Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Free Access
free
Developments in type 1 and type 2 diabetes
1型和2型糖尿病的研究进展
- Pages: 530-531
- First Published: 14 April 2021
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
no
A randomized control trial of duloxetine and gabapentin in painful diabetic neuropathy
度洛西汀与加巴喷丁治疗痛性糖尿病神经病变的随机对照试验
- Pages: 532-541
- First Published: 19 December 2020
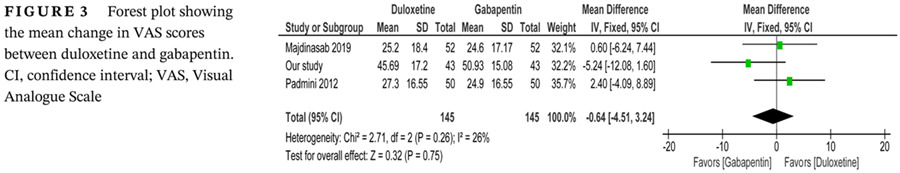
Highlights
- There is significant decrease in pain score and symptom score like diabetic neuropathy symptoms, diabetic neuropathy examination, and neuropathic disability score with duloxetine and gabapentin.
- Equivalence of duloxetine with gabapentin was established with regard to Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) scores.
- Meta-analysis of studies showed comparable efficacy of duloxetine vs gabapentin in terms of VAS scores.
no
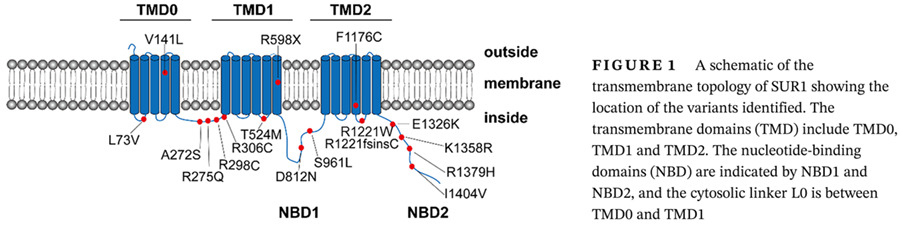
Genetic variants of ABCC8 and phenotypic features in Chinese early onset diabetes
中国早发糖尿病患者ABCC8基因变异的临床特征分析
- Pages: 542-553
- First Published: 09 December 2020
no
Relationship between dietary choline intake and diabetes mellitus in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2010
膳食胆碱摄入量与糖尿病的关系:美国国民健康与营养调查2007-2010
- Pages: 554-561
- First Published: 10 December 2020
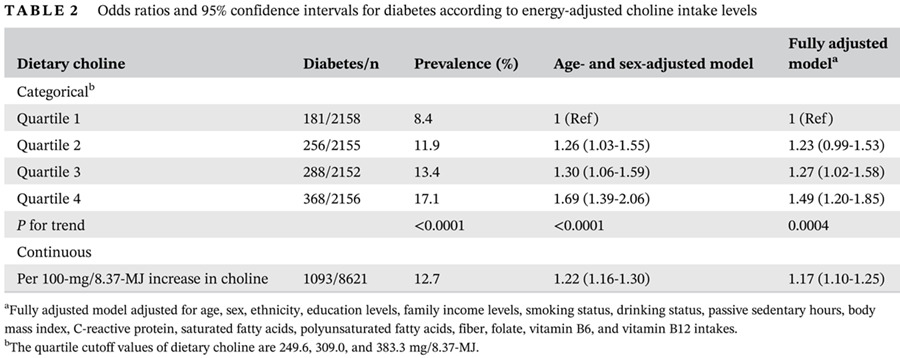
Highlights
- Choline is a major dietary precursor for gut microbiome-derived trimethylamine, but little is known about the relationship between dietary intake of choline and diabetes mellitus.
- There is a linear dose–response relationship between dietary choline intake and the odds of diabetes mellitus.
- Dietary choline should not exceed 331.7 mg/8.37-MJ per day for US adults to achieve potentially lower risks of diabetes mellitus.
