Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Editorial Board
Editorial Board: Chem. Eng. Technol. 6/2023
- Page: 1056
- First Published: 22 May 2023
Overview
Overview Contents: Chem. Eng. Technol. 6/2023
- Page: 1057
- First Published: 22 May 2023
Editorial
CHISA 2022 – 26th Worldwide Meeting of Chemical Engineers
- Page: 1058
- First Published: 22 May 2023
Review Articles
Radiation Models for Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulations of Photocatalytic Reactors
- Pages: 1059-1077
- First Published: 09 March 2023
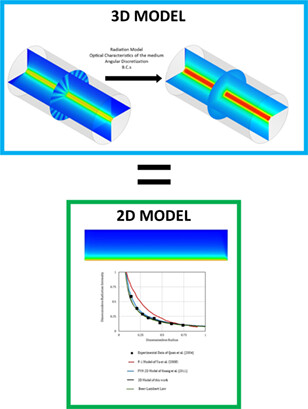
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations applied to photocatalytic systems are reviewed. Simulations of three models for simulating radiation distribution in 3D annular photoreactors and 2D rectangular enclosures with black walls are covered. The discrete ordinates model is selected to find the radiation distribution inside the reactor. CFD models agree excellently with literature results.
Estimating the Ecological Performance of Water and Wastewater Treatment in Africa: A Meta-Analysis
- Pages: 1078-1088
- First Published: 04 May 2023
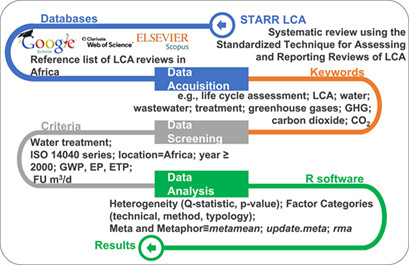
A systematic overview of published life cycle assessment (LCA) studies on water and wastewater treatment in Africa is presented. Unitary estimates for energy use, global warming potential (GWP), and eutrophication potential (EP) are provided for geographical locations and water sources. The meta regression model is fit to predict how these factors influence energy use, GWP, and EP.
Research Articles
Liquefaction of Waste Rendering Fat Using Iron-Containing Catalysts
- Pages: 1089-1097
- First Published: 10 January 2023
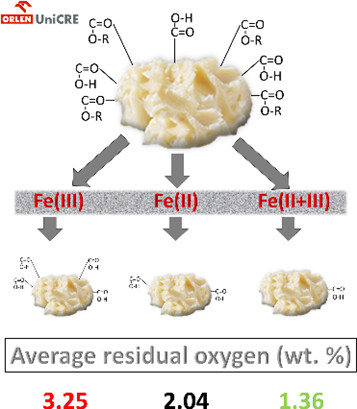
Waste rendering fat (WRF), a solid residuum from rendering plants, consists of a mixture of lipids with a high content of mono-, di-, and triglycerol esters and free fatty acids. Catalytic liquefaction and deoxygenation of WRF with four different iron-based catalysts are proposed, with the aim to prepare new catalysts and use them for upgrading WRF for application in current refineries.
Effect of the Discharging Flap on Particle Separation in a Cyclone
- Pages: 1098-1105
- First Published: 10 January 2023
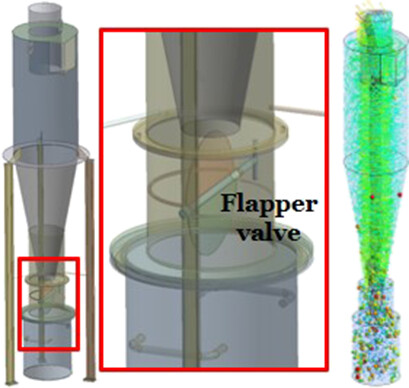
The effects of the flapper valve for particle discharging in an industrial cyclone separator on the flow field, static pressure drop, cut size, and slope of the grade efficiency curve have been investigated using the Reynolds stress model simulation. The cyclone was simulated in three operation regimes, namely, when the flapper valve is open, closed, and without the flapper valve.
