Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Polyprodrug Antimicrobials: Polyprodrug Antimicrobials: Remarkable Membrane Damage and Concurrent Drug Release to Combat Antibiotic Resistance of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (Small 41/2018)
- First Published: 11 October 2018

In article number 1802008, Da Xing, Xianglong Hu, and co-workers propose a strategy of polyprodrug antimicrobials. The triclosan polyprodrug antimicrobials with diverse hydrophilic-hydrophobic balance demonstrate remarkable membrane damage and concurrent triclosan release potency, which can efficiently inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, a highly pathogenic bacteria associated with high mortality rates. Polyprodrug antimicrobials possess excellent antibacterial selectivity and undetectable antibiotic resistance when compared with commercial antibiotics.
Inside Front Cover
Sodium-Ion Batteries: SnS2 Nanosheets Coating on Nanohollow Cubic CoS2/C for Ultralong Life and High Rate Capability Half/Full Sodium-Ion Batteries (Small 41/2018)
- First Published: 11 October 2018

In article number 1802716, Caizhen Zhu and co-workers develop an effective and controllable strategy for preparing a SnS2 nanosheet coating on nano-hollow cubic CoS2/C (CoS2/C@SnS2). As anodes for sodium-ion batteries, the electrode exhibits an ultra-long cycle life and excellent rate performance. This strategy can pave a way for preparing various metal sulfides with excellent performance in the field of energy storage.
Back Cover
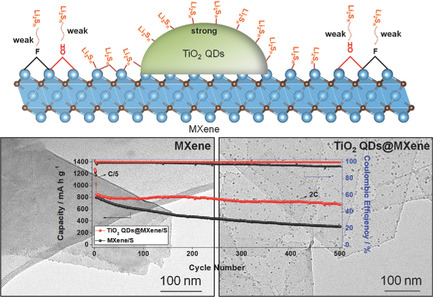
Li–S Batteries: Ultrathin MXene Nanosheets Decorated with TiO2 Quantum Dots as an Efficient Sulfur Host toward Fast and Stable Li–S Batteries (Small 41/2018)
- First Published: 11 October 2018
In article number 1802443, Xiao-Dong Zhu, Yi-Tao Liu, and co-workers report unique solvothermal growth of TiO2 quantum dots (QDs) on ultrathin MXene nanosheets. Through remarkable synergies, the resulting TiO2 QDs@MXene nanohybrids exhibit significantly improved long-term cyclability and rate capability as a sulfur host, disclosing a new opportunity toward fast and stable Li–S batteries.
Masthead
Reviews
Organic Solar Cell Materials toward Commercialization
- First Published: 14 August 2018
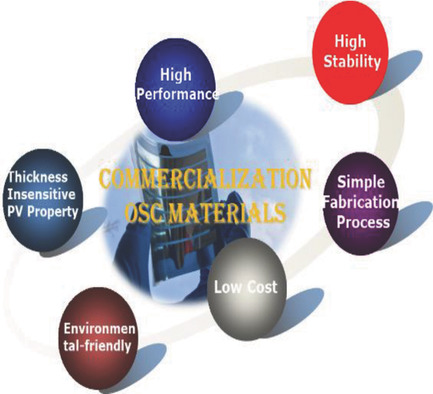
Recent progress of photovoltaic materials toward the commercialization of organic solar cells is in focus. High-performance, thickness-insensitive, low-cost, environmentally friendly, and stable photoactive and interface materials are discussed. Meanwhile, several fundamental challenges and future prospects of organic solar cell materials are proposed.
Synthesis and Progress of New Oxygen-Vacant Electrode Materials for High-Energy Rechargeable Battery Applications
- First Published: 06 August 2018

Oxygen-vacant substances represent one type of promising material for electrochemical energy storage. The synthetic strategies, tailored material properties, and various electrochemical performances of oxygen-deficient materials for use in batteries are described. Oxygen-deficient substances are selectively introduced, and comprehensive summaries and evaluations are presented.
Communications
Ultrathin MXene Nanosheets Decorated with TiO2 Quantum Dots as an Efficient Sulfur Host toward Fast and Stable Li–S Batteries
- First Published: 02 September 2018
Frontispiece
Protective Coatings: Bioinspired Wear-Resistant and Ultradurable Functional Gradient Coatings (Small 41/2018)
- First Published: 11 October 2018

In article number 1802717, Zhengzhi Wang, Houbing Huang, Zuoqi Zhang, and co-workers develop functional gradient nanocomposite coatings with hybrid-sized nanoreinforcements gradiently and discretely distributed towards the coating surface. The coatings exhibit simultaneously high surface hardness, stiffness, and wear resistance, as well as superb coating/substrate interfacial integrity that applies perfectly as ultradurable protective coatings. The design strategy and mechanics of functional gradients in biological materials are well replicated in these coating structures.
