Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Rare Neurological Diseases
Dementia and cognitive disorders
Associations between texture of T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and radiographic pathologies in Alzheimer’s disease
- Pages: 735-744
- First Published: 24 October 2020
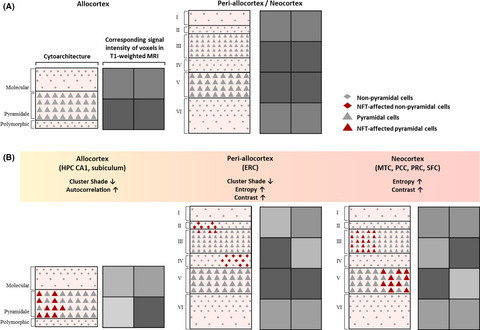
Regional texture features from T1-weighted brain MRI were associated with regional tau burden. Specific texture features showed associations with regional tau burden depending on the region's cytoarchitecture. Study findings suggest that texture of MRI may reflect tau-associated microstructural changes in the brain.
ALS and frontotemporal dementia
Brain metabolic correlates of apathy in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: An 18F-FDG-positron emission tomography stud
- Pages: 745-753
- First Published: 11 November 2020
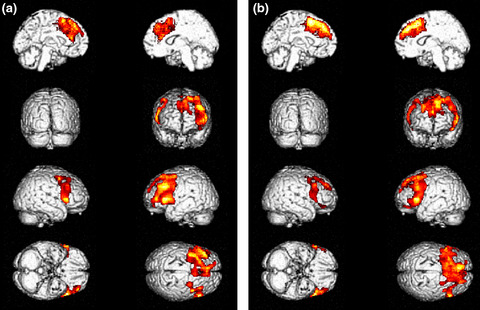
No studies on brain 18F-FDG-PET correlates of apathy have been performed in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). We found that Frontal Systems Behaviour Scale “after” apathy subscore correlated with metabolic changes in brain regions known as neuroanatomical correlates of apathy. Furthermore, our findings support the relevance of the gap between premorbid and morbid conditions to detect behavioural changes due to the neurodegenerative process underlying ALS.
Movement Disorders
Effect of cognitive and motor dual-task on oropharyngeal swallowing in Parkinson's disease
- Pages: 754-762
- First Published: 21 October 2020

This study investigated the effect of cognitive and motor dual-task interference on oropharyngeal swallowing in Parkinson's disease. Dual-task significantly worsened oropharyngeal swallowing function. Additional allocation of attentional resources in the central control of swallowing seems to be an effective compensatory mechanism in Parkinson's disease related dysphagia.
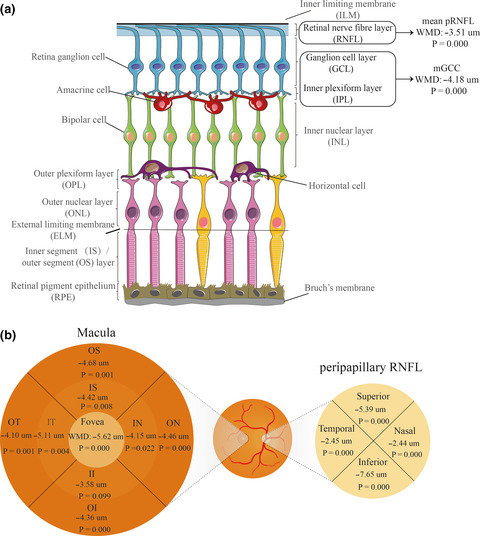
Optical coherence tomography measurements as potential imaging biomarkers for Parkinson's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 763-774
- First Published: 26 October 2020
From trials to clinical practice: Temporal trends in the coverage of specialized allied health services for Parkinson's disease
- Pages: 775-782
- First Published: 03 November 2020
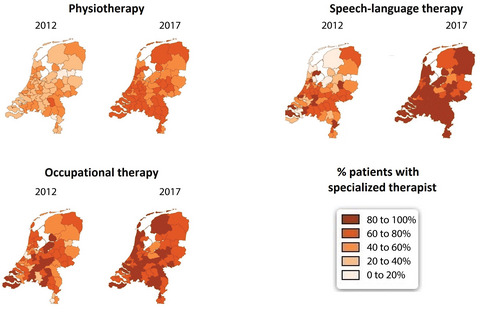
Following the publication of positive trials, the ParkinsonNet approach was successfully introduced on a nationwide scale in the Netherlands as a cost-effective intervention for people with Parkinson's disease. The successful wide-scale implementation of specialized allied healthcare delivery may serve as a template for other healthcare innovations for patients with Parkinson's disease elsewhere.
