Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Presentations at the 81st scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association, part 2
在美国糖尿病协会第81届科学会议上的报告(第二部分)
- Pages: 844-846
- First Published: 15 August 2021
EDITOR'S RECOMMENDATION
Beneficial effects of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on left ventricular mass in patients with diabetes mellitus
钠葡萄糖共转运体2抑制剂对糖尿病患者左心室重量的影响
- Pages: 847-856
- First Published: 07 July 2021
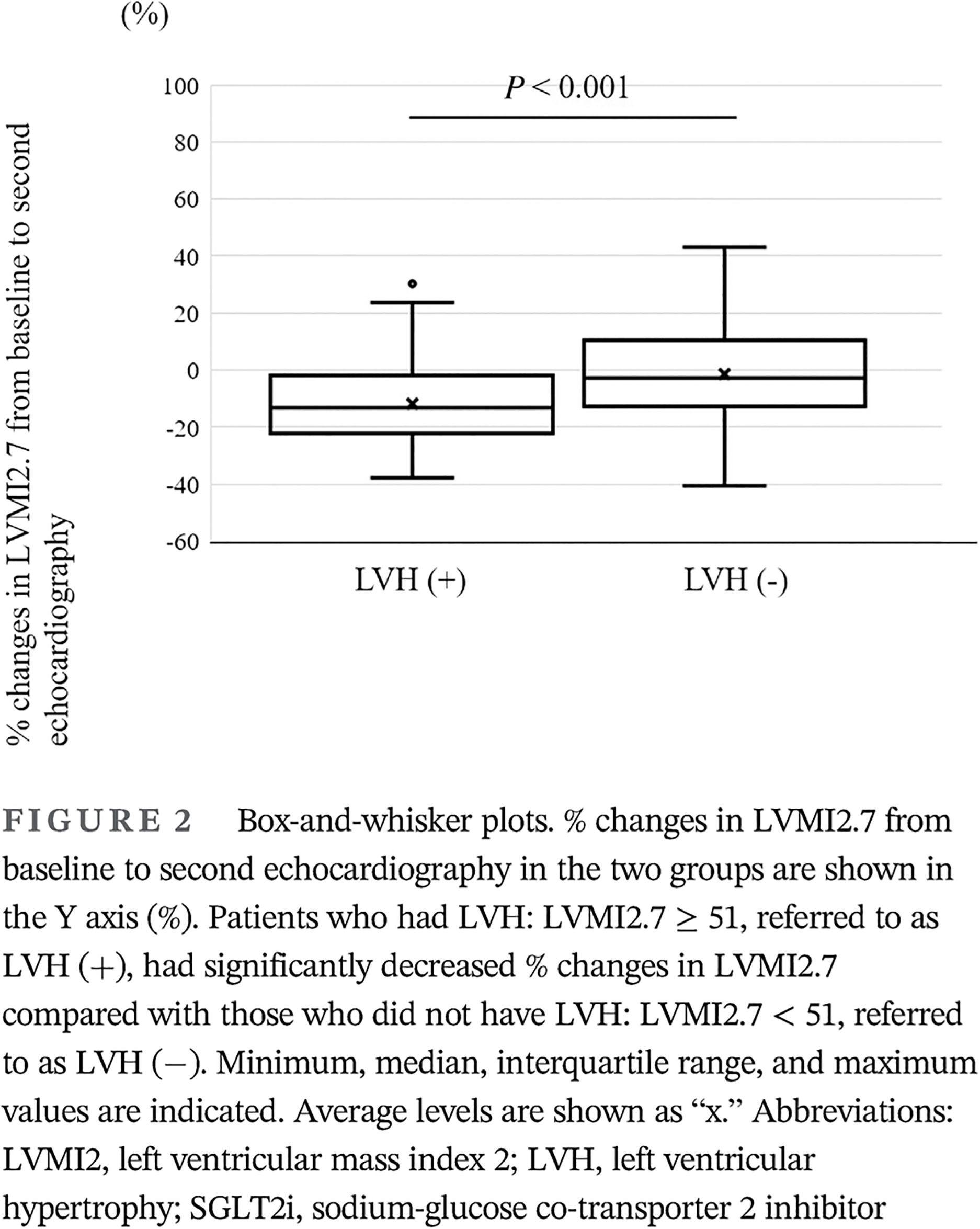
Highlights We evaluated Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) for the effect of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor (SGLT2i) on left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH). Left ventricular mass index (LVMI) was used as an indicator of LVH. LVMI levels