Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Titelbild
Editorial
Andreas Seidel-Morgenstern zum 60. Geburtstag
- Page: 1547
- First Published: 25 October 2016
Inhalt
Corrigendum
Model-Based Optimal Design of Continuous-Flow Reactors for the Synthesis of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
- Page: 1554
- First Published: 25 October 2016
Aus den Gesellschaften
Forum
Reviews
Sol-Gel and Porous Glass-Based Silica Monoliths with Hierarchical Pore Structure for Solid-Liquid Catalysis†
- Pages: 1561-1585
- First Published: 10 August 2016
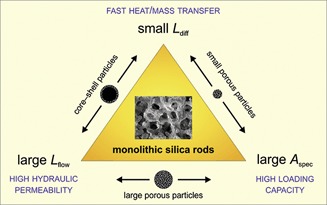
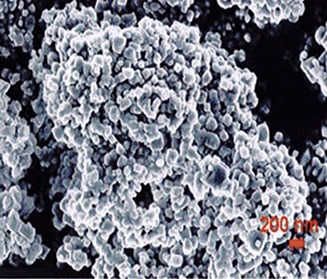
Monolithic support structures are abundantly used in high-throughput catalysis. Compared to fixed beds of small or large fully porous or core-shell particles, silica monoliths with hierarchical pore structure boost the design space spanned by hydraulic permeability, heat/mass transfer resistance, and adsorption/reaction capacity.
Thermodynamics of Multicomponent Liquid Chromatography†
- Pages: 1586-1597
- First Published: 12 August 2016
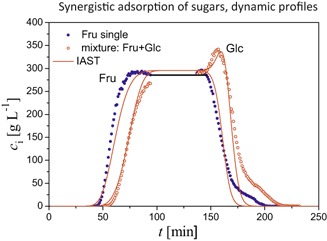
Thermodynamic models of multicomponent liquid chromatography are presented. The competitive and synergistic effects that accompany chromatographic elution are illustrated and described within thermodynamic framework. The effect of the mobile phase modifier on the retention pattern of the chromatographed species is discussed.
Modeling the Kinetics of Protein Conjugation Reactions†
- Pages: 1598-1608
- First Published: 11 October 2016
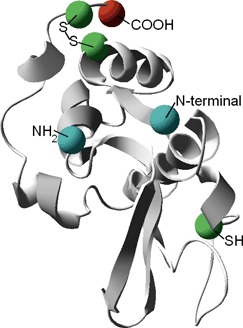
Due to the complex nature of proteins, which often bear multiple reactive sites, the kinetic modeling of conjugation reactions can be quite challenging. This work presents a rigorous approach for modeling these reactions and ultimately gain a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms and design more efficient processes.
Research Article
Crystallization of Nano-Calcium Carbonate: The Influence of Process Parameters†
- Pages: 1609-1616
- First Published: 27 July 2016
Forschungsarbeiten
Dynamische Methode zur Berechnung thermodynamischer Gleichgewichte in reaktiven Mehrphasensystemen†
Dynamic Method for Computation of Thermodynamic Equilibria in Reactive Multiphase Systems
- Pages: 1617-1627
- First Published: 05 September 2016
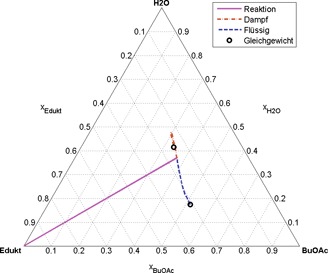
Eine dynamische Methode zur Berechnung thermodynamischer Gleichgewichte in reaktiven Mehrphasensystemen wird vorgestellt. Diese basiert auf der Lösung eines Systems physikalisch motivierter Evolutionsgleichungen. Ihre Anwendung wird am Beispiel verschiedener Fälle im Kontext der Butylacetat-Synthese illustriert.
