Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
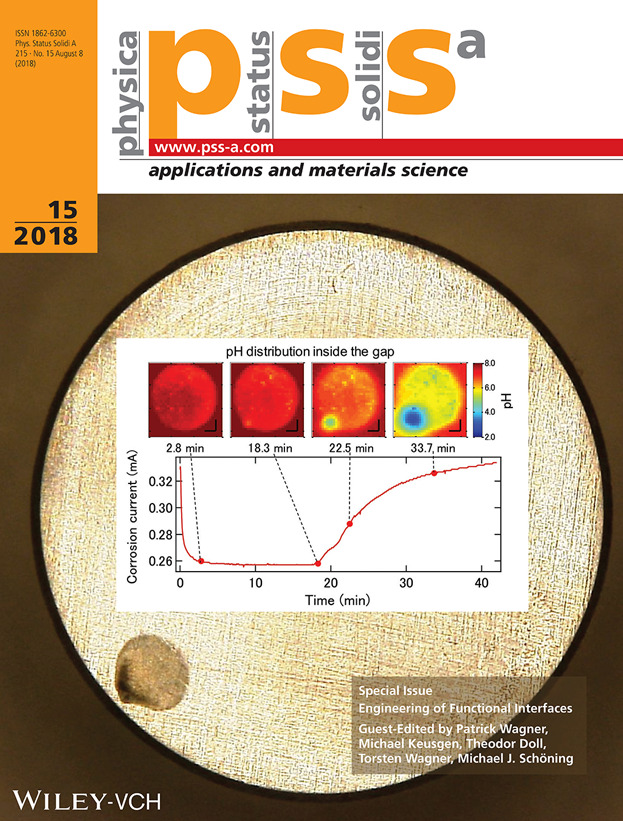
A Modified Chemical Imaging Sensor System for Real-Time pH Imaging of Accelerated Crevice Corrosion of Stainless Steel (Phys. Status Solidi A 15∕2018)
- First Published: 08 August 2018
Chemical Imaging Sensors
In spite of the high corrosion resistance, a surface of stainless steel placed in a narrow gap of the order of microns is known to corrode, which can be a potential hazard, for example, in marine infrastructures. A direct interrogation of this “crevice corrosion” has been difficult due to the very limited accessibility of the confined space. A novel technique visualizes the temporal change of pH distribution inside the gap during corrosion in a geometry where a chemical imaging sensor is placed in the proximity of a steel surface. The observed local decrease of pH down to 2 corresponds to the location where the corrosion is initiated. This is reported by Ko-ichiro Miyamoto and co-workers in article number 1700963.
Masthead
Editorial
Original Papers
Surface Science
Electrochemical Evaluation of Light-Addressable Electrodes Based on TiO2 for the Integration in Lab-on-Chip Systems
- First Published: 05 June 2018
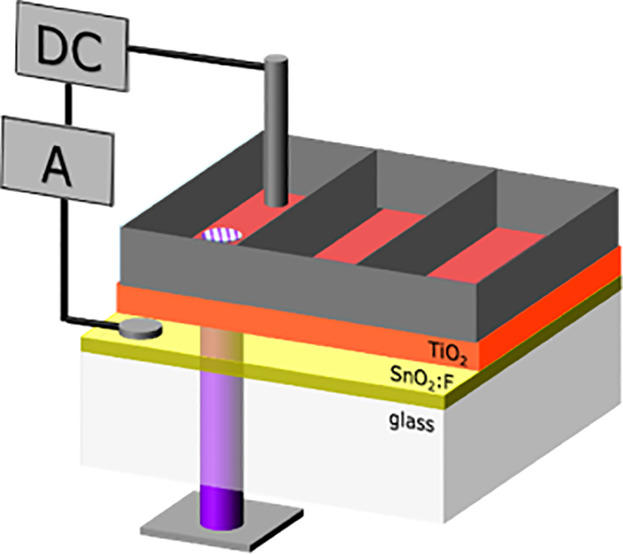
Titanium dioxide layers with different thicknesses are fabricated by a non-aqueous sol–gel approach on fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) glass to work as light-addressable electrodes (LAE). The dependence of the film thickness on the dark- and photocurrent is evaluated and the spatial resolution is successfully tested for the integration of the LAE in lab-on-chip systems.
A Novel N-Substituted Pyrrole Based Surface Modification for Biosensing
- First Published: 18 May 2018
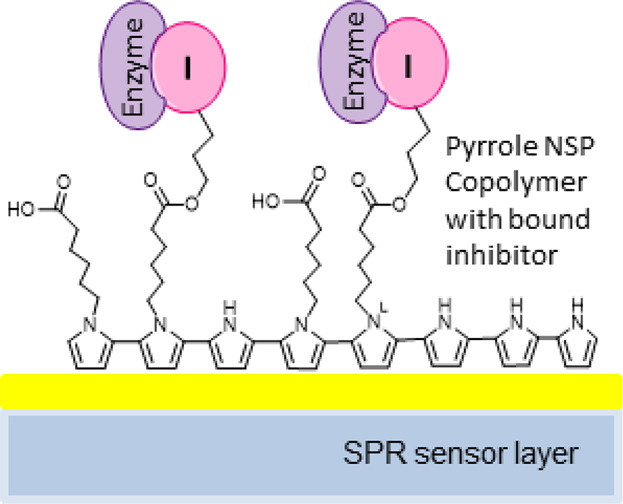
Different N-substituted pyrroles are synthesized and via electro-polymerization deposited on a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor. Their use to create a novel binding surface for development of assays like sugar-lectin binding assays is studied by SPR technology. The pyrrole-N-C16 co-polymer surface as well as the pyrrole/6-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl) hexanoic acid co-polymer (PHCP) with and without chemical activation are suitable for binding assays.
