Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
FRONT COVER
Front Cover
- Page: i
- First Published: 16 February 2020

The cover image is based on the Original Article Phenotypic delineation of the retinal arterial macroaneurysms with supravalvular pulmonic stenosis syndrome by Hisham Alkuraya et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cge.13676.
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
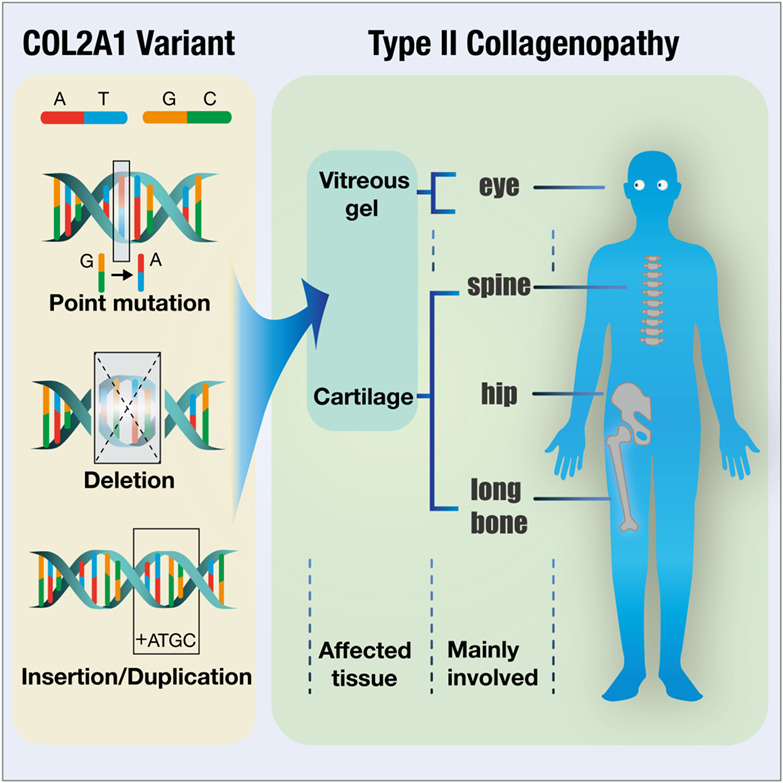
Integrated analysis of COL2A1 variant data and classification of type II collagenopathies
- Pages: 383-395
- First Published: 23 November 2019
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
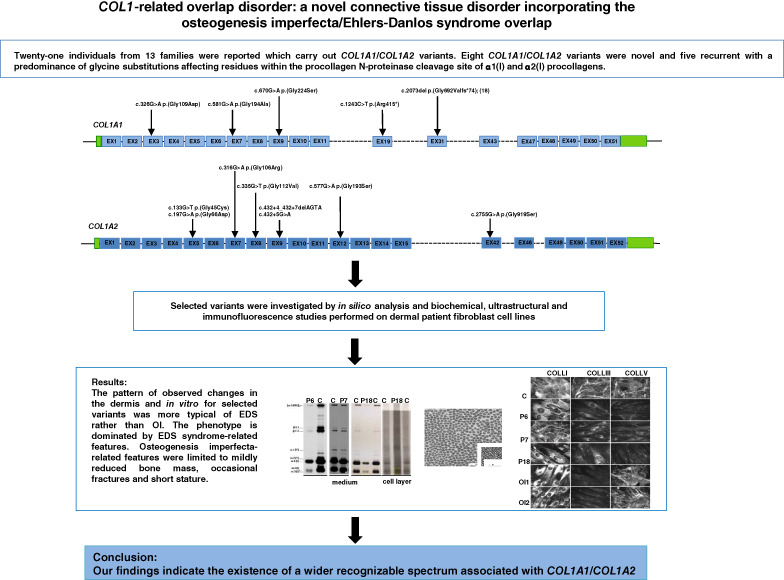
COL1-related overlap disorder: A novel connective tissue disorder incorporating the osteogenesis imperfecta/Ehlers-Danlos syndrome overlap
- Pages: 396-406
- First Published: 03 December 2019
Multicenter study of the clinical features and mutation gene spectrum of Chinese children with Dent disease
- Pages: 407-417
- First Published: 01 November 2019
X-linked intellectual disability: Phenotypic expression in carrier females
- Pages: 418-425
- First Published: 08 November 2019
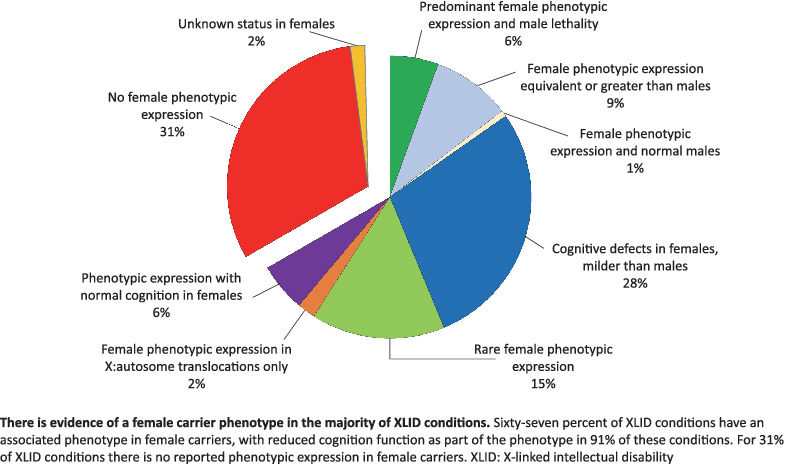
There is evidence of a female carrier phenotype in the majority of XLID conditions. Sixty-seven percent of XLID conditions have an associated phenotype in female carriers, with reduced cognition function as part of the phenotype in 91% of these conditions. For 31% of XLID conditions, there is no reported phenotypic expression in female carriers. XLID, X-linked intellectual disability.
