Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Development and validation of a chewing robot for mimicking human food oral processing and producing food bolus
- Pages: 419-429
- First Published: 26 May 2022
Bionic design of the oral swallowing in vitro and its application in the dysphagia
- Pages: 430-443
- First Published: 13 June 2022
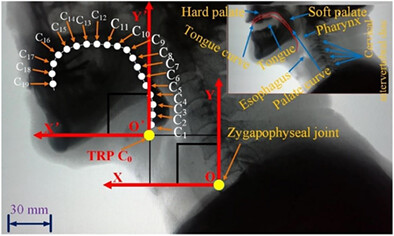
Based on the bionic swallowing device in vitro of similar human-tongue motion during swallowing, the average correlation coefficients between the tongue trajectories of patients at five swallowing grades and those of the BSD were 0.87, proving its effectiveness and potential application. Furthermore, the corn-paste experiments of the bionic swallowing device showed that the dysphagia at five swallowing grades s could be a suitable choice for certain food concentration.
A method for evaluating time-resolved rheological functionalities of fluid foods
- Pages: 444-452
- First Published: 26 March 2022
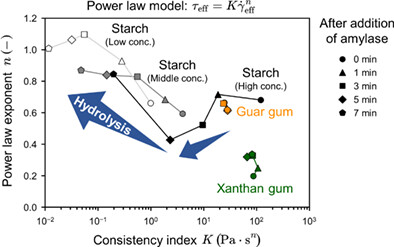
Ultrasonic spinning rheometry described time variation of the instantaneous viscosity curves for typical thickener solutions with alpha-amylase as a digestive enzyme. A K-n diagram was constructed from the obtained viscosity curves for quantitatively characterizing time-resolved rheological functionalities of fluid foods.
Textural thermo-mechanical properties of sweet cherry for postharvest damage analysis
- Pages: 453-464
- First Published: 24 January 2022
The surface mechanics of cooked rice as influenced by gastric fluids measured using a micro texture analyzer
- Pages: 465-477
- First Published: 22 February 2022
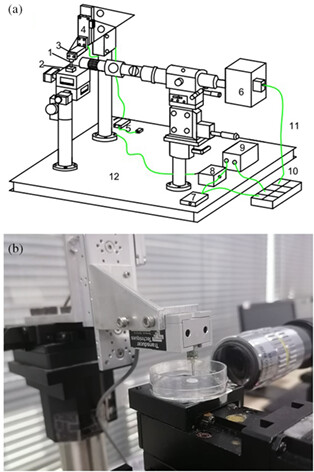
This article introduces a micro texture analyzer in terms of its origin, key features, reliability and data analysis of texture profile. This device was employed to explore the texture characteristics of the surface of an individual steamed rice (SR) and fried rice (FR) grain as influenced by different gastric digestion environments in vitro. Similar mechanical behaviors were shown, but the hardness and elastic modulus of FR were decreased less than that of SR during in vitro digestion in the same digestion condition.
Significance of milling methods on brown teff flour, dough, and bread properties
- Pages: 478-489
- First Published: 22 February 2022
Texture and viscoelastic characteristics of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) surimi affected by combination of washing regimes and hydrogen peroxide
- Pages: 490-502
- First Published: 16 March 2022
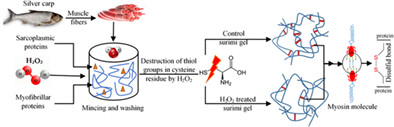
This study investigated the texture and rheological characteristics of silver carp surimi after being exposed to different concentrations of H2O2 and mince:water ratios during different washing cycles. Finally, it was revealed that there is possible texture damage of fish mince after being exposed to H2O2 as it results in a weaker surimi gel compared to the one prepared by the conventional washing method.
