Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Cover Picture: Materials and Corrosion. 11/2020
- Page: 1767
- First Published: 02 November 2020
MASTHEAD
Masthead: Materials and Corrosion. 11/2020
- Page: 1769
- First Published: 02 November 2020
CONTENTS
Contents: Materials and Corrosion. 11/2020
- Pages: 1770-1773
- First Published: 02 November 2020
ARTICLES
Formation of corrosion pockets in FeNiCrAl at high temperatures investigated by 3D FIB-SEM tomography
- Pages: 1774-1782
- First Published: 26 June 2020
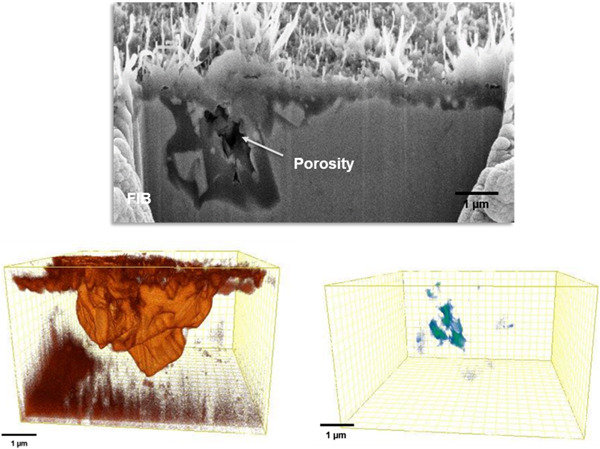
A focused ion beam–scanning electron microscope tomography study has been undertaken on an equally nitrided FeNiCrAl sample to characterize its nitridation corrosion features chemically and morphologically. The alloy is strengthened by a high number of chromium carbide precipitates. Besides the confirmation of the complete encapsulation of the corrosion pocket from the alloy, very large voids have been found in said pockets.
Corrosion behavior of UCX, KHR35, and KHR45 alloys in molten nitrates
- Pages: 1783-1793
- First Published: 23 July 2020
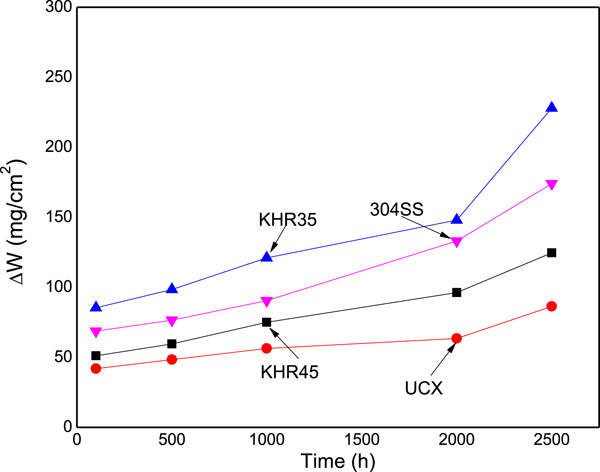
The corrosion behavior of three high-Ni, high-Cr alloys in a mixture of 60% NaNO3–40% KNO3 at 600°C has been evaluated by using weight loss tests, potentiodynamic polarization curves, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The results indicated the formation of a passive layer in all cases and the EIS data have shown that the corrosion mechanism for all the alloys was charge transfer from the alloy to the molten salt.
Ultrathin hydroxyapatite coating on pure magnesium substrate prepared by pulsed electron ablation technique
- Pages: 1794-1801
- First Published: 28 June 2020
In this study, ultrathin hydroxyapatite (HA)-based coating and HA containing Sr coatings are deposited via pulsed electron ablation technique on pure Mg. The materials covered by this layer were characterized by superior corrosion behavior, with corrosion rates of coated samples up to five times lower as compared with the uncoated ones. Such coating is the thinnest coating found in the literature sources.