Stroke
Intensive versus guideline-recommended blood pressure reduction in acute lacunar stroke with intravenous thrombolysis therapy: The ENCHANTED trial
- Pages: 783-793
- First Published: 17 October 2020
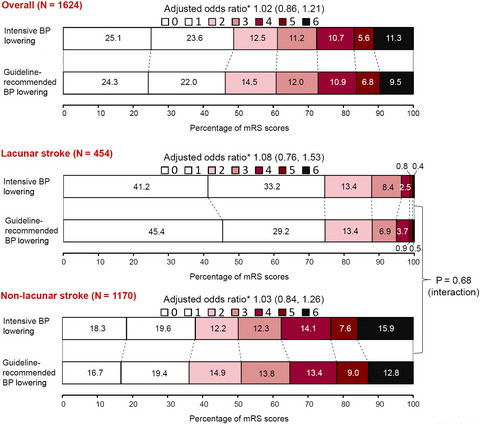
In the ENCHANTED trial, mean blood pressure difference by treatment was comparable across participants with lacunar and non-lacunar acute ischaemic stroke within the first week after randomization. There were no differences in the treatment effect of early intensive versus guideline-recommended blood pressure lowering across the two subgroups.
Association between cortical microinfarcts and total small vessel disease burden in cerebral amyloid angiopathy on 3-Tesla magnetic resonance imaging
- Pages: 794-799
- First Published: 24 October 2020
Social deprivation and 1-year survival after stroke: a prospective cohort study
- Pages: 800-808
- First Published: 24 October 2020
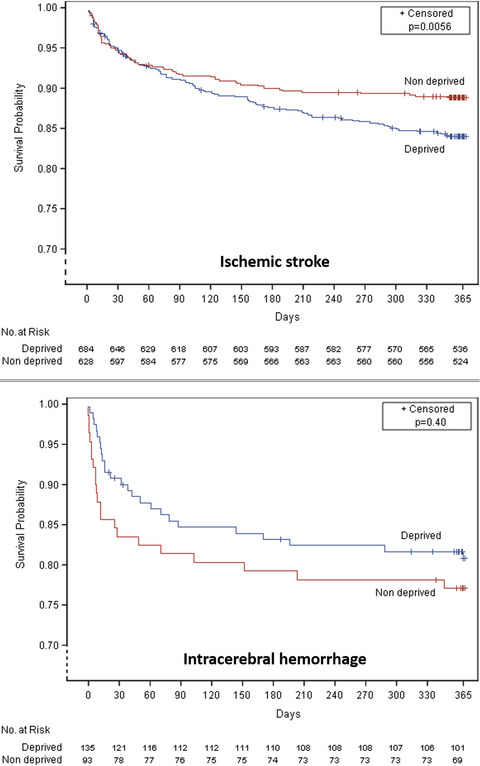
There was no association between deprivation and death occurring within the first 90 days following ischemic stroke. In contrast, an excess in mortality was observed between 90 days and 12 months in deprived compared with non-deprived patients. In patients with intracerebral hemorrhage, mortality at 12 months did not significantly differ according to deprivation status.
Effect of vitamin D and/or omega-3 fatty acid supplementation on stroke outcomes: A randomized trial
- Pages: 809-815
- First Published: 31 October 2020
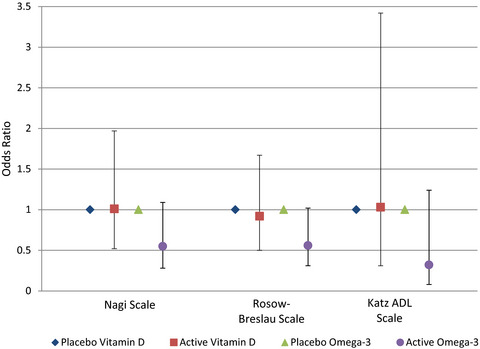
We used data from VITAL (the VITamin D and OmegA-3 TriaL) which randomized middle-aged and older men and women without cardiovascular disease to vitamin D 3 (2000 IU/day) and/or marine n-3 fatty acids (1 g/day) and followed them for incident stroke events. Individuals experiencing a non-fatal stroke were mailed questionnaires assessing functional limitations and physical disability. Vitamin D or omega-3 fatty acid supplementation prior to stroke did not result in significantly improved post-stroke outcomes.
Outcomes and long-term mortality after basilar artery occlusion—A cohort with up to 20 years’ follow-up
- Pages: 816-822
- First Published: 03 November 2020
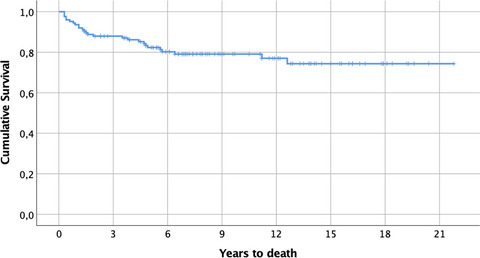
The cumulative mortality rate of basilar artery occlusion (BAO) patients surviving the first 3 months was 25.7% during the long-term follow-up of up to two decades. Older age, coronary artery disease and more extensive ischemic changes on admission brain imaging were independently associated with long-term mortality. After the acute phase, the rate of other vascular causes of death increased in relation to stroke. A trend towards better patient selection for treatment and higher rate of good and/or moderate outcome during later years was seen in our BAO cohort.