Electronic Responses to Humidity in Monolayer and Multilayer AuNP Stripes Fabricated by Convective Self-Assembly
- First Published: 22 February 2018
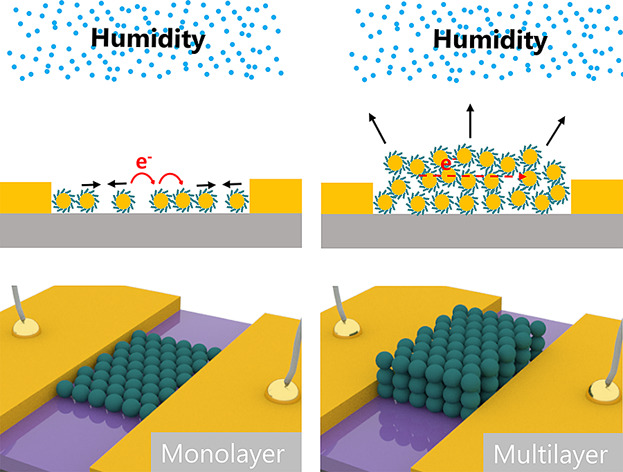
Monolayer and multilayer AuNP stripes are fabricated by convective self-assembly. Their electronic responses to humidity are studied. These AuNP stripes with different layers show different responses to humidity. Studies on charge transport regimes and the morphologies in these AuNP stripes reveal the possible mechanism accounting for their different responses.
Carbon Nanotube-Silicone Rubber on Active Thin-Film Implants
- First Published: 03 July 2018
Neuronal electrode contact surfaces are improved using a carbon nanotube (CNT) silicone rubber compound. This paper presents a new method for defined application of the flexible electrode material onto electrode surfaces with different diameters (300–500 µm). Wet etching techniques are optimized for such small and thin CNT silicone rubber pads and to ensure the electrode itself stays undamaged by the process. Success is examined using impedance measurements and scanning electron microscopy.
Structure and Thermal Stability of Stilbenedithiol SAMs on Au(111)
- First Published: 24 March 2018
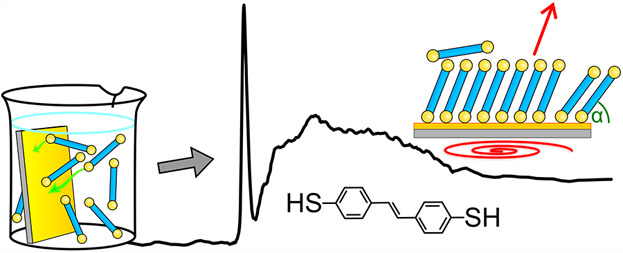
A self-assembling monolayer (SAM) of an aromatic dithiol on Au(111) is investigated, which represents a promising bivalent linker layer. With complementary characterization techniques the dependence of film quality on preparation parameters, such as used solvent, temperature, and ambient conditions is analyzed. Moreover, a remarkably high thermal stability is revealed, ascribed to partial cross-linking inside the film.
On the Electropolishing Mechanism of Nickel Titanium in Methanolic Sulfuric acid − An Electrochemical Impedance Study
- First Published: 24 July 2018
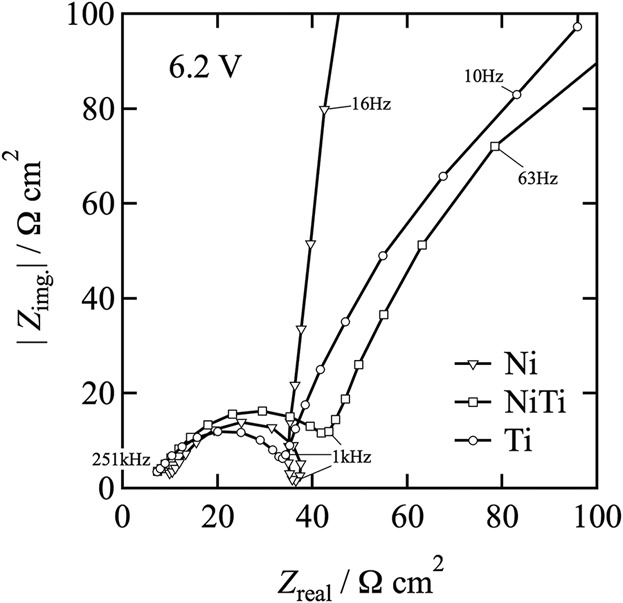
This study demonstrates that electro-dissolution under mass transfer condition follows a compact salt-film mechanism. In order to quantitatively characterize the salt film formed during electropolishing, EIS is performed under stationary conditions. The increase in applied voltage caused an increase in polarization resistance and decrease in capacitance of the interface film.
