Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Free Access
free
The Fifth Annual Heart in Diabetes Conference (Part 1)
第五届心脏病与糖尿病年会(第一部分)
- Pages: 946-948
- First Published: 07 October 2021
EDITOR'S RECOMMENDATION
no
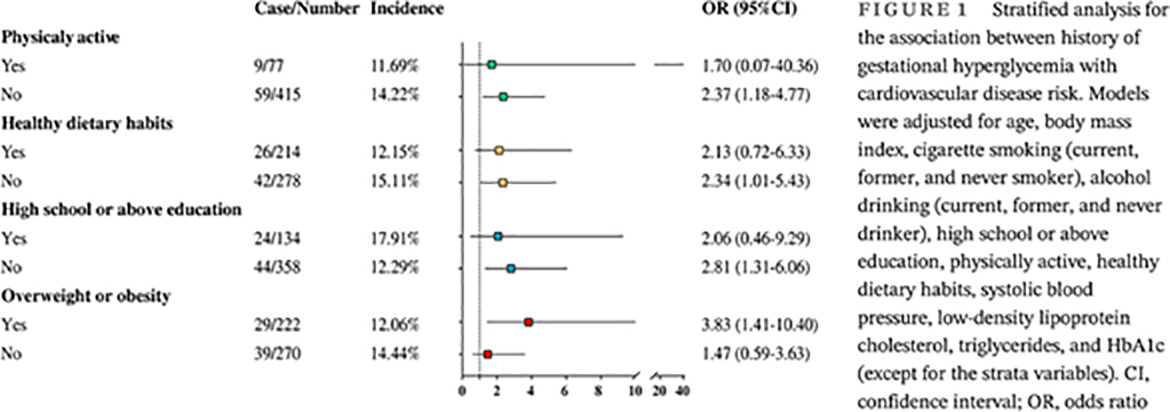
Gestational hyperglycemia and the risk of cardiovascular diseases among elderly Chinese women: Findings from the REACTION study
妊娠高血糖与中国老年女性心血管疾病风险:来自REACTION研究发现
- Pages: 949-959
- First Published: 24 August 2021
Highlights
- Even without progressing to type 2 diabetes, gestational hyperglycemia is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD).
- The association between gestational hyperglycemia and CVD risk could be modified by lifestyle factors and hypertension.
