Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Editorial Board
Masthead
Contents
Short Communication
Research Articles
Effects of Electron Beam Irradiation on the Physicochemical Properties of Quinoa and Starch Microstructure
- First Published: 11 January 2020
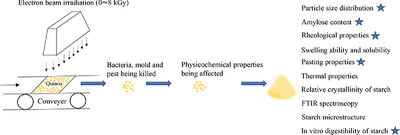
Electron beam irradiation (EBI) can be used as a processing method for quinoa. During the irradiation process, bacteria, mold, and pest in quinoa seeds can be killed. EBI also impacts the physicochemical properties such as particle size, amylose content, rheological properties, and pasting properties of quinoa flour. In this study, the physicochemical properties of quinoa flour before and after irradiation are compared. The results can be used as a guide to ensure the irradiated quinoa products are with desired quality.
A Semi-Empirical Model for Mass Transfer in Carbohydrate Polymers: A Case of Native Cassava Starch Hydration Kinetic in Hot Water Media
- First Published: 14 March 2020
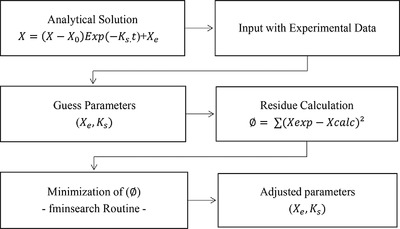
This article aims to determine the parameters of a model based on mass balance to represent the process of native cassava starch hydration. Experimental data on the hydration of natural starch is collected. It is concluded that the hydration of natural starch profile has a logarithmic behavior over time, and the correlation that best describes the behavior of equilibrium moisture content is linear.
Modification of Starches with Different Amylose/Amylopectin-Ratios Using the Dual Approach with Hydroxypropylation and Subsequent Acid-Thinning—Impacts on Morphological and Molecular Characteristics
- First Published: 06 April 2020
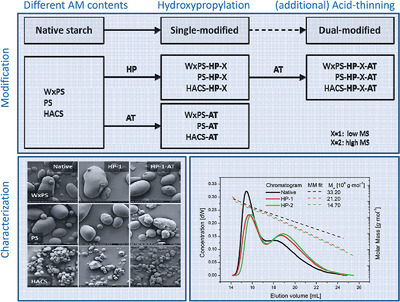
Dual-modified starches: Hydroxypropylation and acid-thinning of commercial starches with different AM/AP-ratios. Investigation using scanning electron microscopy reveals basically intact granular structure with surface defects. The molecular properties are determined by means of size exclusion chromatography techniques. The evaluation using statistical analysis (ANOVA) identifies statistically significant impacts with respect to the starch type, the substitution level, and the acid treatment.
Effect of Crystalline and Double Helical Structures on the Resistant Fraction of Autoclaved Corn Starch with Different Amylose Content
- First Published: 31 March 2020
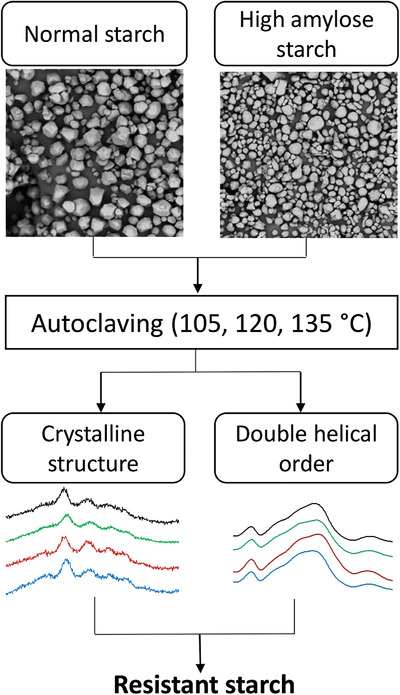
Resistant starch (RS) is a functional compound. Normal and high amylose corn starches are autoclaved to obtain RS. Formation of RS depends more on the organization of the double helical order than on the crystalline structure. Understanding the structural factors determining the formation of RS could help to tailor the properties of autoclaved starch when used as an ingredient.
Preparation and Characterization of a Starch-Based Adsorbent for the Effective Removal of Environmental Pollutants Hg (II)
- First Published: 10 April 2020
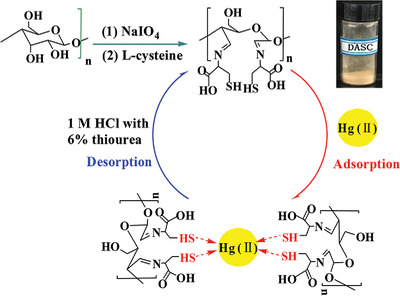
In the present study, a novel dialdehyde starch cysteine Schiff base biosorbent is synthesized and used to remove Hg (II) from aqueous solution. Owing to the advantages of low cost, eco-friendly, high adsorption capacity, and recyclability, this starch-based material may have potential application in the treatment of Hg (II) contaminated water and environmental remediation.