Self-Assembled Functional Nanostructures
Characterization of Nanosized Drug Carriers by Analytical Centrifugation
- First Published: 18 May 2018
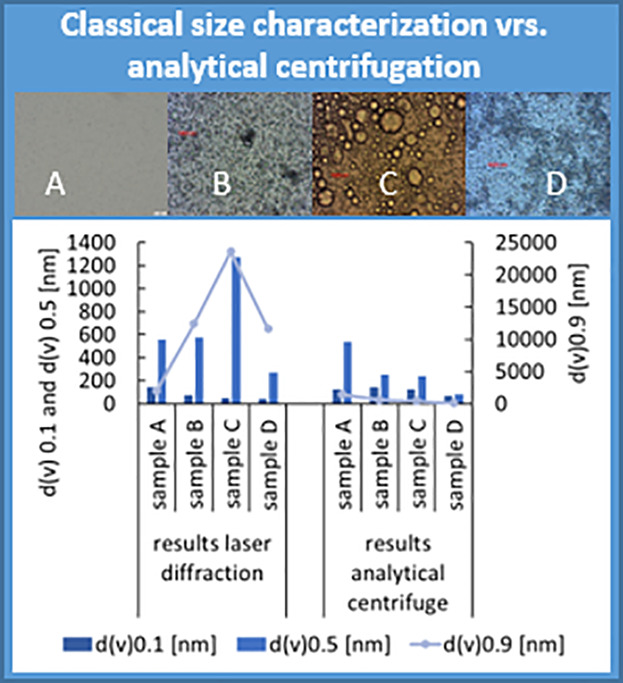
Mixtures from differently sized particle standards with known composition and different drug nanocarrier systems are characterized by dynamic light scattering and analytical centrifugation. Analytical centrifugation led to accurate size results when standard particles are analyzed. Size characterization of the different drug nanocarriers is not superior, when compared to classical sizing methods.
Folding DNA Origami Nanolevers From Differently Prepared Scaffold Strands
- First Published: 14 February 2018
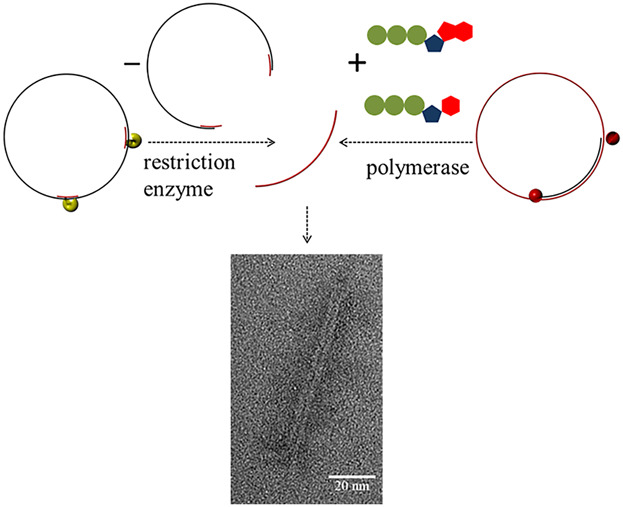
In this paper, a top-down and a bottom-up approach for the fabrication of two scaffold strands of customized length for predefined DNA origami structures are presented. Three different origami structures are synthesized and analyzed in terms of accuracy of shape, yield as well as the costs attributed to each fabrication route.
Multilayer Bacteriostatic Coating for Surface Modified Titanium Implants
- First Published: 22 March 2018
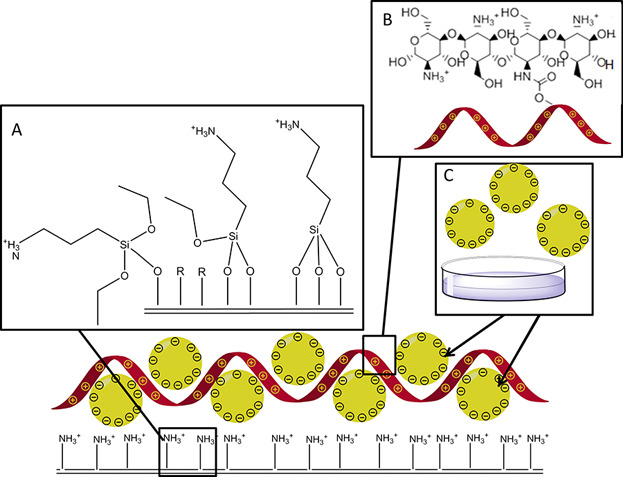
The multilayer coating developed in this study addresses the problems associated with bacterial growth and biofilm formation by two different approaches viz. preventing bacterial adhesion by nanostructured surface modification and by creating an ultra-thin PLGA/norfloxacin nanoparticle coating on the titanium/implant surface. Multi-layered norfloxacin loaded PLGA nanoparticles alternating with chitosan are used to coat titanium surfaces.
