Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Cover Picture: Materials and Corrosion. 10/2020
- Page: 1601
- First Published: 07 October 2020
MASTHEAD
Masthead: Materials and Corrosion. 10/2020
- Page: 1603
- First Published: 07 October 2020
CONTENTS
Contents: Materials and Corrosion. 10/2020
- Pages: 1604-1607
- First Published: 07 October 2020
ARTICLES
Hot corrosion studies of a salt-coated Ni-based superalloy under flowing wet air and sulfur vapor ambient
- Pages: 1608-1618
- First Published: 02 June 2020
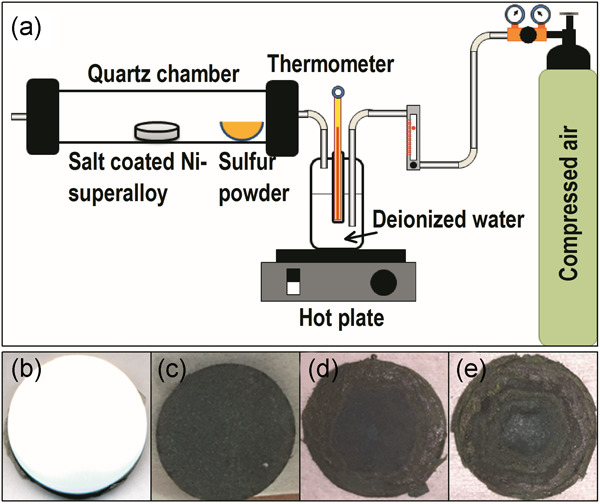
Corrosion of Ni-based single-crystal superalloys, coated with mixed sulfate salts, has been investigated at elevated temperatures upon vaporized sulfur carried in flowing wet air. Morphological and structural evolutions, probed from the cross-sections that exhibit apparently distinguishable corroded zone boundaries beneath the surface of the superalloy, have been studied by increasing the corrosion duration.
Assessment of pitting corrosion in bare and passivated (wet scCO2-induced patination and chemical passivation) hot-dip galvanized steel samples with SVET, FTIR, and SEM (EDS)
- Pages: 1619-1628
- First Published: 14 May 2020
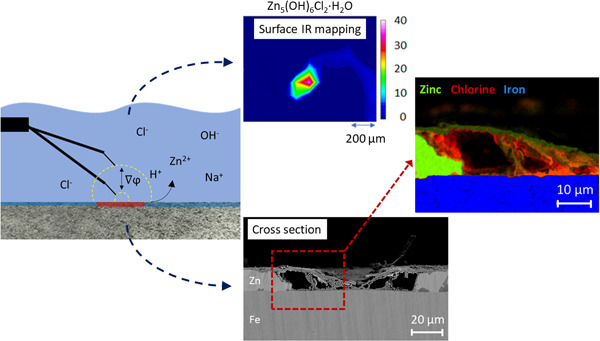
Salt-induced pitting corrosion of hot-dip galvanized steel can be suppressed by suitable passivating layers. Such layers can function by withstanding ion-exchange reactions or reducing ionic diffusion through the barrier layer. A combination of local electrochemical measurements with molecular spectroscopy and high-resolution cross-section element mapping can clarify the root cause for pitting corrosion and facilitate tailoring of appropriate protective layers for specific environments.
Hydrogen-induced stress corrosion cracking studied by the novel tuning-fork test method
- Pages: 1629-1636
- First Published: 08 June 2020
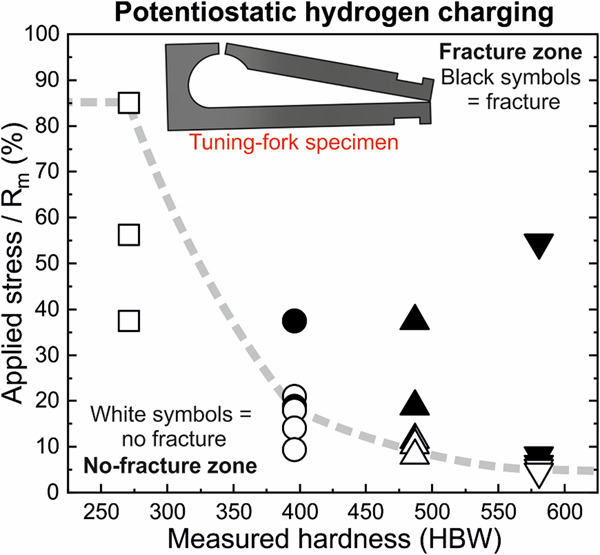
This article presents the development work of the novel tuning-fork test, where direct-quenched steels with a hardness range of 300–550 HBW are investigated with galvanostatic and potentiostatic hydrogen charging techniques. Both hydrogen charging techniques produce similar results. However, the potentiostatic technique produces larger differences between the lowest fracture stress results, thus having a better resolution.