significantly decreased after administration of SGLT2i. After SGLT2i treatment, LVMI levels in the patients who had LVH significantly decreased compared with patients without LVH. SGLT2i was therefore shown to improve LVH in patients with T2DM.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
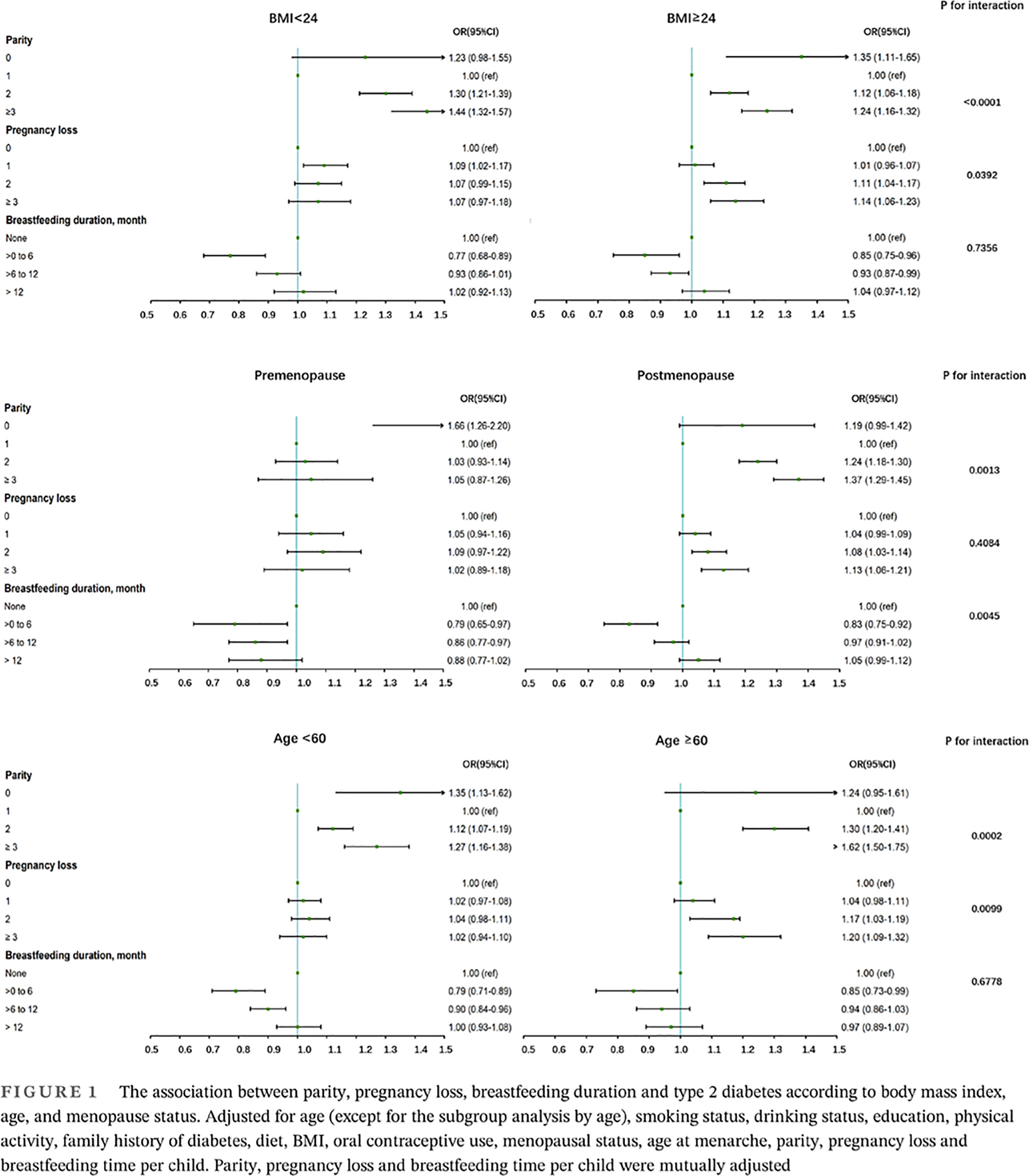
Associations between parity, pregnancy loss, and breastfeeding duration and risk of maternal type 2 diabetes: An observational cohort study
胎次、流产及母乳喂养时间与2型糖尿病风险的关系:一项观察性队列研究
- Pages: 857-867
- First Published: 12 March 2021
Highlights
- The number of parities and breastfeeding duration were positively related to fasting plasma glucose, 2-hour postload glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin, and homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance.