Vereinfachte Auslegung der simulierten Gegenstromchromatographie mittels des Hodographenraums†
Using the Hodograph Space for the Simplified Design of Simulated Moving Bed Chromatography
- Pages: 1628-1642
- First Published: 23 September 2016
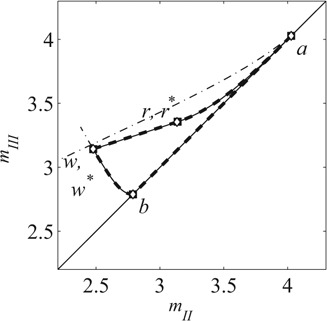
Die Auslegung der simulierten Gegenstromchromatographie (SMB-Verfahren), ist nach wie vor eine Herausforderung für Verfahrensingenieure. Die Grundlagen der Gleichgewichtstheorie für die Gegenstromchromatographie werden detailliert dargestellt und eine einfache explizite Auslegungsmethode für nichtklassische kompetitive Gleichgewichte wird abgeleitet.
Erweiterung des Semenov-Kriteriums auf konzentrationsabhängige Reaktionen†
Extension of the Semenov Criterion to Concentration-Dependent Reactions
- Pages: 1643-1649
- First Published: 10 August 2016
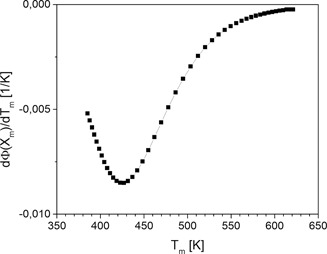
Das Semenov-Kriterium wird häufig als Stabilitätskriterium für exotherme Batch-Reaktoren verwendet. Für konzentrationsabhängige Reaktionen in flüssiger Phase muss dieses jedoch erweitert werden, um einen allgemeineren Ausdruck für die Sensitivität des Temperaturmaximums zu erhalten und somit die thermische Sicherheit dieser Form der Reaktionsführung beurteilen zu können.
Research Articles
1D Model for Coupled Simulation of Steam Cracker Convection Section with Improved Evaporation Model†
- Pages: 1650-1664
- First Published: 15 August 2016
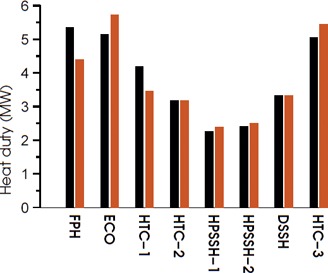
A 1D model is developed to simulate a complete steam cracker convection section enabling fast simulations. Hence, optimization and design of the convection section can be performed. The accuracy of the evaporation model is improved by implementing a mechanistic evaporation model, taking into account the different flow regimes.
Impact of Thermo-Physical Data on the Modeling of High-Pressure Polymerizations†
- Pages: 1665-1675
- First Published: 12 August 2016
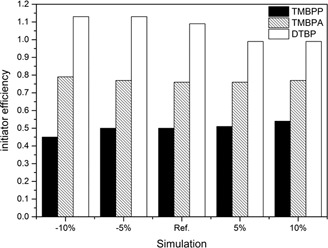
The influence of mixture viscosity and heat capacity on the process modeling of high-pressure polymerization of ethene in tubular reactors is evaluated. Special attention is paid to the heat balance, the conversion and the properties of the resulting LDPE mainly depicted by the molecular weight distribution.
Effective Axial Thermal Conductivity in Catalyst Packings from High Resolution Temperature Profiles†
- Pages: 1676-1683
- First Published: 23 September 2016
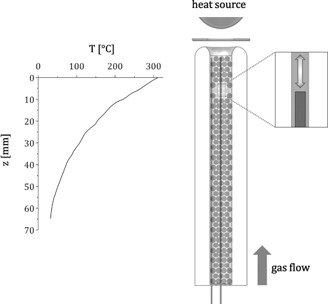
One-dimensional pseudo-homogeneous models are frequently used to describe the heat transport in packed bed reactors. One important parameter in the model is the effective axial thermal conductivity. In this work, experimental results of the axial thermal conductivity of different packings are presented. Moreover, a correlation for spherical packings is recommended.
Kinetics of Multi-Step Redox Processes by Time-Resolved In Situ X-ray Diffraction†
- Pages: 1684-1692
- First Published: 10 August 2016
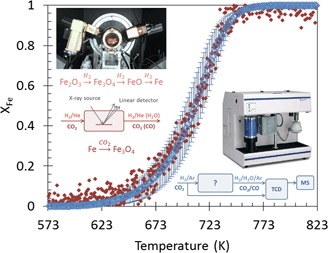
In contrast with conventional monitoring techniques, the application of time-resolved in situ XRD allows for a detailed kinetic investigation of multi-step redox processes. This experimental strategy was applied to the reduction of iron oxide, an active oxygen carrier for chemical looping CO2 utilization.
