Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Editorial Board
Overview
Contents
Contents: Chem. Eng. Technol. 9/2013
- Pages: 1440-1446
- First Published: 22 August 2013
Highlights
Introduction
Review
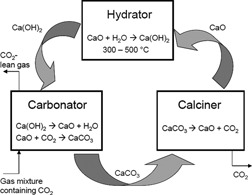
Ca(OH)2-Based Calcium Looping Process Development at The Ohio State University
- Pages: 1451-1459
- First Published: 22 August 2013
Research Articles
The Effect of Bituminous and Lignite Ash on the Performance of Ilmenite as Oxygen Carrier in Chemical-Looping Combustion
- Pages: 1460-1468
- First Published: 22 August 2013

The influence of ash in chemical-looping combustion has been studied in a lab-scale fluidized bed reactor. The gas conversion was clearly affected by the addition of ash, and very similar results were seen both for methane conversion and for CO conversion in solid fuel tests. Additionally, no negative effect of ash addition on the fluidizability of the bed material could be seen.
CO2 Capture and Desulfurization in Chemical Looping Combustion of Coal with a CaSO4 Oxygen Carrier
- Pages: 1469-1478
- First Published: 23 May 2013
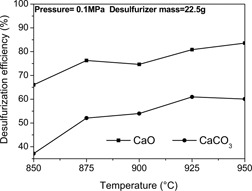
The feasibility of CO2 capture in situ desulfurization using traditional desulfurizers was examined in Ca-based chemical looping combustion (CLC) of coal. The performances of CaSO4 and desulfurizers were assessed under pressurized conditions in CLC of coal and the potential of anhydrite as a promising low-cost oxygen carrier was evaluated.
Thermodynamic Evaluation and Cold Flow Model Testing of an Indirectly Heated Carbonate Looping Process
- Pages: 1479-1487
- First Published: 22 August 2013
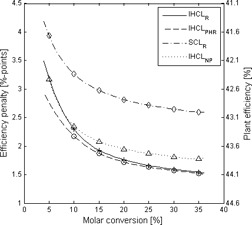
Carbon capture via indirectly heated carbonate looping can decrease the efficiency penalty of the post-combustion capture technology. Thermodynamic mass and energy balances of the process are presented. A concept is proposed based on a fluidized-bed heat exchanger system transferring heat from a combustor to the calciner by means of sodium-filled heat pipes. Cold flow model investiga-tions proved the concept of a 300-kWth pilot plant.
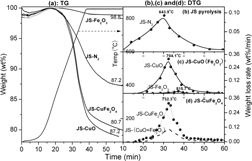
Chemical Looping Combustion of Petroleum Coke with CuFe2O4 as Oxygen Carrier†
- Pages: 1488-1495
- First Published: 26 April 2013
Sorbent-Enhanced Steam Methane Reforming Reaction Studied over a Ca-Based CO2 Sorbent and Ni Catalyst
- Pages: 1496-1502
- First Published: 22 August 2013
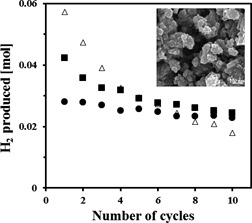
The sorption-enhanced steam methane reforming (SE-SMR) reaction was studied on a Ni-hydrotalcite-derived catalyst synthesized via a precipitation technique. Ca-based materials synthesized by a sol-gel technique served as CO2 sorbents. Under SE-SMR conditions, hydrogen of 99 vol % purity was obtained, i.e., thermodynamic equilibrium was reached.
Modeling of a Chemical Looping Combustion Process in Interconnected Fluidized Beds with a Cu-Based Oxygen Carrier
- Pages: 1503-1510
- First Published: 22 August 2013
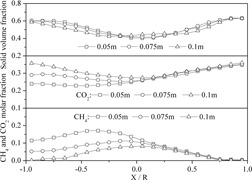
The reactive multiphase model is incorporated into the computational fluid dynamics code to simulate the reactive fluid dynamics in a chemical looping combustion (CLC) reactor with a two-fluid model. This model can recognize the complex gas-solid flow behaviors and chemical reactions in the process of a CLC system.