- Subsequent blood pressure management and lifestyle intervention for women with gestational hyperglycemia are important approaches to prevent CVD.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
no
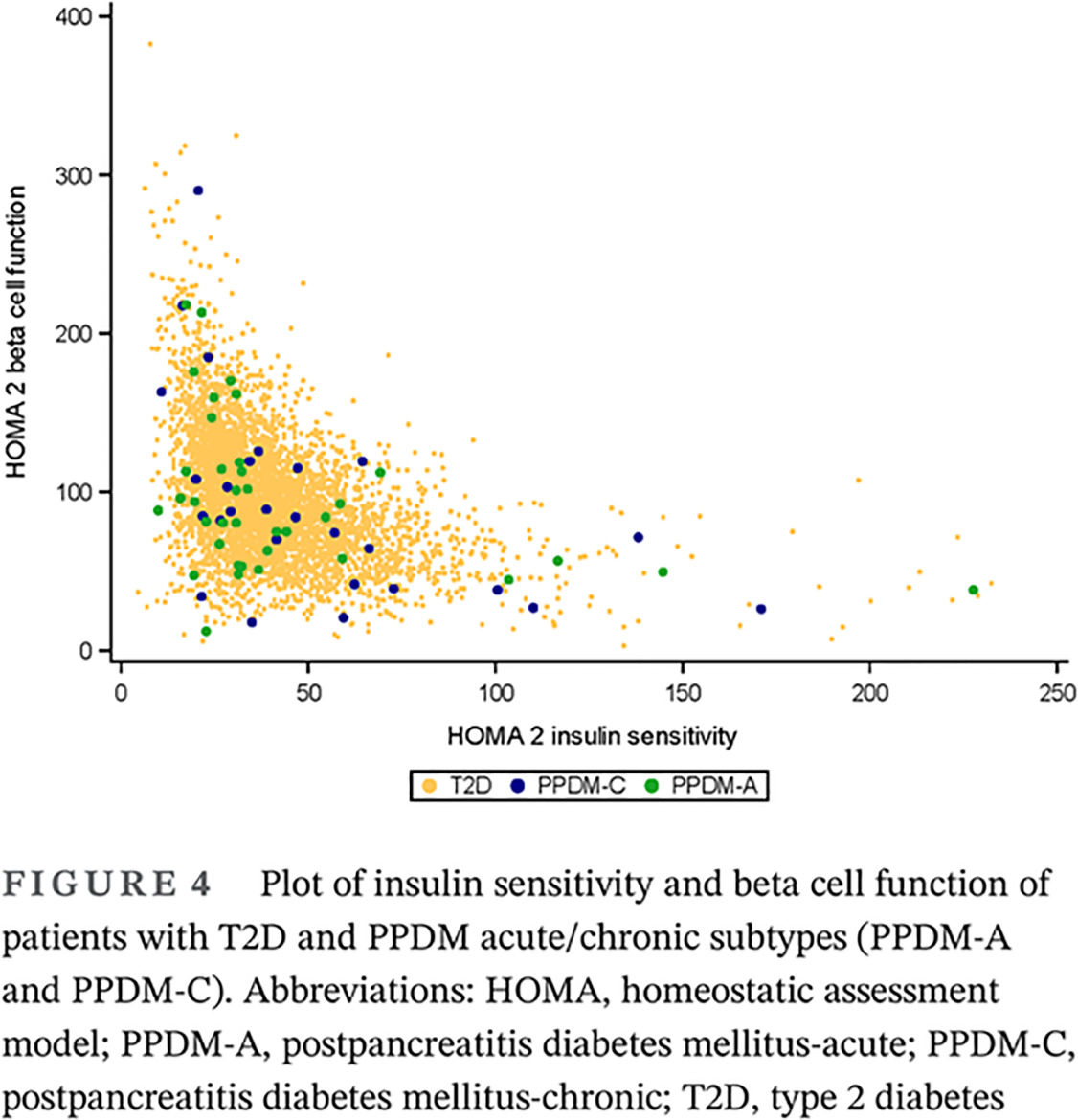
Clinical and biochemical characteristics of postpancreatitis diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study from the Danish nationwide DD2 cohort
胰腺炎后糖尿病的临床和生化特征:一项来自丹麦全国DD2队列的横断面研究
- Pages: 960-974
- First Published: 09 July 2021
Highlights
- Among patients with clinically diagnosed type 2 diabetes, the proportion of postpancreatitis diabetes mellitus (PPDM) is ~1.5% in an everyday clinical care setting.
- Glucose metabolism of PPDM folowing acute pancreatitis is largely indistinguishable from T2D, whereas PPDM associated with chronic pancreatitis differs in relation to insulin secretion, insulin sensitivity, and glycemic control.