Forschungsarbeit
Entwicklung eines optisch zugänglichen Reaktors zur Thermographiemessung in einer Katalysatorschüttung†
Developing an Optically Accessible Reactor for Thermography Measurement in a Catalyst Bed
- Pages: 1693-1702
- First Published: 22 September 2016
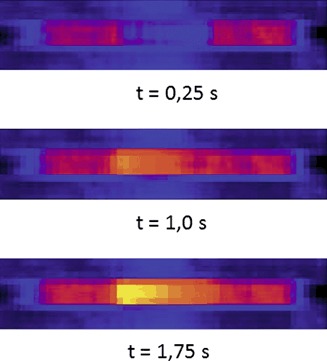
Die Wärmentwicklung in einem Reaktor bei einer stark exothermen Reaktion wurde mithilfe der Thermographie untersucht. Hierbei wurde durch systematische Variation der wichtigsten Parameter der Einfluss auf die Temperaturverteilung bestimmt. Darüber hinaus konnte die Anwendung der Thermographie zur Beobachtung sehr schneller Temperaturänderungen gezeigt werden.
Research Articles
Multiplicity Regions in a Moving-Bed Reactor: Bifurcation Analysis, Model Extension, and Application for the High-Temperature Pyrolysis of Methane†
- Pages: 1703-1714
- First Published: 23 September 2016
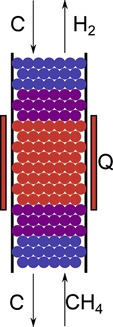
Multiple steady states (MSS) can arise in moving-bed reactors (MBR). In this work, bifurcation curves are used to identify MSS. Mapping these curves, regions of multiplicity can be established. Studies on a generalized model for several test cases and with a heat-integrated MBR for the methane pyrolysis are performed.
Evaluation of Performance of Periodically Operated Reactors for Single Input Modulations of General Waveforms†
- Pages: 1715-1722
- First Published: 06 September 2016
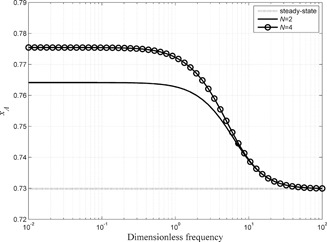
The nonlinear frequency response method was used for evaluating the time-average performance of a weakly nonlinear system when a single input is modulated in a general waveform. As a case study, an isothermal continuous stirred-tank reactor with square-wave modulation of the inlet reactant concentration was used and the reactant conversion was evaluated.
Oxidative Dehydrogenation of a C4 Raffinate-2 towards 1,3-Butadiene in a Two-Zone Fluidized Bed†
- Pages: 1723-1729
- First Published: 20 July 2016
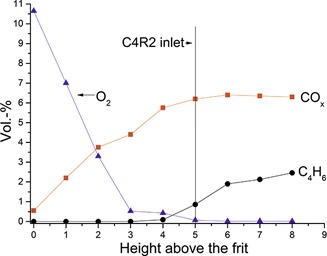
A mixture consisting of 75 vol % n-butenes and 25 vol % n-butane was used as feedstock for oxidative dehydrogenation in a two-zone fluidized bed reactor. The reaction parameters were optimized to maximize the yield of 1,3-butadiene. Furthermore, an axial concentration profile provides insights into the processes inside the fluidized bed.
Adsorption Behavior of Halogenated Anesthetic and Water Vapor on Cr-Based MOF (MIL-101) Adsorbent. Part I. Equilibrium and Breakthrough Characterizations†
- Pages: 1730-1738
- First Published: 13 September 2016
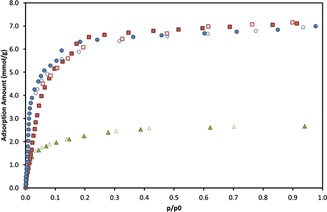
The Cr-based metal organic framework adsorbent (MIL-101) was synthesized and characterized using sevoflurane and water vapor as sorbates. Adsorption isotherms and breakthrough data were collected for MIL-101 and a commercially used reference sample to compare their performances. MIL-101 demonstrated a higher adsorption capacity and far better selectivity for sevoflurane compared.
