A Comparison of Continuum and Kinetic Simulations of Moderate pd Microplasmas Integrated With High Secondary Yield Cathodes
Abhishek Kumar Verma
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of California Merced, 5200 N. Lake Rd., Merced, California, 95343 USA
Search for more papers by this authorArghavan Alamatsaz
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of California Merced, 5200 N. Lake Rd., Merced, California, 95343 USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ayyaswamy Venkattraman
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of California Merced, 5200 N. Lake Rd., Merced, California, 95343 USA
Search for more papers by this authorAbhishek Kumar Verma
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of California Merced, 5200 N. Lake Rd., Merced, California, 95343 USA
Search for more papers by this authorArghavan Alamatsaz
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of California Merced, 5200 N. Lake Rd., Merced, California, 95343 USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ayyaswamy Venkattraman
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of California Merced, 5200 N. Lake Rd., Merced, California, 95343 USA
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
The computational techniques commonly used for low-temperature plasma simulations are compared in the context of modeling microplasmas driven by cathodes with high secondary electron emission coefficient. Simulations of 100 µm argon microplasmas operating at pressures of 100 Torr and secondary electron emission coefficient of 0.1 are performed using particle-in-cell with Monte Carlo collisions (PIC-MCC), and fluid model using the full-momentum equations for both electrons and ions. Results obtained for plasma density, potential, electric field, and electron temperature using continuum simulations are compared with the PIC-MCC simulations as benchmark. The comparison demonstrates significant discrepancies and a need to calibrate continuum simulation parameters based on kinetic simulations.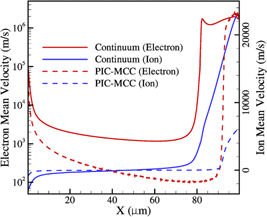
References
- 1 K. H. Schoenbach, K. Becker, Eur. Phys. J. D 2016, 70, 1.
- 2 K. H. Becker, K. H. Schoenbach, J. Phys. D 2006, 39, 55.
- 3 K. H. Becker, H. Kersten, J. Hopwood, J. L. Lopez, Eur. Phys. J. D 2010, 60, 437.
- 4 K. -F. Chen, J. G. Eden, Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 161501.
- 5 W. Yuan, F. K. Chowdhury, M. Tabib-Azar, in IEEE 25th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Paris, France 2012, 293.
- 6 P. Pai, M. Tabib-Azar, in IEEE 27th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), San Francisco, CA, USA 2014, 171.
- 7 P. Pai, M. Tabib-Azar, IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2014, 35, 593.
- 8 L. Lin, Q. Wang, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2015, 35, 925.
- 9 R. Wang, S. Zuo, D. Wu, J. Zhang, W. Zhu, K. H. Becker, J. Fang, Plasma Processes Polym. 2015, 12, 380.
- 10 D. Marriotti, R. M. Sankaran, J. Phys. D 2010, 43, 323001.
- 11 O. Sakai, T. Naito, T. Shimomura, K. Tachibana, Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 3444.
- 12 O. Sakai, K. Tachibana, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2012, 21, 013001.
- 13 T. Chang, S. Lou, H. Chen, C. Chen, C. Lee, N. Tai, I. Lin, Nanoscale 2013, 5, 7467.
- 14 H. C. Chen, I. -N. Lin, S. C. Lou, C. Chen, R. H. Tang, W. C. Shih, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 02B108.
- 15 S. Samukawa, M. Hori, S. Rauf, K. Tachibana, P. Bruggeman, G. Kroesen, J. C. Whitehead, A. B. Murphy, A. F. Gutsol, S. Starikovskaia, U. Kortshagen, J. -P. Boeuf, T. J. Sommerer, M. J. Kushner, U. Czarnetzki, N. Mason, J. Phys. D 2012, 45, 253001.
- 16 M. J. Kushner, J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 846.
- 17 M. J. Kushner, J. Phys. D 2005, 38, 1633.
- 18 Q. Wang, D. Economou, V. M. Donnelly, J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 023301.
- 19 C. K. Birdsall, IEEE T. Plasma Sci. 1991, 19, 65.
- 20 J. P. Verboncoeur, Plasma Phys. Contr. F. 2005, 47, A231.
- 21 Y. J. Hong, S. M. Lee, G. C. Kim, J. K. Lee, Plasma Processes Polym. 2008, 5, 583.
- 22 H. C. Kim, F. Iza, S. S. Yang, M. Radmilovic-Radjenovic, J. K. Lee, J. Phys. D 2005, 38, R283.
- 23 J. A. Rossmanith, D. C. Seal, J. Comput. Phys. 2011, 230, 6203.
- 24 G. J. Hagelaar, L. C. Pitchford, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2005, 14, 722.
- 25
C. K. Birdsall,
A. B. Langdon, “
Plasma Physics via Computer Simulation,”
CRC Press,
Boca Raton, FL, USA
2004.
10.1201/9781315275048 Google Scholar
- 26 V. Vahedi, M. Surendra, Comput. Phys. Comm. 1995, 87, 179.
- 27 J. P. Verboncoeur, M. V. Alves, V. Vahedi, J. Comput. Phys. 1993, 104, 321.
- 28 L. S. Frost, A. V. Phelps, Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, 1538.
- 29 K. Tachibana, A. V. Phelps, J. Chem. Phys. 1981, 75, 3315.
- 30 O. Zatsarinny, K. Bartschat, J. Phys. B 2004, 37, 4693.
- 31 L. C. Pitchford, L. L. Alves, K. Bartschat, S. F. Biagi, M. C. Bordage, A. V. Phelps, C. M. Ferreira, G. J. M. Hagelaar, W. L. Morgan, S. Panchesnyi, V. Puech, A. Stauffer, O. Zatsarinny, J. Phys. D 2013, 46, 334001.
- 32
R. Fitzpatrick, “
Plasma Physics: An Introduction,”
CRC Press,
Boca Raton, FL, USA
2014.
10.1201/b17263 Google Scholar
- 33 G. Chen, L. L. Raja, J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 96, 6073.
- 34 Q. Wang, D. J. Economou, V. M. Donnelly, J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 023301.
- 35 J. Gregorio, A. R. Hoskinson, J. Hopwood, J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 083305.