Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Plasma Process. Polym. 4–5∕2017
- First Published: 25 April 2017
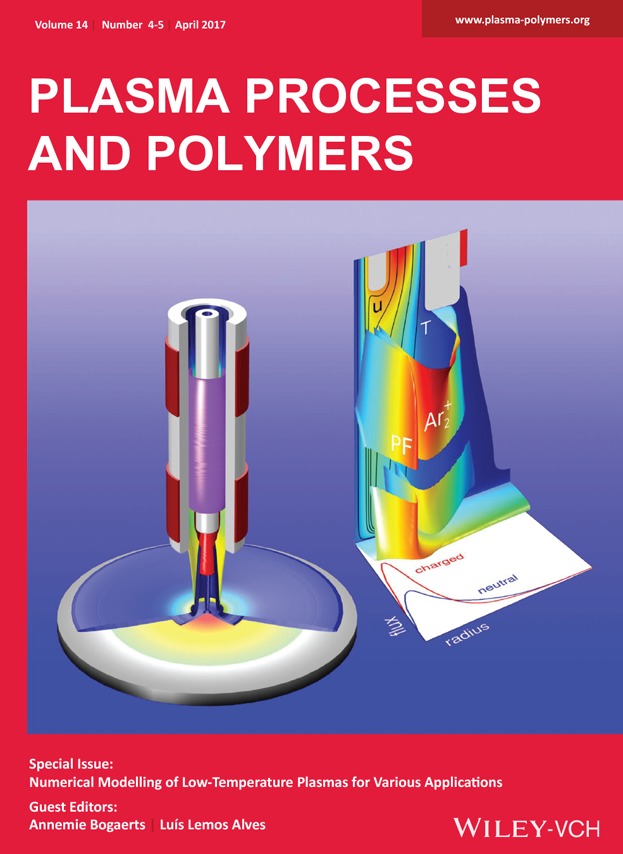
Front Cover: The gas flow, plasma generation and film deposition by a nonthermal plasma jet has been described using a fluid model. The figure illustrates the argon plasma between both electrodes, the charged (red) and neutral (blue) precursor fragments in the effluent and the gas flow. The densities of neutral precursor fragments (PF) and molecular argon ions as well as the flux of fragments to the substrate are shown at the right side. Further details can be found in the article by F. Sigeneger et al. at 1600112.
Issue Information
Back Cover
Back Cover: Plasma Process. Polym. 4–5∕2017
- First Published: 25 April 2017
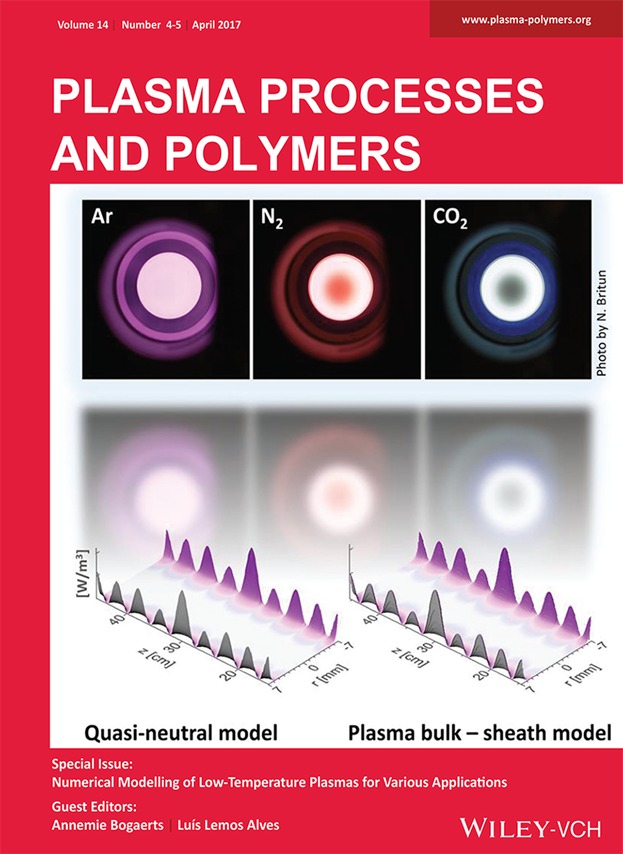
Back Cover: Cross-sectional view of a microwave plasma column at a pressure of 933 Pa. The Ar, N2 or CO2 plasma is sustained by a surfaguide launcher. Modeling shows that the power is deposited along the plasma-dielectric boundary (the tube wall), where the surface wave propagates. This paper presents and benchmarks two 2-dimensional models (quasi-neutral and plasma bulk-sheath, both accounting for the gas flow) for Ar microwave plasma and compares the results with the experiment. Further details can be found in the article by V. Georgieva et al. at 1600185.
