Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Editorial Board
Editorial Board: Chem. Eng. Technol. 4/2018
- Page: 666
- First Published: 25 March 2018
Overview
Overview Contents: Chem. Eng. Technol. 4/2018
- Page: 667
- First Published: 25 March 2018
Highlights
Editorial
Monitoring and Process Control of Anaerobic Digestion Plants
- Page: 670
- First Published: 25 March 2018
Research Articles
Ammonium Chloride vs Urea-Induced Ammonia Inhibition of the Biogas Process Assessed by Stable Isotope Analysis
- Pages: 671-679
- First Published: 09 January 2018
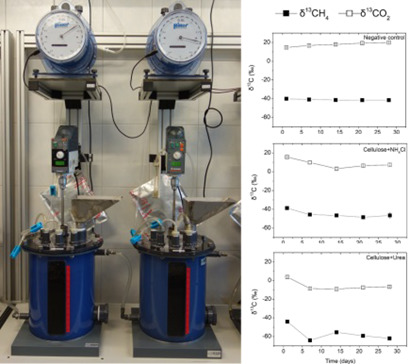
Ammonia, as a major inhibitor of the biogas process, is an important target of process monitoring. Ammonium salts, which are frequently used in laboratory experiments, are shown to lead to misleading results. Stable isotope analysis of the biogas was used to assess the major methanogenic pathway, confirming that ammonium chloride is a less effective biogas inhibitor than urea.
Measuring Biogas Composition with a Compact Microelectromechanical System-Based Spectrometer
- Pages: 680-686
- First Published: 17 January 2018

An online mid-infrared spectroscopic gas sensor with a microelectromechanical system-based interferometer was developed for assessing biogas concentration. The sensor response was evaluated and tests were performed on a pilot-scale digester and at a landfill site. The possible role of this sensor is discussed in the context of the shifting function of anaerobic digestion in the energy market.
Microbial Electrochemical Sensors for Anaerobic Digestion Process Control – Performance of Electroactive Biofilms under Real Conditions
- Pages: 687-695
- First Published: 17 January 2018
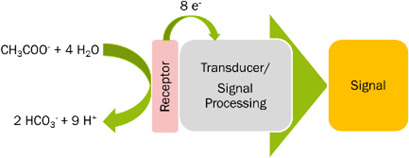
A microbial electrochemical sensor for the quantification of volatile fatty acids is integrated in a real anaerobic digestion process. The sensor signal correlates with the acetate concentration in the process but the sensor stability is affected by the process conditions. Potential inhibitors in the anaerobic digestion process are examined to explain the observed loss of function.
Real-Time Gas Quality Data for On-Demand Production of Biogas
- Pages: 696-701
- First Published: 17 January 2018

The flexible production of biogas makes it a promising candidate to become the first renewable on-demand energy source. One interesting possibility to enable on-demand supply of biogas is to control the output itself via system operation. A non-dispersive infrared absorption spectroscopy setup using an alternative, gas-based detector scheme based on the photoacoustic effect is proposed.
Management of Gas Storages in Biogas Plants
- Pages: 702-710
- First Published: 18 January 2018

Linking multiple biogas storages often causes problems on large-scale biogas plants, especially when they operate demand-driven gas consumers. Methods for the correct design and control of the gas system in biogas plants are reported and illustrated by reference to two specific large-scale industrial biogas plants, in order to overcome these problems by using a dedicated gas management system.
Laboratory Simulation of an Agricultural Biogas Plant Start-up
- Pages: 711-716
- First Published: 18 January 2018
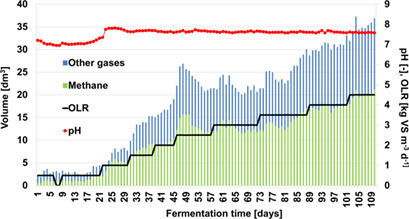
Currently, several biogas plants are started in Poland, using pig slurry as the main substrate. However, there is no up-to-date data on the commissioning of installations using this substrate. The start-up of agricultural biogas plants on a laboratory scale was simulated using pig slurry and maize silage. Similar running conditions like for real-scale biogas installation were assessed.
