Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
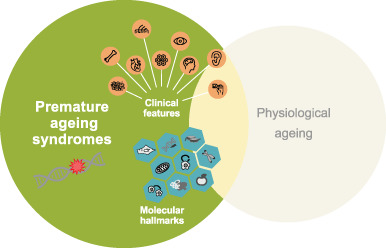
Premature aging disorders: A clinical and genetic compendium
- Pages: 3-28
- First Published: 28 August 2020
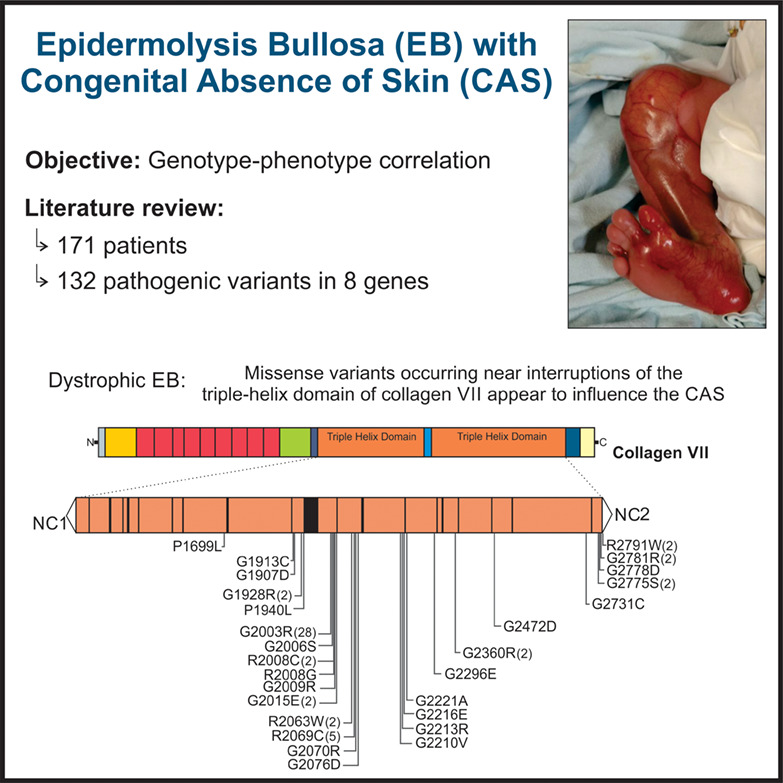
Genotype-phenotype correlations on epidermolysis bullosa with congenital absence of skin: A comprehensive review
- Pages: 29-41
- First Published: 07 June 2020
The evolution of the nosology of osteogenesis imperfecta
- Pages: 42-52
- First Published: 09 September 2020
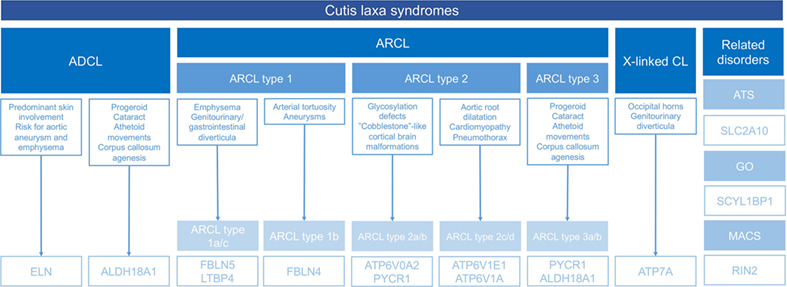
Cutis laxa: A comprehensive overview of clinical characteristics and pathophysiology
- Pages: 53-66
- First Published: 14 October 2020
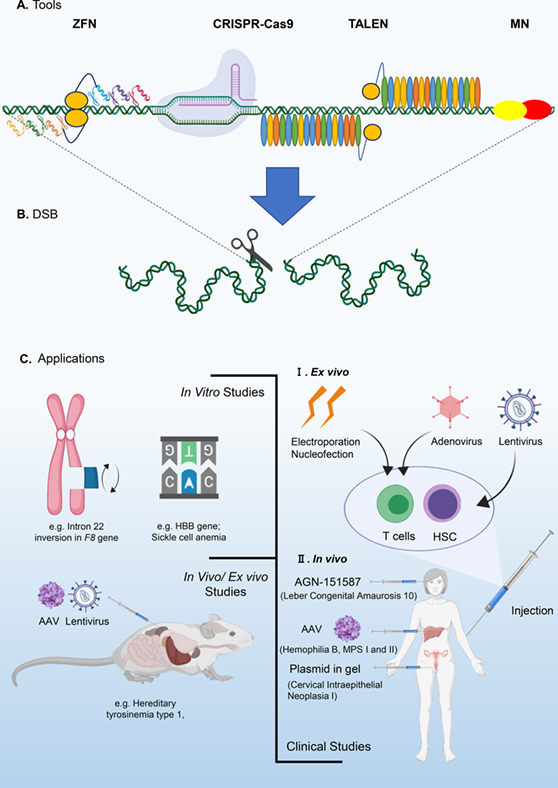
Gene editing technology for improving life quality: A dream coming true?