Editorial
Full Papers
Ion Energy and Angular Distribution in Biased Inductively Coupled Ar/O2 Discharges by Using a Hybrid Model
- First Published: 03 March 2017
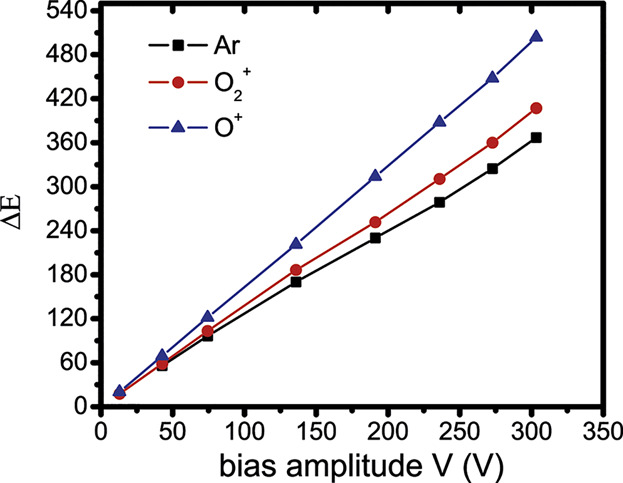
Inductively coupled plasma (ICP) has played critical roles for etching, depositing, and materials surface modification etc. In this work, we extend the previous hybrid model used for electropositive argon discharge to electronegative argon/oxygen discharge. This model could quickly estimate all kinds of species densities in the bulk plasma, ion energy, and angular distribution on the biased electrode.
Multiscale Modeling of Low Pressure Plasma Etching Processes: Linking the Operating Parameters of the Plasma Reactor with Surface Roughness Evolution
- First Published: 28 October 2016

Plasma etching in low pressure reactors has been shown to “induce” surface roughness on polymeric substrates and thus affecting, e.g., the wetting properties of the surface or the surface – cell interactions. Aiming to process recipes delivering desired surface roughness, a multiscale modeling framework, linking the operating parameters of the plasma reactor with the evolution of surface roughness of the etched substrate, is developed.
Comparison of Helical and Helicon Antennas as Sources of Plasma Excitation Using a Full Wave 3D Electromagnetic Analysis in Vacuum
- First Published: 30 September 2016
Observations of Surface Mode Influence on Plasma Uniformity in PIC/MCC Simulations of Large Capacitive Discharges
- First Published: 28 September 2016
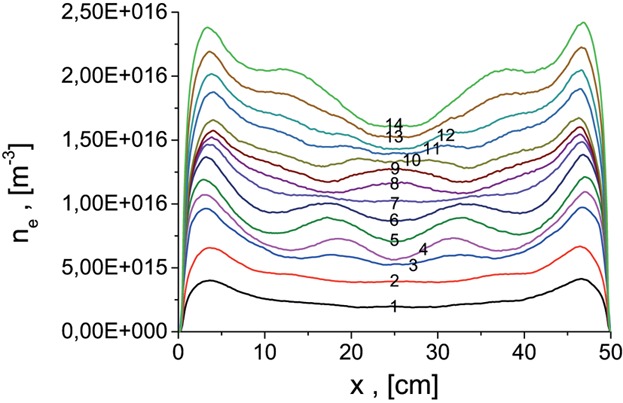
2D electrostatic PIC simulations of a large CCP discharge demonstrate non-uniformities in plasma density profile. A suggested explanation is based on excitation of surface modes, for which a new physics-based terminology is suggested. The surface mode studied in the present work interacts differently with low-energy and high-energy electrons.