Meta-analysis of genotype and phenotype studies to confirm the predictive role of the RNF213 p.R4810K variant for moyamoya disease
- Pages: 823-836
- First Published: 11 November 2020
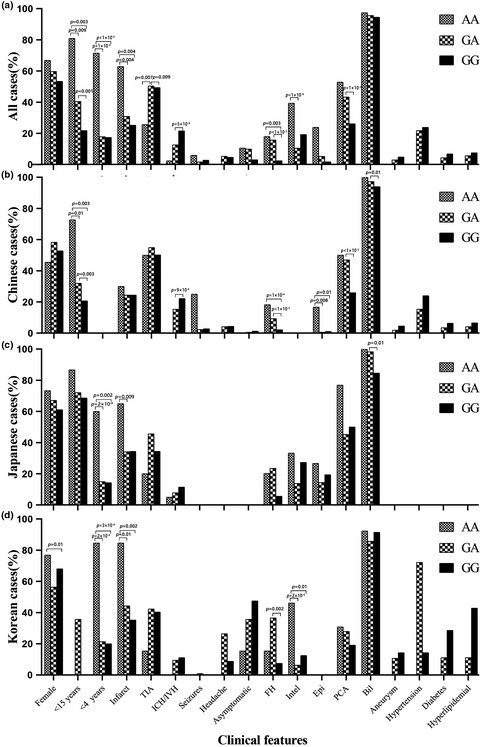
RNF213 p.R4810K may be an efficient biomarker with which to classify different clinical phenotypes of moyamoya disease (MMD). Homozygotes had a significantly earlier age at onset (<4 years) and were more susceptible to infarction and intellectual impairment, and the heterozygous genotype could predict the initial symptoms of transient ischemic attack and posterior cerebral artery involvement. Both homozygosity and heterozygosity had a significant predictive effect in patients younger than 15 years old and patients with a family history. In addition, the predictive effects of RNF213 p.R4810K genotypes on clinical phenotypes of MMD were heterogeneous among different ethnicities.
The Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysm Treatment Score as a predictor of aneurysm growth or rupture
- Pages: 837-843
- First Published: 11 November 2020
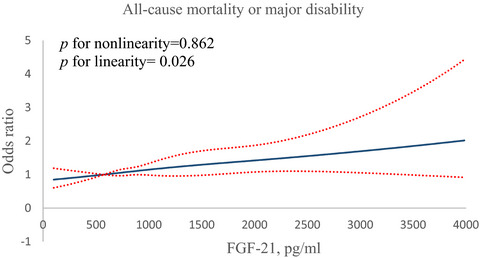
Prognostic value of plasma fibroblast growth factor 21 among patients with acute ischemic stroke
- Pages: 844-851
- First Published: 15 December 2020
Headache at onset of first-ever ischemic stroke: Clinical characteristics and predictors
- Pages: 852-860
- First Published: 16 December 2020
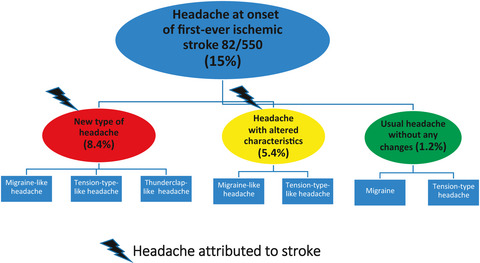
This study examined for the first time prospectively headache at onset of first-ever ischemic stroke (n = 550) in comparison with a large concurrent control group (n = 192). It was found that headache occurred in 15% of patients with first-ever ischemic stroke. More than half (56%) had a new type of headache (mainly migraine-like) simultaneously with stroke onset, and 36% had headache with altered characteristics (mainly tension-type-like headache). These headaches are causally related and attributed to stroke. They are associated with cardioembolism, posterior circulation stroke, infarcts >15 mm, infarcts of cerebellum, good neurological, and low frequency of large-artery atherosclerosis.
Safety and efficacy of mechanical thrombectomy in infective endocarditis: A matched case–control analysis from the German Stroke Registry–Endovascular Treatment
- Pages: 861-867
- First Published: 16 December 2020
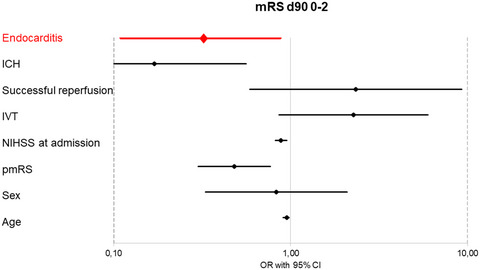
Endovascular stroke treatment in infectious endocarditis patients. Taking data from the German Stroke Registry–Endovascular Treatment (ET), the safety and efficacy of ET in large vessel occlusion (LVO) stroke patients due to infective endocarditis (IE) was analyzed. Although ET results in high successful recanalization rates with acceptable safety profile in these patients, IE was negatively associated with a good outcome (odds ratio = 0.32, 95% CI = 0.11–0.87, p = 0.03, see graphic). However, although the overall clinical outcome in those patients was poor—decisively limited by the underlying IE—ET should not to be withheld in LVO stroke due to IE.
