Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Ecology and evolution of plant chemodiversity
- Pages: 633-636
- First Published: 12 July 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
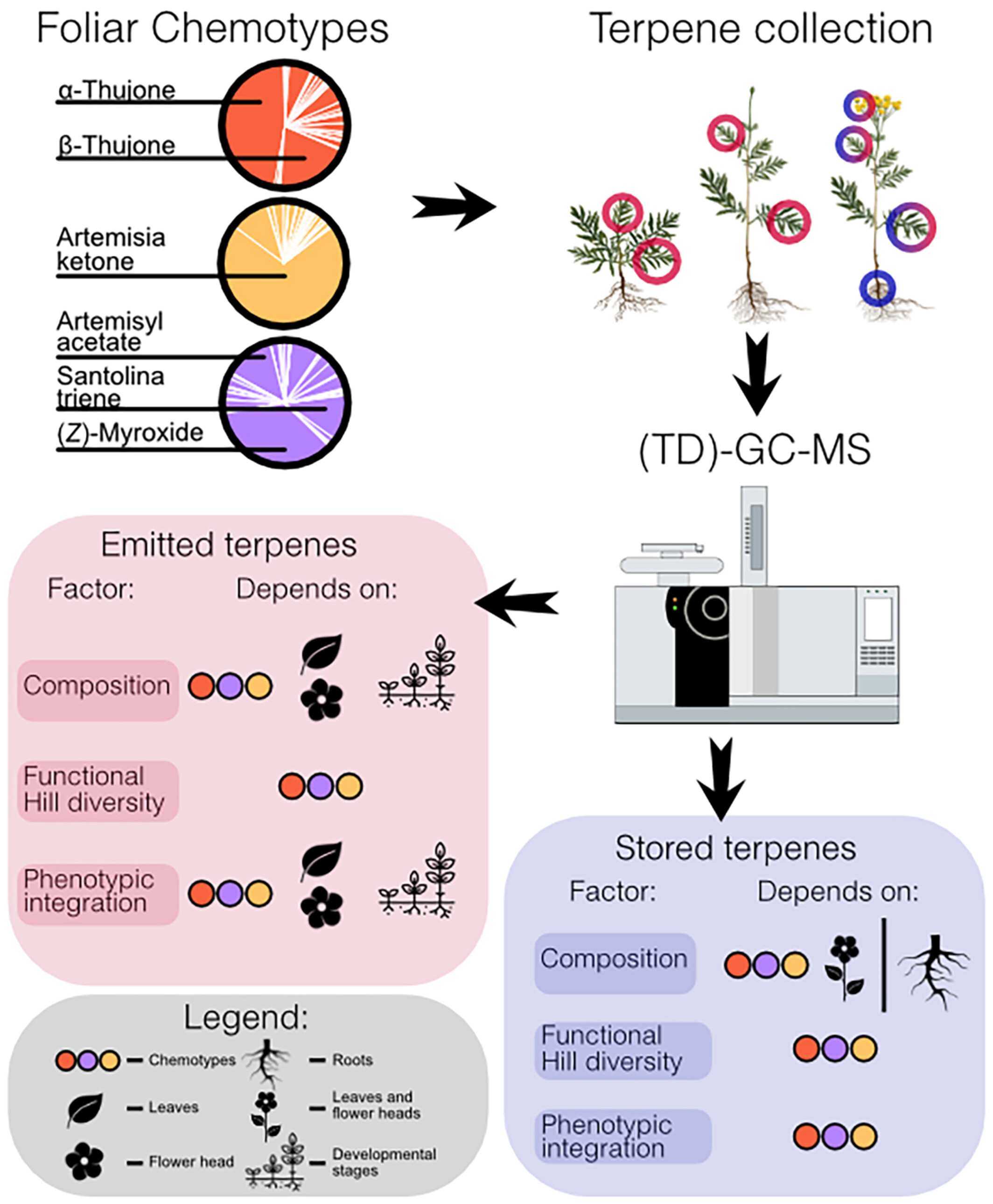
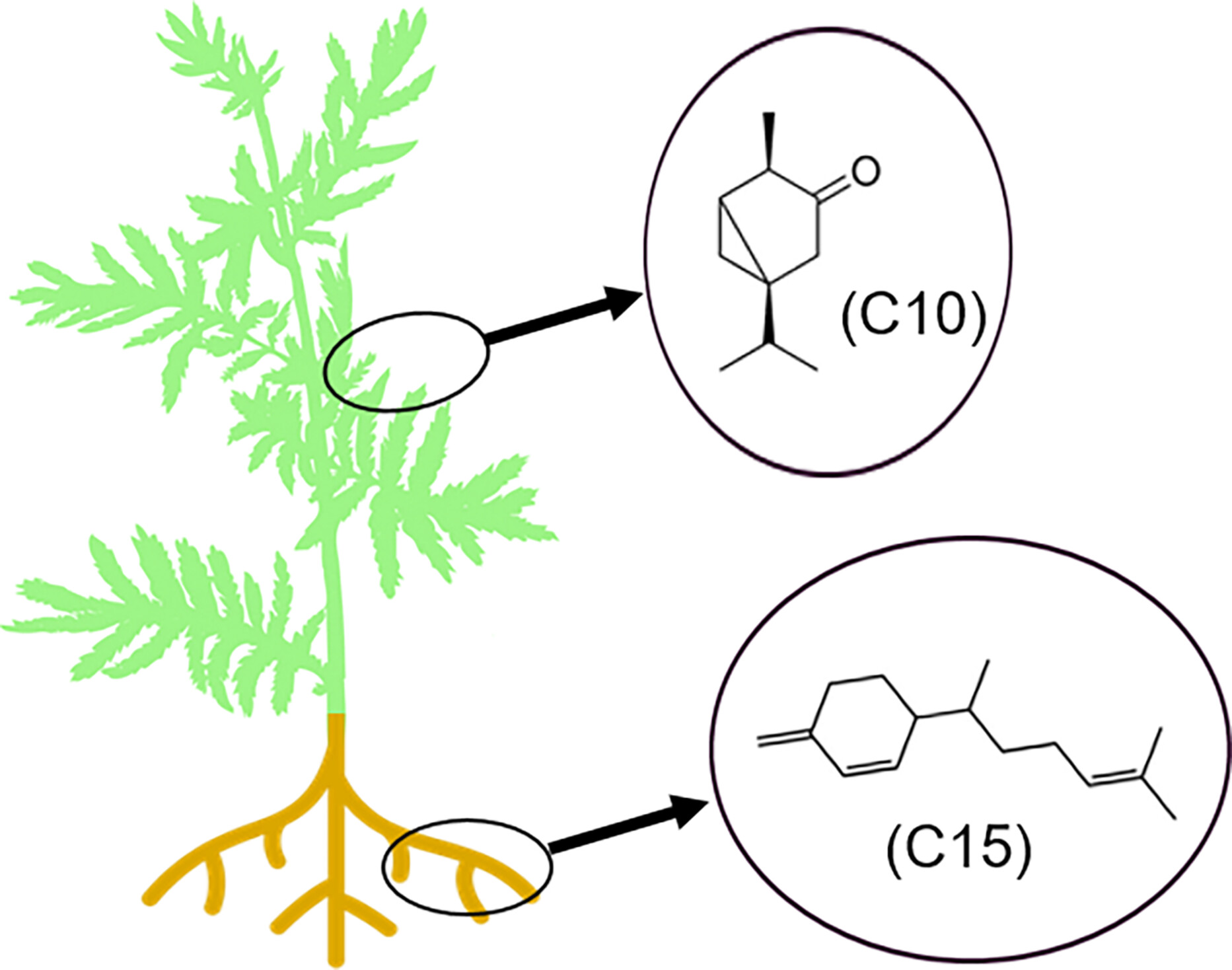
Intraspecific and intra-individual chemodiversity and phenotypic integration of terpenes across plant parts and development stages in an aromatic plant
- Pages: 637-650
- First Published: 07 January 2025
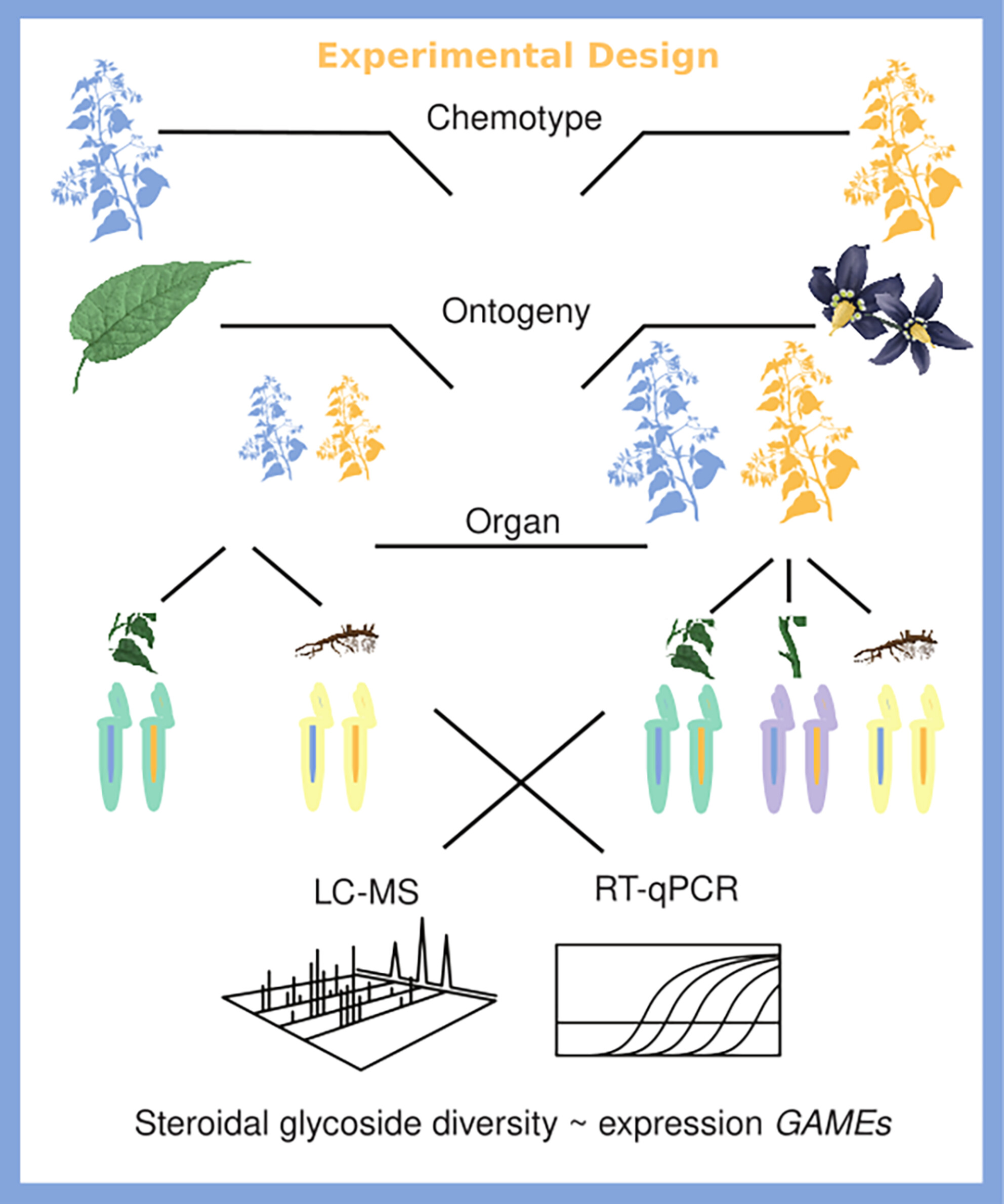
Ontogeny and organ-specific steroidal glycoside diversity is associated with differential expression of steroidal glycoside pathway genes in two Solanum dulcamara leaf chemotypes
- Pages: 651-668
- First Published: 16 August 2024
Secretory structures in Baccharis platypoda DC. inflorescences (Asteraceae) and characterization of the chemical composition of its secretion
