Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Celiac disease: A global survey
乳糜泻:一项全球调查
- Pages: 446-447
- First Published: 14 March 2021
EDITOR'S RECOMMENDATION
Celiac disease in children with type 1 diabetes varies around the world: An international, cross-sectional study of 57 375 patients from the SWEET registry
1型糖尿病儿童的乳糜泻在世界各地各不相同:一项对来自SWEET注册中心的57375名患者进行的国际横断面研究
- Pages: 448-457
- First Published: 29 October 2020
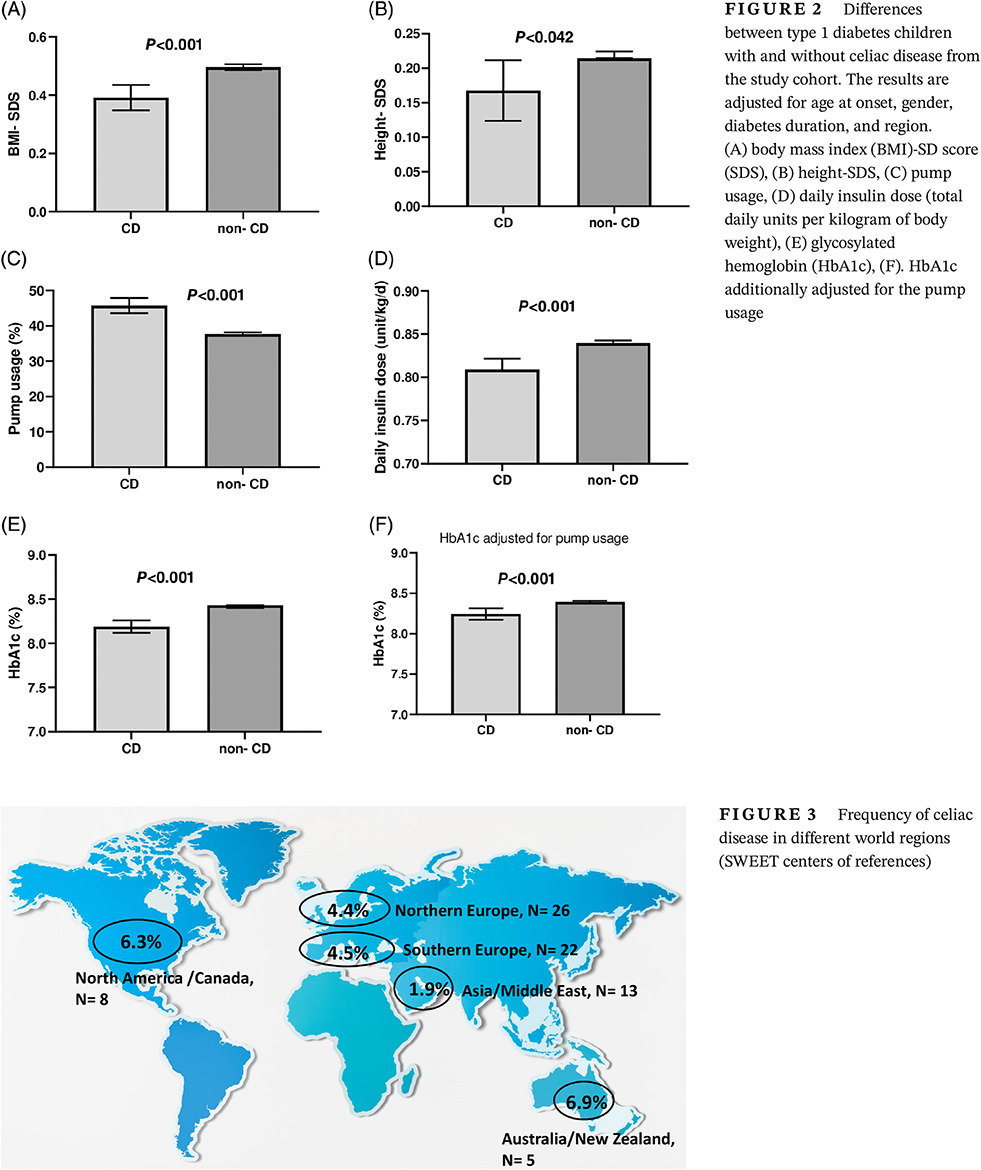
Highlights
- There are worldwide differences in the frequency of CD in children with T1D with higher prevalence in girls and those with young onset. Differences in anthropometric outcomes in children with T1D and CD highlights the importance of close follow-up of growth and antibodies in