Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Organic Donor–Acceptor–Donor Trimers Nanoparticles Stabilized by Amphiphilic Block Copolymers for Photocatalytic Generation of H2
- First Published: 23 September 2024

Front Cover: A versatile platform is developed for creating functional π-conjugated organic nanoparticles stabilized by amphiphilic block copolymers for green H2 photocatalytic generation. The donor–acceptor–donor trimers nanoparticles show enhanced photocatalytic activity (≈0.6 mmol g−1 h−1) for H2 production via water splitting. More details can be found in article 2400395 by Thiago R. Guimarães, Jean-Louis Bobet, Eric Cloutet, and co-workers.
Masthead
Review
Structural Functions of 3D-Printed Polymer Scaffolds in Regulating Cell Fates and Behaviors for Repairing Bone and Nerve Injuries
- First Published: 17 June 2024
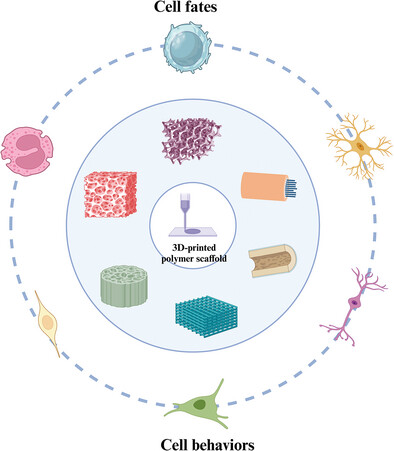
Fabricating 3D-printed polymer scaffolds is a powerful approach in tissue engineering. These scaffolds are crucial for repairing bone and nerve injuries by influencing the fates and behaviors of immune cells, stem cells, and other key cells. Their structural properties promote tissue repair and regeneration, making them pivotal to efficient tissue engineering strategies.
TFE Terpolymers: Once Promising – Are There Still Perspectives in the 21st Century: Synthesis, Characterization, and Properties-Part I
- First Published: 06 August 2024
PTFE decomposes at temperatures close to its melting point. Therefore, TFE terpolymers have emerged as desirable PTFE alternatives, where these TFE terpolymers combine PTFE's advantages with better processability. Currently, fluoropolymers have reached a new era. The present review summarizes the synthesis, detailed characterization, and structure-property correlations of the fluoropolymers and ends with a future perspective on the use of fluoropolymers.
Research Article
Organic Donor–Acceptor–Donor Trimers Nanoparticles Stabilized by Amphiphilic Block Copolymers for Photocatalytic Generation of H2
- First Published: 10 July 2024
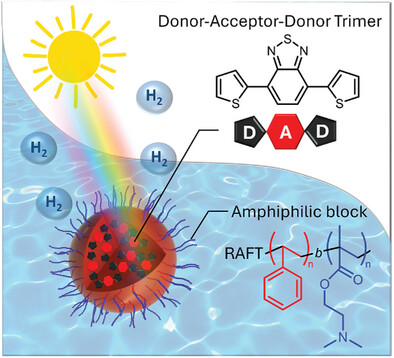
A versatile platform is developed for creating functional π-conjugated organic nanoparticles stabilized by amphiphilic block copolymers for green H2 photocatalytic generation. The donor–acceptor–donor trimers nanoparticles show enhanced photocatalytic activity (≈0.6 mmol g⁻¹ h⁻¹) for H₂ production via water splitting.
A Minimalist Method for Fully Oxygen-Tolerant RAFT Polymerization through Sulfur-Centered Trithiocarbonate Radical Initiation
- First Published: 05 August 2024
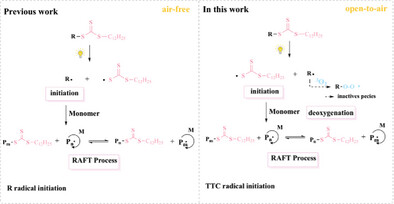
In this work, a minimalist method is successfully employed to accomplish fully oxygen-tolerant reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization using bis(trithiocarbonate) disulfides as iniferter agent. By high-throughput screening, we found that trithiocarbonate (TTC) is responsible for the fully oxygen-tolerant RAFT polymerization through sulfur-centered trithiocarbonate radical initiation and R radical deoxygenation.