Investigation of corrosion behavior at elbow by array electrode and computational fluid dynamics simulation
- Pages: 1637-1650
- First Published: 14 April 2020
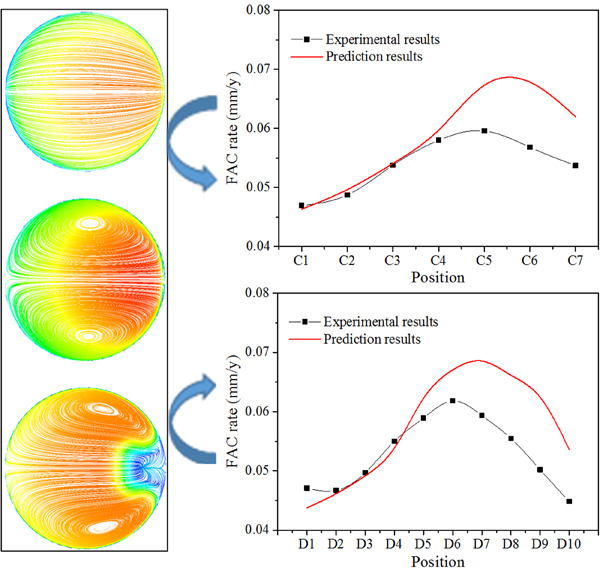
The present work focuses on the flow-accelerated corrosion (FAC) behavior of A106Gr.B steel at 90° elbow by electrochemical measurement and computational fluid dynamics simulation. The FAC rates under turbulent flows were measured by the array electrode technique in a loop system. The experimental results reveal that the maximum FAC rate appears at the extrados of 90° elbow.
Cathodic protection design optimization of a buried vessel by FEM simulation
- Pages: 1651-1659
- First Published: 11 June 2020
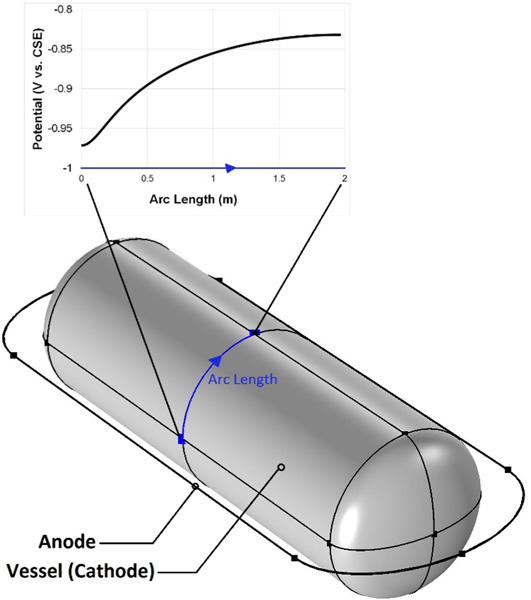
In the present work, using the finite element method simulation, a new generation design of cathodic protection for the buried vessel with a linear anode is comprehensively studied. Besides finding the effective parameters on the design and current distribution, the optima of the variables are extracted.
Stress distribution in thick-walled cylinder due to non-uniform radial pressure on the example of reinforcement corrosion in concrete
- Pages: 1660-1666
- First Published: 15 April 2020
This paper presents an analytical solution to the non-uniform pressure on thick-walled cylinder. The formulation is based on the linear elasticity theory (plain strain) and stress function method. As an example, the proposed solution is used to model the stress distribution due to non-uniform steel reinforcement corrosion in concrete
Investigation of the influence of iron-containing abrasives on the corrosion behaviour of the aluminium alloy AlSi1.2Mg0.4
- Pages: 1667-1679
- First Published: 19 April 2020
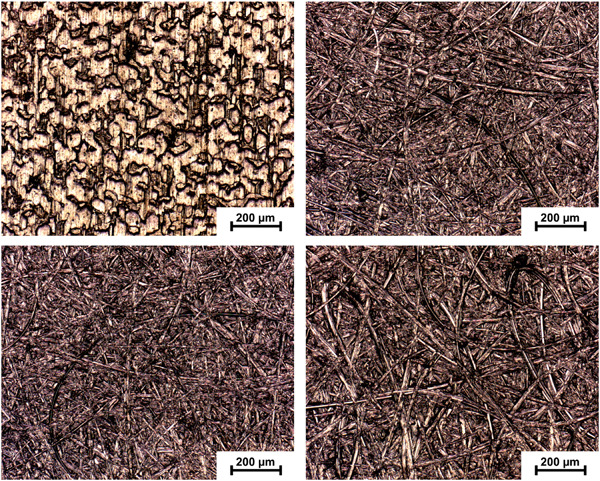

For years, iron-containing abrasive materials were suspected to lead to increased corrosion susceptibility after processing of aluminium surfaces. To prove a possible correlation between the iron content of an abrasive and the corrosion behaviour of aluminium components, different corrosion investigations were performed at mechanically ground aluminium surfaces.
