Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Porous Nanostructures: Boosting Electrochemical Hydrogen Evolution of Porous Metal Phosphides Nanosheets by Coating Defective TiO2 Overlayers (Small 42/2018)
- First Published: 18 October 2018

In article number 1802755, Chuanxin He and co-workers develop a facile yet robust strategy for boosting the electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) of metal phosphides by coating defective TiO2 overlayers. The abundant oxygen vacancies on the defective TiO2 are found to possess high activity for the adsorption and dissociation of water, thereby markedly facilitating the Volmer step of the HER.
Inside Front Cover
Glioma Therapy: Combination Glioma Therapy Mediated by a Dual-Targeted Delivery System Constructed Using OMCN–PEG–Pep22/DOX (Small 42/2018)
- First Published: 18 October 2018

In article number 1801905, Jinlong Shi, Rongqin Huang, Wei Shi, and co-workers describe a novel drug-loaded system, OPPD, which uses PEG and OMCN linked to the Pep22 polypeptide targeting the low-density lipoprotein receptor, that can effectively cross the blood-brain barrier and target glioma cells, exerting an outstanding therapeutic efficacy via both the near-infrared photothermal and chemotherapeutic effects of the loaded DOX. The collective findings support the utility of OPPD, a promising drug-delivery vehicle, for future clinical application in glioma therapy.
Back Cover
Cerium Valence State Distribution: Atomic-Scale Valence State Distribution inside Ultrafine CeO2 Nanocubes and Its Size Dependence (Small 42/2018)
- First Published: 18 October 2018

In article number 1802915, Tadafumi Adschiri, Yuichi Ikuhara, and co-workers report the atomic-scale analysis of the distribution of cerium valence states in surfactant-modified CeO2 nanocubes using scanning transmission electron microscopy and electron energy loss spectroscopy. A nanosized effect induces local lattice expansion, which results in the increasing amount of Ce3+ cations in the central layer of the ultrafine CeO2 nanocubes.
Masthead
Reviews
The Research Development of Quantum Dots in Electrochemical Energy Storage
- First Published: 23 August 2018
Quantum dots represent one promising kind of power materials for electrochemical energy storage. Synthesis strategies, tailored material properties, and different electrochemical performances are prominent characteristics of batteries and electrochemical capacitors. A comprehensive summary and evaluation of the electrode material are provided in this review.
Neutrophil-Based Delivery Systems for Nanotherapeutics
- First Published: 24 August 2018
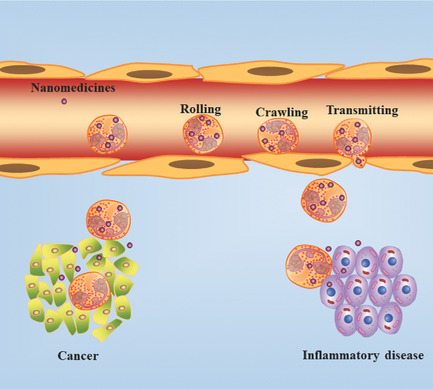
Neutrophils are the major type of leukocytes recruited to sites of inflammation during infection and tumorigenesis. The neutrophil-mediated drug delivery systems are shown to greatly contribute to nanotherapeutics. In this review, the application of neutrophil-based nanomedicine in the treatment of inflammatory diseases and cancers is summarized, and its opportunities, critical challenges, and prospects are discussed.
Frontispiece
Water Splitting: Cobalt Nanocrystals Encapsulated in Heteroatom-Rich Porous Carbons Derived from Conjugated Microporous Polymers for Efficient Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution (Small 42/2018)
- First Published: 18 October 2018

In article number 1803232, Meifang Zhu, Arne Thomas, Yaozu Liao, and co-workers create a series of N,O-dual-doped carbon encapsulated cobalt nanoparticles (CoNOCs) as novel and superior electrocatalysts for water splitting using a conjugated microporous polymer as a precursor. Such CoNOCs represent advances in the design of binder-free membrane-like electrodes, achieving even better hydrogen evolution performance. The work demonstrates that the rational design of scaled-up non-noble-metal-containing carbon electrocatalysts could offer a promising water-splitting setup relevant for industrial applications.