Modeling of Single and Dual Frequency Capacitive Discharge in Argon Hydrogen Mixture − Dynamic Effects and Ion Energy Distribution Functions
- First Published: 26 September 2016
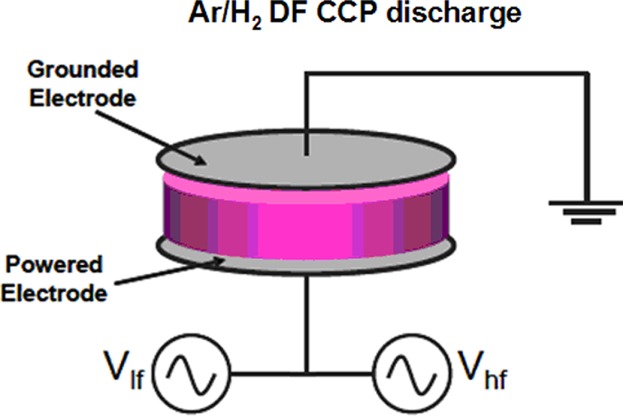
The single and dual frequency capacitively coupled plasma discharges in argon hydrogen mixtures are studied numerically with Particle-in-cell with Monte Carlo Collision method. In single frequency 81 MHz discharge the effect of hydrogen addition from 1 to 50% is shown. In dual frequency 1.76–81 MHz discharge the effect of low-frequency voltage is studied for 20 and 100 mTorr.
A Simple Model for Ion Flux-Energy Distribution Functions in Capacitively Coupled Radio-Frequency Plasmas Driven by Arbitrary Voltage Waveforms
- First Published: 28 October 2016
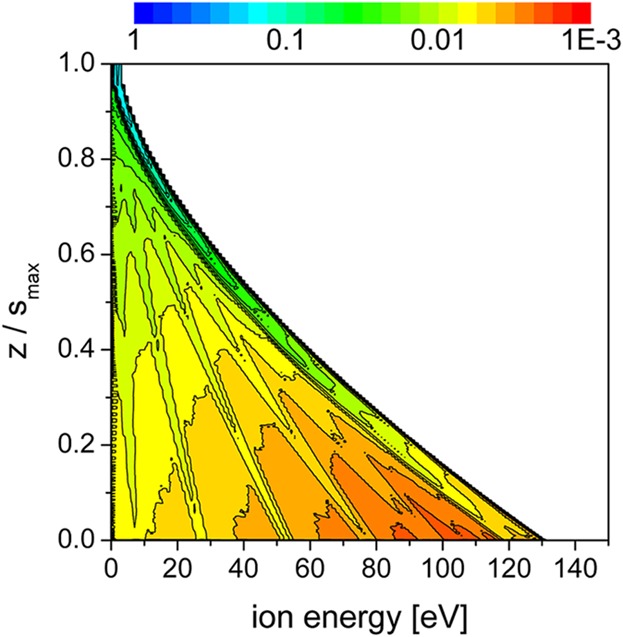
The bombardment by energetic ions plays a key role in surface processing applications of capacitive discharges. We study the complex ion dynamics and the formation of the ion flux-energy distribution function (IFEDF) in the radio-frequency sheath. A simple model is introduced, which allows for the calculation of the IFEDF at various gas pressures, and voltage waveforms. It is validated in comparisons with PIC/MCC simulation results and measurements.
Chemical Kinetics and Reactive Species in Normal Saline Activated by a Surface Air Discharge
- First Published: 05 October 2016
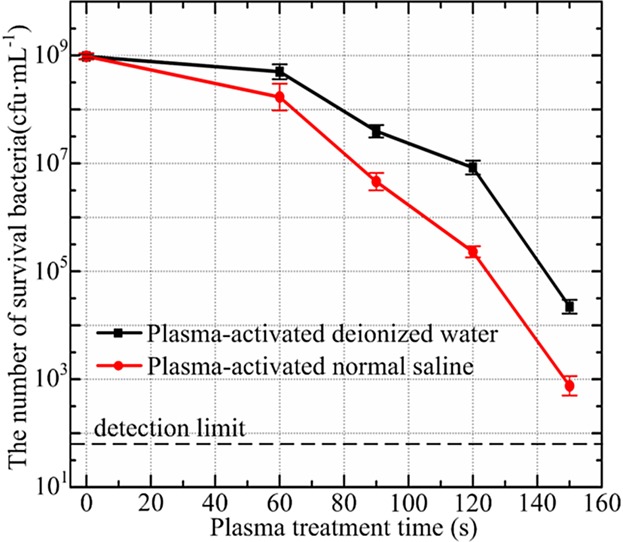
Plasma-activated normal saline is found to have a stronger bactericidal effect than the plasma-activated deionized water, which may be attributed to the production of reactive chlorine/oxy-chlorine species especially for HClO. A model is developed for the interaction between surface air plasmas and normal saline, from which the chemical profile of reactive chlorine/oxy-chlorine species is provided.