Biosurfactant Production by Acinetobacter venetianus and Its Application in Bioremediation
- Pages: 1106-1114
- First Published: 10 January 2023
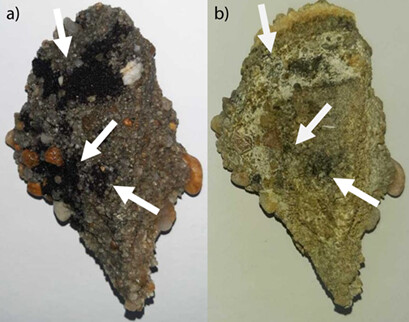
Acinetobacter venetianus isolated from samples of oil spilled on the Brazilian coast was able to produce a biosurfactant with high emulsification potential and stability against variations in temperature, pH, and presence of NaCl. The bioproduct obtained was capable to disperse oil residues present in stones contaminated by oil spills, evidencing its potential for bioremediation.
Interfacial Polymerization Kinetics of Polyurea Microcapsules Formed Using Hexamethylene Diisocyanate Biuret Low Viscosity Isocyanate
- Pages: 1115-1125
- First Published: 10 January 2023
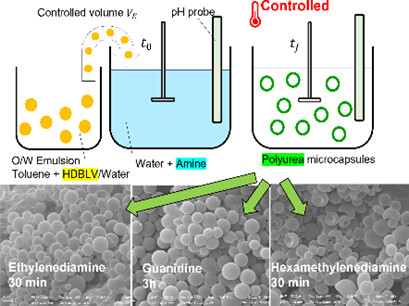
This paper demonstrates how the nontoxic isocyanate hexamethylene diisocyanate biuret low viscosity (HDB-LV) allows the fabrication of polyurea microcapsules for cosmetic applications at decent reaction rates. A theoretical model is presented to fit the experimental data and obtain key parameters of the reaction. Three different amines and various temperatures were tested.
Converting Fuel-Synthesis Process Water to Aquaculture Feed by Purple Non-Sulfur Bacteria
- Pages: 1126-1133
- First Published: 16 January 2023
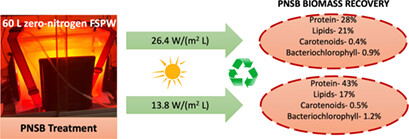
A pilot-scale reactor was set up to determine the feasibility of single-cell protein (SCP) recovery from fuel synthesis process water (FSPW), a zero-nitrogen feedstock, via anaerobic purple non-sulfur bacteria treatment under various light intensities. FSPW treatment efficiency, biomass yield and content were dependent on light intensity. Substantial SCP recovery was achieved at low light intensity.
Non-Isothermal Mass Transfer in Fluid Drops with Internal Circulation
- Pages: 1134-1139
- First Published: 24 January 2023
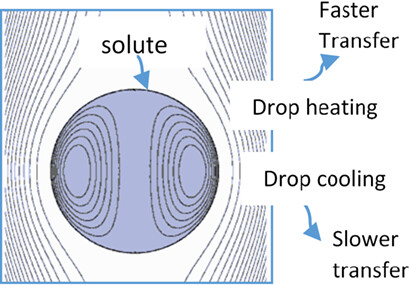
Non-isothermal mass transfer to dispersed fluid drops was studied using the computational fluid dynamics simulation tool ANSYS FLUENT. The temperature-dependent diffusion coefficient was employed with the help of the User-Defined Function. Mass transfer is faster for drop heating than for drop cooling and significant solute transfer occurs at the final higher temperature.
Compartmental Modeling of Biofouling in Industrial Cooling Circuits
- Pages: 1140-1148
- First Published: 23 January 2023
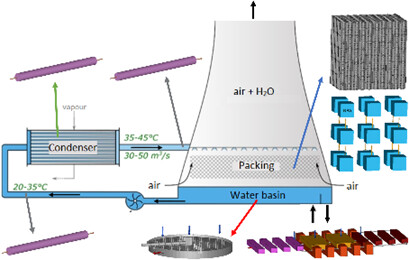
Industrial cooling circuits are strongly susceptible to fouling and particularly biofouling. This work proposes a compartmental model built from a full hydrodynamic characterization of an industrial cooling circuit and implemented with a biofilm growth model which considers kinetic (temperature, concentrations) as well as hydrodynamic (internal and external transfer) limitations.