- Pages: 669-680
- First Published: 04 June 2024
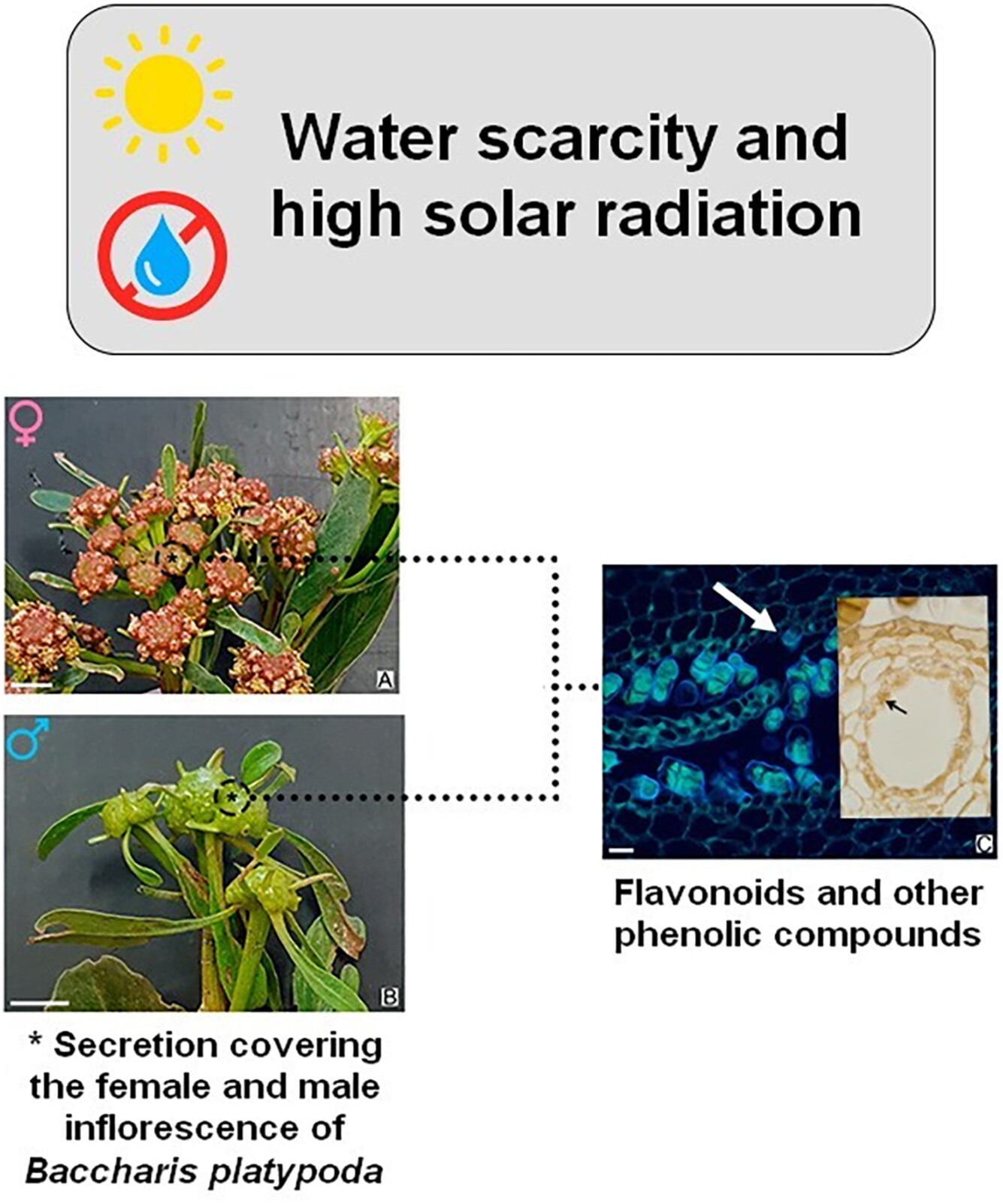
We investigated the secretory structures and chemical composition of Baccharis platypoda inflorescences, revealing similarities between female and male plants and highlighting the presence of phenolic compounds as natural defense mechanisms against high solar radiation in rocky outcrop environments.
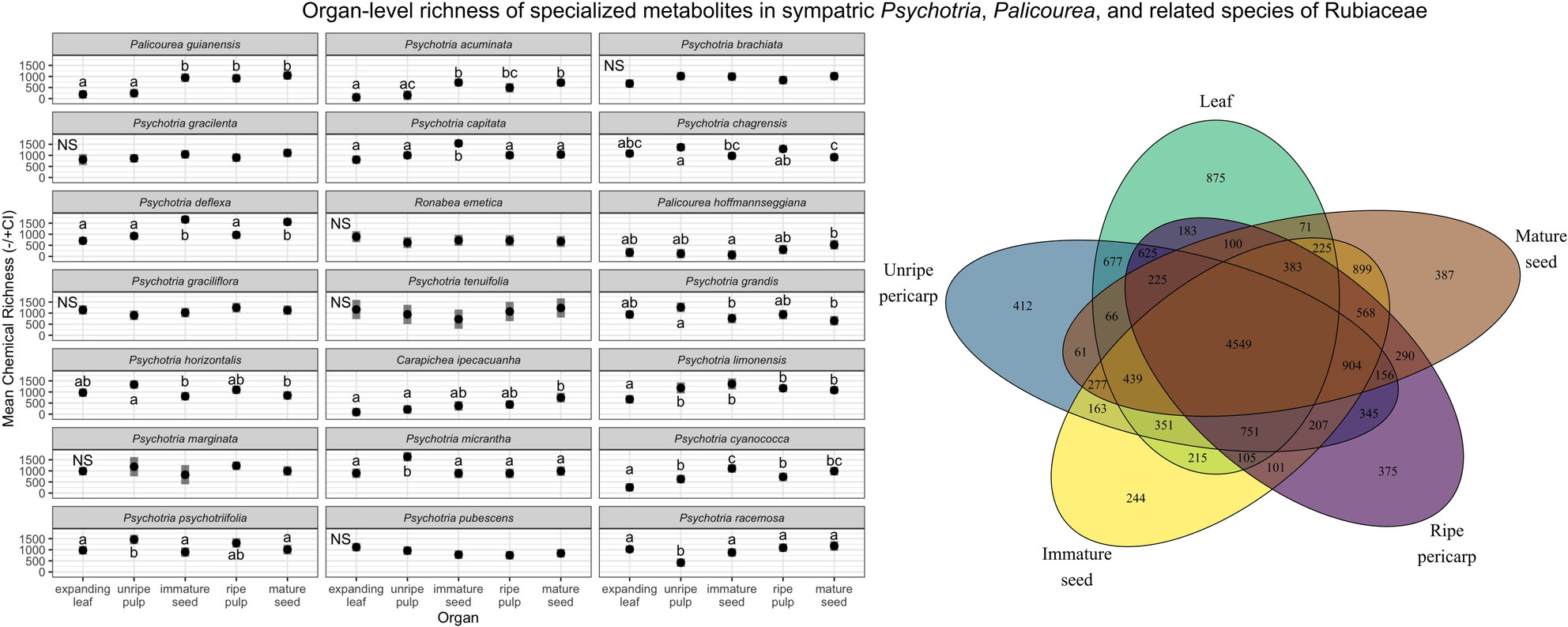
Different tools for different trades: contrasts in specialized metabolite chemodiversity and phylogenetic dispersion in fruit, leaves, and roots of the neotropical shrubs Psychotria and Palicourea (Rubiaceae)
- Pages: 681-697
- First Published: 22 March 2025
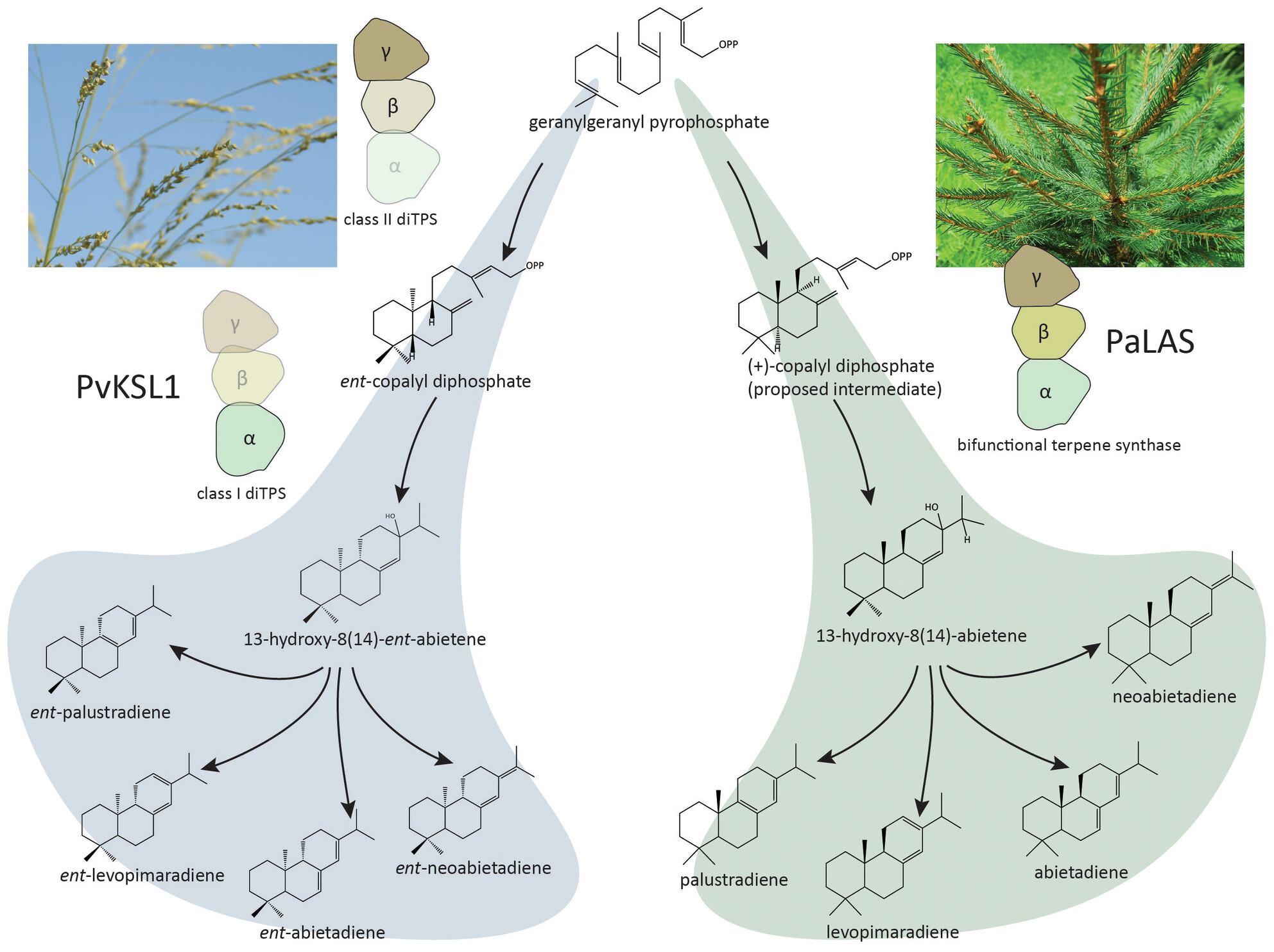
