesey, M. Cooper, Y. Chen, J Innov Opt Health Sci 2014, 7, 1350064.
- 18B. Wang, H. W. Wang, H. Guo, E. Anderson, Q. Tang, T. Wu, R. Falola, T. Smith, P. M. Andrews, Y. Chen, J Biomed Opt 2017, 22, 1.
- 19J. Wierwille, P. M. Andrews, M. L. Onozato, J. Jiang, Y. Chen, Lab Investig 2011, 91, 1596.
- 20P. M. Andrews, W. M. Petroll, H. D. Cavanagh, J. V. Jester, Am J Anat 1991, 191, 95.
- 21M. N. Ghayur, L. J. Janssen, Med Hypotheses Res 2009, 5, 47.
- 22S. L. Ashworth, R. M. Sandoval, G. A. Tanner, B. A. Molitoris, Kidney Int 2007, 72, 416.
- 23T. Hato, S. Winfree, R. Day, R. M. Sandoval, B. A. Molitoris, M. C. Yoder, R. C. Wiggins, Y. Zheng, K. W. Dunn, P. C. Dagher, J Am Soc Nephrol 2017, 28, 2420.
- 24D. M. Small, W. Y. Sanchez, G. C. Gobe, Methods Mol Biol 2016, 1397, 155.
- 25R. Galli, V. Sablinskas, D. Dasevicius, A. Laurinavicius, F. Jankevicius, E. Koch, G. Steiner, J Biophotonics 2014, 7, 23.
- 26P. M. Andrews, J. Wierwille, Y. Chen, Optical Coherence Tomography in Kidney Transplantation, New York: Springer International Publishing, 2015.
10.1007/978-3-319-06419-2_81 Google Scholar
- 27W. Denk, J. H. Strickler, W. W. Webb, Science 1990, 248, 73.
- 28T. Hato, S. Winfree, P. C. Dagher, Methods 2017, 128, 33.
- 29R. Torres, H. Velazquez, J. J. Chang, M. J. Levene, G. Moeckel, G. V. Desir, R. Safirstein, J Am Soc Nephrol 2016, 27, 1102.
- 30C. Baylis, H. R. Rennke, B. M. Brenner, Kidney Int 1977, 12, 344.
- 31H. Hackbarth, D. Büttner, D. Jarck, M. Pothmann, C. Messow, K. Gärtner, Kidney Blood Press Res 1983, 6, 63.
- 32Q. Tang, T. Nagaya, Y. Liu, J. Lin, K. Sato, H. Kobayashi, Y. Chen, J Control Release 2017, 260, 154.
- 33H. Guo, H. W. Wang, Q. Tang, E. Anderson, R. Falola, T. Smith, Y. Liu, M. Levi, P. M. Andrews, Y. Chen, J Innov Opt Health Sci 2018, 11, 1850030.
- 34H. V. Baeyer, J. B. Van Liew, J. Klassen, J. W. Boylan, Kidney Int 1976, 10, 425.
- 35M. Matejovic, C. Ince, L. S. Chawla, R. Blantz, B. A. Molitoris, M. H. Rosner, M. D. Okusa, J. A. Kellum, C. Ronco, A. X. W. Group, J Am Soc Nephrol 2015, 126, 47.
- 36Tubular atrophy. Pittsburgh: Transplant Pathology Internet Services. Available from https://tpis.upmc.com/main.cfm.
- 37Y. Chen, P. M. Andrews, A. D. Aguirre, J. M. Schmitt, J. G. Fujimoto, J Biomed Opt 2007, 12, 034008.
- 38K. W. Samarakoon, J. Y. Ko, J. H. Lee, O. N. Kwon, S. W. Kim, Y. J. Jeon, J Funct Foods 2014, 6, 231.
- 39K. W. Dunn, T. A. Sutton, R. M. Sandoval, Curr Protoc Cytom, Live-Animal Imaging of Renal Function by Multiphoton Microscopy. Current Protocols in Cytometry, 2012, 62, 12.9.1-12.9.18. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142956.cy1209s62.
10.1002/0471142956.cy1209s62 Google Scholar
- 40A. M. Hall, C. Crawford, R. J. Unwin, M. R. Duchen, C. M. Peppiattwildman, J Am Soc Nephrol 2011, 22, 1297.
- 41Normative values for rats. Web.jhu.edu. Baltimore, Maryland: Association ofNormative biochemical values for rats. Available from http://web.jhu.edu/animalcare/procedures/rat.html.