Effect of microstructure on discharge performance of Al–0.8Sn–0.05Ga–0.9Mg–1.0Zn (wt%) alloy as anode for seawater-activated battery
- Pages: 1680-1690
- First Published: 14 April 2020
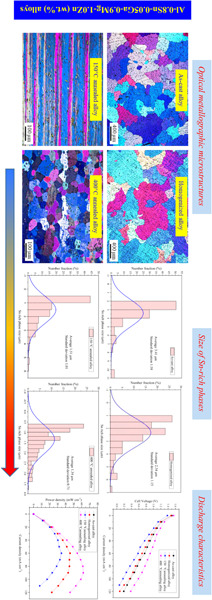
The electrochemical performance and discharge behavior of Al–0.8Sn–0.05Ga–0.9Mg–1.0Zn (wt%) alloys in as-cast, homogenized, and annealed states were investigated through electrochemical means, corrosion rate test, and discharge test in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution. Results suggest that the discharge performance of this alloy is enhanced by rolling and subsequent annealing treatment.
Influence of the surface etching on the corrosion behaviour of a three-dimensional printed Ti–6Al–4V alloy
- Pages: 1691-1696
- First Published: 03 June 2020

Products prepared by additive technology often require further surface treatment, in the case of complex shapes, it is not possible to proceed to classical techniques such as machining and turning. A three-dimensional printed titanium alloy was etched in an acid mixture. Etching has a negative influence on corrosion behaviour in the long term. The corrosion rate is increased for up to 24 hr exposure. The etching did not influence the cytotoxicity.
Design and characterization of selective laser-melted Ti6Al4V–5Cu alloy for dental implants
- Pages: 1697-1710
- First Published: 15 April 2020
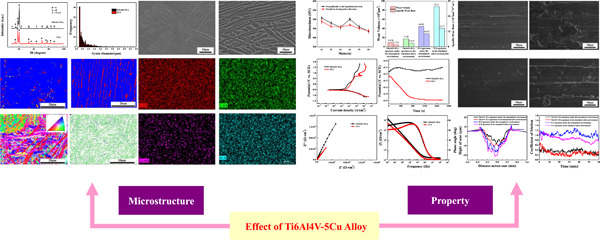
The microstructure changes of Ti6Al4V–5Cu alloys and forged TC4 were observed and the primary reasons were analyzed. The wear mechanism of Ti6Al4V–5Cu alloys in the simulated saliva environment and atmospheric environment was investigated.
Selective laser-melted Ti6Al4V–5Cu alloys exhibited a good corrosion resistance.
High-speed wire electrical discharge machining to create superhydrophobic surfaces for magnesium alloys with high corrosion and wear resistance
- Pages: 1711-1720
- First Published: 08 June 2020
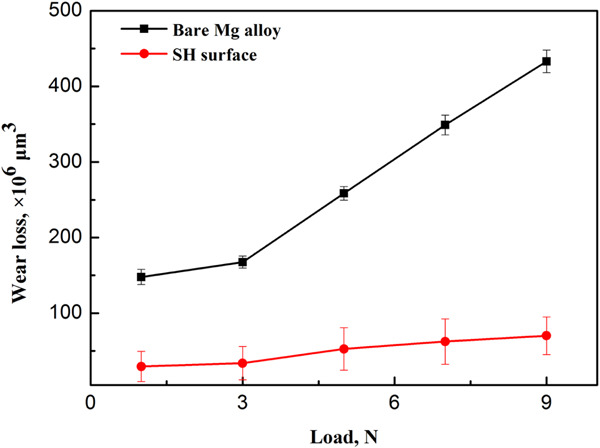
The superhydrophobic surface of a AZ31B magnesium alloy prepared by high-speed wire electrical discharge machining and modification with stearic acid had better corrosion resistance than the bare magnesium alloy. Under both dry and wet friction conditions, the friction coefficient of the superhydrophobic surface was lower than that of the bare magnesium alloy surface, with a much lower wear loss.