Nanoparticles and Liposomes for the Surface Modification of Implants: A Comparative Study of Spraying and Dipping Techniques
- First Published: 27 February 2018
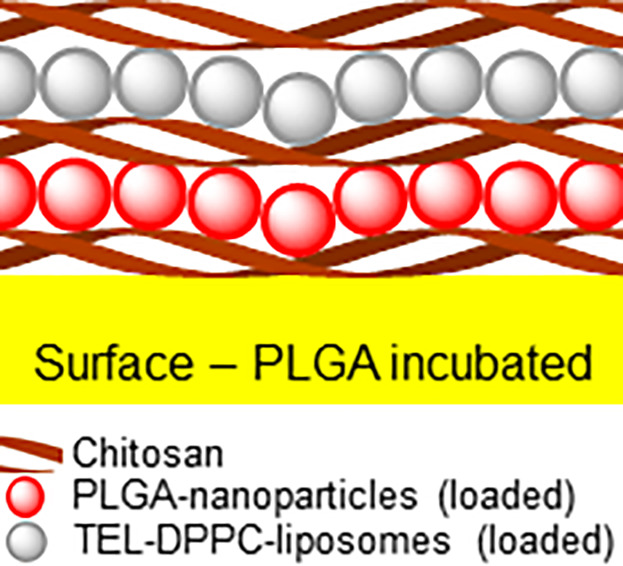
Implant polymers need to be modified for prevention of bacterial attachment, biofilm formation and bloodstream infections. A simple and efficient way for surface modification is the layer-by-layer technique. Using this method anti-adhesive, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory layers can be created. These different layers can be applied by simple yet effective dipping or spraying technique facilitating attachment via electrostatic interactions.
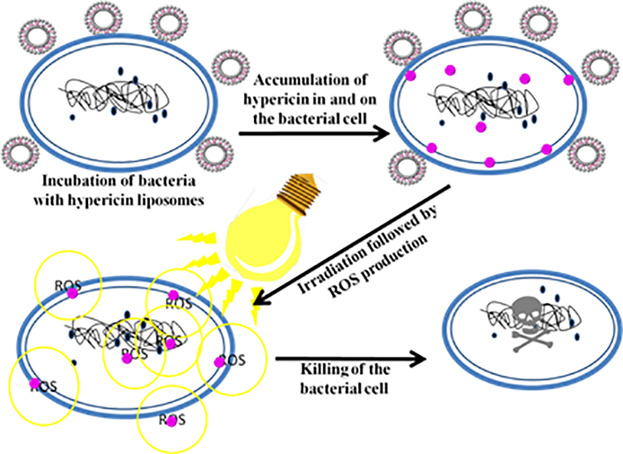
Hypericin Loaded Liposomes for Anti-Microbial Photodynamic Therapy of Gram-Positive Bacteria
- First Published: 27 February 2018
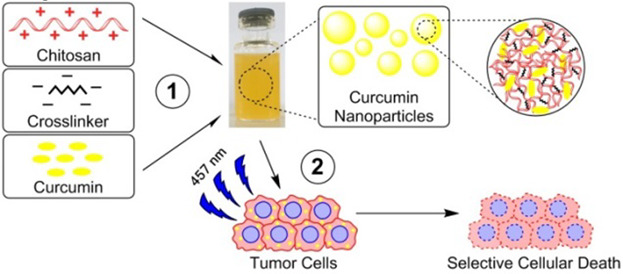
Preparation and Characterization of Curcumin Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles for Photodynamic Therapy
- First Published: 06 November 2017
Surface-Analytical Techniques
A Modified Chemical Imaging Sensor System for Real-Time pH Imaging of Accelerated Crevice Corrosion of Stainless Steel
- First Published: 17 April 2018
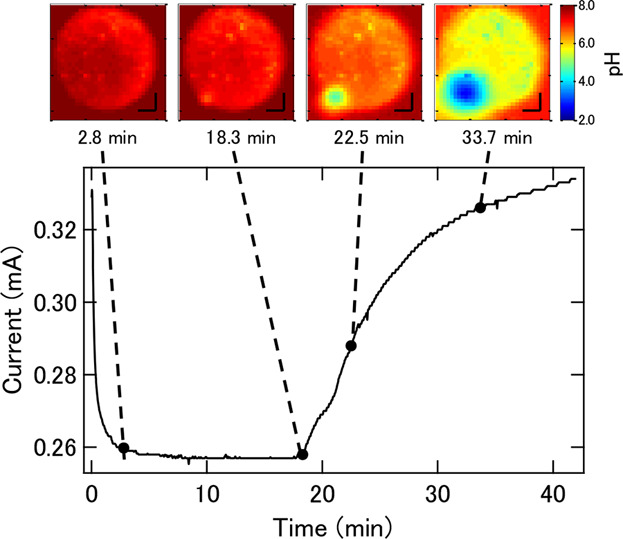
In situ visualization of pH change in the course of crevice corrosion is presented here. The pH distribution in the vicinity of a test piece of stainless steel under potentiostatic polarization is measured by a chemical imaging sensor. In synchronization with the increase of the corrosion current, the pH value drops to about 2 at the location where corrosion is initiated.