- Pages: 67-83
- First Published: 07 June 2020
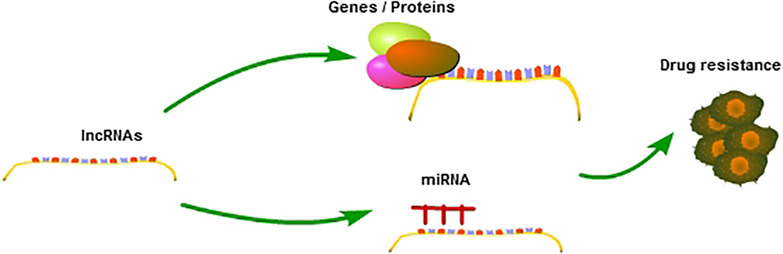
The role of long non-coding RNAs in drug resistance of cancer
- Pages: 84-92
- First Published: 25 June 2020
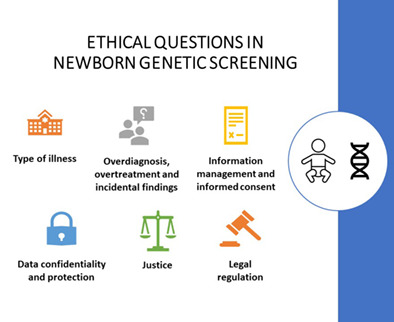
Ethical questions concerning newborn genetic screening
- Pages: 93-98
- First Published: 10 August 2020
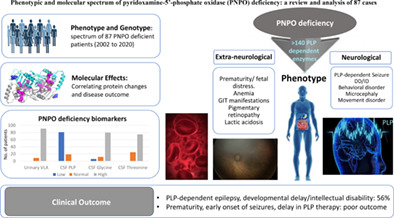
Phenotypic and molecular spectrum of pyridoxamine-5′-phosphate oxidase deficiency: A scoping review of 87 cases of pyridoxamine-5′-phosphate oxidase deficiency
- Pages: 99-110
- First Published: 04 September 2020
Autosomal dominant neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis: Clinical features and molecular basis
- Pages: 111-118
- First Published: 12 August 2020
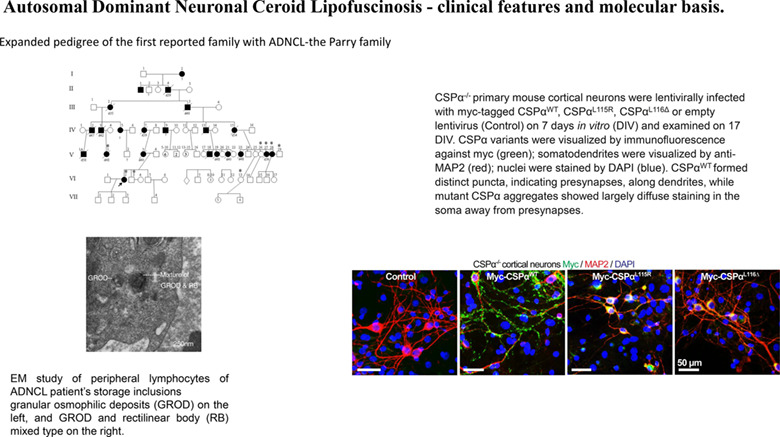
EM study of peripheral lymphocytes of autosomal dominant neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (ADNCL) patient's storage inclusions granular osmophilic deposits (GROD) on the left, and GROD and rectilinear body (RB) mixed type on the right. CSPα−/− primary mouse cortical neurons were lentivirally infected with myc-tagged CSPαWT, CSPαL115R, CSPαL116Δ, or empty lentivirus (control) on 7 days in vitro (DIV) and examined on 17 DIV. CSPα variants were visualized by immunofluorescence against myc (green); somatodendrites were visualized by anti-MAP2 (red); nuclei were stained by DAPI (blue). CSPαWT formed distinct puncta, indicating presynapses, along dendrites, while mutant CSPα aggregates showed largely diffuse staining in the soma away from presynapses.
