Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Cover Picture: Materials and Corrosion. 12/2020
- Page: 1939
- First Published: December 2020
MASTHEAD
Masthead: Materials and Corrosion. 12/2020
- Page: 1941
- First Published: December 2020
CONTENTS
Contents: Materials and Corrosion. 12/2020
- Pages: 1942-1945
- First Published: December 2020
ARTICLES
In situ study of the deep sea electrochemical performance of aluminum-based galvanic anodes
- Pages: 1946-1956
- First Published: 09 July 2020
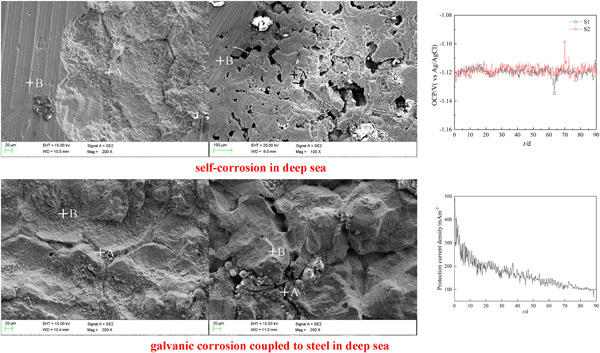
Al–Zn–In–Mg–Ti–Ga–Mn anode degradation mainly occurs via uniform corrosion accompanied with minor pitting and intergranular corrosion in the South China Sea at a depth of 1,420 m, whereas the Al–Zn–In–Si anode is subject to extensive intergranular corrosion. Two types of active anodes are chosen and the protection current density for E355DD is about 120 mA/m2 in the deep sea.
Exfoliation and intergranular corrosion resistance of the 2198 Al–Cu–Li alloy with different thermomechanical treatments
- Pages: 1957-1970
- First Published: 23 July 2020
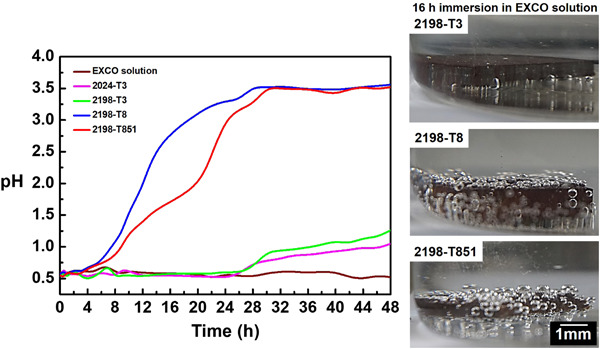
The exfoliation and intergranular corrosion (IGC) resistance of the 2198 Al–Cu–Li alloy with different thermomechanical treatments were investigated. Higher pH values were related to artificially aged alloys in the EXCO solution. Interestingly, a relation between weight loss and pH was established in this solution. Information about the corrosion attack depth in the IGC solution was discussed. This information has great importance for the aeronautical industry.
Atmospheric corrosion behavior of 7A09 aluminum alloy exposed to an industrial environment
- Pages: 1971-1979
- First Published: 29 September 2020

Graphical abstract
The atmospheric corrosion behavior and corrosion mechanism of 7A09 alloy exposed to an industrial environment have been studied. This alloy suffers pitting and intergranular corrosion (IGC) and shows a decreasing tendency of corrosion rate. The occurrence of IGC is mainly due to the preferential dissolution of grain boundary precipitates Mg(ZnAlCu)2 and the precipitate-free zone along grain boundaries.
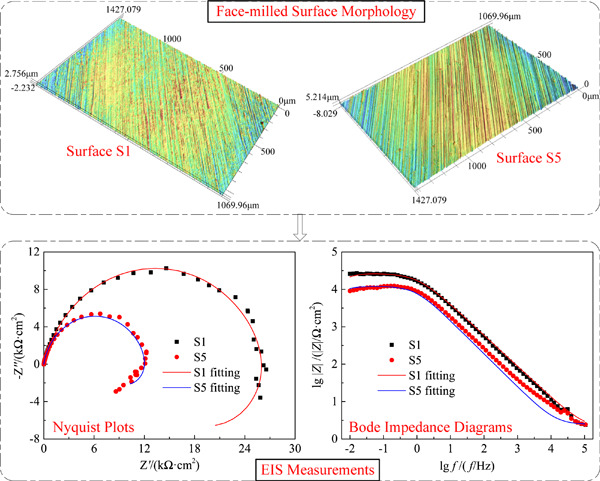
Anticorrosion property enhancement of Al–Li alloy 2A97 by lowering machined surface roughness
- Pages: 1980-1988
- First Published: 26 June 2020
Microstructures and electrochemical behaviors of as-cast magnesium alloys with enhanced compressive strengths and corrosion decomposition
- Pages: 1989-1998
- First Published: 27 July 2020
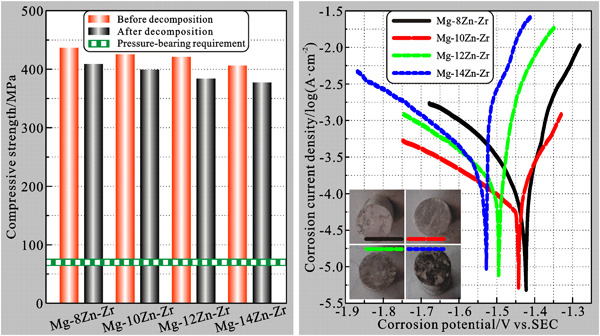
Mg–xZn–Zr alloys designed by regulating Zn contents have been fabricated with extrusion casting. Compressive strengths and electrochemical tests have been investigated to characterize their feasibility as decomposition materials. Results show that as-prepared materials not only guarantee fast dissolution of fracturing balls after oil exploitation but also ensures compressive strength stability in decomposition.