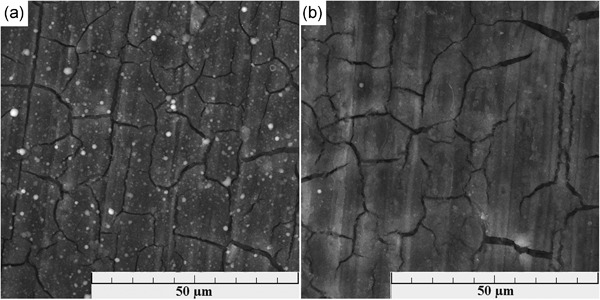
Enhancing the intergranular corrosion resistance of high Mg-alloyed Al–Mg alloy by Y addition
- Pages: 1802-1811
- First Published: 29 June 2020
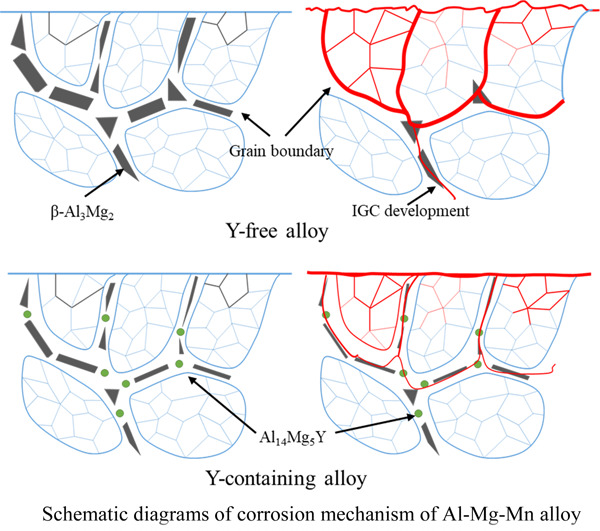
Y presence in the β phase of Al–Mg–Mn alloys could be a factor in the improved intergranular corrosion (IGC) resistance. Furthermore, the formation of the Al14Mg5Y phase inhibits the precipitation of the β-Al3Mg2 at the grain boundaries, which is the dominant mechanism for the enhanced IGC resistance by Y addition.
Revealing the effect of aluminum content on the electrochemical performance of magnesium anodes for aqueous batteries
- Pages: 1812-1823
- First Published: 11 June 2020
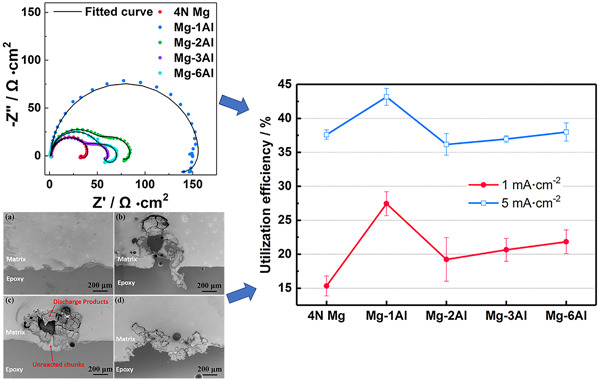
The results show that the Mg–1Al alloy possesses the larger corrosion resistance during discharge, correspondingly, the anode utilization efficiency significantly increased at 1 and 5 mA/cm2 compared with pure Mg. However, further increase of the Al content does not continuously improve the discharge performance of the Mg anode due to the decline of utilization efficiency.
Preparation and corrosion resistance of short basalt fiber/7075 aluminum composite
- Pages: 1824-1831
- First Published: 03 June 2020
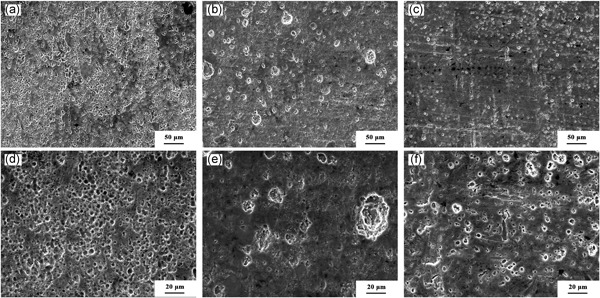
An innovative short basalt fiber/aluminum composite is prepared by vacuum hot-press sintering technique. Also, the corrosion behavior of the composites is investigated by hydrogen evolution and electrochemical tests. The results show that the short basalt fiber improves the strength and density of the oxide film of the composite, thereby improving its corrosion resistance.