Pickering Emulsions Produced with Starch Nanocrystals from Cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz), Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.), and Corn (Zea mays L.)
- First Published: 13 April 2020
The behavior of starch nanocrystals produced from three different sources (cassava, corn, and bean starches) is studied when they are used to stabilize Pickering emulsions. The starch sources influence the crystallinity and the behavior of the nanocrystals. The nanocrystals that are oxidized with hypochlorite have superior performance for stabilizing the emulsions.
Characterization of Functional Properties of Biodegradable Films Based on Starches from Different Botanical Sources
- First Published: 20 April 2020
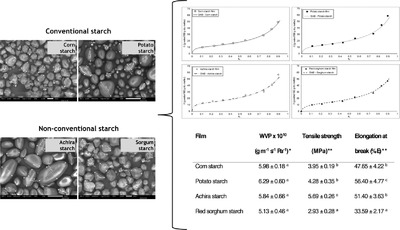
Starch-based biodegradable film properties can be affected by the starch source. Non-gelatinized starch granules can significantly modify the mechanical and barrier performance of films. The hydration properties of starch films are found to vary depending on the botanical source, mainly the solubility, the water vapor adsorption capacity, and the swelling index.
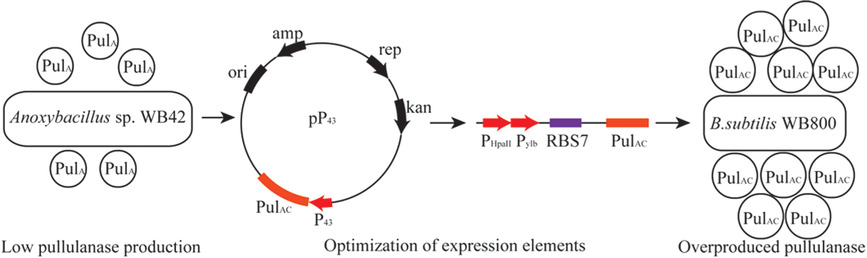
Production of a Thermostable Pullulanase in Bacillus subtilis by Optimization of the Expression Elements
- First Published: 10 April 2020
Physicochemical Properties and Structure of Annealed Sweet Potato Starch: Effects of Enzyme and Ultrasound
- First Published: 25 April 2020
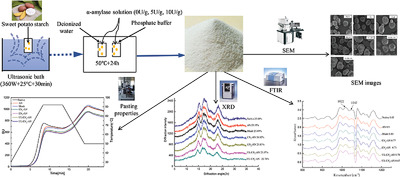
In order to improve properties of native starch, and annealing methods ultrasound and enzymes are applied to enhance the annealing process, and the effects of annealing, enzymatic annealing and ultrasonically enzymatic annealing on the structure and properties of starch are investigated and compared. This work provides a theoretical foundation to develop new modified starches and novel technology for starch modification.
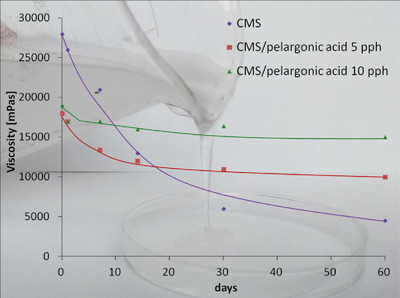
Carboxymethyl Starch/Medium Chain Fatty Acid Compositions: Rheological Changes During Storage and Selected Film Properties
- First Published: 05 May 2020
Luminescent Europium Complex-Grafted Octenyl Succinylated Starch Nanoparticles
- First Published: 07 May 2020
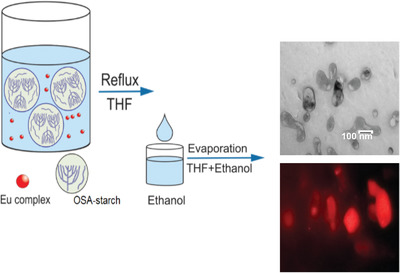
Although several fluorescent nanoparticles have been reported, none of them is based on a modified starch that will allow covalent attachment of lanthanide complexes. In this work, fluorescent octenyl succinic anhydride-starch nanoparticles with a covalently linked europium complex are synthetized. The used method is simple and produced novel hybrid nanomaterials with promising application in biological imaging or cell labeling.