no
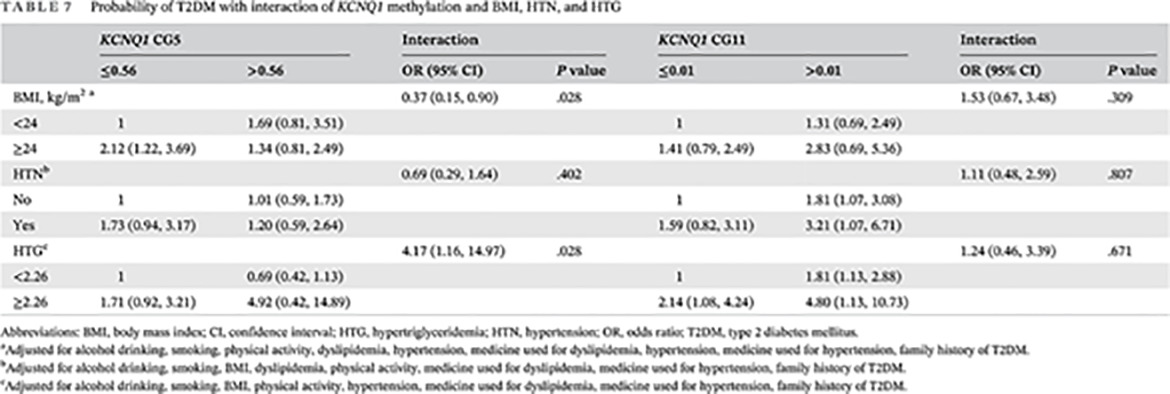
Integrated analysis of probability of type 2 diabetes mellitus with polymorphisms and methylation of KCNQ1 gene: A nested case-control study
KCNQ1基因多态性和甲基化与2型糖尿病发病风险关系的巢氏病例对照研究
- Pages: 975-986
- First Published: 14 July 2021
no
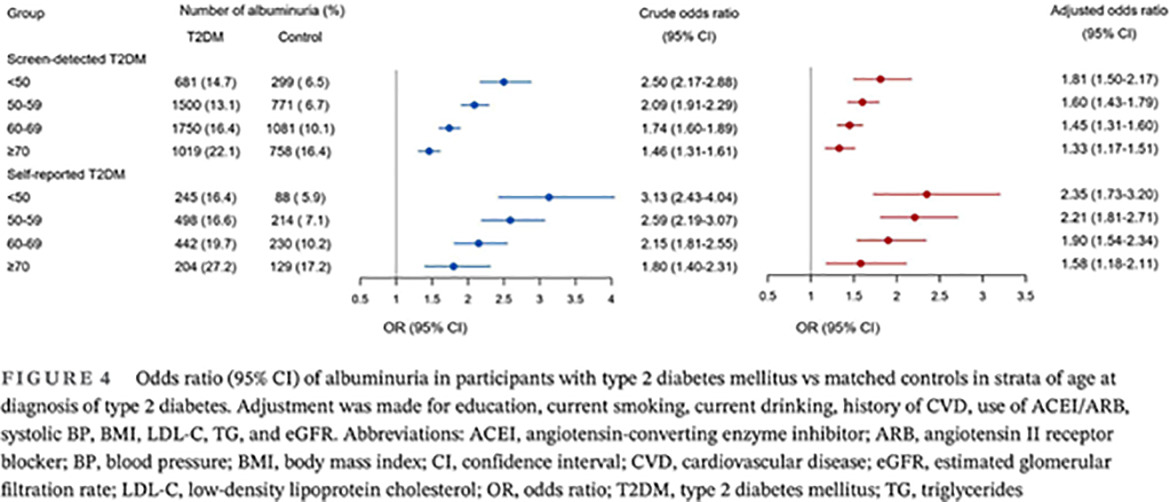
The association between age at diagnosis of type 2 diabetes and albuminuria in Chinese adults: A nationwide population study
中国成人2型糖尿病诊断年龄与白蛋白尿的相关性:一项全国人群研究
- Pages: 987-997
- First Published: 14 July 2021
Highlights
- A younger age at diagnosis of type 2 diabetes is associated with a more significantly elevated risk of albuminuria than an older age at diagnosis in Chinese adults, after fully excluding the confounding effect of actual age or diabetes duration.
- Young adults diagnosed with diabetes were more likely to have an unfavorable metabolic profile compared with normal controls.
- The age at diabetes diagnosis should be considered when evaluating the risk of developing albuminuria in diabetes patients.