A Partially Etched Structure of Light-Addressable Potentiometric Sensor for High-Spatial-Resolution and High-Speed Chemical Imaging
- First Published: 24 March 2018
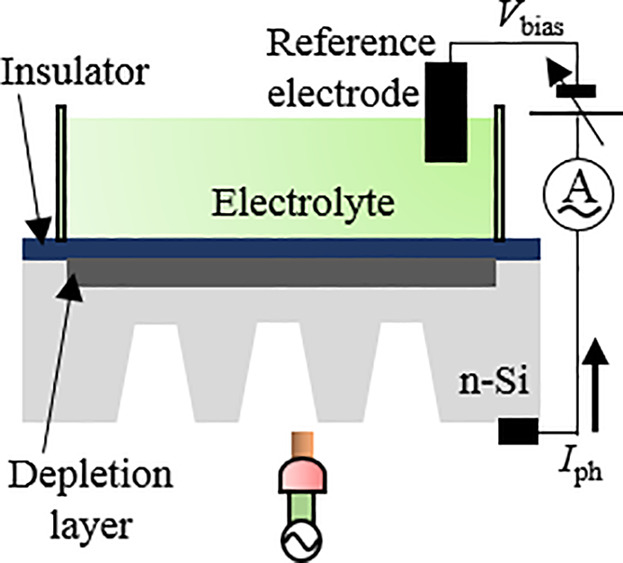
An anisotropic etching process based on tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH) is optimized to fabricate a partially etched structure of a LAPS sensor plate. This structure results in an improved imaging performance inside the etched region while maintaining the mechanical strength of the sensor plate.
Suitability of Various Materials for Probes in Scanning Kelvin Probe Measurements
- First Published: 11 December 2017
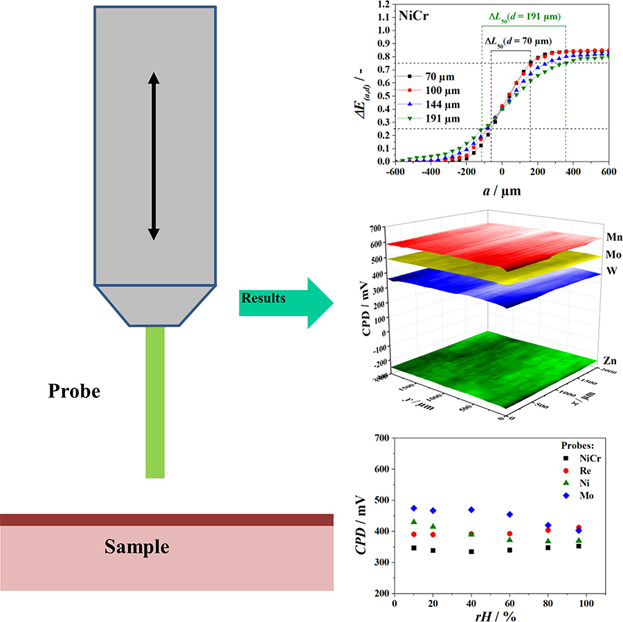
In the present study several materials, namely Re, Ni, and Mo, are tested regarding their suitability for serving as probes in scanning Kelvin probe (SKP) measurements. For comparison purposes NiCr, a commonly used standard material, is also tested. The metals are found to be more suitable than the NiCr alloy probe. High work function of probe materials results in high resolution capacity of Volta potential.
In Situ Mass Spectrometric Reaction Monitoring of Atmospheric Corrosion Processes
- First Published: 28 June 2018
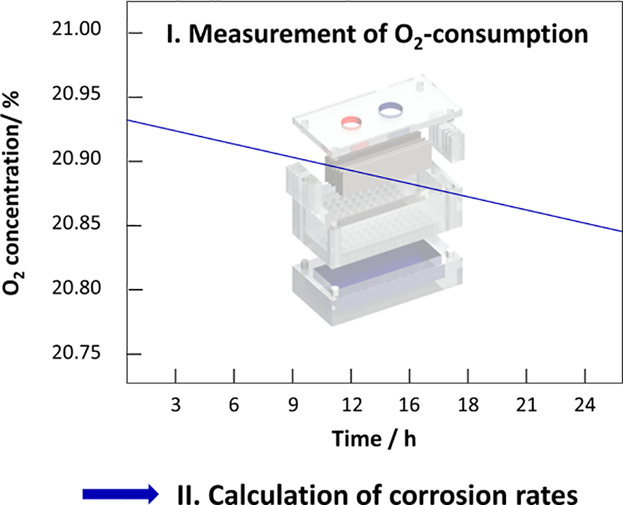
The anodic metal oxidation and the cathodic oxygen reduction are frequently the basis of atmospheric corrosion processes. With the oxygen reduction being the predominant cathodic reaction one can use oxygen consumption rates to determine the corrosion rate of a metal. In this work mass spectrometry is used to in situ measure oxygen consumption rates.
Determination of the Amount of Carbohydrates Adsorbed on Solid Substrates
- First Published: 17 April 2018

Carbohydrates are essential components in biofilms and involved in bacterial adhesion. Thus it is of great importance to find out which amount of carbohydrates binds to surfaces under predefined conditions. The classical phenol-sulfuric acid (PSA) assay is a method to quantify carbohydrates in solution. The presented modified assay allows now to determine the amount of carbohydrates which are adsorbed on a surface.
Comparison of Versatile Immobilization Methods for Gram-Positive Bacteria on a Silicon Cantilever
- First Published: 17 January 2018
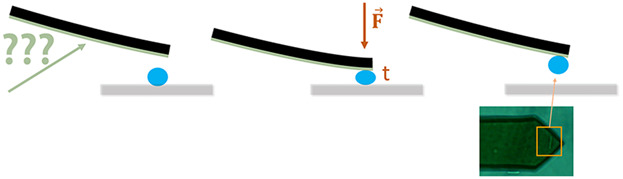
Bacterial adhesion is the first step in the formation of a biofilm and can be studied by single cell force spectroscopy. In this study the potential of different functionalizations to create single cell bacterial probes using gram-positive bacteria and tipless silicon cantilevers are investigated. Even though covalent fixation generally seems to work best, there are big differences between the three tested bacterial strains.