Commercial Starch Behavior When Impregnated with Food Additives by Moderate Temperature Supercritical CO2 Processing
- First Published: 13 March 2020
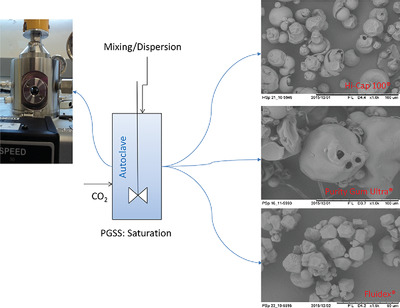
The behavioral analysis of carrier materials in supercritical carbon dioxide (CO2) is important for particle formation applications. In this work, the behavior of modified starches (Hi-Cap 100, Purity Gum Ultra, and Fluidex) in supercritical CO2 at 15 MPa and 60 °C is studied. Although the starches are chemically modified, which gives them hydrophobicity, their interaction with supercritical CO2 are found to be minimal.
Pasting, Rheological, and Thermal Properties and Structural Characteristics of Large and Small Arenga pinnata Starch Granules
- First Published: 30 March 2020
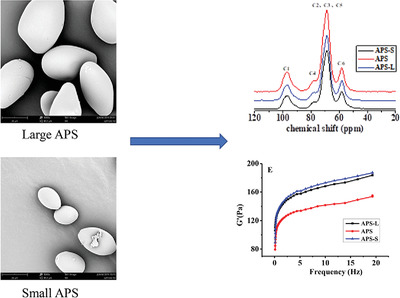
Arenga pinnata starch (APS) is separated into large and small size fractions. The granule size is significantly related to pasting, rheological, and thermal properties of the APS. APS structure–functional relationships might be affected by their morphology, granular size, molecular structures, and interactions between large and small granules. The native APS may be more conducive processing.
Effect of Drought stress on Resistant starch content and Glycemic index of rice (Oryza sativa L.)
- First Published: 15 April 2020
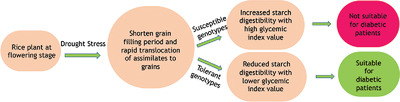
People eating rice as main food component have greater risk of developing type-II diabetes. Rice cultivation encounters mild to moderate drought stress during the grain filling period resulting in increased starch digestibility with high glycemic index value. Identification of rice genotypes having less responsiveness towards increment in glycemic index under drought stress may be useful in this context.
Review
Methods for the Extraction of Roots, Tubers, Pulses, Pseudocereals, and Other Unconventional Starches Sources: A Review
- First Published: 02 May 2020
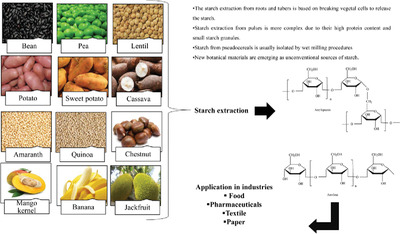
The starch extraction from roots and tubers is based on breaking vegetal cells to release the starch. Starch extraction from pulses is more complex due to their high protein content and small starch granules. Starch from pseudocereals is usually isolated by wet milling procedures. New botanical materials are emerging as unconventional sources of starch.
Short Communication
Co-Joined Starch Modification and β-Carotene Dispersion In Situ by Planetary Ball Milling
- First Published: 04 June 2020
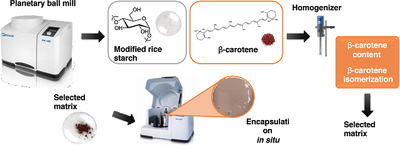
An innovative method to obtain starch modifications and β-carotene dispersion in situ is tested by planetary ball milling. β-carotene structure is partially (69%) preserved, a 16-fold increase in the encapsulated/surface ratio and a threefold increase in the encapsulated β-carotene content are obtained compared to traditional rotor–stator homogenizers.
Research Articles
Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Starch from Cassava Roots Differing in Growing Duration and Ploidy Level
- First Published: 12 May 2020
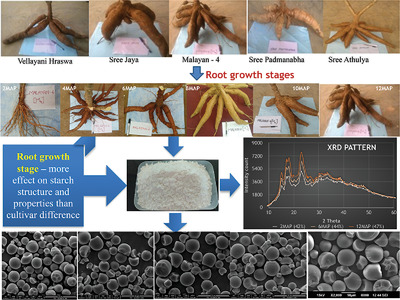
Starch is isolated from five cultivars of cassava at different root harvesting periods starting from root initiation stage. All the starches show A-type X-ray diffraction patterns. Average chain length and molecular weight of the starch show varietal differences. Significant differences in the physicochemical and functional properties of starch with ploidy of the plant are not observed.