A Comprehensive Chemical Model for the Splitting of CO2 in Non-Equilibrium Plasmas
- First Published: 17 October 2016

A graphical overview of the complex CO2 chemistry, including the vibrational modes, which is implemented in the global models of Plasimo and ZDPlasKin. The reaction data set is obtained from literature and reviewed rigorously. The Plasimo compatible model, including the chemistry, is made available via the Plasimo (http://plasimo.phys.tue.nl/resources/index.html) and the publishers websites.
Influence of Gap Size and Dielectric Constant of the Packing Material on the Plasma Behaviour in a Packed Bed DBD Reactor: A Fluid Modelling Study
- First Published: 19 September 2016
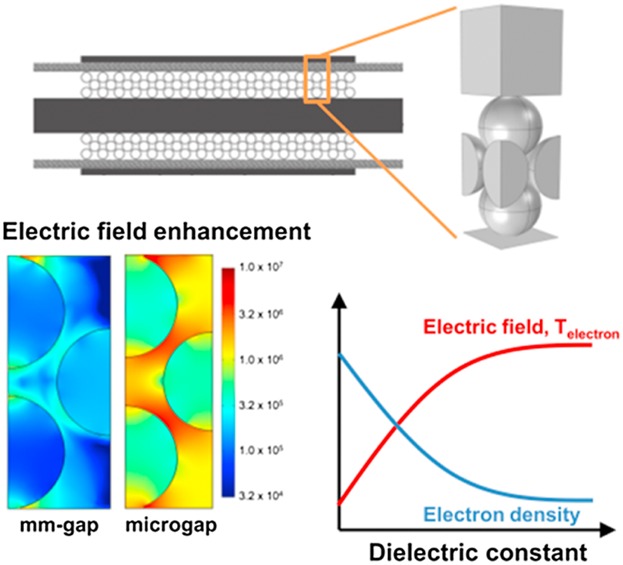
By reducing the size of the gap or by increasing the dielectric constant of the packing, the electric field in the dielectric barrier discharge reactor is significantly enhanced. The electron temperature also increases, but the electron density drops, which can have a negative effect on the rate of CO2 dissociation.
Quasi-Neutral Modeling of Gliding Arc Plasmas
- First Published: 04 October 2016

A gliding arc discharge (GAD) is studied by means of a quasineutral (QN) fluid plasma model. The model reliability is first evaluated against a more elaborate non-quasineutral discharge model at atmospheric pressure in argon. Subsequently, the QN approach is applied for a reverse vortex flow GAD in argon and a GAD in CO2.
Understanding Microwave Surface-Wave Sustained Plasmas at Intermediate Pressure by 2D Modeling and Experiments
- First Published: 17 November 2016
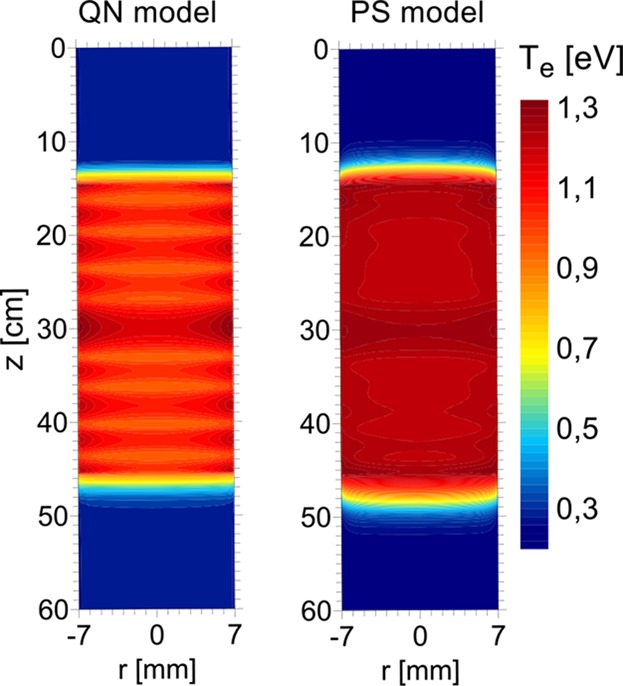
A surface-wave sustained Ar plasma is investigated at intermediate pressure (200–2667 Pa). Two 2D self-consistent models, a quasi-neutral (QN) and a plasma bulk-sheath (PS) model, are developed and benchmarked. The pressure range is extended down to 80 Pa by optical emission spectroscopy (OES) measurements. Comparison with experimental plasma characteristics available from literature for similar operating conditions is also shown and discussed.