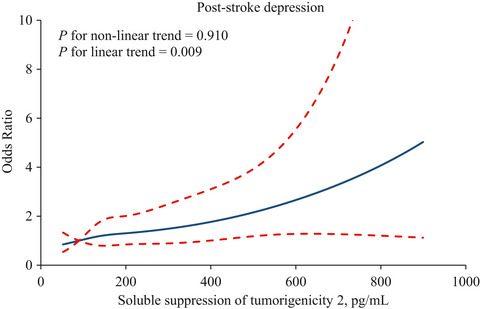
Plasma soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2 and depression after acute ischemic stroke
- Pages: 868-876
- First Published: 25 December 2020
Infectious Diseases
β-Amyloid may accumulate in the human brain after focal bacterial infection: An 18F-flutemetamol positron emission tomography study
- Pages: 877-883
- First Published: 31 October 2020
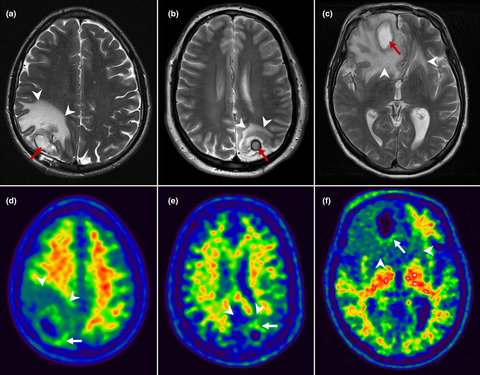
β-Amyloid, which accumulates in the brain in Alzheimer's disease, may be part of the brains antimicrobial response. We asked if β-amyloid would accumulate in brains of patients with a brain abscess. 18F-Flutemetamol positron emission tomography, which visualizes β-amyloid accumulation, detected β-amyloid in the brain tissue surrounding the abscess remains in three out of 17 patients.
Multiple Sclerosis
Impaired consolidation of visuomotor adaptation in patients with multiple sclerosis
- Pages: 884-892
- First Published: 17 October 2020
In a visuomotor adaptation task, persons with multiple sclerosis (MS) show normal adaptation and online learning, but reduced retention after 24 h and 72 h compared to controls. This indicates intact adaptation, but limited consolidation, in the patient group. The individual clinical course of MS might also be influenced by differential capacities to consolidate training achievements.
The Framingham cardiovascular risk score and 5-year progression of multiple sclerosis
- Pages: 893-900
- First Published: 22 October 2020
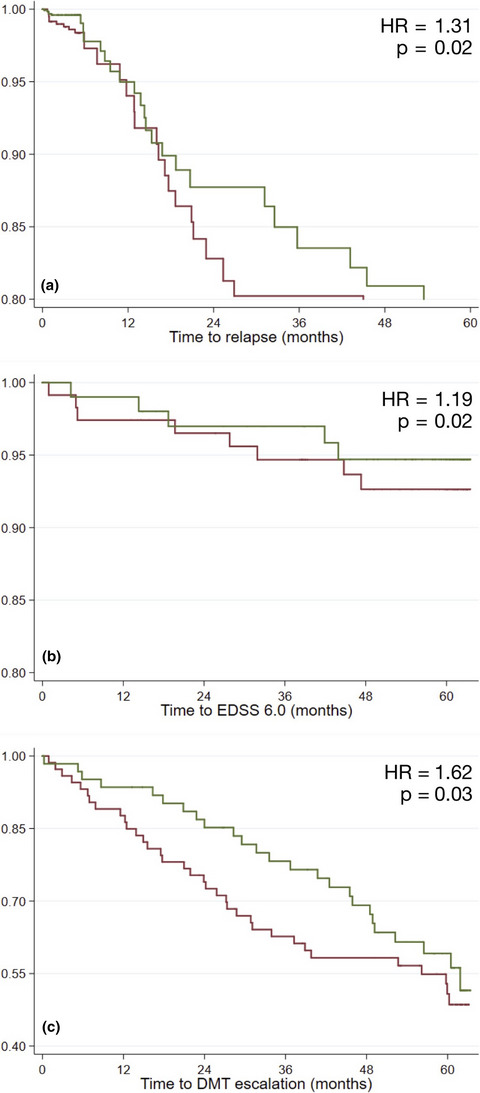
We evaluated the impact of multiple cardiovascular risk factors at baseline, combined in a percent risk score (i.e., the Framingham risk score), on multiple sclerosis (MS) course over 5 years. Each additional percent Framingham risk score was related to a 40% higher relapse rate, 20% higher risk of reaching of Expanded Disability Status Scale 6.0, and 60% higher risk of disease-modifying treatment escalation. Early identification, correction, and treatment of cardiovascular comorbidities should be carefully considered within MS management.