Experimental Study on the Scalability of Planetary Roller Extruders
- Pages: 1149-1155
- First Published: 23 January 2023
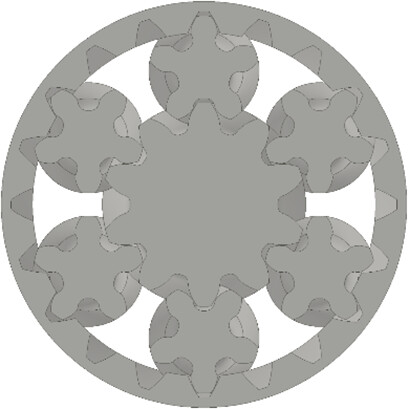
Scaling algorithms for planetary roller extruders on laboratory and production scale are developed in this contribution. In systematic studies, different operating conditions are analyzed with regard to process temperatures, pressure build-up capacity, and residence time distribution. Machine learning models are applied to make predictions of process variables with high accuracy.
Forced Precipitation Experiments for Study of the Electromagnetic Treatment of Water
- Pages: 1156-1162
- First Published: 23 January 2023
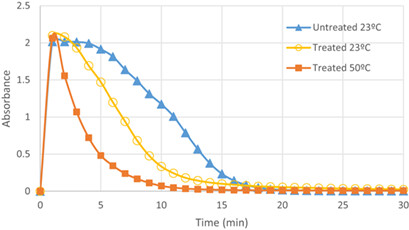
The effect of an electromagnetic equipment to prevent incrustations in pipes is evaluated. An immediate technique of forced precipitation of calcium carbonate to verify this effect is applied to distinguish between electromagnetically treated and untreated tap water, by means of temporal evolution of turbidity, absorbance, and the final size of the particles formed, with temperature control.
Influence of the Distance between Two Catalysts for CO2 to Dimethyl Ether Tandem Reaction
- Pages: 1163-1169
- First Published: 23 January 2023
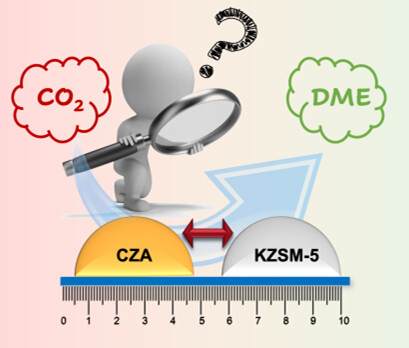
A systematic experimental investigation of the distance between the catalysts for CO2 to dimethyl ether tandem reaction system is presented. The distance mainly causes external mass transfer limitations which affect the overall performance of the catalysts, whereas, if the catalysts are very close to each other, poisoning of the acid catalyst due to high local concentration of water may occur.
Properties of Epoxy Resins-Based Composite Materials with the Addition of Microspheres
- Pages: 1170-1175
- First Published: 29 January 2023
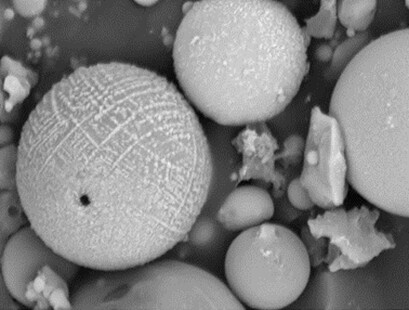
Composite materials based on epoxy resins with microspheres additives were tested for resistance to alternating temperatures, corrosive media like acid, alkali, and gasoline, and to abrasion. The improved chemical resistance, wear capacity, and resistance to temperature drops by adding microspheres allows the application as corrosion-resistant coatings for metal structures and during machine maintenance.
Bi-Reforming of Biogas for Hydrogen Production with Sulfur-Resistant Multimetallic Catalyst
- Pages: 1176-1184
- First Published: 29 January 2023
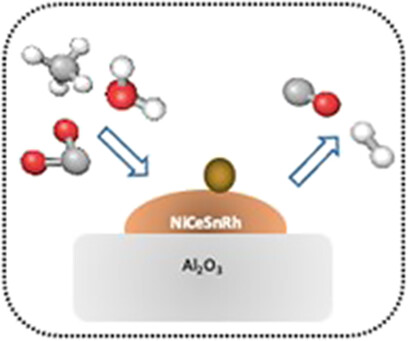
A catalytic technology to produce H2 from biogas was investigated. Since biogas is a wet mixture of methane and CO2, the process currently studied takes advantage of the presence of the two common oxidants used to convert CH4, an approach often known as bi-reforming of methane. The effect of sulfur, a common poison found in biogas streams, was evaluated by adding dimethyl sulfide to the catalysts.