no
Good glycemic control at puberty in boys with type 1 diabetes is important for final height
1型糖尿病男孩青春期良好的血糖控制对最终身高很重要
- Pages: 998-1006
- First Published: 15 July 2021
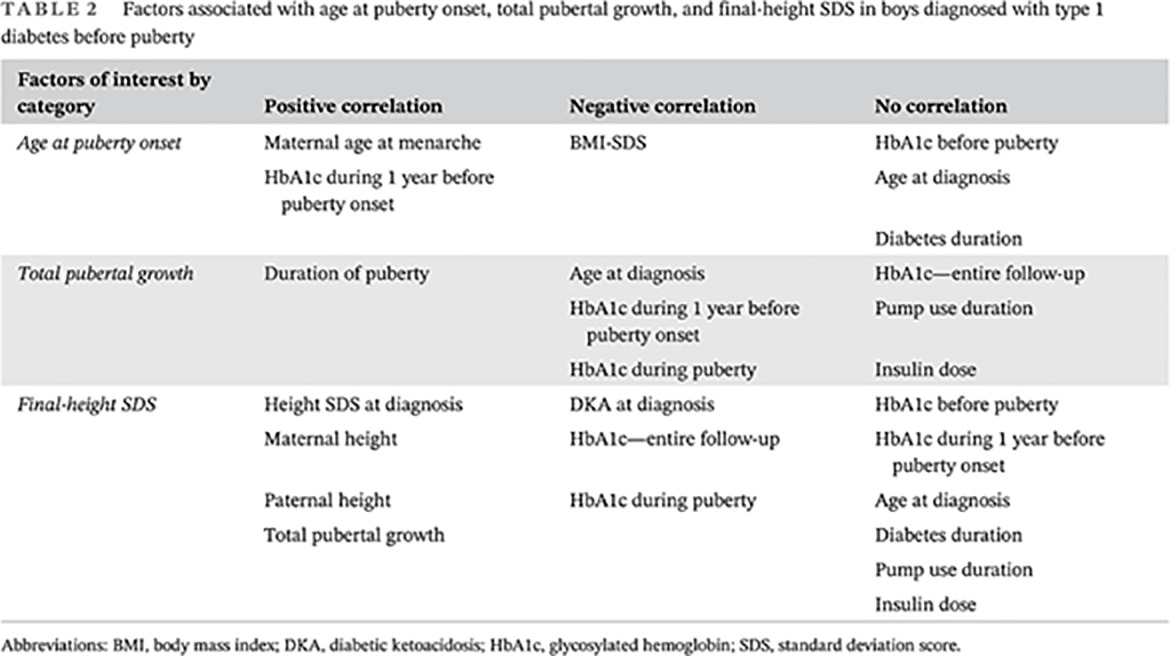
Highlights
- Boys with type 1 diabetes diagnosed before puberty achieved a final height that was similar to that of their target height and the general population.
- The association of good glycemic control with higher total pubertal growth and final height highlights the importance of maintaining tight glycemic control, especially during the stages of maximal growth when boys may be particularly vulnerable.
Open Access
oa
Immune-checkpoint inhibitor-associated diabetes compared to other diabetes types - A prospective, matched control study
免疫检查点抑制剂相关糖尿病与其他糖尿病类型的比较--一项前瞻性配对对照研究
- Pages: 1007-1014
- First Published: 18 July 2021
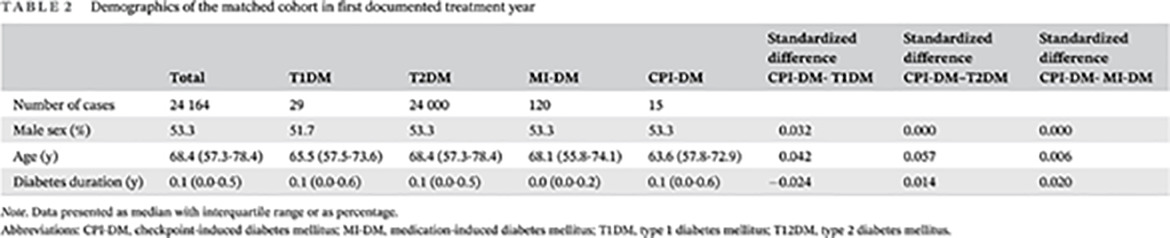
Highlights
- This prospective study compares 15 patients with immune-checkpoint induced diabetes mellitus (CPI-DM) with a propensity score matched cohort of patients with other diabetes types. Diabetic ketoacidosis at onset and autoimmune comorbidity is more frequent in CPI-DM patients. This can be avoided by regular glucose measurements and education on hyperglycemia.
