Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Investigation of Topological and Catalytic Properties of Gold Iodide Monolayer: A Density Functional Theory Study
- First Published: 05 May 2022
The topological and catalytic properties of gold iodide monolayers are investigated using first-principles calculations by Prafulla K. Jha and colleagues in article number 2100657. The non-trivial topology and catalytic activity are at the core of this work offering insights into potential applications of gold iodide monolayers.
Masthead
Reviews
15 years of pss RRL
Rational Control of GeSn Nanowires
- First Published: 31 December 2021
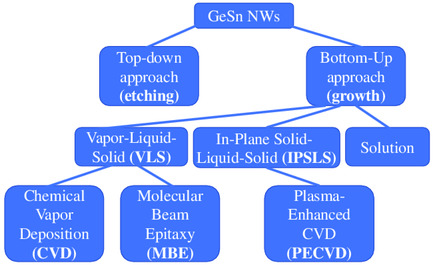
GeSn nanowires can be synthesized via top-down and bottom-up approaches. Top-down involves growing GeSn layers on a Ge buffer layer and combining wet etching with selective dry etching to achieve strain-free GeSn nanowires. Bottom-up methods include i) vapor–liquid–solid processes via chemical vapor deposition and molecular beam epitaxy, ii) plasma-assisted in-plane solid–liquid–solid growth, and iii) solution-based mechanisms.
Organic Semiconductor–Insulator Blends for Organic Field-Effect Transistors
- First Published: 08 February 2022
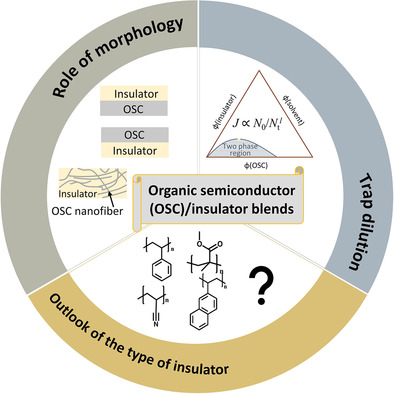
This review focuses on how to use organic semiconductor/insulator blends to achieve better organic field-effect transistors (OFETs). It covers the latest advances in blended OFETs. Then, several schemes, including morphology control, trap dilution, and various insulator types, are proposed to deepen the understanding of the intrinsic properties of insulator blends and provide clinical directions for device optimization.
Monolithic InGaN Multicolor Light-Emitting Devices
- First Published: 31 January 2022
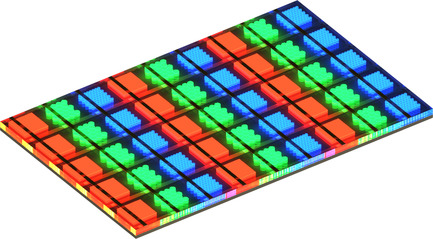
Monolithic full-color microLED display is a feasible and cost-effective solution to overcome the shortcomings of existing “mass transfer” technologies. By realizing multicolor emission from a single wafer, the approach offers a potentially higher yield, scalability, robustness, efficiency, and manufacturability. Herein, an overview of the main monolithic integration approaches including top-down fabrication and bottom-up growth approaches is given.
Perspective
Halide Ions Distribution and Charge Dynamics in Mixed-Halide Perovskites
- First Published: 03 February 2022
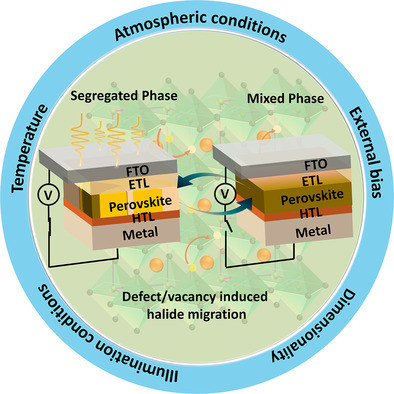
Mixed-halide perovskites are tunable photoabsorbers and emitters because of their compositional-dependent properties. This perspective provides a meticulous understanding of the critical views on how the mixed-halide perovskites are going to be the cutting-edge next-generation materials, focusing on the implications that have become seemingly difficult to extrapolate and predict the realistic performance of optoelectronic devices in working conditions.
