Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
Issue Information - Editorial Board and TOC
- Pages: 1961-1965
- First Published: 18 August 2022
REVIEW
Knee
Small laboratory animal models of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
- Pages: 1967-1980
- First Published: 11 June 2022
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Osteoarthritis
Transient neonatal shoulder paralysis causes early osteoarthritis in a mouse model
- Pages: 1981-1992
- First Published: 23 November 2021
Recovery of balance control in bilateral medial knee osteoarthritis after total knee arthroplasty during level walking
- Pages: 1993-2003
- First Published: 05 December 2021
Assessment of osteoarthritis functional outcomes and intra-articular injection volume in the rat anterior cruciate ligament transection model
- Pages: 2004-2014
- First Published: 07 January 2022
Knee
Intra-articular pressure characteristics of the knee joint: An exploratory study
- Pages: 2015-2024
- First Published: 11 December 2021
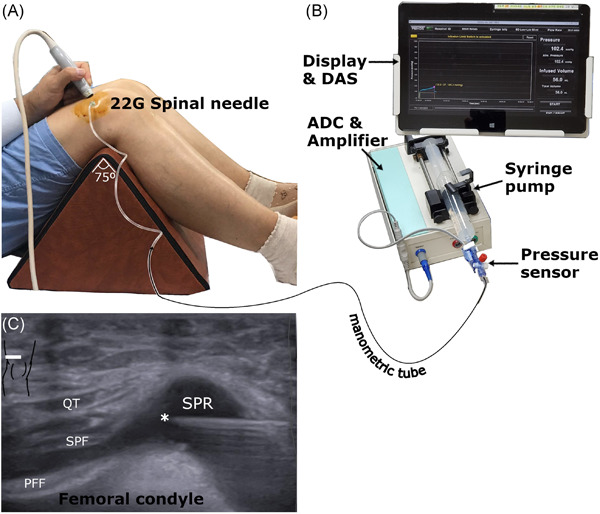
Knee osteoarthritis is a group of heterogeneous pathologies, but physical properties of stiffened synovia were less investigated. Intra-articular pressure changes according to volume infusion were investigated. Early synovial tension, high intra-articular pressure and stiffened synovium was observed in the presence of suprapatellar effusion or radiologically definite osteoarthritis. The development and consequences of stiffened synovia should be investigated further to elucidate their contributions to pain, disability, and disease progression, and in-clinic pressure monitoring could be utilized for its evaluation and treatment.
Knee joint biomechanics during gait improve from 3 to 6 months after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
- Pages: 2025-2038
- First Published: 06 January 2022
Bone
Experimental DVC validation of heterogeneous micro finite element models applied to subchondral trabecular bone of the humeral head
- Pages: 2039-2047
- First Published: 02 December 2021
Full-field experimental analysis of the influence of microstructural parameters on the mechanical properties of humeral head trabecular bone
- Pages: 2048-2056
- First Published: 15 December 2021
Investigation of distal femur microarchitecture and factors influencing its deterioration: An ex vivo high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography study
- Pages: 2057-2064
- First Published: 05 January 2022
Use of computer tomography imaging for analyzing bone remodeling around a percutaneous osseointegrated implant
- Pages: 2065-2075
- First Published: 15 December 2021
Tendon/Ligament
Structural and pathological changes in the enthesis are influenced by the muscle contraction type during exercise
- Pages: 2076-2088
- First Published: 04 December 2021
Spine
A bovine nucleus pulposus explant culture model
- Pages: 2089-2102
- First Published: 23 November 2021
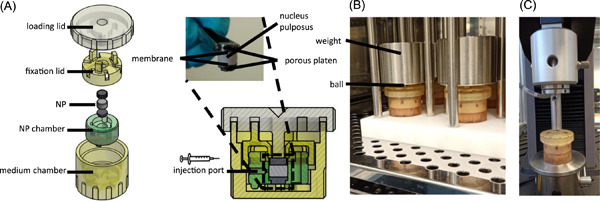
(A) A bovine nucleus pulposus (NP) explant bioreactor chamber. (B) In the volume controllable chamber, the NP tissue volume can be locked physically to an equilibrated pressure to prevent tissue swelling. Enzymes, biomaterials, and fluids containing cells or growth factors can be injected via the injection port. (C) Tissue can be measured biomechanically with a tensile tester.
Cartilage
Deformation behaviors and mechanical impairments of tissue cracks in immature and mature cartilages
- Pages: 2103-2112
- First Published: 16 December 2021
Hip
Prediction of femoral head coverage from articulated statistical shape models of patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip
- Pages: 2113-2126
- First Published: 23 November 2021
Femoral antetorsion after calcar-guided short-stem total hip arthroplasty: A cadaver study
- Pages: 2127-2132
- First Published: 06 December 2021
Ceramic-on-polyethylene hip arthroplasty reduces the risk of postoperative periprosthetic joint infection
- Pages: 2133-2138
- First Published: 23 November 2021
Influence of acetabular cup thickness on seating and primary stability in total hip arthroplasty
- Pages: 2139-2146
- First Published: 02 December 2021
Elevated loading at the posterior acetabular edge of dysplastic hips during double-legged squat
- Pages: 2147-2155
- First Published: 11 January 2022
Shoulder
Development of a framework to assess the biomechanical impact of reverse shoulder arthroplasty placement modifications
- Pages: 2156-2168
- First Published: 08 December 2021
Humeral short stem varus–valgus alignment affects bone stress
- Pages: 2169-2178
- First Published: 16 December 2021
The results of this study show that central positioning of a short stem humeral implant produces the smallest changes in bone stresses compared to the intact state and produces the smallest volume of bone expected to resorb due to stress shielding. If distal contact must occur, valgus malposition resulting in distal medial stem cortical contact may be worse than varus malposition resulting in distal lateral stem contact.
Musculoskeletal modeling-based definition of load cases and worst-case fracture orientation for the design of clavicle fixation plates
- Pages: 2179-2188
- First Published: 21 December 2021
Foot/Ankle
The stability of total talar prosthesis—How stable to dislocation? Cadaveric study
- Pages: 2189-2195
- First Published: 13 December 2021
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction alters the midfoot mechanics and energetics during gait
- Pages: 2196-2208
- First Published: 15 December 2021
The contribution of the ligaments in progressive collapsing foot deformity: A comprehensive computational study
- Pages: 2209-2221
- First Published: 03 January 2022