Observations of Surface Mode Influence on Plasma Uniformity in PIC/MCC Simulations of Large Capacitive Discharges
Corresponding Author
Denis Eremin
Institute of Theoretical Electrotechnics, Ruhr University Bochum, Universitaetsstrasse 150, Bochum, D-44801 Germany
Search for more papers by this authorRalf Peter Brinkmann
Institute of Theoretical Electrotechnics, Ruhr University Bochum, Universitaetsstrasse 150, Bochum, D-44801 Germany
Search for more papers by this authorThomas Mussenbrock
Institute of Theoretical Electrotechnics, Ruhr University Bochum, Universitaetsstrasse 150, Bochum, D-44801 Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Denis Eremin
Institute of Theoretical Electrotechnics, Ruhr University Bochum, Universitaetsstrasse 150, Bochum, D-44801 Germany
Search for more papers by this authorRalf Peter Brinkmann
Institute of Theoretical Electrotechnics, Ruhr University Bochum, Universitaetsstrasse 150, Bochum, D-44801 Germany
Search for more papers by this authorThomas Mussenbrock
Institute of Theoretical Electrotechnics, Ruhr University Bochum, Universitaetsstrasse 150, Bochum, D-44801 Germany
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
Capacitively coupled plasmas with large electrodes, driven at high frequencies, exhibit new physics compared to small scale CCP devices or at low frequencies. This is due to excitation of two types of surface modes which arise as a result of interaction between the bulk plasma and the plasma sheaths separating the plasma from electrodes. Based on the physical effects that these modes cause, they are labeled as “self-bias” (SB) and “plasma-series resonance” (PSR) modes. Results of electrostatic 2d3v PIC/MCC simulations for a model geometry are used to selectively study the SB modes and demonstrate that they lead to non-uniformities of the plasma density profile owing to the influence of the SB modes on the heating of high- and low-energy electrons.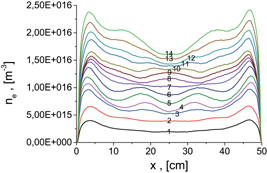
References
- 1 A. Perret, P. Chabert, J. -P. Booth, J. Jolly, J. Guillon, Ph. Auvray, Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 243.
- 2 J. E. Stevens, M. J. Sowa, J. L. Cecchi, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1996, 14, 0734.
- 3 J. Schmitt, M. Elyaakoubi, L. Sansonnens, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2002, 11, A206.
- 4 M. A. Lieberman, J. P. Booth, P. Chabert, J. M. Rax, M. M. Turner, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2002, 11, 283.
- 5 L. Sansonnens, A. A. Howling, Ch. Hollenstein, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2006, 15, 302.
- 6 A. A. Howling, L. Sansonnens, Ch. Hollenstein, Thin Solid Films 2007, 515, 5059.
- 7 P. Chabert, J. Phys. D 2007, 40, R63.
- 8 Y. -X. Liu, Y. -R. Zhang, A. Bogaerts, Y. -N. Wang, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2015, 33, 020801.
- 9 I. Lee, M. A. Lieberman, D. B. Graves, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2008, 17, 015018.
- 10 Y. -R. Zhang, S. X. Zhao, A. Bogaerts, Y. -N. Wang, Phys. Plasmas 2010, 17, 113512.
- 11 S. Rauf, Z. Chen, K. Collins, J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 093302.
- 12 Y. Yang, M. J. Kushner, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2010, 19, 055011.
- 13 D. Eremin, T. Hemke, R. P. Brinkmann, T. Mussenbrock, J. Phys. D 2013, 46, 084017.
- 14 E. Kawamura, M. A. Lieberman, D. B. Graves, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2014, 23, 064003.
- 15 G. A. Hebner, E. V. Barnat, P. A. Miller, A. M. Paterson, J. P. Holland, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2006, 15, 879.
- 16 I. Sawada, P. L. G. Ventzek, B. Lane, T. Ohshita, R. R. Upadhyay, L. L. Raja, Japan. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 53, 03DB01.
- 17 M. A. Lieberman, A. J. Lichtenberg, E. Kawamura, A. M. Marakhtanov, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2015, 24, 055011.
- 18 M. A. Lieberman, A. J. Lichtenberg, E. Kawamura, P. Chabert, Phys. Plasmas 2016, 23, 013501.
- 19 D. Eremin, S. Bienholz, D. Szeremley, J. Trieschmann, S. Ries, P. Awakowicz, T. Mussenbrock, R. P. Brinkmann, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2016, 25, 025020.
- 20 C. K. Birdsall, A. B. Langdon, “ Plasma Physics via Computer Simulation,” McGraw-Hill, New York 2005.
- 21
R. W. Hockney,
J. W. Eastwood, “
Computer Simulation Using Particles,”
Taylor & Francis, Inc,
Bristol, UK
1988.
10.1887/0852743920 Google Scholar
- 22
Y. N. Grigoryev,
V. A. Vshivkov,
M. P. Fedoruk, “
Numerical Particle-in-Cell Methods: Theory and Applications,”
Walter de Gruyter Inc,
Boston
2002.
10.1515/9783110916706 Google Scholar
- 23 Bowers, K.J., High Frequency Electron Resonances and Surface Waves in Unmagnetized Bounded Plasmas, Ph.D. thesis, UC Berkeley, 2001.
- 24
X. Q. Xu,
G. DiPeso,
V. Vahedi,
C. K. Birdsall, “
Theory and simulation of plasma sheath waves,” Memorandum UCB/ERL M92/148,
University of California at Berkeley Electronics Research Lab,
Berkeley, CA
1992.
10.2172/10186872 Google Scholar
- 25 D. J. Cooperberg, Phys. Plasmas 1998, 5, 853.
- 26 T. Mussenbrock, T. Hemke, D. Ziegler, R. P. Brinkmann, M. Klick, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2008, 17, 025018.
- 27 A. A. Howling, L. Sansonnens, J. Ballutaud, Ch. Hollenstein, J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 96, 5429.
- 28 D. Eremin, T. Hemke, T. Mussenbrock, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2016, 25, 015009.
- 29 A. V. Phelps, Z. Lj. Petrovic, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 1999, 8, R21.
- 30 A. V. Phelps, J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 76, 747.
- 31
M. A. Lieberman,
A. J. Lichtenberg, “
Principles of Plasma Discharges and Materials Processing,” 2nd edition,
Wiley,
New York
2005.
10.1002/0471724254 Google Scholar
- 32 J. V. Parker, J. C. Nickel, R. W. Gould, Phys. Fluids 1964, 7, 1489.