Two-Stage Dry Anaerobic Digestion Process Control of Biowaste for Hydrolysis and Biogas Optimization
- Pages: 717-726
- First Published: 19 January 2018
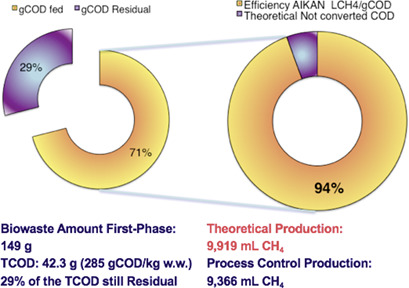
Anaerobic digestion is a promising technology for biowaste management. A highly important target is the overall process control of such plants. The hydrolysis in the first stage for the treatment of biowaste is optimized using the digestate recirculation from the second stage. An advanced management system is proposed with pH sensors to control the process within the optimal range.
Near-Infrared Spectrum Analysis to Determine Relationships between Biochemical Composition and Anaerobic Digestion Performances
- Pages: 727-738
- First Published: 06 February 2018
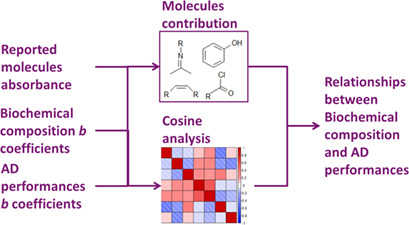
In order to assess the contribution of molecules to anaerobic digestion performances, the application of near-infrared spectroscopy and partial least square b coefficient analysis is proposed as a fast and economical approach. Powerful tools are provided to investigate the influence of the molecules on anaerobic digestion performances which can be extended to other fields of application.
A Scale-up Strategy for the Fluid Flow in Biogas Plants
- Pages: 739-746
- First Published: 07 February 2018
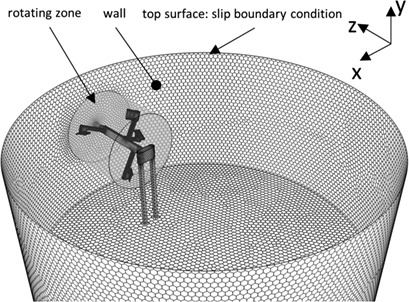
The mixing process in biogas plants is crucial to effectiveness. Difficult test conditions at full scale mean that experiments must be conducted at lab-scale. To cover flow characteristics, scale-up conditions have to be defined to transfer findings from the model to the original scale. Similarity laws are applied to find conditions necessary for achieving equal mixing processes at different scales.
Using Digestate Compost as a Substrate for Anaerobic Digestion
- Pages: 747-754
- First Published: 16 February 2018
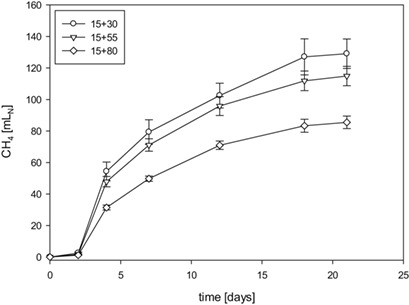
The digestibility of liquid digestate and digestate compost was evaluated using batch reactors in an anaerobic digestion plant. In these experiments, digestate compost turned out to be an interesting substrate for anew anaerobic digestion which can be employed in times of worsening reactor performance because of seasonal changes in the quantity and quality of the feed material.
Process Monitoring and Control for an Anaerobic Covered Lagoon Treating Abattoir Wastewater
- Pages: 755-760
- First Published: 16 February 2018
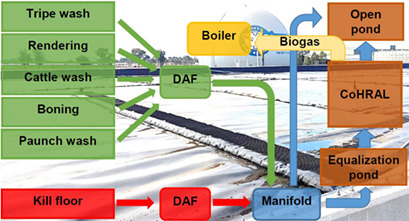
The monitoring of online and offline process parameters allows the efficient operation of anaerobic treatment plants but also requires a profound knowledge of the involved biological processes and regular maintenance and calibration of the sensor technology. Process monitoring and analytical methods at a field-scale biogas facility treating slaughterhouse wastewater are discussed.