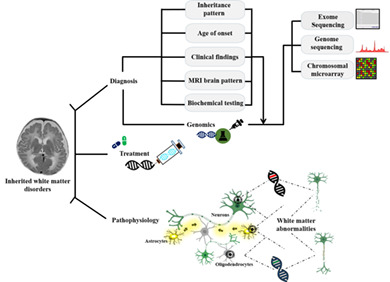
Genetic disorders with central nervous system white matter abnormalities: An update
- Pages: 119-132
- First Published: 12 October 2020
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Age of onset and behavioral manifestations in Huntington's disease: An Enroll-HD cohort analysis
- Pages: 133-142
- First Published: 05 October 2020
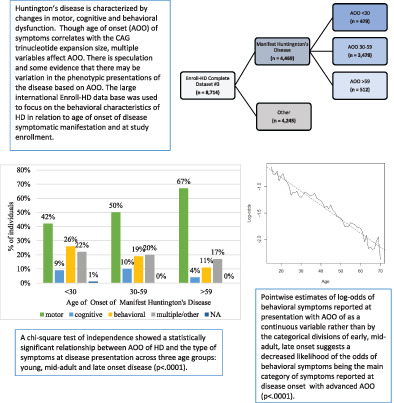
Huntington's disease is a autosomal dominant trinucleotide repeat disorder that results in motor, behavioral and cognitive dysfunction. Onset is usually in midlife but symptoms may start in childhood or late in life. Age of onset in relation to behavioral presentations were explored using a large manifest cohort. An inverse relationship was noted between age of onset and behavioral symptom presentations, highlighting an age associated difference in phenotypic presentations of Huntington's disease.
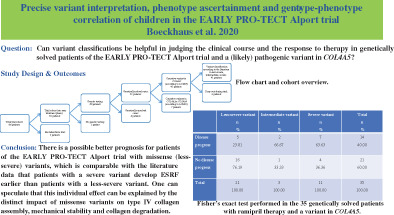
Precise variant interpretation, phenotype ascertainment, and genotype–phenotype correlation of children in the EARLY PRO-TECT Alport trial
- Pages: 143-156
- First Published: 11 October 2020
Exploring genotype-phenotype relationships in the CDKL5 deficiency disorder using an international dataset
- Pages: 157-165
- First Published: 12 October 2020
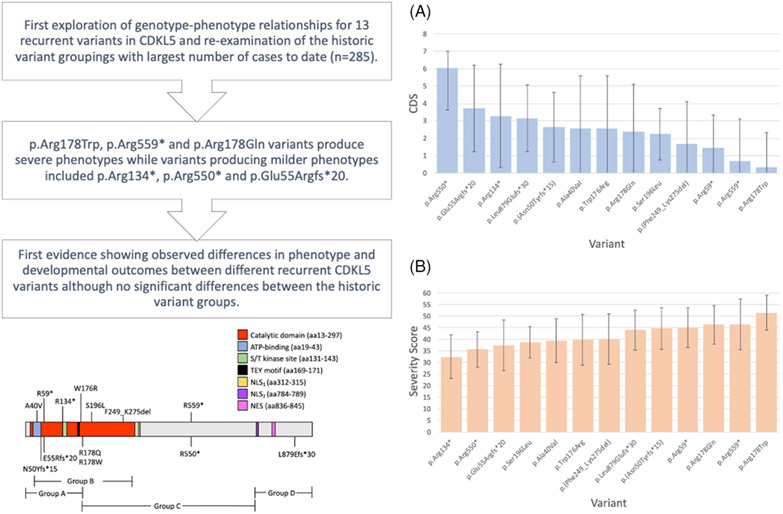
This study is the first exploration of genotype-phenotype relationships for 13 recurrent variants in CDKL5. We also re-examined the historic variant groupings previously used to investigate variants for the CDKL5 deficiency disorder. By applying two recently developed measures, we demonstrated that p.Arg178Trp, p.Arg559* and p.Arg178Gln variants produce severe phenotypes while variants producing milder phenotypes included p.Arg134*, p.Arg550* and p.Glu55Argfs*20. Our novel findings highlight the need for continued international collaboration between research groups to facilitate large study sizes and meaningful results for rare genetic conditions like the CDKL5 deficiency disorder.