- Women who were nulliparas or had more than one birth or experienced more than one pregnancy loss had an increased risk of diabetes. On the other hand, women who breastfed for less than 12 months had a lower risk of diabetes.
- Interaction effects between parity and pregnancy loss with body mass index or age, and breastfeeding duration with menopause status were detected for the risk of diabetes.
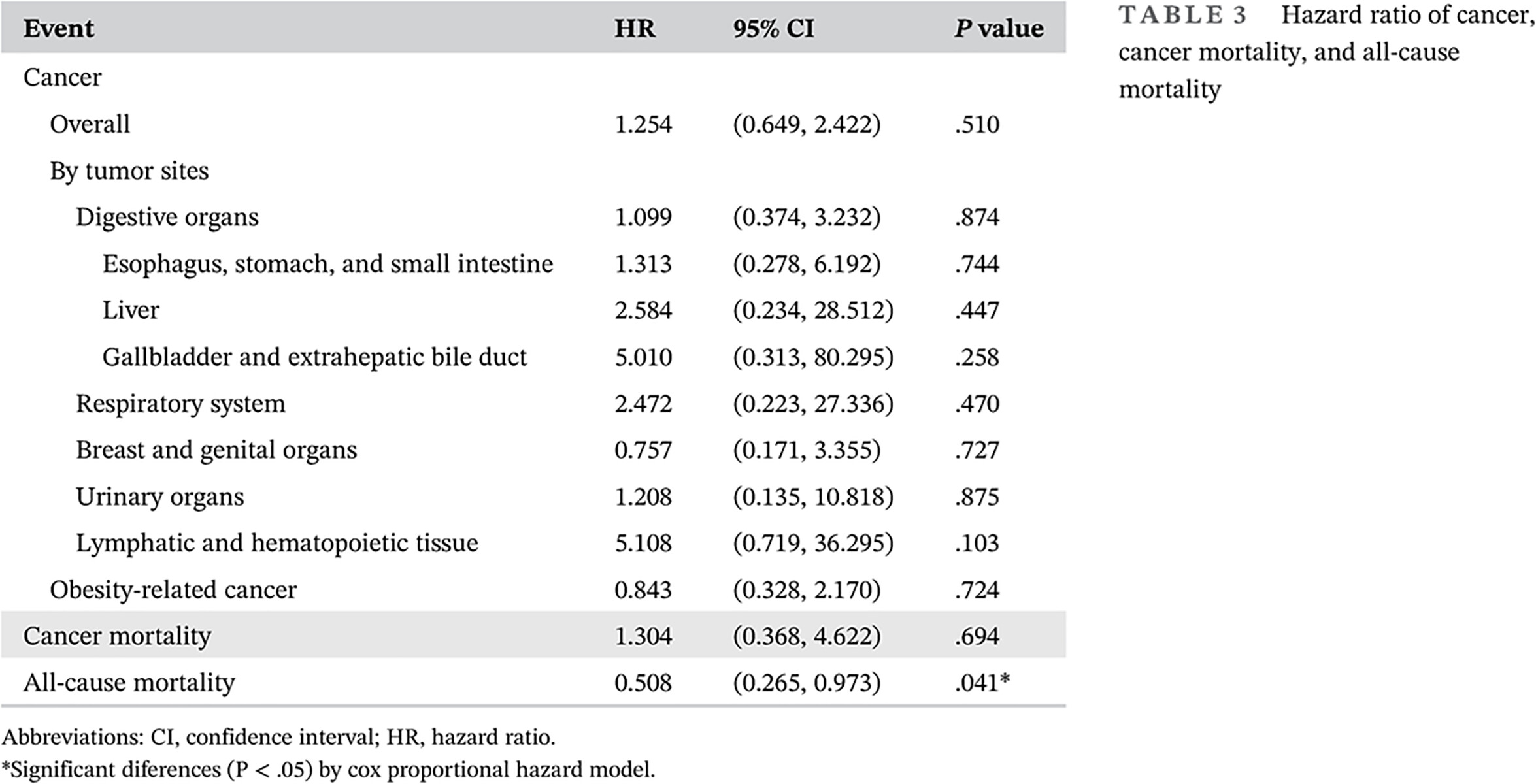
Association between bariatric surgery and risks of cancer among Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A retrospective cohort study
减重手术与患癌风险的关系:一项基于中国2型糖尿病人群的回顾性队列研究
- Pages: 868-881
- First Published: 17 March 2021