Communications
Estimation of Methane Yields in Continuous Biogas Reactors Using Kinetic and Mass Flow Models
- Pages: 761-767
- First Published: 19 January 2018
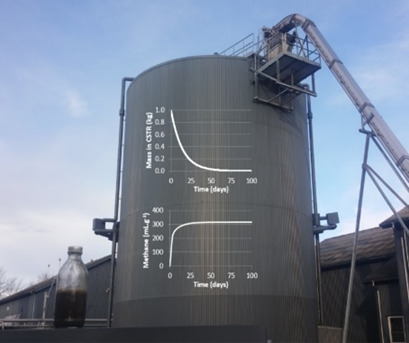
Estimating the methane yield of substrates in continuous anaerobic digestion processes usually requires either complex substrate analysis or labor-intensive laboratory-scale continuous reactors. By modifying simple batch assays and applying the acquired kinetic rates and specific methane yields to mass flow models, satisfactory estimation of continuous process yields was achieved.
Research Articles
Influence of External Forces during Supercooling on Dispersion Stability during Melt Emulsification
- Pages: 768-775
- First Published: 12 January 2018
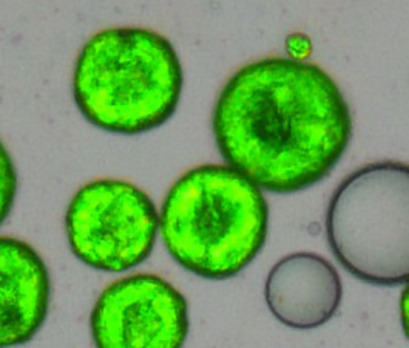
External forces during supercooling of melt-emulsified particles influence the size, shape, and stability of crystalline alkane dispersions. With increasing mechanical treatment during the crystallization, especially in higher alkane emulsions, the stability of the dispersions decreased due to morphological changes within solidifying droplets.
Energy and Exergy Analysis of Power Generation Systems with Chemical Looping Combustion of Coal
- Pages: 776-787
- First Published: 12 January 2018
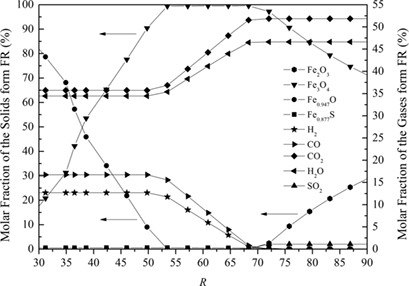
Chemical looping combustion (CLC) is an attractive technology because it allows fuel combustion with inherently pure CO2 separation. Two basic approaches to CLC, coal direct (CD) and coal gasification, are combined into cycle power generation systems and simulated by using the ASPEN Plus software. The CD-CLC combined cycle results in excellent system performance with high CO2 capture efficiency.
Effects of Solute Permeability on Permeation and Solute Rejection in Membrane Filtration
- Pages: 788-797
- First Published: 05 January 2018
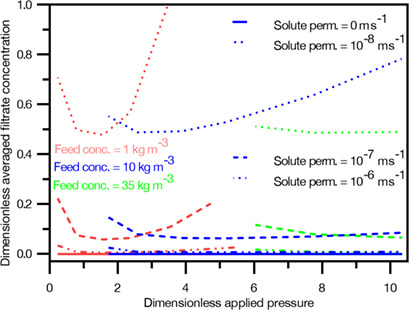
The coupling of concentration polarization, transmembrane solute and solvent fluxes and osmotic pressures was studied by solving the continuity, Navier-Stokes and solute transfer equations. Solvent permeation was found to rise with the value of membrane solute permeability. There is an optimal value of inlet pressure which leads to maximum solute rejection at a given feed concentration.
