Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
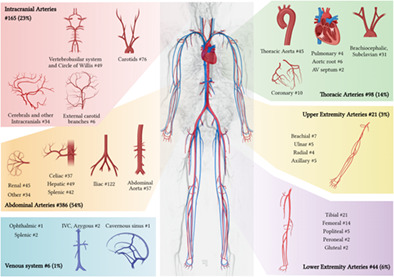
Vascular aneurysms in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome subtypes: A systematic review
- Pages: 261-267
- First Published: 09 October 2022
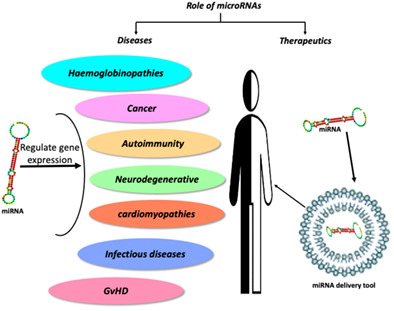
Dynamic interplay of microRNA in diseases and therapeutic
- Pages: 268-276
- First Published: 30 October 2022
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
FGF9 variant in 46,XY DSD patient suggests a role for dimerization in sex determination
- Pages: 277-287
- First Published: 09 November 2022
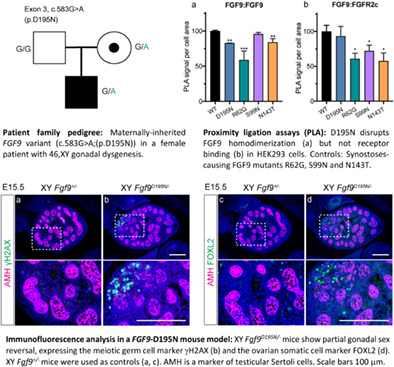
Immunofluorescence analysis in a FGF9-D195N mouse model: XY Fgf9D195N/− mice show partial gonadal sex reversal, expressing the meiotic germ cell marker γH2AX (b) and the ovarian somatic cell marker FOXL2 (d). XY Fgf9+/− mice were used as controls (a, c). AMH is a marker of testicular Sertoli cells. Scale bars 100 μm.
Bridging clinical care and research in Ontario, Canada: Maximizing diagnoses from reanalysis of clinical exome sequencing data
- Pages: 288-300
- First Published: 10 November 2022
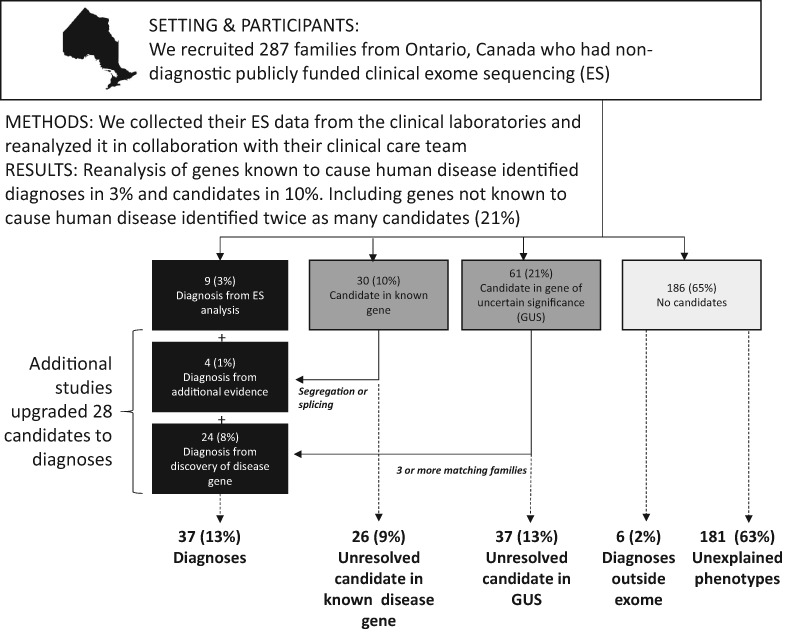
Reanalysis of 287 nondiagnostic clinical exomes from Ontario, Canada revealed few missed diagnoses by the clinical laboratories and the incremental gain from reanalysis of clinically-relevant genes is modest. The highest yield came from translational research methods to validate novel disease-gene associations.