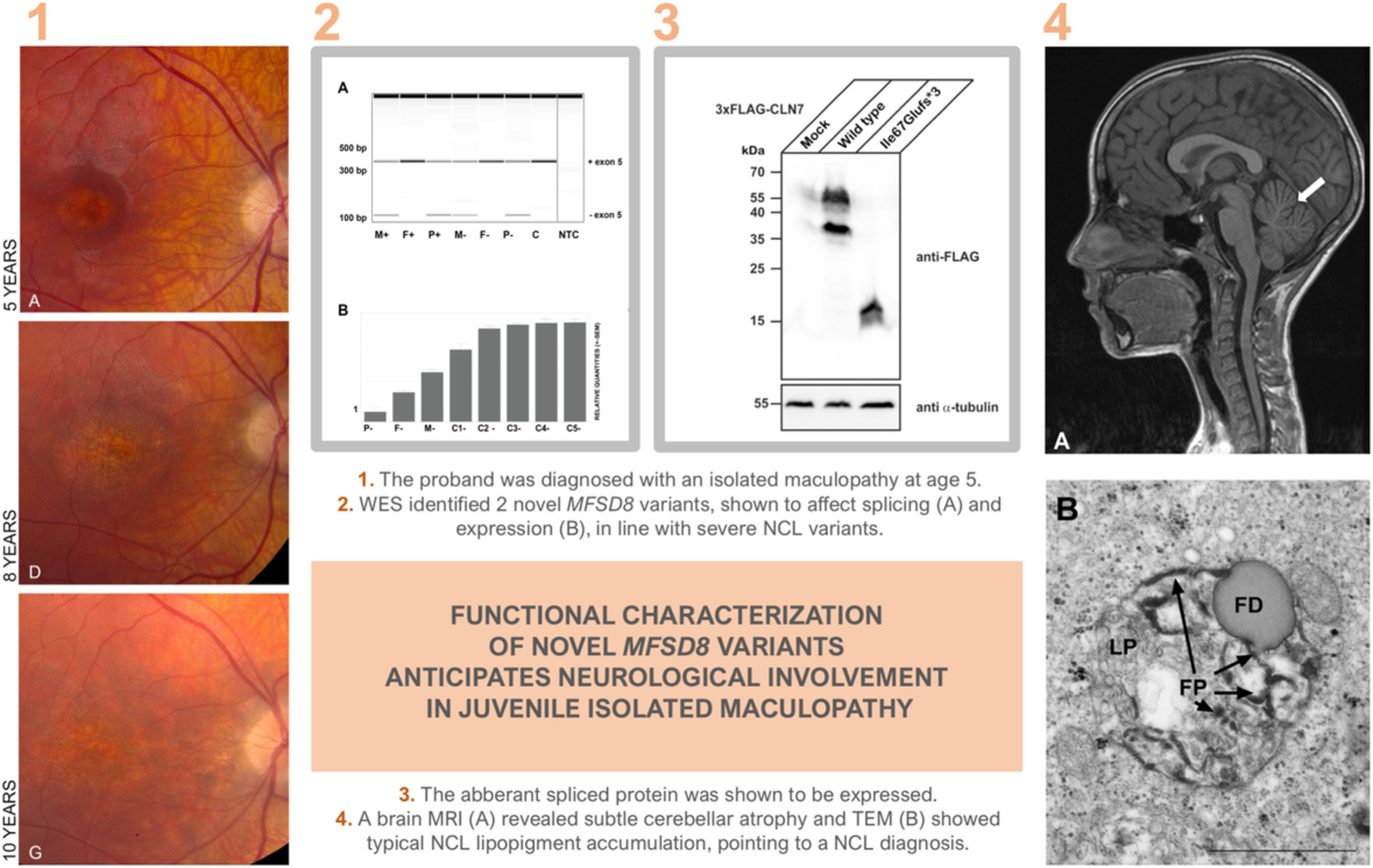
Functional characterization of novel MFSD8 pathogenic variants anticipates neurological involvement in juvenile isolated maculopathy
- Pages: 426-436
- First Published: 13 November 2019
Sorting nexin 27 (SNX27) variants associated with seizures, developmental delay, behavioral disturbance, and subcortical brain abnormalities
- Pages: 437-446
- First Published: 13 November 2019
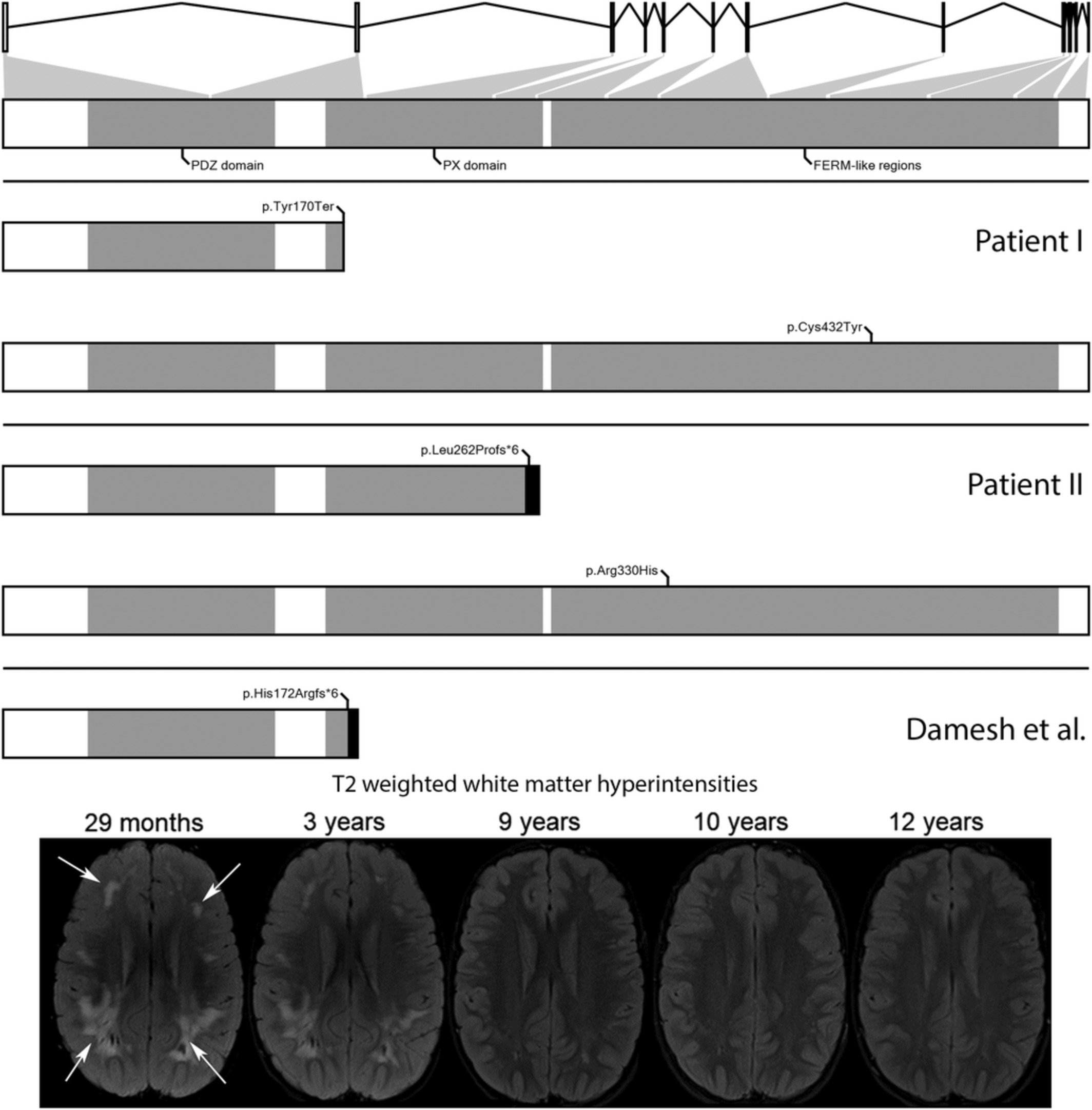
Biallelic sorting nexin 27 (SNX27) variants (top panel) are associated with seizures, developmental delay, intellectual