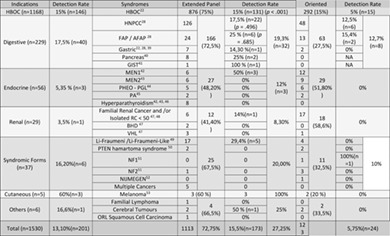
Feedback of extended panel sequencing in 1530 patients referred for suspicion of hereditary predisposition to adult cancers
- Pages: 166-175
- First Published: 12 October 2020
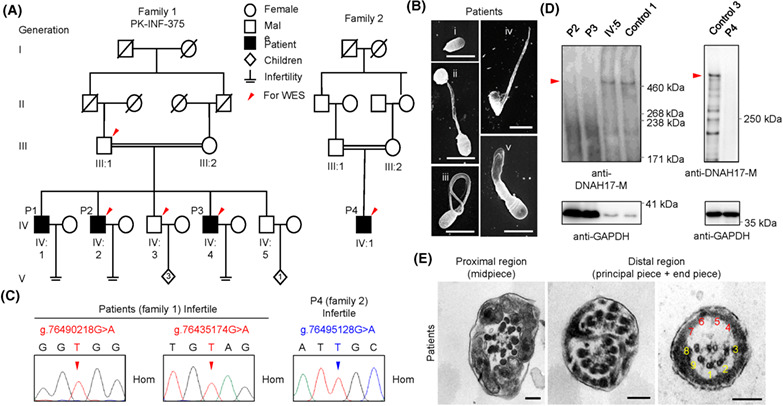
Novel loss-of-function variants in DNAH17 cause multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagella in humans and mice
- Pages: 176-186
- First Published: 17 October 2020
SHORT REPORTS
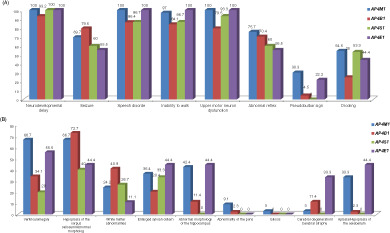
Comprehensive genotype-phenotype correlation in AP-4 deficiency syndrome; Adding data from a large cohort of Iranian patients
- Pages: 187-192
- First Published: 07 September 2020
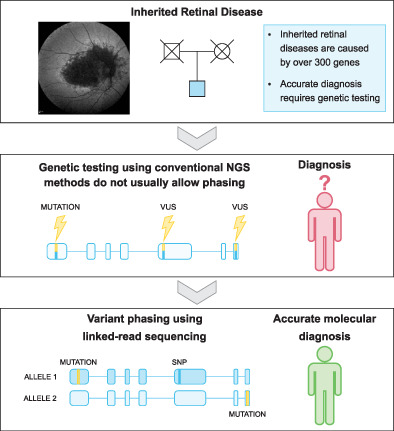
Identifying haplotypes in recessive inherited retinal dystrophies using whole-genome linked-read sequencing
- Pages: 193-198
- First Published: 09 September 2020
QRICH1 variants in Ververi-Brady syndrome—delineation of the genotypic and phenotypic spectrum
- Pages: 199-207
- First Published: 03 October 2020

The Ververi-Brady syndrome is a rare developmental disorder with a lot of hallmarks that are rather unspecific. We tried to further delineate the symptoms in this this study. Speech delay and notable social behaviour deficits seem to be the key symptoms. Our patients, as well as those described in the literature, all show mutations in the QRICH1 gene. We found three new variants that have not yet been described as well as one that has already been identified.
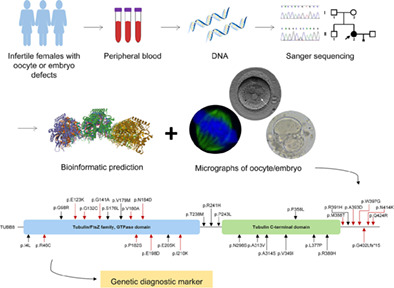
Mutation analysis of tubulin beta 8 class VIII in infertile females with oocyte or embryonic defects
- Pages: 208-214
- First Published: 03 October 2020