these children. In many regions, children with CD and T1D are more likely to use modern technologies compared to non-CD subjects. Diabetes control in children with CD and T1D varies between regions and needs improvement.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Age at menarche, ideal cardiovascular health metrics, and risk of diabetes in adulthood: Findings from the REACTION study
月经初潮年龄、理想的心血管健康指标和成年后糖尿病患病风险:来自REACTION研究的发现
- Pages: 458-468
- First Published: 01 November 2020
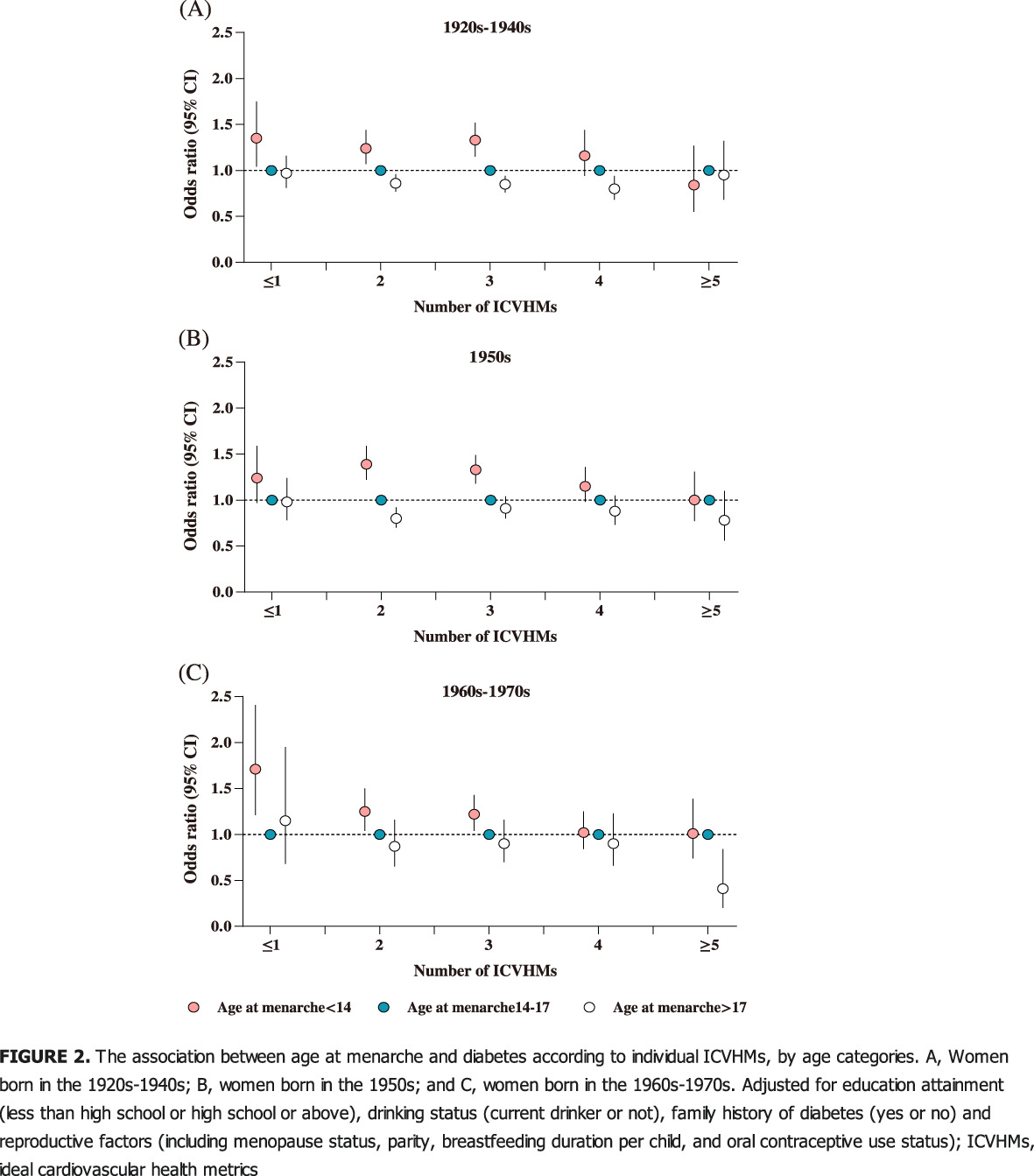
Highlights
- Results from previous studies on the association of age at menarche and the risk of diabetes in adulthood were inconsistent, and the impact of ideal cardiovascular health metrics (ICVHMs) on this association was unclear.