disability, behavioral disturbance, and subcortical white matter abnormalities (bottom panel, white arrows). Severe variants (Damseh et al) can lead to early lethality, while missense variants (Patient I and Patient II) can be associated with late survival.
Phenotypic delineation of the retinal arterial macroaneurysms with supravalvular pulmonic stenosis syndrome
- Pages: 447-456
- First Published: 15 November 2019
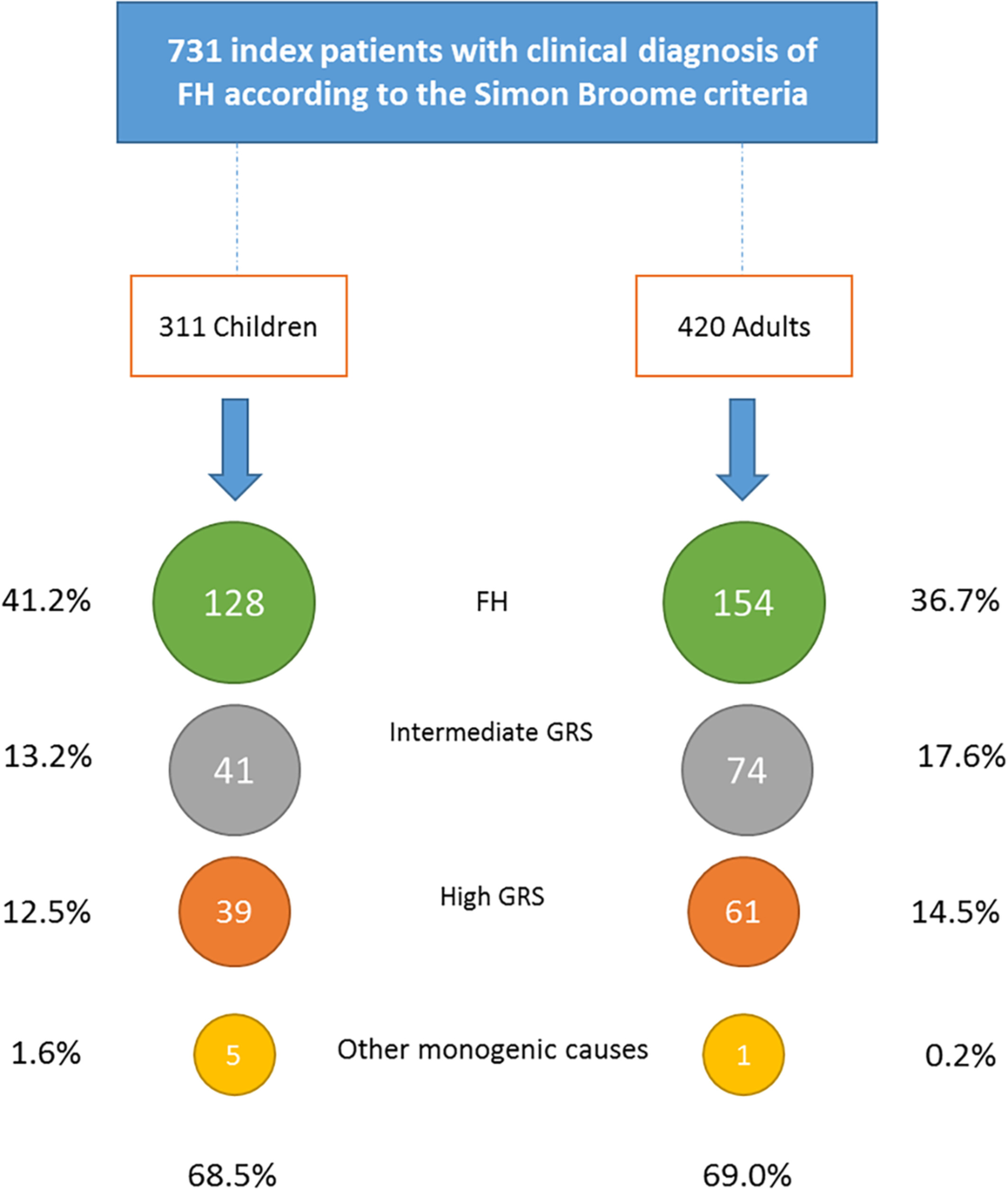
The familial hypercholesterolaemia phenotype: Monogenic familial hypercholesterolaemia, polygenic hypercholesterolaemia and other causes