Open Access
oa
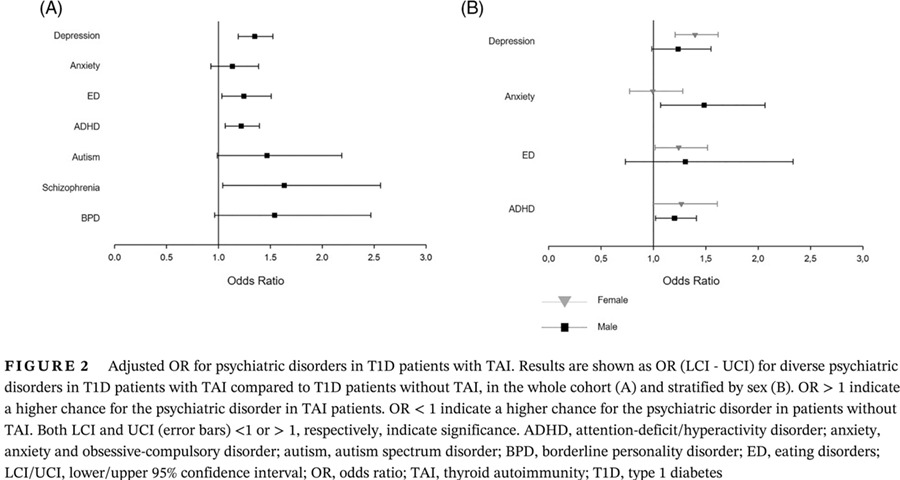
Are psychiatric disorders associated with thyroid hormone therapy in adolescents and young adults with type 1 diabetes?
青少年和青壮年1型糖尿病患者的精神障碍与甲状腺激素治疗有关吗?
- Pages: 562-571
- First Published: 16 December 2020
Open Access
oa
Combining glomerular basement membrane and tubular basement membrane assessment improves the prediction of diabetic end-stage renal disease
联合评估肾小球基底膜厚度和肾小管基底膜厚度可提高糖尿病肾病进展为终末期肾脏病的预测能力
- Pages: 572-584
- First Published: 22 December 2020
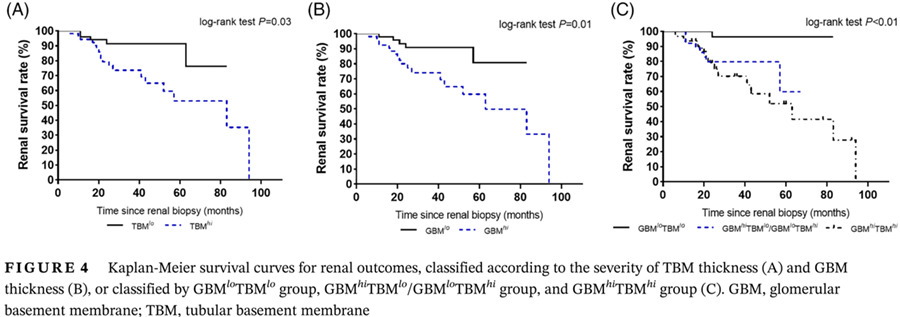
Highlights
- The prognostic value of combining tubular basement membrane (TBM) and glomerular basement membrane (GBM) in diabetic nephropathy (DN) was lacking.
- TBM thickness was strongly correlated with GBM thickness, baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate, and proteinuria.
- The degree of TBM thickness provided additional value to GBM thickness for predicting end-stage renal disease progression in patients with type 2 diabetes and biopsy-proven DN.
no
Clinical characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with type 2 diabetes in Turkey: A nationwide study (TurCoviDia)
土耳其2型糖尿病患者患有COVID-19的临床特征和结果:一项全国性研究(TurcoviDia)
- Pages: 585-595
- First Published: 02 March 2021
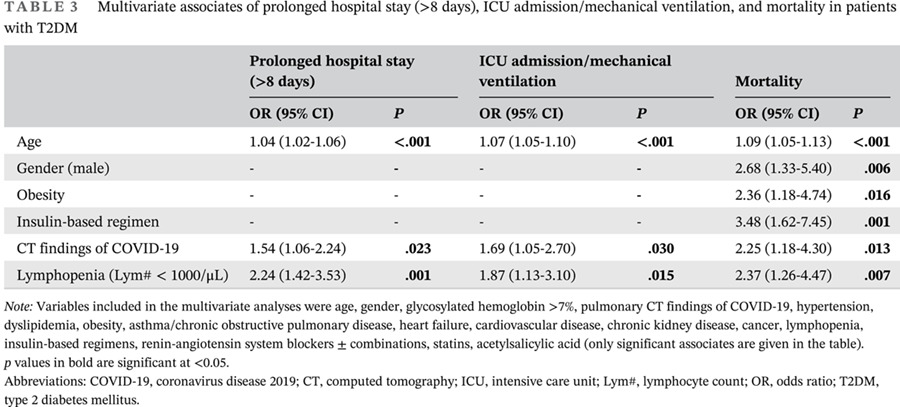
Highlights
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) takes an unfavorable course in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and the risk increases in individuals with certain conditions, some of which are not modifiable.
- This study showed significantly higher mortality due to COVID-19 in hospitalized patients with T2DM than without (13.6% vs 8.7%; hazard ratio 1.75; 95% CI, 1.58-1.93).