Impact of SO2 in the Presence of Steam on Carbonation and Sulfation of Calcium Sorbents
- Pages: 1511-1517
- First Published: 06 August 2013
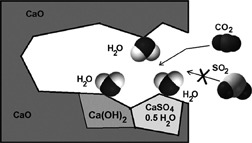
For implementing CaO carbonation and calcination reactions to separate CO2 from the flue gas it is imperative that the calcium sorbent maintains high reactivity over multiple cycles. Multicycle carbonation-calcination tests for three limestone types were carried out under simulated flue gas conditions to investigate the influence of the presence of steam and SO2 on CO2 sorption capacity.
Continuous CO2 Capture in a 1-MWth Carbonate Looping Pilot Plant
- Pages: 1518-1524
- First Published: 06 August 2013
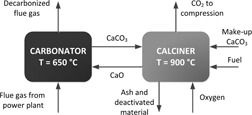
One possibility to minimize CO2 emissions from coal-fired power plants is the use of carbon capture and storage technology. Carbon capture tests using the carbonate looping technology have been performed in a 1-MWth carbonate looping pilot plant. The results from these tests are highly encouraging since very high CO2 capture efficiencies were achieved. The performance of the tests as well as the analysis of the results are presented.
Design and Experimental Investigation of Calcium Looping Process for 3-kWth and 1.9-MWth Facilities
- Pages: 1525-1532
- First Published: 02 August 2013

Calcium looping is a promising concept for post-combustion CO2 capture applications. A long-term test proved the stability and ease of operation of a 3-kWth facility. Detailed design parameters of the 1.9-MWth facility currently under construction in Taiwan are presented. The ambition of this pilot plant is to achieve a CO2 capture rate of 1 t h–1.
Self-Fluidization in an Indirectly Heated Calciner
- Pages: 1533-1538
- First Published: 23 July 2013
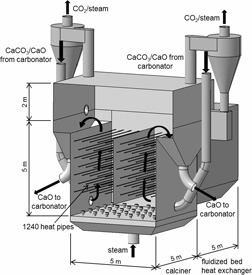
The indirectly heated carbonate looping process is a promising way to reduce CO2 emissions of fossil-fired power plants. Gas release and its possibility to transform a fixed to a fluidized bed during the calcination process are discussed on the basis of experimental investigations in an electrically heated fluidized-bed calciner.
Review
Research on Mass Transfer Columns: passé?
- Pages: 1539-1549
- First Published: 08 August 2013

From an industrial point of view, continuous research activity is important to generate thermodynamic equilibrium data for gas/liquid or gas/liquid/liquid systems and to predict their physical, thermal, and kinetic properties. Standardization of experimental test facilities for distillation, absorption, desorption, and liquid-liquid extraction is essential.
Research Articles
Fabrication and Evaluation of Non-porous Graphene by a Unique Spray Pyrolysis Method
- Pages: 1550-1558
- First Published: 08 August 2013
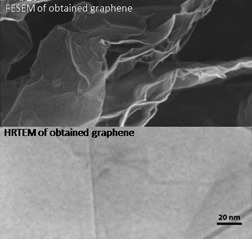
Graphene oxide is reduced by spray pyrolysis and a three-layer graphene is synthesized. Spray pyrolysis reduction proved to be a simple, reproducible, and appropriate synthesis method with great potential to be applied for large-scale production at low cost. Temperature as the most important parameter in this process is investigated and controlled.