The association of energy and macronutrient intake at dinner vs breakfast with the incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in a cohort study: The China Health and Nutrition Survey, 1997-2011
晚餐与早餐能量和宏量营养素摄入与2型糖尿病发病率的关系研究:1997-2011年中国健康与营养调查
- Pages: 882-892
- First Published: 13 April 2021

Highlights
- Higher intake of energy, protein, and fat at dinner than at breakfast increases the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- If 5% of total energy at dinner is substituted by total energy at breakfast, type 2 diabetes mellitus incidence can be decreased.
- If 5% of energy from fat or protein at dinner is isocalorically replaced by energy from carbohydrate, protein, and fat at breakfast, this can also decrease type 2 diabetes mellitus incidence.
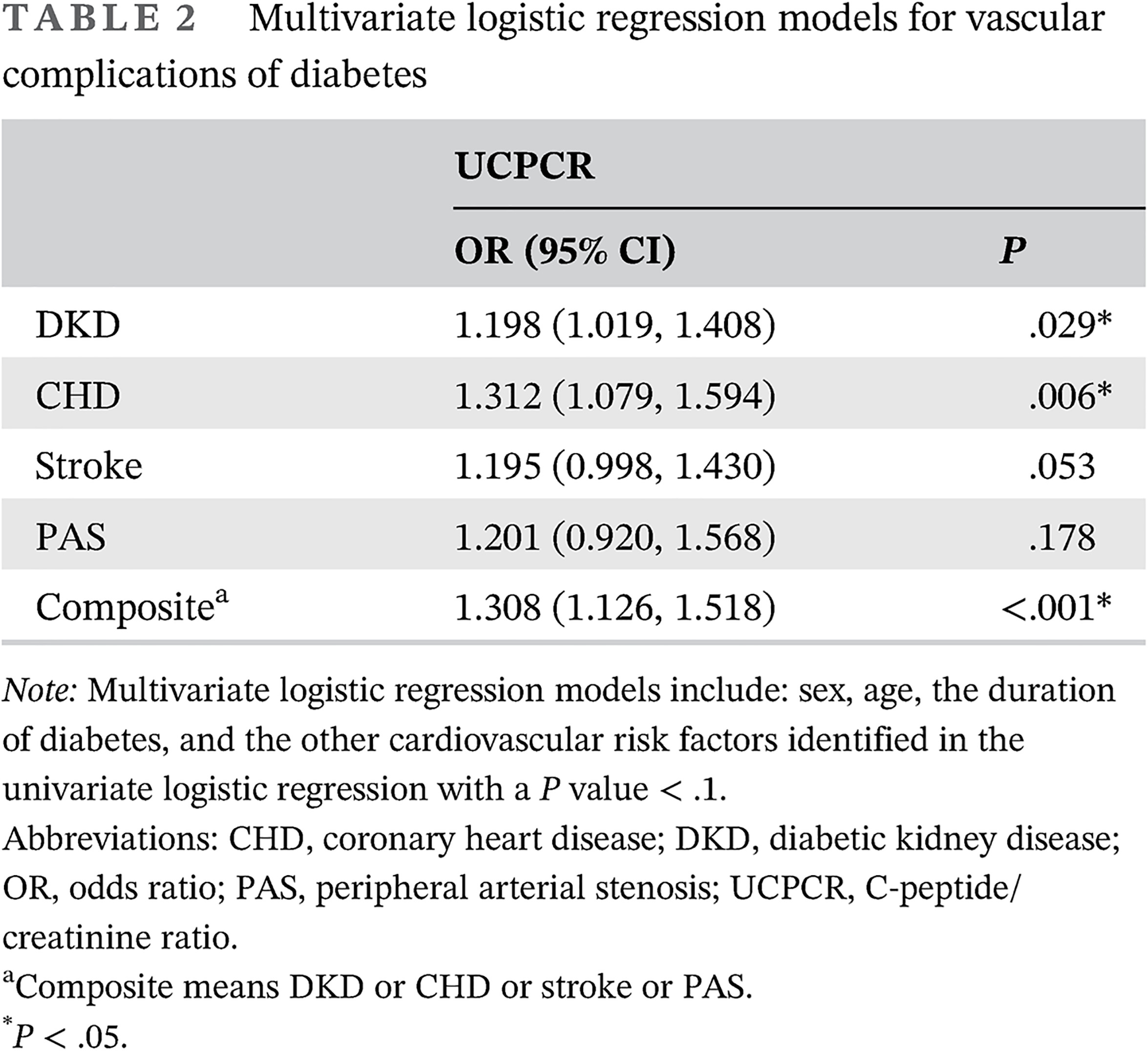
