Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Glycemic treatment: Further concepts
降血糖治疗:进一步的概念
- Pages: 362-363
- First Published: 11 February 2021
EDITOR'S RECOMMENDATION
Association between maternal prepregnancy body mass index and risk of preterm birth in more than 1 million Asian American mothers
在一百万亚裔美国母婴中探讨母亲孕前体重指数与早产的关系
- Pages: 364-374
- First Published: 19 October 2020
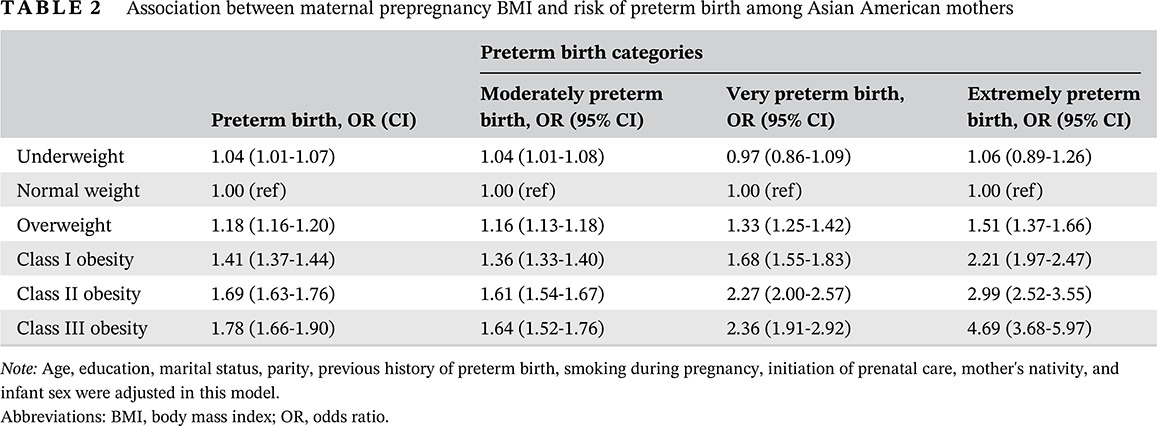
Highlights
- By clarifying the association between prepregnancy obesity and preterm birth among Asian Americans, one of the most fast-growing subpopulations in the United States, our study provides important evidence for tailored clinical recommendations for pregnant women of this race.
- These findings also highlight the importance of using Asian-specific body mass index cutoffs in assessing risk of preterm birth among Asian American mothers.
