Modeling of a Microwave Plasma Driven Biomass Pyrolitic Conversion for Energy Production
Dmitry L. Tsyganov
Brest State Technical University, Moskovskaya 267, 224017 Brest, Belarus
Search for more papers by this authorNeli Bundaleska
Instituto de Plasmas e Fusão Nuclear, Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, 1049-001 Lisbon, Portugal
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Elena Tatarova
Instituto de Plasmas e Fusão Nuclear, Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, 1049-001 Lisbon, Portugal
Search for more papers by this authorDmitry L. Tsyganov
Brest State Technical University, Moskovskaya 267, 224017 Brest, Belarus
Search for more papers by this authorNeli Bundaleska
Instituto de Plasmas e Fusão Nuclear, Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, 1049-001 Lisbon, Portugal
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Elena Tatarova
Instituto de Plasmas e Fusão Nuclear, Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, 1049-001 Lisbon, Portugal
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
The thermal decomposition of biomass particles in a microwave plasma operating at atmospheric pressure conditions has been theoretically investigated. The set of equations, including thermal balance equations for the gas and biomass particles and kinetic rate balance equations for stable and intermediate components of biomass decomposition was solved for two different assumptions: thermal equilibrium and non-equilibrium. The thermal equilibrium assumption is acceptable given the high temperature and high reaction rates achievable in the microwave plasma environment, and although it hides the evolution of the pyrolysis process, it allows the description of the detailed chemical composition of the stable pyrolysis by-products (H2, CO, C2H2, and C [solid]).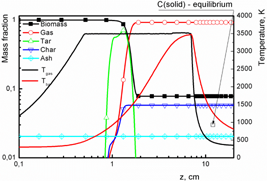
References
- 1 E. Tatarova, N. Bundaleska, J. Ph. Sarrette, C. M. Ferreira, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2014, 23, 063002.
- 2
A. V. Bridgwater,
Thermal Sci.
2004,
8, 21.
10.2298/TSCI0402021B Google Scholar
- 3 D. Mohan, C. U. Pittman, Jr., P. H. Steele, Energy Fuels 2006, 20, 848.
- 4 N. Prakash, T. Karunanithi, J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2008, 4, 1627.
- 5 T. Paulmier, L. Fulcheri, Chem. Eng. J. 2005, 106, 59.
- 6 L. Zhang, C. Ch. Xu, P. Champagne, Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 969.
- 7 B. Peters, C. Bruch, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2003, 70, 233.
- 8 F. Thurner, U. Mann, Ind. Eng. Chem. Proc. Design Dev. 1981, 20, 482.
- 9 S. Alves, J. L. Figueiredo, Chem. Eng. Sci. 1989, 44, 2861.
- 10
F. Shafizadeh,
P. P. S. Chin,
ACS Symp. Ser.
1977, 57.
10.1021/bk-1977-0043.ch005 Google Scholar
- 11 W. R. Chan, M. Kelbon, B. B. Krieger, Fuel 1985, 64, 1505.
- 12 R. Font, A. Marcilla, E. Verdu, J. Devesa, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1990, 29, 846.
- 13 C. Di Blasi, G. Russo, “ Modeling of Transport Phenomena and Kinetics of Biomass Pyrolysis”, in Advances in Thermochemical Biomass Conversion. Vol. 2, A. V. Bridgewater, Ed., Blackie Academic and Professional, Londres 1994, p. 906.
- 14 B. Carmen, C. Di Blasi, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2003, 67, 207.
- 15 B. Carmen, A. Albano, C. Di Blasi, Thermochim. Acta 2005, 429, 133.
- 16 G. Najla, K. Halouani, A. Zoulalian, F. Halouani, Thermochim. Acta 2006, 440, 23.
- 17 D. Tsyganov, N. Bundaleska, E. Tatarova, C. M. Ferreira, Int. J. Hydr. Energy 2013, 38, 14512.
- 18 N. Bundaleska, D. Tsyganov, E. Tatarova, F. M. Dias, C. M. Ferreira, Int. J. Hydr. Energy 2014, 39, 5663.
- 19 N. Bundaleska, D. Tsyganov, R. Saavedra, E. Tatarova, F. M. Dias, C. M. Ferreira, Int. J. Hydr. Energy 2013, 38, 145.
- 20 W. Bizzo, P. C. Lenço, D. J. Carvalho, J. P. S. Veiga, Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2014, 29, 589.
- 21 H. Yang, R. Yan, H. Chen, D. Ho Lee, C. Zheng, Fuel 2007, 86, 1781.
- 22 M. W. van de Weerdhof, J. A. van Oijen, 2010, Modeling the pyrolysis process of biomass particles (Master Thesis, WVT, No. 2010.07). Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, 72 pp.
- 23 L. Canilha, A. K. Chandel, T. S. dos Santos Milessi, F. A. F. Antunes, W. L. C. Freitas, M. G. A. Felipe, S. S. Silva, J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, Article ID 989572 2012, 15.
- 24 J. A. Souza-Correa, C. Oliveira, L. D. Wolf, V. M. Nascimento, G. J. Rocha, J. Amorim, Appl. Biochem Biotechnol. 2013, 171, 104.
- 25NIST chemical kinetics database. http://kinetics.nist.gov
- 26 E. Goos, A. Burcat, B. Ruscic, Third millennium ideal gas and condensed phase thermochemical database for combustion. Haifa, Israel: Technion Aerospace Engineering (TAE); January 2001. Report #867, ftp://ftp.technion.ac.il/pub/supported/aetdd/thermodynamics (January 2005 update).
- 27Reaction design, chemkin thermochemical database. http://reactiondesign.com
- 28 R. S. Miller, J. Bellan, Sci. Tech. 1997, 126, 97.
- 29 C. Di Blasi, Biomass Bioenergy 1984, 7, 87.
- 30 S. M. Ward, J. Braslaw, Comb. Flame 1985, 61, 261.
- 31 C. A. Koufopans, G. Maschio, J. Chem. Eng. 1989, 67, 75.
- 32 D. Mohan, Ch. U. Pittman, P. H. Steele, Jr., Energy Fuels 2006, 20, 848.
- 33 B. V. Kantorovich, “ Osnovy Goreniia i Gazifikatcii Tverdogo Topliva (Fundamentals of the Theory of Combustion and Gasification of Solid Fuel.)”, Izd. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Moscow 1958, p. 600 [in Russian].
- 34 B. V. Kantorovich, “ Vvedenie v Teoriiu Goreniia i Gazifikatcii Tverdogo Topliva (Introduction to the Theory of Combustion and Gasification of Solid Fuels.)”, Metallurgizdat, Moskva 1960, p. 360 [in Russian].
- 35 N. Bundaleska, E. Tatarova, F. M. Dias, M. Lino da Silva, C. M. Ferreira, J. Amorim, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 47, 055201 (10pp).
- 36 A. P. Sokolskii, F. A. Timofeeva, Issledovanie Protcessov Goreniia Naturalnogo Topliva. (Investigation of Natural Fuel Combustion Processes). M.: Gosenergoizdat, 1958, p. 133 [in Russian].
- 37 N. Frössling, Lunds. Univ. Arsskr. N. F. Avd. 1940, 2, 35.
- 38 J. A. Souza-Corrêa, M. A. Ridenti, C. Oliveira, S. R. Araújo, J. Amorim, J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 21, 117.