- Older age, male gender, obesity, preexisting insulin treatment, low lymphocyte count, and pulmonary involvement on admission were the significant associates of COVID-19 mortality.
RESEARCH LETTER
no
Do SGLT-2 inhibitors exhibit similar cardiovascular benefit in patients with heart failure with reduced or preserved ejection fraction?
SGLT-2抑制剂在射血分数降低或保持不变的心力衰竭患者中是否显示出类似的心血管益处?
- Pages: 596-600
- First Published: 01 April 2021
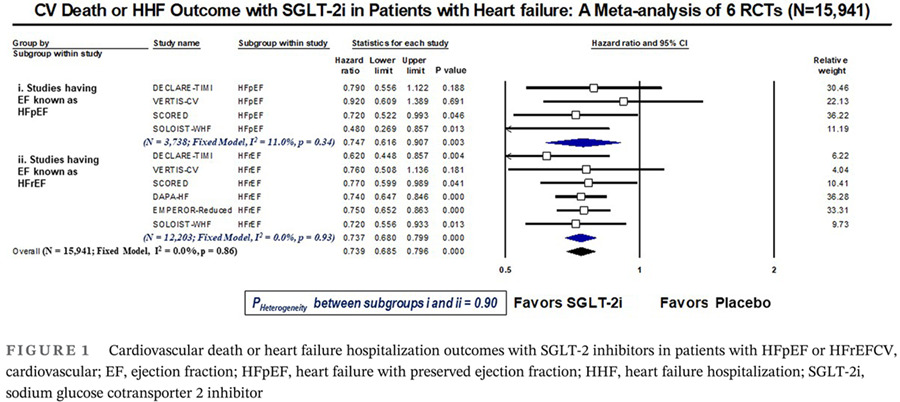
Highlights
- The beneficial cardiovascular (CV) effects of SGLT-2 inhibitors (SGLT-2i) in patients with heart failure are already known.
- Whether SGLT-2i exert similar CV effects in heart failure with reduced or preserved ejection fraction is not known.