- 42V. W. Lee, Y. Wang, X. Qin, Y. Wang, G. Zheng, D. Mahajan, J. Coombes, G. Rangan, S. I. Alexander, D. C. Harris, Nephrol Dial Transplant 2006, 21, 3293.
- 43L. A. Hebert, G. Tom, L. Andrew, M. E. Falkenhain, K. Saulo, Am J Kidney Dis 2003, 41, 962.
- 44L. Raij, R. Tian, J. S. Wong, J. C. He, K. N. Campbell, Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2016, 311, 00162.
- 45J. Wu, M. Dong, C. Rigatto, Y. Liu, F. Lin, NPJ Digital Med 2018, 1, 7.
- 46A. S. Levey, J. Coresh, T. Greene, L. A. Stevens, Y. L. Zhang, S. Hendriksen, J. W. Kusek, L. F. Van Ann, Intern Med 2006, 145, 247.
- 47P. M. Andrews, H. W. Wang, H. Guo, E. Anderson, R. Falola, Y. Chen, Exp Clin Transplant 2016, 14, 617.
- 48J. Yao, Z. Ke, X. Wang, F. Peng, B. Li, R. Wu, Mol Med Rep 2014, 10, 39.
- 49D. Mew, C. K. Wat, G. H. Towers, J. G. Levy, J Immunol 1983, 130, 1473.
- 50S. Paola, M. Tom, Science 2006, 312, 1059.
- 51W. Micah, K. L. Witkin, C. F. Orna, J Cell Sci 2009, 122, 1477.
- 52M. R. Longmire, M. Ogawa, Y. Hama, N. Kosaka, C. A. S. Regino, P. L. Choyke, H. Kobayashi, Bioconjug Chem 2008, 19, 1735.
- 53Y. Hama, Y. Urano, Y. Koyama, M. Bernardo, P. L. Choyke, H. Kobayashi, Bioconjug Chem 2006, 17, 1426.
- 54C. Baylis, J Clin Investig 1994, 94, 1823.
- 55K. Tetsuka, T. Hoshi, E. Sumiya, H. Kitakoji, Y. Yada, F. Hongo, H. Watanabe, M. Saitoh, J Med Ultrason 2003, 30, 247.
- 56E. Yew, C. Rowlands, P. T. C. So, J Innov Opt Health Sci 2014, 07, 1330010.
- 57M. Balu, K. M. Kelly, C. B. Zachary, R. M. Harris, T. B. Krasieva, K. König, A. J. Durkin, B. J. Tromberg, Cancer Res 2014, 74, 2688.
- 58M. T. Myaing, D. J. MacDonald, X. Li, Opt Lett 2006, 31, 1076.
- 59S. Tang, W. Jung, D. McCormick, T. Xie, J. Su, Y. C. Ahn, B. J. Tromberg, Z. Chen, J Biomed Opt 2009, 14, 034005.
- 60Y. Wu, Y. Zhang, J. Xi, M.-J. Li, X. Li, J Biomed Opt 2010, 15, 1.
- 61Y. Zhang, M. L. Akins, K. Murari, J. Xi, M.-J. Li, K. Luby-Phelps, M. Mahendroo, X. Li, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012, 109, 12878.
- 62W. Liang, K. Murari, Y. Y. Zhang, Y. Chen, X. D. Li, M.-J. Li, J Biomed Opt 2012, 17, 1.
- 63W. Liang, G. Hall, B. Messerschmidt, M.-J. Li, X. Li, Light Sci Appl 2017, 6, e17082.
- 64W. Göbel, J. N. D. Kerr, A. Nimmerjahn, F. Helmchen, Opt Lett 2004, 29, 2521.
- 65D. M. Huland, C. M. Brown, S. S. Howard, D. G. Ouzounov, I. Pavlova, K. Wang, D. R. Rivera, W. W. Webb, C. Xu, Biomed Opt Express 2012, 3, 1077.
- 66D. M. Huland, M. Jain, D. G. Ouzounov, B. D. Robinson, D. S. Harya, M. M. Shevchuk, P. Singhal, C. Xu, A. K. Tewari, J Biomed Opt 2014, 19, 1.
- 67A. Li, G. Hall, D. Chen, W. Liang, B. Ning, H. Guan, X. Li, J Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201800229.