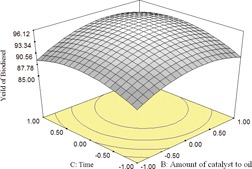
Transesterification of Soybean Oil to Biodiesel by Brønsted-Type Ionic Liquid Acid Catalysts
- Pages: 1559-1567
- First Published: 22 August 2013
Effects of Wall Confinement and Power-Law Fluid Viscosity on Nusselt Number of Confined Spheres
- Pages: 1568-1576
- First Published: 06 August 2013
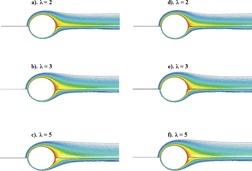
Impacts of wall confinement on heat transfer phenomena of confined spherical particles in Newtonian and power-law fluids are investigated by means of a numerical approach for wide ranges of relevant dimensionless parameters. An empirical correlation for the average Nusselt numbers of confined spheres in such fluids is proposed based on numerical results.
Melt Index Prediction by Fuzzy Functions and Weighted Least Squares Support Vector Machines
- Pages: 1577-1584
- First Published: 08 August 2013
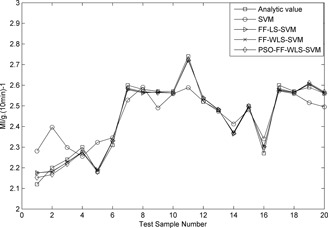
A novel high-precision on-line method for predicting the melt index of propylene polymerization based on fuzzy functions and weighted least squares support vector machines is proposed to overcome the high correlation characteristics and high nonlinear characteristics in the propylene polymerization process. The validity of these methods is demonstrated through practical data in a real factory.
Optimization of a Multiple Impinging Jets Cavitation Reactor Using Zero-Valent Iron Powder as Catalyst
- Pages: 1585-1592
- First Published: 06 August 2013
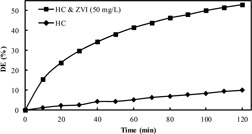
Heterogeneous catalyzed hydrodynamic cavitation (HC) was combined with impinging streams and a pilot-scale multiple impinging jets cavitation reactor was constructed. Zero-valent iron powder served as a cost-efficient catalyst to improve significantly the performance of low-pressure HC. The mechanism of enhancing effects of the catalyst is discussed.
Regeneration of a Commercial Catalyst for the Dehydrogenation of Isobutane to Isobutene
- Pages: 1593-1598
- First Published: 08 August 2013
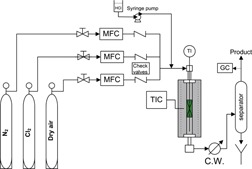
The regeneration of deactivated Pt-Sn/γ-Al2O3 catalyst utilized for the dehydrogenation of isobutane to isobutene in a commercial-scale plant is presented. The activity of the commercial Pt/γ-Al2O3 catalyst is recovered after the regeneration process and the selectivity of the regenerated catalyst for the production of isobutene is similar to that of the fresh one.
Hydrogen Production from Bio-Char via Steam Gasification in a Fluidized-Bed Reactor
- Pages: 1599-1602
- First Published: 06 August 2013
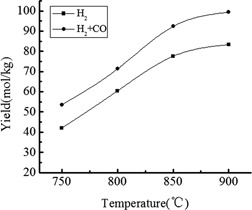
Bio-char served as feedstock to perform hydrogen production by means of steam gasification in a fluidized-bed reactor. The influence of gasification temperature and steam-to-char ratio was evaluated. The optimal contact of bio-char with steam in this reactor leads to enhanced carbon conversion, hydrogen production, and large-scale production.
Communication
Hydrodynamics of High-Pressure Bubble Columns†
- Pages: 1603-1607
- First Published: 06 August 2013
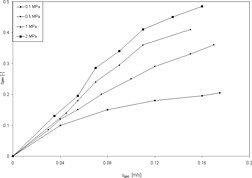
Although bubble columns are applied in many chemical production facilities, only a limited number of experimental studies regarding bubble column hydrodynamics under industrial conditions do exist. An overview of available publications regarding gas holdups and dispersion in bubble columns operated under high pressure is presented and discussed in detail.