Characterization of switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) PvKSL1 as a levopimaradiene/abietadiene-type diterpene synthase
- Pages: 698-709
- First Published: 20 August 2024
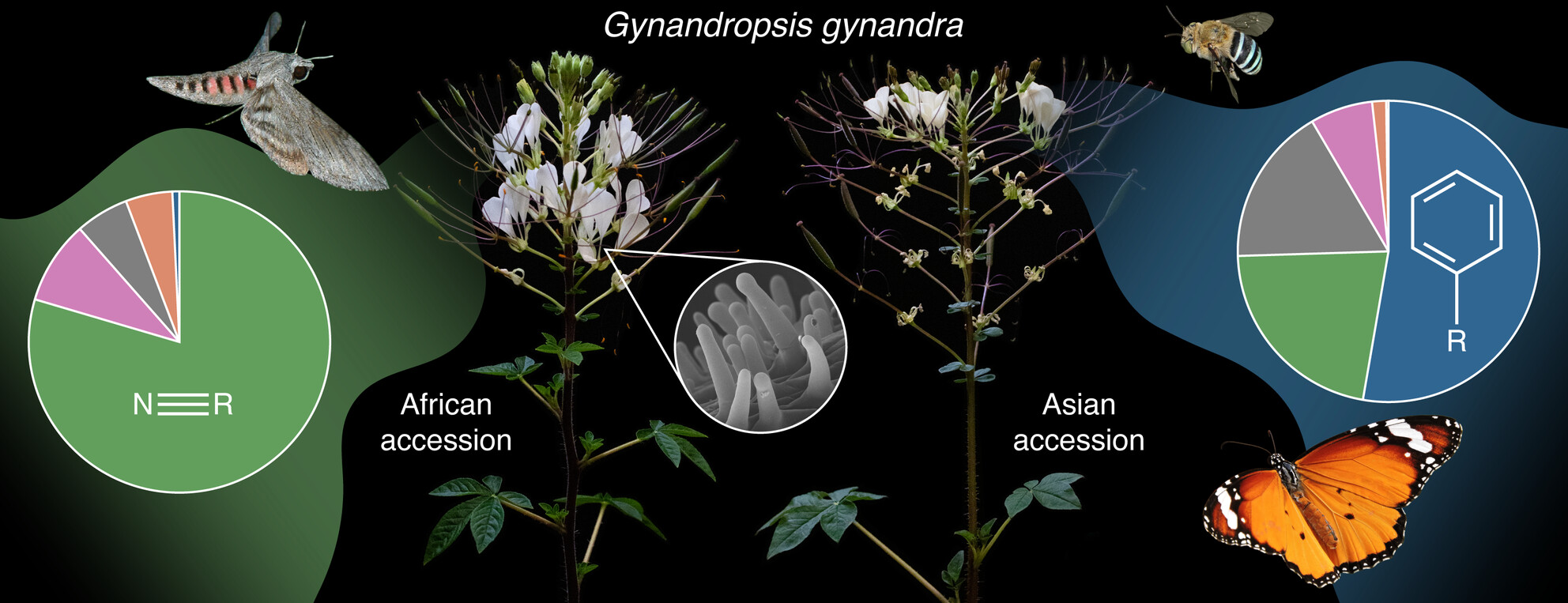
Chemical, morphological, and genetic characterization of the floral scent and scent-releasing structures of Gynandropsis gynandra (Cleomaceae, Brassicales)
- Pages: 710-724
- First Published: 20 March 2025
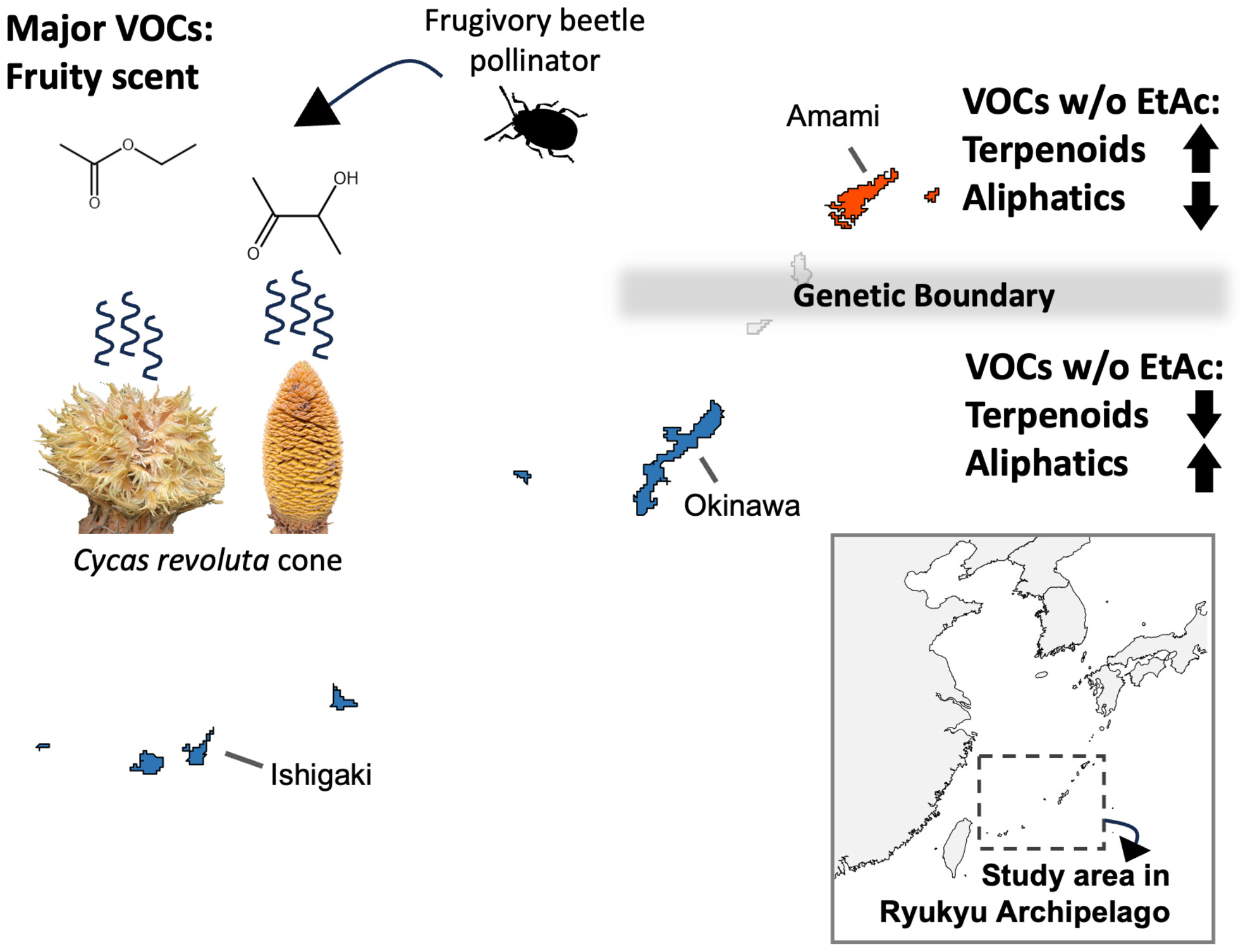
Match of fruit-scented cone volatile composition with genetic boundary in Cycas revoluta and implications for fruit mimicry pollination
- Pages: 725-739
- First Published: 03 July 2025
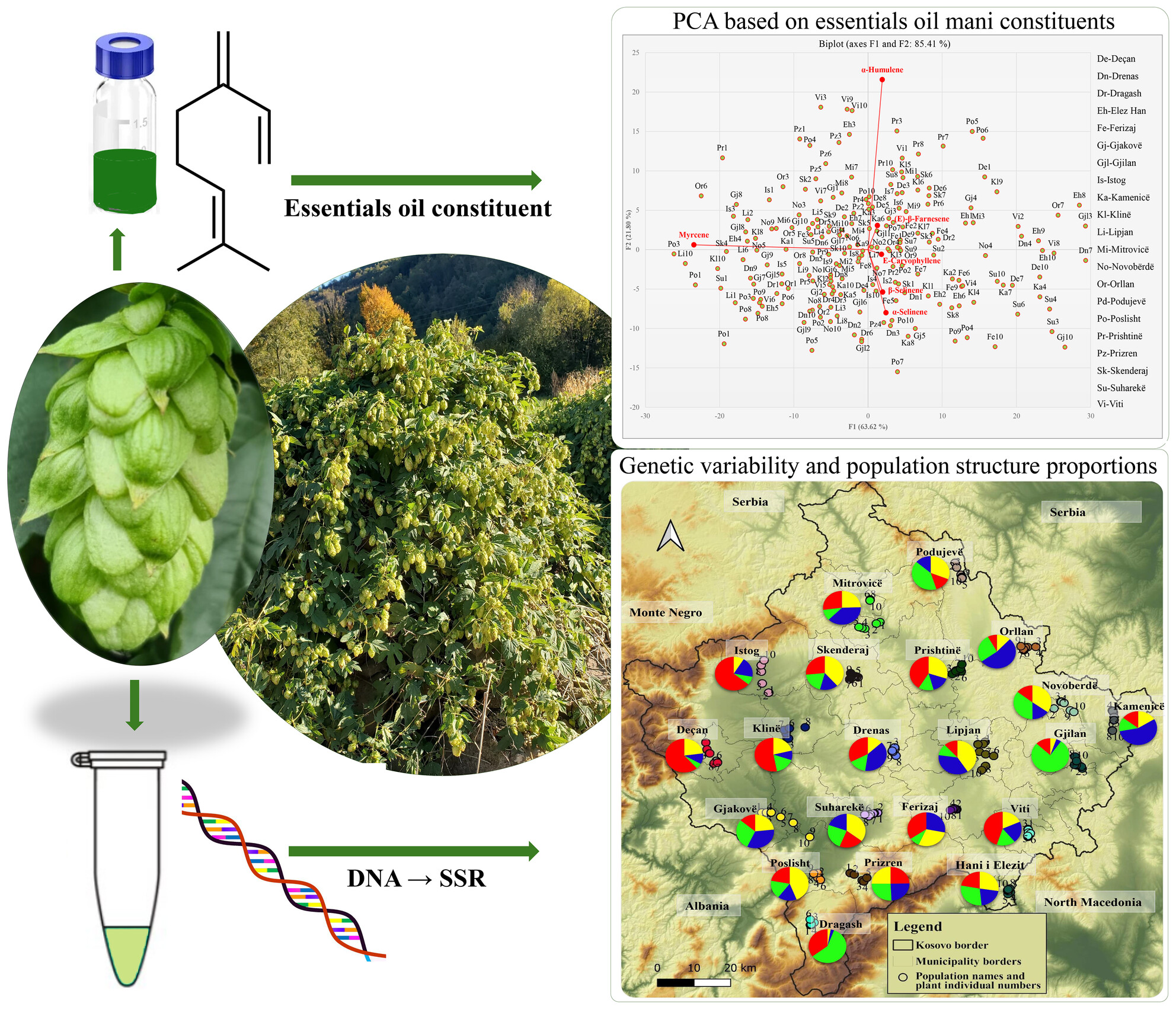
Analysis of chemical and genetic variability in wild hop (Humulus lupulus L.) populations of Kosovo
- Pages: 740-748
- First Published: 01 August 2024