Communications
Cobalt Nanocrystals Encapsulated in Heteroatom-Rich Porous Carbons Derived from Conjugated Microporous Polymers for Efficient Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution
- First Published: 18 September 2018
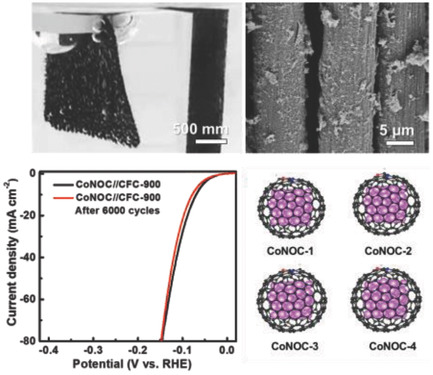
N,O-dual-doped carbon encapsulated cobalt nanocrystals are reported as catalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). A conjugated microporous polymer acts as the precursor, which also allows fabrication of binder-free HER electrodes. Structural analyses and density functional theory calculations indicate that N,O-dual-doping and cobalt nanocrystals encapsulation significantly decrease the free energy of hydrogen adsorption, explaining the superior HER activity of the catalysts.
In Vivo Synthesis of Nanocomposites Using the Recombinant Escherichia coli
- First Published: 17 September 2018
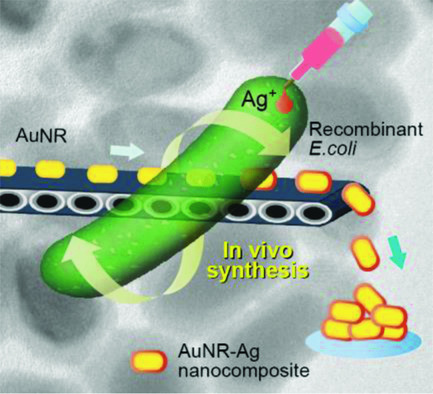
In vivo synthesis of gold nanorod (AuNR)-Ag core–shell nanocomposites is demonstrated for the first time by using recombinant Escherichia coli. Chemically synthesized AuNRs are internalized into the E. coli, then Ag ions are reduced and grown on the surface of the AuNRs with assistance from metal-binding proteins. The biogenic AuNR-Ag nanocomposites with core–shell structure exhibit good plasmonic effects.
Single-Molecule Co-Immunoprecipitation Reveals Functional Inheritance of EGFRs in Extracellular Vesicles
- First Published: 21 September 2018
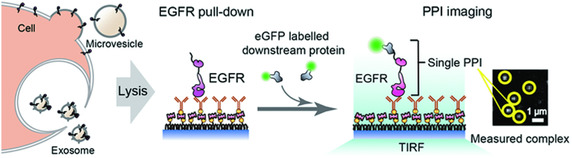
The quantity and protein–protein interaction (PPI) strengths of epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFRs) derived from extracellular vesicles (EVs) and the original lung adenocarcinoma cells are determined using single-molecule immunolabeling and co-immunoprecipitation methods. The EGFR PPI strengths measured for EVs generally show tight correlation with those determined for the original cells.
Room-Temperature Phototransistor with Negative Photoresponsivity of 108 A W−1 Using Fullerene-Sensitized Aligned Carbon Nanotubes
- First Published: 24 September 2018
Full Papers
Atomic-Scale Valence State Distribution inside Ultrafine CeO2 Nanocubes and Its Size Dependence
- First Published: 09 September 2018
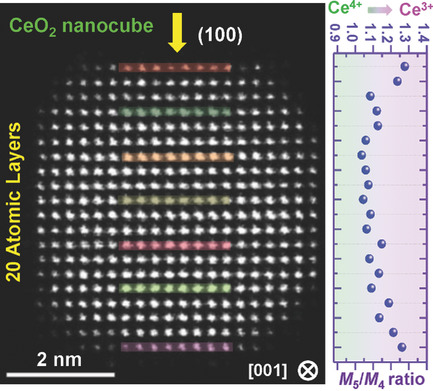
Atomic-scale cerium valence state distribution layer-by-layer in the surfactant-modified CeO2 nanocubes is achieved using scanning transmission electron microscopy and electron energy loss spectroscopy. It is demonstrated that the increasing amount of Ce3+ in the center layers of CeO2 nanocube (as the size reduced to approximately 5 nm) is related to the nanosize-effect induced local lattice expansion.