Modeling of a Microwave Plasma Driven Biomass Pyrolitic Conversion for Energy Production
- First Published: 17 October 2016
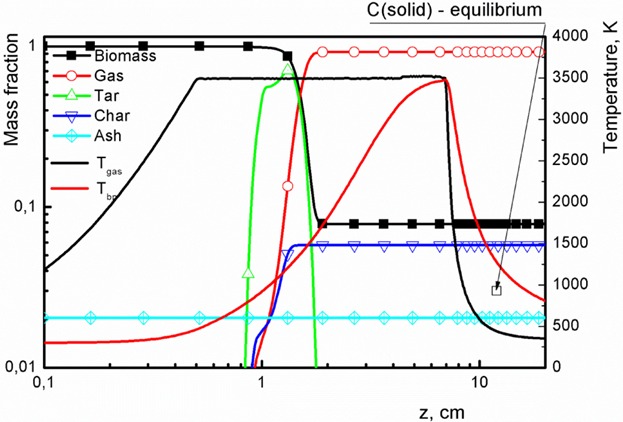
The thermal decomposition of biomass particles in a microwave plasma operating at atmospheric pressure conditions is theoretically investigated. The equilibrium approach provides detailed chemical composition of the final products (CO, CO2, and H2), while the non-equilibrium presents the evolution of the pyrolysis process. A correlation between the two approaches is found.
Computing Different Modes on Cathodes of DC Glow and High-Pressure Arc Discharges: Time-Dependent Versus Stationary Solvers
- First Published: 04 November 2016
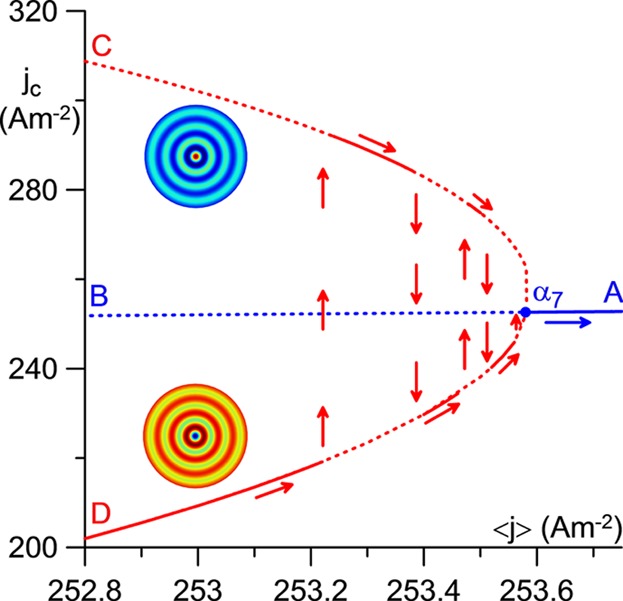
It is shown in this work that time-dependent solvers may fail to deliver essential information when used in the modeling of DC gas discharges, particularly in the presence of complex behavior and/or multiple modes of current transfer to the cathode. Results of time-dependent modeling of complex behavior and different modes of are shown to be at best incomplete. In extreme situations, time-dependent solvers may produce patchy pictures of the pattern of different modes. In most cases numerical stability of time-dependent solvers was found to be not equivalent to physical stability.