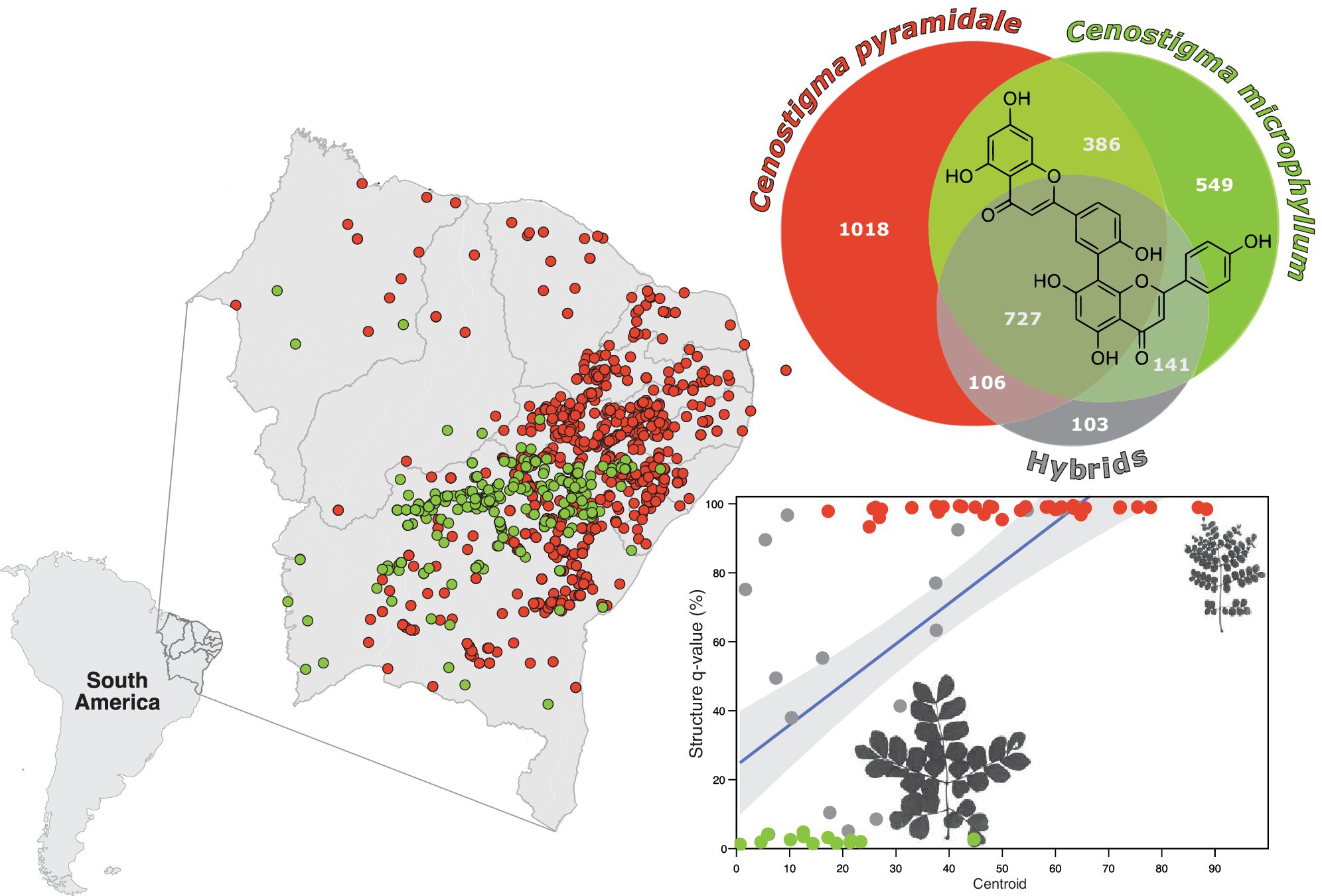
Integrative evidence on the hybridization between Cenostigma microphyllum and C. pyramidale (Leguminosae) in the Caatinga dry forest
- Pages: 749-760
- First Published: 16 December 2024
The influence of aridity on plant intraspecific chemical diversity supports adaptive differentiation and convergent evolution
- Pages: 761-772
- First Published: 25 October 2024
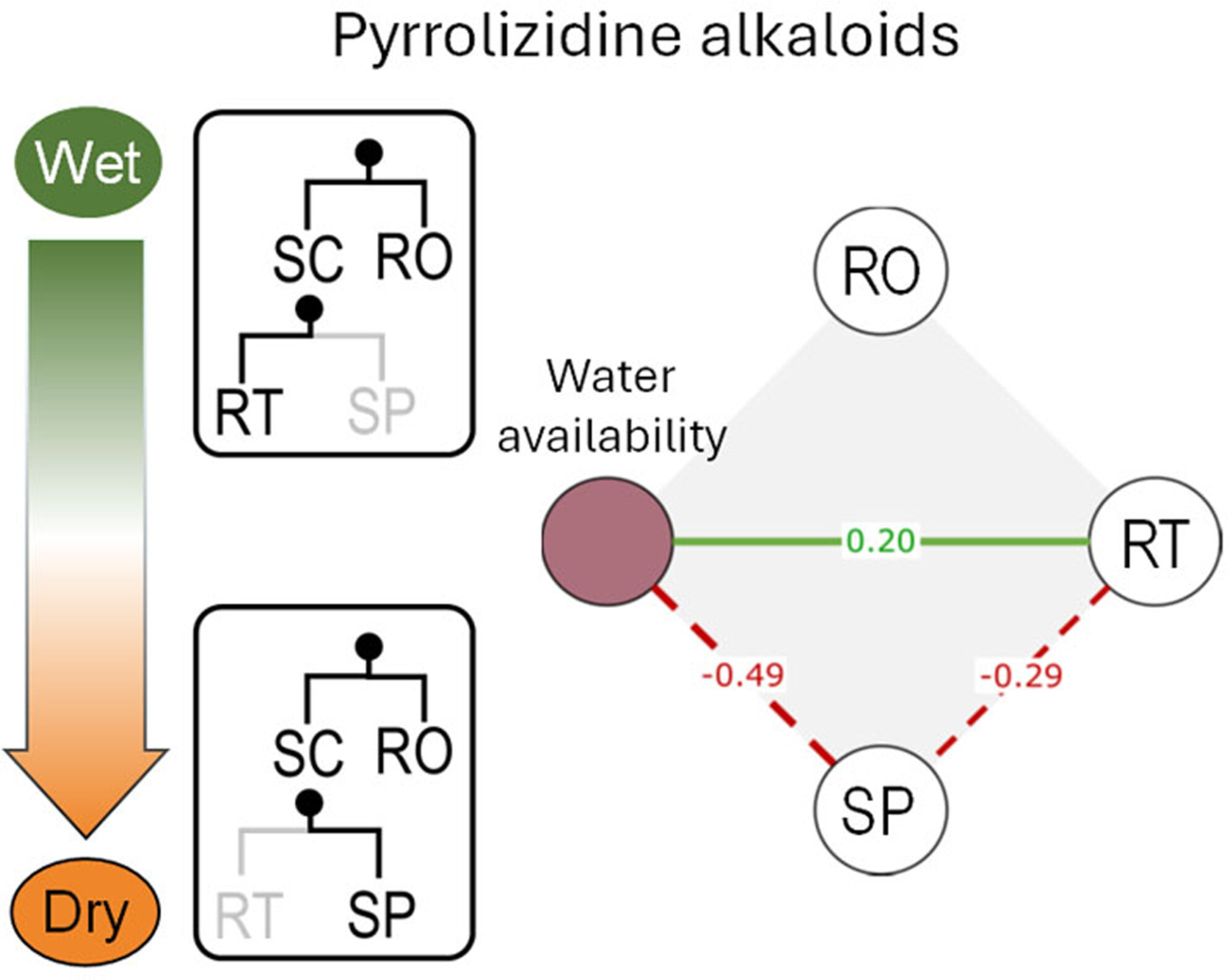
Pyrrolizidine alkaloid composition in the invasive plant Senecio pterophorus is coherent with a pattern of adaptive differentiation in response to aridity, as shown in an environmental gradient in the native range and across three cross-continental introductions, under natural and common garden conditions, by accounting for the population neutral genetic structure.