Dynamically Reconfigurable Micro-Patterned Hydrogels Based on Magnetic Pickering Emulsion Droplets
- First Published: 08 August 2024
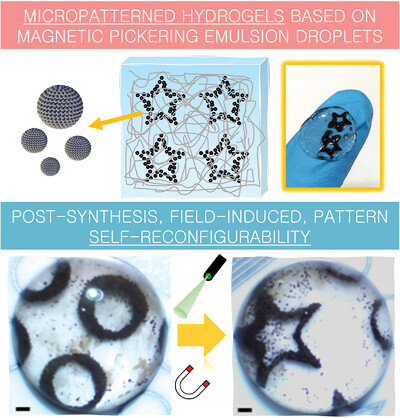
Self-reconfigurable micro-patterned hydrogels based on Pickering emulsion droplets stabilized by magnetic particles are fabricated. These particles harness energy from external fields so that hundreds of droplets organize into field-guided patterns, which are immobilized within the hydrogels. The droplets themselves can drive pattern self-reconfigurability upon laser irradiation. Additionally, they can behave as hydrophobic, liquid-like reservoirs of nutrients for cell growth.
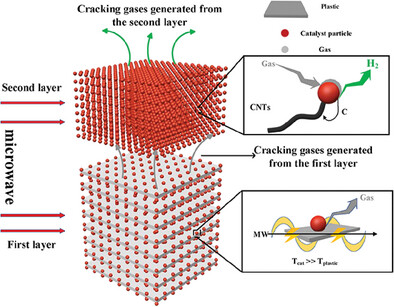
Highly Efficient Recycling Waste Plastic into Hydrogen and Carbon Nanotubes through a Double Layer Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis Method
- First Published: 29 July 2024
Reorganization of Poly(Butylene Succinate) Containing Crystals of Low Stability
- First Published: 14 June 2024
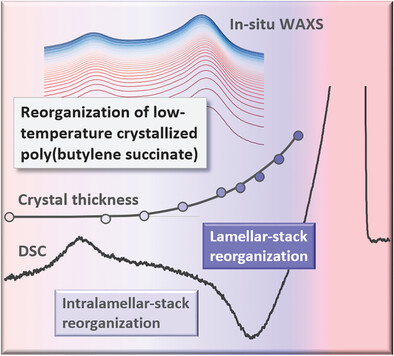
Poly(butylene succinate) forms imperfect crystals on crystallization at low temperature. Analysis of the evolution of unit-cell parameters, long period, and thickness of such crystals during slow heating, in combination with a quantitative evaluation of thermal events, as detected by calorimetry, identifies melting and melt-recrystallization at different length-scales, controlled by temperature, as a mechanism of crystal reorganization.
A Fluorescent Hydrogel with AIE Emission for Dehydration-Visualizable Wearable Sensors
- First Published: 30 May 2024
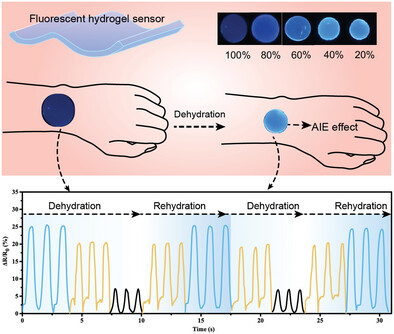
Herein, a novel AIEgen-based fluorescent hydrogel as wearable sensing electronic devices, having the capability to simultaneously track motion signals and hydrogel's water retention rate that depends on fluorescence intensity at various joints of the human body, is successfully prepared by the one-pot strategy.
Synthesis of New Glycine-Based Polymers and their Thermoresponsive Behavior in Water
- First Published: 08 June 2024
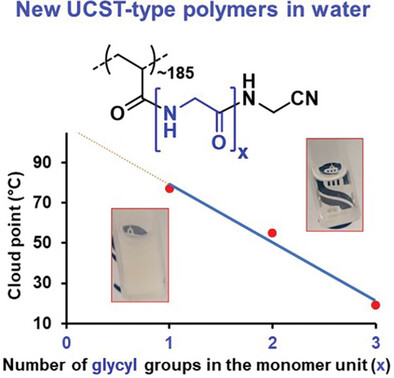
Cyanomethylglycinamide-derived polymers exhibit an upper critical solution temperature-type thermal transition in water. Their cloud point can be adjusted over a large temperature range (from ≈20–85 °C), by tuning the polymer's molar mass and/or the number of amide functional groups in the monomer structure.
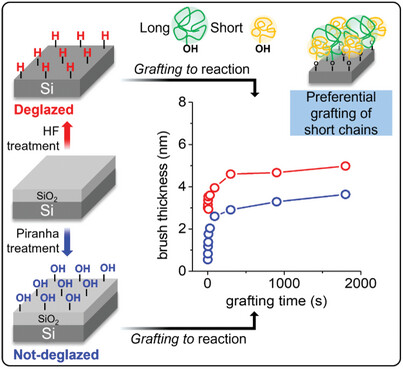
Polystyrene Brush Evolution by Grafting to Reaction on Deglazed and Not-Deglazed Silicon Substrates
- First Published: 16 July 2024
Facile Preparation of Silica/Tannic Acid/Zein Microcapsules Templated from Non-Aqueous Pickering Emulsions and their Application in Cargo Protection
- First Published: 29 July 2024
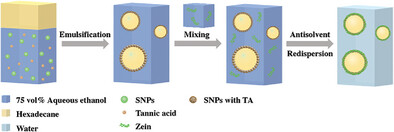
A simple and controllable method is established for preparing oil droplet-filled silica nanoparticle/tannic acid/zein microcapsules using a non-aqueous Pickering emulsion template. Furthermore, the encapsulation and protection of a lipophilic and active compound, β-carotene, within the filled oil droplets is demonstrated.
