Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Microgels: Centering Single Cells in Microgels via Delayed Crosslinking Supports Long-Term 3D Culture by Preventing Cell Escape (Small 22/2017)
- First Published: 07 June 2017

In article number 1603711, Marcel Karperien, Jeroen Leijten, and co-workers present the first microfluidic approach that enables long-term 3D single cell culture by centering cells in microgels in a facile, modular, and widely applicable manner. A typical cell microencapsulation event using the delayed crosslinking approach enables a cell to be positioned at the outer edge of a droplet, and by delaying on-chip crosslinking, the cell is allowed to move towards the center of the droplet. Subsequent crosslinking finally results in an individual cell being encapsulated in the microgel's center.
Inside Front Cover
Energy Storage: A Phase-Separation Route to Synthesize Porous CNTs with Excellent Stability for Na+ Storage (Small 22/2017)
- First Published: 07 June 2017

In article number 1604045, by Ming Zhang, Guozhong Cao, and co-workers, a phase-separation strategy is developed to conveniently synthesize porous carbon nanotubes, which showed excellent rate capacity and cycling performance for sodium-ion storage. This strategy may provide a route for the synthesis and application of core@shell or hollow materials in fields of energy and catalyst.
Back Cover
Characterization: Characterizing Physical Properties of Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles in Liquid Phase Using Brownian Relaxation (Small 22/2017)
- First Published: 07 June 2017

The nonlinear magnetic response of SPIONs to magnetic fields induces harmonic signals that contain information of these nanoparticles. In article number 1604135, Jian-Ping Wang and co-workers, report using the phase lag and harmonic ratios in the SPIONs to analyze the saturation magnetization, average hydrodynamic size, the dominating relaxation processes of SPIONs, and the distinction between single- and multi-core particles.
Masthead
Contents
Communications
Highly Efficient Carbon Dioxide Hydrogenation to Methanol Catalyzed by Zigzag Platinum–Cobalt Nanowires
- First Published: 18 April 2017
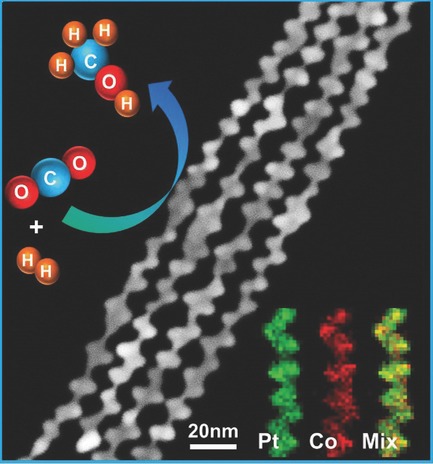
Efficient carbon dioxide (CO2) hydrogenation catalyst: Zigzag Pt–Co nanowires with Pt-rich surface, abundant steps/edges, and high percentages of Pt0 atoms on surface are demonstrated as highly efficient catalysts for CO2 hydrogenation to methanol, in which the appropriate carboxylate intermediates are formed in the methanol production.
Selective Nucleation of GaAs on Si Nanofacets
- First Published: 24 April 2017
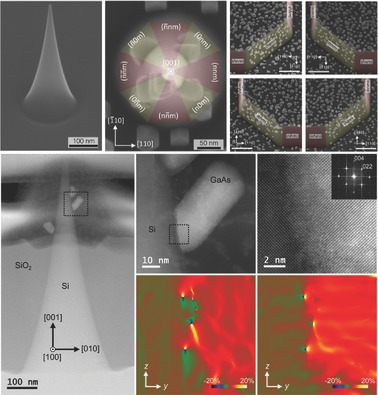
GaAs on Si nanoheteroepitaxy based on a novel Si nanotip wafer is presented. These structures present a curved and smooth morphology composed of {0nm}- and {nnm}-facets. The early stage of the growth reveals a preferential nucleation on the {0nm} micro and nanofacets, which may have an impact on future electronic and photonic devices.