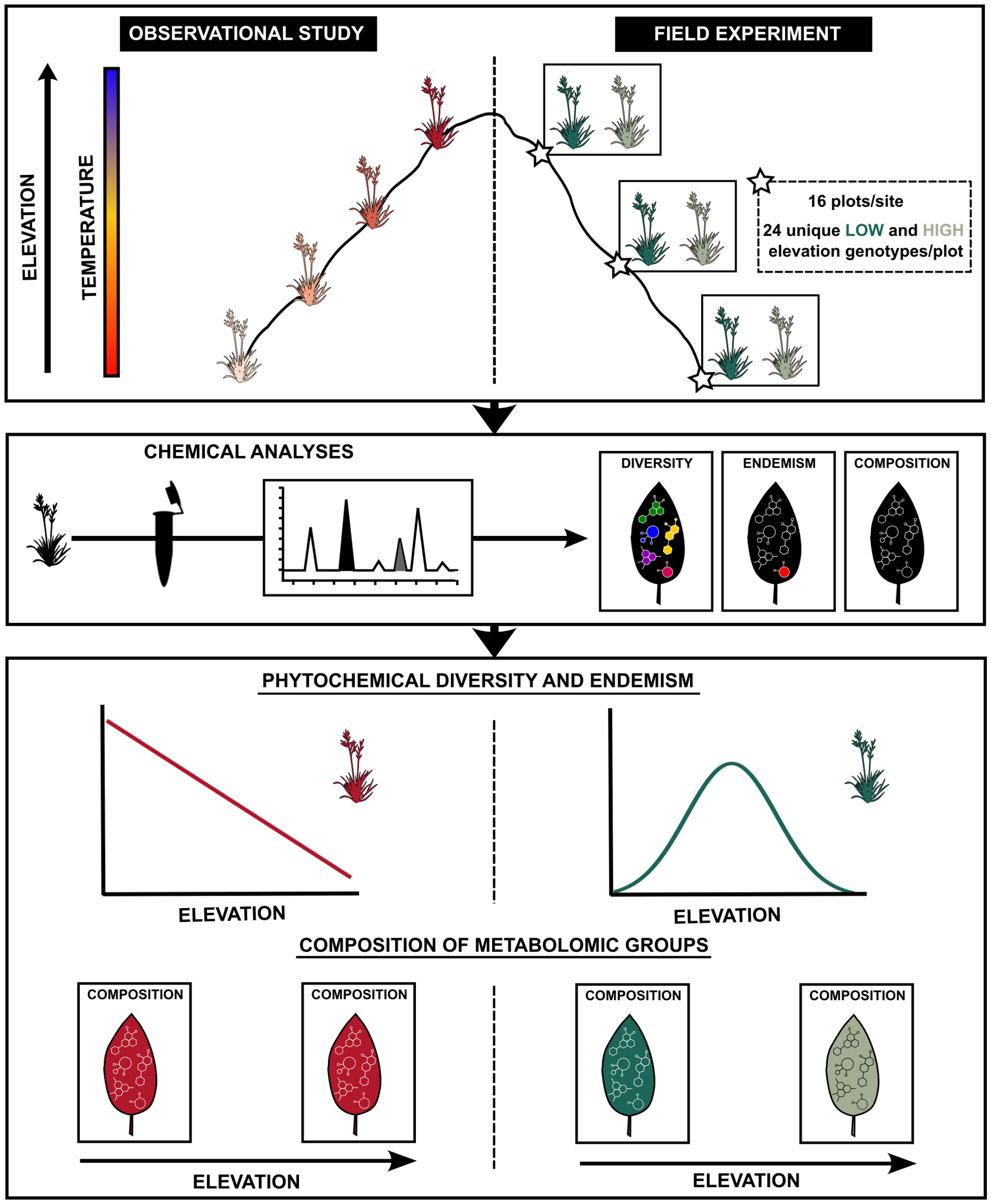
Elevation drives intraspecific metabolomic differentiation in natural and experimental populations
- Pages: 773-784
- First Published: 07 May 2025
Intraspecific chemical variation of Tanacetum vulgare affects plant growth and reproductive traits in field plant communities
- Pages: 785-801
- First Published: 09 April 2024
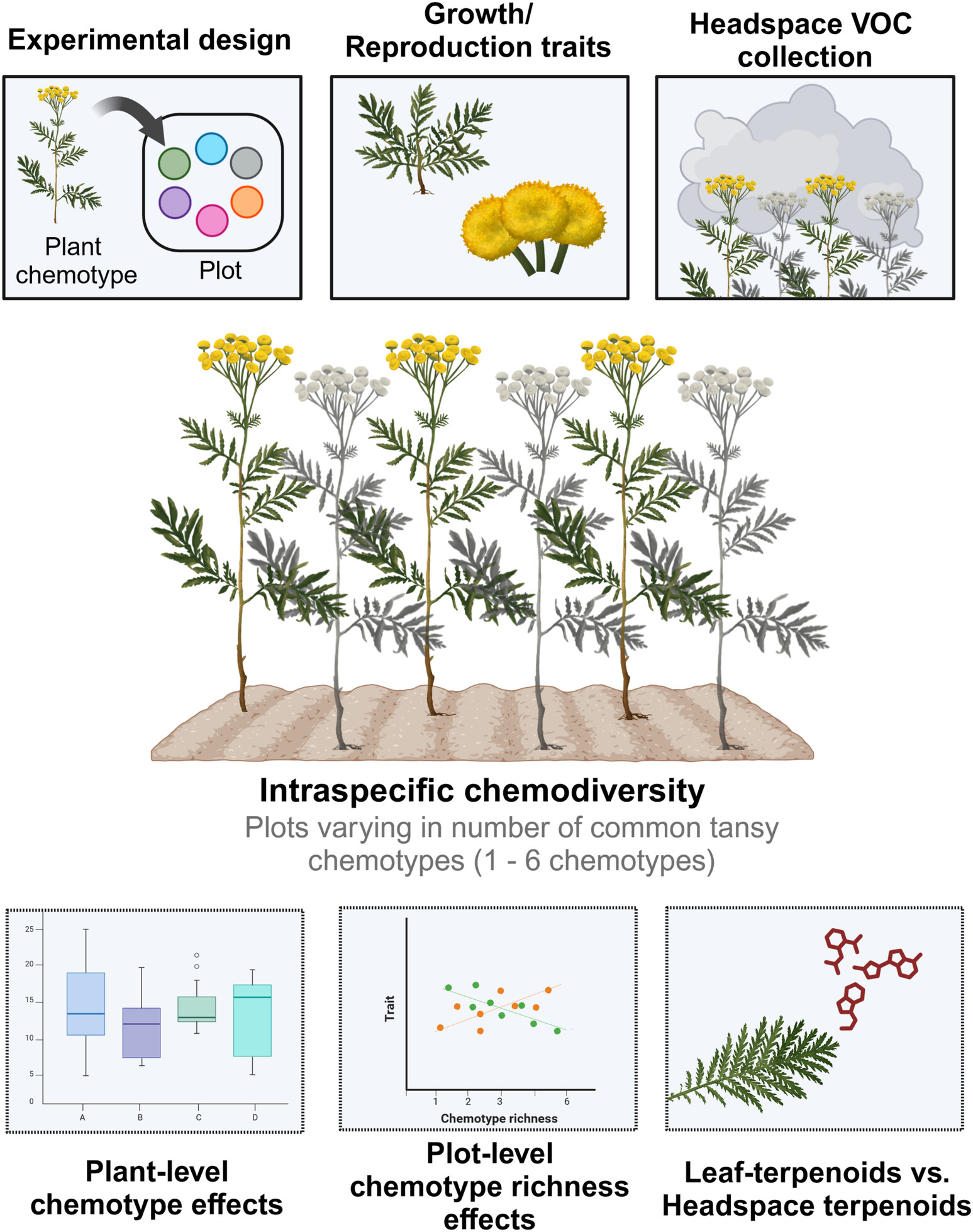
We designed an experiment to test the effects of intraspecific plant chemodiversity at plant and plot level on plant performance, and showed that chemodiversity significantly shapes plant growth and reproductive outputs, with most pronounced interactions between chemotype and plot-level chemotype richness on reproductive traits..
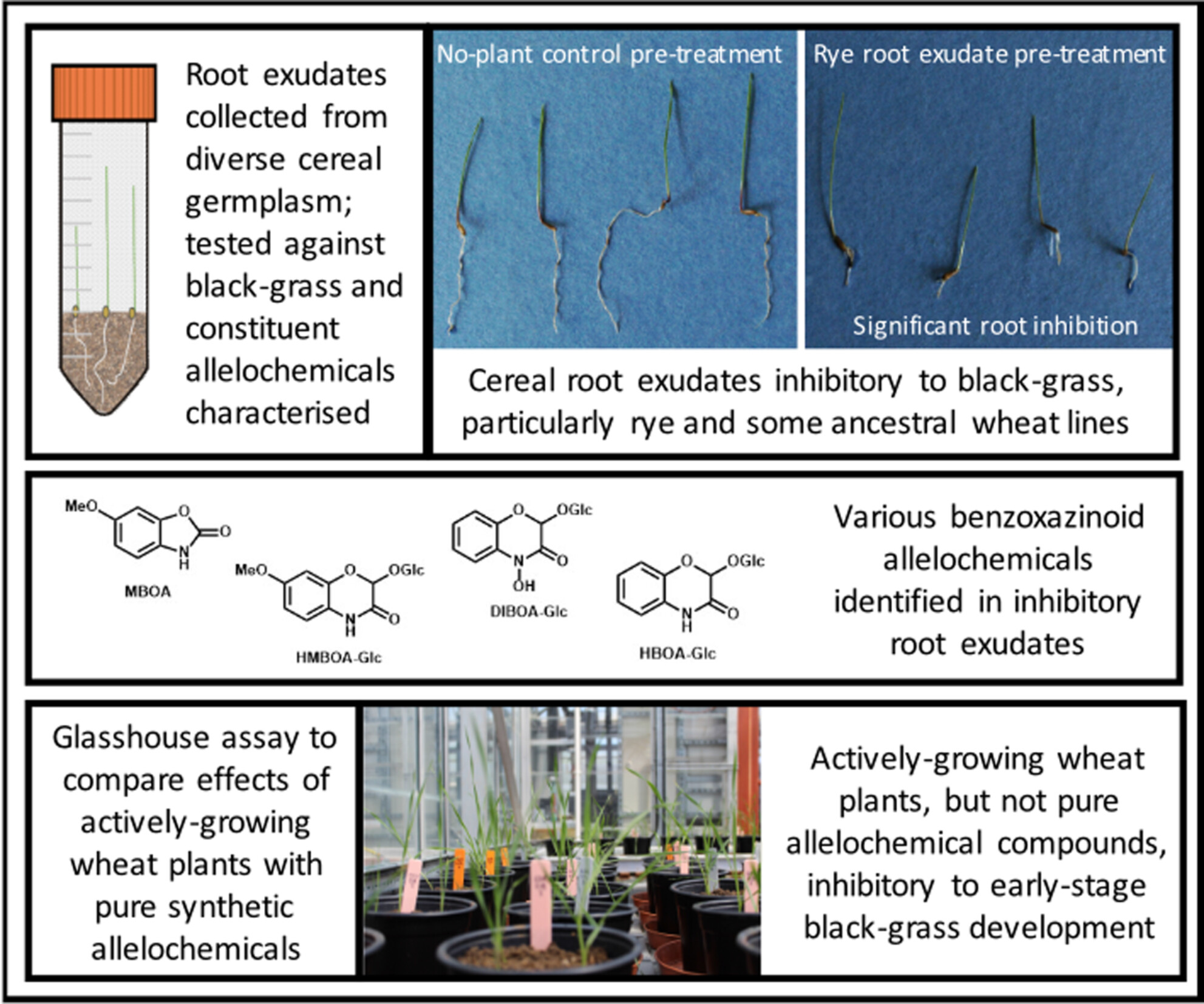