Corrosion of silver in environment containing halides, pseudohalides, or thiourea
- Pages: 1721-1728
- First Published: 14 April 2020
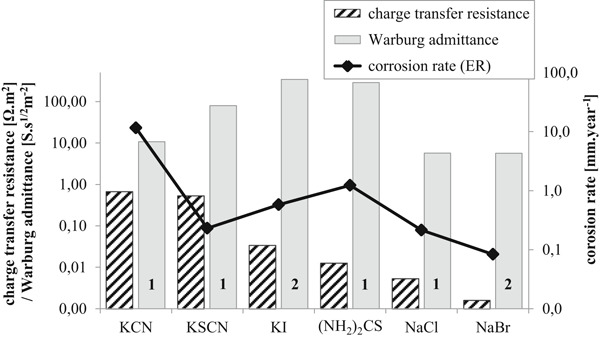
Corrosion stimulants, such as halides, pseudohalides, or thiourea pose a specific threat for historical silver objects like daguerreotypes or coins, for example, during incorrect storing or cleaning method. To better characterize the silver corrosion caused by the solutions, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and electrical resistance technique were used. EIS measurements show that the dissolution of silver in tested solutions is mainly controlled by diffusion.
Effect of relative humidity on the corrosion behavior of Sn–0.7Cu solder under polyvinyl chloride fire smoke atmosphere
- Pages: 1729-1735
- First Published: 23 April 2020
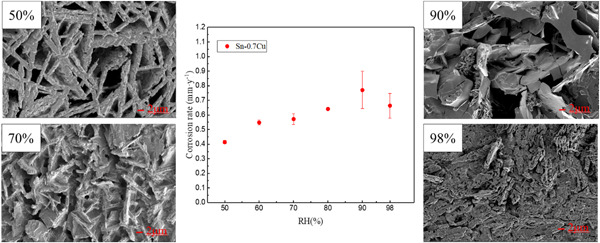
This article investigates the effect of environment relative humidity (RH) on the corrosion kinetics, microstructures, and corrosion process of Sn–0.7Cu solder under a polyvinyl chloride smoke atmosphere. The results show that RH has a great influence on the corrosion of Sn–0.7Cu solder. The corrosion rate increases with the environment RH, from 50% RH to 90% RH, and then decreases from 90% RH to 98% RH.
Corrosion initiation of Hastelloy C-2000 in an HCl-polluted atmosphere
- Pages: 1736-1746
- First Published: 25 May 2020
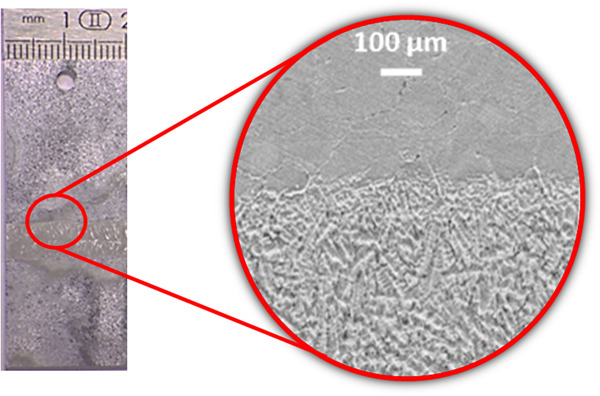
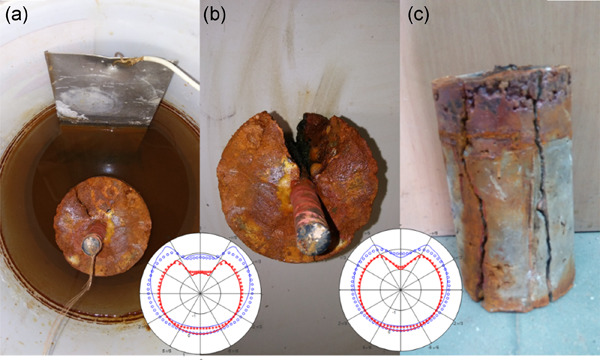
The photograph of an Hastelloy C-2000 welded sample after testing in the 20 wt% HCl vapor phase environment at 935 hr and the Scanning Electron Microscope image of the interface between the base metal and the weld zone. The dissolution of the weld zone materializes by a rough weld seam with the presence of a more or less deep relief. Low-dissolved areas are those rich in molybdenum and weakly concentrated in nickel.
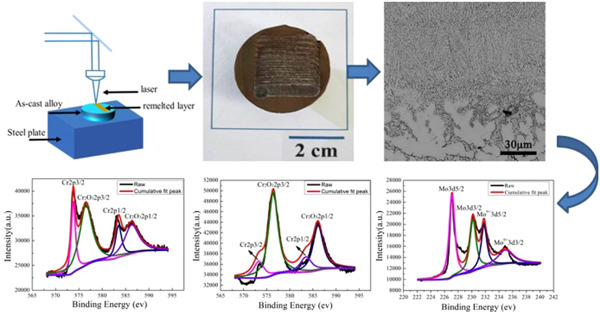
Microstructure and corrosion behavior of FeCrNiMnMox high-entropy alloys fabricated by the laser surface remelting
- Pages: 1747-1754
- First Published: 25 May 2020