- This may have broad implications for Asian countries, which have the largest population in the world.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Efficacy and safety of DPP-IV inhibitors combined with basal insulin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes
DPP-IV抑制剂联合基础胰岛素治疗2型糖尿病的疗效和安全性
- Pages: 375-389
- First Published: 05 October 2020
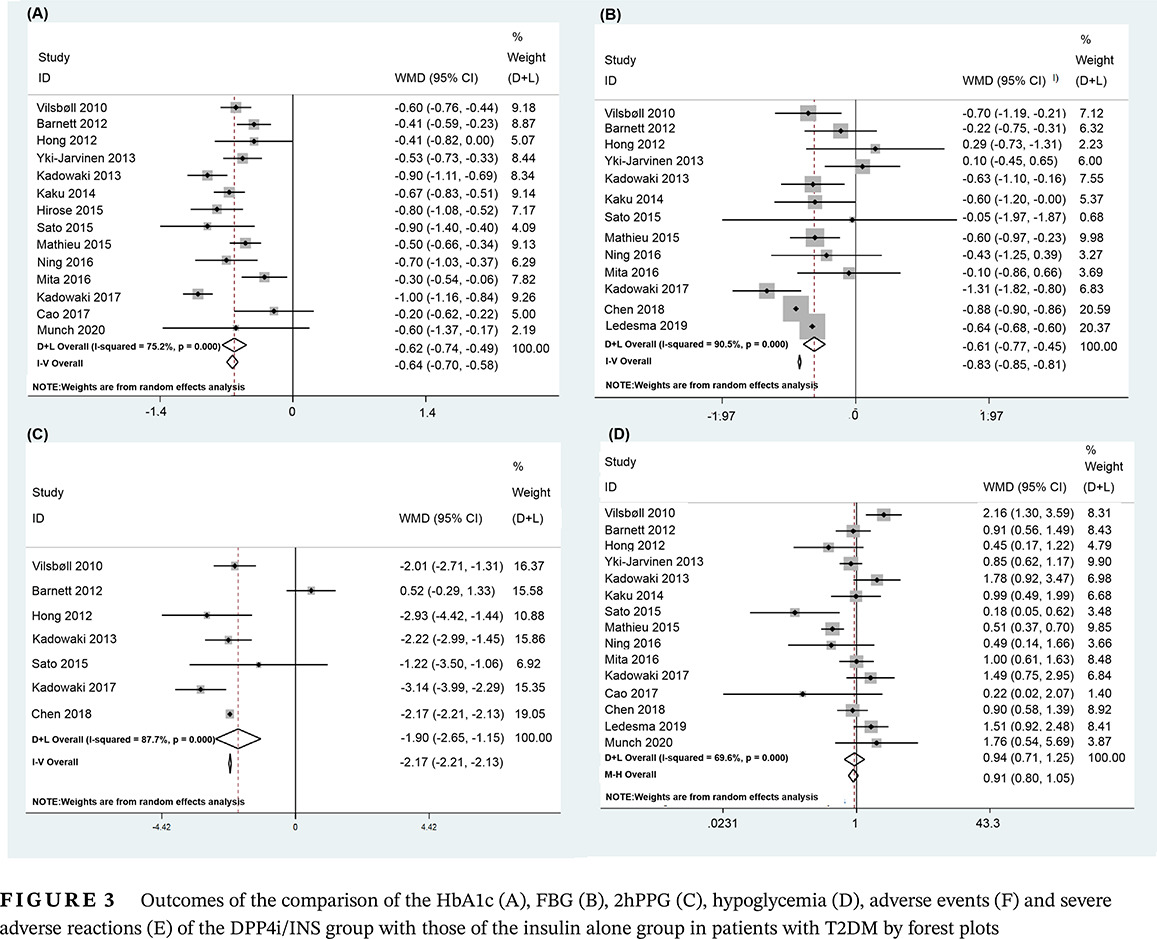
Highlights
- The efficacy and safety of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors combined with insulin (DPP-IVi/INS) were updated in this study.
- The meta-analysis found that compared with the effects in the insulin-alone group, treatment with DPP-IVi/INS improved glycemic control without leading to an increased risk of hypoglycemia and adverse events, which suggests that DPP-IV inhibitors are suitable as an adjunct to insulin to maintain the balance of glucose.