Boosting Electrochemical Hydrogen Evolution of Porous Metal Phosphides Nanosheets by Coating Defective TiO2 Overlayers
- First Published: 09 September 2018
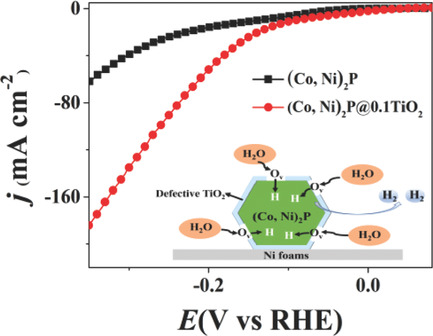
A facile yet effective strategy to boost the alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) of metal phosphides is developed by coating defective TiO2 overlayers. The oxygen vacancies on defective TiO2 overlayers are found to possess high activity for adsorption and dissociation water, thereby significantly promoting the Volmer step of HER.
Combination Glioma Therapy Mediated by a Dual-Targeted Delivery System Constructed Using OMCN–PEG–Pep22/DOX
- First Published: 14 September 2018
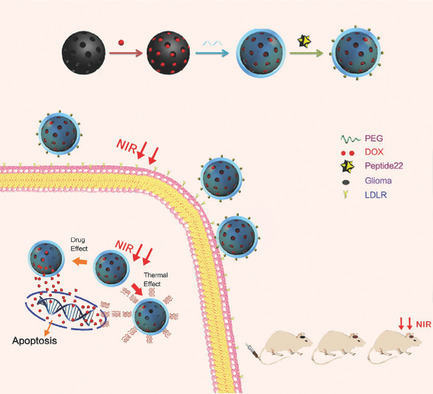
A novel drug-loaded system, OPPD, which uses PEG and OMCN linked to the Pep22 polypeptide targeting the LDLR, can effectively cross the BBB and target glioma cells exerting an outstanding therapeutic efficacy via the near-infrared photothermal and chemotherapeutic effects of loaded DOX. The collective findings support the utility of OPPD, a promising drug-delivery vehicle, for future clinical application in glioma therapy.
Boosting the Electrochemical Performance of Li–S Batteries with a Dual Polysulfides Confinement Strategy
- First Published: 19 September 2018
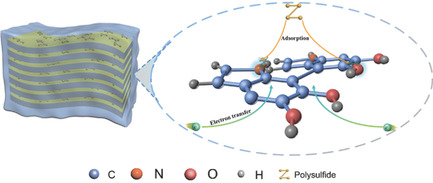
An advanced S@Mxe@PDA electrode with a dual polysulfide confinement strategy is prepared by confinement of sulfur in polydopamine-coated MXene nanosheets for high-performance Li–S batteries. The excellent electrochemical properties of the S@Mxe@PDA cathode can be attributed to their inherently high underlying metallic conductivity and chemical bonding and strong chemical adsorption to lithium polysulfides.
Scalable Multiplexed Drug-Combination Screening Platforms Using 3D Microtumor Model for Precision Medicine
- First Published: 21 September 2018

Combination drug treatment has been widely accepted for better cancer therapeutic efficacy, yet the discovery of combinations is hindered by experimental complexity. A combinatorial drug screening platform is developed, covering all pairwise combinations of 8 drugs with multiple mixing ratios in a linear/logarithmic scale. It facilitates the discovery of synergistic drug combinations by allowing over 1000 experiments per chip at once.