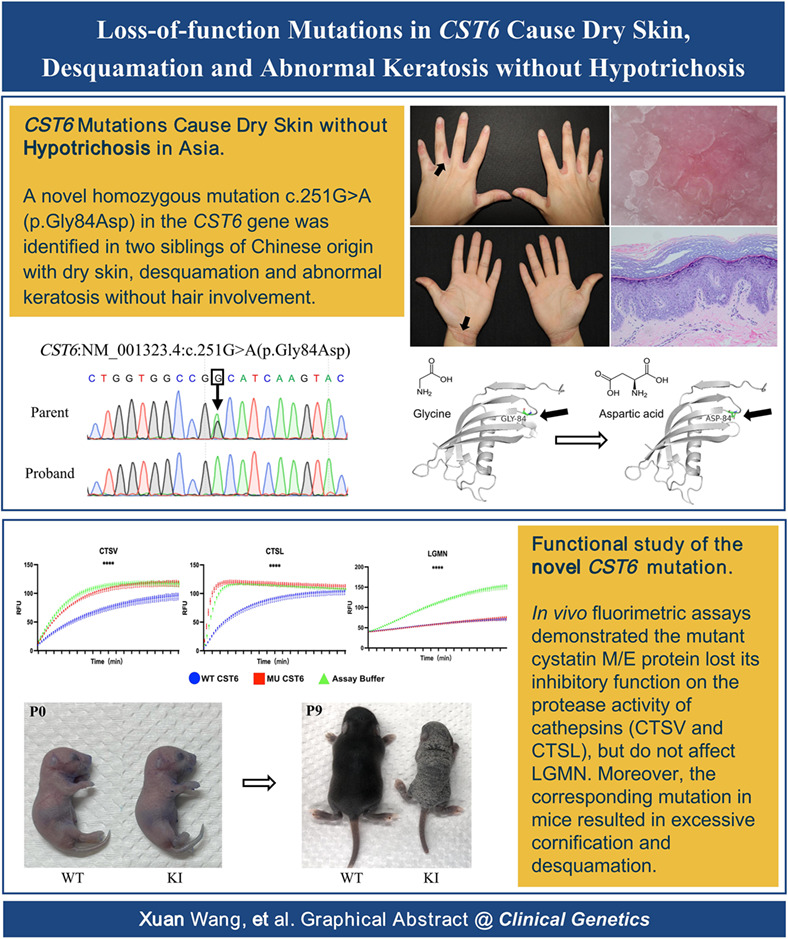
Loss-of-function mutations in CST6 cause dry skin, desquamation and abnormal keratosis without hypotrichosis
- Pages: 301-309
- First Published: 13 November 2022
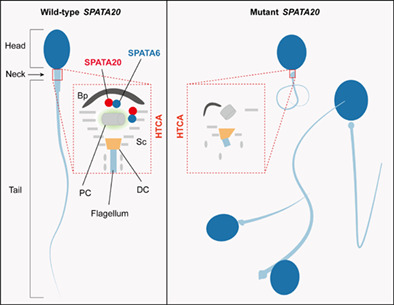
Identification of nonfunctional SPATA20 causing acephalic spermatozoa syndrome in humans
- Pages: 310-319
- First Published: 21 November 2022
A comprehensive functional analysis on the pathogenesis of novel TSPAN12 and NDP variants in familial exudative vitreoretinopathy
- Pages: 320-329
- First Published: 01 December 2022
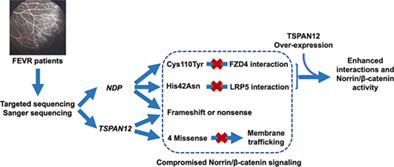
Targeted sequencing and Sanger sequencing identified NDP and TSPAN12 variants from FEVR patients. The four missense variants in TSPAN12 cause defective membrane trafficking ability, leading to decreased Norrin/β-catenin signaling. The Cys119Tyr and His42Asn variants in NDP cause compromised Norrin/β-catenin signaling by disrupting interactions with FZD4 and LRP5, respectively, which can be enhanced by over-expression of TSPAN12.