Variation in suppression of black-grass by modern and ancestral cereal root exudates
- Pages: 802-817
- First Published: 26 March 2025
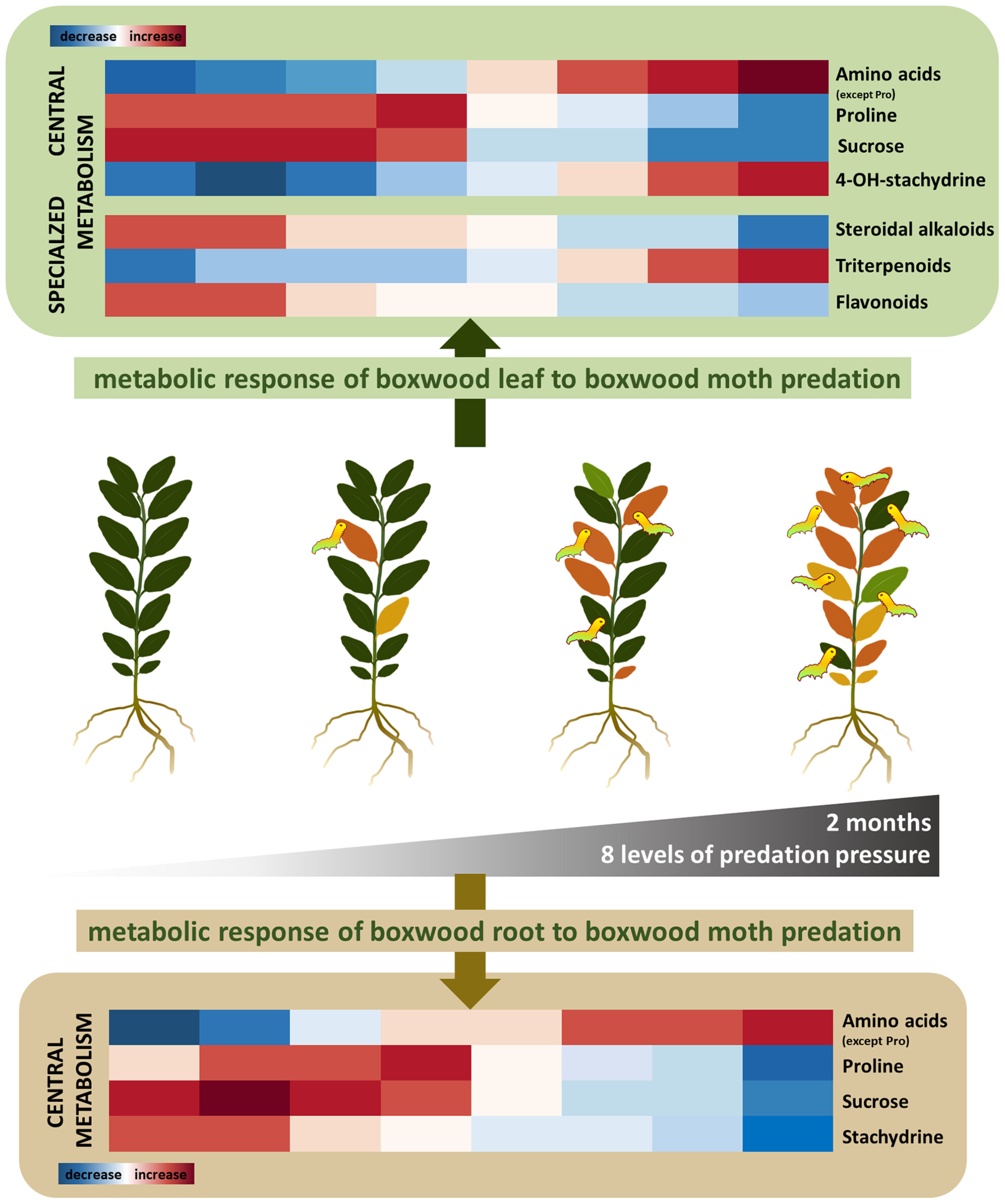
Comparative metabolomics reveals how the severity of predation by the invasive insect Cydalima perspectalis modulates the metabolism re–orchestration of native Buxus sempervirens
- Pages: 818-833
- First Published: 10 July 2024
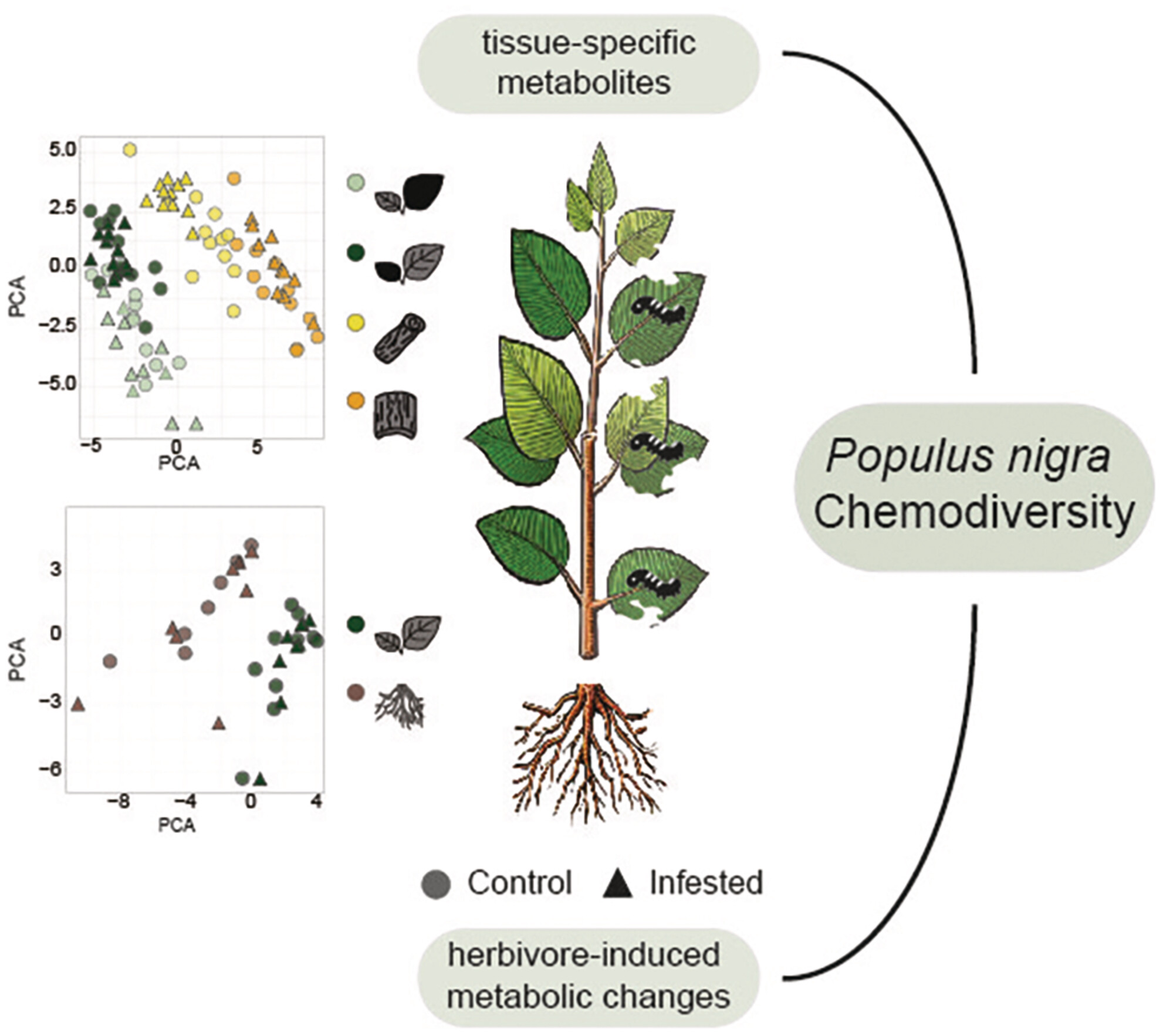
Deciphering organ-specific chemical changes following insect herbivory in Populus nigra using comparative metabolomics
- Pages: 834-846
- First Published: 28 May 2025
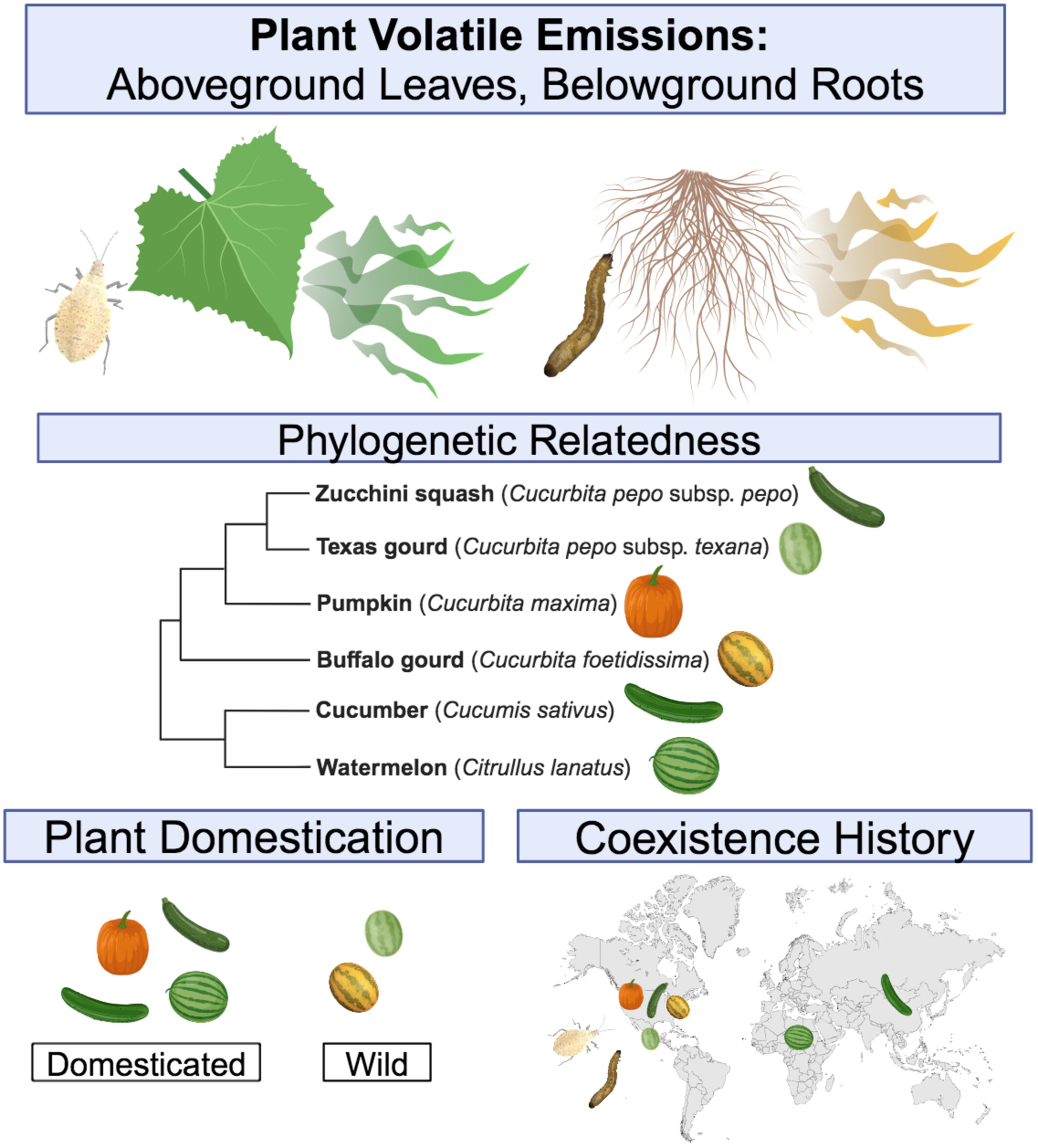
Eco-evolutionary factors contribute to chemodiversity in aboveground and belowground cucurbit herbivore-induced plant volatiles