3D Printing for Chemical Process Laboratories II: Measuring Liquid-Solid Mass Transfer Coefficients
- Pages: 798-805
- First Published: 18 January 2018
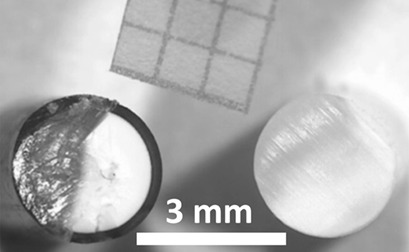
Sulfonated polymers have applications in water softening, acid catalysis, and measuring mass transfer rates. Herein, mass transfer coefficients for laminar flow were determined in a 3D-printed tubular reactor and a fixed bed of spherical particles, both modified by sulfonation, and the obtained values showed good agreement with correlations in the literature.
System Behavior and Predictive Controller Performance Near the Azeotropic Region
- Pages: 806-818
- First Published: 24 January 2018
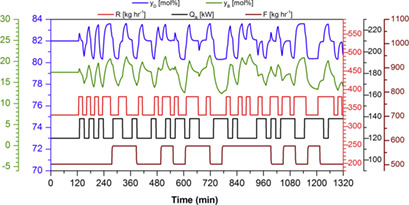
High-purity distillation columns exhibit issues in terms of nonlinearity, interactions, directionality, structural variance, and ill-conditioning for the control systems, leading to poor controller performance. The effects of these challenges on the performance of model predictive control in operations in near-azeotropic regions are evaluated via setpoint tracking and disturbance rejection.
Rheological Behavior of Mixtures of Ionic Liquids with Water
- Pages: 819-826
- First Published: 24 January 2018
Ionic liquids often contain considerable shares of moisture which exert a significant effect on their viscosity. Alterations of viscosity during mixing still mean a major challenge for the prediction of substance properties. The influence of water content on the rheological behavior of ionic liquids is evaluated and an estimation approach is proposed.
Experimental Studies of a Petlyuk Column and Validation of a Non-Equilibrium Stage Model
- Pages: 827-835
- First Published: 24 January 2018
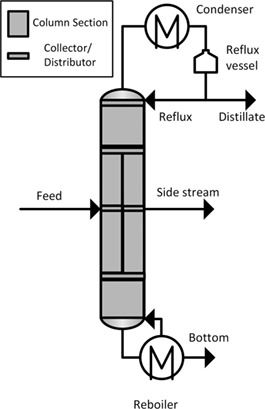
Process integration of unit operations is an important field of current research activities in academia and industry. Integrated distillation equipment like the Petlyuk column exhibits significant energy-saving potential. A pilot-plant scale Petlyuk column was operated for three reference systems, and a non-equilibrium simulation model was validated using the presented experimental data.
Ethyl Lactate Synthesis by Catalytic Membranes in a Pervaporation-Assisted Membrane Reactor
- Pages: 836-844
- First Published: 26 January 2018
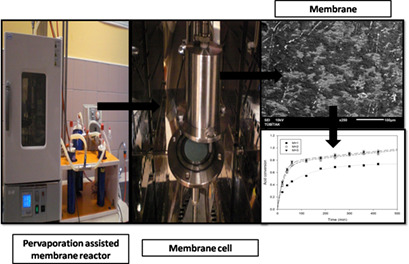
In order to achieve high lactic acid conversion associated with a high-purity final product without the need of a further purification step, a reactive and functional poly(styrenesulfonic acid)-carboxymethylcellulose blend catalytic membrane was developed and applied in a pervaporation-aided membrane reactor for ethyl lactate production. Excellent acid conversion could be realized.
Esterification of Oleic Acid with Methanol Using Zr(SO4)2 as a Heterogeneous Catalyst
- Pages: 845-852
- First Published: 31 January 2018
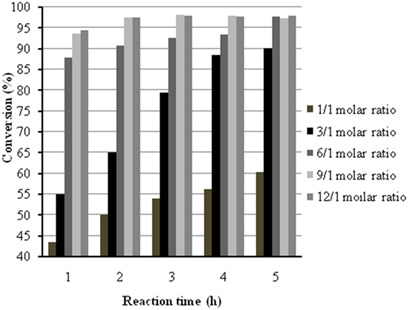
The catalytic performance of the Zr(SO4)2 catalyst was investigated for esterification of oleic acid with methanol. The effects of relevant reaction parameters like methanol-to-oleic acid molar ratio, reaction temperature, and catalyst amount versus reaction time were examined. The kinetics of esterification was studied by applying pseudo-homogeneous and Eley-Rideal models to experimental data.