SHORT REPORTS
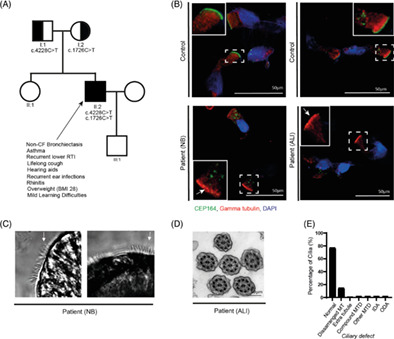
Biallelic variants in CEP164 cause a motile ciliopathy-like syndrome
- Pages: 330-334
- First Published: 23 October 2022
Management of copy number variants associated with incomplete penetrance and variable expressivity—Results of a French survey
- Pages: 335-340
- First Published: 23 October 2022
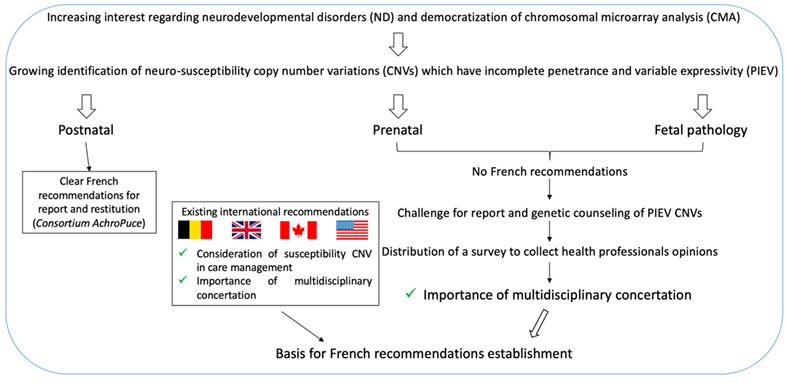
French healthcare professionals have to face with challenging report and genetic counseling regarding PIEV CNVs. Our study consists in purposing them a survey about their opinions and practices of which results highlight that multidisciplinary concertation has to be the main basis for French recommendations.
A novel variant in AFF3 underlying isolated syndactyly
- Pages: 341-345
- First Published: 23 October 2022
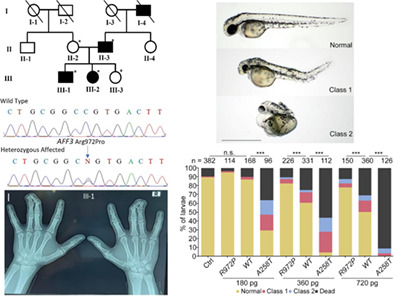
We report a novel heterozygous missense variant in AFF3 (c.2915G > C: p.Arg972Pro) associated with isolated syndactyly. Our zebrafish assay suggested that the variant is loss-of-function. Our results establish the first association of AFF3 with isolated syndactyly and expand the clinical spectrum associated with variants in AFF3.
Putative founder effect of Arg338* AP4M1 (SPG50) variant causing severe intellectual disability, epilepsy and spastic paraplegia: Report of three families
- Pages: 346-351
- First Published: 13 November 2022
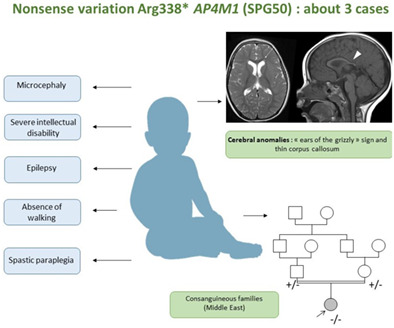
In this study we report three new unrelated patients from Middle-East consanguineous families carrying the previously described NM_004722.4(AP4M1):c.1012C〉T homozygous nonsense variant. We describe their phenotype, and provide evidence that the subjects carrying this variant originate from a common ancestor.