Prognostic value of natural killer cell/T cell ratios for disease activity in multiple sclerosis
- Pages: 901-909
- First Published: 16 December 2020
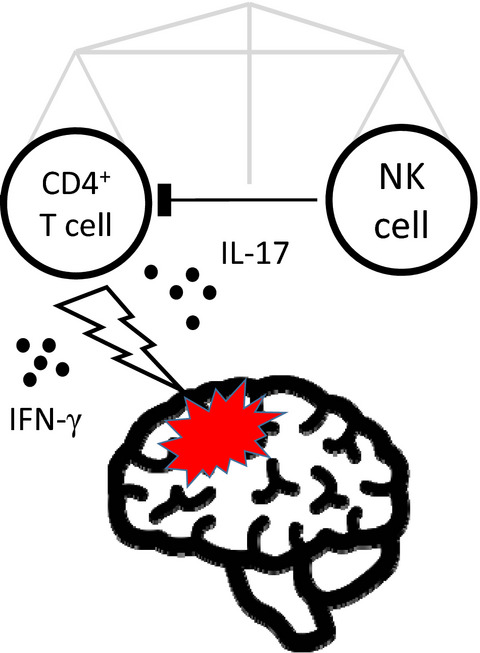
Natural killer (NK) cells may control activation of pathogenic CD4+ T cell subsets in multiple sclerosis (MS). It is shown that circulating NK cell proportions not only correlate negatively with interleukin 17A (IL-17A+) CD4+ T cell proportions but also that a higher abundancy of NK cells relative to IL-17A+ CD4+ T cells is associated with the absence of new magnetic resonance imaging lesions, the absence of new relapses and lower circulating neurofilament light chain levels during 48 weeks of follow-up in relapsing– remitting MS patients treated with interferon beta. Therefore, NK cell/CD4+ T cell ratios may be a prognostic biomarker for disease activity in MS.
Assessing the experience of the quality of care of patients living with multiple sclerosis and their caregivers: The MusiCare questionnaire
- Pages: 910-920
- First Published: 16 December 2020
Neuroimmunology
Course of neuropsychological impairment during natalizumab-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
- Pages: 921-927
- First Published: 21 October 2020
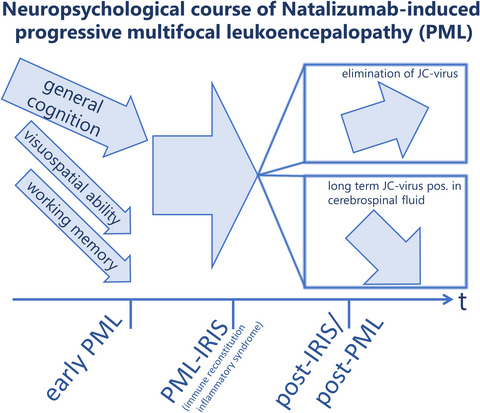
Working memory and visuospatial abilities are found to be core neuropsychological deficits in natalizumab-induced progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). This first evaluation of the neuropsychological disease course in comparison to two non-PML multiple sclerosis cohorts shows these core deficits in a long-term follow-up. Patients with failure to eliminate the John Cunningham virus from the central nervous system showed a progredient cognitive decline, especially in working memory.
Rare Neurological Diseases
A case of Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome with endocrine disorders: Extraordinary efficiency of hydroxychloroquine and mechanism hypothesis
- Pages: 928-933
- First Published: 03 December 2020
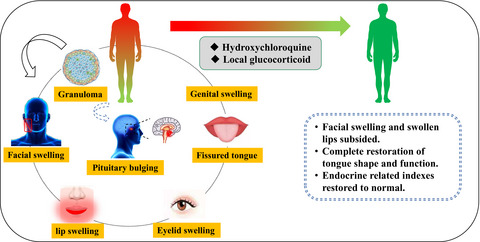
This is a mechanism hypothesis of this case. We report a case of Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome (MRS) with endocrine disorders, which exhibits an extraordinary therapeutic efficiency by using hydroxychloroquine. We propose the first-time hypothesis that MRS may essentially be a systemic granulomatous disease.