- This study showed that early age at menarche was associated with an increased risk of diabetes in middle-aged and elderly Chinese women, but not in women with ≥4 ICVHMs.
- There was a significant interaction between the number of ICVHMs and the age at menarche in modifying the risk of diabetes.
Electrophysiologically verified effects of acupuncture on diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes: The randomized, partially double-blinded, controlled ACUDIN trial
电生理验证针灸对2型糖尿病周围神经病变的影响:随机、部分双盲的ACUDIN对照试验
- Pages: 469-481
- First Published: 04 November 2020
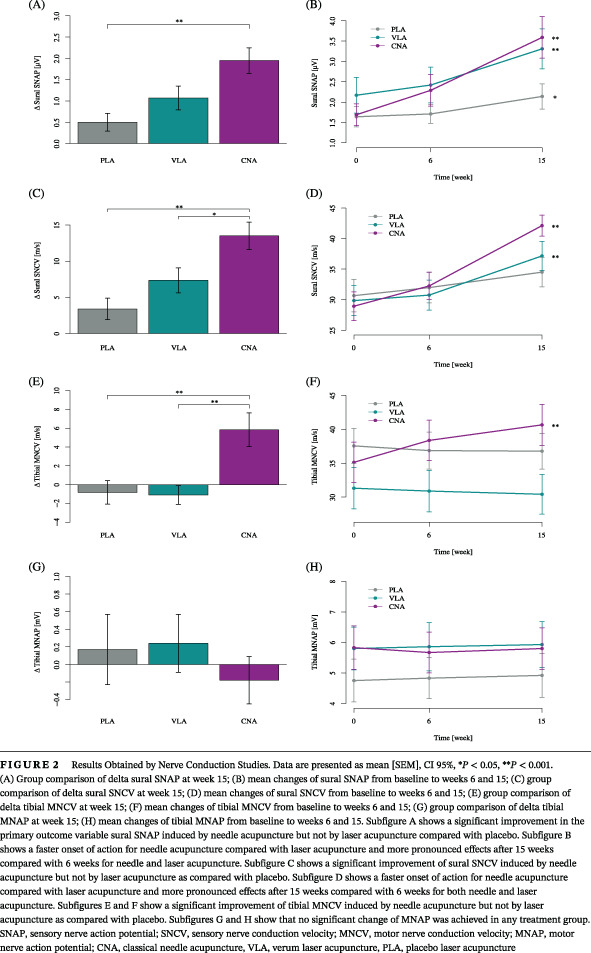
Highlights The ACUDIN (ACUpuncture and laser acupuncture for treatment of DIabetic peripheral Neuropathy) trial showed significant effects of acupuncture compared with placebo on type 2 diabetes-induced DPN, as measured by NCS. Improvement in the primary outcome variable sural SNAP amplitude indicates structural neuroregeneration following acupuncture. Our findings are evidence that acupuncture is an appropriate safe, nonpharmacological complementary treatment option for type 2 diabetic patients with DPN.