Urinary C-peptide/creatinine ratio: A useful biomarker of insulin resistance and refined classification of type 2 diabetes mellitus
尿C肽/肌酐比值:一个评估胰岛素抵抗水平并改善2型糖尿病精准分型的有效生物标志物
- Pages: 893-904
- First Published: 29 May 2021
Highlights
- Urinary C-peptide/creatinine ratio (UCPCR) is a biomarker of insulin resistance.
- High UCPCR is associated with the vascular complications of diabetes.
- The addition of UCPCR could be used to improve the categorization of patients with diabetes, and we present an updated classification comprising subgroups with specific clinical characteristics.
Metabolic risk factors among prediabetic individuals and the trajectory toward the diabetes incidence
糖尿病前期人群代谢危险因素及糖尿病发病轨迹
- Pages: 905-914
- First Published: 15 June 2021
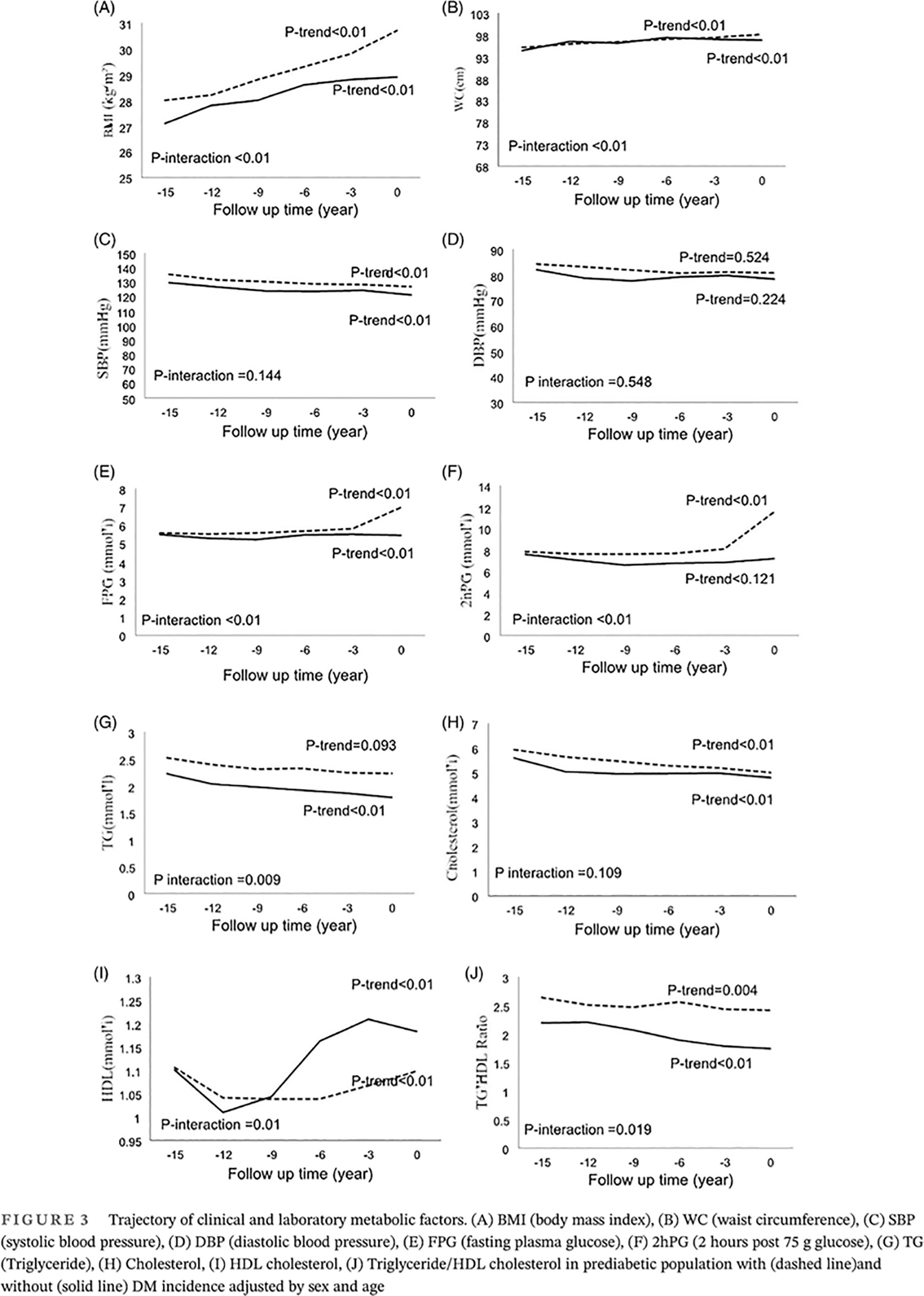