Adsorption Behavior of Halogenated Anesthetic and Water Vapor on Cr-Based MOF (MIL-101) Adsorbent. Part II. Multiple-Cycle Breakthrough Tests†
- Pages: 1739-1745
- First Published: 16 September 2016
Multiple-cycle breakthrough tests of a binary gas mixture (sevoflurane (SF)/water vapor) were performed on a synthesized chromium-based metal organic framework (MIL-101) and a reference adsorbent. A higher stability with lower SF capacity loss was observed for MIL-101 showing its potential as a higher performance replacement for conventional halogenated anesthetics adsorbents.
Kinetic Analysis of the Hydrocarbon Total Oxidation Using Individually Measured Adsorption Isotherms†
- Pages: 1746-1760
- First Published: 20 July 2016
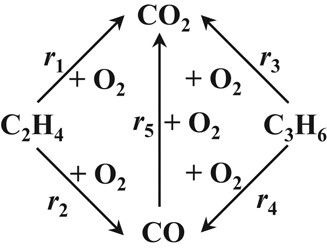
The oxidation of hydrocarbons on a CrOx/γ-Al2O3 catalyst was studied to describe the mechanism of the reaction kinetics based on catalytic cycles. For parameter reduction individually measured adsorption isotherms were used to parameterize adsorption constants to support parameter estimation, to quantify and validate kinetic rate approaches.
Forschungsarbeit
Synthese von porösen Voll- und Core-Shell-Glaskugeln zur Trennung von chiralen Anästhetika†
Synthesis of Porous Glass Beads and Core-Shell Beads for the Separation of Chiral Anesthetic Gases
- Pages: 1761-1769
- First Published: 05 July 2016
Zur Trennung von chiralen Anästhetika werden maßgeschneiderte Materialien, wie z. B. poröse Gläser, benötigt. Es konnten poröse Gläser in Kugelform mit flexibel einstellbaren Partikeldurchmessern, Mikrostrukturen und definierten Porengrößen hergestellt werden. Zudem wurden erstmals Core-Shell-Kugeln mit einem kontrollierbaren Mesoporensystem auf der Basis poröser Gläser synthetisiert.
Research Articles
Hybrid Alginate-Based Cryogels for Life Science Applications†
- Pages: 1770-1778
- First Published: 29 August 2016
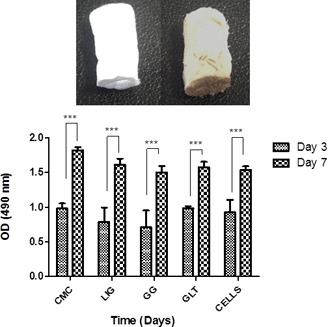
Sodium alginate is known as a good precursor in the hydrogel production for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications. Non-cytotoxic alginate-based cryogels are produced by carbon dioxide induced gelation and freeze-drying and characterized for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications.
Comparison of the Flow of Permanent and Condensable Gases through an Asymmetric Porous Membrane†
- Pages: 1779-1787
- First Published: 13 September 2016
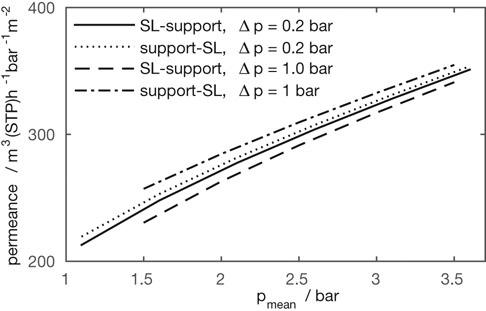
For the flow of nitrogen through an asymmetric inorganic membrane, a weak dependency of the mass flux on the flow direction was observed previously. Conversely, for the flow of propane at pressures close to the saturation pressure, a large difference may arise in the mass flux between the two flow directions through the asymmetric membrane.