no
Combined association of skeletal muscle mass and grip strength with cardiovascular diseases in patients with type 2 diabetes
2型糖尿病患者骨骼肌质量和握力与心血管疾病的联合关系
- Pages: 1015-1024
- First Published: 20 July 2021
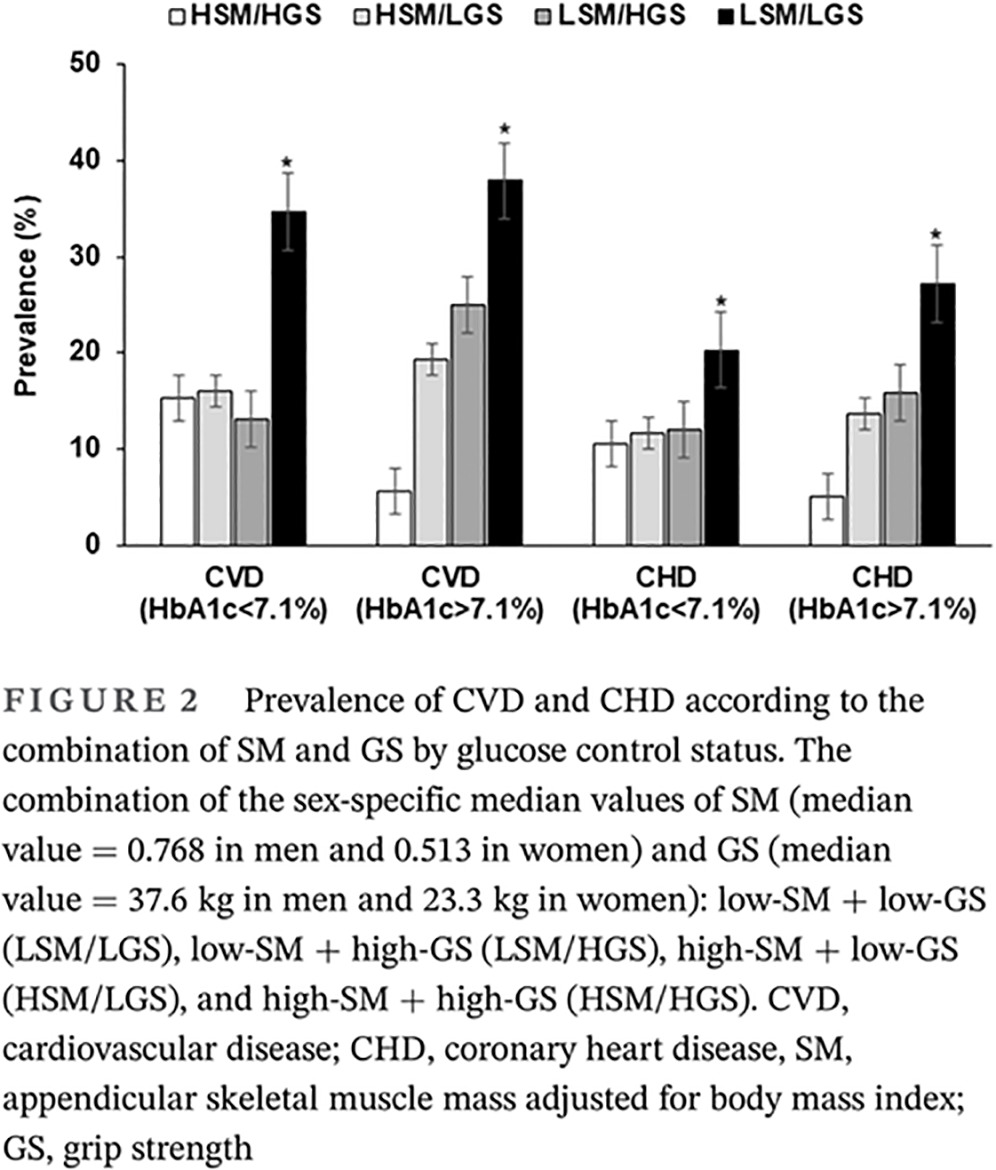
Highlights
- The combination of low appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASM) adjusted with body mass index (ASM/BMI; short: SM) and low grip strength (GS) was more strongly related to cardiovascular disease (CVD), coronary heart disease (CHD), and peripheral arterial disease compared with either low SM or low GS in type 2 diabetic patients.