Communications
Bioinspired Wear-Resistant and Ultradurable Functional Gradient Coatings
- First Published: 11 September 2018
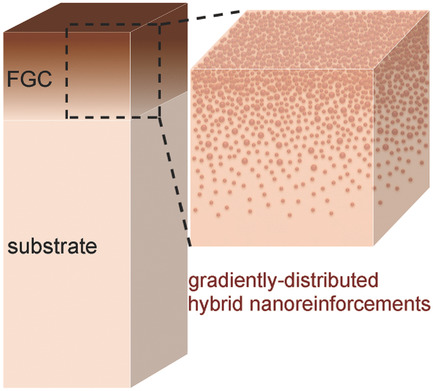
Functional gradient nanocomposite coatings with hybrid nanoreinforcements gradiently and discretely distributed toward the coating surface are presented. The coatings exhibit simultaneously high surface hardness, stiffness, and wear-resistance, as well as superb coating/substrate interfacial integrity that is applied perfectly as ultradurable protective coating. The design strategy and mechanics of functional gradients in biological materials are well replicated in these coating structures.
Microsphere-Based Nanoindentation for the Monitoring of Cellular Cortical Stiffness Regulated by MT1-MMP
- First Published: 14 September 2018
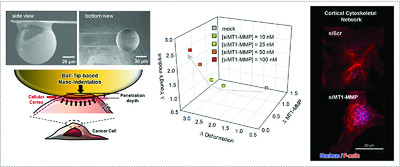
Atomic force microscopy-based nanoindentation is in the limelight to understand cancer mechanobiology because of its potential for the assessment of cellular stiffness. Especially, cellular mechanics has served as a crucial indicator of metastatic cancer. This work eventually describes the novel role of membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase as a key regulator of cellular mechanics brought on by the cytoskeletal network.
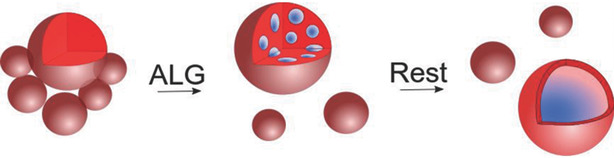
Preparation of Template-Free Robust Yolk–Shell Gelled Particles from Controllably Evolved All-in-Water Emulsions
- First Published: 11 September 2018
Lithography-Free Electrochemical Patterning of Conductive Substrates with Metal Oxides
- First Published: 14 September 2018
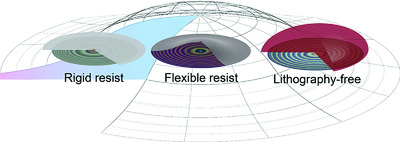
Electrochemical surface-patterning of silicon is achieved with a step potential to oxidize a metal substrate underneath a lithographic mask. Flexible lithographic masks allow for uniform and large metal oxide patterns with submicron precision. The approach is extended to patterning without the need for a lithographic mask. A lacquer–water emulsion serves as a mask and furnishes well-defined patterns.
Air-Stable and Self-Driven Perovskite Photodiodes with High On/Off Ratio and Swift Photoresponse
- First Published: 14 September 2018
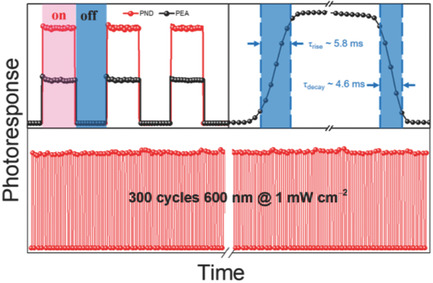
Air-stable and self-driven 2D phenylethylamine perovskite-based vertically structured photodiodes are obtained and exhibit a high on/off ratio up to 2 × 104 under white light irradiation (62 mW cm−2), which is larger than their 3D counterparts, and swift photoresponse under 600 nm light irradiation (0.9 mW cm−2) comparable to those of 2D analogs with lateral configuration.