- This meta-analysis showed SGLT-2i exert similar CV benefits irrespective of the types of heart failure. Future trials will confirm or refute the CV effects of SGLT-2i in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
no
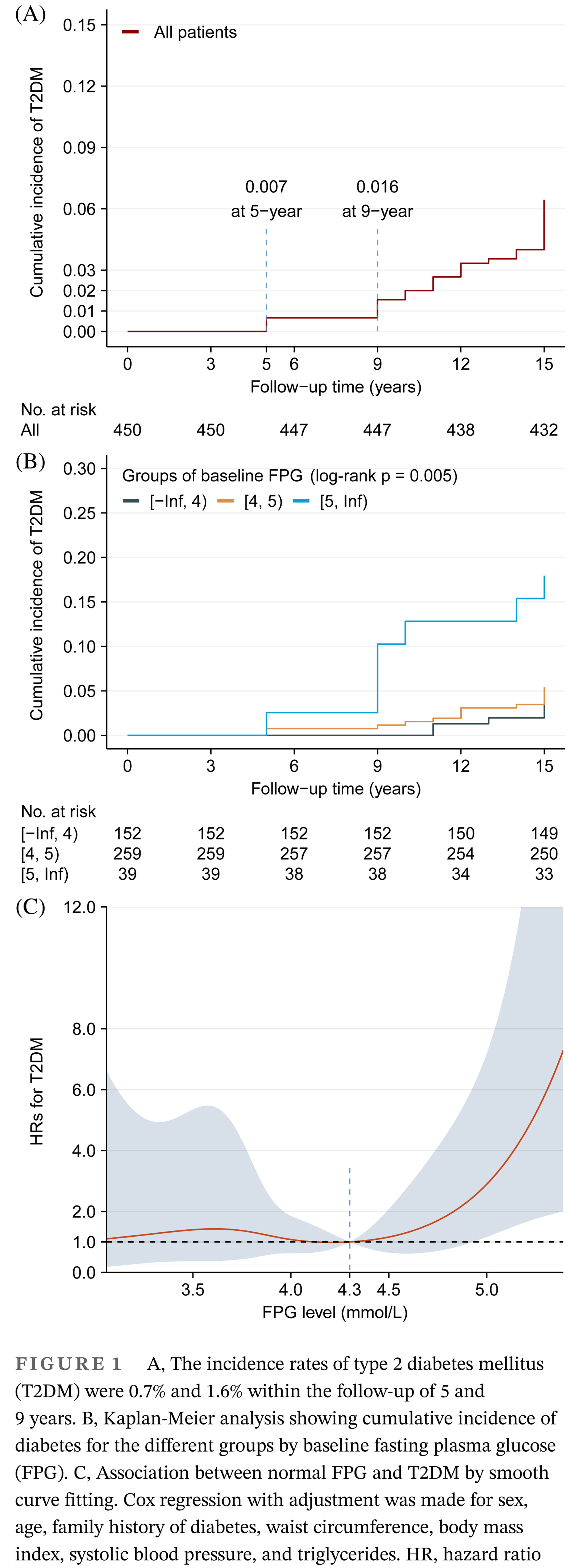
Fasting plasma glucose and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in a group of Chinese people with normoglycemia and without obesity
- Pages: 601-602
- First Published: 17 March 2021
no
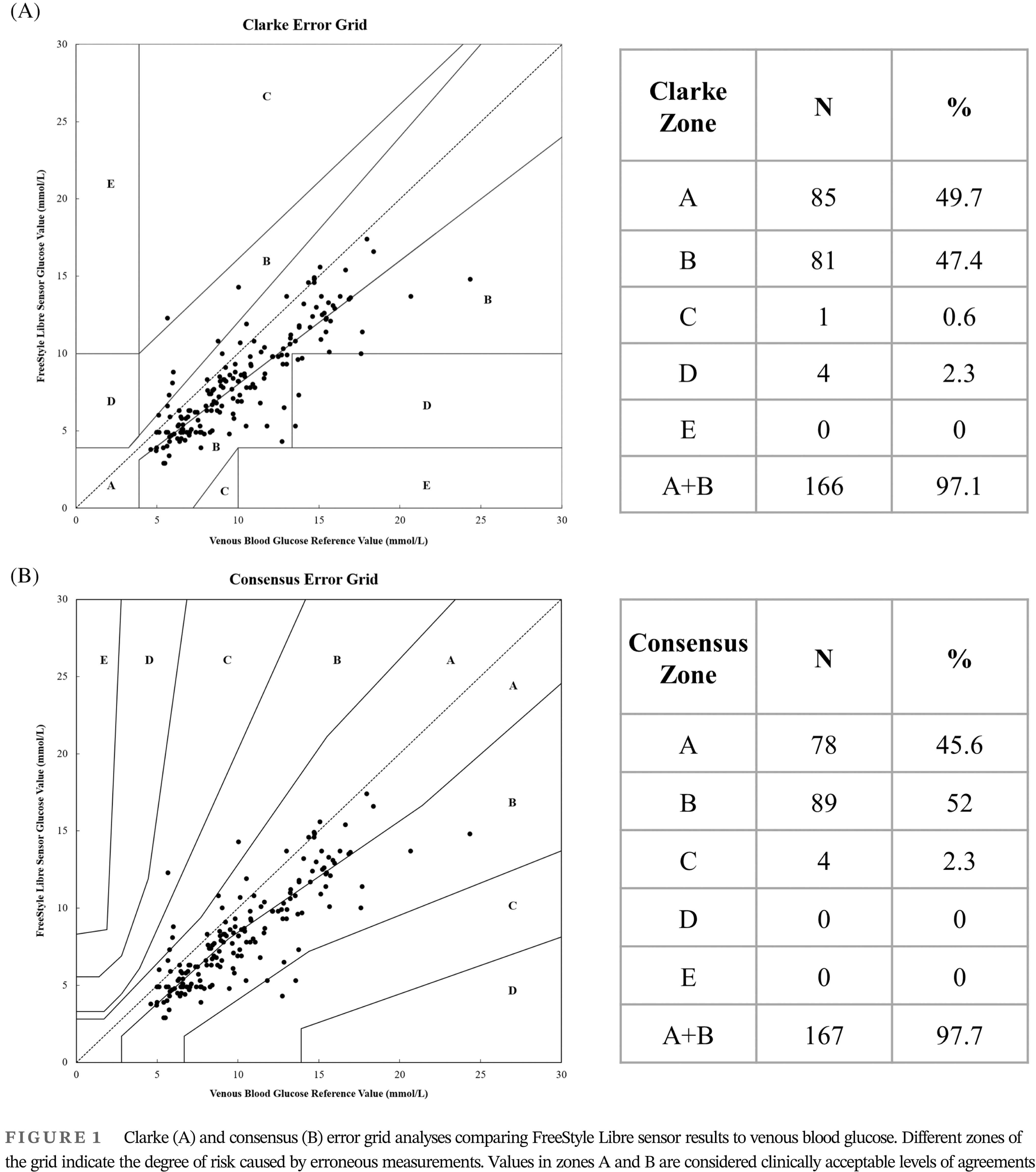
Evaluation for the feasibility and accuracy of Freestyle Libre Flash Glucose Monitoring System used by COVID-19 patients in intensive care unit
- Pages: 603-605
- First Published: 31 March 2021