- Pages: 457-466
- First Published: 31 December 2019
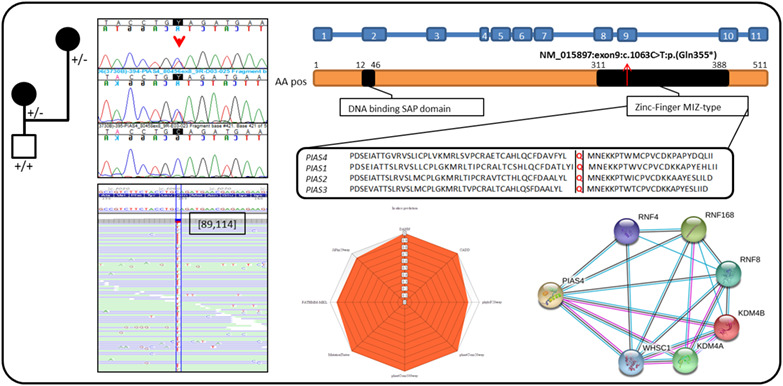
Further definition of the proximal 19p13.3 microdeletion/microduplication syndrome and implication of PIAS4 as the major contributor
- Pages: 467-476
- First Published: 23 January 2020
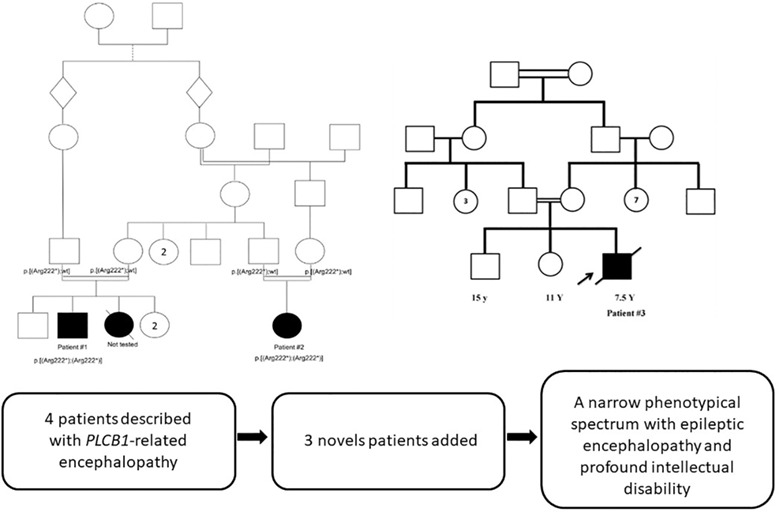
Three novel patients with epileptic encephalopathy due to biallelic mutations in the PLCB1 gene
- Pages: 477-482
- First Published: 27 December 2019
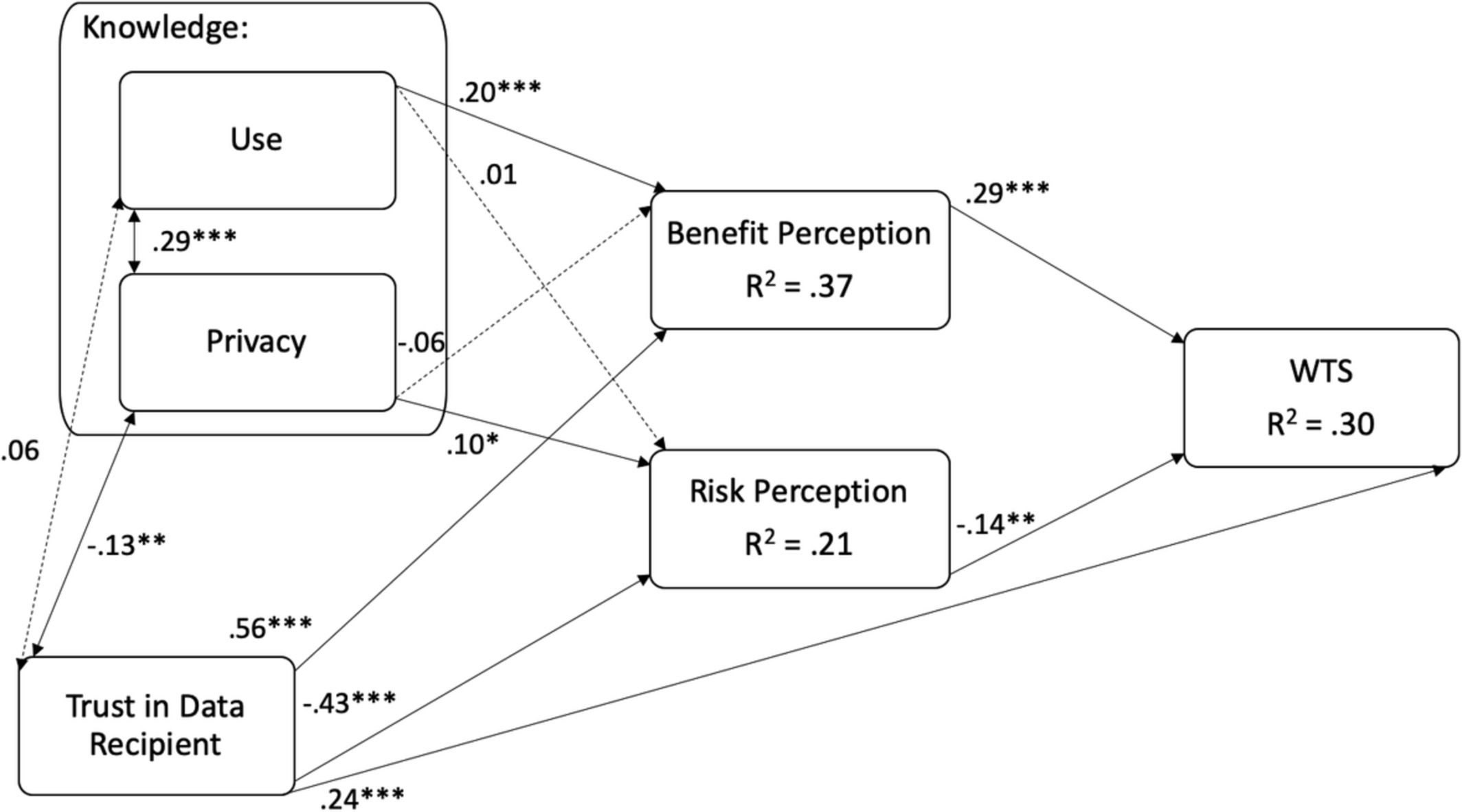
Psychological factors that determine people's willingness-to-share genetic data for research