Size, Shape, and Protein Corona Determine Cellular Uptake and Removal Mechanisms of Gold Nanoparticles
- First Published: 21 September 2018
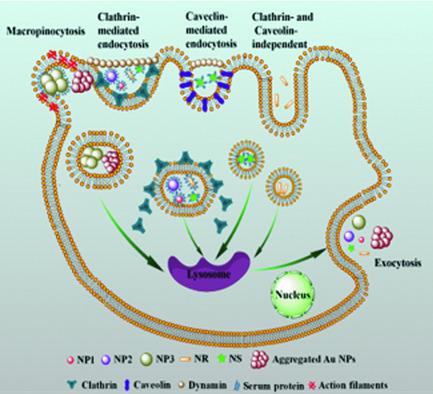
Size, shape, and protein corona play the key role in cellular uptake and removal mechanisms of gold nanoparticles (Au NPs). The uptake mechanisms of five types of Au NPs are different. Size, shape, and protein corona decrease the uptake amount and affect the endocytosis mechanism. However, all of them are released through the lysosomal exocytosis pathway.
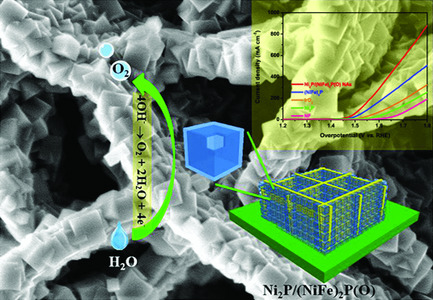
Oxygen-Doped Nickel Iron Phosphide Nanocube Arrays Grown on Ni Foam for Oxygen Evolution Electrocatalysis
- First Published: 21 September 2018
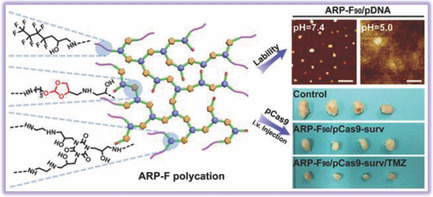
Fluorinated Acid-Labile Branched Hydroxyl-Rich Nanosystems for Flexible and Robust Delivery of Plasmids
- First Published: 20 September 2018
Ultrahigh-Capacity and Long-Life Lithium–Metal Batteries Enabled by Engineering Carbon Nanofiber–Stabilized Graphene Aerogel Film Host
- First Published: 20 September 2018
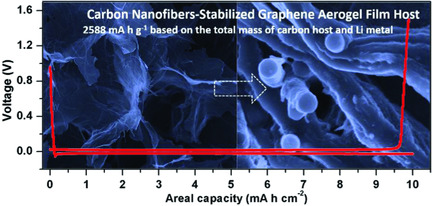
An ultrahigh-capacity and long-life lithium metal anode is achieved by engineering a carbon nanofiber–stabilized graphene aerogel film host for regulating the Li deposition and mitigating the volume change, indicative of an ultrahigh specific capacity of 2588 mA h g−1 based on the total mass and demonstrating a long cycle life up to 1000 h.
Photoacoustic and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Bimodal Contrast Agent Displaying Amplified Photoacoustic Signal
- First Published: 24 September 2018
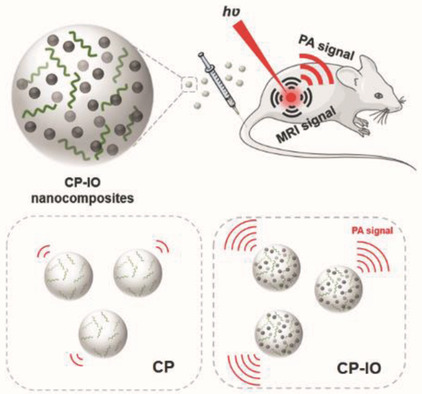
A bimodal contrast agent composed of a conjugated polymer (CP) and iron oxide nanoparticles is developed, displaying 45% amplified photoacoustic signal intensity as compared to bare CP nanoparticles, while the performance for magnetic resonance imaging is not affected. The mechanism of the amplification is investigated through both experimental and theoretical simulation.