Research Articles
15 years of pss RRL
Diode Laser-Crystallization for the Formation of Passivating Contacts for Solar Cells
- First Published: 24 February 2022
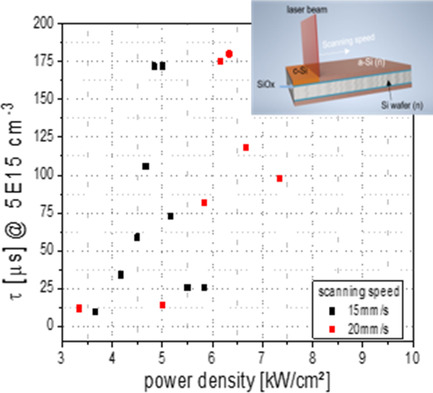
A new method of laser treatment of passivated contacts for wafer solar cell application was investigated. The Czochralski wafer samples were deposited with highly doped amorphous silicon layers on both sides. The samples are scanned with two different speeds and the corresponding power densities. A fitted lifetime above 4.06 ms and an implied open-circuit voltage of 711 mV were achieved.
Orbital Hybridization Induced by Double-Anion Coordination to Enhance Room-Temperature Ferromagnetic Response
- First Published: 22 February 2022
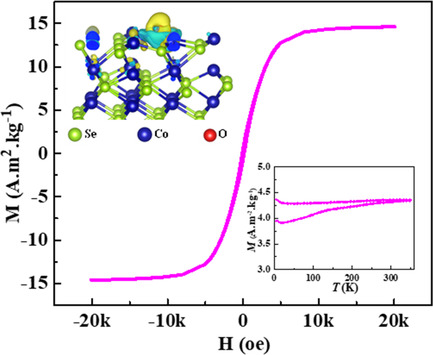
The oxygen introduction can strongly affect magnetic structure, and significantly enhance room-temperature magnetic response for cobalt selenides. The difference in bonding interaction between CoO bonds and CoSe bonds induces electronic reconfiguration in cobalt selenides, altering room-temperature ferromagnetism. This experimental observation can provide a new insight into the role of oxygen incorporation onto magnetic structure transformation.
Demonstration and Evaluation of p-Type and n-Type ZnO Nanoparticles-Based Homojunction UV Light-Emitting Diodes
- First Published: 05 January 2022
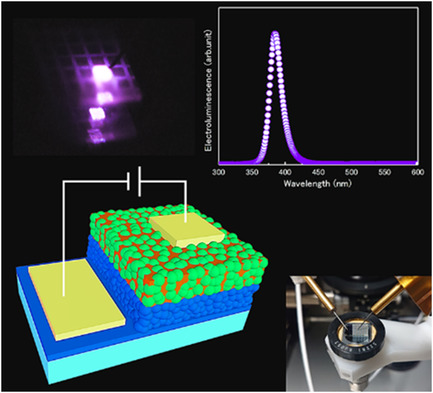
The world's first homojunction UV light-emitting diode (LED) based on both p-type and n-type ZnO nanoparticles (NPs) is demonstrated. Nitrogen-doped ZnO and gallium-doped ZnO NPs are provided to fabricate p-type and n-type NP layers, respectively. The LEDs with these layers show near UV electroluminescence and it can be confirmed that the holes inject from p-type layer to n-type layer.