Complementary EIS/FTIR study of the degradation of adhesives in electronic packaging
- Pages: 1832-1841
- First Published: 08 June 2020
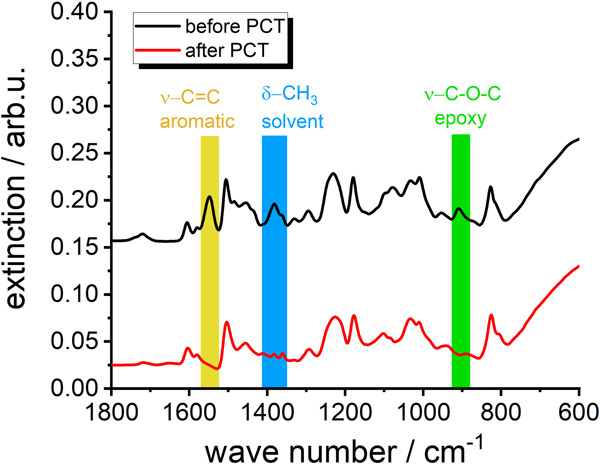
The present approach combines the nondestructive methods, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, as powerful tools in a complementary manner to describe the degradation mechanism and kinetics of two epoxy-based adhesives, which are commonly used in electronic packaging. It is demonstrated that the application quality has a dominant impact on the optimization of the lifetime.
Corrosion damage of 316L steel surface examined using statistical methods and artificial neural network
- Pages: 1842-1855
- First Published: 26 June 2020
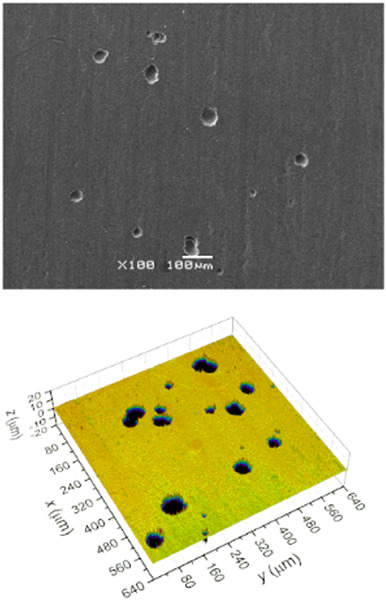
The present work refers to the numerical analysis of the 2D images and 3D maps of 316L steel surface recorded at different stages of the corrosion process. It is shown that using an artificial neural network and 2D grayscale images, instead of black and white images as an input variable, the corrosion degree of 316L steel surface could be predicted. Moreover, 3D surface maps allow to determine the evolution of the stable pit depth with the immersion time.
Experimental study on the corrosion behavior of X70 steel under asymmetric dynamic DC interference
- Pages: 1856-1871
- First Published: 02 July 2020
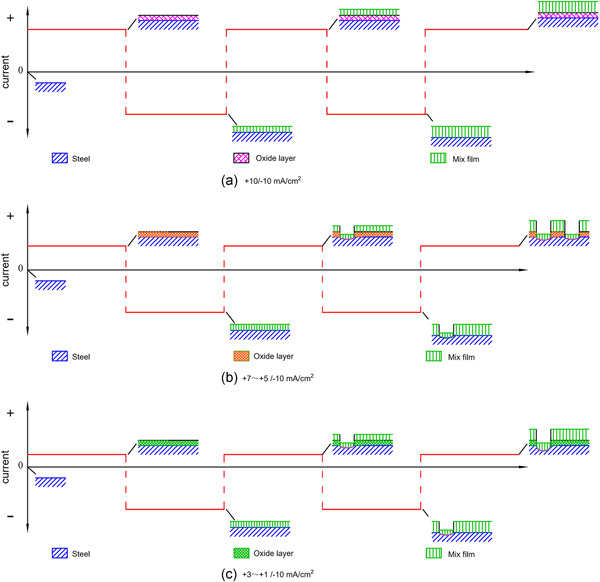
The negatively asymmetric dynamic direct current interference would induce localized corrosion in the experimental conditions. The localized corrosion behavior was probably related to the breakdown of the passive film, which was in an unstable and active condition under the repeated anodic and cathodic polarization.