Full Papers
Polyprodrug Antimicrobials: Remarkable Membrane Damage and Concurrent Drug Release to Combat Antibiotic Resistance of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- First Published: 17 August 2018
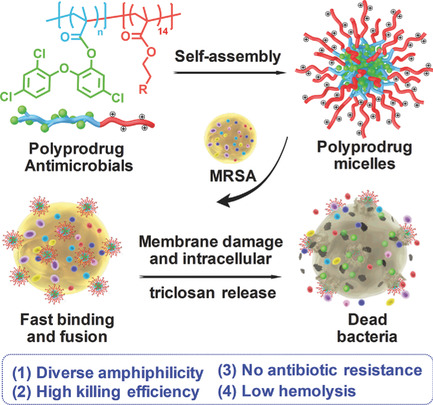
Polyprodrug antimicrobials with remarkable membrane damage and concurrent drug release are proposed to treat the infection and antibiotic resistance of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), exhibiting low hemolysis toward red blood cells and good antibacterial selectivity. Remarkable membrane damage and further intracellular triclosan release synergistically kill MRSA, possessing undetectable resistance compared with commercial antibiotics. Polyprodrug antimicrobials are promising to treat drug-resistant bacteria in biomedicine.
SnS2 Nanosheets Coating on Nanohollow Cubic CoS2/C for Ultralong Life and High Rate Capability Half/Full Sodium-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 28 August 2018
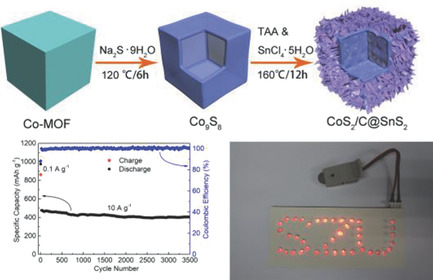
The CoS2/C@SnS2 exhibits ultralong cycle life and high rate capability. The reversible capacity can maintain 854.5 mAh g−1 at a current density of 0.1 A g−1. Even at a high current density of 10 A g−1, the reversible capacity can maintain 400.1 mAh g−1 after 3500 cycles. As for CoS2/C@SnS2-Na3V2(PO4)3 full-cells, one full-cell can light up 41 light-emitting diodes bulbs.
Leveraging Titanium to Enable Silicon Anodes in Lithium-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 14 September 2018
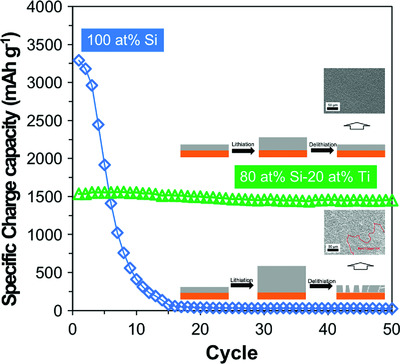
Incorporation of titanium atoms into a silicon matrix significantly enhances the cycling performance of the thin film anode for lithium-ion batteries. The optimal Si–Ti thin film electrode exhibits high gravimetric and volumetric capacities as well as excellent long-term cycling stability even in a full-cell configuration with LiFePO4.
Millerite Core–Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Hollow Shell Structure for Electrochemical Energy Storage
- First Published: 14 September 2018
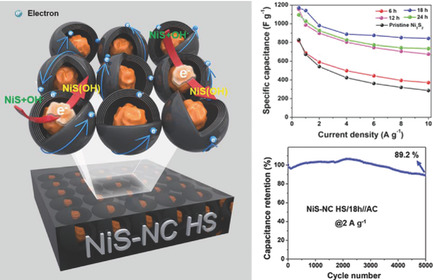
A novel millerite core–nitrogen-doped carbon hollow shell (NiS–NC HS) structure is designed and developed by a simple polydopamine coating, annealing, and hydrothermal synthesis for electrochemical energy storages. The intentionally created void space between the core and the shell accommodates and prevents aggregation of neighboring NiS particles. The NC HS enhances the ion and electron transport and the cycling stability.
Temperature Difference Triggering Controlled Growth of All-Inorganic Perovskite Nanowire Arrays in Air
- First Published: 12 September 2018
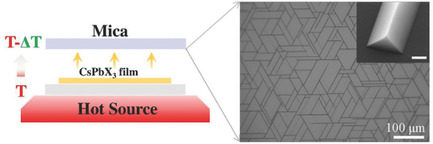
A novel strategy is proposed to integrate the merits of the liquid- and gas-phase method for the fabrication of large-scale all-inorganic perovskites nanowire arrays in air, where uniform solution-prepared precursors and an extremely short vertical mode (<102 µm) rather than long-distance horizontal mode in conventional vapor deposition are employed to provide a uniform and stable mass transport environment.