Advanced SERS Sensor Based on Capillarity-Assisted Preconcentration through Gold Nanoparticle-Decorated Porous Nanorods
- First Published: 25 April 2017
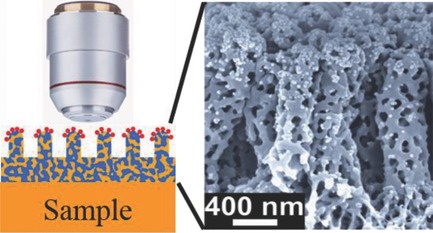
Advanced surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) sensors composed of arrays of porous block copolymer nanorods functionalized with gold nanoparticles are developed for SERS analysis of analytes contained in small pieces of tissue, liquid drops or thin liquid films. The sensor is based on capillarity-assisted preconcentration allowing fast, sensitive SERS detection.
Cobalt Phosphide Double-Shelled Nanocages: Broadband Light-Harvesting Nanostructures for Efficient Photothermal Therapy and Self-Powered Photoelectrochemical Biosensing
- First Published: 26 April 2017
A Phase-Separation Route to Synthesize Porous CNTs with Excellent Stability for Na+ Storage
- First Published: 20 March 2017
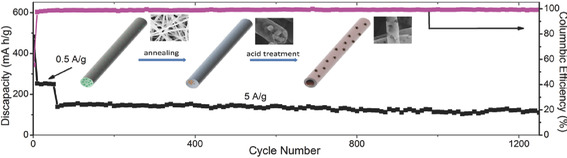
Porous carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are obtained by removing MoO2 nanoparticles from MoO2@C core@shell nanofibers which are synthesized by phase-segregation via a single-needle electrospinning method. As anodes for sodium-ion batteries, the porous CNT electrode displays excellent rate performance and cycling stability, which exhibites 110 mA h g−1 after 1200 cycles at 5 A g−1.
Full Papers
Characterizing Physical Properties of Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles in Liquid Phase Using Brownian Relaxation
- First Published: 04 April 2017
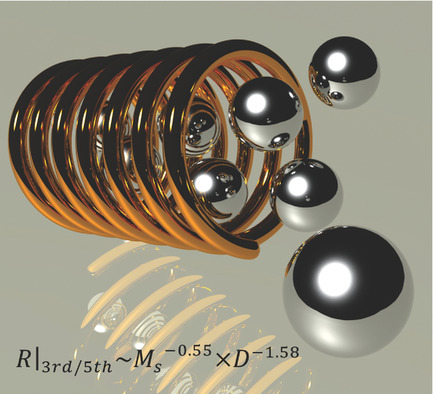
A search-coil-based method is successfully applied to characterize intrinsic properties in superparamagnetic nanoparticles such as saturation magnetization, average hydrodynamic size, dominating relaxation process, and to distinguish between single- and multicore beads. This system and method can be used as building blocks in nanoparticle characterization devices.
Centering Single Cells in Microgels via Delayed Crosslinking Supports Long-Term 3D Culture by Preventing Cell Escape
- First Published: 28 April 2017
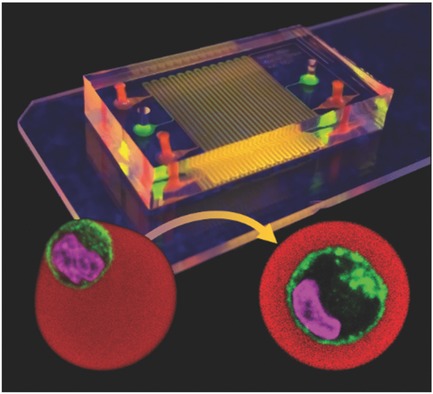
Single-cell-laden microgels support physiological 3D culture conditions while enabling straightforward handling and high-resolution readouts of individual cells. However, state-of-the-art encapsulation strategies suffer from cell escape due to off-center cell encapsulation. Here, the first microfluidic approach that enables long-term 3D single cell culture by centering cells in microgels in a facile, modular, and widely applicable manner is presented.