Stable and Durable Superhydrophobic Cotton Fabrics Prepared via a Simple 1,4-Conjugate Addition Reaction for Ultrahigh Efficient Oil–Water Separation
- First Published: 04 June 2024
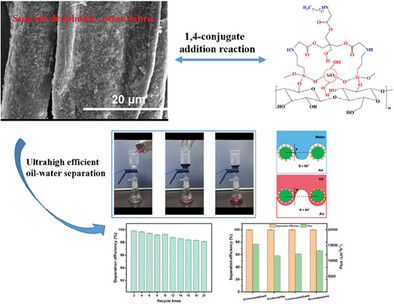
This work reports that stable and durable superhydrophobic cotton fabrics can be prepared using 1,4-conjugate addition reaction by a simple two-step impregnation process. The coated cotton fabric has good physical and chemical stability, self-cleaning, and anti-fouling ability. Importantly, the coated fabric shows excellent oil/water separation efficiency and ultrahigh separation flux.
Separating Charge Centers of Chain Segments in Dielectric Elastomer through Steric Hindrance Engineering
- First Published: 21 May 2024
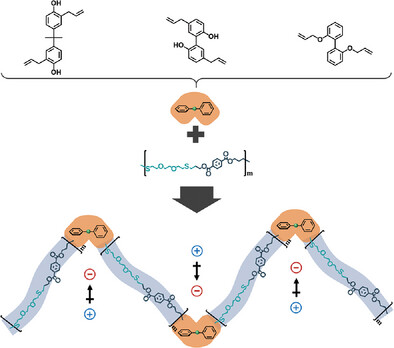
Decoration of polar groups is a direct pathway toward homogeneous dielectric elastomers (DEs) with high dielectric constant (ε′). However, a high grafting degree results in high ε′ together with high dielectric loss ascribes to the interaction of polar groups. Herein, a brand-new method with completely different mechanism is proposed to achieve DEs with both high ε′ and low dielectric loss.
Enhancing CO2 Transport Across the PEG/PPG-Based Crosslinked Rubbery Polymer Membranes with a Sterically Bulky Carbazole-Based ROMP Comonomer
- First Published: 26 July 2024
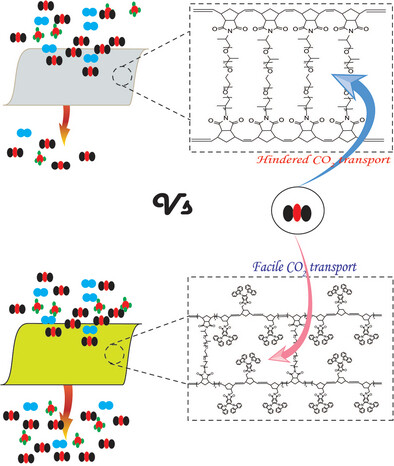
Poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(propylene glycol) (PEG/PPG)- and 5,6-di(9H-carbazol-9-yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione (2CZPImide)-based crosslinked rubbery polymer membranes are newly prepared. Tuning of the microstructure of the PEG/PPG chain segment of the crosslinked system with the sterically bulky NB-2CZPImide comonomer resulted in excellent CO2/N2 and CO2/CH4 selectivities along with long-term stability against physical aging and plasticization resistance.
Enhanced Microstructural Uniformity in Sulfuric-Acid-Treated Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene):Poly(Styrene Sulfonate) Films Using Raman Map Analysis
- First Published: 08 June 2024
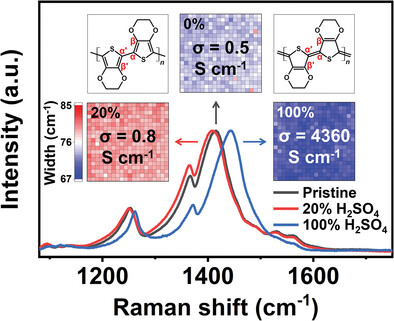
In this study, spatially resolved Raman properties of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrene sulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS) thin films treated with different concentrations of H2SO4 are presented. The results show blueshifted and narrower Raman maps of the Cα═Cβ modes, suggesting a structural transition from coiled to linear conformation and improved crystallinity of the PEDOT chains, indicative of enhanced conductivity.