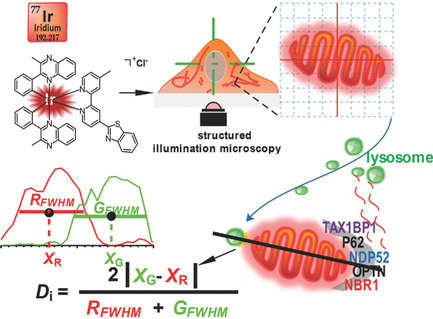
Super-Resolution Tracking of Mitochondrial Dynamics with An Iridium(III) Luminophore
- First Published: 14 September 2018
Disordering the Atomic Structure of Co(II) Oxide via B-Doping: An Efficient Oxygen Vacancy Introduction Approach for High Oxygen Evolution Reaction Electrocatalysts
- First Published: 14 September 2018
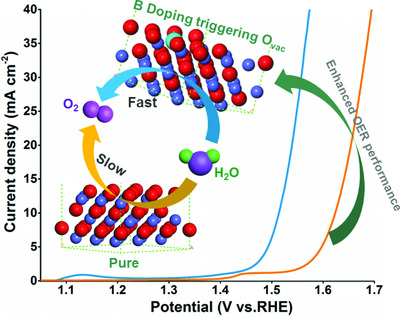
The oxygen vacancies are successfully introduced in CoO nanowires by B-doping using a direct pyrolysis approach. The effective incorporation of oxygen vacancies could not only lower the reaction barrier for breaking the CoO bond, but cause the disordering of local structure, thereby achieving the high active oxygen evolution reaction performance.
Sub-1.5 nm Ultrathin CoP Nanosheet Aerogel: Efficient Electrocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction at All pH Values
- First Published: 14 September 2018
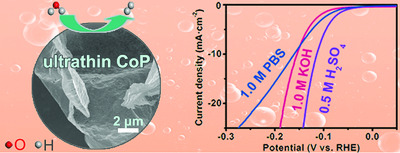
CoP aerogels assembled by sub-1.5 nm nanosheets (CoP-400) derived from alginate biomass are successfully synthesized through an ice-templating strategy. The CoP-400 with a 3D interconnected network of aerogel and nonlayered 2D ultrathin nanosheets can provide a short electron transfer distance and increase exposed active sites, which exhibits remarkable hydrogen evolution reaction performance at all pH values.
Redox-Responsive Nanoparticle-Mediated Systemic RNAi for Effective Cancer Therapy
- First Published: 17 September 2018
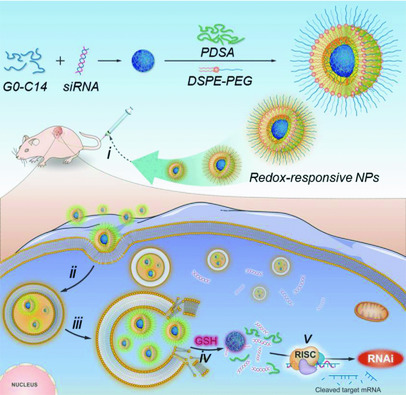
Herein, a biodegradable and fast redox-responsive nanoparticle (NP) platform for systemic small interfering RNA (siRNA) delivery and cancer therapy is developed. This new NP platform shows the unique features of i) long circulation, ii) high tumor accumulation, iii) redox-triggered fast intracellular siRNA release, and iv) effective gene silencing, which can be used as an effective tool for RNA interference-based cancer therapy.
Ultrasmall Ru/Cu-doped RuO2 Complex Embedded in Amorphous Carbon Skeleton as Highly Active Bifunctional Electrocatalysts for Overall Water Splitting
- First Published: 14 September 2018
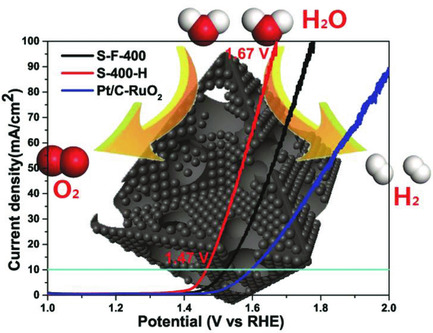
Ultrasmall Ru/Cu-doped RuO2 complex embedded in an amorphous carbon skeleton is synthesized through thermolysis of Ru-modified Cu-BTC. The outstanding oxygen evolution reaction and decent hydrogen evolution reaction catalytic activities endow the complex with impressive overall water splitting performance, superior to that of the state-of-the-art electrocatalysts, which just require 1.47 and 1.67 V to achieve current densities of 10 and 100 mA cm−2.