MOF-Based Mixed-Matrix Membranes in Gas Separation – Mystery and Reality†
- Pages: 1788-1797
- First Published: 27 July 2016
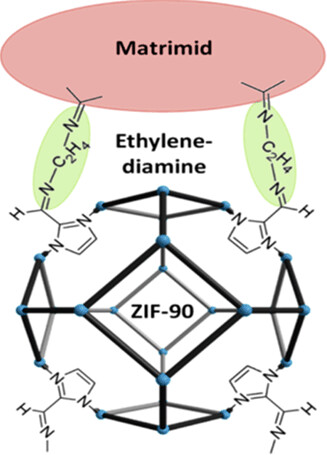
In mixed-matrix membranes (MMMs), suitable microporous nanosized filler like zeolite or carbon can modify the permeation properties of a polymer. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are very promising filler materials for MMMs. The chemistry of MOFs allows for covalent linkage to the polymer. MOFs can be prepared as nanoparticles and as delaminated two-dimensional nanosheets.
ZIF-8 SURMOF Membranes Synthesized by Au-Assisted Liquid Phase Epitaxy for Application in Gas Separation†
- Pages: 1798-1805
- First Published: 14 July 2016
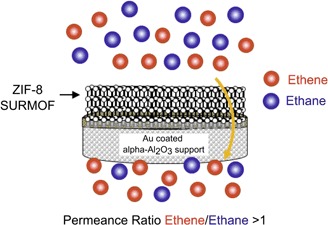
ZIF-8 SURMOF membrane synthesis by liquid phase epitaxial layer-by-layer deposition performed by a dipping procedure proves to deliver remarkably homogeneous and well oriented membranes, when the supporting α-Al2O3 substrates are coated with an Au layer. The membranes are interesting for further investigation regarding the separation of ethane and ethene.
Characteristics of Stable Pickering Emulsions under Process Conditions†
- Pages: 1806-1814
- First Published: 16 September 2016

Stable Pickering emulsions can be used for a lot of applications. However, it is poorly understood how reaction conditions affect the emulsion properties. This work investigates the influence of shear stress, pressure, temperature, and synthesis gas on Pickering emulsion drop size distribution and stability.
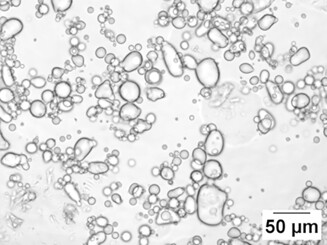
Influence of Nanoparticles and Drop Size Distributions on the Rheology of w/o Pickering Emulsions†
- Pages: 1815-1826
- First Published: 16 September 2016
The rheology of particle/oil suspensions and w/o Pickering emulsions consisting of water, 1-dodecene and silica nanoparticles was investigated. The influence of particle concentration and water content on rheology and drop sizes was determined. Residual particles in the oil phase seem to be the major influencing factor on the emulsion rheology.
Communications
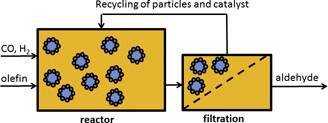
Tuning Pickering Emulsions for Optimal Reaction and Filtration Conditions†
- Pages: 1827-1832
- First Published: 23 September 2016
Pickering emulsions have been studied since 2011 as new possible systems for catalytic multiphase reactions. In order to separate the product and to retain the catalyst in the reactor in a continuous process, the stability of differently prepared Pickering emulsions during ultrafiltration is investigated.
Investigations on the Low Temperature Methanation with Pulse Reaction of CO†
- Pages: 1833-1838
- First Published: 19 August 2016
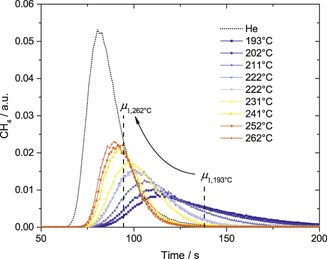
Transient experiments usually provide huge data sets depending on the sampling frequency of the analytics. The analysis and condensation of data is challenging. The application of moment analysis for a pulse-type experiment with chemical reaction is shown to allow data reduction while maintaining meaningful results for interpretation.
Buchbesprechungen
Natural Products in the Chemical Industry. Von B. Schaefer
- Pages: 1839-1840
- First Published: 25 October 2016
Vorschau
Überblick
Überblick Inhalt: Chem. Eng. Technol. 11/2016
- Page: 1843
- First Published: 25 October 2016