- The combined associations of SM and GS with CVD and CHD were more prominent in individuals with glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥ 7.1% than those with HbA1c < 7.1%, indicating that glucose control is critical for ASM and GS.
no
Changes in creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio over 4 years, risk of diabetes, and cardiometabolic control: The China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
肌酐与胱抑素C比值的4年变化值、糖尿病风险和心脏代谢控制:中国健康与养老追踪调查
- Pages: 1025-1033
- First Published: 24 July 2021
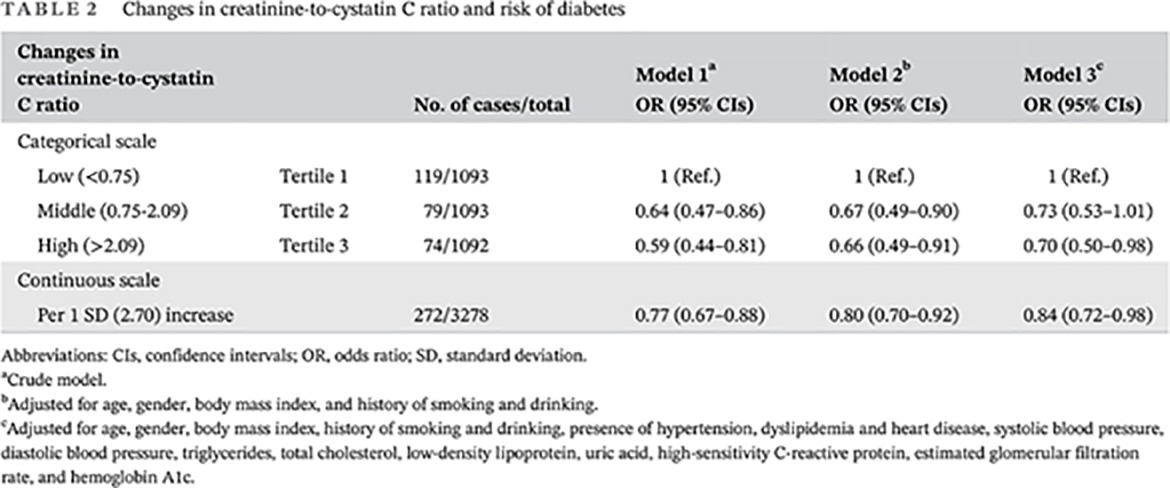
Highlights
- Increases in creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio over 4-year were associated with lower risk of diabetes in middle-aged and older adults.
- Increases in creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio were associated with a favorable cardiometabolic profile at the 4-year follow-up.
- Increases in creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio may benefit cardiometabolic control by improving glycemic control and lowering the degree of inflammation.