High Hydrophilic and Antibacterial Efficient UV−Curable Silicone−Containing Choline Chloride Quaternary Ammonium Salts Functionalized Materials
- First Published: 21 June 2024
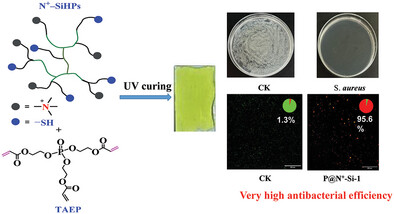
High hydrophilic and antibacterial efficient UV-curable silicone-containing materials are prepared from silicone−containing Choline chloride (ChCl) functionalized hyperbranched quaternary ammonium salts (QAS) and tri−hydroxylethyl acrylate phosphate by UV curing method. The materials possess high hydrophilic performance with a water contact angle as low as 19.3° and quite high antibacterial efficiency against S. aureus over 95.6%.
In Situ Growth of Highly Compatible Cu2O-GO Hybrids Via Amino-Modification for Melt-Spun Efficient Antibacterial Polyamide 6 Fibers
- First Published: 14 June 2024
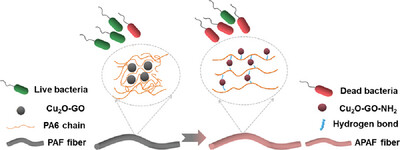
The PA6/Cu2O-GO-NH2 composite fiber, constructed via chemical grafting of aminosilane coupling agent (AEAPTMS) and in situ strategy, exhibits enhanced fracture strength (from 3.0 cN/dtex to 4.2 cN/dtex) and high antimicrobial efficacy (98.85% against Bacillus subtilis, 99.99% against Escherichia coli) after washing 50 times. The in situ concepts and chemical modification improve antimicrobial dispersion and interface bonding, with medical, textile potential.
Reprocessable Polymer Networks Containing Sulfur-Based, Percolated Dynamic Covalent Cross-Links and Percolated or Non-Percolated, Static Cross-Links
- First Published: 11 July 2024
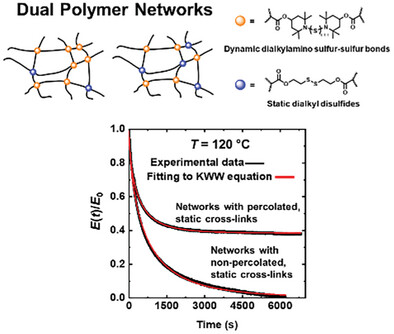
Robust and reprocessable poly(n-hexyl methacrylate) and poly(n-lauryl methacrylate) covalent adaptable networks (CANs) with fractions of percolated or non-percolated, static cross-links are synthesized. The stress relaxation behaviors of CANs are governed either by the dissociative cross-linker chemistry or side-chain motions depending on the amount of percolated, static cross-links.
A Simple Generic Model of Elastin–Like Polypeptides with Proline Isomerization
- First Published: 05 June 2024
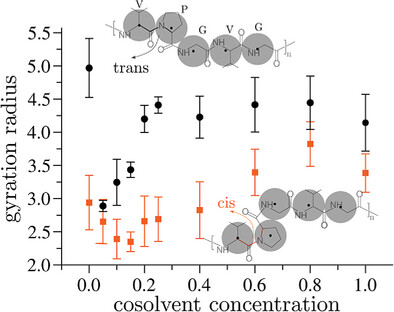
Understanding the solvation behavior of elastin-like polypeptides is crucial in designing high-performance biomaterials for their advanced functional applications. In this work, a simple generic model is derived to investigate the effect of proline isomerization on ELP conformations in binary mixtures. The far-reaching implication of such a simplistic model might be to study the large scale self-assembly of biomolecules.
Clustering-Triggered Emission Mechanism of Sulfur Ester-Polyacrylamide Aqueous Solution
- First Published: 10 July 2024
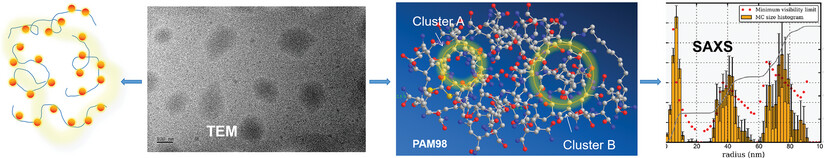
Herein, the photoluminescence properties and mechanism of the gradient aqueous solution of Sulfur ester-polyacrylamide aqueous solution have been successfully elucidated through transmission electron microscopy (TEM), small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), and molecular interaction analysis. It provides a strategy to clarify the clustering-triggered emission (CTE) mechanism of nonconventional luminogens solution more clearly.