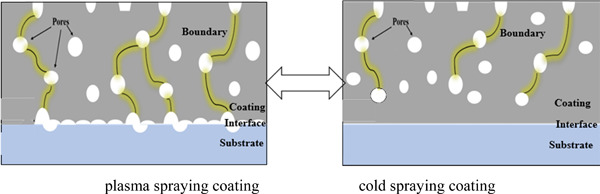
Comparison of a cold-sprayed and plasma-sprayed Fe25Cr20Mo1Si amorphous alloy coatings on 40Cr substrates
- Pages: 1872-1884
- First Published: 29 June 2020
N-methyl-2-hydroxyethylammonium oleate ionic liquid performance as corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in hydrochloric acid medium
- Pages: 1885-1902
- First Published: 02 June 2020
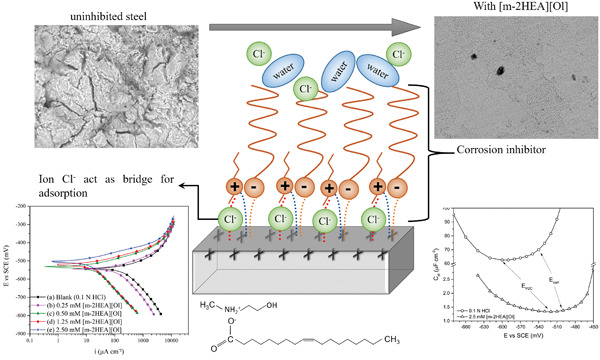
The performance of N-methyl-2-hydroxyethylammonium oleate ([m-2HEA][Ol]) as a corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in a 0.1-mol/L hydrochloric acid solution and the role of chloride in the inhibition mechanism were investigated in this paper. Results revealed that [m-2HEA][Ol] behaves as a mixed-type adsorption inhibitor, by blocking cathodic sites and by modifying the activation energy of the anodic reaction, and it can reach up to 94–97% of inhibition efficiency.
Construction of eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor lignin derivative with excellent corrosion-resistant behavior in hydrochloric acid solution
- Pages: 1903-1912
- First Published: 03 June 2020
Comparative study on two imidazolium-based ionic liquid surfactants as corrosion inhibitors for N80 steel in 15% hydrochloric acid solution
- Pages: 1913-1926
- First Published: 08 June 2020
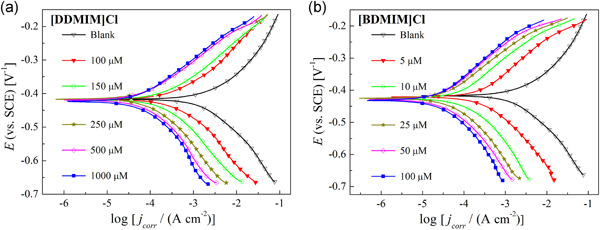
A comparative study on 1-dodecyl-2,3-dimethylimidazolium chloride and 1-benzyl-3-dodecyl-2-methylimidazol-1-ium chloride ([BDMIM]Cl) as corrosion inhibitors for N80 steel in a 15% HCl solution was performed by surface tension tests, electrochemical measurements, weight loss, scanning electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy, and theoretical calculations. The experimental results confirm that [BDMIM]Cl exhibits better inhibitive performance, lower critical micelle concentration, and a lower ratio of saturation adsorption concentration.