Optimization of the Double Electron–Electron Resonance for C-Centers in Diamond
- First Published: 31 December 2021
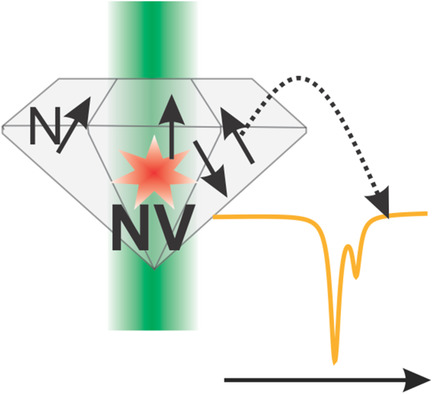
The concentration of C-centers in several diamond plates is measured. The influence of the free precession time of the nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center on the contrast in the double electron–electron resonance spectrum is investigated. The optimal free-precession time is determined for each C-center concentration, showing a strong correlation with both the concentration of C-centers and the NV-center coherence time.
15 years of pss RRL
Disorder-Induced Broadband-Distributed Bragg Reflectors in Dielectric and Nanoporous GaN Systems
- First Published: 15 February 2022
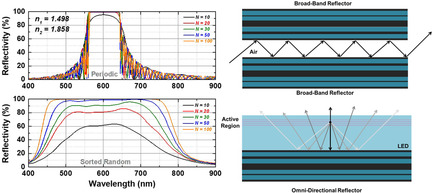
Disordered random distributed Bragg reflectors (DBR) theoretically and experimentally demonstrate a ≈2.5X (from ≈80 to ≈200 nm) enhancement of the stopband width compared with a periodic DBR for both dielectric and nanoporous GaN material systems. The described method is beneficial for various applications, including air-guiding waveguides and light-emitting diodes with improved light extraction efficiency.
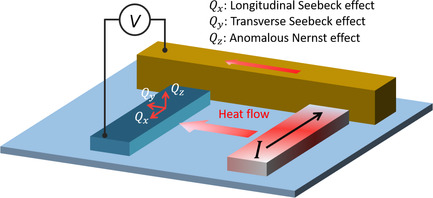
Experimental Evaluation of 3D Heat Flow Using Magneto-Thermoelectric Effects in a Ferromagnetic Nanowire
- First Published: 22 January 2022
Fe- and Co-Doped Tungsten Disulfide Monolayers: 2D Ferromagnetic Half-Metals at Room Temperature
- First Published: 04 February 2022
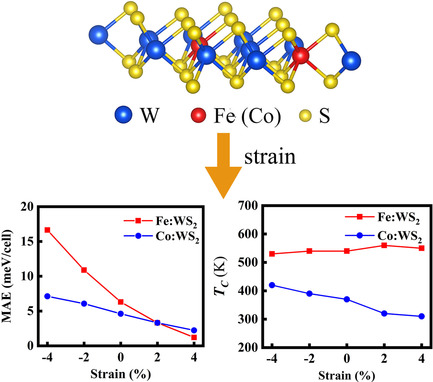
The Fe- and Co-doped tungsten disulfide monolayers are ferromagnetic half-metals with the out-of-plane easy magnetization axis at room temperature. The magnetic anisotropic energy of Fe:WS2 can be larger than 16 meV cell−1 under −4% compressive strain. The strain effect on the Curie temperature is also discussed.
Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Physical Properties of BaSnS2
- First Published: 11 February 2022
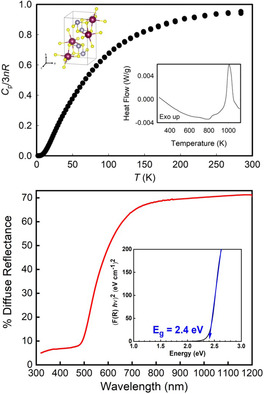
Thermal and optical properties of BaSnS2 are reported for the first time. The herein described analyses show that it is a direct, wide bandgap material (2.4 eV) with a Debye temperature of 198 K and low-frequency Einstein modes at 59 K. The herein described findings lay the foundation for understanding the physical properties of this material.