A More Efficient Fenton Oxidation Method with High Shear Mixing for the Preparation of Cellulose Nanofibers
- First Published: 17 May 2020
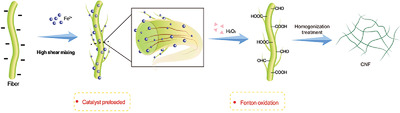
Cellulose nanofiber (CNF) has been widely used in numerous fields due to its distinct features. However, the preparation of CNF has some disadvantages such as high chemical consumption and low efficiency. The objective of this work is to investigate a green facile high shear mixing enhanced Fenton oxidation pretreatment method for the preparation of CNF, and this new process is feasible and has high potential in CNF industrial preparation in the future.
Changes in Structural and Physicochemical Properties of Corn Flour after Fermentation with Lactobacillus plantarum Y1
- First Published: 18 May 2020
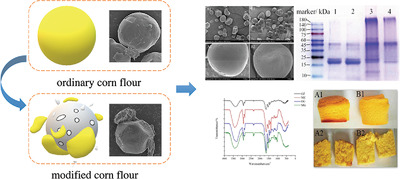
Fermentation with L. plantarum Y1 significantly improves swelling power, solubility, and water binding capacity of corn flour. Also, hardness and retrogradation tendency of corn flour dough reduces after fermentation. The improvements in functional properties of the fermented corn flour may be associated with changes in starch and protein .
Structural Properties Change of Cassava Starch Granule Induced by High Shear Mixer
- First Published: 27 May 2020
Multiple Ethanolic-Precipitation: An Approach to the Separation of Dextrin Fractions with Narrow Molecular Weight Distributions from Acid-Hydrolyzed Waxy Corn Starch
- First Published: 24 May 2020
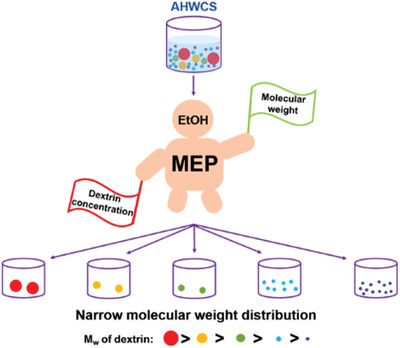
A new ethanolic fractionation method, the multiple ethanolic-precipitation, is established to fractionate acid-hydrolyzed waxy corn starch via weakening the effect of the dextrin concentration on fractionation. Thus, the fractionation only depends on the molecular weight of dextrin. The dextrin fractions with narrow molecular weight distributions and various properties can broaden the application of dextrin in different industries.
Thermal, Morphological, and Functional Characterization of Gros Michel Banana Starch Modified with Octenyl Succinic Anhydride
- First Published: 03 June 2020
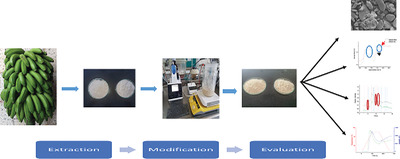
The banana variety Gros Michel modified starch is studied. The physicochemical and structural characteristics of this starch are different from other modified starches, reported in previous works. The starch structure of the Gros Michel banana is altered by chemical modification with octenyl succinic anhydride, evidenced by the changes in the hexagonal and monoclinic conformations of its crystalline structure.
Synthesis and Characterization of Inulin Butyrate Ester, and Evaluation of Its Antioxidant Activity and In Vitro Effect on SCFA Production
- First Published: 12 June 2020
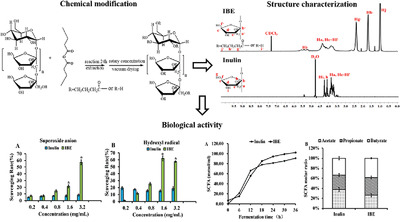
This study presents the synthesis and characterization of inulin butyrate ester which can be used to increase the antioxidant activities of superoxide anion radicals and the amount of short chain fatty acid (SCFA). In vitro experiments show that it may enable delivery of high concentration of SCFA to the colon and may influence intestinal health.