Hypomyelinating leukodystrophies in adults: Clinical and genetic features
- Pages: 934-944
- First Published: 15 November 2020
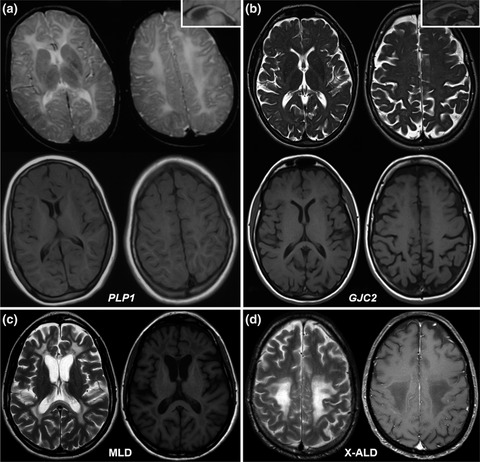
A brain MRI pattern suggestive of hypomyelination can be the prominent feature of adult-onset genetic conditions. Adult neurologists should be trained in recognizing this pattern, as its presence implies different diagnostic work-up and prognosis. An inclusive genetic screening can allow diagnosis in almost half of cases.
Brown−Vialetto−Van Laere and Fazio−Londe syndromes: SLC52A3 mutations with puzzling phenotypes and inheritance
- Pages: 945-954
- First Published: 15 December 2020
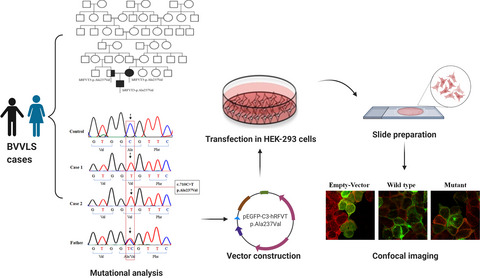
Novel missense mutation c.710C>T (p.Ala237Val) in hRFVT-3 is identified in BVVLS cases of Indian ethnicity for the first time. Pseudodominant pattern of inheritance is identified for the first time among BVVLS cases. Confocal cell imaging of the variant p.Ala237Val showed abrogated expression on the cell surface compared to the wild-type. Though BVVLS and FLD share overlapping phenotypes, a common mutation c.62A>G (p.Asn21Ser) identified in both cases suggesting that they can be caused by the same hRFVT-3 mutation.
Neurogenetics
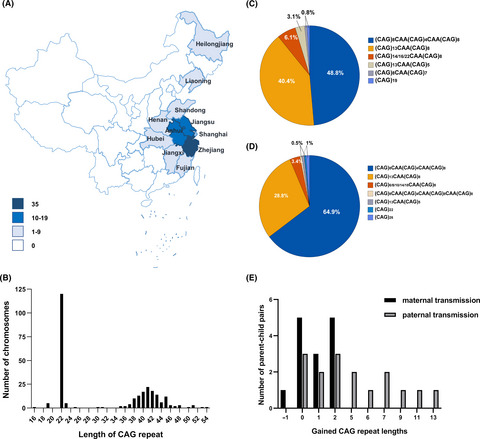
Genetic profile and clinical characteristics of Chinese patients with spinocerebellar ataxia type 2: A multicenter experience over 10 years
- Pages: 955-964
- First Published: 18 October 2020
Neuropathies
Cerebrospinal fluid protein in Guillain–Barré syndrome: Need for age-dependent interpretation
- Pages: 965-973
- First Published: 18 October 2020
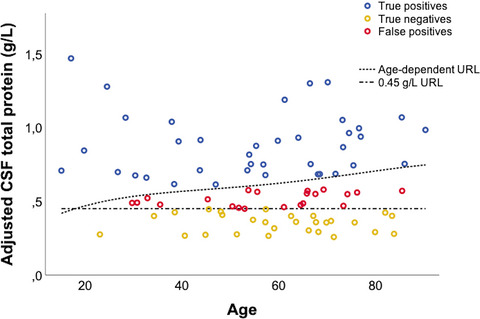
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) total protein and CSF/serum albumin quotient are less frequently elevated in patients with Guillain–Barré syndrome than previously reported, as a result of novel age-dependent upper reference limits that reduce false-positives and avoid over-interpretation of slightly elevated protein levels in the elderly.