15 years of pss RRL
Process–Structure–Properties Relationships of Passivating, Electron-Selective Contacts Formed by Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition of Phosphorus-Doped Polysilicon
- First Published: 27 January 2022
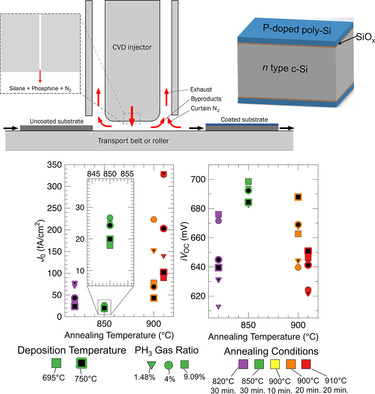
Phosphorus (P) concentration and deposition temperature significantly control the microstructure, electrical properties, and passivation quality of oxide passivated in-situ P-doped poly-Si contact fabricated by atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition process (APCVD). Post-deposition annealing in optimal conditions with hydrogenation yields excellent APCVD poly-Si passivating contact with saturation current density (J 0) of 3 fA cm−2 and implied open-circuit voltage (iV OC) of 712 mV.
Statistics of Nucleation and Growth of Single Monolayers in Nanowires: Towards a Deterministic Regime
- First Published: 14 January 2022
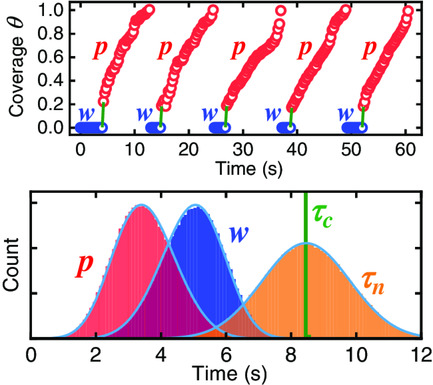
The statistics of nucleation and growth of individual biatomic monolayers in self-catalyzed GaAs nanowires are investigated quantitatively by combining in situ transmission electron microscopy and modeling. When the catalyst droplet is very poor in As, a self-regulated growth regime arises at relatively low growth temperature, despite the stochasticity of the nucleation events.
Electron–Electron Interaction and Weak Antilocalization Effect in a Transition Metal Dichalcogenide Superconductor
- First Published: 28 January 2022
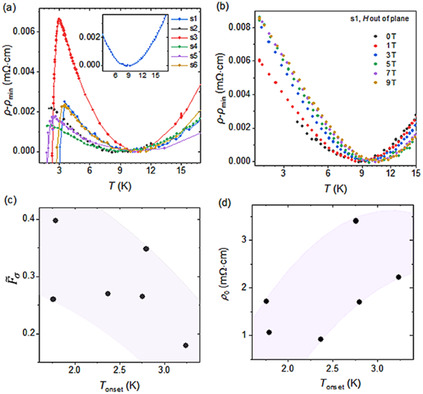
Quantum transport properties of the transition-metal dichalcogenide superconductor 1T-NbSeTe are investigated. The single crystal shows a resistivity upturn at low temperatures before entering the superconducting state. The characteristics of the upturn and the magnetoresistance behavior reveal disorder-enhanced electron–electron interaction and strong spin-orbit coupling-induced weak antilocalization effect. In addition, the material shows anomalous disorder-enhanced superconductivity, calling for further understanding.
Editor's Choice
Electronic Properties of the Weyl Semimetals Co2MnX (X=Si, Ge, Sn)
- First Published: 16 February 2022
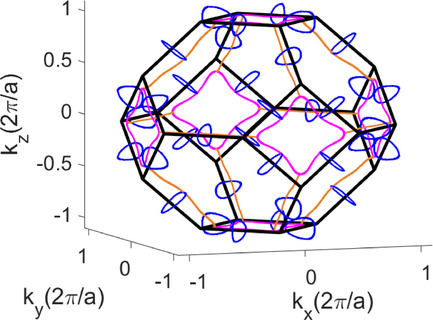
Complex nodal-line geometries, that are topologically protected by crystal mirror planes, are predicted in the family of compounds Co2MnX (X = Si, Ge, Sn), and are classified as Weyl semimetals. Due to presence of ferromagnetism and strong spin–orbit interaction in these materials, time-reversal symmetry is broken, which results in the appearance of Weyl nodes along certain mirror planes. This has important consequences on the experimental observables such as Anomalous Hall conductivity.