- Pages: 847-860
- First Published: 20 August 2024
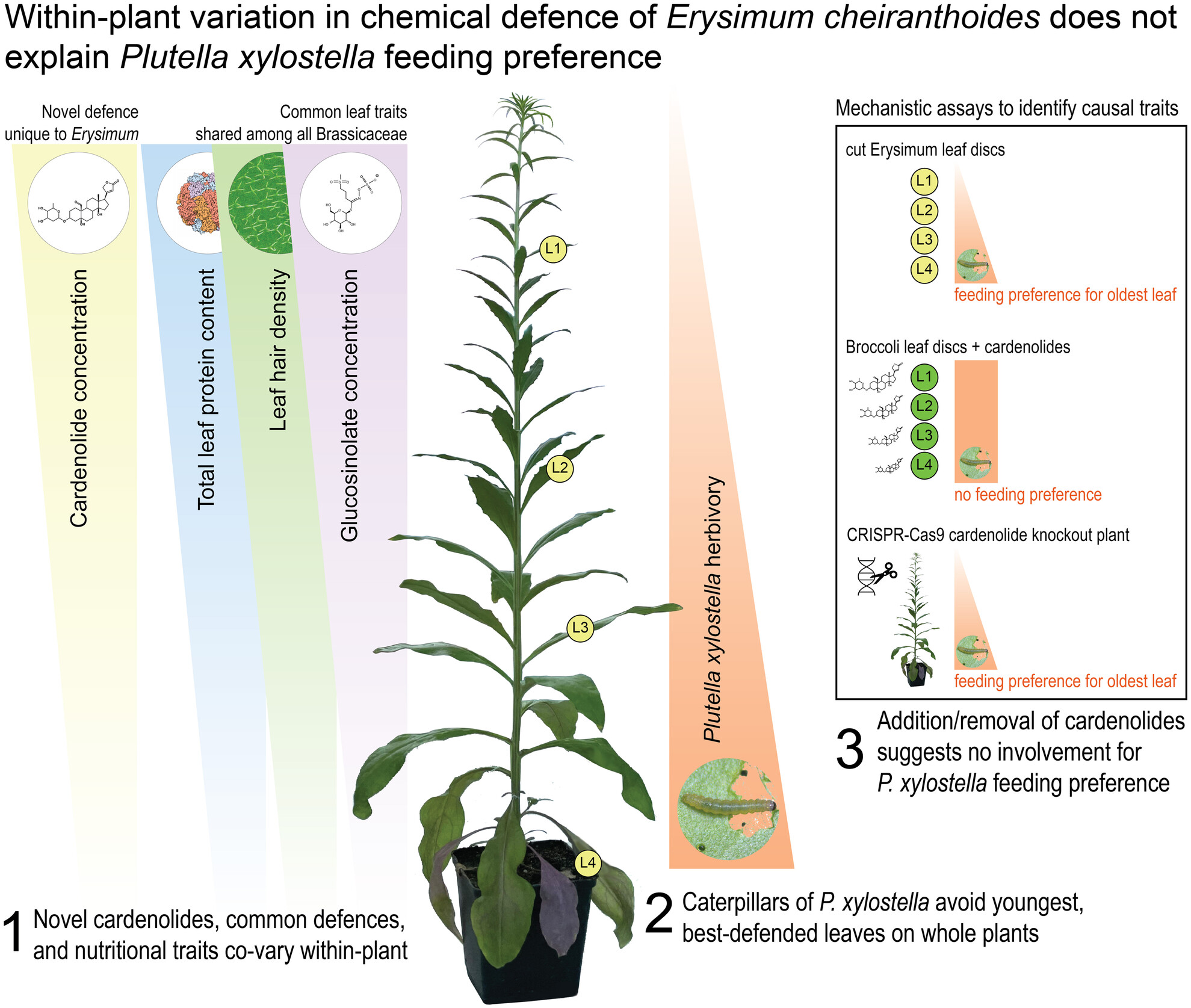
Within-plant variation in chemical defence of Erysimum cheiranthoides does not explain Plutella xylostella feeding preference
- Pages: 861-872
- First Published: 12 February 2025
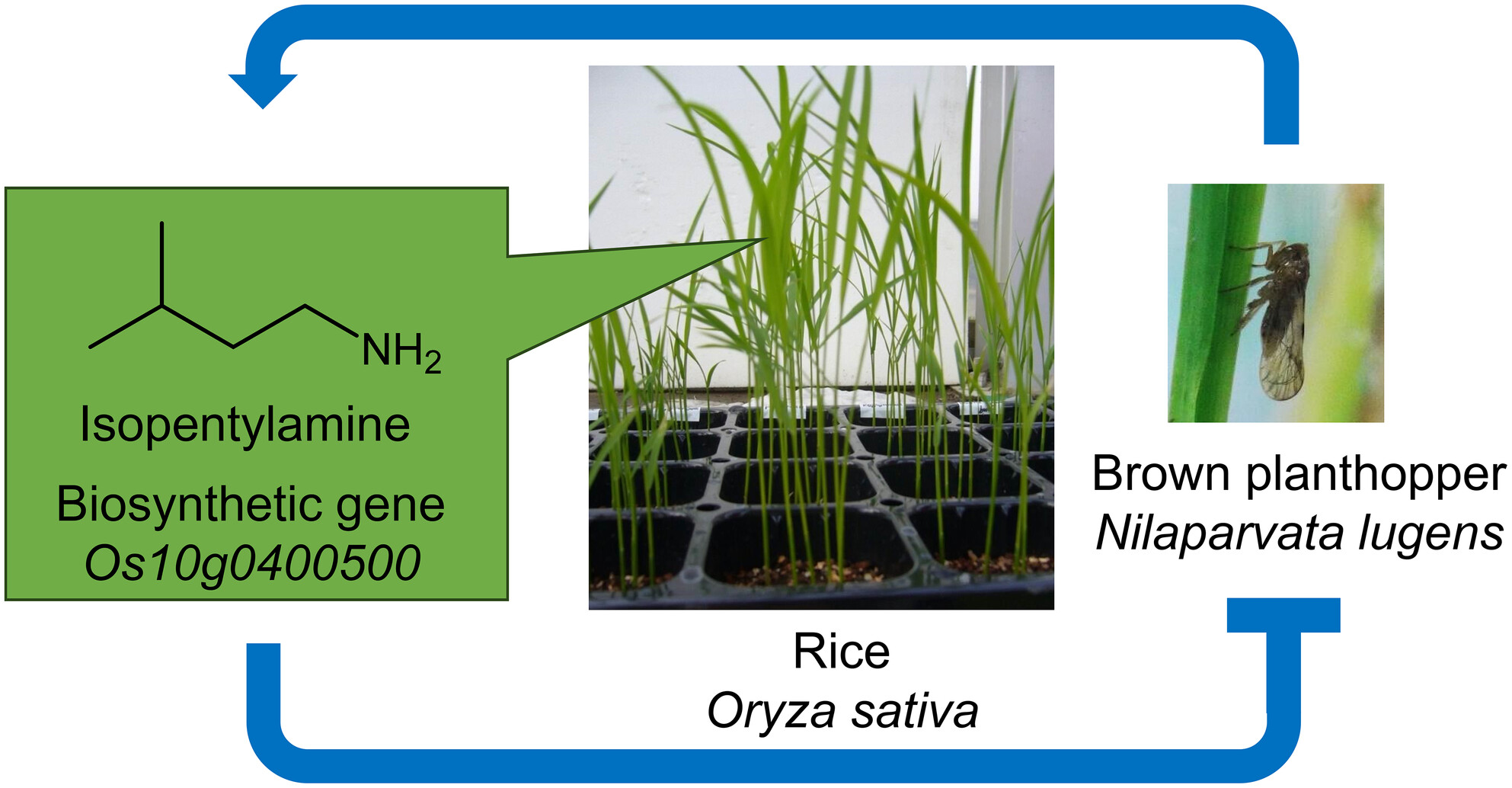
Natural variation-based genetic screen in rice identifies the isopentylamine biosynthetic gene that modulates brown planthopper behaviour
- Pages: 873-882
- First Published: 16 May 2025
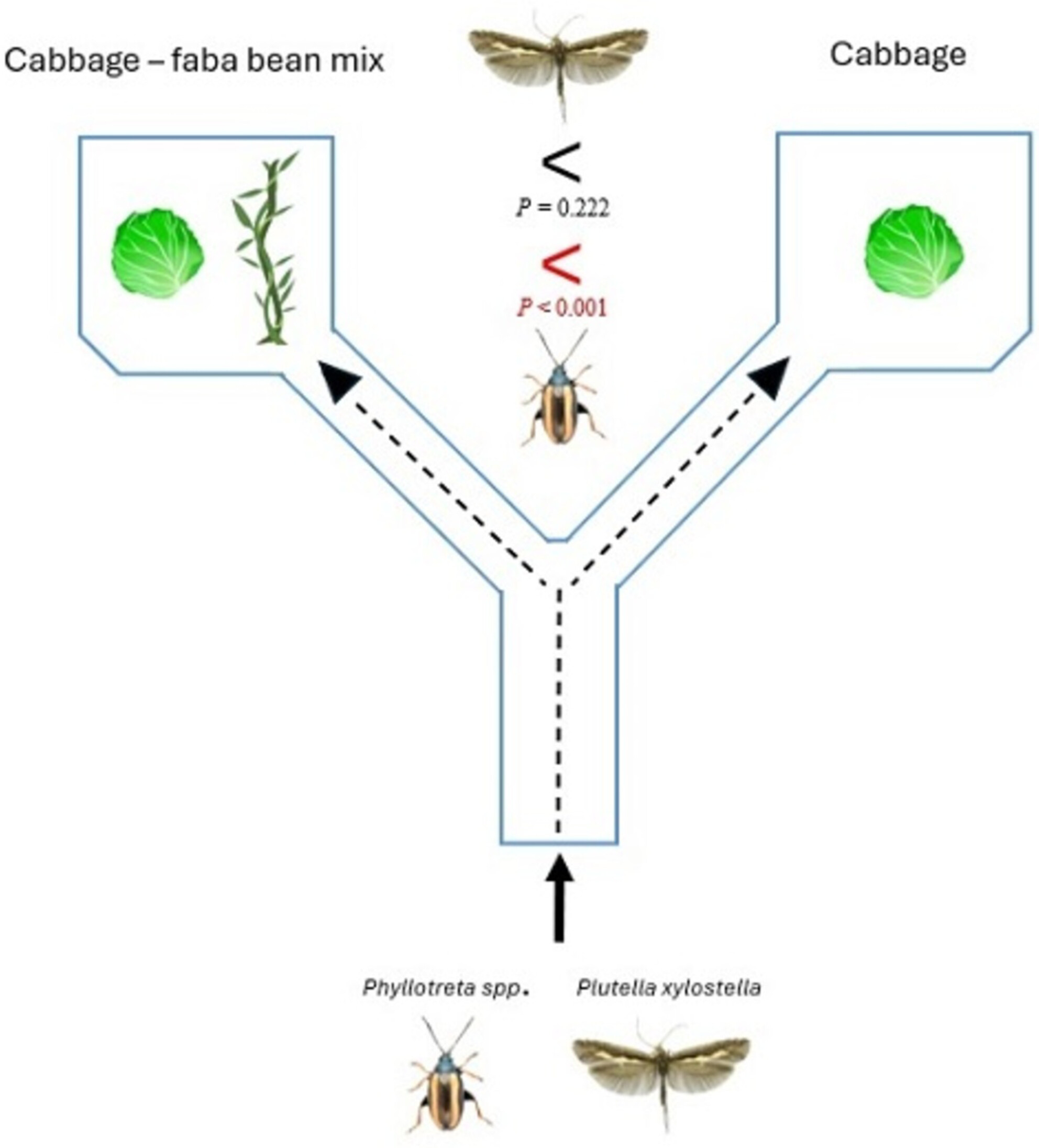
Effects of diversified volatile profiles on olfactory orientation of flea beetles Phyllotreta spp. and the diamondback moth Plutella xylostella
- Pages: 883-890
- First Published: 24 September 2024