A Simulative and Experimental Approach for the Design and Optimization of Atmospheric Pressure Low Power RF Thermal Plasma Processes
- First Published: 20 December 2016
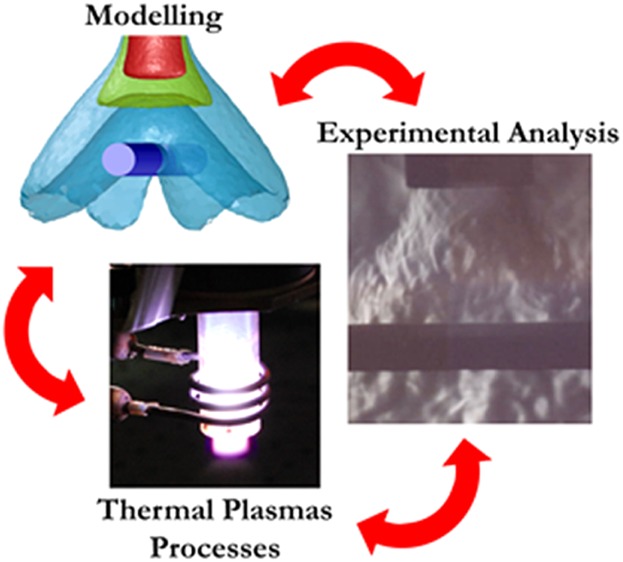
A simulative and experimental approach for the design of processes assisted by atmospheric pressure low power Radio Frequency thermal plasma is presented. A comparison is made between data obtained from diagnostic techniques and simulations in order to characterize the behavior of the effluent of the plasma torch for different operating conditions in a free flow regime or impinging on a substrate.
Modeling of a Non-Thermal RF Plasma Jet at Atmospheric Pressure
- First Published: 07 November 2016
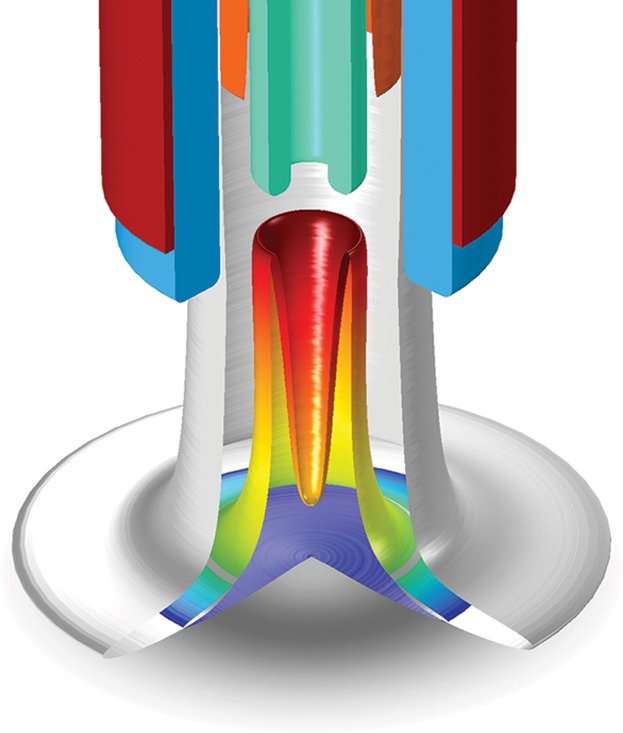
The spatially two-dimensional hydrodynamic model of the plasma jet describes the gas flow and heating, the plasma generation in the active zone, reactions of active plasma particles with precursor molecules in the effluent and the transport of precursor fragments toward the substrate. The impact of flow conditions on the radial profiles of precursor fragments is analyzed.