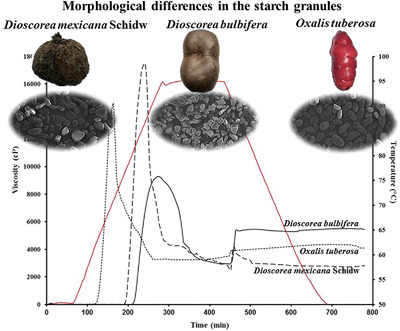
Physicochemical, Morphological, and Molecular Properties of Starch Isolated from Dioscorea and Oxalis Tubers from Hidalgo State, Mexico
- First Published: 13 June 2020
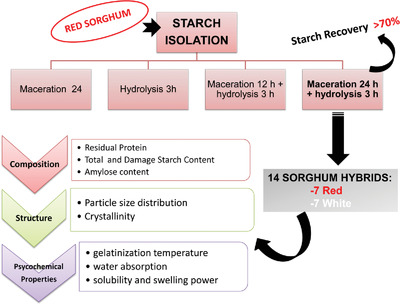
Comparison of Isolation Methods and Physicochemical Characteristics of Starches Isolated from Red and White Sorghum Hybrids
- First Published: 19 June 2020
Morphological, Structural, and Functional Evaluation of Rice Starch Acylated in a System Catalyzed by the B-Lipase of Candida antarctica
- First Published: 26 May 2020
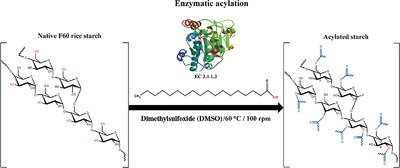
The evaluation of native starches with different fatty acid contents and the effect of the fatty acid type and content on the polymer characteristics of modified starches are reported. This work widens the scope of the applications of rice starches by modifying them for uses in the pharmaceutical and/or food industries, according to the herein reported characteristics.
Purified Starches from 18 Pulses Have Markedly Different Morphology, Oil Absorption and Water Absorption Capacities, Swelling Power, and Turbidity
- First Published: 07 June 2020
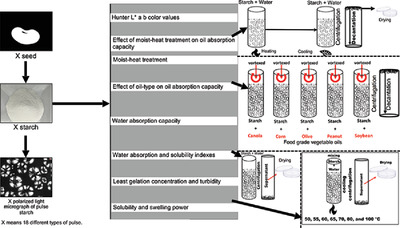
There is high demand for healthier food ingredient with specific functionality. These demands contribute to the potential use of pulse starch as an alternative food ingredient. However, further investigation of pulse starch is still required. Pulse starches are herein studied for specific functionalities. A clear difference is observed among the purified pulse starches. This study provides additional understanding of pulse starch functionalities.
β-Carotene Stability and Some Physicochemical Properties of Apricot Juice Powders Obtained by Using Maltodextrins with Different Dextrose Equivalents
- First Published: 02 May 2020
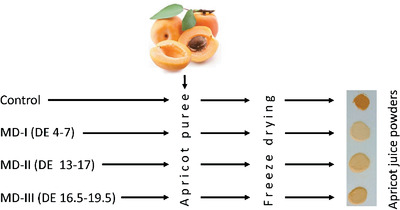
Apricot is a notable source for β-carotene which has important biological functions including provitamin A activity. This study was undertaken to understand the effect of different maltodextrins (MDs) on β-carotene stability and some physicochemical properties of apricot juice powder obtained via freeze drying. The results show that medium-high dextrose equivalence (DE) MD provids better protection for β-carotene while other quality attributes are better in low DE MD.
Effect of Wheat Bran Fiber on the Behaviors of Maize Starch Based Films
- First Published: 02 May 2020
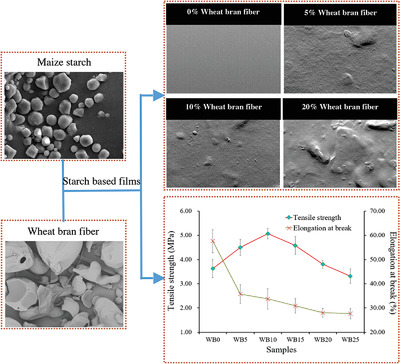
Wheat bran fiber, as the main byproduct of flour milling, is used as filling agent for maize starch based films. The properties of biocomposite films are studied. The results show that the addition of wheat bran fiber improves the mechanical properties of starch-based films, which may meet the requirements of the food packing films.
Stachyose Prevents Intestinal Mucosal Injury in the Immunosuppressed Mice
- First Published: 18 May 2020
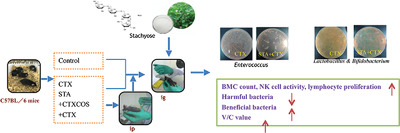
The effects of stachyose (STA) on the immune system and intestinal microbiota in immunosuppressed mice with intestinal mucosal damage induced by cyclophosphamide (CTX), with chitooligosaccharide used as the positive control, are investigated. STA can counteract the side effects of CTX in the immunosuppressed mice. It is a potential prebiotic which exerts indirect and direct effects on the immune system.