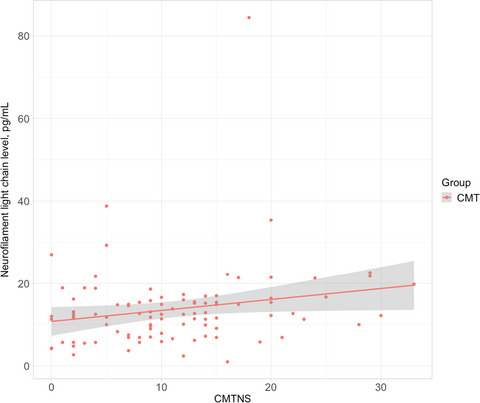
Plasma neurofilament light chain as a potential biomarker in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
- Pages: 974-981
- First Published: 19 December 2020
Early changes of nerve integrity in preclinical carriers of hereditary transthyretin Ala117Ser amyloidosis with polyneuropathy
- Pages: 982-991
- First Published: 28 December 2020
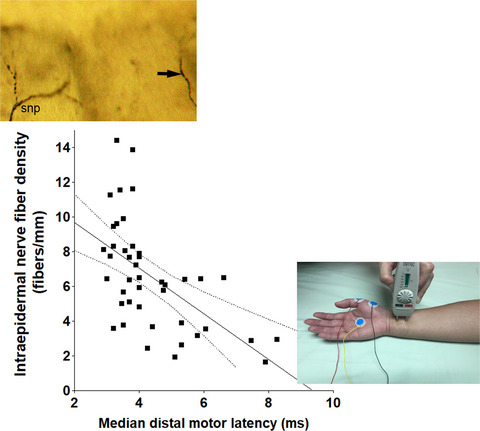
In carriers of late-onset hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis with polyneuropathy, Chiang et al. found that the most common electrophysiological abnormalities were the median nerve conduction parameters, particularly the prolonged distal motor latency, which was correlated with the reductions in the intraepidermal nerve fiber (IENF) density and the changes of the median nerve excitability. Moreover, the nerve dysfunction index, defined by normalizing the median distal motor latency to the IENF density, served as a biomarker to reflect deficits in the large- and small-fiber nerves in carriers and to differentiate carriers from healthy controls.
Muscle and MNJ Disorders
Whole-exome analyses of congenital muscular dystrophy and congenital myopathy patients from India reveal a wide spectrum of known and novel mutations
- Pages: 992-1003
- First Published: 30 October 2020
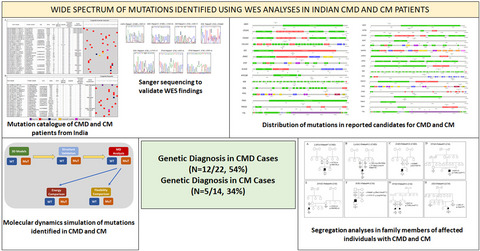
To our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive mutational analyses in congenital muscular dystrophy (CMD) and congenital myopathy (CM) patients from India. Importantly, these findings allowed us to achieve accurate genetic diagnosis of CMD (n = 12/22, 54%) and CM (n = 5/14, 34%) cases, which was difficult using conventional diagnostic tools. Transferring these whole-exome sequencing analyses findings to clinical practice will help guide clinical care of the affected patients and inform genetic counselling.
All neurologists
Serum neurofilament level increases after ascent to 4559 m but is not related to acute mountain sickness
- Pages: 1004-1008
- First Published: 23 October 2020
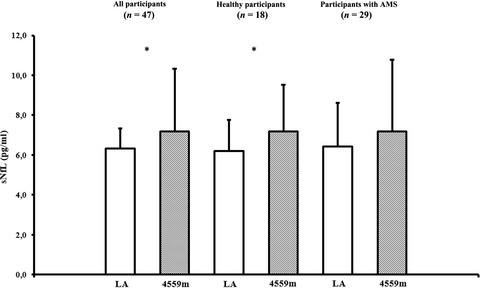
At high altitude the brain is exposed to hypoxic stress, which may result in an alteration of neuro-axonal integrity for which serum neurofilament light (sNfL) is a novel blood biomarker. In the present study, rapid ascent of healthy people to high altitude provoked an increase in sNfL 44 h after arrival at 4559 m, which was not related to the magnitude of hypoxemia or the incidence and severity of the most common high-altitude illness, acute mountain sickness (AMS). Our results suggest that neuro-axonal alterations occur after high-altitude exposure, but do not directly contribute to the pathophysiology of AMS.
Dementia and cognitive disorders
Co-incidental C9orf72 expansion mutation-related frontotemporal lobar degeneration pathology and sporadic Creutzfeldt−Jakob disease
- Pages: 1009-1015
- First Published: 31 October 2020
Rare Neurological Diseases
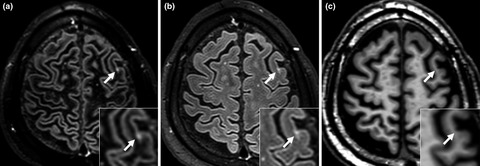
Brainstem progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
- Pages: 1016-1021
- First Published: 30 October 2020
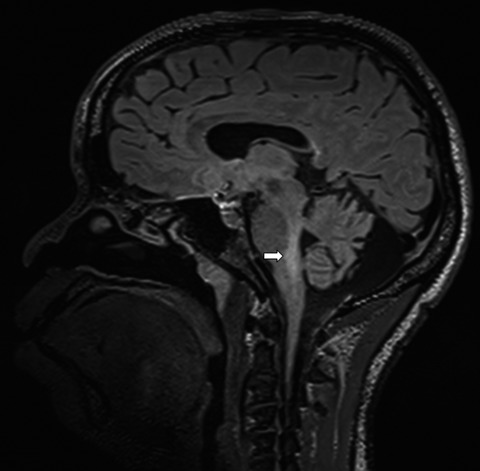
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) is a severe infection caused by the polyomavirus JC that develops in the central nervous system (CNS) of immunosuppressed patients. The infection frequently starts in the brain hemispheres and can spread into other CNS regions. Isolated brainstem lesion is an exceptional presentation of PML at disease onset. Prognosis is reserved because of the surrounding vital structures in the brainstem, but clinical recovery may occur. This case report and literature review emphasize brainstem PML as an atypical presentation of PML at disease onset.