Modeling of Streamer Dynamics in Atmospheric-Pressure Air Plasma Jets
- First Published: 09 August 2016
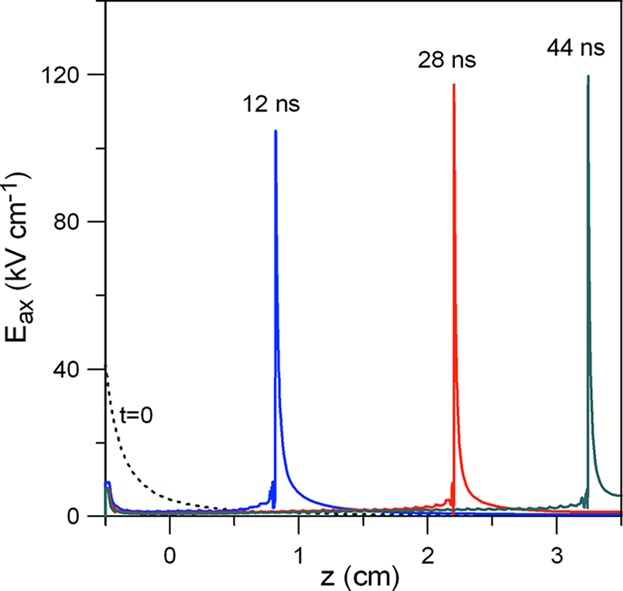
Computational study of atmospheric-pressure air plasma jets formed by pulsed discharges in thin dielectric tubes is performed. The parameters of non-thermal plasma produced by streamers propagating along spatially non-uniform gas density regions inside the jets are evaluated. The profiles of calculated densities of produced oxygen and nitrogen atoms are presented.
Hybrid and Fluid Modeling of Ion Activation Energy and Reactive Fluxes to Particulates Suspended in Air and Residing on Surfaces
- First Published: 22 September 2016
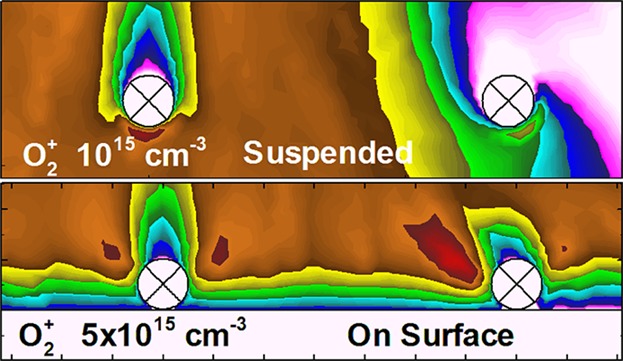
Intersection of plasma filaments with small particulates-bacteria suspended in air or residing on surfaces results in different scenario of their surface treatment. The particulates residing on the substrate can be partially or totally immersed in the sheath formed beneath the filament and the substrate. Ion energies and fluxes to particulates are determined by the sheath properties and the dielectric constant of the substrate.
A Comparison of Continuum and Kinetic Simulations of Moderate pd Microplasmas Integrated With High Secondary Yield Cathodes
- First Published: 16 September 2016
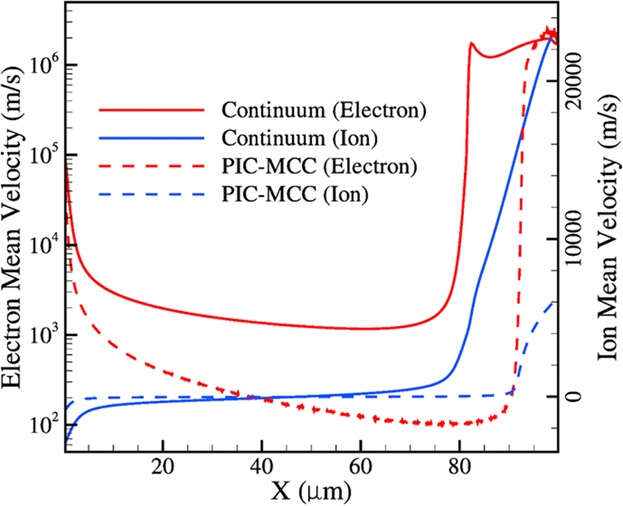
Continuum and kinetic simulations of low-temperature moderate pd microplasmas driven by cathodes with high secondary emission are compared and contrasted with each other. One-dimensional simulations of a 100 μm argon microplasma performed using the momentum equation for both ions and electrons are compared with particle-in-cell with Monte Carlo collision simulations. The discrepancies between the results obtained from the two methods are highlighted.
Calculation of Electron-Scattering Cross Sections Relevant for Hypersonic Plasma Modeling
- First Published: 19 August 2016