Pressure Drop in Emergency Vent Lines with Two-Phase Flow of Gas and Viscous Liquid
- Pages: 853-859
- First Published: 09 February 2018
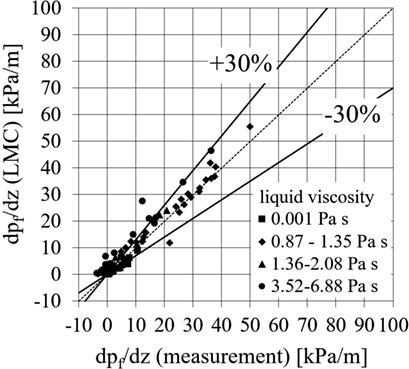
Emergency relief vent lines for polymerization reactors typically need to be sized for a two-phase flow of gas and highly viscous liquid phase. No experimental data are available and the empirical models are not validated in this region. The two-phase pressure drop in a vertically upward straight pipe was measured and the results were compared to literature models.
Flue-Gas Desulfurization by Using a HiGee Electric-Field Device
- Pages: 860-866
- First Published: 02 February 2018

SO2 is one of the major causes of acid rain and is mainly generated from coal combustion systems. SO2 is removed from flue gas by using a system composed of a rotating packed bed and an electric-field device. The effects of operating conditions on SO2 removal efficiency and gas-phase overall volumetric mass-transfer coefficient are revealed.
Correlation between Liquid Product Distribution and H2 Selectivity in Lignin Depolymerization
- Pages: 867-874
- First Published: 02 February 2018
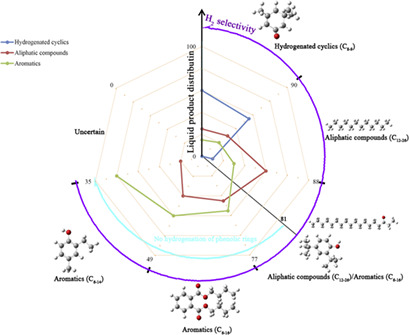
A correlation between the liquid product distribution and the H2 selectivity during catalytic depolymerization of kraft lignin is proposed, which can be used to predict the composition of the liquid products based on H2 selectivity detection or to convert kraft lignin to the desired liquid products. Different solvents, temperatures, and catalysts are viable options for this relationship.
Communications
Laplace Transform Treatment for Chemical Engineering Systems: Whether to Use 0− or 0+?
- Pages: 875-882
- First Published: 12 January 2018
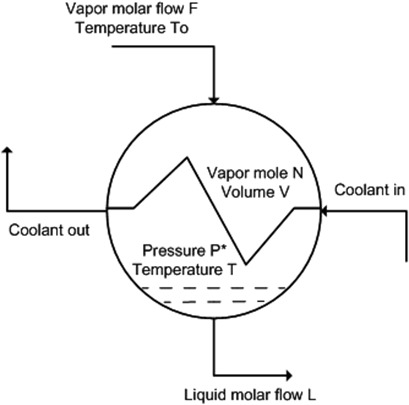
Consistent initialization issues in the Laplace transform treatment for nontrivial chemical engineering systems are addressed. Two application examples of a surge tank and a condenser that contain interacting capacities are used for illustration. The accuracy of the 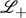 approach over
approach over 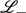 approach is verified and the popular
approach is verified and the popular 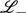 approach is found to be inconsistent and inexact.
approach is found to be inconsistent and inexact.
Overview
Overview Contents: Chemie Ingenieur Technik 4/2018
- Pages: 883-884
- First Published: 25 March 2018