Effect of Fatigue Fracture on Resistive Switching of ZnO and NiO Stacking Films
- First Published: 22 February 2022
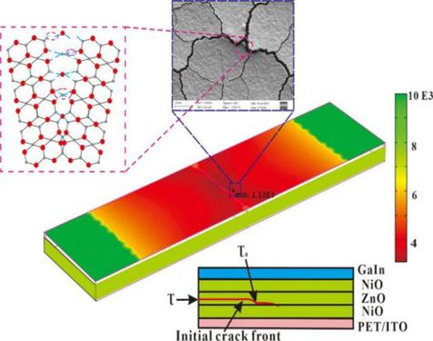
The ZnO and NiO stacking films are prepared by sol–gel spin-coating to explore the impact of bending on device resistive switching. Fatigue life analysis of bent sample is studied to predict the fracture position and to validate the cycle failure times, a modified compliance calibration method is reported to determine the film breakdown threshold.
15 years of pss RRL
Investigation of Topological and Catalytic Properties of Gold Iodide Monolayer: A Density Functional Theory Study
- First Published: 25 February 2022
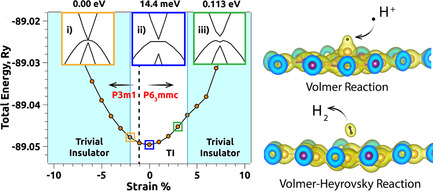
Topological and catalytic properties of gold iodide (AuI) monolayer are explored and predicted for the first time. It is observed that AuI exhibits strain-induced large-gap (0.113 eV) topological insulating nature along with decent catalytic activity toward hydrogen evolution reaction with Gibb's free energy as low as −0.4 eV. The findings open up broader research avenues for nano-electronic and catalytic applications.
Layered MoSi2N4 as Electrode Material of Zn–Air Battery
- First Published: 15 February 2022
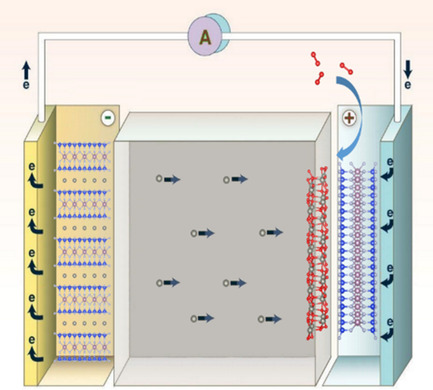
Layered MoSi2N4 is proposed as an electrode material of Zn–air battery. As the anode and the Zn storage material, a phase transition from state I to state III occurs in MoSi2N4 with increasing Zn loading. With MoSi2N4 as the cathode, the two-electron mechanism of O2 reduction to ZnO2 is more efficient than general sluggish four-electron aqueous O2 redox reactions.
Multicolor Invisible Patterns Encrypted in Double-Inverse-Opal Films Based on Thermally Induced Structural Deformation
- First Published: 16 February 2022
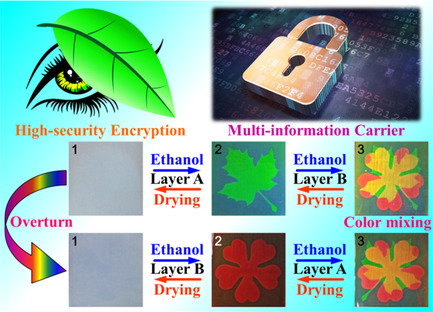
Herein, multicolor invisible patterns encrypted in double-inverse opal films based on thermally induced structural deformation for anti-counterfeiting applications are prepared. The current film material can reveal different patterns on the front and back sides during the solvent-responsive decryption, and simultaneously the overlapping part of the patterns can achieve color mixing based on the bilayer structure.