Effect of Ti3SiC2 content on the corrosion behavior of Al/Ti3SiC2 composite coatings
- Pages: 1999-2010
- First Published: 20 July 2020
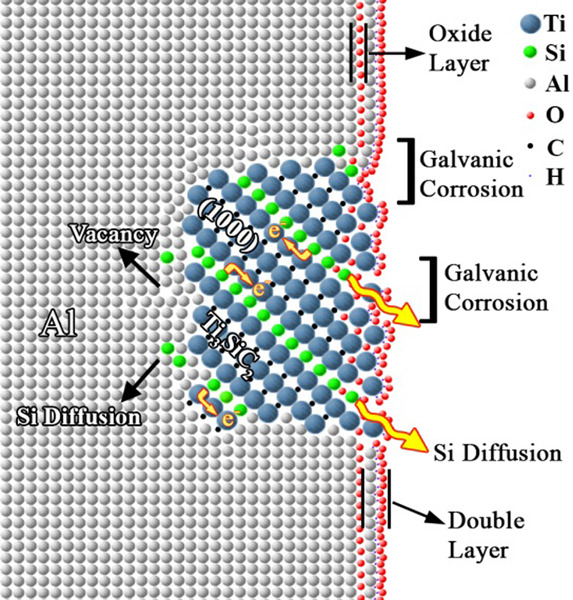
The electrochemical corrosion properties of flame-sprayed Al and Al/(5, 10, 15)% Ti3SiC2 coatings in a 3.5% NaCl solution were investigated. The results revealed that Al/Ti3SiC2 coating is nobler than the pure aluminum coating and that the presence of Ti3SiC2 particles significantly enhances the corrosion resistance of the coatings.
One-pot fluorine-free superhydrophobic surface towards corrosion resistance and water droplet bouncing
- Pages: 2011-2020
- First Published: 25 June 2020
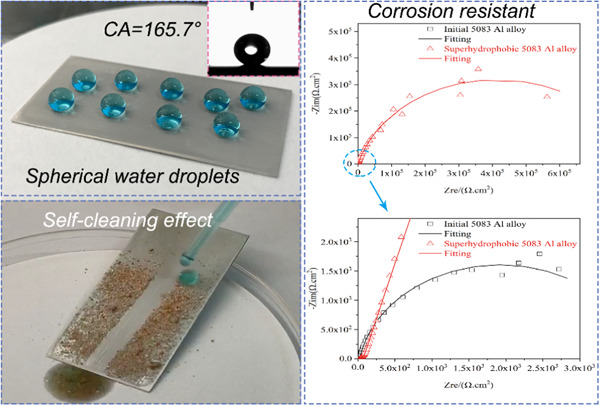
Stearic acid (STA)-based one-pot hydrothermal treatment provides an eco-friendly and cost-effective method for construction of superhydrophobic surface. The prepared superhydrophobic surface exhibits superior water repellency, self-cleaning, and corrosion-resisting properties, which broadens the multifunctional applications.
Electrochemical corrosion behavior of LDX 2101® duplex stainless steel in a fluoride-containing environment
- Pages: 2021-2028
- First Published: 26 June 2020
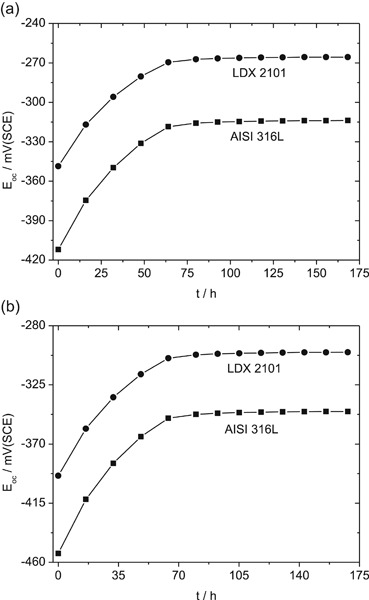
The effect of fluoride on the electrochemical corrosion behavior of an LDX 2101 duplex stainless steel was studied. Open-circuit potential (EOC) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements were carried out in artificial saliva and with the addition of fluoride (1 wt% NaF). LDX 2101 exhibits superior corrosion resistance as compared to AISI 316L.