Genetic screening in patients with ovarian dysfunction
- Pages: 352-357
- First Published: 13 November 2022
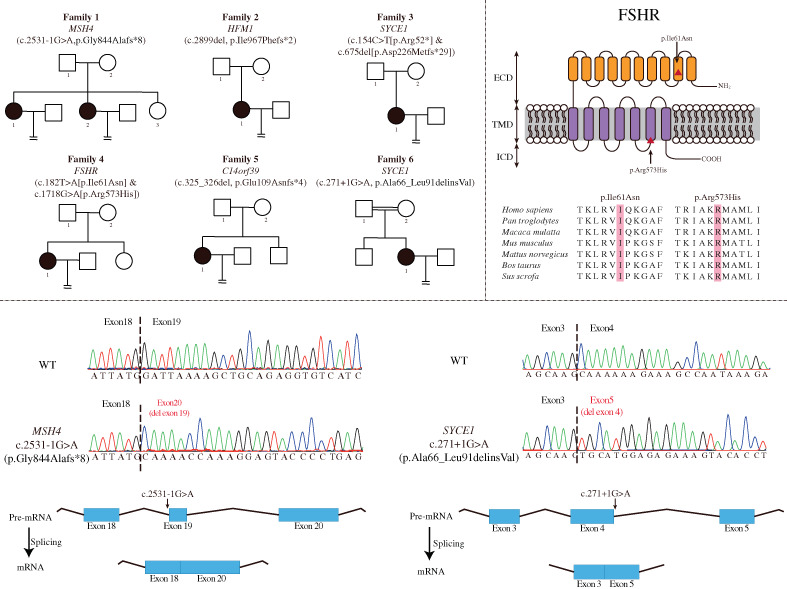
We identified eight potential variants in five genes (MSH4, HFM1, SYCE1, FSHR and C14orf39) from six independent families in infertile females characterized by ovarian dysfunction with exome sequencing. The missense variants in FSHR were conserved across species. And the splice-site variants in MSH4 and SYCE1 affected canonical splicing isoforms, leading to missing protein domains or premature termination.
Aminoacylation-defective bi-allelic mutations in human EPRS1 associated with psychomotor developmental delay, epilepsy, and deafness
- Pages: 358-363
- First Published: 21 November 2022
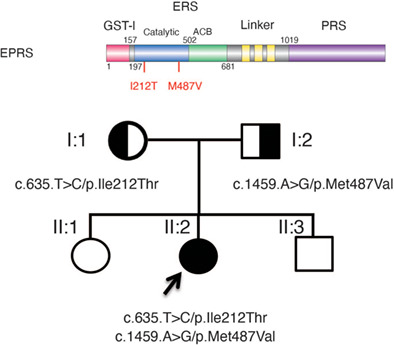
We report compound heterozygous variants in a bifunctional aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, EPRS1, in a 4-year-old female patient presenting with psychomotor developmental delay, seizures and deafness. Functional studies of these two missense mutations support major defects in enzymatic function in vitro and contributed to confirmation of the diagnosis.