Amino-Acid-Induced Preferential Orientation of Perovskite Crystals for Enhancing Interfacial Charge Transfer and Photovoltaic Performance
- First Published: 12 April 2017
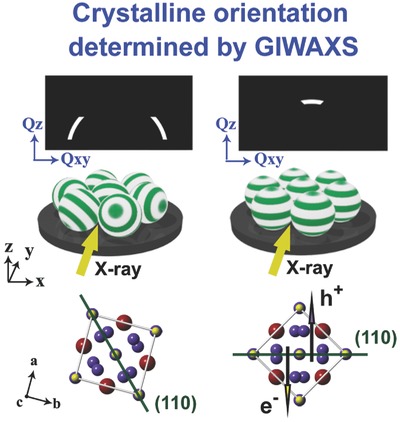
The (110) plane of CH3NH3PbI3 crystallites adjacent to the amino-acid-modified TiO2 surface tends to align in the direciton perpendicular to the TiO2 surface. Such crystalline orientation significantly enhances charge transfer efficiency at the TiO2/CH3NH3PbI3 interface and greatly improves the photovotaic performance of perovskite solar cells.
A Multifunctional Tb-MOF for Highly Discriminative Sensing of Eu3+/Dy3+ and as a Catalyst Support of Ag Nanoparticles
- First Published: 18 April 2017
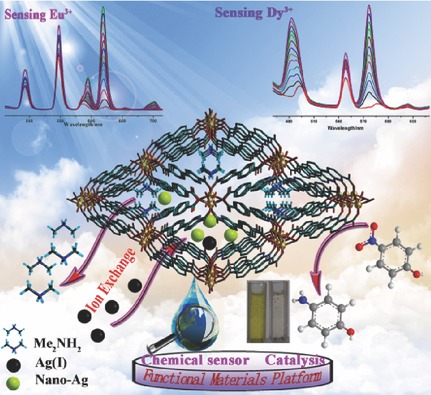
A new porous, anionic Tb-metal–organic-framework, China Three Gorges University (CTGU-1), can serve as a turn-on sensor for detection of Eu3+ and Dy3+, with different detection limits. Additionally, spontaneous in situ reduction and immobilization of ion-exchanged Ag(I) to Ag nanoparticles in the anionic framework result in an Ag@CTGU-1 composite, which can remarkably catalyze the reduction of 4-nitrophenol.
Vertically Oriented Graphene Nanoribbon Fibers for High-Volumetric Energy Density All-Solid-State Asymmetric Supercapacitors
- First Published: 18 April 2017
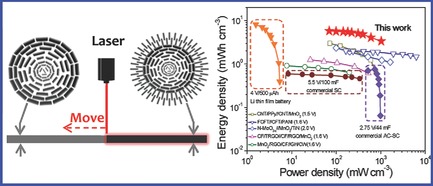
Vertically oriented graphene nanoribbon fiber (VGR) with highly exposed surface area displays high length/volumetric specific capacitances, excellent rate capability, and outstanding cycling performance (≈96% capacitance retention after 10 000 cycles). Moreover, the assembled VGR//VGR/MnO2 all-solid-state asymmetric supercapacitor exhibits high volumetric energy density of 5.7 mWh cm−3 and excellent cycling stability.
Novel Structure for High Performance UV Photodetector Based on BiOCl/ZnO Hybrid Film
- First Published: 18 April 2017
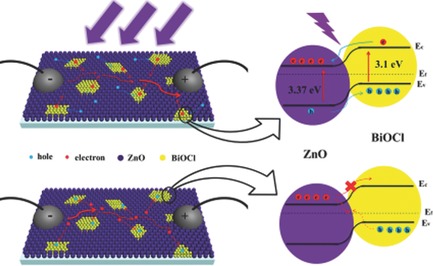
A novel structure ultraviolet photodetector based on a ZnO film is prepared by incorporating a BiOCl nanostructure into the film, which has high responsivity and short decay time. The BiOCl nanostructure not only provides electrons to enhance the photocurrent, but also forms barriers to accelerate the attenuation process of the current after the UV light is turned off.