Enhancement of Wastewater Treatment Using Mist and Photocatalyst
- Pages: 1185-1190
- First Published: 29 January 2023
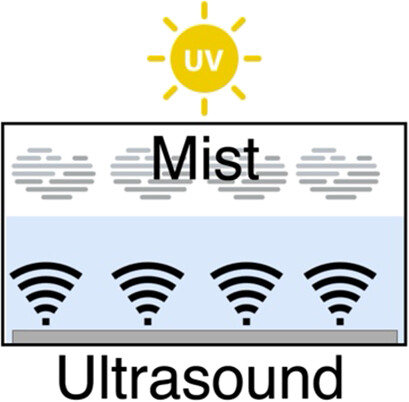
In the reactor proposed for treating wastewater containing refractory organic substances, the roles of ultraviolet (UV) irradiation, ultrasound, ultrasonic mist, and photocatalyst were investigated by comparing the pollutant removal performance under different operating conditions. The results show that the use of UV, ultrasound, and photocatalyst is necessary to utilize mist as a reaction field.
Impact of Curved-Blade Impellers on Gas Holdup and Liquid Homogenization Dynamics in Stirred Tanks
- Pages: 1191-1197
- First Published: 06 February 2023
The local values of gas holdup together with the liquid mixing time were investigated with the specific purpose of assessing the difference in gas-liquid mixing performances obtained with the standard Rushton turbine and the asymmetric concave blade design, namely, the Bakker turbine, in single and multiple impeller configurations. The latter was more energetically efficient for gas-liquid mixing.
Hydrogen Sensor to Monitor the Conditions in the Primary Circuit of a Nuclear Reactor
- Pages: 1198-1203
- First Published: 06 February 2023
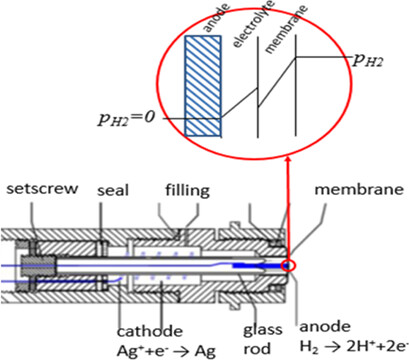
A hydrogen concentration measurement device for nuclear power plants is under development. The experience on the device preparation complexity is shared by the Mass Transfer Laboratory at UCT Prague. The amperometric hydrogen sensor tests illustrate how to enhance the sensor durability. A successful improvement is confirmed by the operational test at the Dukovany nuclear power plant.
Evaluation of the Dry Deposition of Particles Emitted by Biomass Combustion
- Pages: 1204-1211
- First Published: 06 February 2023
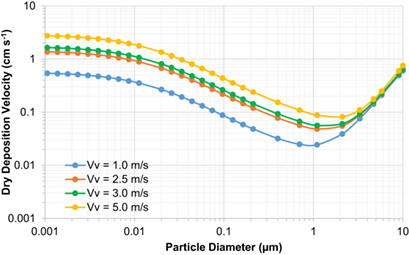
The role of biomass considering the occurrence of pollution remains still understudied. The deposition flux of different ionic compounds to fine particulate matter for urban, agricultural, and forest regions was determined. Possible sources, concentrations, and ionic composition of atmospheric particulate matter present in the atmosphere of Araraquara were analyzed and related to emission sources.
Solid-Phase Extraction of the Aromatic By-Products Obtained by Fast Pyrolysis of Pretreated Lignocellulose
- Pages: 1212-1217
- First Published: 06 February 2023
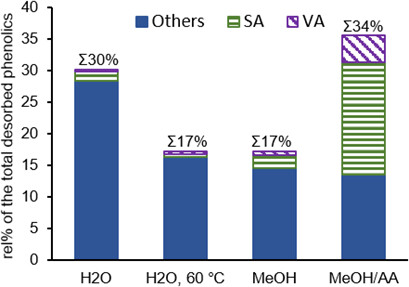
Pyrolysis liquids obtained by fast pyrolysis of birch wood pretreated with diluted sulfuric acid have been separated by solid-phase extraction to valorize the aromatic by-products which arise during levoglucosan production. Solid-phase extraction offers good separation between sugars and phenols, also allowing further selective extraction of different aromatic species.