Chemo- and Biosensors
Flexible Calorimetric Gas Sensors for Detection of a Broad Concentration Range of Gaseous Hydrogen Peroxide: A Step Forward to Online Monitoring of Food-Package Sterilization Processes
- First Published: 21 May 2018
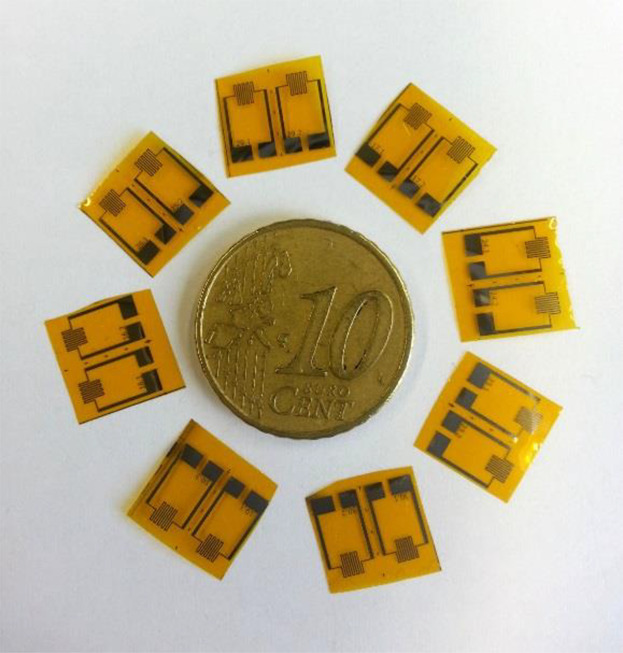

Flexible calorimetric gas sensors are fabricated on flexible polyimide films to specifically detect gaseous hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in sterilization processes for aseptic packaging industry. These sensors successfully detect high as well as low H2O2 concentrations with high sensitivity. The novelty of low H2O2 concentration detections is in the best interest of future inline monitoring of food-package sterilization.
Experimental and Numerical Analyzes of a Sensor Based on Interdigitated Electrodes for Studying Microbiological Alterations
- First Published: 17 May 2018
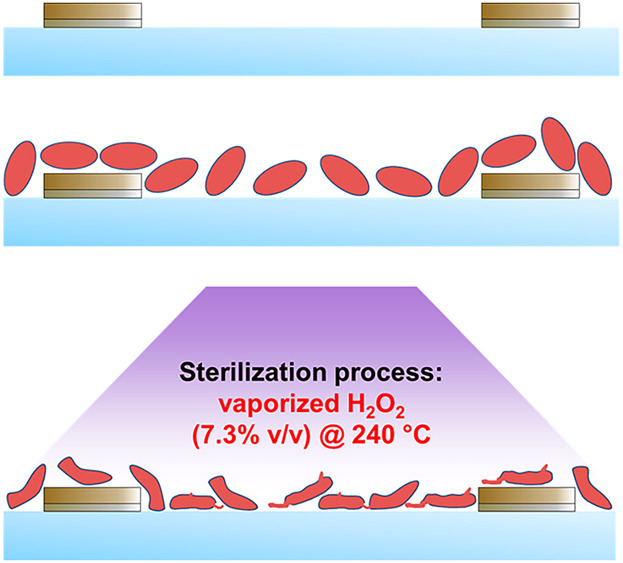
A biosensor to evaluate sterilization efficacy using hydrogen peroxide vapor is characterized. The biosensor is based on interdigitated gold electrodes. Experimental methods are applied to evaluate sensor behavior and alteration of test microorganisms (Bacillus atrophaeus). Numerical models of the sensor at different states are designed in COMSOL® Multiphysics and validated by the application of known material data. Numerical optimizations are applied to the numerical model in combination with experimental data to derive and tabulate frequency-dependent electrical parameters.
SIP-Based Thermal Detection Platform for the Direct Detection of Bacteria Obtained from a Contaminated Surface
- First Published: 15 January 2018
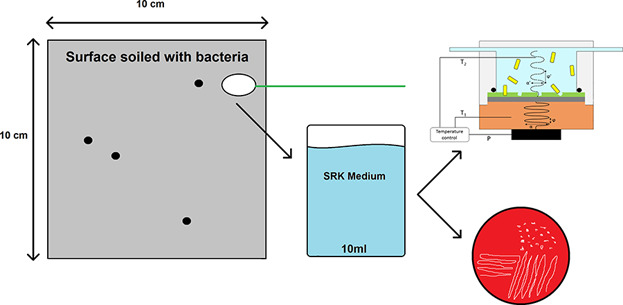
The research presented in this paper demonstrates the application of a fast, low-cost sensor for surface detection of bacteria. Bacteria are obtained from a contaminated surface using commercial swab rinse kits and the biomimetic sensor is able to detect the bacteria in a qualitative and quantitative manner within the hour. In this way, it offers a low-cost, fast alternative for the current labor-intensive and expensive gold standard detection techniques.