- Pages: 483-491
- First Published: 12 December 2019
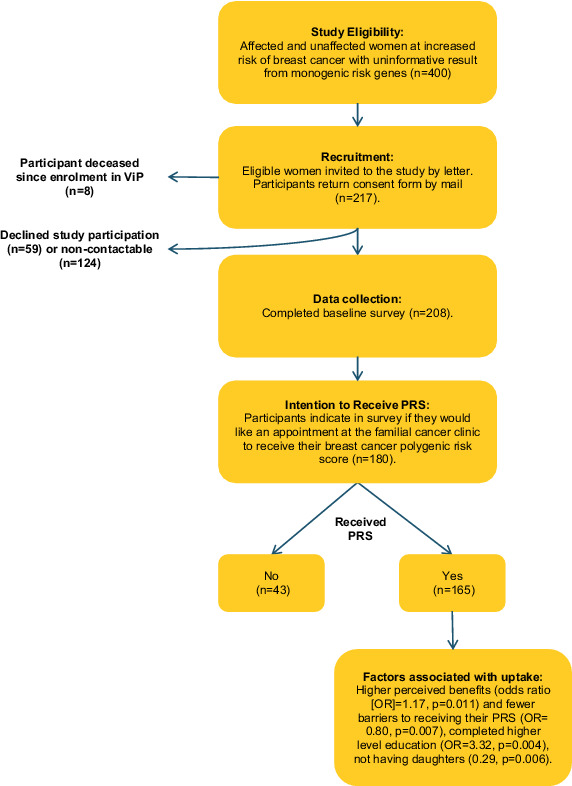
Uptake of polygenic risk information among women at increased risk of breast cancer
- Pages: 492-501
- First Published: 12 December 2019
SHORT REPORTS
Novel variants in CDH2 are associated with a new syndrome including Peters anomaly
- Pages: 502-508
- First Published: 24 October 2019
Clinical and genetic spectrum in 33 Egyptian families with suspected primary ciliary dyskinesia
- Pages: 509-515
- First Published: 24 October 2019
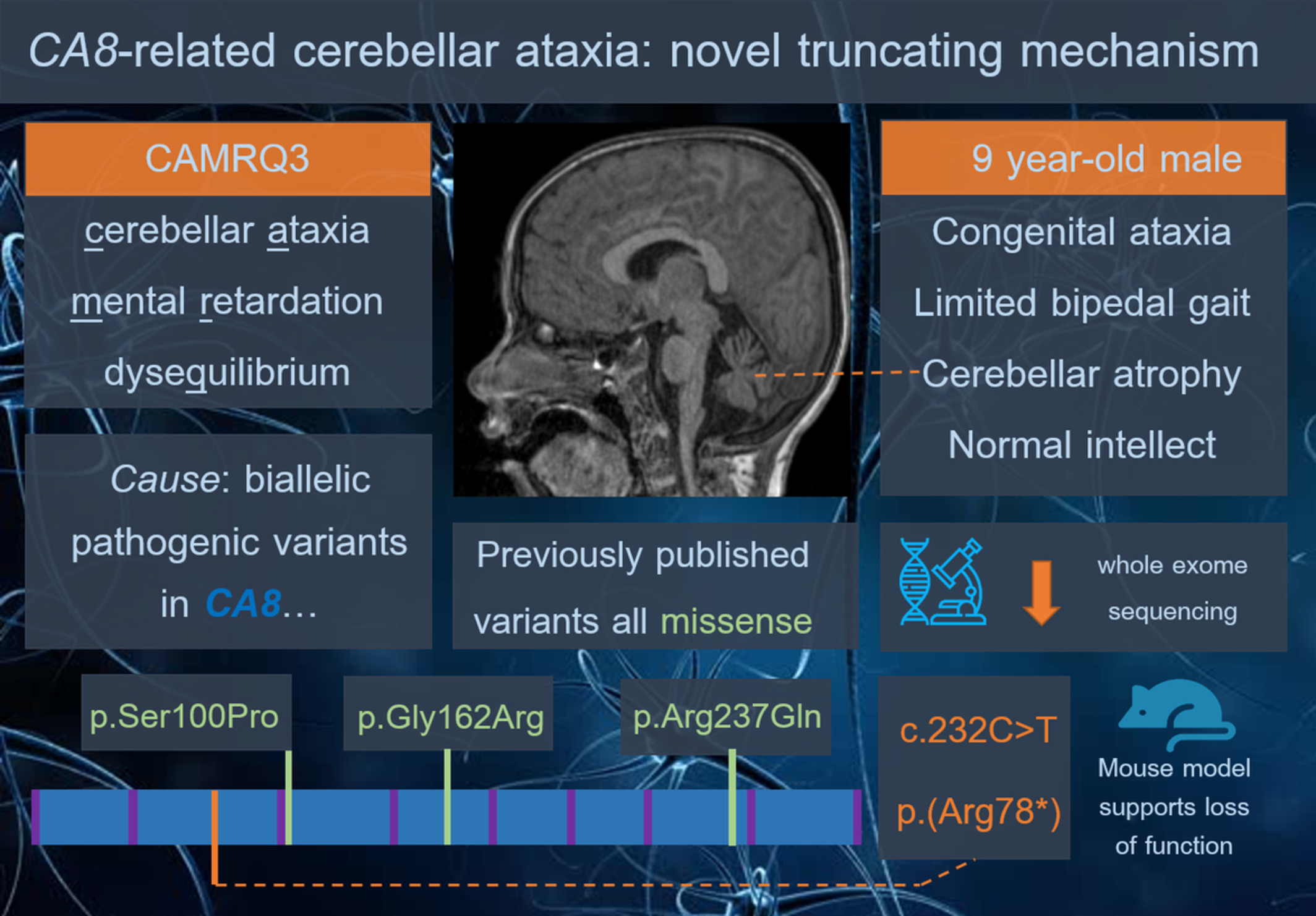
