Effective use of computerized insulin dose adjustment algorithms on continuous glucose monitoring results by a clinical pharmacist - Proof-of-concept
计算机化胰岛素剂量调整算法在连续血糖监测结果中的有效应用——一位临床药剂师的概念验证
Graphical Abstract
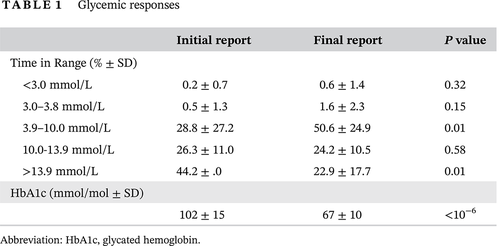
Highlights A clinical pharmacist using recommendations of Food and Drug Administration-cleared computerized insulin dose adjustment algorithms based on analyses of glucose readings from continuous glucose monitoring (Abbot Free Style Pro) in 13 poorly controlled insulin-requiring diabetic patients increased time in target range of 3.9 to 10.0 mmol/L from 29% to 51% and decreased time in range of >13.9 mmol/L from 43% to 23% (both P = 0.01) after 3 months. Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels (±SD) fell from 102 (±15) to 67 (±10) mmol/mol (P < 10−6).