Impedimetric Sensing of DNA with Silicon Nanowire Transistors as Alternative Transducer Principle
- First Published: 08 January 2018
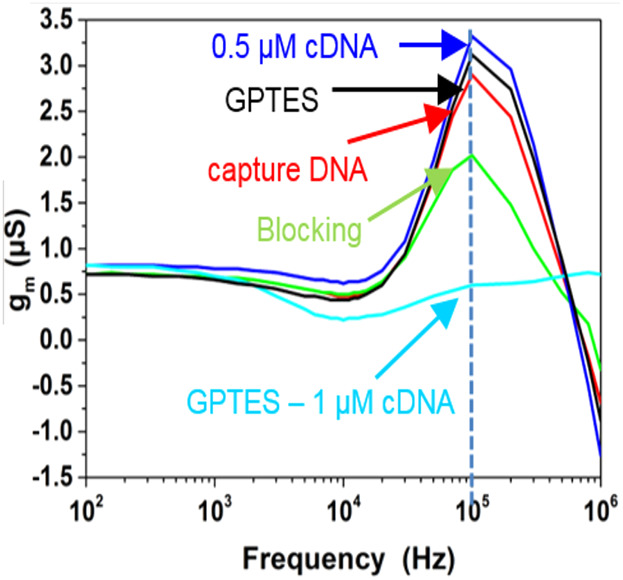
In this work, an alternative transducer principle for silicon nanowire biosensors to detect DNA by the transistor-transfer function (TTF) method is presented. The spectra are influenced by the biomolecule charges, which change the liquid–solid interface impedance. It is shown that this transducer principle is also influenced by Debye screening, but shifting to higher frequencies of 100 kHz and above might overcome this limitation.
Two-Protein Modified Gold Nanoparticles for One-Step Serological Diagnosis
- First Published: 15 February 2018
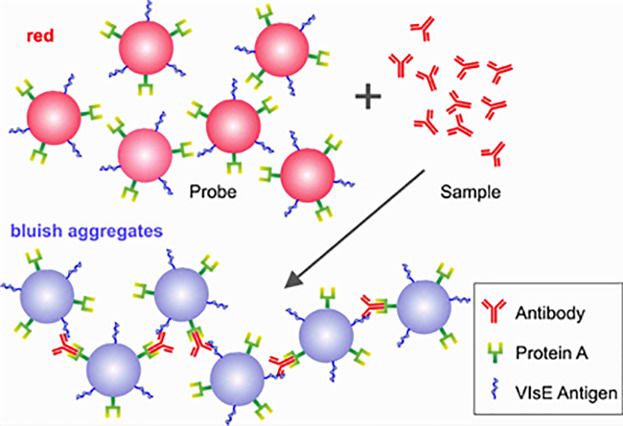
A successful employment of a new platform for proteins detection in body fluid can be established. AuNPs modified with two proteins (protein A and VlsE Borrelia antigen) are utilized to detect antibodies directed to Lyme borreliosis in human sera samples. AuNPs show a very specific style in the detection of the antibodies; furthermore, the assay can be performed only in one step in a rapid manner.
Wafer-Scale Nanoimprint Lithography Process Towards Complementary Silicon Nanowire Field-Effect Transistors for Biosensor Applications
- First Published: 27 June 2018
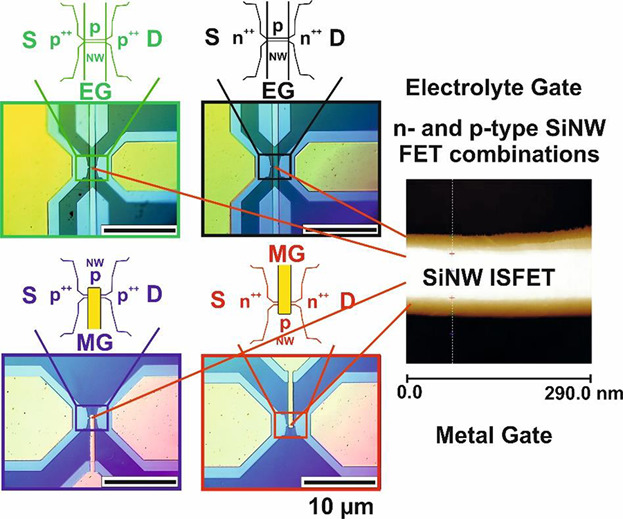
A novel, wafer-scale fabrication process for combined n-type and p-type silicon nanowire field-effect transistors (SiNW FET) is presented. The sensors are fabricated with nanoimprint lithography (NIL) while the nano- and micro-scale structures are realized in one step. The SiNW FET platform can be utilized for various biomedical applications with very precise electronic control of the nanoscale transducer elements.