Gas Holdup and Flow Regimes in a Thin-Gap Bubble Column with Newtonian and Non-Newtonian Liquid Phase
- Pages: 1218-1227
- First Published: 10 February 2023
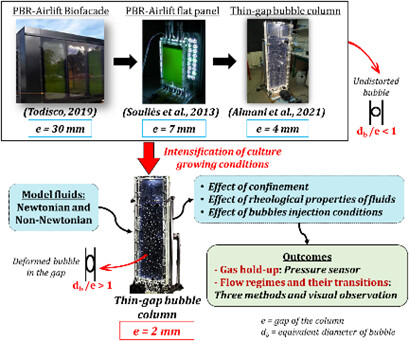
Intensification work is carried out using a thin-gap bubble column intended as a photobioreactor, with high confinement ratio and cell concentration. Consequences of this geometrical condition and rheological properties of the liquid phase on the gas holdup and flow regimes are studied for different model fluids, having the same rheological properties as microalgae suspensions at high concentrations.
Fractionation of a Three-Particle Mixture by Brownian Sieving Hydrodynamic Chromatography
- Pages: 1228-1234
- First Published: 10 February 2023
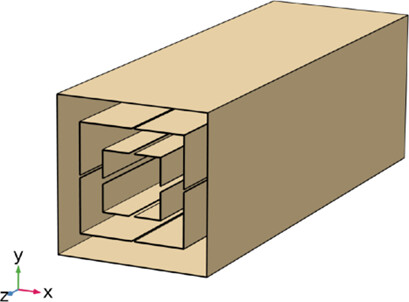
An innovative separation microdevice based on a Brownian sieving effect coupled with hydrodynamic chromatography is proposed to investigate and optimize a modified geometry suitable for obtaining the simultaneous separation of a three-size diluted suspension. The results prove a significant improvement of up to 3000 % over the standard hydrodynamic chromatography.
Hydrodynamic Behavior of Natural Adsorbents Filters for Water Treatment Technology
- Pages: 1235-1240
- First Published: 10 February 2023
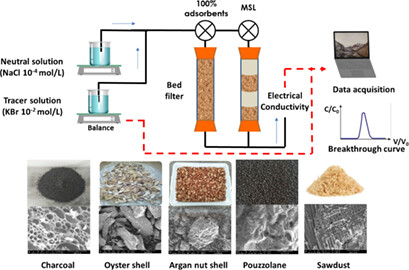
Quantification of water flow in natural low-cost adsorbents employed as multilayer filters for wastewater treatment by the infiltration-percolation technology was investigated. Laboratory tracer experiments and mathematical modeling were performed for such adsorbents. The choice of the appropriate adsorbent is crucial to improve flow uniformity, which in turn will impact the treatment efficiency.
ChannelCOMB Device for Mesostructured Reactors and Networks of Reactors
- Pages: 1241-1250
- First Published: 10 February 2023
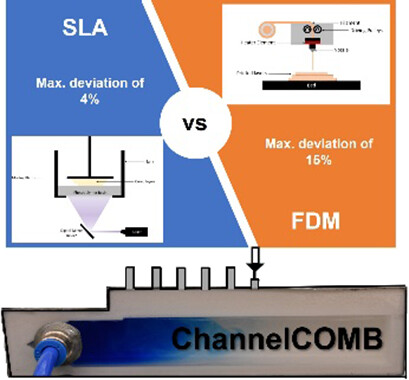
Stereolithography (SLA) and fused deposition modeling were used to additively manufacture ChannelCOMB, a consecutive flow distributor. The SLA ChannelCOMB shows a smaller flow deviation, because SLA promotes better flow uniformity due to the lower fabrication tolerance and material impermeability. The flow distribution can be well predicted by CFD simulations and the resistance analog model.
Process Simulation of Twin-Screw Granulator: Effect of Screw Configuration on Size Distribution
- Pages: 1251-1259
- First Published: 10 February 2023
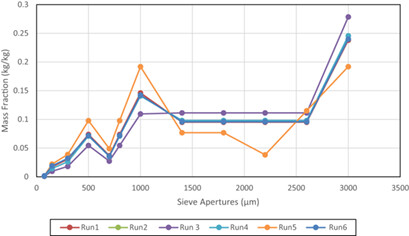
The significant impact of screw configuration on the final granule size distribution was investigated by means of gPROMS FormulatedProduct software to perform optimization, estimation of complex processes, and analyses. Twin-screw granulation modeling was applied to evaluate the contribution of screw configuration and liquid-to-solid ratio on granule size distribution.