Highlights
- Metabolic risk factors are present in a prediabetic population and start worsening on an ascending trend many years prior to diabetes mellitus (DM) occurrence.
- The changes in metabolic risk factors were significant over time for body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), triglyceride (TG), TG:HDL ratio, and plasma glucose between DM convertors and nonconvertors.
- The most prominent differences were observed from 3 years before diabetes occurrence for fasting plasma glucose and 2-hour plasma glucose, 6 years for WC, 9 years for HDL, and even earlier for BMI, TG, and TG:HDL ratio.
- HDL-C and WC trajectories are independent predictors of diabetes incidence.
Changes in body mass index, glycosylated hemoglobin A1C, blood pressure, and LDL-cholesterol among type 2 diabetes patients in Malaysia: A population-based longitudinal study
马来西亚2型糖尿病患者体重指数, 糖化血红蛋白, 血压和低密度脂蛋白-胆固醇的变化:一项基于人群的纵向研究
- Pages: 915-929
- First Published: 17 June 2021
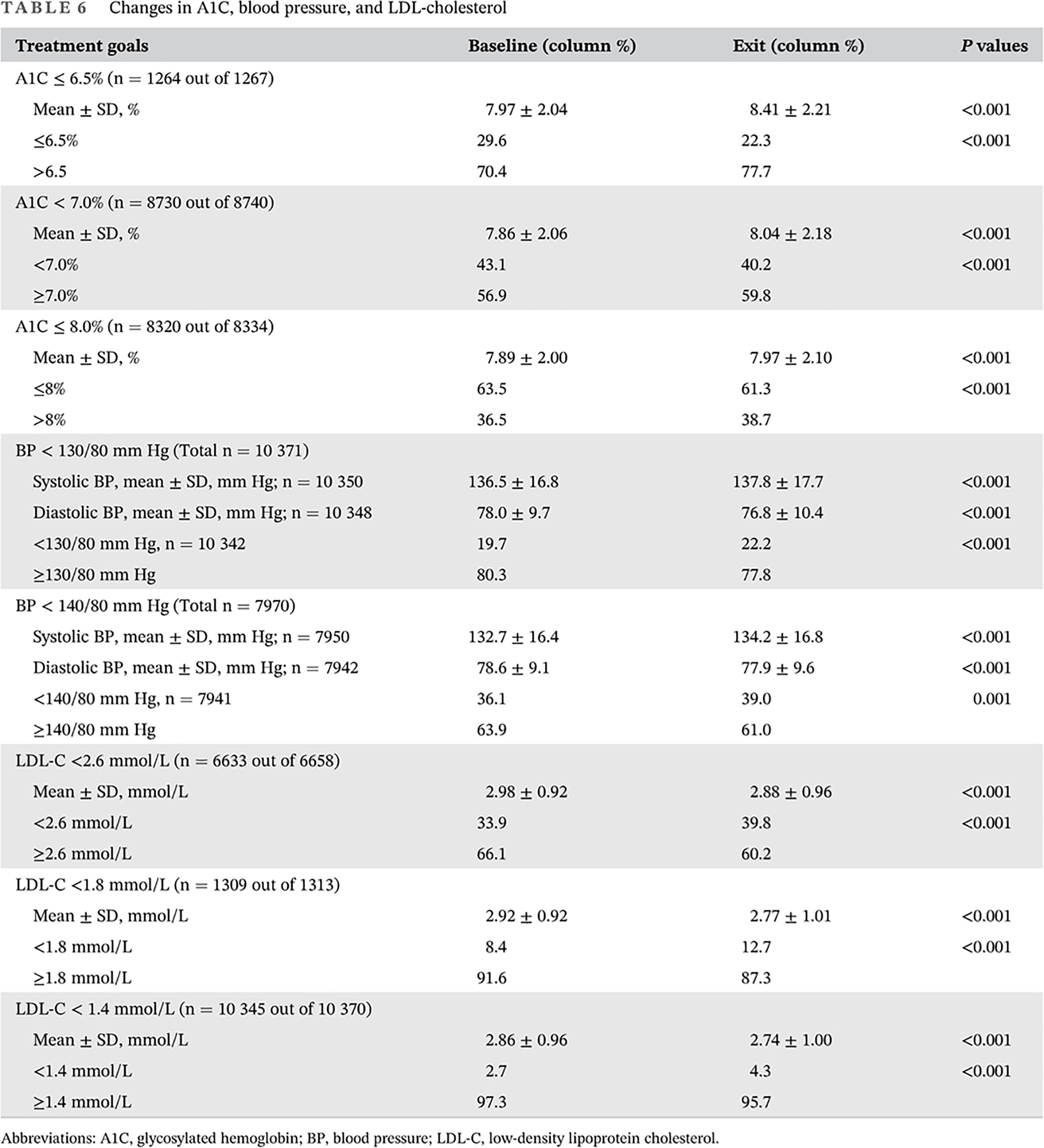
Highlights
- Changes in body mass index, glycosylated hemoglobin A1C, blood pressure, and LDL-cholesterol over an average of 2.5 person-years of follow-up were not encouraging in the real-world clinical settings in Malaysia.
- The standards of care for body mass index, A1C, blood pressure, and LDL-cholesterol remain to be achieved by the majority of diabetes patients.
- There appears to be a disconnection between clinical recommendations and real-world practice in public health clinics.