Integrative analysis of hepatic metabolomic and transcriptomic data reveals potential mechanism of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in high-fat diet–fed mice
高脂饮食小鼠的肝脏代谢组学及转录组学联合分析揭示非酒精性脂肪肝炎的潜在机制
- Pages: 390-401
- First Published: 06 October 2020
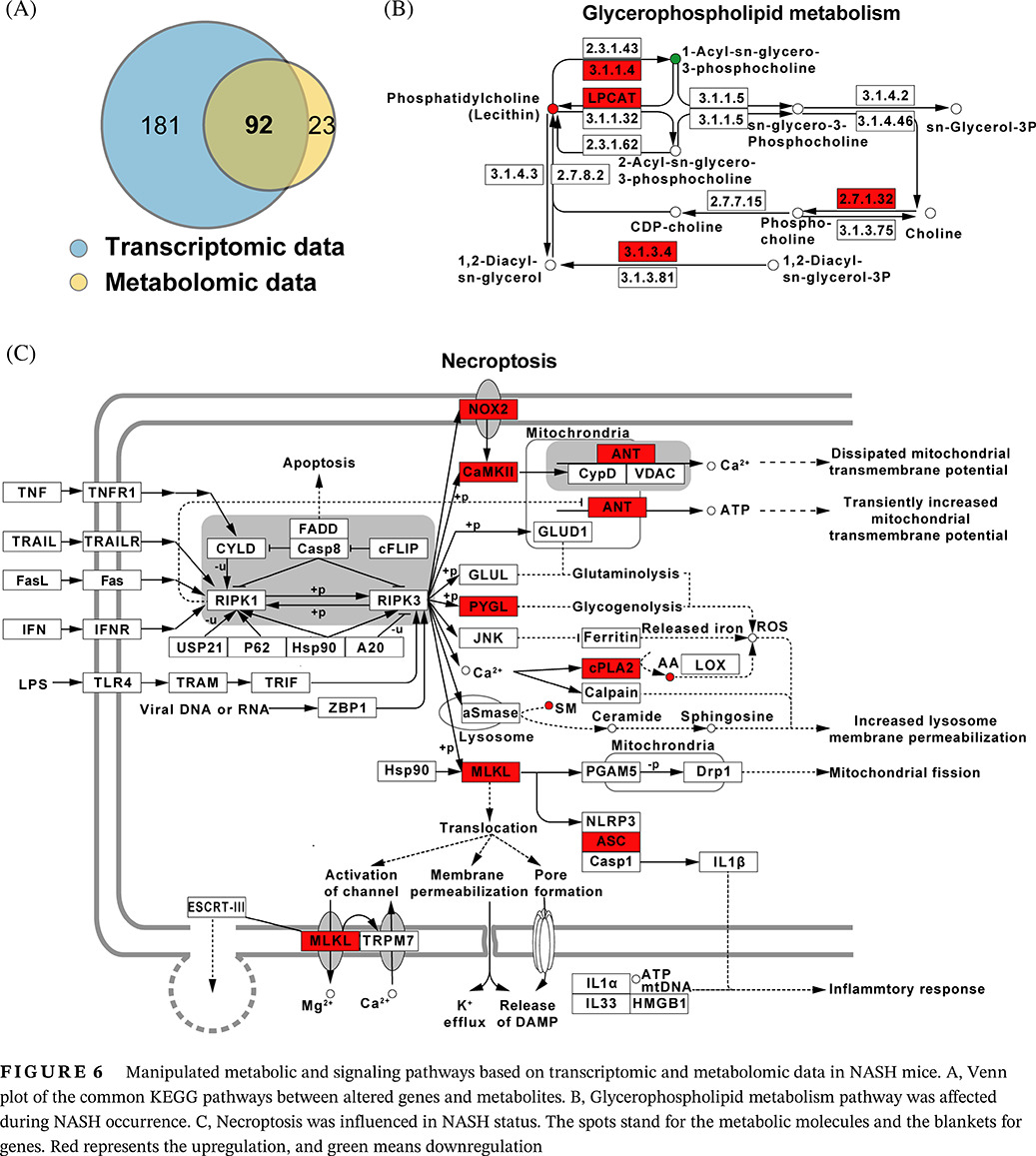
Highlights
- This study integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic data to explore potential molecular changes during nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
- Major inflammatory biomarkers and fatty acid metabolism in NASH mice were investigated.
- Necroptosis played a crucial role in the occurrence of NASH
In this paper, hepatic metabolomic and transcriptomic data were integrated for molecular mechanism on the occurrence of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. And the results highlighted the crucial alteration of glycerophospholipid metabolism and necroptosis signaling.