Exogenous stimulation of Tanacetum vulgare roots with pipecolic acid leads to tissue-specific responses in terpenoid composition
- Pages: 891-902
- First Published: 16 August 2024
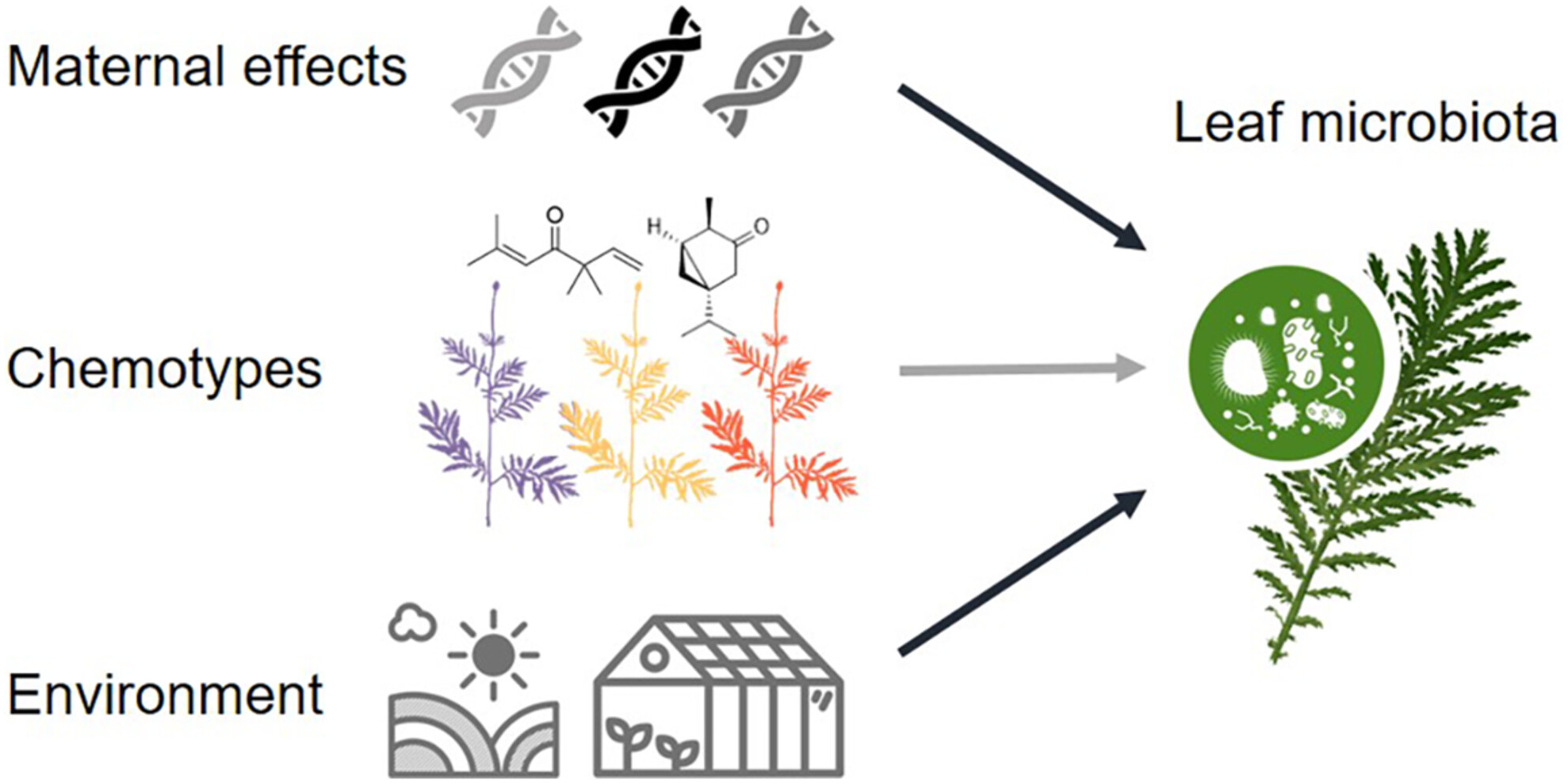
Influences of plant maternal effects, chemotype, and environment on the leaf bacterial community
- Pages: 903-912
- First Published: 17 January 2025
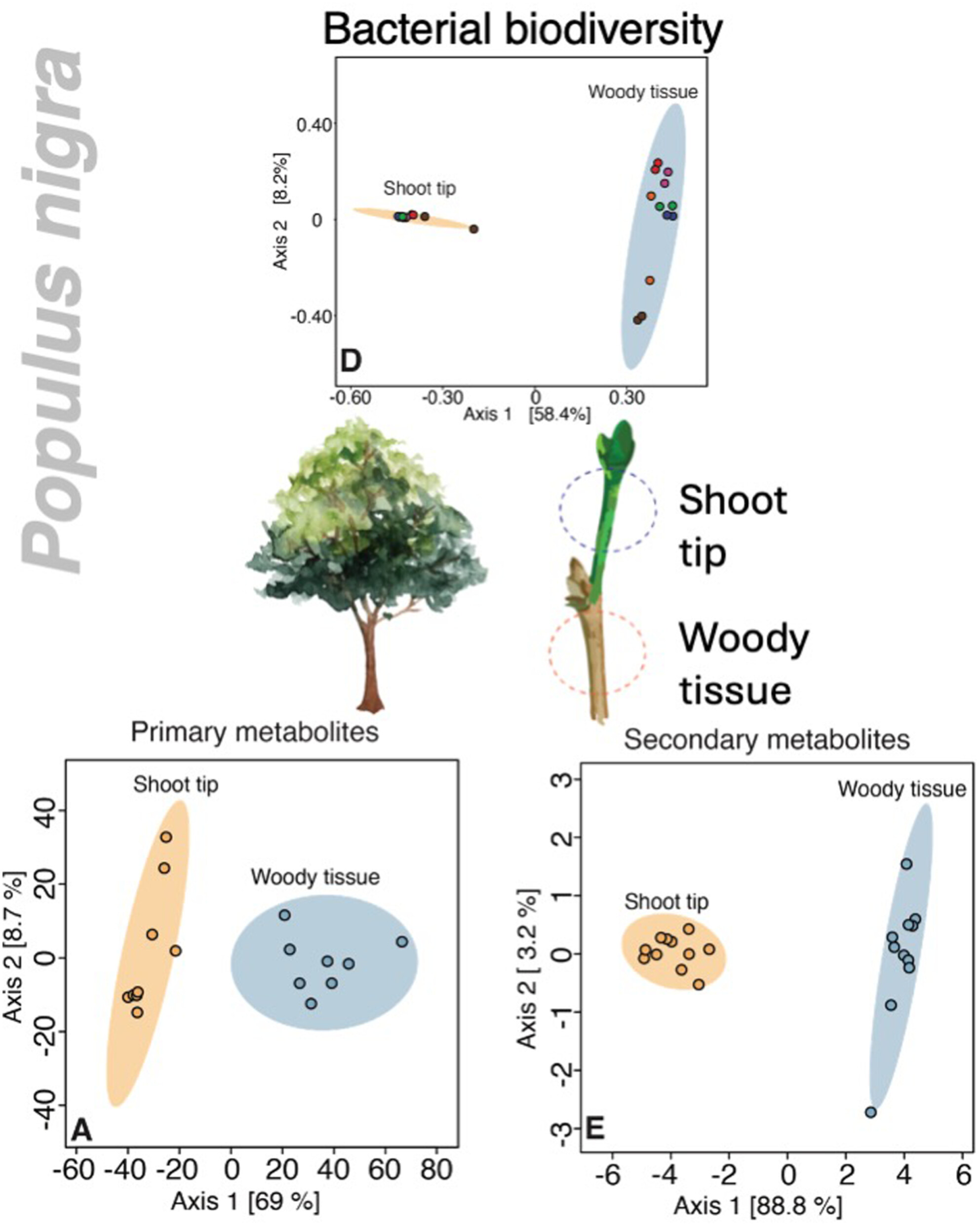
Tissue ontogeny and chemical composition influence bacterial biodiversity in the wood and shoot tip of Populus nigra
- Pages: 913-923
- First Published: 02 October 2024
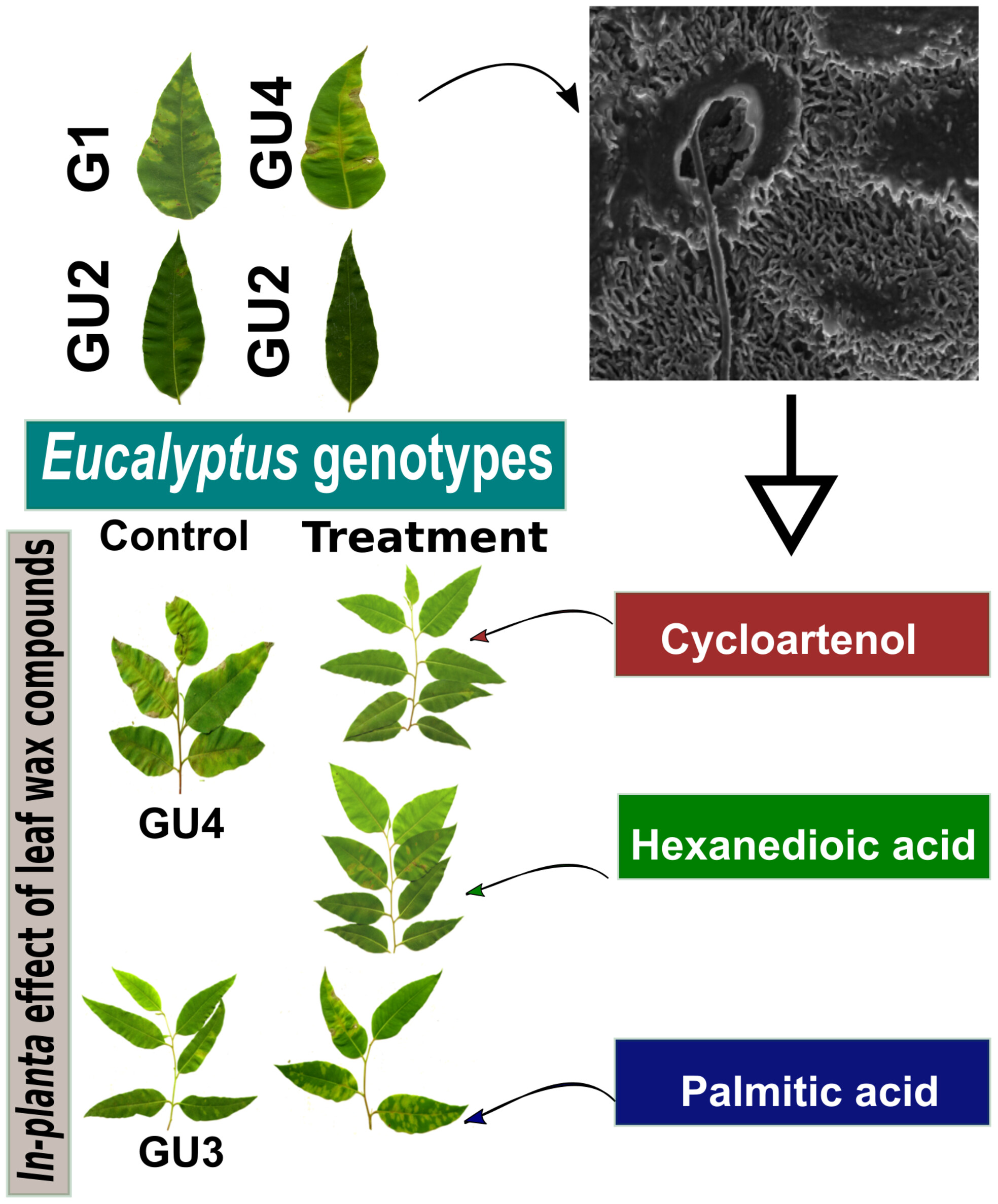
First line of defence: Eucalyptus leaf waxes influence infection by an aggressive fungal leaf pathogen
- Pages: 924-932
- First Published: 20 August 2024