The burden of ischemic heart disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus attributable to diet high in sugar-sweetened beverages in China: An analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017
中国归因于高糖饮料的缺血性心脏病和2型糖尿病的疾病负担:一项基于2017年全球疾病负担研究的分析
- Pages: 482-493
- First Published: 05 November 2020
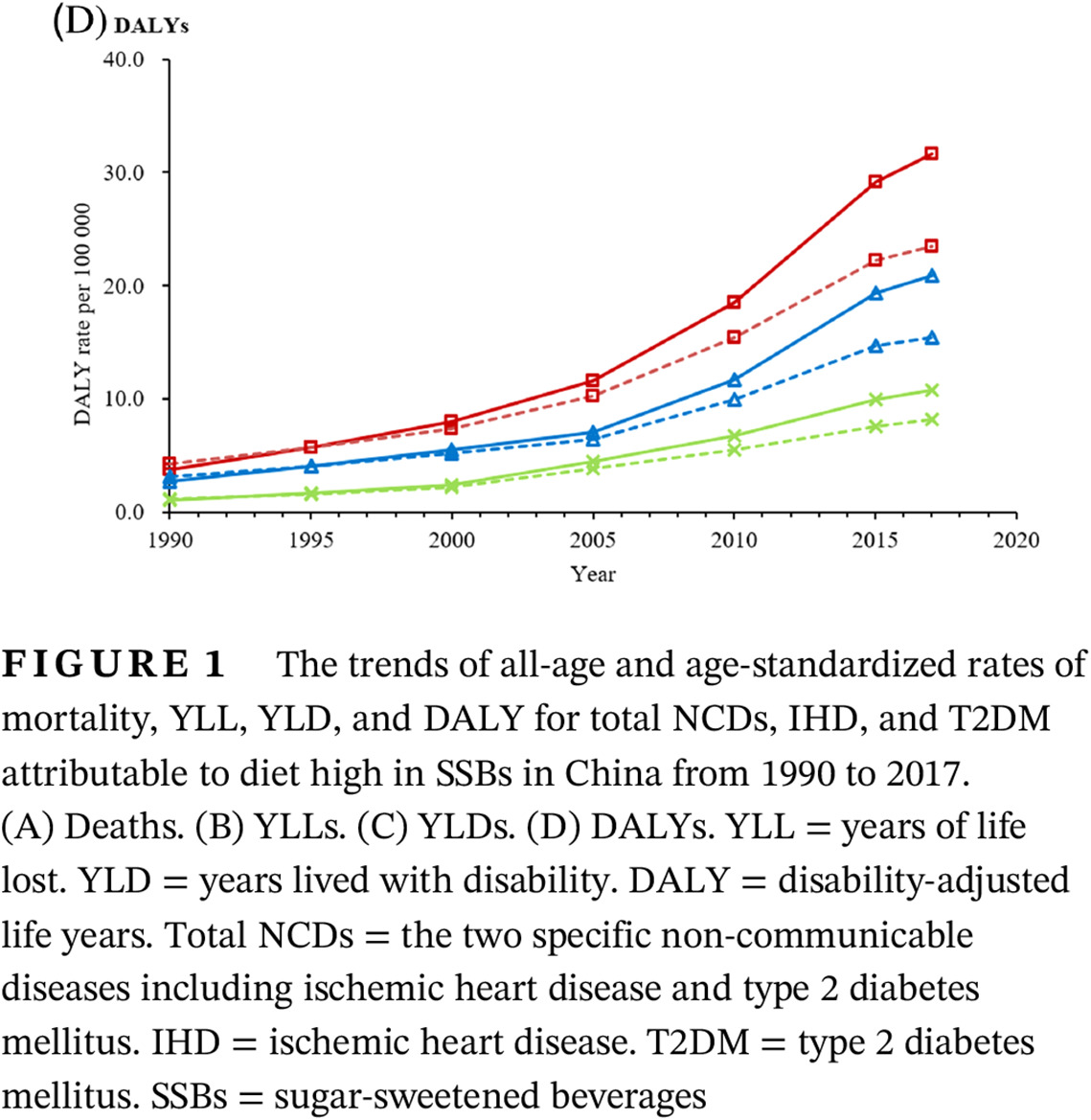
Highlights
- We found that China has an enormous and increasing burden of ischemic heart disease (IHD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) attributable to diet high in SSBs among specific groups, that is, young and middle-aged male adults in provinces with higher economic growth.
- These findings can be used as reference for making public health policies and intervention programs for IHD and T2DM at the national and provincial levels.