Association of TG/HDLC ratio trajectory and risk of type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study in China
TG/HDL-C比值变化轨迹与2型糖尿病发病风险的关系:一项中国回顾性队列研究
- Pages: 402-412
- First Published: 19 October 2020
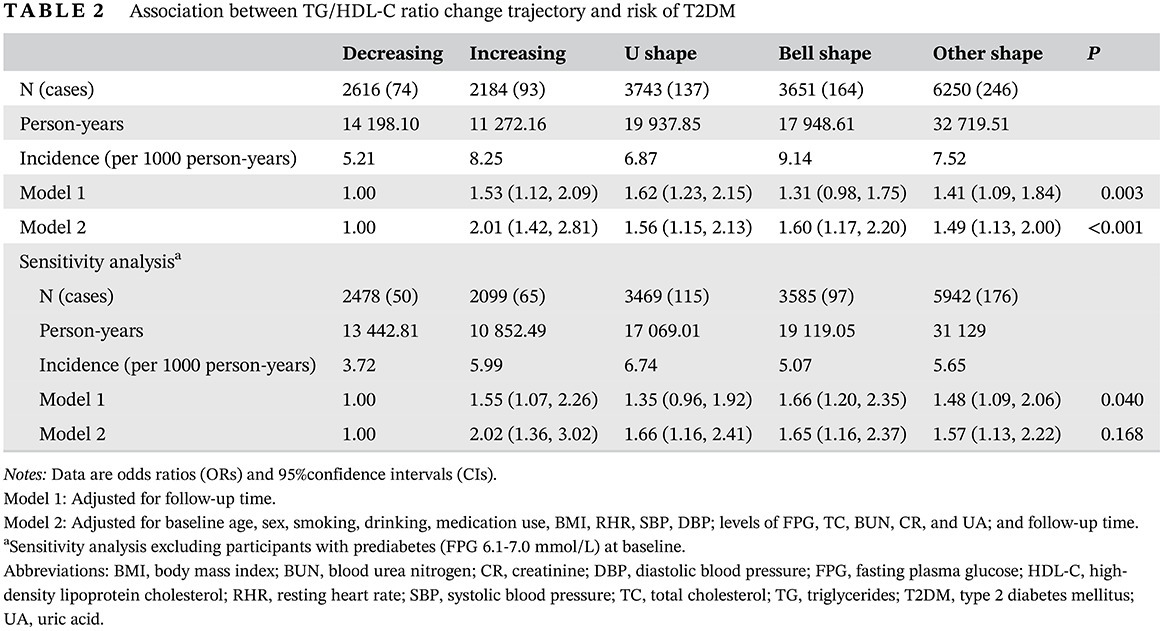
Highlights
- TG/HDL-C ratio change trajectory, long-term high TG/HDL-C ratio level, variability of TG/HDL-C ratio level and annual increasing rate of TG/HDL-C ratio level were significantly associated with risk of T2DM.
- Understanding interactions between TG/HDL-C ratio change trajectory and T2DM could open up useful avenues for future intervention.
- Maintaining low and stable level of TG/HDL-C ratio is important for preventing T2DM.
Association between thiamine deficiency and hyperlactatemia among critically ill patients with diabetes infected by SARS-CoV-2
重症糖尿病患者感染SARS-CoV-2后硫胺素缺乏与高乳酸血症的关系
- Pages: 413-419
- First Published: 15 January 2021
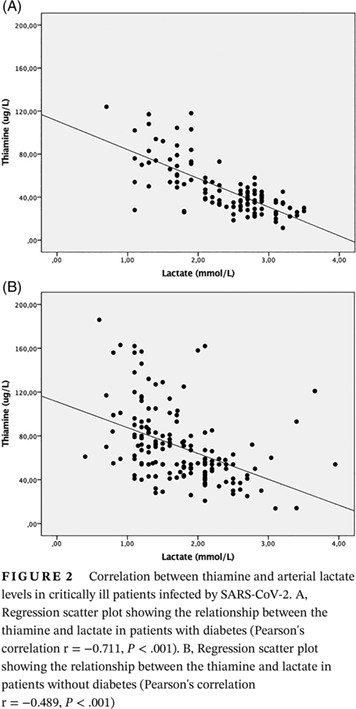
Highlights
- Thiamine is important for cellular metabolism and energy homeostasis. There are no data yet in the literature that have reported thiamine deficiency in coronavirus disease 2019.
- Thiamine insufficiency may exist in critically ill patients not only due to reduced intake and very impaired absorptive processes during the critical stage but also due to the high consumption by hypermetabolism. Severe thiamine deficiency may cause lactic acidosis, hyperlactatemia, and even worsen diabetic ketoacidosis.
- There is a negative correlation between thiamine levels and arterial lactate, especially among critically ill patients with diabetes.
Metabolic syndrome and clinical outcomes in patients infected with COVID-19: Does age, sex, and race of the patient with metabolic syndrome matter?