Choice of basal insulin therapy is associated with weight and height development in type 1 diabetes: A multicenter analysis from the German/Austrian DPV registry in 10 338 children and adolescents
基础胰岛素治疗的选择与1型糖尿病患者的体重和身高发育有关:来自德国/奥地利DPV登记的10338名儿童和青少年的多中心分析
- Pages: 930-939
- First Published: 28 June 2021
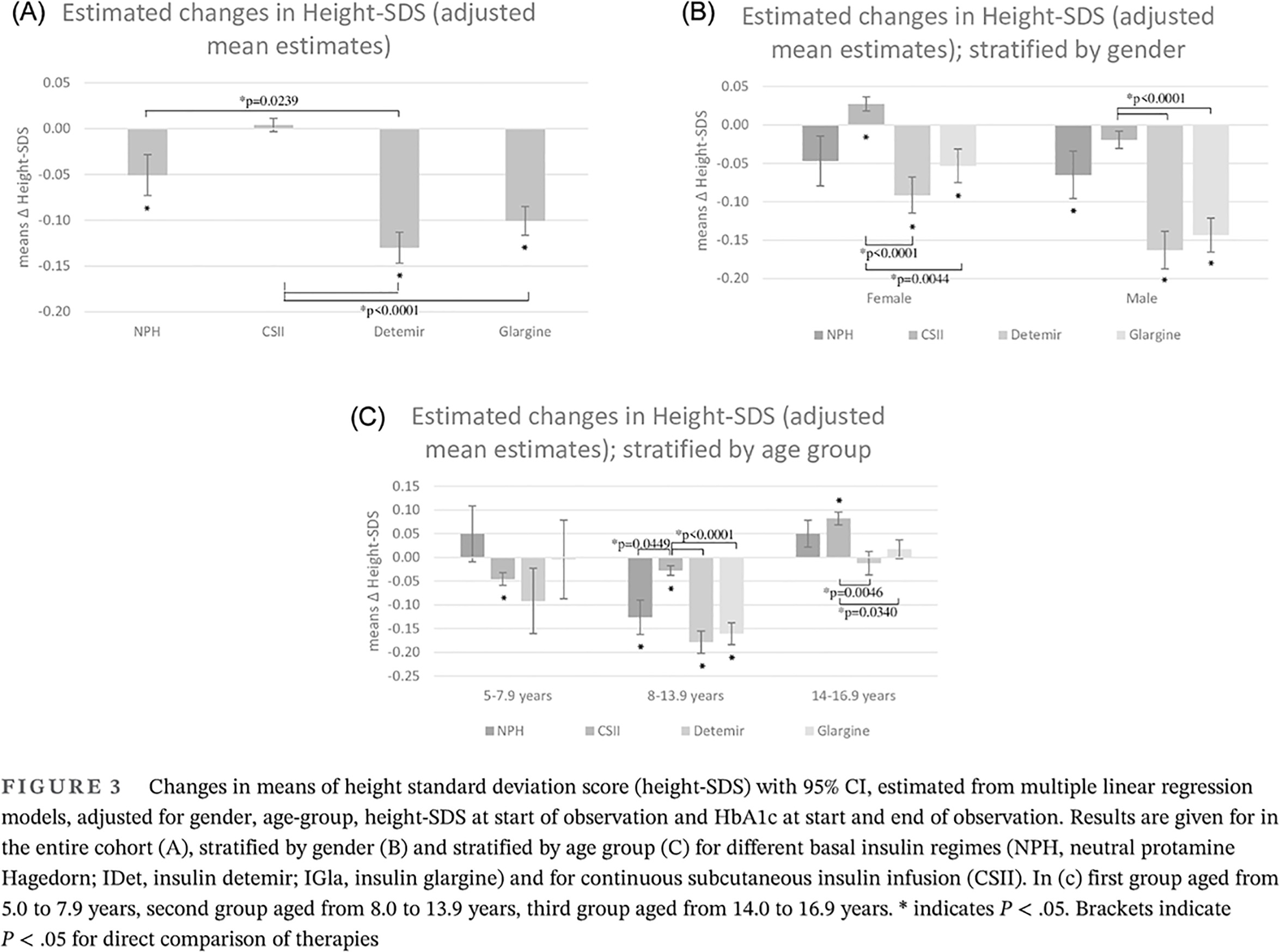
Highlights
- Choice of basal insulin regimen might influence height development; continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion appeared to have a favorable effect on growth trajectories.
- All therapies were associated with an increase in body mass index standard deviation score (BMI-SDS), most evident in females.
- In the context of BMI-SDS, there were no consistent findings to support one therapy regimen over another in pediatric type 1 diabetes.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Efficacy and safety of total pancreatectomy with islet autotransplantation: A clinical study in Japan
- Pages: 940-942
- First Published: 29 July 2021