Open Access
oa
A comparison of the stress hyperglycemia ratio, glycemic gap, and glucose to assess the impact of stress-induced hyperglycemia on ischemic stroke outcome
比较应激性高血糖比率, 血糖间隙和葡萄糖评估应激性高血糖对缺血性卒中预后的影响
- Pages: 1034-1042
- First Published: 18 September 2021
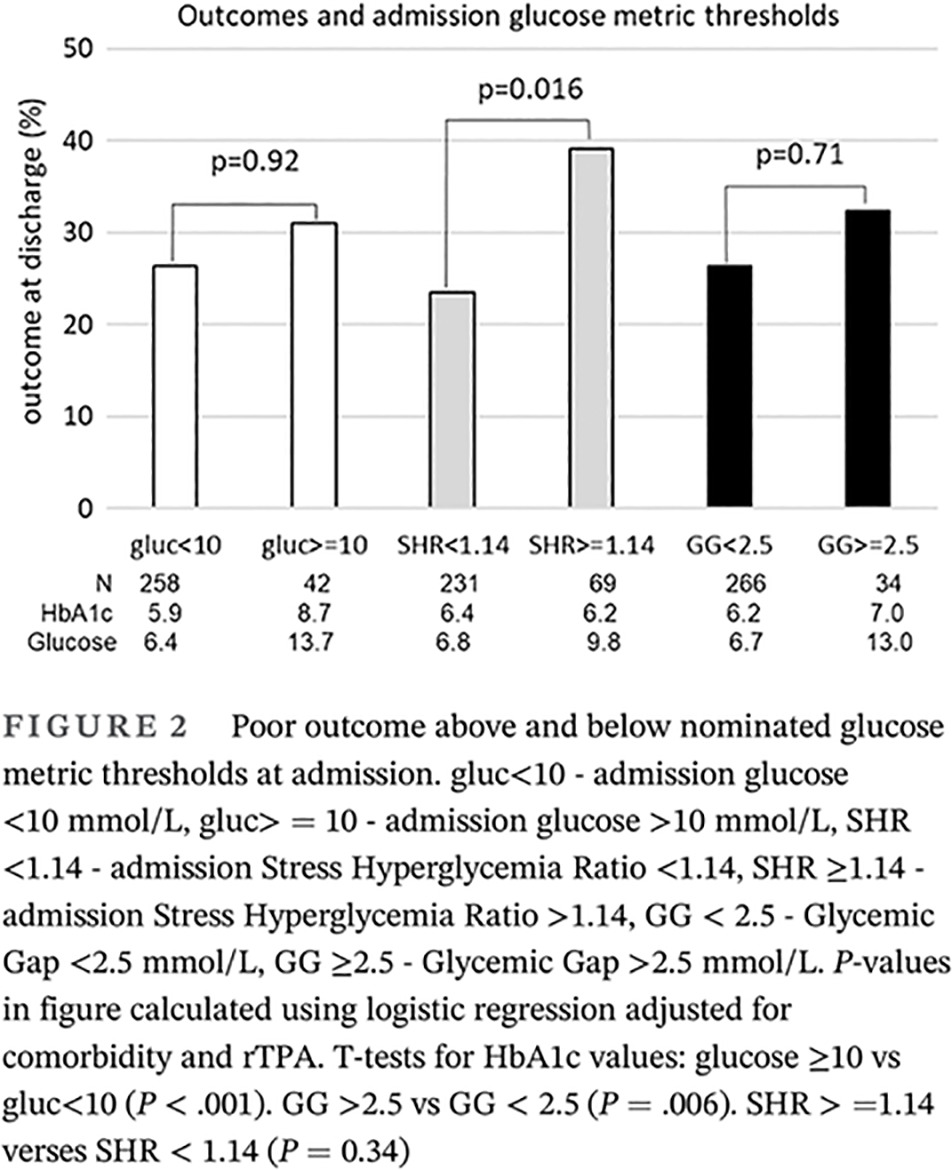
Highlights
- The impact of stress-induced hyperglycemia on outcome is poorly reflected by absolute glucose levels.
- The stress hyperglycemia ratio (SHR) biomarker discriminates between interpatient variation in normal premorbid background glycemia related to glycosylated hemoglobin and the acute relative increase in glucose related to physiological stress that truly represents stress-induced hyperglycemia.
- SHR at admission was superior to glucose in predicting ischemic stroke outcome.
- There is a need for interventional studies based on SHR rather than glucose to best assess management of stress-induced hyperglycemia.