COVID-19患者的代谢综合征和临床结局:代谢综合征患者的年龄、性别和种族重要吗?
- Pages: 420-429
- First Published: 16 January 2021
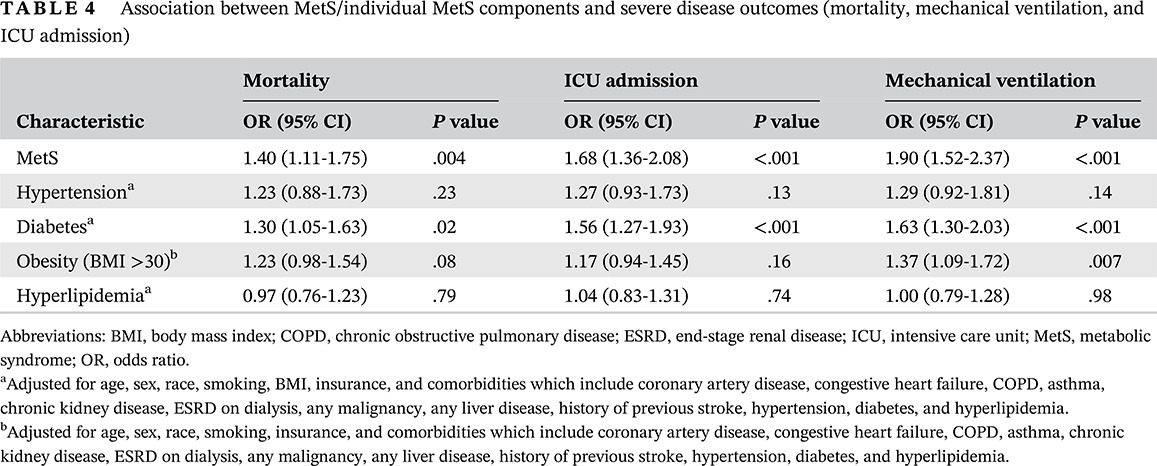
Highlights
- Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a vital prognostic indicator of outcomes in coronavirus disease 2019.
- Patients with MetS had worse clinical outcomes compared with the ones without MetS.
- Patients with MetS had a higher need for intensive care unit irrespective of their age, sex, or race.
- Need for mechanical ventilation was higher for all patients with MetS except Caucasians.
- Females, younger patients (<65), and African Americans with MetS had higher mortality.
Predictors of mortality in a multiracial urban cohort of persons with type 2 diabetes and novel coronavirus 19
城市多种族患有2型糖尿病的新型冠状病毒肺炎患者死亡率的预测因素
- Pages: 430-438
- First Published: 23 January 2021
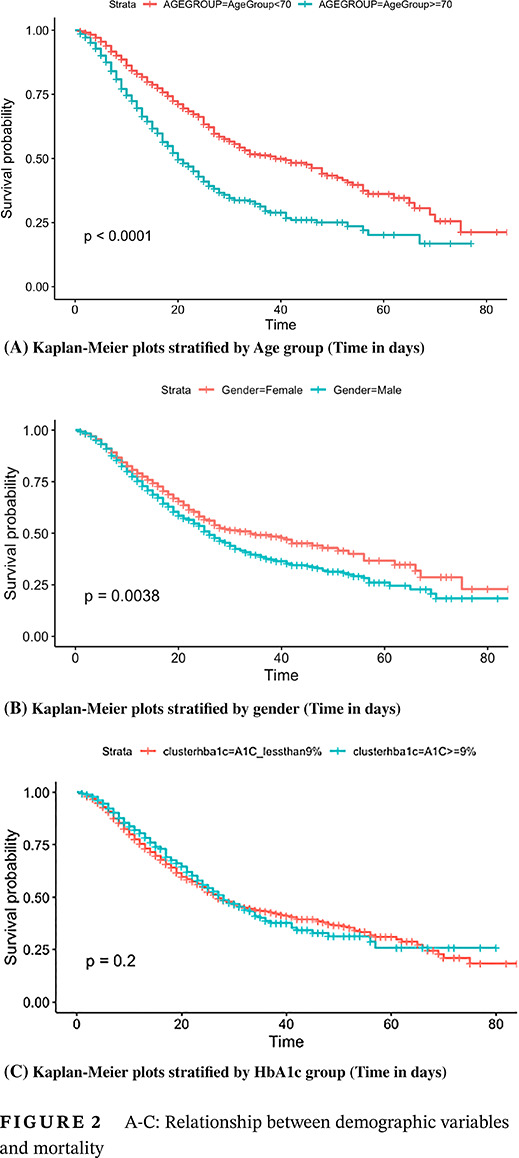
Highlights
- Admission serum or point-of-care glucose is a greater predictor of mortality than glycosylated hemoglobin in persons with type 2 diabetes and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
- Those with diabetes and COVID-19 who were intubated had a higher morality than those who were not intubated.