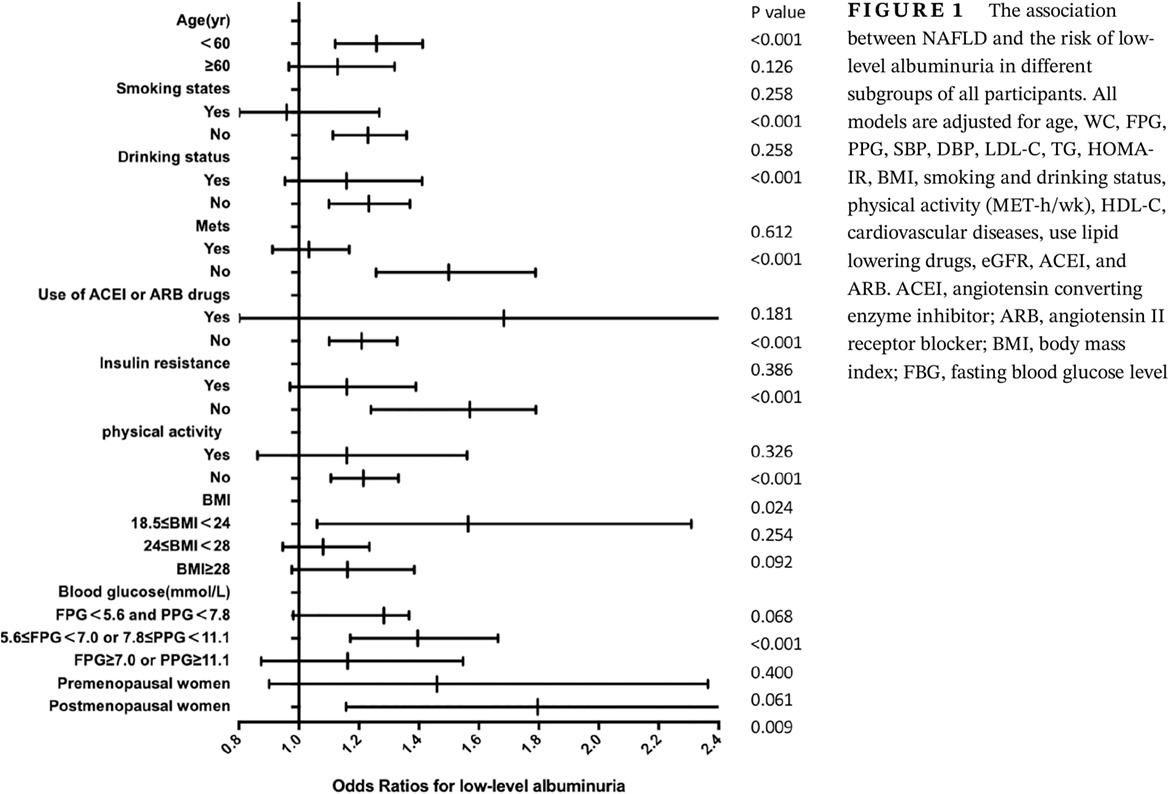
Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver and increased low-level albuminuria in postmenopausal women in China: A cross-sectional study
中国绝经后的女性非酒精性脂肪肝与低水平白蛋白尿增加的相关性:一项横断面研究
- Pages: 494-505
- First Published: 16 November 2020
Incretins in fibrocalculous pancreatic diabetes: A unique subtype of pancreatogenic diabetes
肠促胰岛素在纤维结石性胰腺糖尿病中的作用:胰源性糖尿病的一种独特亚型
- Pages: 506-511
- First Published: 28 November 2020
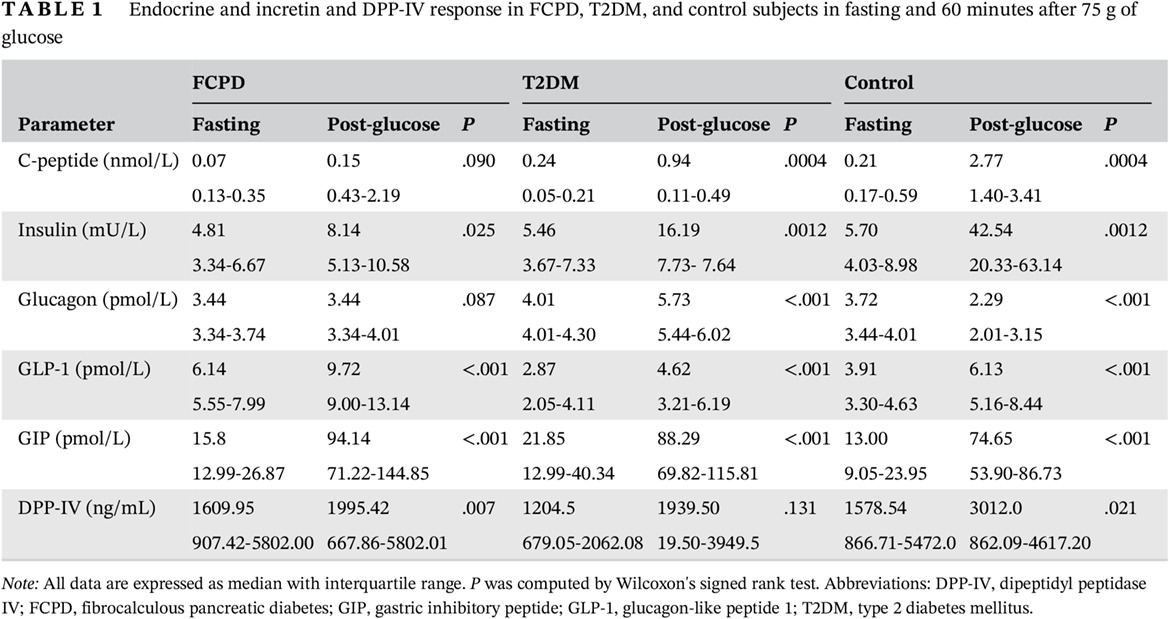
Highlights
- Incretins in pancreatogenic diabetes have been studied in chronic pancreatitis; however, incretins in fibrocalculous pancreatic diabetes (FCPD), a unique form of pancreatogenic diabetes, have not been explored previously.