Open Access
oa
Cardiovascular disease and risk of incident diabetes mellitus: Findings from the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos (HCHS/SOL)
心血管疾病与糖尿病发病风险:拉美裔社区健康研究/拉丁裔研究(HCHS/SOL)的研究结果
- Pages: 1043-1053
- First Published: 18 September 2021
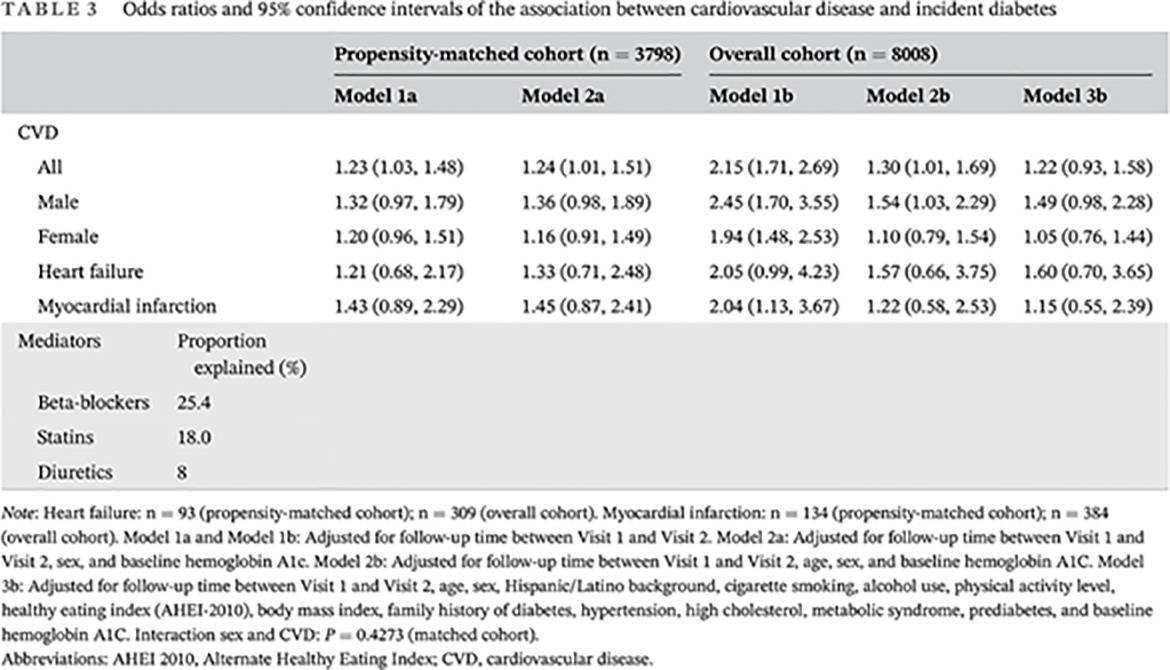
Highlights
- Prior studies have reported an association between cardiovascular disease and risk of incident diabetes mellitus. However, factors that may explain the association remain unclear.
- Using propensity score matching, we reinforced the concern that cardiovascular disease may increase the risk of developing diabetes mellitus.
- We further showed that the association between cardiovascular disease and incident diabetes mellitus was partially explained by cardiovascular medications such as beta-blockers, statins, and diuretics.
RESEARCH LETTER
Open Access
oa
Early gut dysbiosis could be an indicator of unsuccessful diet control in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Pages: 1054-1058
- First Published: 21 September 2021
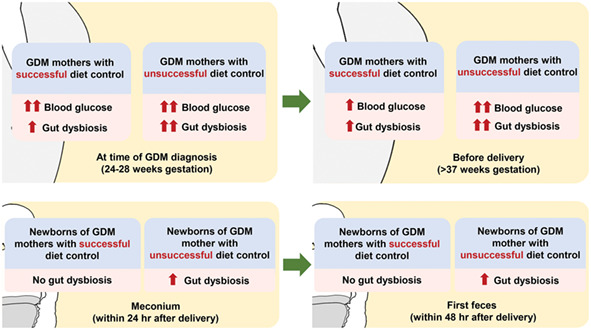
Highlights
- At the time of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) diagnosis, gut dysbiosis was severer in mothers who ended up with diet control failure than those who ended up with successful diet control.
- This finding was noticed even when the glycemic profile at the time of GDM diagnosis was similar between these two groups.
- Interestingly, gut dysbiosis in GDM mothers with diet control failure was shown associated with gut dysbiosis in their newborns.
COMMENTARY
Free Access
free
Precision nutrition for gut microbiome and diabetes research: Application of nutritional n-of-1 clinical trials
- Pages: 1059-1061
- First Published: 28 August 2021