Cerebellar ataxia with normal intellect associated with a homozygous truncating variant in CA8
- Pages: 516-520
- First Published: 06 November 2019
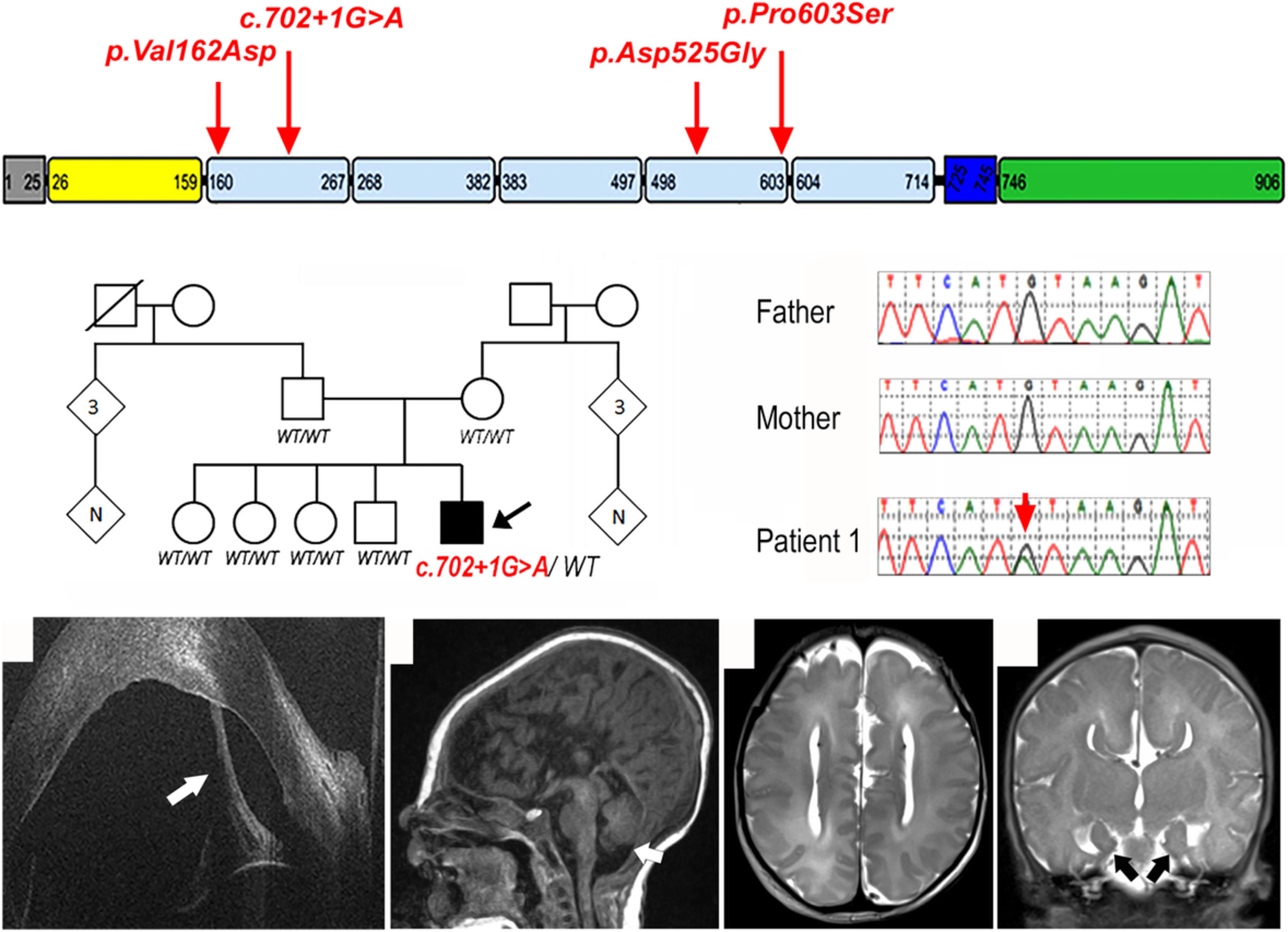
Hereditary spastic paraplegia is a novel phenotype for germline de novo ATP1A1 mutation
- Pages: 521-526
- First Published: 08 November 2019
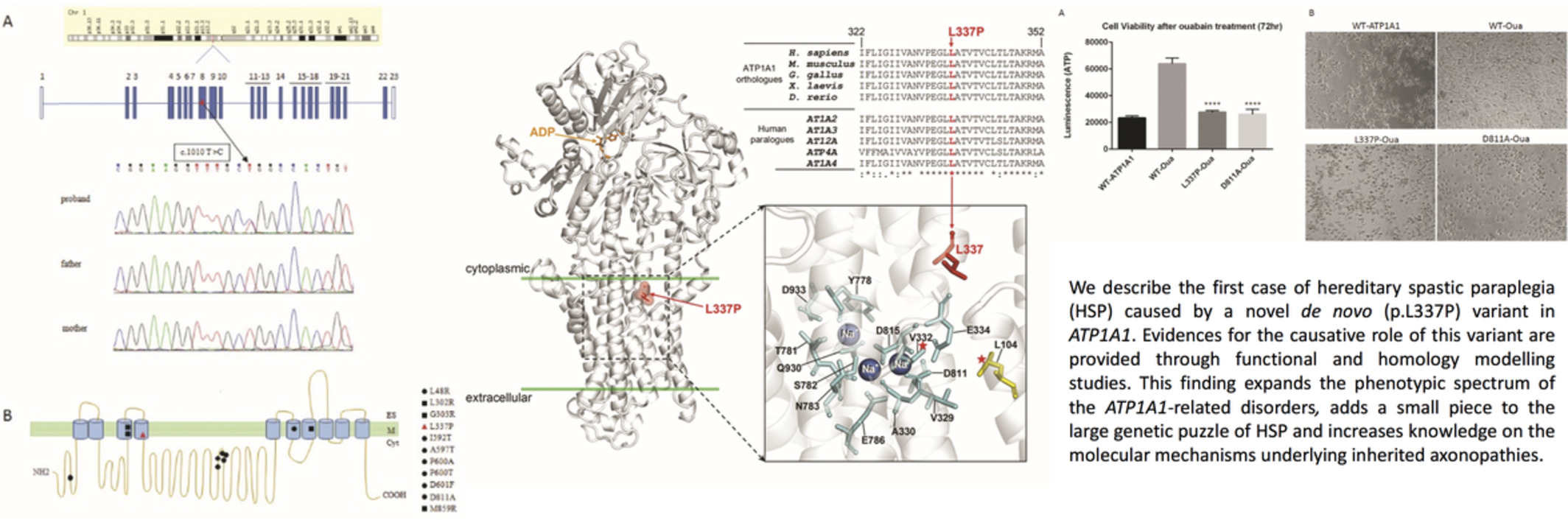
We describe the first case of hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP) caused by a novel de novo (p.L337P) variant in ATP1A1. Evidences for the causative role of this variant are provided