- This study would significantly help in incretin biology in FCPD and may help bridge the knowledge gap in current understanding.
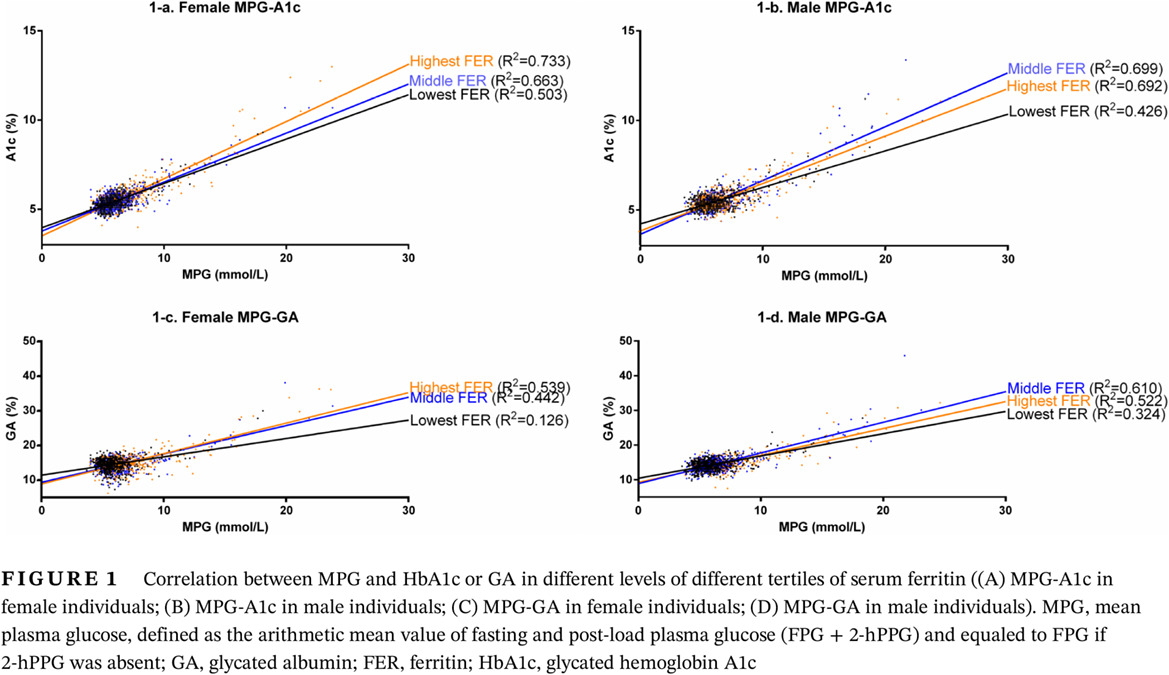
The impact of ferritin on the disassociation of HbA1c and mean plasma glucose
铁蛋白水平对糖化血红蛋白与平均血糖关系的影响
- Pages: 512-520
- First Published: 29 November 2020
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Is prediabetes a risk factor for severe COVID-19?
- Pages: 521-522
- First Published: 09 February 2021
Screening for celiac disease in youth with type 1 diabetes: Are current recommendations adequate?
- Pages: 525-526
- First Published: 12 March 2021