Lipid Flip-Flop and Pore Nucleation on Zwitterionic Bilayers are Asymmetric under Ionic Imbalance
- First Published: 20 April 2017
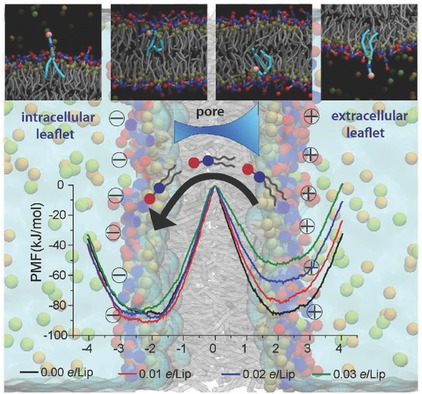
Ionic imbalance across cell membranes affects the energy barrier of lipid flip-flop, imposing a directionality on the translocation of lipids between bilayer leaflets. The asymmetry indicates that lipid accumulates at the cytoplasmic side of the cell membrane under physiological conditions. The linear reduction of the energy barrier of lipid flip-flop explains the observed increase in conductance of bilayers under external voltage.
Efficiency of Cathodoluminescence Emission by Nitrogen-Vacancy Color Centers in Nanodiamonds
- First Published: 18 April 2017
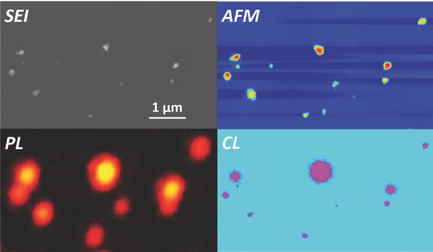
The cathodoluminescence (CL) emission properties of nanodiamonds containing nitrogen-vacancy centers are investigated. Coregistered images of nanodiamonds obtained by secondary electron imaging, atomic force microscopy, photoluminescence, and cathodoluminescence, enable precise characterization of CL intensity as a function of nanodiamond size and doping concentration, for applications in correlative microscopy.
Multichannel Porous TiO2 Hollow Nanofibers with Rich Oxygen Vacancies and High Grain Boundary Density Enabling Superior Sodium Storage Performance
- First Published: 18 April 2017
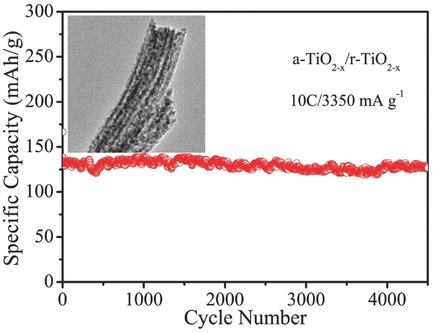
A 1D, multichannel, porous binary-phase anatase-TiO2–rutile-TiO2 composite with oxygen-deficient and high grain-boundary density (a-TiO2−x/r-TiO2−x) are fabricated via electrospinning and subsequent vacuum treatment. The introduction of numerous oxygen vacancies and the high density of grain boundaries between the anatase- and rutile-phase TiO2 are favorable for enhanced electrochemical performance with excellent long cycling stability and superior rate performance.