Effects of variety, early harvest, and germination on pasting properties and cooked grain texture of brown rice
- Pages: 503-516
- First Published: 21 March 2022
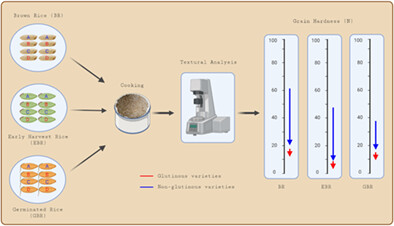
Early harvest had a greater effect on reducing the hardness of cooked whole grain while germination substantially reduced viscosities of flour paste. The softer texture of brown rice, about 10 N (32%) lower, could be achieved by germination and a further 5 N (46%) by harvesting early. Desired characteristics in rice flour as ingredients in the food industry and of whole grain for direct consumption can be achieved by selecting a suitable variety and by harvesting the grain early or germination.
Wheatgrass powder-enriched functional pasta: Techno-functional, phytochemical, textural, sensory, and structural characterization
- Pages: 517-530
- First Published: 01 April 2022
Mechanical properties of gellan gum beads prepared with potassium or calcium ions
- Pages: 531-539
- First Published: 15 April 2022
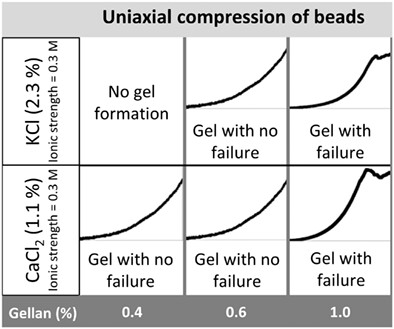
Beads of low acyl gellan gum were produced using extrusion technique (dripping) followed by an ionotropic gelation step with calcium or potassium chloride. Gellan and salts concentrations suitable to gel beads formation were determined and mechanical properties of gellan beads were measured by uniaxial compression. Maximum force or force at failure was mainly dependent on the type and salt concentration. Young modulus, determined using Hertz approach, showed values between 445 and 840 kPa depending on polysaccharide concentration and cation type added.
Physicochemical and sensory properties of biscuits formulated with Tenebrio molitor and Alphitobius diaperinus flours
- Pages: 540-549
- First Published: 12 May 2022
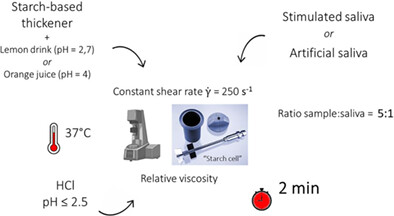
Effect of α-amylase and pH on the rheological properties of thickened liquids containing starch in in vitro conditions relevant to oral processing and swallowing
- Pages: 550-557
- First Published: 12 May 2022
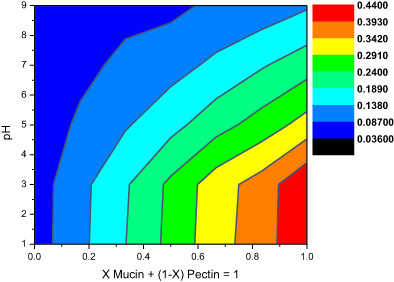
Stability and rheology of plant-derived hydrocolloid–mucin mixtures
- Pages: 558-562
- First Published: 16 May 2022
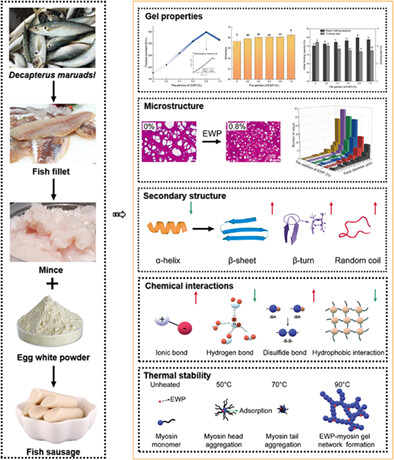
Gel properties of blue round scad (Decapterus maruadsi) mince as influenced by the addition of egg white powder
- Pages: 563-576
- First Published: 17 May 2022