Creep rupture life assessment of superheater tube with oxide formation in power plant
- Pages: 2029-2037
- First Published: 29 June 2020
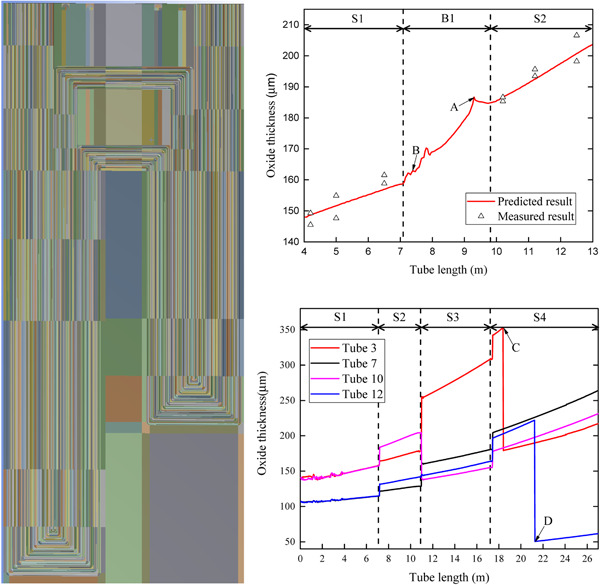
This paper proposes a method for predicting the creep rupture life of superheater tubes, considering the continuous increasing metal temperature and stress as a result of oxide formation. The steam-side oxide growth was assessed by the parabolic oxidation rate law, and the temperature profiles of superheater tubes was calculated combining the 3D computational fluid dynamics simulation and the 1D analytical models.
The effect of cathodic polarization on the corrosion behavior of X65 steel in seawater containing sulfate-reducing bacteria
- Pages: 2038-2051
- First Published: 26 July 2020
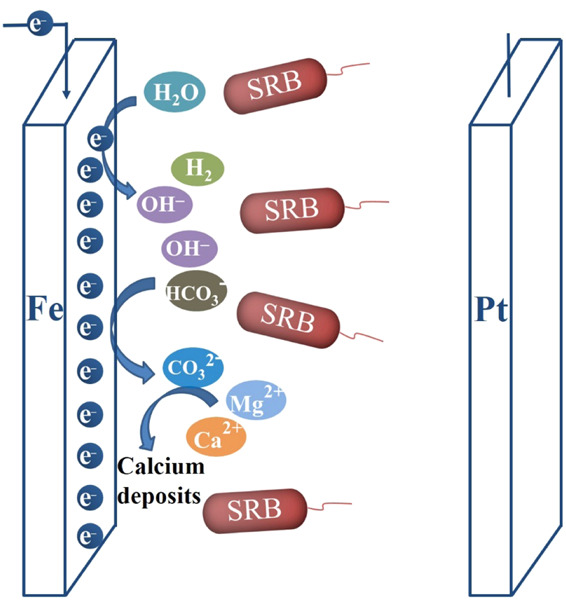
The cathodic potential of −1,050 mV/SCE has an obvious inhibitory effect on sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB)-induced pitting corrosion. When the potential of −1,050 mV/SCE is applied, the number of SRB cells attached to the electrode surface decreases significantly. The impressed charges, the increase of pH, and the formation of calcareous deposits on the electrode surface are the driving forces to inhibit the attachment of SRB.
Physicochemical studies of galvanized steel corrosion in urban, industrial, and marine environments, and corrosion mapping of Karachi city: An important coastal city of the 21st-century modern maritime silk route
- Pages: 2052-2069
- First Published: 22 July 2020
Effect of substituents on the inhibitive properties of newly synthesized 5-benzoyl-4-methyl-1,3,4,5-tetrahydro-2H-1,5-benzodiazepin-2-one derivatives against mild steel corrosion in an acidic medium
- Pages: 2070-2082
- First Published: 28 July 2020
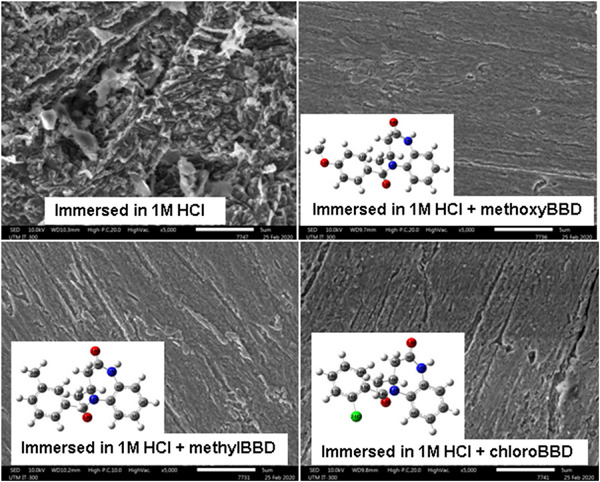
The effect of methoxy, methyl, and chloride substituents on the inhibitive performance of three 1,5-benzodiazepine derivatives as corrosion inhibitors was investigated. The best inhibition performance of the derivative with methoxy substituent is due to the presence of the –OCH3 as a stronger electron-donating group, compared with the other two derivatives with –CH3 and –Cl.