Novel de novo ZNF148 truncating variant causing autism spectrum disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and intellectual disability
- Pages: 364-368
- First Published: 28 November 2022
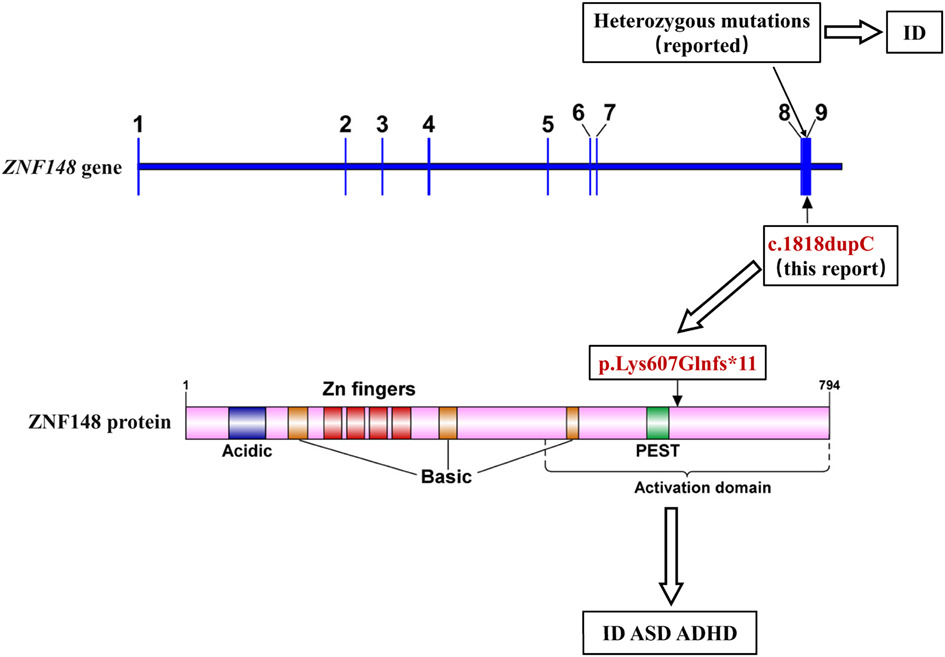
We first identify a novel ZNF148 heterozygous truncating variant c.1818dupC (p.Lys607Glnfs*11) in a patient with distinct phenotypes of ASD and ADHD. This variation produces a ZNF148 truncated protein with a deletion of the C-terminal activation domain and may destabilize the protein by affecting the transcriptional activation function.
RESEARCH LETTERS
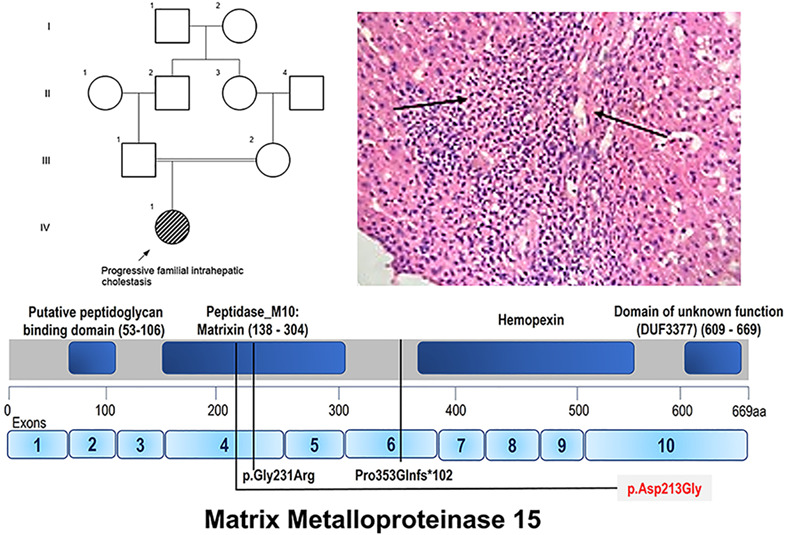
A bi-allelic missense change c.638A > G in matrix metalloproteinase 15 in a patient with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis without cardiac anomalies
- Pages: 369-370
- First Published: 09 November 2022
New insights in efficacy of different enzyme replacement therapy dosages in Fabry disease: Switch studies data following agalsidase beta shortage
- Pages: 371-376
- First Published: 13 November 2022

The update of the review on the effects of switching from agalsidase beta to alfa showed, in comparison to the previous review, an increased number of clinical events, a significant loss of renal function, and an increase in lyso Gb-3 levels, underscoring the importance of dose in the treatment of FD.
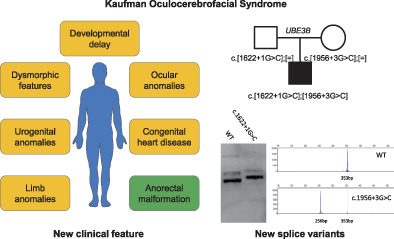
A new case of Kaufman Oculocerebrofacial syndrome caused by two splicing variants in UBE3B and review of the literature
- Pages: 377-379
- First Published: 28 November 2022