through functional and homology modeling studies. This finding expands the phenotypic spectrum of the ATP1A1-related disorders, adds a small piece to the large genetic puzzle of HSP and increases knowledge on the molecular mechanisms underlying inherited axonopathies.
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
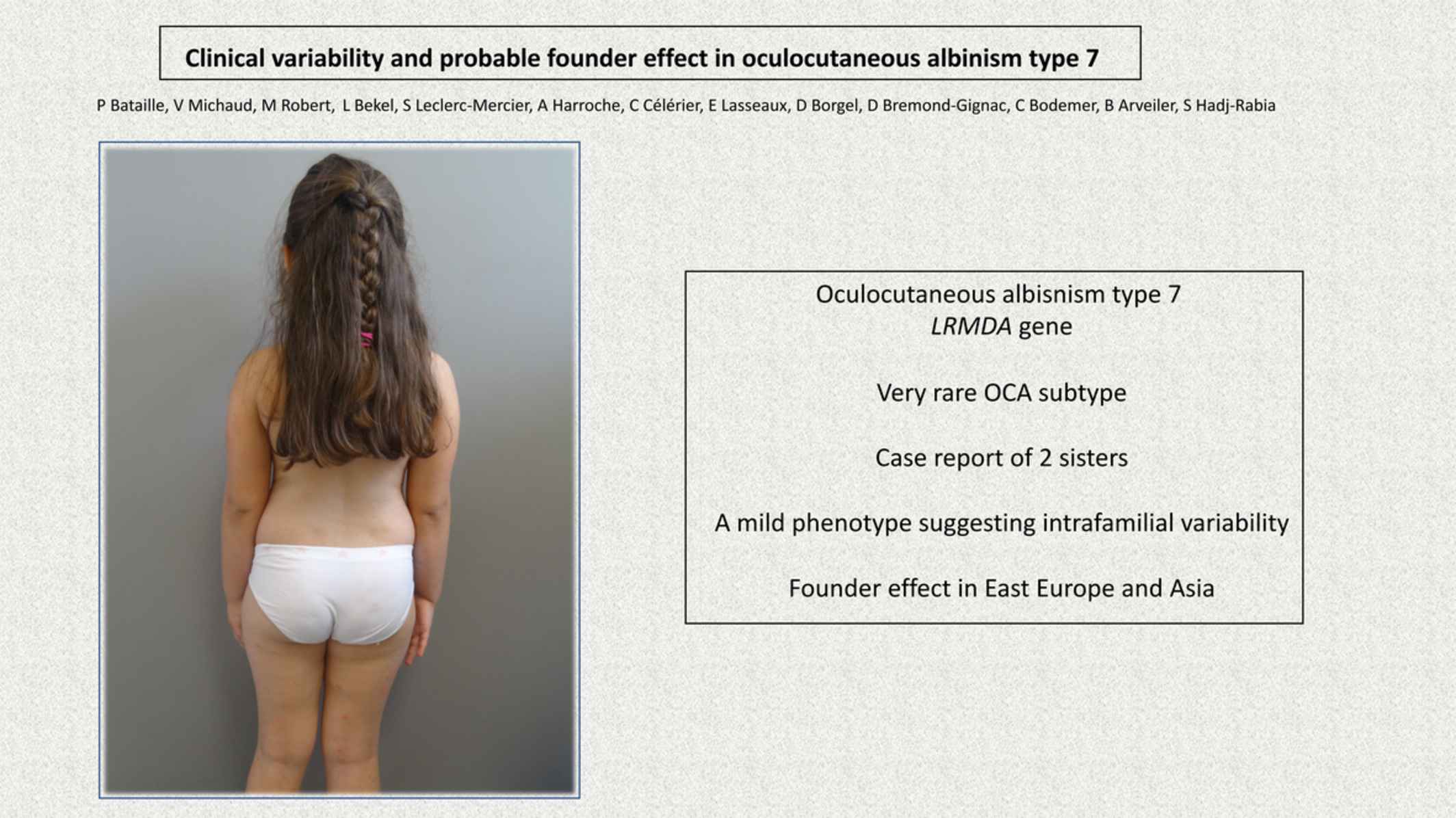
Clinical variability and probable founder effect in oculocutaneous albinism type 7
- Pages: 527-528
- First Published: 06 November 2019
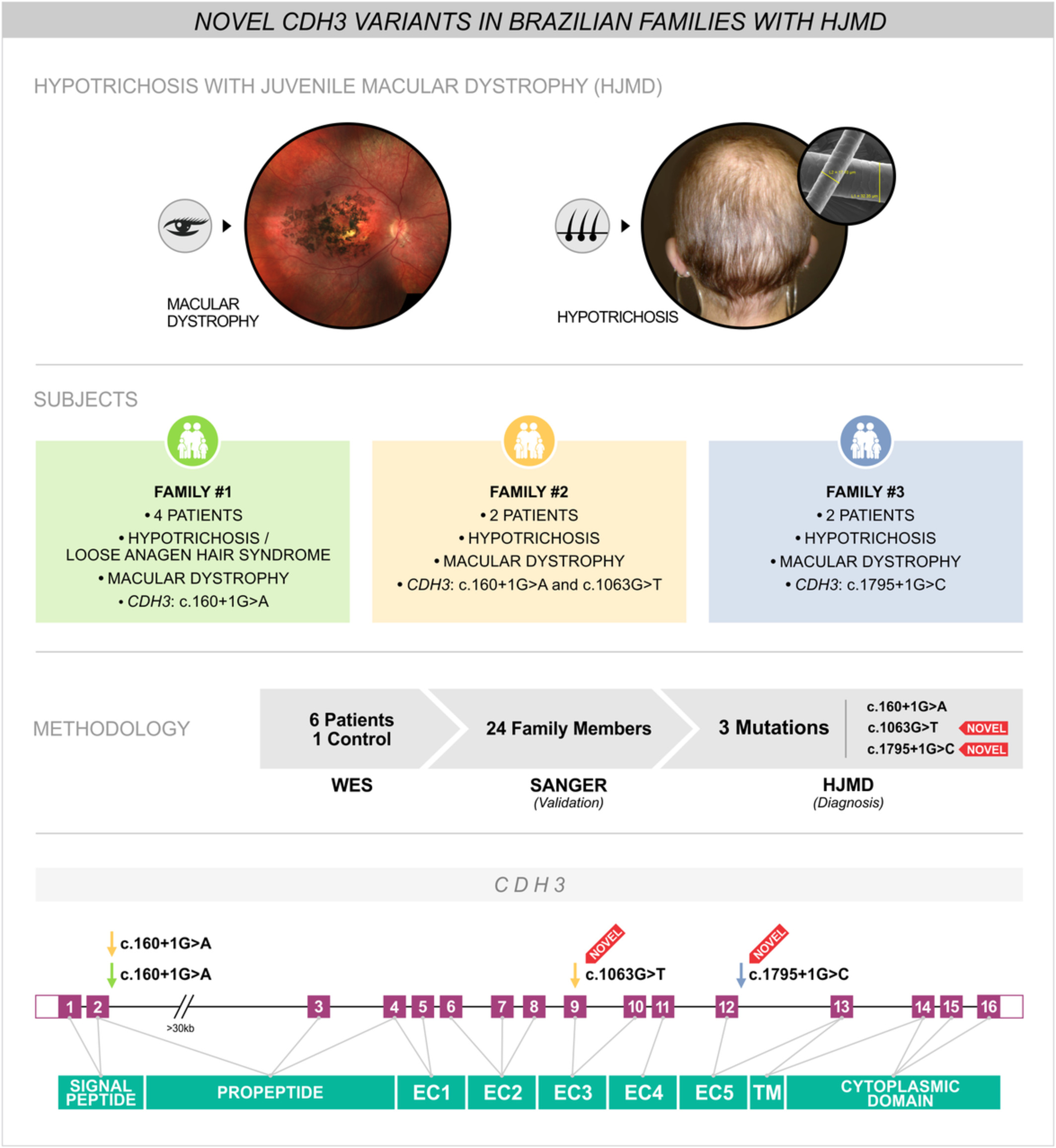
Novel CDH3 variants in Brazilian families with hypotrichosis and juvenile macular dystrophy revealed by exome sequencing
- Pages: 529-531
- First Published: 06 November 2019
Clinical and genetic findings in a cohort of Chinese patients with autosomal recessive spinocerebellar ataxia
- Pages: 532-535
- First Published: 19 November 2019
CORRESPONDENCE
Toni Mochty: Bardet Biedl syndrome “avant la lettre”
- Pages: 536-537
- First Published: 09 October 2019
“RE: Lin JL, et al. ‘Immunologic assessment and KMT2D mutation detection in Kabuki syndrome.’ Clin Genet. 2015;88(3):255-260”
- Pages: 538-539
- First Published: 16 February 2020