Movement Disorders
Nonpharmacological interventions for respiratory health in Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 1022-1040
- First Published: 24 October 2020
Biological fluid levels of iron and iron-related proteins in Parkinson’s disease: Review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 1041-1055
- First Published: 24 October 2020
Neuroscience/translational neurology
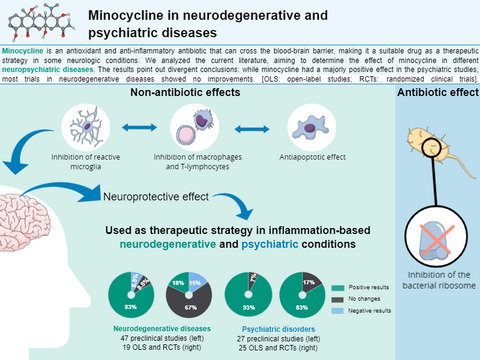
Minocycline in neurodegenerative and psychiatric diseases: An update
- Pages: 1056-1081
- First Published: 12 November 2020
Movement Disorders
Whispering dysphonia in TUBB4A-related disorders responsive to bipallidal deep brain stimulation
- Pages: 1082-1083
- First Published: 21 October 2020
Mutations in TUBB4A are associated with a wide phenotypic spectrum including generalized dystonia with whispering dysphonia (DYT-TUBB4A). We report the case of a patient with DYT-TUBB4A who experienced improvement of dystonia after bipallidal deep brain stimulation (DBS), especially of the cervical and facial components. We suggest that bipallidal DBS should be considered in patient with disabling dystonia related to TUBB4A variants.
Stroke
Cerebral aneurysm: De novo genesis and rupture within 15 days
- Pages: 1084-1085
- First Published: 13 November 2020
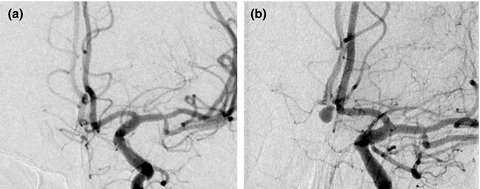
We report the first case of de novo formation of a small 4- × 3-mm symptomatic aneurysm with subsequent subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) within 15 days. A pre-existing aneurysm was excluded by magnetic resonance angiography, as well as conventional angiography. In this case, there was no history of SAH, which is in contrast to other reported cases of de novo aneurysms that developed after previous aneurysm rupture.
Neuroimmunology
Neurofilament light chain levels reflect outcome in a patient with glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 antibody–positive autoimmune encephalitis under immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy
- Pages: 1086-1089
- First Published: 08 February 2021
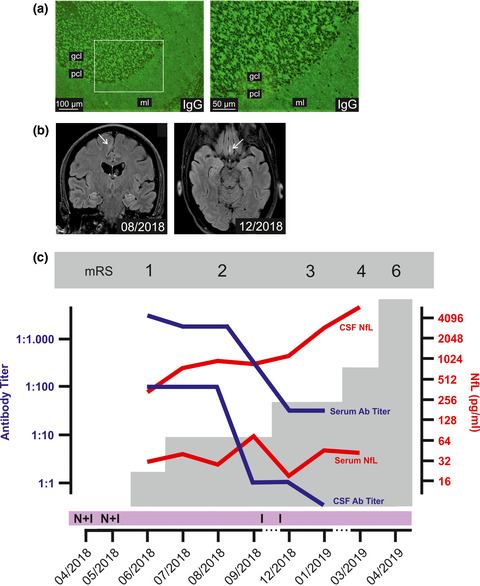
Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapies are highly effective for the treatment of cancer, but are associated with rare but often severe and therapy-limiting complications. Among the emerging spectrum of neurological immune-mediated side effects, our report describes a case of nivolumab/ipilimumab–associated glutamic acid decarboxylase 65–positive autoimmune encephalitis. It proposes neurofilament light chain (NfL) levels, a biomarker indicating axonal damage, in the cerebrospinal fluid and serum as a putative novel biomarker for this diagnostically and therapeutically challenging entity with an often unfavorable outcome.
All neurologists
Dementia and cognitive disorders
Movement Disorders
Sulfate reducing gut bacteria and Parkinson's disease
- Page: e21
- First Published: 03 November 2020
Stroke
Neurogenetics
Expanding the genotypic and phenotypic spectrum of Beta-propeller protein-associated neurodegeneration
- Pages: e25-e27
- First Published: 12 December 2020