Development of Instrumentation
Optimization of Cell-Based Multi-Chamber LAPS Measurements Utilizing FPGA-Controlled Laser-Diode Modules
- First Published: 13 May 2018
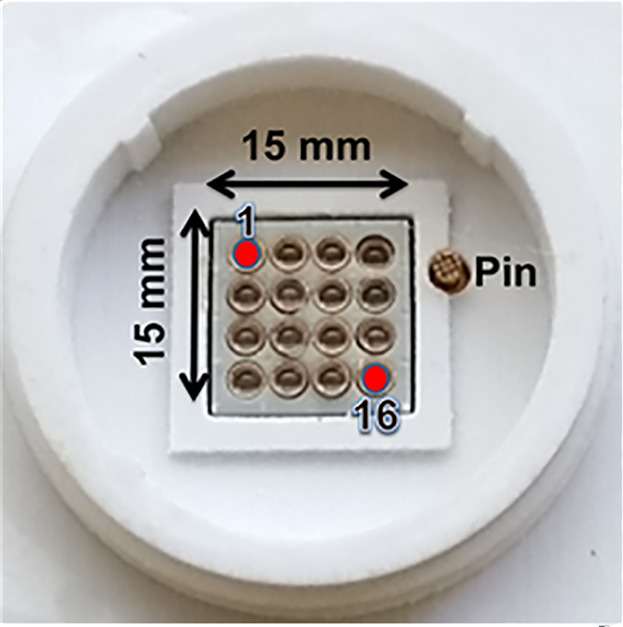
The present work introduces a novel illumination unit for light-addressable potentiometric sensors (LAPS) based on a field programmable gate array (FPGA) consisting of 16 fixed-focus tunable infrared laser-diode modules minimizing undesirable scattering effects in multi-chamber differential measurements in comparison with light-emitting diodes for investigations of the metabolic activity of microorganisms (e.g., Escherichia coli K12).
A Novel Modular Device for Biological Impedance Measurements: The Differential Impedimetric Sensor Cell (DISC)
- First Published: 25 April 2018
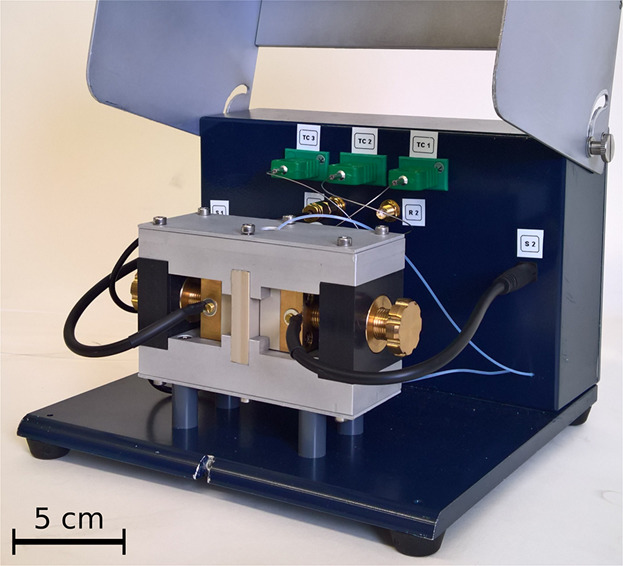
In medical diagnostics, food-safety analysis, and detection of environmental pollutants, simultaneous detection and quantification of multiple target molecules can be invaluable. Furthermore, the ability to perform differential measurements enables analysis of undiluted patient samples, which significantly simplifies sample preparation. In this work, a successful prototype system based on impedance spectroscopy that meets these requirements is presented and validated.
Electrical Impedance Tomography With a Lab-on-Chip for Imaging Cells in Culture
- First Published: 17 April 2018
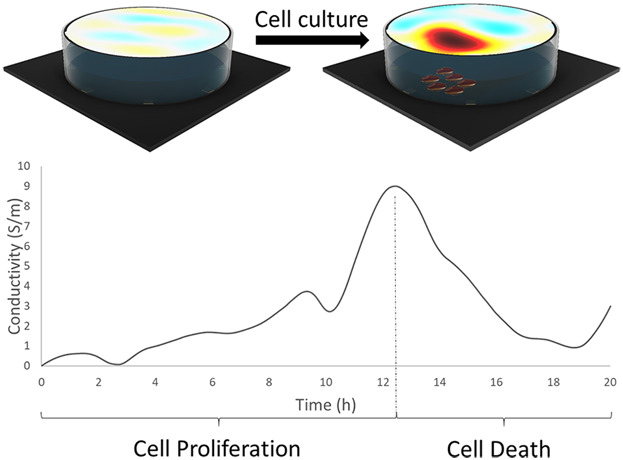
This research explores the benefits and limitations on how impedance tomography can help in the analysis of cell–drug interaction. Results show that real-time monitoring of cellular growth in culture is possible. It is possible to take a tomographical image of the culture well at any given moment and this in a non-invasive and contactless way. This results into a spatial reconstructed image which shows the conductivity distribution within this well.
Flexible High Density Active Neural Implants Combining a Distributed Multiplexing Transceiver Architecture with Biocompatible Technology
- First Published: 07 May 2018
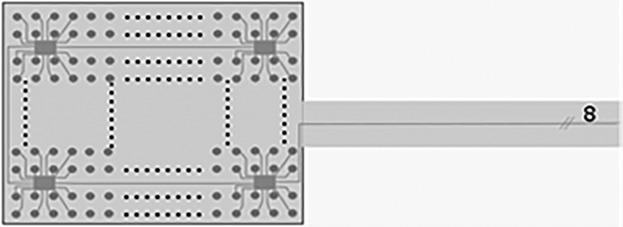
In order to increase spatial resolution without increasing the number of wires in neurological ECoG grids a new de-multiplexing system using a distributed electronic architecture is presented. This architecture is enabled by chip arrays that jointly multiplex the electrode signals using a combination of analog and digital data transmission.