Drop Size Distributions as a Function of Dispersed Phase Viscosity: Experiments and Modeling
- Pages: 1260-1270
- First Published: 12 February 2023
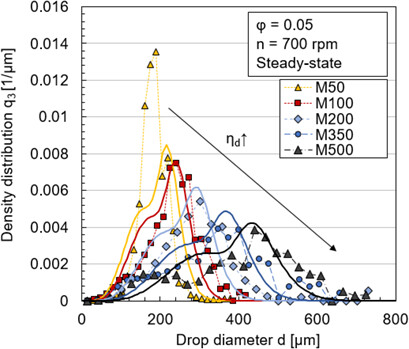
Measurements of dynamic and steady-state drop size distributions were performed in silicone oil-in-water systems with rising dispersed phase viscosity using an in situ endoscope technique in a stirred tank. The predictive power of a population balance model for partly mobile interfaces is evaluated critically. The fitting procedure and impact of daughter drop size distribution shape are discussed.
Templated Crystallization of Glycine Homopeptides: Experimental and Computational Developments
- Pages: 1271-1278
- First Published: 22 February 2023
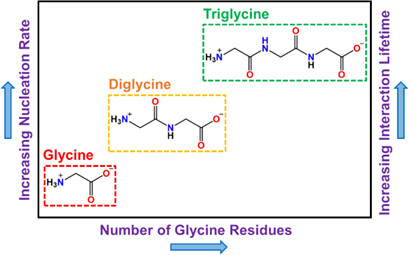
The rate of nucleation of (poly)glycine molecules increases with the number of glycine residues added. This may be attributed to more interactions between the (poly)glycine molecule and the heterosurface. Molecular dynamics simulations confirmed the existence of more interaction sites, resulting in an increase in hydrogen bond interaction lifetime of (poly)glycine with heterosurfaces.
Bunno's Fabulous Soap-Making Challenge – Educational Concept, Game Design, and Initial Evaluation
- Pages: 1279-1288
- First Published: 28 February 2023

Bunno's Fabulous Soap-Making Challenge is a resource-managing game in which players plan, organize, and execute the production of soap. The game concept, educational theory, design, educational content, and projected learning outcomes are described and discussed. A first mixed-method evaluation collects and identifies players' game-playing experiences. Results indicate that players enjoyed playing it.
Chemical Recycling of Waste Polypropylene via Thermocatalytic Pyrolysis over HZSM-5 Catalysts
- Pages: 1289-1297
- First Published: 06 March 2023
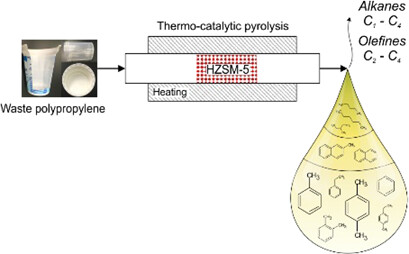
Chemical recycling allows for the transformation of waste polyolefins into valuable products which can be employed as secondary feedstocks for chemical and petrochemical industries. The acid site density of HZSM-5 catalysts can be used as a tool for tuning the product selectivity during thermocatalytic pyrolysis of polyolefins.
Possibilities of Optimizing the Purity of Mannose in Continuous Chromatographic Separation
- Pages: 1298-1306
- First Published: 27 April 2023
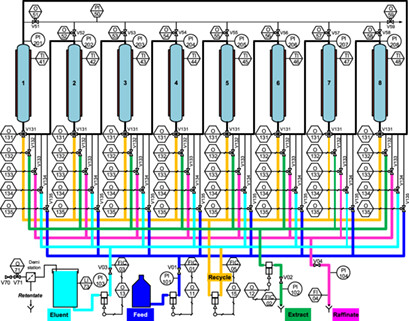
The design of continuous simulated moving-bed chromatography and its optimization for the separation of mannose from natural sources are described. The results are compared based on the purities of mannose in the extract stream and galactose in the raffinate stream. The developed method can be extended to more feed compounds and separation of aqueous solutions not only in carbohydrate technologies.
In Situ Bioreduction of Hexavalent Chromium-Contaminated Water Using a Microbial Culture Barrier
- Pages: 1307-1311
- First Published: 05 May 2023

Bioremediation of Cr(VI)-contaminated effluents is an economical and environment-friendly treatment method. Cr(VI) removal in a bench-scale bioreactor was investigated using municipal dried sludge as a permeable bioreactive barrier. The indigenous bacteria obtained from a wastewater treatment plant were able to effectively remove Cr(VI) with or without any biostimulation.
Overview
Overview Contents: Chemie Ingenieur Technik 6/2023
- Page: 1312
- First Published: 22 May 2023