Hierarchical TiO2/SnO2 Hollow Spheres Coated with Graphitized Carbon for High-Performance Electrochemical Li-Ion Storage
- First Published: 18 April 2017
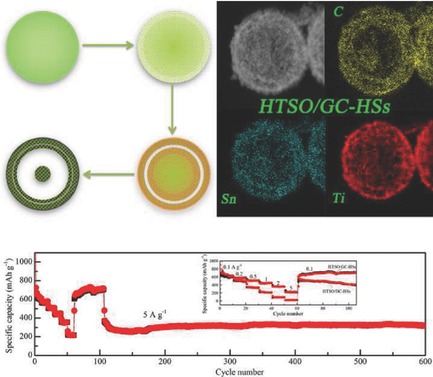
Hierarchical TiO2/SnO2 hollow spheres coated with graphitized carbon (HTSO/GC-HSs) are synthesized based on a self-templated method. The as-prepared mesoporous HTSO/GC-HSs present an approximate yolk-double–shell structure, with high specific area and small nanocrystals of TiO2 and SnO2, and thus exhibit superior electrochemical reactivity and stability when used as anode materials for Li-ion batteries.
Reprogrammable Assembly of Molecular Motor on Solid Surfaces via Dynamic Bonds
- First Published: 24 April 2017
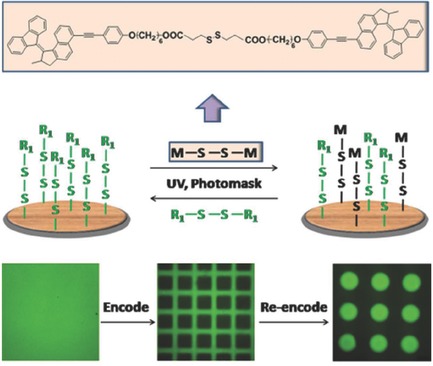
Dynamic disulfide bonds are introduced into the chemical structure of molecular motors and the surface of solid substrates so that molecular motors can reversibly and selectively assemble on solid surfaces regardless of their chemical compositions and microstructures, while maintaining photochemistry isomerization behavior. Due to the reversible photoinduced exchange reaction, molecular motors can be reformatted and reprogramed repeatedly on solid surfaces.
Biomass Derived N-Doped Porous Carbon Supported Single Fe Atoms as Superior Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction
- First Published: 25 April 2017
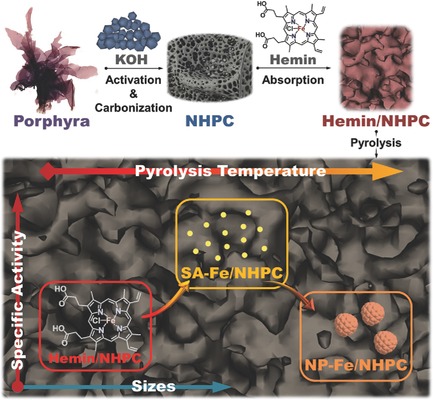
Single Fe atom electrocatalyst, derived from biomass resource of porphyra as the biocarbon source and hemin as the natural iron source, presents atomic dispersion of Fe atoms in the N-doped hierarchically porous carbon. The as-prepared electrocatalyst exhibits much higher catalytic activity, durability, and methanol-tolerance than the commercial Pt/C catalyst for oxygen reduction.
Coordinated Membrane Fusion of Proteinosomes by Contact-Induced Hydrogel Self-Healing
- First Published: 25 April 2017
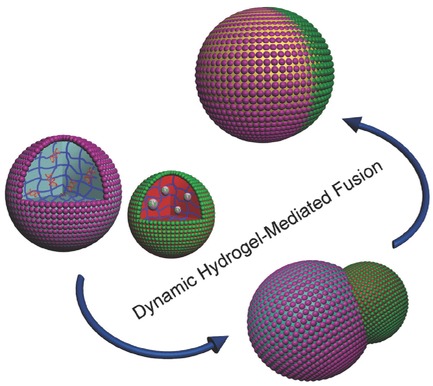
Proteinosome membrane fusion: Controlled membrane fusion of proteinosome-based protocells is achieved via a hydrogel-mediated process involving dynamic covalent binding, self-healing, and membrane reconfiguration at the contact interface, with a concomitant transportation and redistribution of entrapped payloads such as DNA and dextran.