- Older age, male gender, and history of chronic kidney disease, hypertension, or coronary artery disease increased the risk of mortality. Race and insurance type had no impact on mortality.
RESEARCH LETTER
Effective use of computerized insulin dose adjustment algorithms on continuous glucose monitoring results by a clinical pharmacist - Proof-of-concept
计算机化胰岛素剂量调整算法在连续血糖监测结果中的有效应用——一位临床药剂师的概念验证
- Pages: 439-441
- First Published: 05 January 2021
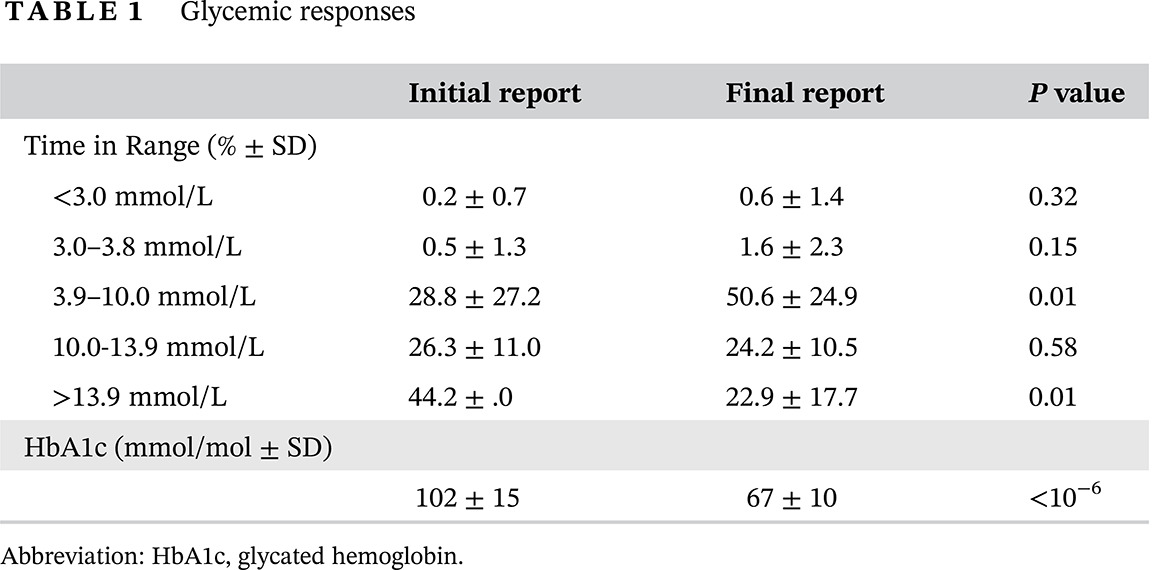
Highlights A clinical pharmacist using recommendations of Food and Drug Administration-cleared computerized insulin dose adjustment algorithms based on analyses of glucose readings from continuous glucose monitoring (Abbot Free Style Pro) in 13 poorly controlled insulin-requiring diabetic patients increased time in target range of 3.9 to 10.0 mmol/L from 29% to 51% and decreased time in range of >13.9 mmol/L from 43% to 23% (both P = 0.01) after 3 months. Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels (±SD) fell from 102 (±15) to 67 (±10) mmol/mol (P < 10−6).









